Deck 5: Why Linking Exposure and Disease
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/10
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Why Linking Exposure and Disease
1
1000 adults who presented to their local emergency department with a possible heart attack had a blood sample collected for laboratory tests.It was later found that 300 of
These people had not had a heart attack and the levels of triglycerides in the blood of
This group were compared with the levels among the 700 who had had a heart attack
Giving the following results: The odds ratio for the association between high triglycerides and heart attack is:
The odds ratio for the association between high triglycerides and heart attack is:
A)3.0
B)6.0
C)12.0
D)2.3
E)It cannot be calculated from the data shown
These people had not had a heart attack and the levels of triglycerides in the blood of
This group were compared with the levels among the 700 who had had a heart attack
Giving the following results:
 The odds ratio for the association between high triglycerides and heart attack is:
The odds ratio for the association between high triglycerides and heart attack is:A)3.0
B)6.0
C)12.0
D)2.3
E)It cannot be calculated from the data shown
12.0
2
In the first 12 years of follow‐up of the Framingham Heart Study, the observed number of cases of angina was 1.6 times higher than the number expected based on
Population rates.What type of measure is this?
A)Prevalence rate
B)Incidence rate ratio
C)Risk ratio
D)Adjusted incidence rate
E)Standardised incidence (or morbidity) ratio
Population rates.What type of measure is this?
A)Prevalence rate
B)Incidence rate ratio
C)Risk ratio
D)Adjusted incidence rate
E)Standardised incidence (or morbidity) ratio
Standardised incidence (or morbidity) ratio
3
A randomised, placebo‐controlled trial was conducted in Indonesia to study the effects of vitamin A in preventing deaths among children with measles.The investigators
Reported a relative risk of 0.60 for the intervention versus control group.This means
That:
A)Children receiving vitamin A were 40% less likely to die from measles than children receiving placebo
B)Children receiving vitamin A were 60% less likely to die from measles than children receiving placebo
C)The chance of dying from measles in the placebo group was 60%
D)60% of the children who died received vitamin A; the other 40% received placebo
E)None of the above statements is true
Reported a relative risk of 0.60 for the intervention versus control group.This means
That:
A)Children receiving vitamin A were 40% less likely to die from measles than children receiving placebo
B)Children receiving vitamin A were 60% less likely to die from measles than children receiving placebo
C)The chance of dying from measles in the placebo group was 60%
D)60% of the children who died received vitamin A; the other 40% received placebo
E)None of the above statements is true
Children receiving vitamin A were 40% less likely to die from measles than children receiving placebo
4
Which of the following factors will influence the population attributable fraction? (Select all that apply)
A)The relative risk of disease associated with exposure
B)The incidence of the disease
C)The prevalence of the exposure
D)The prevalence of the disease
E)All of the above
A)The relative risk of disease associated with exposure
B)The incidence of the disease
C)The prevalence of the exposure
D)The prevalence of the disease
E)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The following table shows data from an epidemiological study.What is the rate difference? 
A)22.6 per 100 py
B)22.6 per 100,000 py
C)12.1 per 100,000 py
D)10.5 per 100 py
E)2.7
F)0.37

A)22.6 per 100 py
B)22.6 per 100,000 py
C)12.1 per 100,000 py
D)10.5 per 100 py
E)2.7
F)0.37

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In a study to determine whether tonsillectomy is associated with subsequent development of Hodgkin's disease, the estimated relative risk for those with prior
Tonsillectomy was found to be 1.9.From this we can conclude:
A)The case fatality rate is higher among patients who have had a prior tonsillectomy
B)The incidence of Hodgkin's disease is higher among those who had a prior tonsillectomy
C)Tonsillectomy appears to protect against the development of Hodgkin's disease
D)Tonsillectomy should not be performed because it increases the risk of Hodgkin's disease
E)None of the above
Tonsillectomy was found to be 1.9.From this we can conclude:
A)The case fatality rate is higher among patients who have had a prior tonsillectomy
B)The incidence of Hodgkin's disease is higher among those who had a prior tonsillectomy
C)Tonsillectomy appears to protect against the development of Hodgkin's disease
D)Tonsillectomy should not be performed because it increases the risk of Hodgkin's disease
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the population attributable risk in the same study? 
A)22.6 per 100 py
B)22.6 per 100,000 py
C)2.7
D)12.1 per 100 py
E)10.5 per 100 py
F)Noneoftheabove

A)22.6 per 100 py
B)22.6 per 100,000 py
C)2.7
D)12.1 per 100 py
E)10.5 per 100 py
F)Noneoftheabove

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following measures is most useful for assessing the potential benefits of a preventive programme?
A)Relative risk
B)Odds ratio
C)Attributable fraction
D)Population attributable fraction
E)Case fatality rate
A)Relative risk
B)Odds ratio
C)Attributable fraction
D)Population attributable fraction
E)Case fatality rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
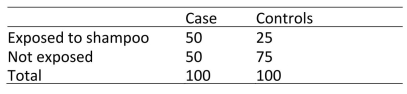
To assess the association between Kawasaki syndrome (KS) and carpet shampoo, investigators conducted a case‐control study with 100 cases (children with KS) and 100
Controls (children without KS).Among the children with KS, 50 had a history of recent
Exposure to carpet shampoo.Among the controls, the number with a recent history of
Exposure to carpet shampoo was 25.For this study, the odds ratio was:
A)1.0
B)2.0
C)3.0
D)Cannot be calculated from the information given
Controls (children without KS).Among the children with KS, 50 had a history of recent
Exposure to carpet shampoo.Among the controls, the number with a recent history of
Exposure to carpet shampoo was 25.For this study, the odds ratio was:
A)1.0
B)2.0
C)3.0
D)Cannot be calculated from the information given


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The strength of an association between exposure and disease is best measured by the:
A)Incidence rate of disease in the exposed group
B)Attributable risk
C)Attributable fraction
D)Population attributable risk
E)Relative risk
A)Incidence rate of disease in the exposed group
B)Attributable risk
C)Attributable fraction
D)Population attributable risk
E)Relative risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



