Deck 10: Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/78
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis
1
A cell is dividing by binary fission. What can you conclude?
A) Mitosis has taken place without cytokinesis.
B) Homologous chromosomes have already paired.
C) The cyclin-Cdk complex is no longer phosphorylating enzymes.
D) The cell is undergoing uncontrolled cell division.
E) The cell is prokaryotic.
A) Mitosis has taken place without cytokinesis.
B) Homologous chromosomes have already paired.
C) The cyclin-Cdk complex is no longer phosphorylating enzymes.
D) The cell is undergoing uncontrolled cell division.
E) The cell is prokaryotic.
E
2
What is not a hallmark of prophase?
A) Nuclear envelope is visible with the light microscope.
B) Nucleolus disappears.
C) Mitotic spindle is beginning to assemble.
D) Spindle fibers pull chromosomes to opposite sides of the cell.
E) Duplicated chromosomes become visible with the light microscope.
A) Nuclear envelope is visible with the light microscope.
B) Nucleolus disappears.
C) Mitotic spindle is beginning to assemble.
D) Spindle fibers pull chromosomes to opposite sides of the cell.
E) Duplicated chromosomes become visible with the light microscope.
D
3
Duplicated centrioles move to opposite poles of a dividing ____ cell during the ____ of the cell cycle.
A) plant; metaphase
B) plant; anaphase
C) prokaryotic; metaphase
D) animal; interphase
E) animal; prophase
A) plant; metaphase
B) plant; anaphase
C) prokaryotic; metaphase
D) animal; interphase
E) animal; prophase
E
4
Cytokinesis in animal cells involves contraction of a ring of ____ microfilaments.
A) tubulin plus actin
B) actin plus myosin
C) cyclin plus myosin
D) cohesin plus actin
E) cyclin plus actin
A) tubulin plus actin
B) actin plus myosin
C) cyclin plus myosin
D) cohesin plus actin
E) cyclin plus actin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When is a cell in metaphase?
A) The chromosomes are visible as threadlike structures.
B) The nuclear envelope is clearly visible.
C) The chromosomes are aligned at the midplane of the cell.
D) The chromosomes are separated into distinct groups at opposite cell poles.
E) Cytokinesis is occurring.
A) The chromosomes are visible as threadlike structures.
B) The nuclear envelope is clearly visible.
C) The chromosomes are aligned at the midplane of the cell.
D) The chromosomes are separated into distinct groups at opposite cell poles.
E) Cytokinesis is occurring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A bacterial chromosome consists of a
A) linear DNA molecule many times larger than the cell.
B) circular DNA molecule many times larger than the cell.
C) circular DNA molecule smaller than the cell.
D) linear DNA molecule smaller than the cell.
E) linear or circular DNA molecule smaller than the cell.
A) linear DNA molecule many times larger than the cell.
B) circular DNA molecule many times larger than the cell.
C) circular DNA molecule smaller than the cell.
D) linear DNA molecule smaller than the cell.
E) linear or circular DNA molecule smaller than the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In unwound chromatin, nucleosomes are organized into large coiled loops held together by
A) histones.
B) centromeres.
C) kinetochore proteins.
D) scaffolding proteins.
E) condensins.
A) histones.
B) centromeres.
C) kinetochore proteins.
D) scaffolding proteins.
E) condensins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following are surrounded by fibrils that make up the pericentriolar material?
A) Mitotic spindle
B) Centrioles
C) Kinetochore
D) Microtubules
E) Centromere
A) Mitotic spindle
B) Centrioles
C) Kinetochore
D) Microtubules
E) Centromere

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
____ ______________organized on chromosomes carry the information that controls the functions of the cell.
A) Proteins
B) Nucleosomes
C) Asters
D) Genes
E) Histones
A) Proteins
B) Nucleosomes
C) Asters
D) Genes
E) Histones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The cell cycle of a typical somatic cell consists of the ____ and M phases.
A) interphase
B) meiosis I
C) crossing-over
D) meiosis II
E) mitosis
A) interphase
B) meiosis I
C) crossing-over
D) meiosis II
E) mitosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the function of kinetochores?
A) Kinetochores anchor spindle fibers to the centrioles.
B) Kinetochores are the site of DNA synthesis.
C) Kinetochores regulate the length of the cell cycle.
D) Kinetochores attach to microtubules during mitosis.
E) Kinetochores are involved in cytokinesis.
A) Kinetochores anchor spindle fibers to the centrioles.
B) Kinetochores are the site of DNA synthesis.
C) Kinetochores regulate the length of the cell cycle.
D) Kinetochores attach to microtubules during mitosis.
E) Kinetochores are involved in cytokinesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Eukaryotic chromosomes consist of
A) circular DNA molecules complexed with positively charged nonhistone proteins.
B) circular DNA molecules complexed with negatively charged histone proteins.
C) linear DNA molecules complexed with positively charged histone proteins.
D) linear DNA molecules complexed with negatively charged histone proteins.
E) circular DNA molecules folded to fit inside a bacterial cell.
A) circular DNA molecules complexed with positively charged nonhistone proteins.
B) circular DNA molecules complexed with negatively charged histone proteins.
C) linear DNA molecules complexed with positively charged histone proteins.
D) linear DNA molecules complexed with negatively charged histone proteins.
E) circular DNA molecules folded to fit inside a bacterial cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The function of nucleosomes is to
A) prevent DNA strands from tangling.
B) help DNA replicate.
C) make RNA synthesis possible.
D) prevent RNA from tangling with DNA during transcription.
E) prevent histones from tangling.
A) prevent DNA strands from tangling.
B) help DNA replicate.
C) make RNA synthesis possible.
D) prevent RNA from tangling with DNA during transcription.
E) prevent histones from tangling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The ____ is responsible for the separation of the chromosomes during the ____ of mitosis.
A) cell wall; anaphase
B) mitotic spindle; interphase
C) mitotic spindle; anaphase
D) kinetochore; prophase
E) centromere; telophase
A) cell wall; anaphase
B) mitotic spindle; interphase
C) mitotic spindle; anaphase
D) kinetochore; prophase
E) centromere; telophase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Nucleosomes are best described as
A) eukaryotic DNA associated with histone proteins.
B) prokaryotic DNA associated with nonhistone proteins.
C) eukaryotic DNA associated with nonhistone proteins.
D) prokaryotic DNA associated with histone proteins.
E) eukaryotic DNA associated with scaffolding proteins.
A) eukaryotic DNA associated with histone proteins.
B) prokaryotic DNA associated with nonhistone proteins.
C) eukaryotic DNA associated with nonhistone proteins.
D) prokaryotic DNA associated with histone proteins.
E) eukaryotic DNA associated with scaffolding proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The mitotic spindle is made of
A) motor proteins.
B) condensin.
C) histones.
D) Z rings.
E) microtubules.
A) motor proteins.
B) condensin.
C) histones.
D) Z rings.
E) microtubules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Eukaryotic chromosomes are composed of
A) proteins only.
B) chromatin.
C) DNA only.
D) circular chromatin.
E) karyotypes.
A) proteins only.
B) chromatin.
C) DNA only.
D) circular chromatin.
E) karyotypes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
During prophase, ____ is(are) compacted into visible chromosomes.
A) chromatin
B) centrioles
C) centromeres
D) kinetochores
E) tetrads
A) chromatin
B) centrioles
C) centromeres
D) kinetochores
E) tetrads

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
____ contain identical DNA sequences and are held together by ____ during mitosis.
A) Daughter chromosomes; hydrogen bonding
B) Daughter chromosomes; ionic bonding
C) Sister chromatids; spindle fibers
D) Sister chromosomes; histone proteins
E) Sister chromatids; cohesin proteins
A) Daughter chromosomes; hydrogen bonding
B) Daughter chromosomes; ionic bonding
C) Sister chromatids; spindle fibers
D) Sister chromosomes; histone proteins
E) Sister chromatids; cohesin proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Cytokinesis in plant cells occurs via the formation of a(n)
A) aster.
B) mitotic spindle.
C) Golgi complex.
D) cell wall.
E) cell plate.
A) aster.
B) mitotic spindle.
C) Golgi complex.
D) cell wall.
E) cell plate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
To control the cell cycle,
A) the activity of Cdks stays the same throughout the cell cycle.
B) cyclins fluctuate during the cell cycle.
C) Cdks are active only when they are released from cyclins.
D) the anaphase-promoting complex stimulates DNA replication.
E) M-Cdk inhibits mitosis.
A) the activity of Cdks stays the same throughout the cell cycle.
B) cyclins fluctuate during the cell cycle.
C) Cdks are active only when they are released from cyclins.
D) the anaphase-promoting complex stimulates DNA replication.
E) M-Cdk inhibits mitosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Homologous chromosomes undergo synapsis during
A) anaphase I.
B) prophase I.
C) anaphase II.
D) telophase II.
E) prophase II.
A) anaphase I.
B) prophase I.
C) anaphase II.
D) telophase II.
E) prophase II.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
During which stage of meiosis do the sister chromatids separate?
A) Metaphase I
B) Anaphase I
C) Metaphase II
D) Anaphase II
E) telophase II
A) Metaphase I
B) Anaphase I
C) Metaphase II
D) Anaphase II
E) telophase II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Figure 10-1
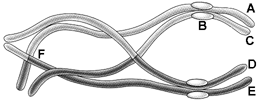
Which phase of cell division is depicted in the accompanying figure?
A) Prophase of mitosis
B) Metaphase of mitosis
C) Prophase I of meiosis
D) Prophase II of meiosis
E) Metaphase I of meiosis
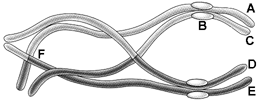
Which phase of cell division is depicted in the accompanying figure?
A) Prophase of mitosis
B) Metaphase of mitosis
C) Prophase I of meiosis
D) Prophase II of meiosis
E) Metaphase I of meiosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
During prophase I of meiosis, homologous chromosomes lie side by side. This phenomenon is known as
A) chromatid pairing.
B) DNA replication.
C) tetrad formation.
D) paternal pairing.
E) parental pairing.
A) chromatid pairing.
B) DNA replication.
C) tetrad formation.
D) paternal pairing.
E) parental pairing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A cell in the G2 phase
A) has twice the amount of DNA present in a telophase nucleus.
B) has visibly distinct chromosomes.
C) lacks a visible nuclear membrane.
D) is in mitosis.
E) is in cytokinesis.
A) has twice the amount of DNA present in a telophase nucleus.
B) has visibly distinct chromosomes.
C) lacks a visible nuclear membrane.
D) is in mitosis.
E) is in cytokinesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Homologous chromosomes can be identified and/or characterized by
A) their similar and characteristic staining patterns.
B) the different centromere positions in the maternal versus paternal chromosomes.
C) those chromosomes that do not have partners.
D) paternal chromosomes only.
E) maternal chromosomes only.
A) their similar and characteristic staining patterns.
B) the different centromere positions in the maternal versus paternal chromosomes.
C) those chromosomes that do not have partners.
D) paternal chromosomes only.
E) maternal chromosomes only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What evolutionary advantage is provided by sexual reproduction?
A) Increased genetic diversity
B) Generation of clones
C) Production of genetically identical offspring
D) Possibility of polyploidy in the progeny
E) Removal of all genetic mutations
A) Increased genetic diversity
B) Generation of clones
C) Production of genetically identical offspring
D) Possibility of polyploidy in the progeny
E) Removal of all genetic mutations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Plant hormones known as ____ stimulate mitosis.
A) scaffolding proteins
B) growth factors
C) cytokinins
D) cyclins
E) cohesins
A) scaffolding proteins
B) growth factors
C) cytokinins
D) cyclins
E) cohesins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Once nerve cells become mature, they do not typically undergo cell division. Based on your knowledge of the cell cycle, you might predict that mature nerve cells become arrested in the ____ of the cell cycle.
A) G0 phase
B) S phase
C) prophase
D) G1 phase
E) G2 phase
A) G0 phase
B) S phase
C) prophase
D) G1 phase
E) G2 phase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Chromosomes are duplicated during the ____ of the cell cycle.
A) G1 phase
B) G2 phase
C) S phase
D) metaphase
E) prophase
A) G1 phase
B) G2 phase
C) S phase
D) metaphase
E) prophase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is produced by meiosis?
A) Somatic cells
B) Animal gametes
C) Polyploid cells
D) Diploid cells
E) Zygotes
A) Somatic cells
B) Animal gametes
C) Polyploid cells
D) Diploid cells
E) Zygotes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Figure 10-1
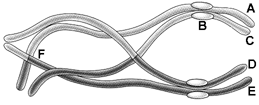
In the accompanying figure, which combination of letters accurately represents two homologous chromosomes?
A) A and B
B) A and C
C) A and D
D) B and F
E) D and E
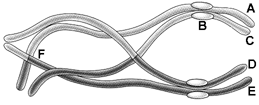
In the accompanying figure, which combination of letters accurately represents two homologous chromosomes?
A) A and B
B) A and C
C) A and D
D) B and F
E) D and E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
During prophase I, each chiasma represents
A) the remnants of the nuclear envelope.
B) the remnant of the nucleolus.
C) a newly formed haploid gamete.
D) a site of crossing-over.
E) the site where sister chromatids are connected.
A) the remnants of the nuclear envelope.
B) the remnant of the nucleolus.
C) a newly formed haploid gamete.
D) a site of crossing-over.
E) the site where sister chromatids are connected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In a human cell at prophase I, there are ____ tetrads.
A) 92
B) 46
C) 23
D) 2
E) 4
A) 92
B) 46
C) 23
D) 2
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The M phase of the cell cycle involves two main processes:
A) mitosis and cytokinesis.
B) meiosis I and meiosis II.
C) homologous pairing and crossing over.
D) interphase and mitosis.
E) mitosis and meiosis.
A) mitosis and cytokinesis.
B) meiosis I and meiosis II.
C) homologous pairing and crossing over.
D) interphase and mitosis.
E) mitosis and meiosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
To prevent disastrous consequences, the eukaryotic cell cycle is controlled by
A) the mitochondria.
B) replication.
C) environmental signals.
D) a very detailed, rigid genetic program.
E) a series of cell cycle checkpoints.
A) the mitochondria.
B) replication.
C) environmental signals.
D) a very detailed, rigid genetic program.
E) a series of cell cycle checkpoints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An animal with a diploid number of 36 chromosomes will have ____ chromosomes in its gametes and ____ chromosomes in its somatic cells.
A) 18; 18
B) 18; 36
C) 36; 18
D) 36; 36
E) 36; 72
A) 18; 18
B) 18; 36
C) 36; 18
D) 36; 36
E) 36; 72

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What would happen if meiosis did not occur in sexually reproducing organisms?
A) The growth of the zygote would be halted.
B) Mitosis would be sufficient to produce haploid gametes.
C) The gametes would remain haploid.
D) The chromosome number would double in each generation.
E) The eggs would be haploid, but the sperm would be diploid.
A) The growth of the zygote would be halted.
B) Mitosis would be sufficient to produce haploid gametes.
C) The gametes would remain haploid.
D) The chromosome number would double in each generation.
E) The eggs would be haploid, but the sperm would be diploid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Figure 10-1
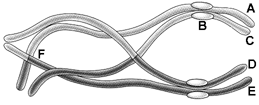
In the accompanying figure, which combination of letters accurately represents two sister chromatids?
A) A and B
B) A and C
C) A and D
D) A and E
E) B and F
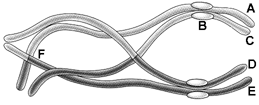
In the accompanying figure, which combination of letters accurately represents two sister chromatids?
A) A and B
B) A and C
C) A and D
D) A and E
E) B and F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Microtubules of the mitotic spindle attach directly to each chromosome at the centromere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An animal zygote is a haploid cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In fungi and protists, gametes produced by ____ of haploid cells fuse to form a ____ zygote, which then undergoes ____ to restore the haploid chromosome number.
A) mitosis, diploid, meiosis
B) meiosis, diploid, mitosis
C) mitosis, haploid, meiosis
D) meiosis, haploid, mitosis
E) mitosis, diploid, mitosis
A) mitosis, diploid, meiosis
B) meiosis, diploid, mitosis
C) mitosis, haploid, meiosis
D) meiosis, haploid, mitosis
E) mitosis, diploid, mitosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Briefly describe the advantages of asexual reproduction of unicellular organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Briefly explain the difference between meiosis I and mitosis. Also, explain the reasons for these differences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Cell-cycle checkpoints temporarily block key events from being initiated during the cell cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Figure 10-2

The process occurring at arrow 3 in the accompanying figure is
A) fertilization.
B) G1.
C) meiosis.
D) mitosis.
E) fusion.

The process occurring at arrow 3 in the accompanying figure is
A) fertilization.
B) G1.
C) meiosis.
D) mitosis.
E) fusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The nuclear envelope fragments during the prometaphase stage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
At the completion of oogenesis, ____ are produced.
A) male gametes
B) four sperm cells
C) four egg cells
D) one egg cell and three polar bodies
E) haploid spores
A) male gametes
B) four sperm cells
C) four egg cells
D) one egg cell and three polar bodies
E) haploid spores

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
List the stages in the eukaryotic cell cycle, and identify the principal events that occur during each stage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the cell cycle, DNA is replicated during the G2 phase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Homologous pairs of chromosomes separate during meiosis I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Enzymes required for DNA replication are synthesized during the G1 phase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Draw and label the parts of a sister chromatid. List the function of each structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A nucleosome consists of DNA wrapped around scaffolding proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A pair of centrioles is found at the center of the microtubule-organizing center in plant cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In animal cells, cytokinesis occurs via the formation of a cell plate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Gametophyte plants produce gametes using
A) mitosis.
B) meiosis.
C) fertilization.
D) polyploidy.
E) sporogenesis.
A) mitosis.
B) meiosis.
C) fertilization.
D) polyploidy.
E) sporogenesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Bacteria divide asexually by mitosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which event occurs in prophase II?
A) Disappearance of the spindle
B) Condensation of the chromatin into chromosomes
C) Formation of the chiasmata
D) Crossing over occurs.
E) Formation of the cleavage furrow
A) Disappearance of the spindle
B) Condensation of the chromatin into chromosomes
C) Formation of the chiasmata
D) Crossing over occurs.
E) Formation of the cleavage furrow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
For each animal cell that begins oogenesis, the number of ova produced is four.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Sketch the life cycle of a plant and label the ploidy of each stage. You may use n to represent the haploid number of chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Why do the cells produced by meiosis undergo two nuclear divisions but only have a haploid number of chromosomes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Briefly describe how the cell cycle is controlled and why phosphorylation of proteins plays a major role.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



