Deck 3: The Chemistry of Life: Organic Compounds
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: The Chemistry of Life: Organic Compounds
1
What group of molecules is represented in this structure?
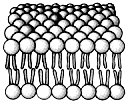
A) structural proteins
B) polysaccharides
C) triacylglycerols
D) phospholipids
E) polypeptides

A) structural proteins
B) polysaccharides
C) triacylglycerols
D) phospholipids
E) polypeptides
D
2
Why are hydrocarbons considered hydrophobic?
A) Hydrocarbons exist as isomers.
B) Hydrocarbons contain oxygen atoms.
C) The covalent bonds between carbon atoms are polar.
D) The covalent bonds between hydrogen and carbon are nonpolar.
E) The hydrogen bonds between hydrogen and carbon are nonpolar.
A) Hydrocarbons exist as isomers.
B) Hydrocarbons contain oxygen atoms.
C) The covalent bonds between carbon atoms are polar.
D) The covalent bonds between hydrogen and carbon are nonpolar.
E) The hydrogen bonds between hydrogen and carbon are nonpolar.
D
3
Which of the following is sometime referred to as animal starch?
A) cellulose
B) sugars
C) starch
D) fatty acid
E) glycogen
A) cellulose
B) sugars
C) starch
D) fatty acid
E) glycogen
E
4
What carbohydrate energy storage molecule is found in animal liver and muscle cells?
A) starch
B) cellulose
C) glycogen
D) a fatty acid
E) cholesterol
A) starch
B) cellulose
C) glycogen
D) a fatty acid
E) cholesterol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A steroid consists of carbon atoms arranged in four attached rings. How many carbon atoms do three of the rings contain?
A) six carbon atoms
B) five carbon atoms
C) three carbon atoms
D) seven carbon atoms
E) two carbon atoms
A) six carbon atoms
B) five carbon atoms
C) three carbon atoms
D) seven carbon atoms
E) two carbon atoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When we know what kinds of ____ are present in an organic compound, we can predict its chemical behavior.
A) proteins
B) enzymes
C) triacylglycerols
D) macromolecules
E) functional groups
A) proteins
B) enzymes
C) triacylglycerols
D) macromolecules
E) functional groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Figure 3-1
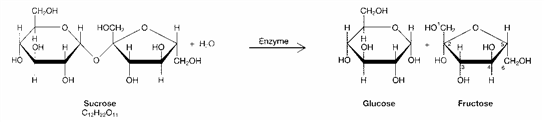
Which is the main structural component of the walls that surround plant cells?
A) cellulose
B) sugars
C) starches
D) fatty acid
E) glucose

Which is the main structural component of the walls that surround plant cells?
A) cellulose
B) sugars
C) starches
D) fatty acid
E) glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Glucose and fructose are ____ because they have identical molecular formulas but their atoms are arranged differently.
A) polar
B) tertiary
C) enantiomers
D) structural isomers
E) geometric isomers
A) polar
B) tertiary
C) enantiomers
D) structural isomers
E) geometric isomers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Most animals convert carotenoids to which vitamin?
A) Vitamin K
B) Vitamin A
C) Vitamin D
D) Vitamin E
E) Vitamin B
A) Vitamin K
B) Vitamin A
C) Vitamin D
D) Vitamin E
E) Vitamin B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
You isolate a compound that is insoluble in water, has alternating single and double bonds and has a bright orange color. You correctly conclude that this compound is a:
A) protein
B) nucleic acid
C) polysaccharide
D) steroid
E) carotenoid
A) protein
B) nucleic acid
C) polysaccharide
D) steroid
E) carotenoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which carbohydrate is the most structurally complex?
A) polymer
B) monomer
C) phospholipid
D) polysaccharide
E) monosaccharide
A) polymer
B) monomer
C) phospholipid
D) polysaccharide
E) monosaccharide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following describes an amphipathic molecule?
A) A phospholipid with two polar ends
B) A phospholipid with two hydrophobic ends
C) A steroid with a hydrophilic functional group
D) A steroid with a hydrophobic functional group
E) A phospholipid with both a hydrophobic end and a hydrophilic end
A) A phospholipid with two polar ends
B) A phospholipid with two hydrophobic ends
C) A steroid with a hydrophilic functional group
D) A steroid with a hydrophobic functional group
E) A phospholipid with both a hydrophobic end and a hydrophilic end

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What substance is removed during a condensation reaction?
A) water
B) a dimer
C) a polymer
D) a hydrocarbon
E) a carboxyl group
A) water
B) a dimer
C) a polymer
D) a hydrocarbon
E) a carboxyl group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What are compounds that have the same molecular formulas but different structures and different molecules?
A) Thiols
B) Monomers
C) Hexoses
D) Amyloplasts
E) Isomers
A) Thiols
B) Monomers
C) Hexoses
D) Amyloplasts
E) Isomers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which is a property of unsaturated fats?
A) They are more common in animals.
B) They are generally liquid at room temperature.
C) They have no double bonds in the carbon chains of their fatty acids.
D) They have fewer fatty acids per fat molecule than do saturated fats.
E) They contain more hydrogen than saturated fats that have the same number of carbon atoms.
A) They are more common in animals.
B) They are generally liquid at room temperature.
C) They have no double bonds in the carbon chains of their fatty acids.
D) They have fewer fatty acids per fat molecule than do saturated fats.
E) They contain more hydrogen than saturated fats that have the same number of carbon atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following fatty acids include one or more adjacent pairs of carbon atoms joined by a double bond?
A) saturated fatty acids
B) monounsaturated fatty acids
C) unsaturated fatty acids
D) polyunsaturated fatty acids
E) trans fatty acids
A) saturated fatty acids
B) monounsaturated fatty acids
C) unsaturated fatty acids
D) polyunsaturated fatty acids
E) trans fatty acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Unlike lipids, hydrophilic functional groups typically contain ____ atoms, which make them more soluble in water.
A) carbon
B) oxygen
C) hydrogen
D) nitrogen
E) phosphate
A) carbon
B) oxygen
C) hydrogen
D) nitrogen
E) phosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A molecule of a saturated triacylglycerol contains:
A) the maximum number of double bonds between carbons in the fatty acid chains
B) the maximum number of triple bonds between carbons in the fatty acid chains
C) the maximum number of hydrogen atoms in the fatty acid chains
D) fatty acid chains with both amino and carboxyl groups
E) alternating single and double bonds between carbons in the fatty acid chains
A) the maximum number of double bonds between carbons in the fatty acid chains
B) the maximum number of triple bonds between carbons in the fatty acid chains
C) the maximum number of hydrogen atoms in the fatty acid chains
D) fatty acid chains with both amino and carboxyl groups
E) alternating single and double bonds between carbons in the fatty acid chains

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
How many covalent bonds are formed by carbon atoms, producing a wide variety of molecular shapes and sizes?
A) Six
B) Two
C) Three
D) Four
E) Seven
A) Six
B) Two
C) Three
D) Four
E) Seven

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Figure 3-1
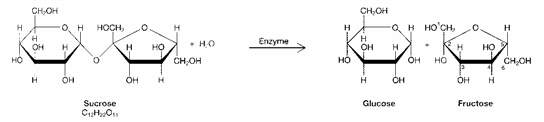
The products of the process in the accompanying figure are:
A) enzymes
B) amino acids
C) monosaccharides
D) molecules of glycerol
E) representative of a glycoside linkage

The products of the process in the accompanying figure are:
A) enzymes
B) amino acids
C) monosaccharides
D) molecules of glycerol
E) representative of a glycoside linkage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following describes the tertiary structure of a protein molecule?
A) bonding of two amino acids to form a dipeptide
B) folding of a peptide chain to form an alpha helix
C) association of several polypeptide chains by weak bonds
D) order in which amino acids are joined in a peptide chain
E) three-dimensional shape of an individual polypeptide chain
A) bonding of two amino acids to form a dipeptide
B) folding of a peptide chain to form an alpha helix
C) association of several polypeptide chains by weak bonds
D) order in which amino acids are joined in a peptide chain
E) three-dimensional shape of an individual polypeptide chain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Figure 3-2
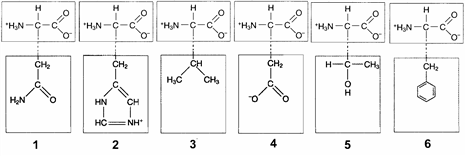
In the accompanying figure, ionic bonds would form between the R groups of which amino acids?
A) 1 and 3
B) 2 and 4
C) 3 and 5
D) 4 and 6
E) 3 and 6

In the accompanying figure, ionic bonds would form between the R groups of which amino acids?
A) 1 and 3
B) 2 and 4
C) 3 and 5
D) 4 and 6
E) 3 and 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When two amino acids combine in a condensation reaction, a ____________ is formed.
A) peptide bond
B) dipeptide bond
C) polypeptide chain
D) trans bond
E) cis bond
A) peptide bond
B) dipeptide bond
C) polypeptide chain
D) trans bond
E) cis bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the functionality of regulatory proteins?
A) strengthen and protect cells and tissues
B) store nutrients
C) control the activities of proteins, genes, cells, and tissues
D) generate movement in cells and tissues
E) move substances between cells and across cell membranes
A) strengthen and protect cells and tissues
B) store nutrients
C) control the activities of proteins, genes, cells, and tissues
D) generate movement in cells and tissues
E) move substances between cells and across cell membranes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the purpose of regulatory proteins?
A) To store nutrients
B) To defend against foreign invaders
C) To catalyze a specific chemical reaction
D) To control the expression of specific genes
E) To strengthen and protect cells and tissues
A) To store nutrients
B) To defend against foreign invaders
C) To catalyze a specific chemical reaction
D) To control the expression of specific genes
E) To strengthen and protect cells and tissues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
_____________ is a region where a polypeptide chain forms a uniform helical coil.
A) Beta globin
B) Alpha globin
C) Beta turns
D) α-helix
E) Beta-pleated sheet
A) Beta globin
B) Alpha globin
C) Beta turns
D) α-helix
E) Beta-pleated sheet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
At which level of protein structure are peptide bonds most important?
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary
E) globular
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary
E) globular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What type of protein accelerates the thousands of different chemical reactions that take place in an organism?
A) enzyme
B) amino acid
C) transport protein
D) regulatory protein
E) protective protein
A) enzyme
B) amino acid
C) transport protein
D) regulatory protein
E) protective protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Assume that the shaded portions of the molecule in the accompanying figure each represent different polypeptide chains. What does this represent?

A) Cellulose
B) A carotenoid
C) An amino acid
D) A steroid hormone
E) The quaternary structure of a protein

A) Cellulose
B) A carotenoid
C) An amino acid
D) A steroid hormone
E) The quaternary structure of a protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When a nucleic acid undergoes hydrolysis, the resulting subunits are:
A) fatty acids
B) amino acids
C) nucleotides
D) carotenoids
E) monosaccharides
A) fatty acids
B) amino acids
C) nucleotides
D) carotenoids
E) monosaccharides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Analysis of a certain polymer shows that it contains phosphate groups, ribose groups, and pyrimidines. Based on this information, what statement best describes this compound?
A) It is RNA.
B) It is DNA.
C) It is cylic AMP.
D) It is a polypeptide.
E) It is an inorganic compound.
A) It is RNA.
B) It is DNA.
C) It is cylic AMP.
D) It is a polypeptide.
E) It is an inorganic compound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Figure 3-3
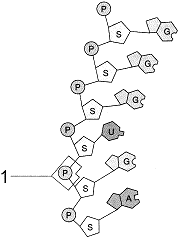
The molecular fragment, represented in the accompanying figure is:
A) ATP
B) RNA
C) DNA
D) a nucleotide
E) a polysaccharide

The molecular fragment, represented in the accompanying figure is:
A) ATP
B) RNA
C) DNA
D) a nucleotide
E) a polysaccharide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which functional group in cysteine residues can form bridges that help stabilize a protein's tertiary structure?
A) amino
B) carbonyl
C) hydroxyl
D) phosphate
E) sulfhydryl
A) amino
B) carbonyl
C) hydroxyl
D) phosphate
E) sulfhydryl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The helical coil shape of an α-helix fibrous protein provides what type of property to that protein?
A) rigidity
B) strength
C) elasticity
D) heat tolerance
E) water retention
A) rigidity
B) strength
C) elasticity
D) heat tolerance
E) water retention

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Figure 3-2
In the accompanying figure, hydrophobic interactions would occur between the R groups of which two amino acids?
A) 1 and 4
B) 2 and 5
C) 3 and 6
D) 2 and 4
E) 3 and 5

In the accompanying figure, hydrophobic interactions would occur between the R groups of which two amino acids?
A) 1 and 4
B) 2 and 5
C) 3 and 6
D) 2 and 4
E) 3 and 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which pair matches the correct macromolecule with the bond that joins its subunits?
A) protein−ester linkage
B) steroid−peptide bond
C) polysaccharide−peptide bond
D) triacylglycerol−glycosidic linkage
E) nucleic acid−phosphodiester linkage
A) protein−ester linkage
B) steroid−peptide bond
C) polysaccharide−peptide bond
D) triacylglycerol−glycosidic linkage
E) nucleic acid−phosphodiester linkage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is responsible for the alpha-helical structure of proteins?
A) hydrogen bonds
B) ionic interactions
C) polar covalent bonds
D) hydrophobic interactions
E) nonpolar covalent bonds
A) hydrogen bonds
B) ionic interactions
C) polar covalent bonds
D) hydrophobic interactions
E) nonpolar covalent bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the purpose of molecular chaperones?
A) To transfer an amino acid
B) To attach a carboxyl group
C) To straighten other molecular proteins
D) To strengthen the tertiary structure of a protein
E) To assist the folding of other molecular proteins
A) To transfer an amino acid
B) To attach a carboxyl group
C) To straighten other molecular proteins
D) To strengthen the tertiary structure of a protein
E) To assist the folding of other molecular proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The primary difference between the amino acids commonly found in proteins is in their:
A) R or variable groups
B) number of potassium groups
C) number of phosphate groups
D) number of carbonyl groups
E) number of asymmetric carbons
A) R or variable groups
B) number of potassium groups
C) number of phosphate groups
D) number of carbonyl groups
E) number of asymmetric carbons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
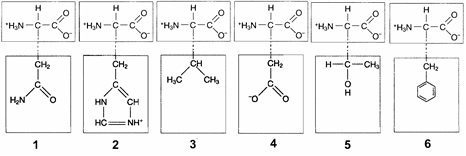
The following amino acid would be characterized as ____ based on the chemical properties of its side chain.
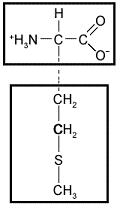
A) basic
B) acidic
C) nonpolar
D) hydrophilic
E) electrically charged

A) basic
B) acidic
C) nonpolar
D) hydrophilic
E) electrically charged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which lipid can be identified by its isoprene units?
A) Fats
B) Steroids
C) Carotenoids
D) Amino acids
E) Phospholipids
A) Fats
B) Steroids
C) Carotenoids
D) Amino acids
E) Phospholipids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is a purine base found in nucleotides?
A) uracil
B) steroid
C) guanine
D) cytosine
E) thymine
A) uracil
B) steroid
C) guanine
D) cytosine
E) thymine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
_______________________ are isomers that are mirror images of each other.
A) Geometric isomers
B) Structural isomers
C) Disaccharides
D) Enantiomers
E) Amino groups
A) Geometric isomers
B) Structural isomers
C) Disaccharides
D) Enantiomers
E) Amino groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Since a carbon atom has 4 valence electrons, it can complete its valence shell by forming a total of 4 hydrogen bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The carboxyl group can exist in either an ionized or nonionized form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What does the term "functional group" mean in the context of organic molecules? Briefly describe two types of functional groups and their chemical properties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Cellulose is the main structural component of the walls that surround plant cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which organic compound is not only responsible for energy storage, but can also provide thermal insulation?
A) Lipids
B) Proteins
C) Nucleic acids
D) Carbohydrates
E) Monosaccharides
A) Lipids
B) Proteins
C) Nucleic acids
D) Carbohydrates
E) Monosaccharides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
By definition, geometric isomers are mirror images of each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Hemoglobin consists of 574 amino acids arranged in four polypeptide chains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Why is ATP important in living organisms?
A) It is easily converted to starch for long-term storage.
B) It can transfer some of its energy to other chemicals.
C) It is an important structural component of cell membranes.
D) Like all other nucleic acids, it stores hereditary information.
E) Like RNA, it acts as a source code for the formation of proteins.
A) It is easily converted to starch for long-term storage.
B) It can transfer some of its energy to other chemicals.
C) It is an important structural component of cell membranes.
D) Like all other nucleic acids, it stores hereditary information.
E) Like RNA, it acts as a source code for the formation of proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When glucose and fructose undergo condensation, maltose is produced as a product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A phosphate group is weakly acidic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An essential amino acid is one that the body cannot synthesize in sufficient amounts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Fats and steroids have very different functions. However, both are structurally related and share some of the same characteristics. Briefly, describe the similarities and differences between the two molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
You have discovered a protein that consists of three identical subunits (polypeptide chains). Each subunit has an alpha helix and two different domains that are connected by two cysteine residues. Describe the four levels of organization for this protein and list the type(s) of bond(s) involved in establishing each structural level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A disaccharide is composed of two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The hydroxyl group is weakly acidic because of the presence of a strongly electronegative oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Condensation and hydrolysis reactions are catalyzed by the same enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Briefly describe three functions of proteins other than enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A pyrimidine is a double-ring molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disease caused by the deletion of one amino acid in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein. This deletion changes the shape of the protein in dramatic ways, causing serious health issues. How can the deletion of one amino acid lead to such drastic results?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Cyclic AMP is a type of nucleotide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Methane, which is composed of one carbon and four hydrogens is a gas at room temperature. Upon replacing one of the hydrogen atoms with a hydroxyl group, methane is converted to methanol, which is a liquid at room temperature. Explain the reason behind this difference in physical properties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What factors allow carbon to be ideally suitable to serve as the "backbone" for large molecules?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A beta-pleated sheet is an example of a protein's tertiary structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Molecular chaperones mediate the folding of other protein molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



