Deck 16: Human Genetics and the Human Genome
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/82
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Human Genetics and the Human Genome
1
Autosomal monosomy is not seen in live births because:
A) its effects are so small as to be overlooked.
B) its effects do not set in until adulthood.
C) its effects are so lethal as to cause spontaneous abortion early in pregnancy.
D) it only occurs in sex chromosomes and therefore does affect nonreproductive function.
E) the births lead to the establishment of a clone of abnormal cells.
A) its effects are so small as to be overlooked.
B) its effects do not set in until adulthood.
C) its effects are so lethal as to cause spontaneous abortion early in pregnancy.
D) it only occurs in sex chromosomes and therefore does affect nonreproductive function.
E) the births lead to the establishment of a clone of abnormal cells.
C
2
The human genome contains about ____ genes, which comprises about _____ of the genome.
A) 25,000; 2%
B) 45,000; 2%
C) 25,000; 50%
D) 80,000; 2%
E) 100,000; 1%
A) 25,000; 2%
B) 45,000; 2%
C) 25,000; 50%
D) 80,000; 2%
E) 100,000; 1%
A
3
What was revealed with the completion of the Human Genome Project?
A) the sequence of the entire human genome
B) the functions of all human genes
C) the knowledge that all genetic variations lead to genetic disease
D) the knowledge that all genetic variations are found outside of protein-coding regions
E) the number, but not the locations, of genes in the human genome
A) the sequence of the entire human genome
B) the functions of all human genes
C) the knowledge that all genetic variations lead to genetic disease
D) the knowledge that all genetic variations are found outside of protein-coding regions
E) the number, but not the locations, of genes in the human genome
A
4
Karyotyping is useful for determining:
A) the number of chromosomes in an individual
B) the presence of recessive traits
C) whether a specific gene is missing from a chromosome
D) whether gene mutations have occurred
E) the presence of sickle cell anemia
A) the number of chromosomes in an individual
B) the presence of recessive traits
C) whether a specific gene is missing from a chromosome
D) whether gene mutations have occurred
E) the presence of sickle cell anemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Persons having an XO karyotype are sterile females. They have ____ syndrome.
A) Turner
B) Klinefelter
C) Down (trisomy form)
D) Phenylketonuria
E) Down (translocation form)
A) Turner
B) Klinefelter
C) Down (trisomy form)
D) Phenylketonuria
E) Down (translocation form)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The sperm in the figure below were most likely produced by:
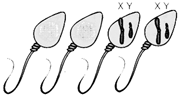
A) nondisjunction
B) mutation
C) X-linkage
D) translocation
E) normal meiosis

A) nondisjunction
B) mutation
C) X-linkage
D) translocation
E) normal meiosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Nearly half of the pregnancies that end in miscarriage have:
A) trisomy of chromosome 21
B) homozygosity for a recessive lethal allele
C) major chromosomal abnormalities
D) Klinefelter syndrome
E) Down syndrome
A) trisomy of chromosome 21
B) homozygosity for a recessive lethal allele
C) major chromosomal abnormalities
D) Klinefelter syndrome
E) Down syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Human genetics can be most effectively studied using:
A) offspring raised under controlled conditions
B) experimental matings between true-breeding strains
C) controlled matings
D) population studies of large extended families
E) population studies of small extended families
A) offspring raised under controlled conditions
B) experimental matings between true-breeding strains
C) controlled matings
D) population studies of large extended families
E) population studies of small extended families

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Figure 16-2
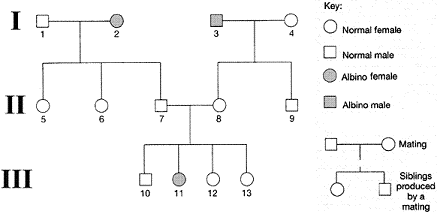
The genotypes of the normal females in the second generation in accompanying figure are:
A) homozygous for albinism
B) heterozygous for hair color
C) heterozygous for albinism
D) X-linked
E) unknown

The genotypes of the normal females in the second generation in accompanying figure are:
A) homozygous for albinism
B) heterozygous for hair color
C) heterozygous for albinism
D) X-linked
E) unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Figure 16-2
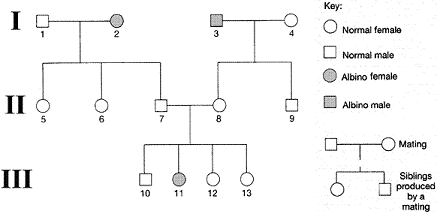
The inheritance pattern demonstrated by the pedigree in accompanying figure is:
A) autosomal recessive
B) autosomal dominant
C) X-linked recessive
D) X-linked dominant
E) undeterminable from these data

The inheritance pattern demonstrated by the pedigree in accompanying figure is:
A) autosomal recessive
B) autosomal dominant
C) X-linked recessive
D) X-linked dominant
E) undeterminable from these data

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Turner syndrome is an example of a __________ condition.
A) monosomic
B) disomic
C) trisomic
D) polyploid
E) fragile site
A) monosomic
B) disomic
C) trisomic
D) polyploid
E) fragile site

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In genomic imprinting:
A) a gene is imprinted in the progeny, depending upon the phenotype of the parent.
B) the expression of a gene depends on the parental phenotype.
C) a gene is imprinted in the progeny, depending upon the age of the parent.
D) the expression of a gene in the progeny depends upon which parent the gene is inherited from.
E) only dominant traits are expressed.
A) a gene is imprinted in the progeny, depending upon the phenotype of the parent.
B) the expression of a gene depends on the parental phenotype.
C) a gene is imprinted in the progeny, depending upon the age of the parent.
D) the expression of a gene in the progeny depends upon which parent the gene is inherited from.
E) only dominant traits are expressed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Figure 16-2
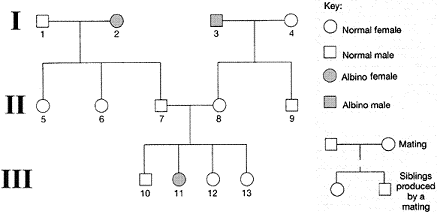
Refer to the accompanying figure. Based on the phenotypes of the third generation, the genotype of the father in the second generation must be:
A) homozygous for albinism
B) heterozygous for hair color
C) heterozygous for albinism
D) X-linked
E) dominant

Refer to the accompanying figure. Based on the phenotypes of the third generation, the genotype of the father in the second generation must be:
A) homozygous for albinism
B) heterozygous for hair color
C) heterozygous for albinism
D) X-linked
E) dominant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The normal human karyotype contains ____ total chromosomes, consisting of ____ autosomes and ____ sex chromosomes.
A) 23; 22; 1
B) 44; 22; 1
C) 46; 22; 2
D) 46; 23; 0
E) 22; 20; 2
A) 23; 22; 1
B) 44; 22; 1
C) 46; 22; 2
D) 46; 23; 0
E) 22; 20; 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Gene targeting has been used in mice to produce strains that were either homozygous or heterozygous for ____.
A) PKU
B) cystic fibrosis
C) Huntington's disease
D) sickle cell anemia
E) Tay-Sachs disease
A) PKU
B) cystic fibrosis
C) Huntington's disease
D) sickle cell anemia
E) Tay-Sachs disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Down syndrome is an example of a ____ condition.
A) monosomic
B) disomic
C) trisomic
D) polyploid
E) transgenic
A) monosomic
B) disomic
C) trisomic
D) polyploid
E) transgenic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Colchicine is a drug that:
A) arrests cells in mitotic telophase
B) stimulates meiosis
C) prevents DNA replication
D) arrests cells in mitotic metaphase
E) prevents cells from entering prophase
A) arrests cells in mitotic telophase
B) stimulates meiosis
C) prevents DNA replication
D) arrests cells in mitotic metaphase
E) prevents cells from entering prophase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The position of a specific gene on a chromosome can be determined by:
A) preparing a karyotype
B) southern blotting
C) genomic hybridization
D) chromosome sorting
E) fluorescent in situ hybridization
A) preparing a karyotype
B) southern blotting
C) genomic hybridization
D) chromosome sorting
E) fluorescent in situ hybridization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Down syndrome is characterized by:
A) single base mutations
B) the presence of 47 chromosomes per somatic cell
C) increasing risk with younger maternal age
D) the presence of an extra chromosome 18 in each somatic cell
E) the same symptoms observed in each individual
A) single base mutations
B) the presence of 47 chromosomes per somatic cell
C) increasing risk with younger maternal age
D) the presence of an extra chromosome 18 in each somatic cell
E) the same symptoms observed in each individual

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Comparing the human and mouse genomes has revealed that the mouse and human:
A) share few genes
B) genomes are identical
C) genomes have no genes in common
D) share most genes
E) genomes have identical noncoding DNA
A) share few genes
B) genomes are identical
C) genomes have no genes in common
D) share most genes
E) genomes have identical noncoding DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Huntington's disease is caused by a:
A) rare recessive allele
B) nucleotide triplet repeat
C) monosomic condition
D) dominant X-linked allele
E) deletion of part of chromosome 4
A) rare recessive allele
B) nucleotide triplet repeat
C) monosomic condition
D) dominant X-linked allele
E) deletion of part of chromosome 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following are inborn errors of metabolism?
A) PKU and alkaptonuria
B) sickle cell anemia and hemophilia
C) cystic fibrosis and Tay-Sachs disease
D) Huntington's disease and fragile X syndrome
E) cri du chat syndrome and Down syndrome
A) PKU and alkaptonuria
B) sickle cell anemia and hemophilia
C) cystic fibrosis and Tay-Sachs disease
D) Huntington's disease and fragile X syndrome
E) cri du chat syndrome and Down syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Aneuploidies describe:
A) a phenomenon that only occurs in plants
B) a condition in which an extra chromosome is present or one is absent
C) a defect that is always fatal in humans
D) an uncommon condition in humans
E) mutations that almost always have a beneficial effect on an individual
A) a phenomenon that only occurs in plants
B) a condition in which an extra chromosome is present or one is absent
C) a defect that is always fatal in humans
D) an uncommon condition in humans
E) mutations that almost always have a beneficial effect on an individual

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Maternal PKU can result in serious effects in fetuses. This problem occurs because:
A) the fetus is homozygous for PKU and therefore cannot metabolize phenylalanine.
B) the fetus is usually homozygous dominant and therefore has PKU.
C) the mother is heterozygous for PKU and therefore cannot metabolize phenylalanine.
D) the mother is homozygous dominant for PKU and cannot metabolize phenylalanine.
E) the mother is homozygous recessive for PKU and cannot metabolize phenylalanine.
A) the fetus is homozygous for PKU and therefore cannot metabolize phenylalanine.
B) the fetus is usually homozygous dominant and therefore has PKU.
C) the mother is heterozygous for PKU and therefore cannot metabolize phenylalanine.
D) the mother is homozygous dominant for PKU and cannot metabolize phenylalanine.
E) the mother is homozygous recessive for PKU and cannot metabolize phenylalanine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Hemophilia A is an example of a(n) _____ disease and is characterized by a lack of blood-clotting factor ____.
A) X-linked; VIII
B) sex-linked recessive; V
C) autosomal dominant; VIII
D) sex-linked dominant; V
E) autosomal recessive; VIII
A) X-linked; VIII
B) sex-linked recessive; V
C) autosomal dominant; VIII
D) sex-linked dominant; V
E) autosomal recessive; VIII

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Cri du chat syndrome arises from:
A) trisomy for chromosome 5
B) deletion of part of chromosome 5
C) a 14/21 reciprocal translocation
D) nondisjunction
E) a duplication of part of chromosome 15
A) trisomy for chromosome 5
B) deletion of part of chromosome 5
C) a 14/21 reciprocal translocation
D) nondisjunction
E) a duplication of part of chromosome 15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Autosomal aneuploidies arise by:
A) chromosome breakage and rejoining
B) meiotic nondisjunction
C) errors in crossing-over
D) mistakes in chromosome replication
E) mitotic nondisjunction
A) chromosome breakage and rejoining
B) meiotic nondisjunction
C) errors in crossing-over
D) mistakes in chromosome replication
E) mitotic nondisjunction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A fragile site:
A) is found only on the X chromosome
B) occurs in only one of the sister chromatids
C) is associated with cancerous cells
D) is usually not inherited
E) is the result of genomic imprinting
A) is found only on the X chromosome
B) occurs in only one of the sister chromatids
C) is associated with cancerous cells
D) is usually not inherited
E) is the result of genomic imprinting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What explains the viability of individuals with aneuploidies for the sex chromosomes?
A) Sex chromosomes carry less information than autosomes.
B) The lack of crossing-over between the X and the Y chromosomes.
C) Sex chromosomes are smaller than most autosomes.
D) The information on sex chromosomes is duplicated on the autosomes.
E) Dosage compensation, by which one X chromosome per cell is inactivated.
A) Sex chromosomes carry less information than autosomes.
B) The lack of crossing-over between the X and the Y chromosomes.
C) Sex chromosomes are smaller than most autosomes.
D) The information on sex chromosomes is duplicated on the autosomes.
E) Dosage compensation, by which one X chromosome per cell is inactivated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Nondisjunction during mitosis leads to:
A) an individual with a clone of abnormal cells
B) an individual with all abnormal cells
C) death of the daughter cells
D) nonviable sperm
E) normal daughter cells
A) an individual with a clone of abnormal cells
B) an individual with all abnormal cells
C) death of the daughter cells
D) nonviable sperm
E) normal daughter cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Translocation occurs when:
A) part of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to a nonhomologous chromosome
B) part of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to a homologous chromosome
C) crossing-over events occur
D) genes move from one area on a chromosome to another area on the same chromosome
E) a Y chromosome replaces an X chromosome in a female cell
A) part of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to a nonhomologous chromosome
B) part of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to a homologous chromosome
C) crossing-over events occur
D) genes move from one area on a chromosome to another area on the same chromosome
E) a Y chromosome replaces an X chromosome in a female cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Polyploidy:
A) may be the result of more than one sperm fertilizing an egg
B) is not lethal in humans
C) may be the result of the failure of a chromosome to separate during meiosis
D) can be due to nondisjunction for a chromosome
E) is the mechanism of dosage compensation
A) may be the result of more than one sperm fertilizing an egg
B) is not lethal in humans
C) may be the result of the failure of a chromosome to separate during meiosis
D) can be due to nondisjunction for a chromosome
E) is the mechanism of dosage compensation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In a chromosomal inversion, a segment of a chromosome is:
A) reversed
B) duplicated
C) lost
D) attached to a nonhomologous chromosome
E) deleted
A) reversed
B) duplicated
C) lost
D) attached to a nonhomologous chromosome
E) deleted

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
An individual who inherits the specific chromosome ____ deletion from his/her ____ will most likely have Prader-Willi syndrome rather than Angelman syndrome.
A) 15; mother
B) 15; father
C) 21; mother
D) 21; father
E) 12; father
A) 15; mother
B) 15; father
C) 21; mother
D) 21; father
E) 12; father

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Fragile X syndrome:
A) results in learning, attention, and hyperactivity disabilities in males
B) is not inherited from the parents
C) is characterized by a fragile site at the tip of the Y chromosome
D) results from a deletion of CGG sequences in the fragile X gene
E) is due to genomic imprinting
A) results in learning, attention, and hyperactivity disabilities in males
B) is not inherited from the parents
C) is characterized by a fragile site at the tip of the Y chromosome
D) results from a deletion of CGG sequences in the fragile X gene
E) is due to genomic imprinting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Polyploidy is the:
A) presence of more than two of a certain chromosome
B) presence of only one of each chromosome
C) presence of one extra chromosome
D) presence of multiple sets of chromosomes
E) general term for conditions such as Down or Turner syndrome
A) presence of more than two of a certain chromosome
B) presence of only one of each chromosome
C) presence of one extra chromosome
D) presence of multiple sets of chromosomes
E) general term for conditions such as Down or Turner syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following must be true for a female to have hemophilia?
A) Her mother is not a carrier and her father has the disease.
B) Her mother is homozygous normal and her father is a carrier.
C) Her father and mother are heterozygous.
D) Her mother is a carrier and her father has the disease.
E) Her father is heterozygous.
A) Her mother is not a carrier and her father has the disease.
B) Her mother is homozygous normal and her father is a carrier.
C) Her father and mother are heterozygous.
D) Her mother is a carrier and her father has the disease.
E) Her father is heterozygous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A karyotype reveals that an individual is XYY. Based on your knowledge of human genetics, you correctly conclude that this individual has ____, and is a phenotypically _____.
A) Turner syndrome; sterile female
B) Turner syndrome; fertile female
C) Klinefelter syndrome; sterile male
D) Klinefelter syndrome; fertile male
E) XXY karyotype; fertile male
A) Turner syndrome; sterile female
B) Turner syndrome; fertile female
C) Klinefelter syndrome; sterile male
D) Klinefelter syndrome; fertile male
E) XXY karyotype; fertile male

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Individuals who are ____ for sickle cell hemoglobin tend to be ____ resistant to falciparum malaria but do not experience the effects of sickled red blood cells.
A) homozygous dominant; more
B) homozygous dominant; less
C) homozygous recessive; less
D) heterozygous; more
E) heterozygous; less
A) homozygous dominant; more
B) homozygous dominant; less
C) homozygous recessive; less
D) heterozygous; more
E) heterozygous; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A couple in which the woman is homozygous dominant for clotting ability and the man has hemophilia A will produce:
A) carrier daughters and affected sons
B) affected daughters and affected sons
C) carrier daughters and normal sons
D) normal daughters and normal sons
E) offspring of unknown genotype for this gene
A) carrier daughters and affected sons
B) affected daughters and affected sons
C) carrier daughters and normal sons
D) normal daughters and normal sons
E) offspring of unknown genotype for this gene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The selective advantage linked to the high frequency of the cystic fibrosis allele in Caucasians is:
A) an increased resistance to falciparum malaria
B) the prevention of excessive water loss associated with certain types of diarrhea
C) production of an enzyme to break down cholera toxin
D) increased mucous secretions for the removal of infectious cells
E) an increased probability of Salmonella infection
A) an increased resistance to falciparum malaria
B) the prevention of excessive water loss associated with certain types of diarrhea
C) production of an enzyme to break down cholera toxin
D) increased mucous secretions for the removal of infectious cells
E) an increased probability of Salmonella infection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the current status of gene therapy?
A) It is currently being used effectively to cure cystic fibrosis.
B) It has been terminated because clinical trials have shown it to be ineffective.
C) It is being evaluated to assess the risks associated with potential side effects.
D) The number of clinical trials is increasing at an almost uncontrollable rate.
E) It may be considered in the future, but currently the technology is not available.
A) It is currently being used effectively to cure cystic fibrosis.
B) It has been terminated because clinical trials have shown it to be ineffective.
C) It is being evaluated to assess the risks associated with potential side effects.
D) The number of clinical trials is increasing at an almost uncontrollable rate.
E) It may be considered in the future, but currently the technology is not available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis is done:
A) on cells of an in vitro fertilized embryo
B) in the womb, before birth
C) after a woman is pregnant, but before the embryo implants
D) with the help of ultrasound
E) before fertilization on the sperm and the egg
A) on cells of an in vitro fertilized embryo
B) in the womb, before birth
C) after a woman is pregnant, but before the embryo implants
D) with the help of ultrasound
E) before fertilization on the sperm and the egg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Briefly illustrate how nondisjunction in meiosis can result in Down syndrome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Why are most infants with phenylketonuria usually healthy at birth?
A) The defect causing the condition has usually been repaired by that time.
B) The mother breaks down phenylalanine for both herself and her fetus.
C) The infant can produce sufficient quantities of the enzymes needed by birth.
D) Phenylalanine can be completely excreted in infants.
E) Phenylalanine is completely metabolized in infants.
A) The defect causing the condition has usually been repaired by that time.
B) The mother breaks down phenylalanine for both herself and her fetus.
C) The infant can produce sufficient quantities of the enzymes needed by birth.
D) Phenylalanine can be completely excreted in infants.
E) Phenylalanine is completely metabolized in infants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Tay-Sachs disease is a(n) ____ disease that results in blindness, intellectual disability, and death due to ____.
A) sex-linked; the absence of one of the sex chromosomes
B) autosomal recessive; accumulation of lipids in brain cells
C) X-linked; accumulation of acetyltransferases in brain cells
D) autosomal; sickled red blood cells
E) autosomal dominant; accumulation of mucus in the lungs
A) sex-linked; the absence of one of the sex chromosomes
B) autosomal recessive; accumulation of lipids in brain cells
C) X-linked; accumulation of acetyltransferases in brain cells
D) autosomal; sickled red blood cells
E) autosomal dominant; accumulation of mucus in the lungs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What are the predicted phenotypes of the children from a union of a woman who is heterozygous for hemophilia and a man who is normal? (Use the Punnett square to verify your answer.) 
A) 100% normal
B) 75% hemophilia: 25 % normal
C) 50% hemophilia: 50% normal
D) 25 % hemophilia: 75% normal
E) 100% hemophilia

A) 100% normal
B) 75% hemophilia: 25 % normal
C) 50% hemophilia: 50% normal
D) 25 % hemophilia: 75% normal
E) 100% hemophilia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which statement accurately characterizes an ethical consideration surrounding human genetics?
A) Nonrelatives are more likely than relatives to carry the same harmful alleles.
B) Genetic discrimination is not yet possible, even with all the known effects of genetic information.
C) In the current ethical climate, genetic privacy is not a significant concern.
D) Consanguineous matings are prohibited by half of U.S. states due to the increased risk of autosomal recessive alleles.
E) Most insurance companies have instituted policies against keeping genetic information on their policy holders.
A) Nonrelatives are more likely than relatives to carry the same harmful alleles.
B) Genetic discrimination is not yet possible, even with all the known effects of genetic information.
C) In the current ethical climate, genetic privacy is not a significant concern.
D) Consanguineous matings are prohibited by half of U.S. states due to the increased risk of autosomal recessive alleles.
E) Most insurance companies have instituted policies against keeping genetic information on their policy holders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Briefly explain the different purposes for genetic screening in newborns and adults.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
FISH distinguishes chromosomes by using more than one fluorescent-tagged RNA strand, which will bind to complementary DNA sequences on a specific chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
According to data from the ENCODE project, approximately 80% of the human genome is associated with biological function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Genetic screening can be used to identify:
A) only diseases caused by more than one gene
B) diseases caused by single gene mutations
C) nongenetic conditions
D) chromosomal abnormalities
E) predicted date of birth
A) only diseases caused by more than one gene
B) diseases caused by single gene mutations
C) nongenetic conditions
D) chromosomal abnormalities
E) predicted date of birth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In individuals with cystic fibrosis:
A) the mucus enhances the action of the cilia that line the bronchi.
B) the mucus prevents the growth of dangerous bacteria in the respiratory system.
C) the mucus in the respiratory system is thinner than in unaffected individuals.
D) abnormal mucous secretions occur throughout the body systems.
E) abnormal mucous secretions inhibit infections by bacteria.
A) the mucus enhances the action of the cilia that line the bronchi.
B) the mucus prevents the growth of dangerous bacteria in the respiratory system.
C) the mucus in the respiratory system is thinner than in unaffected individuals.
D) abnormal mucous secretions occur throughout the body systems.
E) abnormal mucous secretions inhibit infections by bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Briefly illustrate how genomic imprinting affects development of Prader-Willi syndrome and Angelman syndrome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Why has the dominant mutant allele for Huntington's disease been able to persist in human populations despite its devastating effects?
A) It has a heterozygote advantage.
B) Its symptoms do not typically show until after the individual has had children.
C) Its effects are not expressed in heterozygous individuals.
D) Its effects are only expressed in homozygous recessive individuals.
E) Its effects are only expressed in homozygous dominant individuals.
A) It has a heterozygote advantage.
B) Its symptoms do not typically show until after the individual has had children.
C) Its effects are not expressed in heterozygous individuals.
D) Its effects are only expressed in homozygous recessive individuals.
E) Its effects are only expressed in homozygous dominant individuals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
An advantage of chorionic villus sampling (compared with amniocentesis) is that:
A) chorionic villus sampling detects a much wider range of genetic defects than does amniocentesis.
B) chorionic villus sampling is much less expensive than is amniocentesis.
C) chorionic villus sampling is much less invasive than amniocentesis.
D) chorionic villus sampling is much easier to perform than amniocentesis.
E) chorionic villus sampling can be performed much earlier than amniocentesis.
A) chorionic villus sampling detects a much wider range of genetic defects than does amniocentesis.
B) chorionic villus sampling is much less expensive than is amniocentesis.
C) chorionic villus sampling is much less invasive than amniocentesis.
D) chorionic villus sampling is much easier to perform than amniocentesis.
E) chorionic villus sampling can be performed much earlier than amniocentesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Geneticists study pedigrees in order to predict how traits determined by phenotype are inherited from one generation to the next.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A genetic counselor will know that the probability of having a child affected with a condition inherited as an autosomal recessive would be:
A) 0.5 or 50% if both parents were homozygous normal
B) 0.5 or 50% if both parents were heterozygous
C) 0.25 or 25% if both parents were homozygous normal
D) 0.25 or 25% if both parents were heterozygous
E) 0% if both parents were heterozygous
A) 0.5 or 50% if both parents were homozygous normal
B) 0.5 or 50% if both parents were heterozygous
C) 0.25 or 25% if both parents were homozygous normal
D) 0.25 or 25% if both parents were heterozygous
E) 0% if both parents were heterozygous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Gene therapy involves:
A) replacing all mutant alleles in body cells
B) replacing poor copies of alleles with normal alleles
C) replacing a mutant allele in certain body cells with a normal allele
D) repairing mutant alleles in certain body cells
E) improving gene expression in key body cells
A) replacing all mutant alleles in body cells
B) replacing poor copies of alleles with normal alleles
C) replacing a mutant allele in certain body cells with a normal allele
D) repairing mutant alleles in certain body cells
E) improving gene expression in key body cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Genome-wide association scans compare the proteins of individuals with a disease to individuals without the disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Polyploidy may arise from the failure of chromosomes to separate during cell division or by the fertilization of an egg by more than one sperm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Sickle cell anemia and cystic fibrosis are examples of a homozygote advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Compare the following three terms: polyploidy, aneuploidy, and nondisjunction. Briefly discuss examples of each of these conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Discuss the necessity and benefits of the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GIN
A) of 2008.
A) of 2008.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The Human Genome Project was completed in 2012 and revealed a genomic map of 38 million SNPs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The science of comparative genomics to study human gene function is possible because much of the human genome is conserved among other closely related species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Nondisjunction of the XY pair during the first meiotic division can produce sperm with 2 X chromosomes and 2 Y chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In reciprocal translocation, two homologous chromosomes exchange segments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In trisomy 21, while all genetic information is intact, a abnormal copy of this chromosome creates a genetic imbalance that causes abnormal physical and mental development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Compare the benefits and risks associated with amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Identify and briefly describe the potential disadvantages of gene therapy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Males with Klinefelter syndrome lack a Barr Body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In fragile X syndrome, the fragile X gene contains a nucleotide triplet that repeats 200 to 1000 times.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



