Deck 9: Monetary Policy Tools
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/34
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Monetary Policy Tools
1
One emergency lending procedure put into place in 2008 was the creation of the Term Securities Lending Facility. This entity was set up to
A)lend up to $50 billion of Treasury securities to primary securities dealers for a fee.
B)lend up to $200 billion of Treasury securities to primary securities dealers for a fee.
C)lend funding to the Money Market Investor Funding Facility
D)lend funding to any commercial bank that needed it.
A)lend up to $50 billion of Treasury securities to primary securities dealers for a fee.
B)lend up to $200 billion of Treasury securities to primary securities dealers for a fee.
C)lend funding to the Money Market Investor Funding Facility
D)lend funding to any commercial bank that needed it.
B
2
If GDP is $20 trillion and the money supply is $4 trillion, what is the velocity of money?
A)2
B)5
C)16
D)80
A)2
B)5
C)16
D)80
B
3
Which of these is the most often used and the most flexible monetary tool used by the Federal Reserve?
A)Discount window lending
B)Dynamic transactions
C)Open market operations
D)Quantitative easing
A)Discount window lending
B)Dynamic transactions
C)Open market operations
D)Quantitative easing
C
4
Which of these statements best describes why the required reserve ratio is no longer relevant in most cases today?
A)Sweep accounts eliminated the need for the required reserve ratio.
B)Changes in the required reserve ratio can affect the size of the money multiplier.
C)About 70% of banks already have reserves that exceed their level of required reserves.
D)The required reserve ratio rarely had a positive effect in most situations.
A)Sweep accounts eliminated the need for the required reserve ratio.
B)Changes in the required reserve ratio can affect the size of the money multiplier.
C)About 70% of banks already have reserves that exceed their level of required reserves.
D)The required reserve ratio rarely had a positive effect in most situations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When the economy is caught in a liquidity trap, expansionary monetary policy will
A)result in inflation.
B)result in a significant contraction in economic activity.
C)result in a significant expansion of economic activity.
D)have little impact on the economy.
A)result in inflation.
B)result in a significant contraction in economic activity.
C)result in a significant expansion of economic activity.
D)have little impact on the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Irving Fisher's equation of exchange is expressed as
A)MS × PL = V × T.
B)MS/V = PL × T.
C)MS × T = PL × V.
D)V = (PL × T)/MS.
A)MS × PL = V × T.
B)MS/V = PL × T.
C)MS × T = PL × V.
D)V = (PL × T)/MS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Why is it easier for the Fed to manage the level of bank reserves using the term auction facility (TAF)as opposed to using discount window lending?
A)Banks do not need to overcome the stigma of requesting a loan when using the TAF.
B)Banks receive TAF proceeds on a 3-day delay, rather than on the day they are requested.
C)Banks that use seasonal credit are more likely to use the term auction facility.
D)Banks receive TAF proceeds after a lengthy verification process.
A)Banks do not need to overcome the stigma of requesting a loan when using the TAF.
B)Banks receive TAF proceeds on a 3-day delay, rather than on the day they are requested.
C)Banks that use seasonal credit are more likely to use the term auction facility.
D)Banks receive TAF proceeds after a lengthy verification process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the figure below, the loanable funds market is in equilibrium at C with the interest rate IR 1 . In conducting monetary policy, the Federal Reserve engages in the selling of US Treasury securities on the open market, which causes

A)no change in the loanable funds market, so the equilibrium interest rate remains at IR1.
B)the demand for loanable funds to decrease to D, causing the equilibrium interest rate to decrease to IR3.
C)both the demand for loanable funds and the supply of loanable funds to decrease to D and S, respectively, keeping the equilibrium interest rate at IR1.
D)the supply of loanable funds to decrease to S, causing the equilibrium interest rate to increase to IR2.

A)no change in the loanable funds market, so the equilibrium interest rate remains at IR1.
B)the demand for loanable funds to decrease to D, causing the equilibrium interest rate to decrease to IR3.
C)both the demand for loanable funds and the supply of loanable funds to decrease to D and S, respectively, keeping the equilibrium interest rate at IR1.
D)the supply of loanable funds to decrease to S, causing the equilibrium interest rate to increase to IR2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Alistair tells a friend that he likes to deposit his entire paycheck into his checking account just in case prices fall. This is an example of the __________ demand for money.
A)inflationary
B)transactions
C)speculative
D)precautionary
A)inflationary
B)transactions
C)speculative
D)precautionary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
John Maynard Keynes argued that people demand money for three reasons. What are these three reasons?
A)Transactions motive, precautionary motive, and speculative motive
B)Quantity motive, speculative motive, and philanthropic motive
C)Transactions motive, precautionary motive, and familial motive
D)Precautionary motive, speculative motive, and wealth motive
A)Transactions motive, precautionary motive, and speculative motive
B)Quantity motive, speculative motive, and philanthropic motive
C)Transactions motive, precautionary motive, and familial motive
D)Precautionary motive, speculative motive, and wealth motive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The purchase of direct debt and mortgage-backed securities by the Federal Reserve in November 2008 is referred to as
A)qualitative easing.
B)quantitative easing.
C)a repurchase agreement.
D)liquidity easing.
A)qualitative easing.
B)quantitative easing.
C)a repurchase agreement.
D)liquidity easing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If the goal of monetary policy is to keep interest rates stable, the Federal Reserve's response to increases in the demand for money will be to
A)decrease the supply of money.
B)increase the supply of money.
C)hold the supply of money constant.
D)decrease the demand for money.
A)decrease the supply of money.
B)increase the supply of money.
C)hold the supply of money constant.
D)decrease the demand for money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The Federal Reserve notices an increase in the public's desire to hold cash and fears that it may cause an increase in interest rates. To keep interest rates steady, the Federal Reserve would likely execute which of these plans?
A)A repurchase agreement to provide a short-term reduction in the money supply
B)A reverse repurchase agreement to provide a short-term reduction in the money supply
C)A repurchase agreement to provide a short-term boost to the money supply
D)A matched-sale purchase agreement to provide a short-term boost to the money supply
A)A repurchase agreement to provide a short-term reduction in the money supply
B)A reverse repurchase agreement to provide a short-term reduction in the money supply
C)A repurchase agreement to provide a short-term boost to the money supply
D)A matched-sale purchase agreement to provide a short-term boost to the money supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Banks that have some financial difficulty and borrow from the Federal Reserve in what is known as secondary credit will pay an interest rate equal to the
A)discount rate.
B)discount rate plus a penalty.
C)federal funds rate.
D)federal funds rate plus a penalty.
A)discount rate.
B)discount rate plus a penalty.
C)federal funds rate.
D)federal funds rate plus a penalty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Three rounds of extraordinary expansionary monetary policy (QE1, QE2, and QE3)were undertaken by the Fed beginning in November 2008 and ending when?
A)November 2009
B)2011
C)2014
D)2017
A)November 2009
B)2011
C)2014
D)2017

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When the Federal Reserve increases the required reserve ratio, the impact will be to
A)increase the size of the spending multiplier.
B)decrease the size of the spending multiplier.
C)increase the size of the money multiplier.
D)decrease the size of the money multiplier.
A)increase the size of the spending multiplier.
B)decrease the size of the spending multiplier.
C)increase the size of the money multiplier.
D)decrease the size of the money multiplier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A financially healthy bank borrowing overnight from the Federal Reserve is known as
A)seasonal credit.
B)secondary credit.
C)primary credit.
D)discount window borrowing.
A)seasonal credit.
B)secondary credit.
C)primary credit.
D)discount window borrowing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In order to overcome the stigma that might come from borrowing from the Federal Reserve following the 2007 financial crisis, the Federal Reserve first created
A)the discount window.
B)quantitative easing.
C)the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC).
D)the term auction facility (TAF).
A)the discount window.
B)quantitative easing.
C)the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC).
D)the term auction facility (TAF).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When the Federal Reserve buys US Treasury securities on the open market, it is attempting to
A)lower interest rates.
B)raise interest rates.
C)reduce inflation.
D)slow economic growth.
A)lower interest rates.
B)raise interest rates.
C)reduce inflation.
D)slow economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the figure below, the loanable funds market is in equilibrium at A with the interest rate IR 1 . In conducting monetary policy, the Federal Reserve engages in the buying of US Treasury securities on the open market, which causes
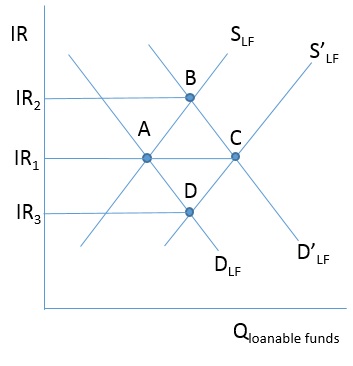
A)no change in the loanable funds market, so the equilibrium interest rate remains at IR1.
B)the demand for loanable funds to increase to D', causing the equilibrium interest rate to increase to IR2.
C)both the demand for loanable funds and the supply of loanable funds to increase to D' and S' respectively, keeping the equilibrium interest rate at IR1.
D)the supply of loanable funds to increase to S', causing the equilibrium interest rate to fall to IR3.

A)no change in the loanable funds market, so the equilibrium interest rate remains at IR1.
B)the demand for loanable funds to increase to D', causing the equilibrium interest rate to increase to IR2.
C)both the demand for loanable funds and the supply of loanable funds to increase to D' and S' respectively, keeping the equilibrium interest rate at IR1.
D)the supply of loanable funds to increase to S', causing the equilibrium interest rate to fall to IR3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Of the policy tools available to the European Central Bank, the most frequently used are the
A)discount rates.
B)standing lending facilities.
C)minimum reserve requirements.
D)open market operations (OMOs).
A)discount rates.
B)standing lending facilities.
C)minimum reserve requirements.
D)open market operations (OMOs).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When a negative shock to the economy becomes more intense due to worsening financial market conditions, it's known as a negative shock accelerator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of these open market operations in the European Central Bank is most central to overall monetary policy and carried out weekly?
A)Longer-term refinancing
B)Structural liquidity-reducing
C)Main refinancing
D)Structural liquidity-providing
A)Longer-term refinancing
B)Structural liquidity-reducing
C)Main refinancing
D)Structural liquidity-providing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
One of the Federal Reserve's most used tools of monetary policy is the buying and selling of US government securities in the secondary market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Times of financial uncertainty tend to cause an increase in the overall demand for money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Open market operations in which the European Central Bank specifies an interest rate at which it will lend and then participating banks submit bids on the amount of money they wish to borrow at that rate are known as __________ tenders.
A)fixed-rate reverse
B)fixed-rate standard
C)variable-rate standard
D)variable-rate reverse
A)fixed-rate reverse
B)fixed-rate standard
C)variable-rate standard
D)variable-rate reverse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of these statements is the most accurate description of a liquidity trap?
A)Borrowers are willing to borrow, and expansionary policy is used to stimulate the economy as needed.
B)Lenders are willing to lend, but high interest rates keep borrowing slightly lower than needed.
C)Borrowers are unwilling to borrow, and lenders are unwilling to lend due to pessimism about the future.
D)Lenders are willing to lend, but borrowers borrow too much due to increased optimism about the future.
A)Borrowers are willing to borrow, and expansionary policy is used to stimulate the economy as needed.
B)Lenders are willing to lend, but high interest rates keep borrowing slightly lower than needed.
C)Borrowers are unwilling to borrow, and lenders are unwilling to lend due to pessimism about the future.
D)Lenders are willing to lend, but borrowers borrow too much due to increased optimism about the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Government deficits can complicate monetary policy because government borrowing can lead to
A)"crowding out," which leads to lower interest rates.
B)"crowding out," which leads to higher interest rates.
C)"crowding in," which leads to lower interest rates.
D)"crowding in," which leads to higher interest rates.
A)"crowding out," which leads to lower interest rates.
B)"crowding out," which leads to higher interest rates.
C)"crowding in," which leads to lower interest rates.
D)"crowding in," which leads to higher interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What was the significance and the immediate effect of the quantitative easing announced on November 25, 2008, in response to the 2007-2008 financial crisis unfolding in the United States?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the purpose of the term auction facility (TAF)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the significance of Fisher's equation of exchange? How did the assumption of a constant velocity of money not match up with ongoing real-world observations?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If the European Central Bank is pursuing a contractionary monetary policy, it will
A)raise the minimum reserve requirement.
B)lower the interest rate paid by its deposit facility.
C)use quantitative easing.
D)lower the minimum reserve requirement.
A)raise the minimum reserve requirement.
B)lower the interest rate paid by its deposit facility.
C)use quantitative easing.
D)lower the minimum reserve requirement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Federal government budget surpluses can lead to a "crowding out" effect, which pushes interest rates upward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Imagine you live in a country with huge public debt and an uncertain future. Monetization of this public debt is most likely to lead to which of these outcomes?
A)Inflation
B)Stagflation
C)Reduced money supply
D)High interest rates
A)Inflation
B)Stagflation
C)Reduced money supply
D)High interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



