Deck 12: Entering Foreign Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/11
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Entering Foreign Markets
1
Entering Foreign Markets
Use the globalEDGE Resource Desk (http://globaledge.msu.edu/Reference-Desk) to complete the following exercises:
Entrepreneur magazine annually publishes a ranking of America's top 200 franchisers seeking international franchisees. Provide a list of the top 10 companies that pursue franchising as a mode of international expansion. Study one of these companies in detail, and provide a description of its business model, its international expansion pattern, the qualifications it looks for in its franchisees, and the type of support and training it provides.
Use the globalEDGE Resource Desk (http://globaledge.msu.edu/Reference-Desk) to complete the following exercises:
Entrepreneur magazine annually publishes a ranking of America's top 200 franchisers seeking international franchisees. Provide a list of the top 10 companies that pursue franchising as a mode of international expansion. Study one of these companies in detail, and provide a description of its business model, its international expansion pattern, the qualifications it looks for in its franchisees, and the type of support and training it provides.
The Entrepreneur magazine gives a list of the top 200 international franchise operations in the US. According to them the top 10 are as listed below.
Top 10 International Franchise Operations in the US
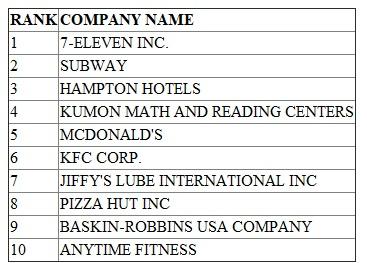 (Source: Entrepreneur Magazine web site http://www.entrepreneur.com/franchises/topglobal/index.html)The one company chosen for describing the business model is Baskin-Robbins USA Company.
(Source: Entrepreneur Magazine web site http://www.entrepreneur.com/franchises/topglobal/index.html)The one company chosen for describing the business model is Baskin-Robbins USA Company.
Brief Details about the company
Products Services : Ice cream, frozen yogurt, frozen beverages
Number of Locations : 7,075
Founded : 1945
Began Franchising : 1948
Startup Costs and Fees
This gives some details of the type of investment required to start a franchise
Total Investment : $100,700 - $390,200 (Depends on country and size of store)Franchise Fee : $25,000
Ongoing Royalty Fee : 5.9%
Term of Franchise Agreement : Term of agreement not renewable
FINANCIAL REQUIREMENTS (Minimum)Net Worth : $250,000
Liquid Cash Available : $125,000
Support to Franchisees
Training : Available at headquarters. Period varies as per requirements.
Ongoing Support : Newsletter, Meetings, Toll-free phone line, Grand opening, Security/safety procedures, Field operations/evaluations.
Marketing Support : Regional advertising.
Top 10 International Franchise Operations in the US
 (Source: Entrepreneur Magazine web site http://www.entrepreneur.com/franchises/topglobal/index.html)The one company chosen for describing the business model is Baskin-Robbins USA Company.
(Source: Entrepreneur Magazine web site http://www.entrepreneur.com/franchises/topglobal/index.html)The one company chosen for describing the business model is Baskin-Robbins USA Company.Brief Details about the company
Products Services : Ice cream, frozen yogurt, frozen beverages
Number of Locations : 7,075
Founded : 1945
Began Franchising : 1948
Startup Costs and Fees
This gives some details of the type of investment required to start a franchise
Total Investment : $100,700 - $390,200 (Depends on country and size of store)Franchise Fee : $25,000
Ongoing Royalty Fee : 5.9%
Term of Franchise Agreement : Term of agreement not renewable
FINANCIAL REQUIREMENTS (Minimum)Net Worth : $250,000
Liquid Cash Available : $125,000
Support to Franchisees
Training : Available at headquarters. Period varies as per requirements.
Ongoing Support : Newsletter, Meetings, Toll-free phone line, Grand opening, Security/safety procedures, Field operations/evaluations.
Marketing Support : Regional advertising.
2
Why do you think that GE has come to prefer joint ventures in recent years? Do you think that the global economic crisis of 2008-2009 might have impacted upon this preference in any way? If so, how?
The case depicts the scenario where a company adopted different policies as per different needs. Change is the only constant in the business world. It is must to consider the importance of introducing new policies as and when required.Company G has changed its strategy of entering in the market. It used to prefer acquisitions or green field ventures at first but during present times joint ventures are the most profitable tools for the same. It is done keeping the present scenario under consideration. The place where company does not have knowledge of local policies, the best option to make its settlement is joint venture. Besides this, the acquisitions require a lot of money without giving any assurance of profit. The company thinks that joint ventures will free it from this risk. The company will not be responsible alone to face the loss if any.
The global economic crisis of 2008-2009 was definitely one of the major reasons behind switching the strategy. The acquisitions became too expensive to consider as a source for market entry. Company's started to go global. This created the need to abide by the local laws of the countries. To understand these laws, Company G was in the need of local people; no other option was as suitable as joint ventures.
The global economic crisis of 2008-2009 was definitely one of the major reasons behind switching the strategy. The acquisitions became too expensive to consider as a source for market entry. Company's started to go global. This created the need to abide by the local laws of the countries. To understand these laws, Company G was in the need of local people; no other option was as suitable as joint ventures.
3
Licensing propriety technology to foreign competitors is the best way to give up a firm's competitive advantage. Discuss.
The statement is basically correct - licensing proprietary technology to foreign competitors does significantly increase the risk of losing the technology. Therefore licensing should generally be avoided in these situations. Yet licensing still may be a good choice in some instances. When a licensing arrangement can be structured in such a way as to reduce the risks of a firm's technological know-how being expropriated by licensees, then licensing may be appropriate. A further example is when a firm perceives its technological advantage as being only transitory, and it considers rapid imitation of its core technology by competitors to be likely. In such a case, the firm might want to license its technology as rapidly as possible to foreign firms in order to gain global acceptance for its technology before imitation occurs. Such a strategy has some advantages. By licensing its technology to competitors, the firm may deter them from developing their own, possibly superior, technology. And by licensing its technology the firm may be able to establish its technology as the dominant design in the industry. In turn, this may ensure a steady stream of royalty payments. Such situations apart, however, the attractions of licensing are probably outweighed by the risks of losing control over technology, and licensing should be avoided
4
Entering Foreign Markets
Use the globalEDGE Resource Desk (http://globaledge.msu.edu/Reference-Desk) to complete the following exercises:
The U.S. Commercial Service prepares a series of reports titled the Country Commercial Guide (or, CCG )for each country of interest to U.S. investors. Utilize this guide to gather information on India. Imagine that your company is in health technologies and is considering entering this country. Select the most appropriate entry method, supporting your decision with the information collected from the commercial guide.
Use the globalEDGE Resource Desk (http://globaledge.msu.edu/Reference-Desk) to complete the following exercises:
The U.S. Commercial Service prepares a series of reports titled the Country Commercial Guide (or, CCG )for each country of interest to U.S. investors. Utilize this guide to gather information on India. Imagine that your company is in health technologies and is considering entering this country. Select the most appropriate entry method, supporting your decision with the information collected from the commercial guide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What are the risks that GE must assume when it enters into a joint venture? Is there any way for GE to reduce these risks?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Discuss how the need for control over foreign operations varies with firms' strategies and core competencies. What are the implications for the choice of entry mode?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The case mentions that GE has a well-earned reputation for being a good partner. What are the likely benefits of this reputation to GE? If GE were to tarnish its reputation by, for example, opportunistically taking advantage of a partner, how might this impact the company going forward?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A small Canadian firm that has developed some valuable new medical products using its unique biotechnology know-how is trying to decide how best to serve the European Community market. Its choices are given below. The cost of investment in manufacturing facilities will be a major one for the Canadian firm, but it is not outside its reach. If these are the firm's only options, which one would you advise it to choose? Why?
• Manufacture the product at home and let foreign sales agents handle marketing.
• Manufacture the products at home but set up a wholly owned subsidiary in Europe to handle marketing.
• Enter into a strategic alliance with a large European pharmaceutical firm. The product would be manufactured in Europe by a 50/50 joint venture, and marketed by the European firm.
• Manufacture the product at home and let foreign sales agents handle marketing.
• Manufacture the products at home but set up a wholly owned subsidiary in Europe to handle marketing.
• Enter into a strategic alliance with a large European pharmaceutical firm. The product would be manufactured in Europe by a 50/50 joint venture, and marketed by the European firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In addition to its reputation for being a good partner, what other assets do you think GE brings to the table that make it an attractive joint-venture partner?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
GE used to have a preference for acquisitions or greenfield ventures as an entry mode, rather than joint ventures. Why do you think this was the case?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Review the Management Focus on Tesco. Then answer the following questions:
a) Why did Tesco's initial international expansion strategy focus on developing nations?
b) How does Tesco create value in its international operations?
c) In Asia, Tesco has a long history of entering into joint venture agreements with local partners. What are the benefits of doing this for Tesco? What are the risks? How are those risks mitigated?
d) In March 2006, Tesco announced that it would enter the United States. This represents a departure from its historic strategy of focusing on developing nations. Why do you think Tesco made this decision? How is the U.S. market different from others Tesco has entered? What are the risks here? How do you think Tesco will do?
a) Why did Tesco's initial international expansion strategy focus on developing nations?
b) How does Tesco create value in its international operations?
c) In Asia, Tesco has a long history of entering into joint venture agreements with local partners. What are the benefits of doing this for Tesco? What are the risks? How are those risks mitigated?
d) In March 2006, Tesco announced that it would enter the United States. This represents a departure from its historic strategy of focusing on developing nations. Why do you think Tesco made this decision? How is the U.S. market different from others Tesco has entered? What are the risks here? How do you think Tesco will do?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



