Deck 7: Banks and Money
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/35
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Banks and Money
1
Which of these statements is most true of the function of banks?
A)Banks are a safe way to save, and savers earn high interest.
B)Banks lend money and help with the problem of symmetric information.
C)Banks play a key role in creating money, and they help with the problem of adverse selection.
D)Banks lend money and help with the problem of free-riders.
A)Banks are a safe way to save, and savers earn high interest.
B)Banks lend money and help with the problem of symmetric information.
C)Banks play a key role in creating money, and they help with the problem of adverse selection.
D)Banks lend money and help with the problem of free-riders.
C
2
The principal of a school hires Daniel to teach eighth grade students. One goal the principal has is to prepare the students to do well on standardized tests, as he will be judged based on the results of those tests. Daniel prefers to teach in a more creative way, so the students learn a lot, but perform poorly on their standardized tests. This is an example of what problem?
A)Adverse selection
B)Moral hazard
C)Free-riding
D)Adverse hazard
A)Adverse selection
B)Moral hazard
C)Free-riding
D)Adverse hazard
B
3
The result of asymmetric information in a market is __________ selection.
A)irrational
B)diverse
C)adverse
D)careful
A)irrational
B)diverse
C)adverse
D)careful
C
4
Rachel goes for a job interview and knows a lot about the job she is applying for. The woman who interviews her is filling in for another employee and knows very little about Rachel. We might say the woman conducting the interview is likely to have what kind of situation?
A)The interviewer is in a situation of moral hazard, since Rachel may turn out to be a poor employee.
B)The interviewer is facing adverse selection, since she knows nothing about Rachel.
C)The interviewer has systemic information, since she can ask probing questions of Rachel.
D)The interviewer has asymmetric information as she knows less about Rachel than Rachel knows of herself.
A)The interviewer is in a situation of moral hazard, since Rachel may turn out to be a poor employee.
B)The interviewer is facing adverse selection, since she knows nothing about Rachel.
C)The interviewer has systemic information, since she can ask probing questions of Rachel.
D)The interviewer has asymmetric information as she knows less about Rachel than Rachel knows of herself.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Cleo is hired as the CEO of Wolfstarter Company, a publicly owned corporation. After she is hired, she authorizes the purchase of a company limousine to chauffeur her around town, purchases a skybox at the stadium of the local NFL team, and provides herself with a company-paid membership at the local country club. This behavior could be an example of
A)adverse selection.
B)the free-rider problem.
C)the principal-agent problem.
D)undisclosed information.
A)adverse selection.
B)the free-rider problem.
C)the principal-agent problem.
D)undisclosed information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In Vance's homeowner's insurance policy, it states that he is required to pay out-of-pocket the first $5,000 for any homeowner's insurance claim that he submits before the insurance company will reimburse for any loss. This is an example of using
A)a restrictive covenant to mitigate the problem of moral hazard.
B)incentives to overcome the principal-agent problem.
C)screening to overcome the adverse selection problem.
D)a deductible to try to mitigate the problem of moral hazard.
A)a restrictive covenant to mitigate the problem of moral hazard.
B)incentives to overcome the principal-agent problem.
C)screening to overcome the adverse selection problem.
D)a deductible to try to mitigate the problem of moral hazard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of these is an example of asymmetric information in banking?
A)Borrowers and lenders have different expectations about financial markets.
B)Lenders know more about the capacity of borrowers to repay loans than borrowers.
C)Borrowers' goals are short-term while lenders' goals are long-term.
D)Borrowers know more about their capacity to repay loans than lenders.
A)Borrowers and lenders have different expectations about financial markets.
B)Lenders know more about the capacity of borrowers to repay loans than borrowers.
C)Borrowers' goals are short-term while lenders' goals are long-term.
D)Borrowers know more about their capacity to repay loans than lenders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The loan application process that banks require potential borrowers to go through is an attempt to deal with
A)adverse hazard.
B)moral selection.
C)free-riders.
D)adverse selection.
A)adverse hazard.
B)moral selection.
C)free-riders.
D)adverse selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The bond rating system, in which companies like Moody's and Standard & Poor's provide ratings for a company's default risk, is one way to deal with
A)symmetric information.
B)adverse hazard.
C)adverse selection.
D)moral selection.
A)symmetric information.
B)adverse hazard.
C)adverse selection.
D)moral selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An example of asymmetric information in financial markets is that, in equity markets, directors __________ than shareholders.
A)have a better sense of future profitability
B)have a different rate of time preference
C)are less optimistic about the future
D)are less certain about the future
A)have a better sense of future profitability
B)have a different rate of time preference
C)are less optimistic about the future
D)are less certain about the future

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Holly goes to her bank to take out a loan, and the bank agrees to the loan on the condition that Holly maintain a balance of $1,000 in her savings account with the bank. This is an example of a bank using a
A)deductible as a way to mitigate the problem of moral hazard.
B)compensating balance as a way to mitigate the problem of moral hazard.
C)compensating balance as a way to mitigate the problem of adverse selection.
D)restrictive covenant as a way to mitigate the problem of moral hazard.
A)deductible as a way to mitigate the problem of moral hazard.
B)compensating balance as a way to mitigate the problem of moral hazard.
C)compensating balance as a way to mitigate the problem of adverse selection.
D)restrictive covenant as a way to mitigate the problem of moral hazard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of these describes an example of asymmetric information in the bond market?
A)Bond issuers have longer-term goals than bond buyers.
B)Bond issuers have better insight about their future profitability than bond buyers.
C)Bond issuers and bond buyers have different experiences in the bond market.
D)Bond issuers are more conservative about the future than bond buyers.
A)Bond issuers have longer-term goals than bond buyers.
B)Bond issuers have better insight about their future profitability than bond buyers.
C)Bond issuers and bond buyers have different experiences in the bond market.
D)Bond issuers are more conservative about the future than bond buyers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What would be expected in a market for used cars, assuming asymmetric information and buyers who have little way to determine good used cars from poor used cars?
A)The average price for used cars would go down and drive the clunker used cars out of the market.
B)The average price for used cars would go down and drive the better used cars out of the market.
C)There would be little to no impact on the market for used cars.
D)The asymmetric information would lead to a fair and efficient market.
A)The average price for used cars would go down and drive the clunker used cars out of the market.
B)The average price for used cars would go down and drive the better used cars out of the market.
C)There would be little to no impact on the market for used cars.
D)The asymmetric information would lead to a fair and efficient market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When the parties to a transaction have different levels of knowledge about each other and/or the nature and implications of the transaction, it is said that there exists __________ information.
A)asymmetric
B)symmetric
C)adverse
D)ad hoc
A)asymmetric
B)symmetric
C)adverse
D)ad hoc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The business of banking solves the problem of
A)moral hazard.
B)a liquidity mismatch with savers desiring illiquidity and borrowers desiring liquid loans.
C)a liquidity mismatch with savers desiring liquidity and borrowers desiring illiquid loans.
D)adverse selection.
A)moral hazard.
B)a liquidity mismatch with savers desiring illiquidity and borrowers desiring liquid loans.
C)a liquidity mismatch with savers desiring liquidity and borrowers desiring illiquid loans.
D)adverse selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Petra has an automobile accident and finds that as a result her auto insurance premium will increase by 25%. This is an example of an adjustable premium that insurance companies often use as a mechanism to combat
A)short-sightedness.
B)adverse selection.
C)free-riders.
D)moral hazard.
A)short-sightedness.
B)adverse selection.
C)free-riders.
D)moral hazard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following qualifies as a liability to a bank?
A)A business loan
B)A mortgage
C)Demand deposits
D)A Treasury bond
A)A business loan
B)A mortgage
C)Demand deposits
D)A Treasury bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of these is not a likely result if banks hold onto excess reserves?
A)The economy may enter into a recession.
B)Demands for loans may increase, but lending will be insufficient.
C)Demand for loans will increase, and business activity will increase.
D)Consumers and businesses will not be able to get loans as easily as before.
A)The economy may enter into a recession.
B)Demands for loans may increase, but lending will be insufficient.
C)Demand for loans will increase, and business activity will increase.
D)Consumers and businesses will not be able to get loans as easily as before.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of these statements best describes the function of banks as part of the aggregate economy?
A)Banks take deposits and make loans.
B)Banks create or reduce the amount of money available in the economy.
C)Banks reduce moral hazard.
D)Banks lend money to those business firms most in need of it.
A)Banks take deposits and make loans.
B)Banks create or reduce the amount of money available in the economy.
C)Banks reduce moral hazard.
D)Banks lend money to those business firms most in need of it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Liquidity is the term that has which of these meanings?
A)A measure of the ease with which one asset can be converted into another asset, usually money
B)A measure of the ease with which one can use money to purchase goods
C)A measure of the ease with which one can borrow money
D)A measure of the ease in which one can get out of debt to become a lender
A)A measure of the ease with which one asset can be converted into another asset, usually money
B)A measure of the ease with which one can use money to purchase goods
C)A measure of the ease with which one can borrow money
D)A measure of the ease in which one can get out of debt to become a lender

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A one-time deposit in a bank will result in
A)no expansion in the money supply.
B)an expansion in the money supply that is smaller than the size of the one-time deposit.
C)an expansion in the money supply that is equal in size to the one-time deposit.
D)an expansion in the money supply that is larger than the size of the one-time deposit.
A)no expansion in the money supply.
B)an expansion in the money supply that is smaller than the size of the one-time deposit.
C)an expansion in the money supply that is equal in size to the one-time deposit.
D)an expansion in the money supply that is larger than the size of the one-time deposit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the difference between adverse selection and moral hazard?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Deductibles are one way insurance companies protect themselves from careless drivers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the required reserve ratio is 3%, an initial demand deposit made in a bank of $100,000 can result in an expansion in the money supply of
A)$1,300,000.
B)$3,000,000.
C)$3,333,000.
D)$3,500,000.
A)$1,300,000.
B)$3,000,000.
C)$3,333,000.
D)$3,500,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Explain the simple deposit multiplier process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A simple deposit multiplier of 10 suggests that a one-time bank deposit of $100,000 will lead to an expansion of the money supply 10 times larger, or a $1,000,000 expansion of the money supply. Identify and explain two real-world problems with this theoretical analysis that could cause the money supply to expand less than that.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following would be considered an asset on a bank's balance sheet?
A)A consumer loan
B)Demand deposits
C)Loans from other banks
D)Savings accounts
A)A consumer loan
B)Demand deposits
C)Loans from other banks
D)Savings accounts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A significant fault of the bond rating system is the free-rider problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Imagine that Roland goes to his bank and deposits $10,000 in cash into his savings account. The bank, wanting to use those funds to generate revenue for itself, will look to make a loan with this cash. An important determinant of how much of that $10,000 the bank can lend is the
A)interest rate the bank is paying Roland on his deposit balance.
B)bank's net worth.
C)required reserve ratio.
D)interest rate the bank will charge on the loan that it makes.
A)interest rate the bank is paying Roland on his deposit balance.
B)bank's net worth.
C)required reserve ratio.
D)interest rate the bank will charge on the loan that it makes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If bankers have reason to feel optimistic about the future, they may become very eager to loan money. If insufficient regulations are in place, this could most likely cause what?
A)Very little change in the short run, as higher interest rates will simply compensate
B)A credit crunch, which will reduce household consumption and business investment spending, leading to a decline in real output
C)A higher percentage of loans in default, as riskier borrowers are attracted to easy loans
D)A credit crunch, as riskier borrowers take out loans
A)Very little change in the short run, as higher interest rates will simply compensate
B)A credit crunch, which will reduce household consumption and business investment spending, leading to a decline in real output
C)A higher percentage of loans in default, as riskier borrowers are attracted to easy loans
D)A credit crunch, as riskier borrowers take out loans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Liquidity is a term that refers to the ease with which one asset can be converted into another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When interest rates on loans and mortgages are low, the huge rush of easy borrowing is sometimes referred to as a credit crunch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What problem may occur if an economy has too few banks or none at all?
A)The economy will support nearly the same standard of living as banks.
B)The economy will be subject to periods of high unemployment alternating with periods of high employment but very high inflation.
C)The economy will be underdeveloped, with a possible increase in unemployment and business failures.
D)The economy may "overheat" and inflation may become a problem.
A)The economy will support nearly the same standard of living as banks.
B)The economy will be subject to periods of high unemployment alternating with periods of high employment but very high inflation.
C)The economy will be underdeveloped, with a possible increase in unemployment and business failures.
D)The economy may "overheat" and inflation may become a problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the public's confidence in the banking system is shaken, it may cause
A)a run on banks.
B)moral hazard.
C)adverse selection.
D)an increase in banking regulation.
A)a run on banks.
B)moral hazard.
C)adverse selection.
D)an increase in banking regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Consider the figure below. The initial equilibrium in the loanable funds market in Etopia is at A. If the banks in Etopia begin to see an upsurge in deposits, this will result in a new equilibrium at what point?
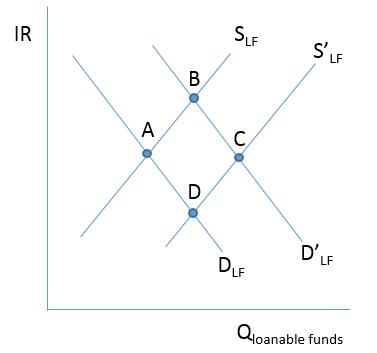
A)Initially, point B with an increase in the interest rate, then point D with a decrease in the interest rate
B)Point B with an increase the interest rate
C)Point C with no change in the interest rate
D)Point D with a decrease in the interest rate

A)Initially, point B with an increase in the interest rate, then point D with a decrease in the interest rate
B)Point B with an increase the interest rate
C)Point C with no change in the interest rate
D)Point D with a decrease in the interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



