Deck 4: Interest Rates in More Detail
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/35
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Interest Rates in More Detail
1
A yield curve illustrates the relationship between the
A)default risk associated with bonds of a given maturity and the interest rate they pay, at a particular point of time.
B)term to maturity of bonds and the interest rate they pay, at a particular point of time.
C)marginal tax rate and the after-tax interest rate of return on taxable bonds.
D)rate of inflation and the real rate of return on bonds.
A)default risk associated with bonds of a given maturity and the interest rate they pay, at a particular point of time.
B)term to maturity of bonds and the interest rate they pay, at a particular point of time.
C)marginal tax rate and the after-tax interest rate of return on taxable bonds.
D)rate of inflation and the real rate of return on bonds.
B
2
Imagine you run a company that produces recycled paper products. The selling price for items you produce is going up, so you increase production. After a time, you see that you have increased production more than the market is actually demanding. Which of these is the most likely reason for less demand than you had estimated based on a higher price for your items?
A)Changing interest rates
B)Inflation
C)Default risk
D)Scarcity of alternatives
A)Changing interest rates
B)Inflation
C)Default risk
D)Scarcity of alternatives
B
3
If the before-tax rate of return on a corporate bond is 7%, an individual in the 25% marginal tax bracket would earn a _____ rate of return on the bond.
A)7%
B)5.95%
C)5.25%
D)4.55%
A)7%
B)5.95%
C)5.25%
D)4.55%
C
4
The best way to measure the default risk premium that a borrower is paying is to
A)look at the borrower's bond rating as reported by Moody's Investors Services.
B)look at the borrower's bond rating as reported by Standard and Poor's Bond Rating Services.
C)compare the interest rate the borrower pays with the risk-free premium, usually represented by the rate on US Treasury Securities.
D)look at the profitability of the lender relative to its industry.
A)look at the borrower's bond rating as reported by Moody's Investors Services.
B)look at the borrower's bond rating as reported by Standard and Poor's Bond Rating Services.
C)compare the interest rate the borrower pays with the risk-free premium, usually represented by the rate on US Treasury Securities.
D)look at the profitability of the lender relative to its industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of these groups of people is most hurt by inflation?
A)Borrowers and the wealthy
B)The very wealthy
C)Lenders and working class people
D)Working class people
A)Borrowers and the wealthy
B)The very wealthy
C)Lenders and working class people
D)Working class people

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Emmel is the CFO for ABC Corporation. Ten years ago, under Emmel's instructions, the company invested in 10-year US Treasury bonds that paid 3% interest. At the time, Emmel's projection was that inflation over the 10-year period would be 0.5% per year. As it turns out, the average annual rate of inflation over the 10-year period was 1.5%. As a result, the ex-post rate of return on ABC Corporation's investment was _____, instead of the _____ return that Emmel expected ex-ante.
A)3%; 2.5%
B)2.5%; 1.5%
C)3%; 0.5%
D)1.5%; 2.5%
A)3%; 2.5%
B)2.5%; 1.5%
C)3%; 0.5%
D)1.5%; 2.5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Inflation is a benefit in the short run to
A)no one.
B)borrowers.
C)lenders.
D)both borrowers and lenders.
A)no one.
B)borrowers.
C)lenders.
D)both borrowers and lenders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A flight to quality is most likely to have which of these effects?
A)It will be more difficult for individual borrowers to borrow, but ease borrowing for businesses.
B)It will be easier for both individuals and businesses that want to sell high-risk bonds.
C)It will decrease the default risk premium that higher risk borrowers have to pay and may bring about economic growth.
D)It will increase the default risk premium that higher risk borrowers will pay and may cause some businesses to cut costs.
A)It will be more difficult for individual borrowers to borrow, but ease borrowing for businesses.
B)It will be easier for both individuals and businesses that want to sell high-risk bonds.
C)It will decrease the default risk premium that higher risk borrowers have to pay and may bring about economic growth.
D)It will increase the default risk premium that higher risk borrowers will pay and may cause some businesses to cut costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Atwood and Spearman, Inc. bonds are selling for more than Boehm and Bull, Inc. bonds. The difference in yields between these two bond options is known as the
A)default risk premium.
B)default risk premium spread.
C)expected yield premium.
D)anticipated yield stretch.
A)default risk premium.
B)default risk premium spread.
C)expected yield premium.
D)anticipated yield stretch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Armand buys a 10-year, $10,000 bond that pays him $500 every year for 10 years and repays the face value in year 10. During the 10-year period, the rate of inflation holds steady at 3% per year. The real rate of return on Armand's investment is
A)5%.
B)3%.
C)2%.
D)0%.
A)5%.
B)3%.
C)2%.
D)0%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A major advantage that municipal bonds have over corporate bonds for investors is that
A)municipal bonds have a lower default risk.
B)the income earned on municipal bonds is not subject to federal income tax.
C)corporate bonds are not as readily available as municipal bonds.
D)municipal bonds have a shorter term to maturity.
A)municipal bonds have a lower default risk.
B)the income earned on municipal bonds is not subject to federal income tax.
C)corporate bonds are not as readily available as municipal bonds.
D)municipal bonds have a shorter term to maturity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Harper just got a big raise at work, which pushed her from the 15% federal marginal tax bracket to the 25% marginal tax bracket. Which of the following best describes how this might affect her decision to buy municipal bonds?
A)This will make her more likely to buy municipal bonds rather than corporate bonds because she is wealthier.
B)This will make her more likely to buy municipal bonds because it will increase the difference between the nominal interest rate paid on the bonds and the after-tax interest rate she will receive relative to corporate bonds.
C)This will make her less likely to buy municipal bonds rather than corporate bonds because the increase in taxes will reduce her wealth.
D)This will make her neither more nor less likely to buy municipal bonds rather than corporate bonds.
A)This will make her more likely to buy municipal bonds rather than corporate bonds because she is wealthier.
B)This will make her more likely to buy municipal bonds because it will increase the difference between the nominal interest rate paid on the bonds and the after-tax interest rate she will receive relative to corporate bonds.
C)This will make her less likely to buy municipal bonds rather than corporate bonds because the increase in taxes will reduce her wealth.
D)This will make her neither more nor less likely to buy municipal bonds rather than corporate bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Sarah is considering the purchase of a 10-year, $10,000 bond being issued by Disreputable, Inc. The bond offers an interest rate of 5.5%. The rate on a similar US Treasury bond is 2.5%. All else equal, what will Sarah's default premium be if she purchases the Disreputable, Inc. bond?
A)3.5%
B)2.5%
C)3.0%
D)5.5%
A)3.5%
B)2.5%
C)3.0%
D)5.5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Carlos is considering buying either a corporate bond or a municipal bond that are exactly the same except for their yield. Carlos is in the 33% marginal tax bracket, and the municipal bond he is considering pays a 4% interest rate. To make Carlos indifferent between the two bonds, the corporate bond must offer an interest rate of how much?
A)5.97%.
B)6.52%.
C)4.97%.
D)5.52%.
A)5.97%.
B)6.52%.
C)4.97%.
D)5.52%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The figure below shows the supply and demand for bonds for Charter Corp. (SC and DC)and US Treasury Securities (SUS and DUS). The default risk premium paid by Charter Corp. in this market is represented by
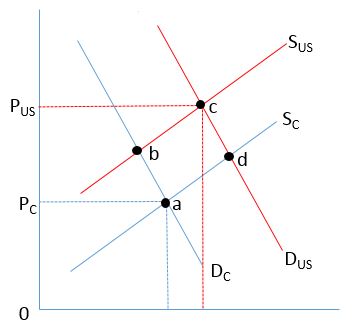
A)PUS0.
B)PC0.
C)PUSPC.
D)PCa.

A)PUS0.
B)PC0.
C)PUSPC.
D)PCa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Emily is in the 10% marginal income tax bracket and earned a 2.5% return on the corporate bonds that just matured. The nominal interest rate paid on these bonds was
A)2.96%.
B)3.28%.
C)2.78%.
D)3.96%.
A)2.96%.
B)3.28%.
C)2.78%.
D)3.96%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The risk that a bond issuer will not be able to live up to the promise they make when they issue a bond is known as __________ risk.
A)inflation
B)default premium
C)bankruptcy
D)default
A)inflation
B)default premium
C)bankruptcy
D)default

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Consider the figure below, which shows the supply and demand for US Treasury Securities (SUS and DUS)and for Charter Corp. bonds (SC and DC), as well as the corresponding equilibrium price (PUS and PC). What is the most likely reason that the market price for US Treasury Securities is higher than the market price for Charter Corp. bonds?
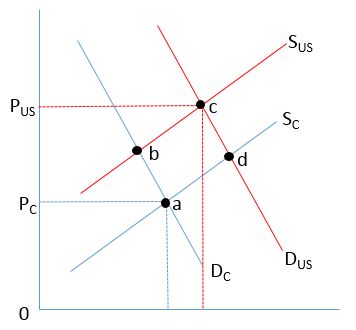
A)There is a higher risk that Charter Corp. will default on its obligation.
B)There is a lower risk that Charter Corp. will default on its obligation.
C)The US government has a monopoly on US Treasury securities.
D)There is a higher risk that the US Treasury will default on its obligation.

A)There is a higher risk that Charter Corp. will default on its obligation.
B)There is a lower risk that Charter Corp. will default on its obligation.
C)The US government has a monopoly on US Treasury securities.
D)There is a higher risk that the US Treasury will default on its obligation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The advantage of municipal bonds over corporate bonds increases as the federal marginal tax rate
A)is eliminated.
B)remains unchanged.
C)decreases.
D)increases.
A)is eliminated.
B)remains unchanged.
C)decreases.
D)increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
According to the pure expectations theory, a flat yield curve means the market
A)thinks that future interest rates will be higher than current interest rates.
B)thinks that future interest rates will be lower than current interest rates.
C)does not know what will happen to future interest rates.
D)thinks that future interest rates will be exactly the same as current interest rates.
A)thinks that future interest rates will be higher than current interest rates.
B)thinks that future interest rates will be lower than current interest rates.
C)does not know what will happen to future interest rates.
D)thinks that future interest rates will be exactly the same as current interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Your friend Jacob is looking at a steep yield curve and makes an attempt to understand the implications using segmented market theory. He says more information will be needed to make economic predictions, as this type of yield curve could be either good news or bad news. Are his comments about this yield curve, using segmented market theory, true or false?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Why is it important to distinguish between nominal and real interest rates in the bond market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A yield curve generally slopes upward but may slope downward if short-term interest rates on bonds are higher than longer-term interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Suppose that the interest rate on a one-year bond is currently 3% and the market believes that the rate on a one-year bond one year from now will be 5%. If you follow the pure expectations theory of interest rates, then you would expect to see a(n)__________ yield curve.
A)upward-sloping
B)downward-sloping
C)horizontal
D)vertical
A)upward-sloping
B)downward-sloping
C)horizontal
D)vertical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An inverted yield curve likely means the
A)economy is expanding rapidly.
B)economy is headed for recession.
C)economy is experiencing increasing inflationary pressure.
D)Federal Reserve is conducting expansionary policy.
A)economy is expanding rapidly.
B)economy is headed for recession.
C)economy is experiencing increasing inflationary pressure.
D)Federal Reserve is conducting expansionary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
You read a review written by a well-respected financial analyst who says that the steep yield curve we currently see suggests that borrowers require a relatively higher premium to hold longer-term bonds now, compared to short-term bonds. This analyst is most likely a proponent of which theory of interest rates?
A)Segmented market
B)Pure expectations
C)Term premium
D)Default risk
A)Segmented market
B)Pure expectations
C)Term premium
D)Default risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
You are having a conversation with your friend Jasmine about the inverted yield curve that currently exists in the bond market. She explains this by saying that the inverted yield curve is because the Federal Reserve is implementing a contractionary monetary policy, which usually impacts only the short-term bond market . Her observation means that she is a proponent of the __________ theory of interest rates.
A)term premium
B)default premium
C)pure expectations
D)segmented market
A)term premium
B)default premium
C)pure expectations
D)segmented market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A corporate bond offering an interest rate of 5% is as good a deal as a municipal bond offering the same interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The three theories that economists have developed to explain the shape of the yield curve are
A)the term premium theory, the pure expectations theory, and the default premium theory.
B)the pure expectations theory, the term premium theory, and the segmented market theory.
C)the segmented market theory, the default premium theory, and the inflationary expectations theory.
D)the pure expectations theory, the inflationary expectations theory, and the term premium theory.
A)the term premium theory, the pure expectations theory, and the default premium theory.
B)the pure expectations theory, the term premium theory, and the segmented market theory.
C)the segmented market theory, the default premium theory, and the inflationary expectations theory.
D)the pure expectations theory, the inflationary expectations theory, and the term premium theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Lenders benefit from inflation in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the difference between the pure expectations, term premium, and segmented market theories of the term structure of interest rates?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is meant by a flight to quality? What is its impact on the bond market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An inverted yield occurs when
A)long-term interest rates are higher than short-term interest rates.
B)long-term interest rates are the same as short-term interest rates.
C)long-term interest rates are lower than short-term interest rates.
D)short-term interest rates are lower than mid-term interest rates, which are higher than long-term interest rates.
A)long-term interest rates are higher than short-term interest rates.
B)long-term interest rates are the same as short-term interest rates.
C)long-term interest rates are lower than short-term interest rates.
D)short-term interest rates are lower than mid-term interest rates, which are higher than long-term interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A person who believes the pure expectations theory of interest rates would explain a steeply upward-sloping yield curve is suggesting that
A)savers currently have a better use for funds, or savers are worried about the future.
B)central banks have cut short-term interest rates and home sales have increased, or central banks have cut interest rates out of a fear of a slowdown in economic activity.
C)the economy is headed for a slowdown, or relief from inflationary pressure is imminent.
D)higher inflation is in the future, or more rapid economic growth is on the horizon.
A)savers currently have a better use for funds, or savers are worried about the future.
B)central banks have cut short-term interest rates and home sales have increased, or central banks have cut interest rates out of a fear of a slowdown in economic activity.
C)the economy is headed for a slowdown, or relief from inflationary pressure is imminent.
D)higher inflation is in the future, or more rapid economic growth is on the horizon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
You are having a conversation with your friend Yvonne about the upward-sloping yield curve that currently exists in the bond market. She explains this to you by saying that the upward slope to the yield curve is because the market expects future short-term interest rates to be higher than current interest rates. Her observation means that she is a proponent of the __________ theory of interest rates.
A)term premium
B)default premium
C)pure expectations
D)segmented market
A)term premium
B)default premium
C)pure expectations
D)segmented market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



