Deck 6: The Risk and Term Structure of Interest Rates
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/25
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: The Risk and Term Structure of Interest Rates
1
Prior to 2008, mortgage lenders required a house inspection to assess a home's value, and often used the same one or two inspection companies in the same geographical market. Following the collapse of the housing market in 2008, mortgage lenders required a house inspection, but this inspection was arranged through a third party. How does the pre-2008 scenario illustrate a conflict of interest similar to the role that credit-rating agencies played in the global financial crisis?
Conflicts of interest occur when an individual or institution has multiple objectives that conflict and is a type of moral hazard problem. This makes the asymmetric information problem worse because the competing interests give incentive for the individual or institution to either hide or give misleading information.
Mortgage lenders' goal is to extend loans to prospective homeowners. They profit from the interest collected on these loans (mortgages) so they have incentive to loan to as many people as possible. These lenders are also supposed to screen out bad credit risks so that they are more likely to be repaid their loans. However, their incentive to profit from issuing as many mortgages as possible overshadows their concern of lending to the wrong people; this represents a conflict of interest for the mortgage lenders.
Credit-rating agencies in the global financial crisis faced similar problems. They received money for analyzing the riskiness of assets and the more investments made in these assets, the more they receive. This gave the agencies incentive to rate up assets that are not as safe as they appeared rating-wise and contributed to the lack of information in the financial market. Investors would purchase highly rated assets thinking that it was a safe investment, but take on more risk than expected in reality.
Mortgage lenders' goal is to extend loans to prospective homeowners. They profit from the interest collected on these loans (mortgages) so they have incentive to loan to as many people as possible. These lenders are also supposed to screen out bad credit risks so that they are more likely to be repaid their loans. However, their incentive to profit from issuing as many mortgages as possible overshadows their concern of lending to the wrong people; this represents a conflict of interest for the mortgage lenders.
Credit-rating agencies in the global financial crisis faced similar problems. They received money for analyzing the riskiness of assets and the more investments made in these assets, the more they receive. This gave the agencies incentive to rate up assets that are not as safe as they appeared rating-wise and contributed to the lack of information in the financial market. Investors would purchase highly rated assets thinking that it was a safe investment, but take on more risk than expected in reality.
2
"According to the expectations theory of the term structure, it is better to invest in one-year bonds, reinvested over two years, than to invest in a two-year bond if interest rates on one-year bonds are expected to be the same in both years." Is this statement true, false, or uncertain?
Expectation Theory:
The expectation theory can be defined as the interest rate on a long-term bond will be equal to an average of the short-term interest rates that are expected to occur over the life.
Based on this definition, it can be said that the given statement is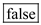 . This is because the two-year term bond would have the same interest rate as the average of the one-year bonds.
. This is because the two-year term bond would have the same interest rate as the average of the one-year bonds.
Since the interest rates on one-year bonds are expected to be the same in both years, for example 5%, then the two-year bond would have an interest rate of 5%. This would make both of the investment choices equally as appealing. Therefore, it is not better to invest in one over the other based on the expectation theory of the term structure.
The expectation theory can be defined as the interest rate on a long-term bond will be equal to an average of the short-term interest rates that are expected to occur over the life.
Based on this definition, it can be said that the given statement is
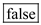 . This is because the two-year term bond would have the same interest rate as the average of the one-year bonds.
. This is because the two-year term bond would have the same interest rate as the average of the one-year bonds. Since the interest rates on one-year bonds are expected to be the same in both years, for example 5%, then the two-year bond would have an interest rate of 5%. This would make both of the investment choices equally as appealing. Therefore, it is not better to invest in one over the other based on the expectation theory of the term structure.
3
If bond investors decide that 30-year bonds are no longer as desirable an investment as they were previously, predict what will happen to the yield curve, assuming (a) the expectations theory of the term structure holds; and (b) the segmented markets theory of the term structure holds.
a. The expectation theory of the term structure states that the interest rate on a long-term bond will equal an average of the short-term interest rates expected to occur over the life of the long-term bond. Suppose that investors decide that 30-year (long-term) bonds are no longer as desirable an investment. This would cause the price of 30-year bonds to decrease due to a decrease in their demand, and their interest rate to increase. Assuming that the expectations theory of the term structure holds, the yield curve would 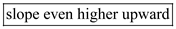 to reflect the increase in the interest rate as maturity increases toward 30 years.
to reflect the increase in the interest rate as maturity increases toward 30 years.
b. The segmented markets theory of the term structure states that the interest rate for bonds with different maturities is determined by the supply and demand of each individual bond. It assumes that there are no effects from expected returns on other bonds with other maturities. Unlike the expectation theory, the segmented markets theory sees markets for bonds with different maturities as separate markets. Since the yield curve depicts the yields on bonds with different maturities but same risk, liquidity, and tax considerations, a decrease in demand for 30-year bonds would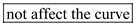 because this theory states that the market for these 30-year bonds are separate from ones with differing maturities.
because this theory states that the market for these 30-year bonds are separate from ones with differing maturities.
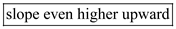 to reflect the increase in the interest rate as maturity increases toward 30 years.
to reflect the increase in the interest rate as maturity increases toward 30 years.b. The segmented markets theory of the term structure states that the interest rate for bonds with different maturities is determined by the supply and demand of each individual bond. It assumes that there are no effects from expected returns on other bonds with other maturities. Unlike the expectation theory, the segmented markets theory sees markets for bonds with different maturities as separate markets. Since the yield curve depicts the yields on bonds with different maturities but same risk, liquidity, and tax considerations, a decrease in demand for 30-year bonds would
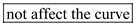 because this theory states that the market for these 30-year bonds are separate from ones with differing maturities.
because this theory states that the market for these 30-year bonds are separate from ones with differing maturities. 4
Suppose the interest rates on one-, five-, and ten-year U.S. Treasury bonds are currently 3%, 6%, and 6%, respectively. Investor A chooses to hold only one-year bonds, and Investor B is indifferent with regard to holding five- and ten-year bonds. How can you explain the behavior of Investors A and B?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a yield curve looks like the one shown here, what is the market predicting about the movement of future short-term interest rates? What might the yield curve indicate about the market's predictions about the inflation rate in the future? 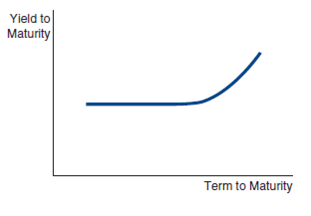


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If junk bonds are "junk," then why do investors buy them?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If a yield curve looks like the one below, what is the market predicting about the movement of future short-term interest rates? What might the yield curve indicate about the market's predictions about the inflation rate in the future? 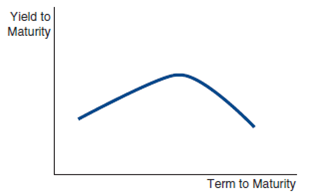


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which should have the higher risk premium on its interest rates, a corporate bond with a Moody's Baa rating or a corporate bond with a C rating? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If yield curves, on average, were flat, what would this say about the liquidity (term) premiums in the term structure? Would you be more or less willing to accept the expectations theory?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Why do U.S. Treasury bills have lower interest rates than large-denomination negotiable bank CDs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If the yield curve suddenly became steeper, how would you revise your predictions of interest rates in the future?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the fall of 2008, AIG, the largest insurance company in the world at the time, was at risk of defaulting due to the severity of the global financial crisis. As a result, the U.S. government stepped in to support AIG with large capital injections and an ownership stake. How would this affect, if at all, the yield and risk premium on AIG corporate debt?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If expectations of future short-term interest rates suddenly fell, what would happen to the slope of the yield curve?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Risk premiums on corporate bonds are usually anticyclical, that is, they decrease during business cycle expansions and increase during recessions. Why is this so?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Following a policy meeting on March 19, 2009, the Federal Reserve made an announcement that it would purchase up to $300 billion of longer-term Treasury securities over the following six months. What effect might this policy have on the yield curve?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
"If bonds of different maturities are close substitutes, their interest rates are more likely to move together." Is this statement true, false, or uncertain? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In 2010 anD₂011, the government of Greece risked defaulting on its debt due to a severe budget crisis. Using bond market graphs, compare the effects on the risk premium between U.S. Treasury debt and comparable-maturity Greek debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The U.S. Treasury offers some of its debt as Treasury Inflation Protected Securities, or TIPS, in which the price of bonds is adjusted for inflation over the life of the debt instrument. TIPS bonds are traded on a much smaller scale than nominal U.S. Treasury bonds of equivalent maturity. What can you conclude about the liquidity premiums of TIPS versus nominal U.S. bonds?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Assuming the expectations theory is the correct theory of the term structure, calculate the interest rates in the term structure for maturities of one to five years, and plot the resulting yield curves for the following paths of one-year interest rates over the next five years:
a. 5%, 7%, 7%, 7%, 7%
b. 5%, 4%, 4%, 4%, 4%
How would your yield curves change if people preferred shorter-term bonds to longer-term bonds?
a. 5%, 7%, 7%, 7%, 7%
b. 5%, 4%, 4%, 4%, 4%
How would your yield curves change if people preferred shorter-term bonds to longer-term bonds?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Predict what will happen to interest rates on a corporation's bonds if the federal government guarantees today that it will pay creditors if the corporation goes bankrupt in the future. What will happen to the interest rates on Treasury securities?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Assuming the expectations theory is the correct theory of the term structure, calculate the interest rates in the term structure for maturities of one to five years, and plot the resulting yield curves for the following paths of one-year interest rates over the next five years:
a. 5%, 6%, 7%, 6%, 5%
b. 5%, 4%, 3%, 4%, 5%
How would your yield curves change if people preferred shorter-term bonds over longer-term bonds?
a. 5%, 6%, 7%, 6%, 5%
b. 5%, 4%, 3%, 4%, 5%
How would your yield curves change if people preferred shorter-term bonds over longer-term bonds?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Predict what would happen to the risk premiums on corporate bonds if brokerage commissions were lowered in the corporate bond market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The table below shows current and expected future one-year interest rates, as well as current interest rates on multiyear bonds. Use the table to calculate the liquidity premium for each multiyear bond. 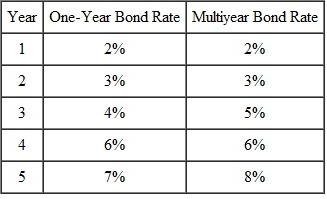


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
During 2008, the difference in yield (the yield spread ) between three-month AA-rated financial commercial paper and three-month AA-rated nonfinancial commercial paper steadily increased from its usual level of close to zero, spiking to over a full percentage point at its peak in October 2008. What explains this sudden increase?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If the income tax exemption on municipal bonds were abolished, what would happen to the interest rates on these bonds? What effect would it have on interest rates on U.S. Treasury securities?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



