Deck 6: Aggregate Supply Aggregate Demand
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/35
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Aggregate Supply Aggregate Demand
1
How did John Maynard Keynes explain the Great Depression, and what did he suggest?
A)Keynes explained that a market-clearing equilibrium would happen eventually; he suggested providing financial help to those who needed it and then waiting for the market to self-correct.
B)Keynes came up with a theory stressing many supply and demand curves within the economy.
C)Keynes explained that a market-clearing equilibrium only happens on its own in the long run; additional action was needed to get the economy out of the Depression.
D)Keynes explained the Depression as a loss of faith or optimism among businessmen; he suggested economic encouragement for businessmen to end the Great Depression.
A)Keynes explained that a market-clearing equilibrium would happen eventually; he suggested providing financial help to those who needed it and then waiting for the market to self-correct.
B)Keynes came up with a theory stressing many supply and demand curves within the economy.
C)Keynes explained that a market-clearing equilibrium only happens on its own in the long run; additional action was needed to get the economy out of the Depression.
D)Keynes explained the Depression as a loss of faith or optimism among businessmen; he suggested economic encouragement for businessmen to end the Great Depression.
C
2
The three reasons that the economy-wide price level and the level of real GDP move in opposite directions are
A)the Pigou effect, the foreign trade effect, and the real savings effect.
B)the foreign trade effect, Keynes's interest rate effect, and the price effect.
C)the Pigou effect, Keynes's interest rate effect, and the foreign trade effect.
D)the foreign trade effect, the government intervention effect, and the real savings effect.
A)the Pigou effect, the foreign trade effect, and the real savings effect.
B)the foreign trade effect, Keynes's interest rate effect, and the price effect.
C)the Pigou effect, Keynes's interest rate effect, and the foreign trade effect.
D)the foreign trade effect, the government intervention effect, and the real savings effect.
C
3
Which of these statements best explains the Great Depression according to Karl Marx?
A)The use of machines to do work was replacing human labor; decreasing consumption by unemployed workers would lead to still more unemployment, ending capitalism and ending the Depression as workers took over the means of production.
B)The increasing use of machines to do work was replacing human labor; at some point, the working class would be able to live on wages earned in just a very short work day, ending the Depression.
C)A temporary imbalance between the very wealthy and the working class was to blame, but would correct itself in time, leading to greater consumption and the end of the Depression.
D)An imbalance between the very wealthy and the working class was to blame and could be fixed through taxation of the earnings of the very wealthy, thus ending the Depression.
A)The use of machines to do work was replacing human labor; decreasing consumption by unemployed workers would lead to still more unemployment, ending capitalism and ending the Depression as workers took over the means of production.
B)The increasing use of machines to do work was replacing human labor; at some point, the working class would be able to live on wages earned in just a very short work day, ending the Depression.
C)A temporary imbalance between the very wealthy and the working class was to blame, but would correct itself in time, leading to greater consumption and the end of the Depression.
D)An imbalance between the very wealthy and the working class was to blame and could be fixed through taxation of the earnings of the very wealthy, thus ending the Depression.
A
4
It is found that when the disposable income of Elvania increases by $100 billion, household consumption spending increases by $70 billion. In Elvania, the marginal propensity to consume is
A)0.3.
B)0.5.
C)0.7.
D)1.0.
A)0.3.
B)0.5.
C)0.7.
D)1.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Aggregate demand is equal to
A)C + I + G + (X + M).
B)C + G + (X - M).
C)C + I + G + (X - M).
D)S + I + G + (X - M).
A)C + I + G + (X + M).
B)C + G + (X - M).
C)C + I + G + (X - M).
D)S + I + G + (X - M).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Originally, Keynes conceived of the aggregate supply curve as consisting of two distinct segments. In this conception, below the full-employment level of output the aggregate supply curve is __________, and once the economy reaches the full-employment level of output it becomes __________.
A)upward sloping; vertical
B)horizontal; vertical
C)upward sloping; horizontal
D)downward sloping; vertical
A)upward sloping; vertical
B)horizontal; vertical
C)upward sloping; horizontal
D)downward sloping; vertical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
At the time of the Great Depression, the __________ believed that the economic disruptions being experienced were temporary and that market forces would eventually reestablish prosperity.
A)Marxists
B)classical economists
C)Keynesian economists
D)supply-side economists
A)Marxists
B)classical economists
C)Keynesian economists
D)supply-side economists

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Consider the figure below . Which of the following would cause a shift in the aggregate demand curve from AD 1 to AD 2 ?
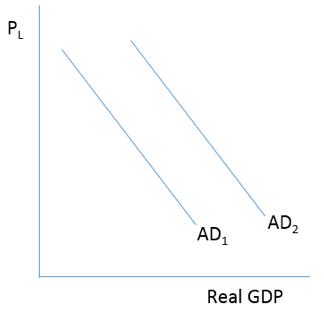
A)An increase in federal government spending on Social Security
B)An increase in federal government spending on drones
C)A decrease in federal government spending on highway infrastructure
D)A decrease in state government spending

A)An increase in federal government spending on Social Security
B)An increase in federal government spending on drones
C)A decrease in federal government spending on highway infrastructure
D)A decrease in state government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The relationship between the economy-wide price level and the level of real GDP illustrated by the aggregate demand curve is
A)neutral.
B)positive.
C)direct.
D)inverse.
A)neutral.
B)positive.
C)direct.
D)inverse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Economic theorists expanded on the Keynesian aggregate supply model in the late 1940s, broadening it into a three-part aggregate supply curve. Which of the following best describes that three-part supply curve?
A)A flat initial segment, followed by a modestly upward-sloping middle segment until full-employment GDP is reached, and finally a more steeply upward-sloping segment beyond full-employment GDP
B)A flat initial segment, followed by an upward-sloping middle segment until full-employment GDP is reached, and finally a vertical segment at full-employment GDP
C)A flat initial segment until full-employment is reached, followed by a vertical segment at full-employment GDP, and finally followed by another flat segment once the full-employment price level is reached
D)An upward-sloping initial segment, followed by an upward-sloping segment until full-employment GDP is reached, and finally followed by another flat segment beyond full-employment GDP
A)A flat initial segment, followed by a modestly upward-sloping middle segment until full-employment GDP is reached, and finally a more steeply upward-sloping segment beyond full-employment GDP
B)A flat initial segment, followed by an upward-sloping middle segment until full-employment GDP is reached, and finally a vertical segment at full-employment GDP
C)A flat initial segment until full-employment is reached, followed by a vertical segment at full-employment GDP, and finally followed by another flat segment once the full-employment price level is reached
D)An upward-sloping initial segment, followed by an upward-sloping segment until full-employment GDP is reached, and finally followed by another flat segment beyond full-employment GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the country of Trivia, it is widely believed that the marginal propensity to consume is 0.75. This means that a onetime increase in spending of $50 billion will result in an increase in GDP equal to
A)$50 billion
B)$66.67 billion
C)$100 billion
D)$200 billion
A)$50 billion
B)$66.67 billion
C)$100 billion
D)$200 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Using a two-part aggregate supply curve, an increase in aggregate demand when the economy is at less than full employment would be expected to lead to __________ in real GDP and __________ in the price level.
A)an increase; an increase
B)an increase; a decrease
C)an increase; no increase
D)no change; an increase
A)an increase; an increase
B)an increase; a decrease
C)an increase; no increase
D)no change; an increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
According to Keynes, when the price level rises, it causes the interest rate to do what? It causes the level of business spending to do what?
A)It causes an increase in the interest rate, due to a greater consumer demand for money to spend; business spending decreases.
B)It causes an increase in the interest rate, due to greater consumer demand for money to spend; business spending goes up as well.
C)It causes a decrease in the interest rate, as people adjust to higher prices and purchase less; business spending decreases as well.
D)It causes a decrease in the interest rate, as people adjust to higher prices and purchase less; business spending goes up.
A)It causes an increase in the interest rate, due to a greater consumer demand for money to spend; business spending decreases.
B)It causes an increase in the interest rate, due to greater consumer demand for money to spend; business spending goes up as well.
C)It causes a decrease in the interest rate, as people adjust to higher prices and purchase less; business spending decreases as well.
D)It causes a decrease in the interest rate, as people adjust to higher prices and purchase less; business spending goes up.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Consider the figure below. Which of the following will cause a shift in aggregate demand from AD2 to AD1?
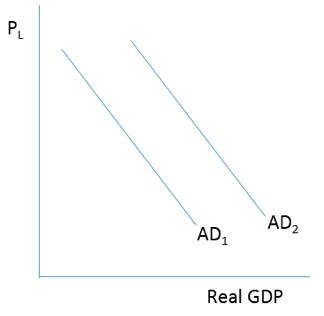
A)An increase in business optimism
B)An increase in business investment spending
C)A decrease in interest rates
D)An increase in interest rates

A)An increase in business optimism
B)An increase in business investment spending
C)A decrease in interest rates
D)An increase in interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The Keynesian aggregate supply model does not take into account what aspect of human behavior that is factored into later assumptions?
A)People adapt to what happens after it happens.
B)People sometimes make irrational choices.
C)People anticipate the future and plan for it.
D)People are largely unpredictable in their preference for saving versus spending.
A)People adapt to what happens after it happens.
B)People sometimes make irrational choices.
C)People anticipate the future and plan for it.
D)People are largely unpredictable in their preference for saving versus spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In which of the following situations did the three-part aggregate supply model not perform well?
A)Explaining the Great Depression
B)Managing the economy during World War II
C)Understanding the post-World War II economic boom
D)Understanding the stagflation of the late 1960s and early 1970s
A)Explaining the Great Depression
B)Managing the economy during World War II
C)Understanding the post-World War II economic boom
D)Understanding the stagflation of the late 1960s and early 1970s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Keynes suggested that what kind of spending would be necessary to move the economy out of the Depression?
A)Consumer spending
B)Increased exports
C)Government spending of some kind
D)Consumer and government spending
A)Consumer spending
B)Increased exports
C)Government spending of some kind
D)Consumer and government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The Pigou effect is one of the reasons that the aggregate demand curve slopes downward. According to this argument, when the price level
A)goes down, interest rates will fall resulting in an increase in the total level of spending.
B)goes down, peoples' savings are able to purchase more stuff so the total level of spending increases.
C)goes down, peoples' savings are able to purchase more stuff, but spending tends to stay steady, while savings increase.
D)in the United States goes down, US goods and services become relatively cheaper compared to things produced overseas, so the total level of spending on US goods and services increases.
A)goes down, interest rates will fall resulting in an increase in the total level of spending.
B)goes down, peoples' savings are able to purchase more stuff so the total level of spending increases.
C)goes down, peoples' savings are able to purchase more stuff, but spending tends to stay steady, while savings increase.
D)in the United States goes down, US goods and services become relatively cheaper compared to things produced overseas, so the total level of spending on US goods and services increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Consider the figure below . Which of the following will cause a shift in the aggregate demand curve from AD 1 to AD 2 ?
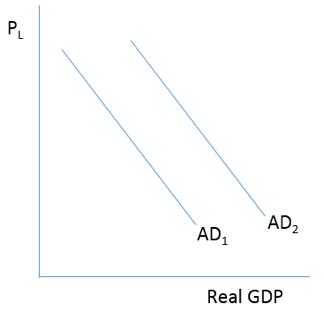
A)An increase in personal savings
B)An increase in personal income taxes
C)A reduction in personal income taxes
D)Increased consumer pessimism about the future

A)An increase in personal savings
B)An increase in personal income taxes
C)A reduction in personal income taxes
D)Increased consumer pessimism about the future

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of these would cause a decrease in aggregate demand?
A)A decrease in imports
B)An increase in imports
C)An increase in net exports
D)An increase in exports
A)A decrease in imports
B)An increase in imports
C)An increase in net exports
D)An increase in exports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Several factors can cause the SRAS curve to shift; these factors include a change in the cost of inputs, a change in taxes, and even a change in seller expectations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Consider the figure below . A decrease in the cost of productive inputs would lead to a movement from
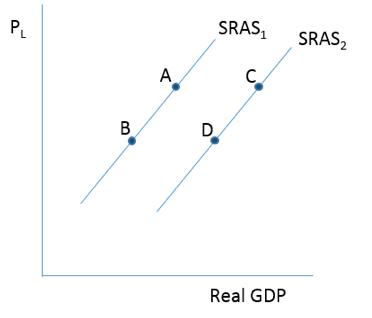
A)A to B.
B)D to C.
C)A to C.
D)D to B.

A)A to B.
B)D to C.
C)A to C.
D)D to B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When resource markets are efficient, recessionary gaps close by themselves without any government intervention.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Consider the figure below . If the price level turns out to be lower than expected, it would result in a movement from
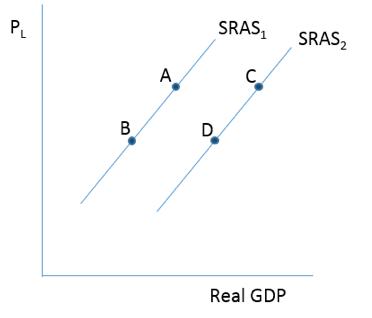
A)A to B.
B)B to A.
C)C to A.
D)D to B.

A)A to B.
B)B to A.
C)C to A.
D)D to B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Consider the figure below. An increase in uncertainty would lead to a movement from
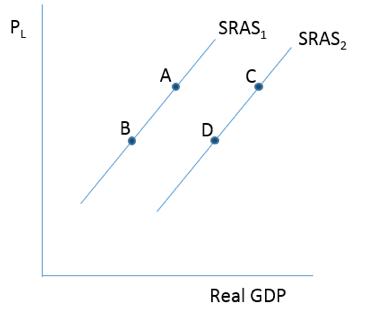
A)A to B.
B)D to C.
C)A to C.
D)D to B.

A)A to B.
B)D to C.
C)A to C.
D)D to B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the logic behind the spending multiplier? Provide an example.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The rational expectations approach postulates what two aggregate supply curves?
A)An upward-sloping short-run aggregate supply curve and a horizontal long-run supply curve at the maximum price level
B)An upward-sloping short-run aggregate supply curve and a vertical long-run supply curve at zero unemployment rate level of GDP
C)An upward-sloping short-run aggregate supply curve and a vertical long-run supply curve at the full-employment level of GDP .
D)A vertical short-run aggregate supply curve at the full-employment level of GDP and an upward-sloping long-run supply curve
A)An upward-sloping short-run aggregate supply curve and a horizontal long-run supply curve at the maximum price level
B)An upward-sloping short-run aggregate supply curve and a vertical long-run supply curve at zero unemployment rate level of GDP
C)An upward-sloping short-run aggregate supply curve and a vertical long-run supply curve at the full-employment level of GDP .
D)A vertical short-run aggregate supply curve at the full-employment level of GDP and an upward-sloping long-run supply curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the term for using all available information to form expectations about the future to make decisions in the present?
A)Rational expectations
B)Adaptive planning
C)Ex ante planning
D)Informed expectations
A)Rational expectations
B)Adaptive planning
C)Ex ante planning
D)Informed expectations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
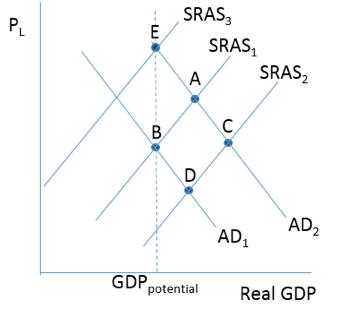
Consider the figure below. The situation in Noprovia is represented by SRAS 1 and AD 1 . The long-run equilibrium real GDP and price level for the economy is represented by point
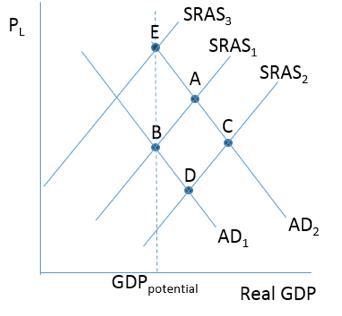
A)E.
B)B.
C)A.
D)D.

A)E.
B)B.
C)A.
D)D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When the actual level of output is less than the potential level of output, there is an output gap, sometimes called a recessionary gap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Explain how an economy might close a recessionary gap without any government intervention.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Why does the aggregate demand curve slope downward?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Real Business Cycle models, or RBCs, assume there is one perfectly rational household that represents all households, and one firm that represents all firms. Thus, these models are also referred to as representative agent models.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Consider the figure below representing the current economic situation in Tilantia. The economy of Tilantia is currently in short-run equilibrium and is thereby experiencing a(n)
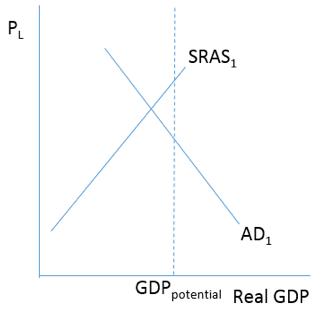
A)inflationary gap.
B)recessionary gap.
C)resource gap.
D)overheated economy.

A)inflationary gap.
B)recessionary gap.
C)resource gap.
D)overheated economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Consider the figure below . The situation in Trombli is characterized by SRAS 1 and AD 1 when there is an increase in the money supply shifting the short-run aggregate supply curve to SRAS 2 . This will create __________ in the economy.
A)a depression
B)recessionary pressure
C)stagflationary pressure
D)inflationary pressure

A)a depression
B)recessionary pressure
C)stagflationary pressure
D)inflationary pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



