Deck 17: The Weighted Cost of Capital and Adjusted Present Value in an Imperfect Market With Taxes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: The Weighted Cost of Capital and Adjusted Present Value in an Imperfect Market With Taxes
1
A $20 million project is expected to return $23 million next year. Your firm is in a 40% combined federal and state marginal income tax bracket. You finance the project with $10 million in debt at a rate of 8%.
Refer to the information above. If the appropriate project interest rate is 10%, what is the present value of the tax savings due to financing the project with debt?
A)$727,273
B)$290,909
C)$72,727
D)$436,364
Refer to the information above. If the appropriate project interest rate is 10%, what is the present value of the tax savings due to financing the project with debt?
A)$727,273
B)$290,909
C)$72,727
D)$436,364
$290,909
2
A $20 million project is expected to return $23 million next year. Your firm is in a 40% combined federal and state marginal income tax bracket. You finance the project with $10 million in debt at a rate of 8%.
Refer to the information above. What amount do you save in taxes by using debt instead of cash to finance the project?
A)$480,000
B)$800,000
C)$80,000
D)$320,000
Refer to the information above. What amount do you save in taxes by using debt instead of cash to finance the project?
A)$480,000
B)$800,000
C)$80,000
D)$320,000
$320,000
3
A firm issues debt of $1 million at an interest rate of 10%. The debt has a 10-year maturity, and the first interest payment is due next year. The principal repayment and the last interest
Payment will be made at the end of year 10. If the firm is in the 40% tax bracket and the
Appropriate discount rate is 10%, what is the present value of the tax savings? Round your
Answer to the nearest dollar.
A)$245,783
B)$368,674
C)$363,636
D)$545,455
Payment will be made at the end of year 10. If the firm is in the 40% tax bracket and the
Appropriate discount rate is 10%, what is the present value of the tax savings? Round your
Answer to the nearest dollar.
A)$245,783
B)$368,674
C)$363,636
D)$545,455
$245,783
4
In a world in which only corporate income taxes matter, the optimal capital structure is
A)100% equity financing.
B)25% debt financing and 75% equity financing.
C)50% debt financing and 50% equity financing.
D)99.99% debt financing.
A)100% equity financing.
B)25% debt financing and 75% equity financing.
C)50% debt financing and 50% equity financing.
D)99.99% debt financing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A firm is making a payment of $1,000 to its investors. The firm is in the 34% marginal tax bracket. If this payment is made in the form of interest to its bondholders, how much does the
Firm have to have in earnings to be able to make the payment? Round your answer to the
Nearest dollar.
A)$1,340
B)$1,515
C)$2,941
D)none of the above
Firm have to have in earnings to be able to make the payment? Round your answer to the
Nearest dollar.
A)$1,340
B)$1,515
C)$2,941
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A firm issues debt of $1 million at an interest rate of 10%. If the firm is in the 40% tax bracket, what is the annual tax savings on this debt?
A)$60,000
B)$400,000
C)$40,000
D)$600,000
A)$60,000
B)$400,000
C)$40,000
D)$600,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A project costs $20,000 today and is expected to return 20% before corporate income taxes. The appropriate after-tax cost of capital is 12%, and the firm pays taxes at the marginal rate of 35%.
What is the project's NPV? Round your answer to the nearest dollar.
A)$179
B)$2,679
C)$1,429
D)none of the above
What is the project's NPV? Round your answer to the nearest dollar.
A)$179
B)$2,679
C)$1,429
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Your investors require a 15% after-tax return, and your firm pays taxes at the marginal rate of 34%. Which of the following scenarios will provide them with the 15% after-tax return they
Require?
A)Your projects cost $500,000 and return $613,650. All of the profit is fully taxable.
B)Your projects cost $500,000 and return $550,000. Only one-fourth of the profit is taxable under current tax laws.
C)Your projects cost $500,000 and return $590,000. Only half of the profit is taxable under current tax laws.
D)All of the above will provide a 15% after-tax return.
Require?
A)Your projects cost $500,000 and return $613,650. All of the profit is fully taxable.
B)Your projects cost $500,000 and return $550,000. Only one-fourth of the profit is taxable under current tax laws.
C)Your projects cost $500,000 and return $590,000. Only half of the profit is taxable under current tax laws.
D)All of the above will provide a 15% after-tax return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The method that allows you to compute the value of a firm today under both current and alternative capital structures that involves constructing pro formas for the firm is the
A)flow-to-equity.
B)weighted average cost of capital.
C)adjusted present value.
D)M&M theory.
A)flow-to-equity.
B)weighted average cost of capital.
C)adjusted present value.
D)M&M theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A $20 million project is expected to return $23 million next year. Your firm is in a 40% combined federal and state marginal income tax bracket. You finance the project with $10 million in debt at a rate of 8%.
Refer to the information above. How much will you pay in taxes?
A)$8,880,000
B)$13,320,000
C)$1,320,000
D)$880,000
Refer to the information above. How much will you pay in taxes?
A)$8,880,000
B)$13,320,000
C)$1,320,000
D)$880,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A project costs $500,000 today and is expected to return 10% before corporate income taxes. The appropriate after-tax cost of capital is 12%, and the firm pays taxes at the marginal rate of
30%. What is this project's NPV? Round your answer to the nearest dollar.
A)-$66,964
B)-$22,321
C)-$115,000
D)-$8,929
30%. What is this project's NPV? Round your answer to the nearest dollar.
A)-$66,964
B)-$22,321
C)-$115,000
D)-$8,929

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following statements regarding current U.S. tax laws is true?
A)Both dividend payments and interest payments are tax-deductible for a firm.
B)Only dividend payments are tax deductible; interest is never tax deductible.
C)Only dividend payments on preferred stock and interest payments on debt are tax-deductible for a firm.
D)Only interest payments are tax deductible; dividends are paid out of after-tax income.
A)Both dividend payments and interest payments are tax-deductible for a firm.
B)Only dividend payments are tax deductible; interest is never tax deductible.
C)Only dividend payments on preferred stock and interest payments on debt are tax-deductible for a firm.
D)Only interest payments are tax deductible; dividends are paid out of after-tax income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Assume that your firm announces that it is going to issue debt and use the funds to
repurchase some of its outstanding shares within the next year. Explain how and why
this is likely to affect the market price per share of your stock today, all else equal.
repurchase some of its outstanding shares within the next year. Explain how and why
this is likely to affect the market price per share of your stock today, all else equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A firm's investments cost $100,000 and are expected to return $118,000 before taxes at the end of 1 year. The firm is financed with $30,000 debt at an expected rate of 8%. The firm pays taxes at the marginal rate of 40%, and the appropriate cost of capital is 12%.
Refer to the information above. What is the NPV of the firm if it is all equity financed?
A)-$5,357
B)-$4,643
C)+$5,357
D)-$1,071
Refer to the information above. What is the NPV of the firm if it is all equity financed?
A)-$5,357
B)-$4,643
C)+$5,357
D)-$1,071

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The method that allows you to compute the value of a firm today under both current and alternative capital structures that decomposes the value of the firm into its value as if all
Equity-financed plus the value of the tax subsidies is
A)M&M theory.
B)weighted average cost of capital.
C)flow-to-equity.
D)adjusted present value.
Equity-financed plus the value of the tax subsidies is
A)M&M theory.
B)weighted average cost of capital.
C)flow-to-equity.
D)adjusted present value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A firm is making a payment of $1,000 to its investors. The firm is in the 34% marginal tax bracket. If this
Payment is made in the form of dividends to its shareholders, how much does the firm have to
Have in earnings to be able to make the payment? Round your answer to the nearest dollar.
A)$2,941
B)$1,340
C)$1,515
D)none of the above
Payment is made in the form of dividends to its shareholders, how much does the firm have to
Have in earnings to be able to make the payment? Round your answer to the nearest dollar.
A)$2,941
B)$1,340
C)$1,515
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When using the adjusted present value (APV)valuation method you should
A)discount expected after-tax cash flows as if 100% equity-financed at the firm's overall cost of capital and add the present value of the interest tax subsidy, using the firm's overall cost
Of capital as the discount rate.
B)discount the expected after-tax cash flows, based on the firm's expected capital structure, at the firm's overall cost of capital and subtract the present value of the interest tax
Subsidy, using the firm's overall cost of capital as the discount rate.
C)discount expected after-tax cash flows as if 100% equity-financed using the firm's WACC and add the present value of the interest tax subsidy, using the firm's cost of debt capital as
The discount rate.
D)discount expected before-tax cash flows as if 100% equity-financed at the cost of equity for the firm and add the present value of the interest tax subsidy, using the firm's cost of debt
As the discount rate.
A)discount expected after-tax cash flows as if 100% equity-financed at the firm's overall cost of capital and add the present value of the interest tax subsidy, using the firm's overall cost
Of capital as the discount rate.
B)discount the expected after-tax cash flows, based on the firm's expected capital structure, at the firm's overall cost of capital and subtract the present value of the interest tax
Subsidy, using the firm's overall cost of capital as the discount rate.
C)discount expected after-tax cash flows as if 100% equity-financed using the firm's WACC and add the present value of the interest tax subsidy, using the firm's cost of debt capital as
The discount rate.
D)discount expected before-tax cash flows as if 100% equity-financed at the cost of equity for the firm and add the present value of the interest tax subsidy, using the firm's cost of debt
As the discount rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Your firm earns $800,000 a year before taxes on its investments and is in the 30%
marginal tax bracket. How much will you pay in taxes if you use 100% equity
financing and pay out 50% of your earnings as dividends to your shareholders? How
much will you pay in taxes if your investments are financed by $200,000 in long-term
debt at an interest rate of 9%?
marginal tax bracket. How much will you pay in taxes if you use 100% equity
financing and pay out 50% of your earnings as dividends to your shareholders? How
much will you pay in taxes if your investments are financed by $200,000 in long-term
debt at an interest rate of 9%?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If investors require a 14% after-tax return, how much does your firm have to return on a pre-tax basis if your firm pays taxes at the marginal rate of 34%?
A)21.2%
B)23.0%
C)41.2%
D)9.0%
A)21.2%
B)23.0%
C)41.2%
D)9.0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If the appropriate after-tax cost of capital for your firm is 10% and your firm pays taxes
at the marginal rate of 39%, how much does an average-risk project have to return on a
before-tax basis before your firm should consider accepting it?
at the marginal rate of 39%, how much does an average-risk project have to return on a
before-tax basis before your firm should consider accepting it?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A 3-year project will cost $180 at the end of year 1 and is expected to produce operating profit before depreciation and amortization (EBITDA)of $80 in year 1, $100 in year 2, and $60 in year 3. Depreciation, both real and financial, will be calculated using straight-line depreciation over 3 years. The cost of capital is 10%, and the firm's marginal tax rate is 25%.
Refer to the information above. Assume the firm will issue $100 of debt in year 1 with an expected interest rate of 8%. Interest must be paid each of the 3 years, and the principal is
Repaid at the end of year 3. What is the project IRR? (Ignore any tax laws allowing the carry
Forward or carry back of net operating losses, and round your answer to the nearest tenth of a
Percent.)
A)16.0%
B)33.1%
C)25.8%
D)7.1%
Refer to the information above. Assume the firm will issue $100 of debt in year 1 with an expected interest rate of 8%. Interest must be paid each of the 3 years, and the principal is
Repaid at the end of year 3. What is the project IRR? (Ignore any tax laws allowing the carry
Forward or carry back of net operating losses, and round your answer to the nearest tenth of a
Percent.)
A)16.0%
B)33.1%
C)25.8%
D)7.1%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The overall cost of capital for Canton Corporation is 10%. The firm is financed with 30% debt that offers a promised return of 15% and has an expected return of 8%. Canton is in the 40% marginal tax bracket.
Refer to the information above. What is Canton's expected cost of equity financing? Round all interim answers and the final answer to the nearest tenth of a percent.
A)10.9%
B)8.8%
C)9.5%
D)10.0%
Refer to the information above. What is Canton's expected cost of equity financing? Round all interim answers and the final answer to the nearest tenth of a percent.
A)10.9%
B)8.8%
C)9.5%
D)10.0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Your firm has a before-tax return of $1,800 on an investment of $800 and a marginal tax rate of 25%. The overall cost of capital is 10%. The firm currently uses 30% debt financing with an expected return of 7%. If it increases its use of debt to 40%, the expected return on the debt will be 8%.
Refer to the information above. Calculate your firm's WACC under the current capital structure. Round your answer to the nearest tenth of a percent.
A)7.9%
B)8.3%
C)9.5%
D)none of the above
Refer to the information above. Calculate your firm's WACC under the current capital structure. Round your answer to the nearest tenth of a percent.
A)7.9%
B)8.3%
C)9.5%
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Your firm has a before-tax return of $1,800 on an investment of $800 and a marginal tax rate of 25%. The overall cost of capital is 10%. The firm currently uses 30% debt financing with an expected return of 7%. If it increases its use of debt to 40%, the expected return on the debt will be 8%.
Refer to the information above. By how much will the present value of the tax subsidy increase (decrease)if the firm adopts the new capital structure?
A)decreases $6.78
B)increases $3.53
C)increases $4.26
D)decreases $4.00
Refer to the information above. By how much will the present value of the tax subsidy increase (decrease)if the firm adopts the new capital structure?
A)decreases $6.78
B)increases $3.53
C)increases $4.26
D)decreases $4.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Your firm has a before-tax return of $1,800 on an investment of $800 and a marginal tax rate of 25%. The overall cost of capital is 10%. The firm currently uses 30% debt financing with an expected return of 7%. If it increases its use of debt to 40%, the expected return on the debt will be 8%.
Refer to the information above. Calculate your firm's WACC under the proposed capital structure. Round your answer to the nearest tenth of a percent.
A)6.8%
B)9.2%
C)8.0%
D)none of the above
Refer to the information above. Calculate your firm's WACC under the proposed capital structure. Round your answer to the nearest tenth of a percent.
A)6.8%
B)9.2%
C)8.0%
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A firm is currently financed with $300 of debt and $700 of equity. The expected return on the debt is 9%. The market beta of the firm's equity is 1.50; the risk-free rate is 4%; and the equity premium is 6%. The firm pays taxes at the marginal rate of 35%.
Refer to the information above. The firm is considering increasing its debt to $400 and using the funds to repurchase some of its stock. This is likely to increase the expected return on debt
To 10%. All else equal, what will the new market beta of the firm's equity be? Round your
Answer to the nearest tenth.
A)1.6
B)1.0
C)2.3
D)The market beta of the equity will be unchanged.
Refer to the information above. The firm is considering increasing its debt to $400 and using the funds to repurchase some of its stock. This is likely to increase the expected return on debt
To 10%. All else equal, what will the new market beta of the firm's equity be? Round your
Answer to the nearest tenth.
A)1.6
B)1.0
C)2.3
D)The market beta of the equity will be unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A firm's investments cost $5,000 today and are expected to return $6,250 before taxes at the end of one year. The firm is financed with $3,000 in debt that promises a return of 18%. The expected return on the debt is 10%. The firm pays taxes at a marginal rate of 30%, and the appropriate cost of capital is 12%.
Refer to the information above. Calculate the firm's adjusted present value (APV). Round your answer to the nearest dollar.
A)$5,391
B)$5,326
C)$5,728
D)$5,514
Refer to the information above. Calculate the firm's adjusted present value (APV). Round your answer to the nearest dollar.
A)$5,391
B)$5,326
C)$5,728
D)$5,514

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Your firm has a before-tax return of $1,800 on an investment of $800 and a marginal tax rate of 25%. The overall cost of capital is 10%. The firm currently uses 30% debt financing with an expected return of 7%. If it increases its use of debt to 40%, the expected return on the debt will be 8%.
Refer to the information above. By what percent will the value of the firm increase (decrease) if the firm decides to adopt the new capital structure? Round your answer to the nearest tenth
Of a percent.
A)decreases 0.2%
B)increases 1.1%
C)decreases 1.0%
D)increases 0.3%
Refer to the information above. By what percent will the value of the firm increase (decrease) if the firm decides to adopt the new capital structure? Round your answer to the nearest tenth
Of a percent.
A)decreases 0.2%
B)increases 1.1%
C)decreases 1.0%
D)increases 0.3%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is the correct method to use to calculate firm value using the WACC method?
A)Discount the expected cash flows based on all-equity financing at the firm's weighted average cost of capital, WACC.
B)Calculate the expected cash flows for the firm based on the firm's expected capital structure, and then discount them at the overall cost of capital for the firm,
C)Calculate the expected cash flows for the firm based on the firm's expected capital structure, and then discount them at the firm's weighted average cost of capital, WACC.
D)Discount the expected cash flows based on all-equity financing at the overall cost of capital for the firm,
A)Discount the expected cash flows based on all-equity financing at the firm's weighted average cost of capital, WACC.
B)Calculate the expected cash flows for the firm based on the firm's expected capital structure, and then discount them at the overall cost of capital for the firm,

C)Calculate the expected cash flows for the firm based on the firm's expected capital structure, and then discount them at the firm's weighted average cost of capital, WACC.
D)Discount the expected cash flows based on all-equity financing at the overall cost of capital for the firm,


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A firm's investments cost $5,000 today and are expected to return $6,250 before taxes at the end of one year. The firm is financed with $3,000 in debt that promises a return of 18%. The expected return on the debt is 10%. The firm pays taxes at a marginal rate of 30%, and the appropriate cost of capital is 12%.
Refer to the information above. What is the NPV of the firm if it uses 100% equity financing? Round your answer to the nearest dollar.
A)+$246
B)+$580
C)-$201
D)+$326
Refer to the information above. What is the NPV of the firm if it uses 100% equity financing? Round your answer to the nearest dollar.
A)+$246
B)+$580
C)-$201
D)+$326

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The pro forma income statement and cash flow statement for OneShot, Inc., are provided below. The firm has a cost of capital of 10%. 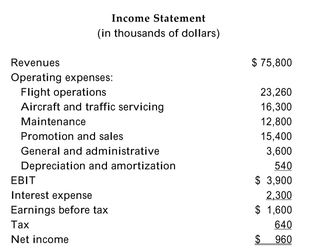
 Cash flows from investing activities:
Cash flows from investing activities:  Cash flows from financing activities:
Cash flows from financing activities: 

Refer to the income statement and cash flow statement above. Assume that OneShot's project cash flows are a perpetuity, and calculate its NPV.
A)$28,000
B)$72,000
C)$5,000
D)$49,000

 Cash flows from investing activities:
Cash flows from investing activities:  Cash flows from financing activities:
Cash flows from financing activities: 

Refer to the income statement and cash flow statement above. Assume that OneShot's project cash flows are a perpetuity, and calculate its NPV.
A)$28,000
B)$72,000
C)$5,000
D)$49,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A firm has expected before-tax earnings of $100 million a year forever, starting next year. It is financed with 30% debt at an expected interest rate of 6% a year and 70% equity with an
Expected cost of 11% a year. If the firm is in the 35% tax bracket, what is its NPV?
A)$684.21 million
B)$1,052.63 million
C)$732.81 million
D)$1,123.60 million
Expected cost of 11% a year. If the firm is in the 35% tax bracket, what is its NPV?
A)$684.21 million
B)$1,052.63 million
C)$732.81 million
D)$1,123.60 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A 3-year project will cost $180 at the end of year 1 and is expected to produce operating profit before depreciation and amortization (EBITDA)of $80 in year 1, $100 in year 2, and $60 in year 3. Depreciation, both real and financial, will be calculated using straight-line depreciation over 3 years. The cost of capital is 10%, and the firm's marginal tax rate is 25%.
Refer to the information above. Assume the firm will issue $100 of debt in year 1 with an expected interest rate of 8%. Interest must be paid each of the 3 years, and the principal is
Repaid at the end of year 3. What is the project NPV? (Ignore any tax laws allowing the carry
Forward or carry back of net operating losses.)
A)+$22.22
B)-$8.78
C)+$27.48
D)+$8.34
Refer to the information above. Assume the firm will issue $100 of debt in year 1 with an expected interest rate of 8%. Interest must be paid each of the 3 years, and the principal is
Repaid at the end of year 3. What is the project NPV? (Ignore any tax laws allowing the carry
Forward or carry back of net operating losses.)
A)+$22.22
B)-$8.78
C)+$27.48
D)+$8.34

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Assume that your firm's investments will earn $500,000 before tax and that your firm
pays taxes at the marginal rate of 40%. Assume, too, that your firm is partially
financed with $100,000 in debt with an expected return of 10%. Your firm's overall cost
of capital is 14%. Compute the firm value using both the APV and WACC methods.
(Assume a one-year life.)
pays taxes at the marginal rate of 40%. Assume, too, that your firm is partially
financed with $100,000 in debt with an expected return of 10%. Your firm's overall cost
of capital is 14%. Compute the firm value using both the APV and WACC methods.
(Assume a one-year life.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A 3-year project will cost $180 at the end of year 1 and is expected to produce operating profit before depreciation and amortization (EBITDA)of $80 in year 1, $100 in year 2, and $60 in year 3. Depreciation, both real and financial, will be calculated using straight-line depreciation over 3 years. The cost of capital is 10%, and the firm's marginal tax rate is 25%.
Refer to the information above. Calculate the project IRR if 100% equity financing is used.
A)13.4%
B)29.8%
C)11.1%
D)12.5%
Refer to the information above. Calculate the project IRR if 100% equity financing is used.
A)13.4%
B)29.8%
C)11.1%
D)12.5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A firm is currently financed with $300 of debt and $700 of equity. The expected return on the debt is 9%. The market beta of the firm's equity is 1.50; the risk-free rate is 4%; and the equity premium is 6%. The firm pays taxes at the marginal rate of 35%.
Refer to the information above. What is the firm's WACC? Round your answer to the nearest tenth of a percent.
A)7.7%
B)10.0%
C)11.8%
D)none of the above
Refer to the information above. What is the firm's WACC? Round your answer to the nearest tenth of a percent.
A)7.7%
B)10.0%
C)11.8%
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A 3-year project will cost $180 at the end of year 1 and is expected to produce operating profit before depreciation and amortization (EBITDA)of $80 in year 1, $100 in year 2, and $60 in year 3. Depreciation, both real and financial, will be calculated using straight-line depreciation over 3 years. The cost of capital is 10%, and the firm's marginal tax rate is 25%.
Refer to the information above. Calculate the project NPV if 100% equity financing is used.
A)$7.64
B)$38.40
C)$24.00
D)$187.64
Refer to the information above. Calculate the project NPV if 100% equity financing is used.
A)$7.64
B)$38.40
C)$24.00
D)$187.64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A firm's investments cost $100,000 and are expected to return $118,000 before taxes at the end of 1 year. The firm is financed with $30,000 debt at an expected rate of 8%. The firm pays taxes at the marginal rate of 40%, and the appropriate cost of capital is 12%.
Refer to the information above. What is the firm's adjusted present value (APV)?
A)$99,786
B)$99,889
C)$109,643
D)$101,072
Refer to the information above. What is the firm's adjusted present value (APV)?
A)$99,786
B)$99,889
C)$109,643
D)$101,072

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The overall cost of capital for Canton Corporation is 10%. The firm is financed with 30% debt that offers a promised return of 15% and has an expected return of 8%. Canton is in the 40% marginal tax bracket.
Refer to the information above. What is Canton's weighted average cost of capital?
A)9.0%
B)7.6%
C)9.7%
D)8.6%
Refer to the information above. What is Canton's weighted average cost of capital?
A)9.0%
B)7.6%
C)9.7%
D)8.6%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A 3-year project will cost $180 at the end of year 1 and is expected to produce operating profit before depreciation and amortization (EBITDA)of $80 in year 1, $100 in year 2, and $60 in year 3. Depreciation, both real and financial, will be calculated using straight-line depreciation over 3 years. The cost of capital is 10%, and the firm's marginal tax rate is 25%.
Refer to the information above. Assume the firm will issue $100 of debt in year 1 with an expected interest rate of 8%. Interest must be paid each of the 3 years, and the principal is
Repaid at the end of year 3. What is the present value of the tax savings?
A)$19.89
B)$4.97
C)$3.47
D)$24.00
Refer to the information above. Assume the firm will issue $100 of debt in year 1 with an expected interest rate of 8%. Interest must be paid each of the 3 years, and the principal is
Repaid at the end of year 3. What is the present value of the tax savings?
A)$19.89
B)$4.97
C)$3.47
D)$24.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The pro forma income statements and excerpts from the pro forma cash flow statements of Lazy R Stables for the next 5 years are provided below. The overall cost of capital of the firm is 18%. 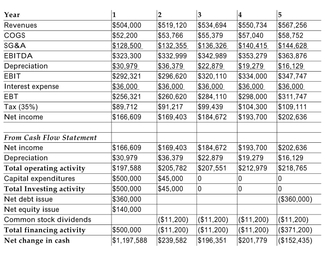
Refer to the information above. Calculate the value of the firm using NPV.

Refer to the information above. Calculate the value of the firm using NPV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If Congress were to pass a law allowing only half a firm's interest expense to be tax deductible, how would this affect the relative value of firms, all else equal?
A)It would increase the value of firms with lower marginal tax rates the most.
B)It would affect only the net income, not firm value.
C)It would decrease the value of firms with higher marginal tax rates the most.
D)It would increase the value of firms with higher marginal tax rates the most.
A)It would increase the value of firms with lower marginal tax rates the most.
B)It would affect only the net income, not firm value.
C)It would decrease the value of firms with higher marginal tax rates the most.
D)It would increase the value of firms with higher marginal tax rates the most.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Under which of the following circumstances might the WACC valuation method be the most useful?
A)when the firm negotiates a better interest rate on its debt than it should have received
B)when the firm is forced to pay a higher interest rate on its debt than is "fair"
C)when the firm's debt ratio is expected to remain fairly constant in the future
D)Both B and C are instances in which the WACC valuation method will be the most useful.
A)when the firm negotiates a better interest rate on its debt than it should have received
B)when the firm is forced to pay a higher interest rate on its debt than is "fair"
C)when the firm's debt ratio is expected to remain fairly constant in the future
D)Both B and C are instances in which the WACC valuation method will be the most useful.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The advantage of the adjusted present value valuation method is that
A)it makes it easier to determine how an extra dollar of debt will increase firm value than do the other two methods.
B)it makes it easier to determine how a target ratio change in capital structure will affect the firm value than do the other two methods.
C)it makes it easier to determine how an extra percentage in debt will increase firm value than do the other two methods.
D)it makes it less likely that you will use an incorrect expected cash flow in your calculation than do the other two methods.
A)it makes it easier to determine how an extra dollar of debt will increase firm value than do the other two methods.
B)it makes it easier to determine how a target ratio change in capital structure will affect the firm value than do the other two methods.
C)it makes it easier to determine how an extra percentage in debt will increase firm value than do the other two methods.
D)it makes it less likely that you will use an incorrect expected cash flow in your calculation than do the other two methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Assume a U.S. company is in a 45% marginal tax bracket. The company has found a small Caribbean island on which corporate income is taxed at only 5% and has opened a branch on
The island. If the company now has a patent worth $25 million a year that it transfers to the
Island branch, how much will it save a year in taxes?
A)$10 million
B)$11.25 million
C)$1.25 million
D)$1 million
The island. If the company now has a patent worth $25 million a year that it transfers to the
Island branch, how much will it save a year in taxes?
A)$10 million
B)$11.25 million
C)$1.25 million
D)$1 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
You have collected the following information for your firm: 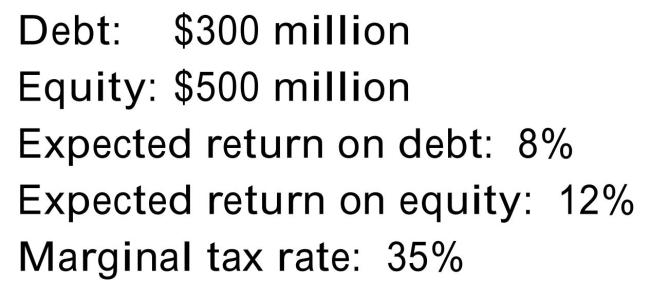 Your firm is contemplating increasing its debt by $100 million and using the funds to repurchase $100 million in equity. The debt would be perpetual and would have a perpetual
Your firm is contemplating increasing its debt by $100 million and using the funds to repurchase $100 million in equity. The debt would be perpetual and would have a perpetual
Expected return of 8.5%. The firm's current marginal tax is also expected to be permanent.
What will this change do to the value of the firm?
A)It will decrease firm value by $20 million.
B)It will increase firm value by 35 million.
C)It will increase firm value by $140 million.
D)It will decrease firm value by about $12 million.
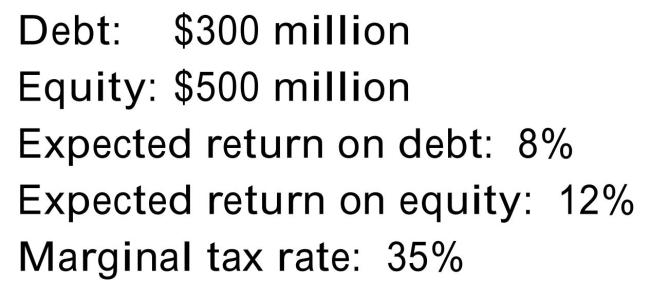 Your firm is contemplating increasing its debt by $100 million and using the funds to repurchase $100 million in equity. The debt would be perpetual and would have a perpetual
Your firm is contemplating increasing its debt by $100 million and using the funds to repurchase $100 million in equity. The debt would be perpetual and would have a perpetualExpected return of 8.5%. The firm's current marginal tax is also expected to be permanent.
What will this change do to the value of the firm?
A)It will decrease firm value by $20 million.
B)It will increase firm value by 35 million.
C)It will increase firm value by $140 million.
D)It will decrease firm value by about $12 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The ForeverMore Corporation plans to issue $600,000 in additional debt. The debt will be a perpetuity with an interest rate of 6%. The firm expects to be in a 35% marginal tax bracket
Permanently. How much will this debt issue increase the value of the firm?
A)$12,600
B)$210,000
C)$390,000
D)$23,400
Permanently. How much will this debt issue increase the value of the firm?
A)$12,600
B)$210,000
C)$390,000
D)$23,400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following statements is true regarding the correct discount rate to use when discounting a firm's expected tax obligations.
A)Tax obligations should be discounted separately using the risk-free rate of interest since management has no control over them.
B)Tax obligations should usually be discounted separately using the firm's weighted average cost of capital, WACC.
C)Tax obligations should be discounted using the firm's overall cost of capital,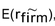 , since they are risky and are positively correlated with the firm's return, regardless of the
, since they are risky and are positively correlated with the firm's return, regardless of the
Financing method used.
D)Tax obligations should be discounted with the cash flows from debt obligations at the expected rate of return on debt.
A)Tax obligations should be discounted separately using the risk-free rate of interest since management has no control over them.
B)Tax obligations should usually be discounted separately using the firm's weighted average cost of capital, WACC.
C)Tax obligations should be discounted using the firm's overall cost of capital,
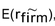 , since they are risky and are positively correlated with the firm's return, regardless of the
, since they are risky and are positively correlated with the firm's return, regardless of theFinancing method used.
D)Tax obligations should be discounted with the cash flows from debt obligations at the expected rate of return on debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What two assumptions are made when calculating how much an increase in debt will
increase firm value using the following formula: Value Increase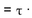 Debt?
Debt?
increase firm value using the following formula: Value Increase
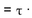 Debt?
Debt?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Calculate the IRR of the firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The Feline Corporation has $50,000 debt with a required return of 9%. The firm is in
the 40% marginal tax bracket, and the debt is perpetual. What is the annual interest tax
shield? What is the present value of the interest tax shield?
the 40% marginal tax bracket, and the debt is perpetual. What is the annual interest tax
shield? What is the present value of the interest tax shield?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The pro forma income statement and cash flow statement for OneShot, Inc., are provided below. The firm has a cost of capital of 10%. 




Refer to the income statement and cash flow statement above. What is the value of OneShot's tax shield in the year for which the pro formas are estimated?
A)$2,300
B)$920
C)$1,541
D)none of the above





Refer to the income statement and cash flow statement above. What is the value of OneShot's tax shield in the year for which the pro formas are estimated?
A)$2,300
B)$920
C)$1,541
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Calculate the value of the firm using the APV method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If you have limited time in which to conduct you analysis, to which should you devote
more attention: estimating expected cash flows or estimating the discount rate to use
on the expected cash flow? Why?
more attention: estimating expected cash flows or estimating the discount rate to use
on the expected cash flow? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The advantage of the Flow-to-Equity valuation method is that
A)it makes it easier to determine how an extra dollar of debt will increase firm value than do the other two methods.
B)it makes it less likely that you will use an incorrect expected cash flow in your calculation than do the other two methods.
C)it makes it easier to determine how a target ratio change in capital structure will affect the firm value than do the other two methods.
D)it makes it easier to consider the tax-induced consequences of proposed capital structure changes than do the other two methods.
A)it makes it easier to determine how an extra dollar of debt will increase firm value than do the other two methods.
B)it makes it less likely that you will use an incorrect expected cash flow in your calculation than do the other two methods.
C)it makes it easier to determine how a target ratio change in capital structure will affect the firm value than do the other two methods.
D)it makes it easier to consider the tax-induced consequences of proposed capital structure changes than do the other two methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following statements regarding capital structure decisions in a world with taxes is true?
A)Even if the same amount of investment dollars is required, one project may offer a higher tax shelter than another project.
B)Firms with higher marginal tax rates will not receive as much benefit from using debt as firms with lower marginal tax rates.
C)Even in a world with taxes, the investment and financing decisions can remain separate.
D)None of the above is a true statement.
A)Even if the same amount of investment dollars is required, one project may offer a higher tax shelter than another project.
B)Firms with higher marginal tax rates will not receive as much benefit from using debt as firms with lower marginal tax rates.
C)Even in a world with taxes, the investment and financing decisions can remain separate.
D)None of the above is a true statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If the U.S. government were able to eliminate all possible corporate tax avoidance schemes, which of the following is likely to occur?
A)Investors in U.S. corporations will be better off.
B)Investors in U.S. corporations will be worse off.
C)More corporations will want to be domiciled in the U.S. because they will face a fairer competitive environment.
D)Both B and C are likely to occur.
A)Investors in U.S. corporations will be better off.
B)Investors in U.S. corporations will be worse off.
C)More corporations will want to be domiciled in the U.S. because they will face a fairer competitive environment.
D)Both B and C are likely to occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How can the common practice of using a firm's overall cost of capital rather than its cost of debt as a discount rate when calculating the present value of tax savings be justified?
A)The debt policy of the firm will cause the amount of its tax shelter to increase as the firm grows larger and the firm borrows more debt. Thus, the tax shelter will grow as firm
Value increases.
B)Because tax savings are usually relatively small, the difference in the discount rate used doesn't make a large difference in the present value.
C)It is never justifiable; tax savings should always be discounted using the firm's cost of debt since these cash flows are in the same risk category as the firm's debt cash flows.
D)Both A and B are legitimate justifications.
A)The debt policy of the firm will cause the amount of its tax shelter to increase as the firm grows larger and the firm borrows more debt. Thus, the tax shelter will grow as firm
Value increases.
B)Because tax savings are usually relatively small, the difference in the discount rate used doesn't make a large difference in the present value.
C)It is never justifiable; tax savings should always be discounted using the firm's cost of debt since these cash flows are in the same risk category as the firm's debt cash flows.
D)Both A and B are legitimate justifications.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The advantage of the WACC valuation method is that
A)it makes it easier to determine how an extra dollar of debt will increase firm value than do the other two methods.
B)it is more adaptable for multi-period use than the other two methods.
C)it makes it easier to determine how a target ratio change in capital structure will affect the firm value than do the other two methods.
D)it makes it less likely that you will use an incorrect expected cash flow in your calculation than do the other two methods.
A)it makes it easier to determine how an extra dollar of debt will increase firm value than do the other two methods.
B)it is more adaptable for multi-period use than the other two methods.
C)it makes it easier to determine how a target ratio change in capital structure will affect the firm value than do the other two methods.
D)it makes it less likely that you will use an incorrect expected cash flow in your calculation than do the other two methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is true regarding a reasonable choice for a discount rate to apply to interest tax savings?
A)If the firm is expected to increase its debt ratio, you should use the expected return on the firm's debt,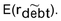
B)If the firm is expected to maintain a constant debt ratio, you should use the firm's weighted average cost of capital, WACC.
C)If the firm is expected to decrease its debt ratio, you should use the expected return on the firm's equity,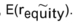
D)None of the above is a true statement.
A)If the firm is expected to increase its debt ratio, you should use the expected return on the firm's debt,
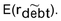
B)If the firm is expected to maintain a constant debt ratio, you should use the firm's weighted average cost of capital, WACC.
C)If the firm is expected to decrease its debt ratio, you should use the expected return on the firm's equity,
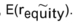
D)None of the above is a true statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



