Deck 11: Pure Competition in the Long Run
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/250
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Pure Competition in the Long Run
1
In purely competitive market, the entry and exit of firms will push price toward equality with marginal revenue.
False
2
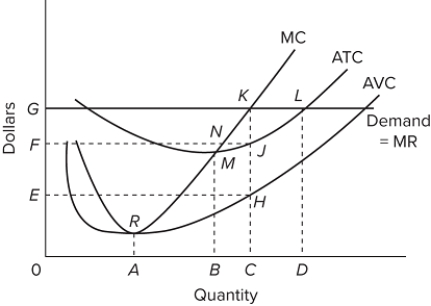 If this diagram represents a typical firm in the industry and the firm is producing at the profit-maximizing level of output in the short run, then in the long run we would expect economic profits in this market to rise.
If this diagram represents a typical firm in the industry and the firm is producing at the profit-maximizing level of output in the short run, then in the long run we would expect economic profits in this market to rise.False
3
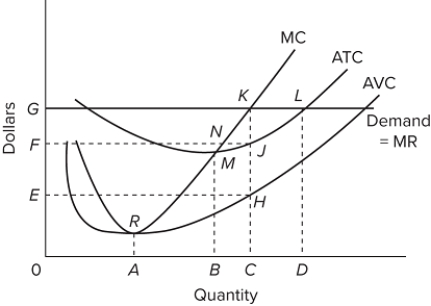 If the firm shown in this graph is producing at the profit-maximizing level of output in the short run, then it is achieving productive and allocative efficiency.
If the firm shown in this graph is producing at the profit-maximizing level of output in the short run, then it is achieving productive and allocative efficiency.False
4
When a competitive firm sees losses because the product price falls below the minimum average cost of production at its current plant, it may decide to expand if there are economies of scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the long run for a purely competitive market, firms will earn only normal profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When a competitive firm is in long-run equilibrium, its accounting profits are greater than zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When entrepreneurs in competitive industries successfully innovate to lower production costs, it usually results in long-run economic profits for the firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The long-run supply curve for a decreasing-cost industry is downsloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
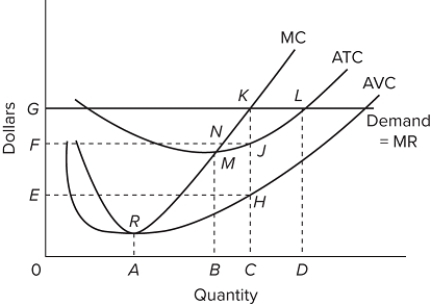 If this diagram represents a typical firm in the industry and the firm is producing at the profit-maximizing level of output in the short run, then in the long run we would expect more firms to enter the market.
If this diagram represents a typical firm in the industry and the firm is producing at the profit-maximizing level of output in the short run, then in the long run we would expect more firms to enter the market.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Marginal cost is a measure of the alternative goods that society forgoes in using resources to produce an additional unit of some specific product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The process by which new firms and new products destroy existing dominant firms and their products is called creative destruction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When a competitive firm sees the price fall below the minimum possible average total cost in the long run, then it will decide that it could do better by moving to a different industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
It is possible for a competitive firm that is maximizing profits in the short run to make its profits even bigger in the long run by expanding its plant, assuming that the product price stays the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Allocative efficiency is achieved by equalizing consumer surplus and producer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When a profit-maximizing competitive firm decides to produce at a loss because its price is below average cost but above average variable cost, that is a long-run decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Long-run supply curves for a purely competitive industry can never be downsloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the long run, assuming that market demand stays the same, if firms in a competitive industry expand, then the product price will tend to fall as a result.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Because the equilibrium position of a purely competitive seller entails an equality of price and marginal costs, competition produces an efficient allocation of economic resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Suppose that a competitive firm finds that in its short-run equilibrium situation, its marginal cost is higher than its average total cost. If things are not expected to change and there are constant returns to scale, then the firm will exit the industry in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the long run for a purely competitive market, firms may enter or exit the industry, but the firms that stay in the industry will maintain their initial plant sizes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An underallocation of resources is occurring in a purely competitive industry whenever the price of the product is greater than marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The transformative effects of competition that foster the development of new products or new production methods benefit everyone in society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
An upward-sloping long-run supply curve indicates a constant-cost industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the long run, pure competition forces firms to produce at the minimum possible average total cost and the firms will charge a product price equal to that cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When firms in a purely competitive industry are earning profits that are greater than normal, the supply of the product will tend to decrease in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The long-run supply curve for a competitive, decreasing-cost industry is downward-sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When some firms leave a purely competitive industry, the market supply curve will shift in such a way that the remaining firms' profits will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The operation of the invisible hand means the pursuit of private interests promotes social interests in pure competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Producer surplus is the difference between the market price a producer receives for a product and the minimum price producers are willing to accept for a product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The reason why the long-run supply curve for a purely competitive industry may be upward-sloping is because of diminishing marginal returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A purely competitive firm that is earning positive profits in its short-run equilibrium situation will continue to earn positive profits at the long-run equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In pure competition, resources are optimally or efficiently allocated when production occurs at the output level where P = MC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The short-run supply curve of a purely competitive industry tends to be steeper than the long-run supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When new firms enter a purely competitive industry, the market supply curve will shift to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In long-run equilibrium, a competitive firm produces where P = MR = MC = minimum ATC and the firm earns normal economic profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Productive efficiency refers to a condition where marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Efficiency or deadweight losses occur in purely competitive markets when P = MC = lowest ATC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the price in a competitive market falls and goes below the equilibrium price, then consumer surplus might increase, but producer surplus will definitely decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Consumer surplus is the difference between the maximum price a consumer is willing to pay for a good and the market price of the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Competitive markets produce equilibrium prices and quantities that minimize the sum of consumer and producer surpluses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Creative destruction is something that our society should try to avoid, through government regulation of business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The costs of competition's creative destruction are often widespread, while the benefits often accrue to only a few.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The primary force encouraging the entry of new firms into a purely competitive industry is
A)normal profits earned by firms already in the industry.
B)economic profits earned by firms already in the industry.
C)government subsidies for start-up firms.
D)a desire to provide goods for the betterment of society.
A)normal profits earned by firms already in the industry.
B)economic profits earned by firms already in the industry.
C)government subsidies for start-up firms.
D)a desire to provide goods for the betterment of society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In a purely competitive industry,
A)there will be no economic profits in either the short run or the long run.
B)economic profits may persist in the long run if consumer demand is strong and stable.
C)there may be economic profits in the short run but not in the long run.
D)there may be economic profits in the long run but not in the short run.
A)there will be no economic profits in either the short run or the long run.
B)economic profits may persist in the long run if consumer demand is strong and stable.
C)there may be economic profits in the short run but not in the long run.
D)there may be economic profits in the long run but not in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Augi's Art Shack sells art supplies in a perfectly competitive market. The firm is currently realizing economic profits of $85,000 in the short run. In the long run we would expect Augi's to
A)realize economic profits greater than $0 but less than $85,000.
B)realize economic profits of $0.
C)realize economic losses greater than $0 but smaller than $85,000
D)shut down.
A)realize economic profits greater than $0 but less than $85,000.
B)realize economic profits of $0.
C)realize economic losses greater than $0 but smaller than $85,000
D)shut down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Balin's Burger Barn operates in a perfectly competitive market. Balin's is currently earning economic profits of $20,000 per year. Based on this information, we can conclude that
A)Balin's profits will discourage new firms from entering.
B)Balin's will increase its market price over the coming months.
C)Balin's is operating in the short run, but not the long run.
D)Balin's is operating in the long run.
A)Balin's profits will discourage new firms from entering.
B)Balin's will increase its market price over the coming months.
C)Balin's is operating in the short run, but not the long run.
D)Balin's is operating in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Assume a purely competitive decreasing-cost industry is in long-run equilibrium. If an increase in demand occurs, firms will
A)enter the industry, price will rise, and quantity produced will fall.
B)leave the industry and price and quantity will both fall.
C)enter the industry and price and quantity will both rise.
D)enter the industry, price will fall, and quantity produced will rise.
A)enter the industry, price will rise, and quantity produced will fall.
B)leave the industry and price and quantity will both fall.
C)enter the industry and price and quantity will both rise.
D)enter the industry, price will fall, and quantity produced will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following distinguishes the short run from the long run in pure competition?
A)Firms can enter and exit the market in the long run but not in the short run.
B)Firms attempt to maximize profits in the long run but not in the short run.
C)Firms use the MR = MC rule to maximize profits in the short run but not in the long run.
D)The quantity of labor hired can vary in the long run but not in the short run.
A)Firms can enter and exit the market in the long run but not in the short run.
B)Firms attempt to maximize profits in the long run but not in the short run.
C)Firms use the MR = MC rule to maximize profits in the short run but not in the long run.
D)The quantity of labor hired can vary in the long run but not in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Purely competitive industry X has decreasing costs and its product is an inferior good. The industry is currently in long-run equilibrium. The economy now goes into a recession and average incomes decline. The result will be
A)an increase in output and in the price of the product.
B)an increase in output, but not in the price of the product.
C)a decrease in the output, but not in the price of the product.
D)a decrease in output and in the price of the product.
A)an increase in output and in the price of the product.
B)an increase in output, but not in the price of the product.
C)a decrease in the output, but not in the price of the product.
D)a decrease in output and in the price of the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Assume a purely competitive constant-cost industry is initially in long-run equilibrium, producing 9 million units at a market price of $18.00. Suppose that an increase in consumer demand occurs. After all economic adjustments have been completed, which output and price combination is most likely to occur?
A)9.5 units at a price of $19.25.
B)10 units at a price of $18.00.
C)9 units at a price of $20.00.
D)8 units at a price of $18.00.
A)9.5 units at a price of $19.25.
B)10 units at a price of $18.00.
C)9 units at a price of $20.00.
D)8 units at a price of $18.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
From the viewpoint of a firm, competition can come even from other firms that are not in the same industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Suppose that Betty's Beads is a typical firm operating in a perfectly competitive market. Currently Betty's MR = $25, MC = $23, ATC = $20, and AVC = $16. Based on this information, we can conclude that
A)Betty's is in long-run equilibrium.
B)Betty's experience will encourage new firms to enter the market.
C)Betty's experience will encourage some existing firms in this market to leave.
D)Betty's experience will discourage firms from entering the market.
A)Betty's is in long-run equilibrium.
B)Betty's experience will encourage new firms to enter the market.
C)Betty's experience will encourage some existing firms in this market to leave.
D)Betty's experience will discourage firms from entering the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If the price of bottled water is $1.00 and the marginal cost of producing it is $1.50,
A)bottled water is being produced in an increasing-cost industry.
B)society will realize a net gain if more bottled water is produced.
C)resources are being overallocated to bottled water.
D)resources are being underallocated to all other goods.
A)bottled water is being produced in an increasing-cost industry.
B)society will realize a net gain if more bottled water is produced.
C)resources are being overallocated to bottled water.
D)resources are being underallocated to all other goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Creative destruction entails both costs as well as benefits to society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Suppose a firm in a purely competitive market discovers that the price of its product is above its minimum AVC point but everywhere below ATC. Given this, the firm
A)minimizes losses by producing at the minimum point of its AVC curve.
B)maximizes profits by producing where MR = ATC.
C)should close down immediately.
D)should continue producing in the short run but leave the industry in the long run if the situation persists.
A)minimizes losses by producing at the minimum point of its AVC curve.
B)maximizes profits by producing where MR = ATC.
C)should close down immediately.
D)should continue producing in the short run but leave the industry in the long run if the situation persists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Suppose that the corn market is purely competitive. If the corn farmers are currently earning negative economic profits, then we would expect that in the long run the firm's
A)demand will increase.
B)demand will decrease.
C)supply will increase.
D)supply will decrease.
A)demand will increase.
B)demand will decrease.
C)supply will increase.
D)supply will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If a purely competitive increasing-cost industry is realizing economic losses, we can expect industry supply to
A)decrease, output to fall, price to rise, and profits to rise.
B)decrease, output to fall, price to fall, and profits to rise.
C)increase, output to rise, price to fall, and profits to rise.
D)decrease, output to rise, price to rise, and profits to rise.
A)decrease, output to fall, price to rise, and profits to rise.
B)decrease, output to fall, price to fall, and profits to rise.
C)increase, output to rise, price to fall, and profits to rise.
D)decrease, output to rise, price to rise, and profits to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If the price of product Y is $14 and its marginal cost is $18,
A)Y is being produced with the least-cost combination of resources.
B)society will realize a net gain if more of Y is produced.
C)resources are being overallocated to Y.
D)resources are being underallocated to Y.
A)Y is being produced with the least-cost combination of resources.
B)society will realize a net gain if more of Y is produced.
C)resources are being overallocated to Y.
D)resources are being underallocated to Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In pure competition, if the market price of the product is lower than the minimum average total cost of the firms, then
A)some firms will enter the industry and the industry supply will increase.
B)other firms will exit the industry and the industry supply will decrease.
C)some firms will exit the industry and the industry supply will increase.
D)other firms will enter the industry and the industry supply will decrease.
A)some firms will enter the industry and the industry supply will increase.
B)other firms will exit the industry and the industry supply will decrease.
C)some firms will exit the industry and the industry supply will increase.
D)other firms will enter the industry and the industry supply will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
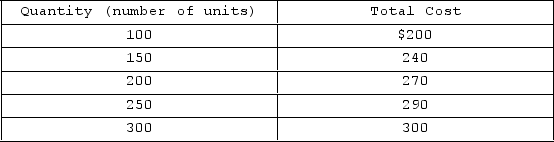 Suppose the table above represents the long-run cost structure for a firm in a perfectly competitive industry. Based on this information we can conclude that this firm operates in
Suppose the table above represents the long-run cost structure for a firm in a perfectly competitive industry. Based on this information we can conclude that this firm operates inA)an industry incapable of reaching long-run equilibrium.
B)a decreasing- cost industry.
C)an increasing-cost industry.
D)a constant-cost industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Long-run adjustments in purely competitive markets primarily take the form of
A)variations in the cost curves of different firms in the market.
B)entry or exit of firms in the market.
C)evolution of the market from a constant-cost to an increasing-cost industry.
D)product differentiation.
A)variations in the cost curves of different firms in the market.
B)entry or exit of firms in the market.
C)evolution of the market from a constant-cost to an increasing-cost industry.
D)product differentiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following is true concerning purely competitive industries?
A)There will be economic losses in the long run because of cut-throat competition.
B)Economic profits will persist in the long run if consumer demand is strong and stable.
C)In the short run, firms may incur economic losses or earn economic profits, but in the long run they earn normal profits.
D)There are economic profits in the long run but not in the short run.
A)There will be economic losses in the long run because of cut-throat competition.
B)Economic profits will persist in the long run if consumer demand is strong and stable.
C)In the short run, firms may incur economic losses or earn economic profits, but in the long run they earn normal profits.
D)There are economic profits in the long run but not in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Karlee's Kreations sells handbags in a purely competitive market. Karlee's is currently breaking even. Based on this information, we can conclude that Karlee's Kreations
A)must be operating in long-run equilibrium.
B)will leave this market in the long run because no economic profits are being earned.
C)will continue operating in this market only if the market price rises.
D)may be operating in either short-run or long-run equilibrium.
A)must be operating in long-run equilibrium.
B)will leave this market in the long run because no economic profits are being earned.
C)will continue operating in this market only if the market price rises.
D)may be operating in either short-run or long-run equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Long-run competitive equilibrium
A)is realized only in constant-cost industries.
B)will never change once it is realized.
C)is not economically efficient.
D)results in zero economic profits.
A)is realized only in constant-cost industries.
B)will never change once it is realized.
C)is not economically efficient.
D)results in zero economic profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If a purely competitive firm is producing at the MR = MC output level and earning an economic profit, then
A)the selling price for this firm is above the market equilibrium price.
B)new firms will enter this market.
C)some existing firms in this market will leave.
D)there must be price fixing by the industry's firms.
A)the selling price for this firm is above the market equilibrium price.
B)new firms will enter this market.
C)some existing firms in this market will leave.
D)there must be price fixing by the industry's firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
We would expect an industry to expand if firms in that industry are
A)earning normal profits.
B)earning economic profits.
C)breaking even.
D)earning accounting profits.
A)earning normal profits.
B)earning economic profits.
C)breaking even.
D)earning accounting profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If the entry or exit of firms does not affect the resource prices in an industry, we refer to it as a
A)fixed-price industry.
B)price-controlled industry.
C)constant-cost industry.
D)price-taking industry.
A)fixed-price industry.
B)price-controlled industry.
C)constant-cost industry.
D)price-taking industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
All of the following are long-run changes, except
A)an industry expanding as more firms enter it.
B)a firm moving into larger production facilities to expand production.
C)some firms deciding to leave an industry and the industry contracts.
D)a firm producing more output by acquiring more raw materials for its existing factory.
A)an industry expanding as more firms enter it.
B)a firm moving into larger production facilities to expand production.
C)some firms deciding to leave an industry and the industry contracts.
D)a firm producing more output by acquiring more raw materials for its existing factory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is not a factor that automatically pushes firms in pure competition to earn only normal profits in the long run?
A)entry of new firms
B)exit of some firms
C)changes in the firms' plant size
D)changes in the market demand
A)entry of new firms
B)exit of some firms
C)changes in the firms' plant size
D)changes in the market demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
All of the following statements apply to a purely competitive market in the long run, except
A)in the long run, all inputs are variable in quantity.
B)firms can expand their plant capacities in the long run.
C)total fixed costs remain constant even when output expands in the long run.
D)firms may enter or leave the industry in the long run.
A)in the long run, all inputs are variable in quantity.
B)firms can expand their plant capacities in the long run.
C)total fixed costs remain constant even when output expands in the long run.
D)firms may enter or leave the industry in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Assume that the market for soybeans is purely competitive. Currently, firms growing soybeans are earning positive economic profits. In the long run, we can expect
A)new firms to enter, causing the market price of soybeans to fall.
B)new firms to enter, causing the market price of soybeans to rise.
C)some firms to exit, causing the market price of soybeans to fall.
D)some firms to exit, causing the market price of soybeans to rise.
A)new firms to enter, causing the market price of soybeans to fall.
B)new firms to enter, causing the market price of soybeans to rise.
C)some firms to exit, causing the market price of soybeans to fall.
D)some firms to exit, causing the market price of soybeans to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Augi's Art Shack sells art supplies in a perfectly competitive market. The firm is currently realizing economic profits of $25,000 in the short run. In the long run we would expect Augi's to
A)realize economic profits greater than $0 but less than $25,000.
B)realize economic profits of $0.
C)realize economic losses greater than $0 but smaller than $25,000
D)shut down.
A)realize economic profits greater than $0 but less than $25,000.
B)realize economic profits of $0.
C)realize economic losses greater than $0 but smaller than $25,000
D)shut down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The representative firm in a purely competitive industry
A)will always earn a profit in the short run.
B)may earn either an economic profit or a loss in the long run.
C)will always earn an economic profit in the long run.
D)will earn zero economic profit in the long run.
A)will always earn a profit in the short run.
B)may earn either an economic profit or a loss in the long run.
C)will always earn an economic profit in the long run.
D)will earn zero economic profit in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Assume that the market for corn is purely competitive. Currently, firms growing corn are suffering economic losses. In the long run, we can expect
A)new firms to enter, causing the market price of corn to fall.
B)new firms to enter, causing the market price of corn to rise.
C)some firms to exit, causing the market price of corn to fall.
D)some firms to exit, causing the market price of corn to rise.
A)new firms to enter, causing the market price of corn to fall.
B)new firms to enter, causing the market price of corn to rise.
C)some firms to exit, causing the market price of corn to fall.
D)some firms to exit, causing the market price of corn to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following is true of normal profits?
A)They are necessary to keep a firm in the industry in the long run.
B)They are zero under pure competition in the long run.
C)They are excluded from a firm's costs of production.
D)They are what attract other firms to enter an industry.
A)They are necessary to keep a firm in the industry in the long run.
B)They are zero under pure competition in the long run.
C)They are excluded from a firm's costs of production.
D)They are what attract other firms to enter an industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following statements about pure competition in the long run is not true?
A)Entry and exit of firms will push economic profits of firms in the industry toward zero.
B)Entry and exit of firms will shift the demand curve facing the representative firm in the industry.
C)The long-run adjustment in pure competition happens through shifts in the industry supply curve.
D)The long-run adjustment in pure competition happens through shifts in the industry demand curve.
A)Entry and exit of firms will push economic profits of firms in the industry toward zero.
B)Entry and exit of firms will shift the demand curve facing the representative firm in the industry.
C)The long-run adjustment in pure competition happens through shifts in the industry supply curve.
D)The long-run adjustment in pure competition happens through shifts in the industry demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In pure competition, if the market price of the product is higher than the minimum average total cost of the firms, then
A)some firms will exit the industry and the industry supply will decrease.
B)other firms will enter the industry and the industry supply will increase.
C)some firms will exit the industry and the industry supply will increase.
D)other firms will enter the industry and the industry supply will decrease.
A)some firms will exit the industry and the industry supply will decrease.
B)other firms will enter the industry and the industry supply will increase.
C)some firms will exit the industry and the industry supply will increase.
D)other firms will enter the industry and the industry supply will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following is not an assumption that we make in analyzing pure competition in the long run?
A)Firms are free to enter into or exit from a purely competitive market.
B)We may talk about a "representative" firm by assuming that competitive firms all have identical cost curves.
C)Firms may increase output by expanding their plant sizes.
D)Profits are not relevant to firm behavior anymore, because competitive firms earn zero profits in the long run.
A)Firms are free to enter into or exit from a purely competitive market.
B)We may talk about a "representative" firm by assuming that competitive firms all have identical cost curves.
C)Firms may increase output by expanding their plant sizes.
D)Profits are not relevant to firm behavior anymore, because competitive firms earn zero profits in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Suppose that Betty's Beads is a typical firm operating in a perfectly competitive market. Currently Betty's MR = $15, MC = $12, ATC = $10, and AVC = $8. Based on this information, we can conclude that
A)Betty's is in long-run equilibrium.
B)Betty's experience will encourage new firms to enter the market.
C)Betty's experience will encourage some existing firms in this market to leave.
D)Betty's experience will discourage firms from entering the market.
A)Betty's is in long-run equilibrium.
B)Betty's experience will encourage new firms to enter the market.
C)Betty's experience will encourage some existing firms in this market to leave.
D)Betty's experience will discourage firms from entering the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Economic profits induce firms to enter an industry; losses encourage firms to leave.
B)Economic profits induce firms to leave an industry; profits encourage firms to leave.
C)Economic profits and losses have no significant impact on the growth or decline of an industry.
D)Normal profits will cause an industry to expand.
A)Economic profits induce firms to enter an industry; losses encourage firms to leave.
B)Economic profits induce firms to leave an industry; profits encourage firms to leave.
C)Economic profits and losses have no significant impact on the growth or decline of an industry.
D)Normal profits will cause an industry to expand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



