Deck 10: Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/14
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
1
CHARACTERISTICS OF MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION Why does the demand curve facing a monopolistically competitive firm slope downward in the long run, even after the entry of new firms?
Monopolistic competition:
Monopolistic competition refers to the market structure with the feature of more firms producing differentiated goods. These goods are called substitute goods: but they are not perfect substitutes. There is no restriction to enter the business. Firms are price makers.
Price elasticity:
Price elasticity refers to the degree of sensitivity of change in demand due to change in the price level.
Downward slope curve for monopolistic competition:
The products produced in the monopolistic competition are differentiated goods. Even though the goods are somewhat substitutes, firms differentiate the product with some features like shape, color, and brand name. Therefore, the firm can sell more products by decreasing the price of the product. Hence, in the long run, even though the new firms enter in to the market, monopolistic firm's demand curve slopes downward.
Monopolistic competition refers to the market structure with the feature of more firms producing differentiated goods. These goods are called substitute goods: but they are not perfect substitutes. There is no restriction to enter the business. Firms are price makers.
Price elasticity:
Price elasticity refers to the degree of sensitivity of change in demand due to change in the price level.
Downward slope curve for monopolistic competition:
The products produced in the monopolistic competition are differentiated goods. Even though the goods are somewhat substitutes, firms differentiate the product with some features like shape, color, and brand name. Therefore, the firm can sell more products by decreasing the price of the product. Hence, in the long run, even though the new firms enter in to the market, monopolistic firm's demand curve slopes downward.
2
PRODUCT DIFFERENTIATION What are four ways in which a firm can differentiate its product? What role can advertising play in product differentiation? How can advertising become a barrier to entry?
Four ways of differentiate the goods:
Four ways of differentiating the goods are given below:
• Physical differences: The products are differentiated by different shapes, packages, color, weights, quality, and so on.
• Availability in regions: Differentiation can be made by the availability of the product in some regions. Some products are available in particular shops only.
• Branding of the product: Producers create the brand loyalty by advertisement and product promotion.
• Provision of services: The product differentiation is done by providing various kinds of services like door delivery, cash on delivery, and free service for some period of time.Role of advertisement in product differences:
Advertisement provides the information of the product, that is, how a product is different from its competitor's product. It highlights the special features of the product like attracting shape, color, and quality of the product. Advertisement is also fostering the image of the product to the consumers.
Advertisement and barriers to entry:
Advertisement is a high-cost product promotion method. Therefore, it increases the cost of production. If the new firm enters in to the market, then it should employ all the product promotion methods which are used by the existing firms to compete effectively with the competitors. Since the advertisement expenditure increases the cost of production, it restricts the entry of new firms in to the market.
Four ways of differentiating the goods are given below:
• Physical differences: The products are differentiated by different shapes, packages, color, weights, quality, and so on.
• Availability in regions: Differentiation can be made by the availability of the product in some regions. Some products are available in particular shops only.
• Branding of the product: Producers create the brand loyalty by advertisement and product promotion.
• Provision of services: The product differentiation is done by providing various kinds of services like door delivery, cash on delivery, and free service for some period of time.Role of advertisement in product differences:
Advertisement provides the information of the product, that is, how a product is different from its competitor's product. It highlights the special features of the product like attracting shape, color, and quality of the product. Advertisement is also fostering the image of the product to the consumers.
Advertisement and barriers to entry:
Advertisement is a high-cost product promotion method. Therefore, it increases the cost of production. If the new firm enters in to the market, then it should employ all the product promotion methods which are used by the existing firms to compete effectively with the competitors. Since the advertisement expenditure increases the cost of production, it restricts the entry of new firms in to the market.
3
TO PRODUCE OR NOT TO PRODUCE What's the difference between shutting down and going out of business?
Difference between shutting down and going out of business:
The difference between shutting down and going out of business is shown below:
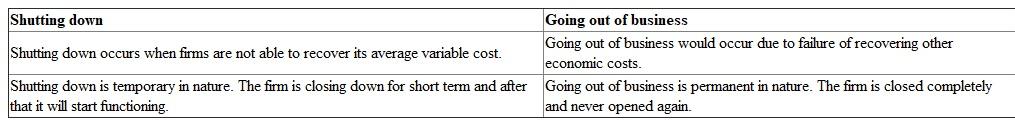
The difference between shutting down and going out of business is shown below:

4
ZERO ECONOMIC PROFIT IN THE LONG RUN In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm earns zero economic profit, which is exactly what would occur if the industry were perfectly competitive. Assuming that the cost curves for each firm are the same whether the industry is perfectly or monopolistically competitive, answer the following questions.
a. Why don't perfectly and monopolistically competitive firms produce the same equilibrium quantity in the long run?
b. Why is a monopolistically competitive industry said to be economically inefficient?
c. What benefits might cause consumers to prefer the monopolistically competitive result to the perfectly competitive result?
a. Why don't perfectly and monopolistically competitive firms produce the same equilibrium quantity in the long run?
b. Why is a monopolistically competitive industry said to be economically inefficient?
c. What benefits might cause consumers to prefer the monopolistically competitive result to the perfectly competitive result?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
VARIETIES OF OLIGOPOLY Do the firms in an oligopoly act independently or interdependently? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
COLLUSION AND CARTELS Why would each of the following induce some members of OPEC to cheat on their cartel agreement?
a. Newly joined cartel members are poor countries.
b. The number of cartel members doubles from 12 to 24.
c. International debts of some members grow.
d. Expectations grow that some members will cheat.
a. Newly joined cartel members are poor countries.
b. The number of cartel members doubles from 12 to 24.
c. International debts of some members grow.
d. Expectations grow that some members will cheat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
PRICE LEADERSHIP Why might a price-leadership model of oligopoly not be an effective means of collusion in an oligopoly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
MARKET STRUCTURES Determine whether each of the following is a characteristic of perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and/or monopoly:
a. A large number of sellers
b. Product is a commodity
c. Advertising by firms
d. Barriers to entry
e. Firms are price makers
f. Many buyers
a. A large number of sellers
b. Product is a commodity
c. Advertising by firms
d. Barriers to entry
e. Firms are price makers
f. Many buyers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
SHORT-RUN PROFIT MAXIMIZATION A monopolistically competitive firm faces the following demand and cost structure in the short run:
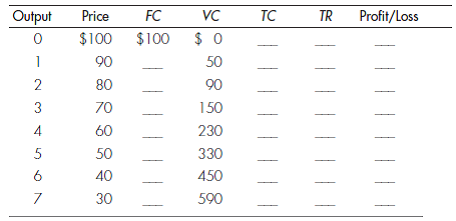
b. What is the highest profit or lowest loss available to this firm?
c. Should this firm operate or shut down in the short run? Why?
d. What is the relationship between marginal revenue and marginal cost as the firm increases output?

b. What is the highest profit or lowest loss available to this firm?
c. Should this firm operate or shut down in the short run? Why?
d. What is the relationship between marginal revenue and marginal cost as the firm increases output?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Case Study: Fast Forward to Creative Destruction
Use a cost-and-revenue graph to illustrate and explain the initial short-run profits in the video rental business in monopolistic competition. Then, use a second graph to illustrate the long-run situation. Explain fully.
Use a cost-and-revenue graph to illustrate and explain the initial short-run profits in the video rental business in monopolistic competition. Then, use a second graph to illustrate the long-run situation. Explain fully.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION AND PERFECT COMPETITION COMPARED Illustrated below are the marginal cost and average total cost curves for a small firm that is in long-run equilibrium.
a. Locate the long-run equilibrium price and quantity if the firm is perfectly competitive.
b. Label the price and quantity p 1 and q 1.
c. Draw in a demand and marginal revenue curve to illustrate long-run equilibrium if the firm is monopolistically competitive. Label the price and quantity p 2 and q 2.
d. How do the monopolistically competitive firm's price and output compare to those of the perfectly competitive firm?
e. How do long-run profits compare for the two types of firms?
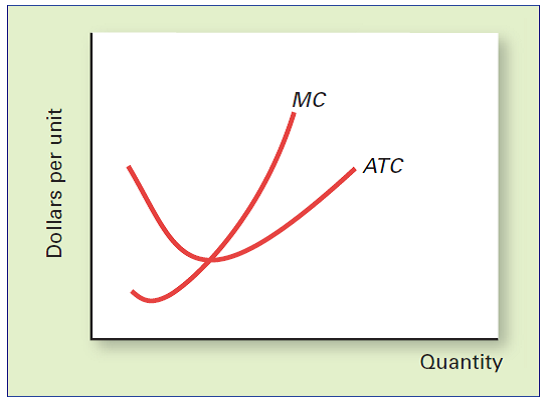
a. Locate the long-run equilibrium price and quantity if the firm is perfectly competitive.
b. Label the price and quantity p 1 and q 1.
c. Draw in a demand and marginal revenue curve to illustrate long-run equilibrium if the firm is monopolistically competitive. Label the price and quantity p 2 and q 2.
d. How do the monopolistically competitive firm's price and output compare to those of the perfectly competitive firm?
e. How do long-run profits compare for the two types of firms?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
COLLUSION AND CARTELS Use revenue and cost curves to Illustrate and explain how a cartel behaves like a monopolist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
GAME THEORY Suppose there are only two automobile companies, Ford and Chevrolet. Ford believes that Chevrolet will match any price it sets, but Chevrolet too is interested in maximizing profit. Use the following price and profit data to answer the following questions.
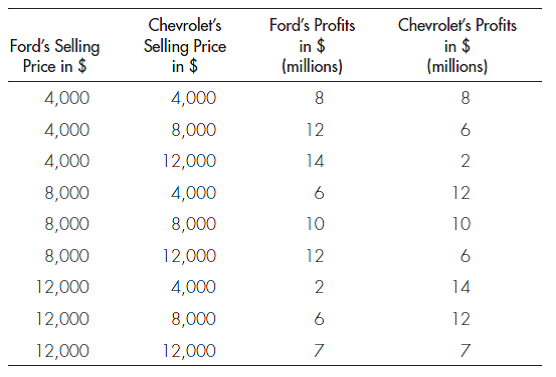
a. What price will Ford charge?
b. What price will Chevrolet charge once Ford has set its price?
c. What is Ford's profit after Chevrolet's response?
d. If the two firms cooperate to maximize joint profits, what prices would they set?
e. Given your answer to part (d), how could undetected cheating on price cause the cheating firm's profit to rise?

a. What price will Ford charge?
b. What price will Chevrolet charge once Ford has set its price?
c. What is Ford's profit after Chevrolet's response?
d. If the two firms cooperate to maximize joint profits, what prices would they set?
e. Given your answer to part (d), how could undetected cheating on price cause the cheating firm's profit to rise?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
GAME THEORY While grading a final exam, an economics professor discovers that two students have virtually identical answers. She is convinced the two cheated but cannot prove it. The professor speaks with each student separately and offers the following deal: Sign a statement admitting to cheating. If both students sign the statement, each will receive an "F" for the course. If only one signs, he is allowed to withdraw from the course while the other student is expelled. If neither signs, both receive a "C" because the professor does not have sufficient evidence to prove cheating.
a. Draw the payoff matrix.
b. Which outcome do you expect? Why?
a. Draw the payoff matrix.
b. Which outcome do you expect? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



