Deck 12: Dna the Carrier of Genetic Information
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Premises:
produces breaks in the DNA molecules and then rejoins the strands to prevent supercoiling
produces breaks in the DNA molecules and then rejoins the strands to prevent supercoiling
produces breaks in the DNA molecules and then rejoins the strands to prevent supercoiling
produces breaks in the DNA molecules and then rejoins the strands to prevent supercoiling
produces breaks in the DNA molecules and then rejoins the strands to prevent supercoiling
produces breaks in the DNA molecules and then rejoins the strands to prevent supercoiling
prevents formation of hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs
prevents formation of hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs
prevents formation of hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs
prevents formation of hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs
prevents formation of hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs
prevents formation of hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs
catalyzes formation of sugar-phosphate bonds in adjacent Okazaki fragments
catalyzes formation of sugar-phosphate bonds in adjacent Okazaki fragments
catalyzes formation of sugar-phosphate bonds in adjacent Okazaki fragments
catalyzes formation of sugar-phosphate bonds in adjacent Okazaki fragments
catalyzes formation of sugar-phosphate bonds in adjacent Okazaki fragments
catalyzes formation of sugar-phosphate bonds in adjacent Okazaki fragments
joins successive nucleotides to a growing polynucleotide strand, complementary to the template strand
joins successive nucleotides to a growing polynucleotide strand, complementary to the template strand
joins successive nucleotides to a growing polynucleotide strand, complementary to the template strand
joins successive nucleotides to a growing polynucleotide strand, complementary to the template strand
joins successive nucleotides to a growing polynucleotide strand, complementary to the template strand
joins successive nucleotides to a growing polynucleotide strand, complementary to the template strand
catalyzes the synthesis of an RNA primer at both leading and lagging strand
catalyzes the synthesis of an RNA primer at both leading and lagging strand
catalyzes the synthesis of an RNA primer at both leading and lagging strand
catalyzes the synthesis of an RNA primer at both leading and lagging strand
catalyzes the synthesis of an RNA primer at both leading and lagging strand
catalyzes the synthesis of an RNA primer at both leading and lagging strand
Responses:
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/68
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Dna the Carrier of Genetic Information
1
DNA:
A) is composed of nucleotide building blocks.
B) contains uracil instead of thymine.
C) is single-stranded.
D) contains pyrimidines and purines in a 2:1 ratio.
E) contains the sugar ribose.
A) is composed of nucleotide building blocks.
B) contains uracil instead of thymine.
C) is single-stranded.
D) contains pyrimidines and purines in a 2:1 ratio.
E) contains the sugar ribose.
A
2
Figure 12-1 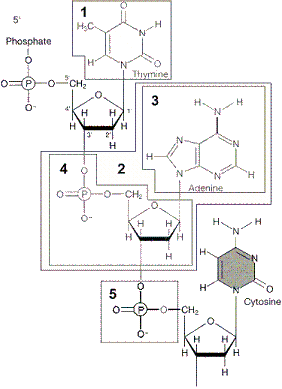 The chemical group in box 5 of the accompanying figure is a:
The chemical group in box 5 of the accompanying figure is a:
A) hydrogen bond.
B) phosphate.
C) nucleotide.
D) pyrimidine.
E) protein.
 The chemical group in box 5 of the accompanying figure is a:
The chemical group in box 5 of the accompanying figure is a:A) hydrogen bond.
B) phosphate.
C) nucleotide.
D) pyrimidine.
E) protein.
B
3
Figure 12-1 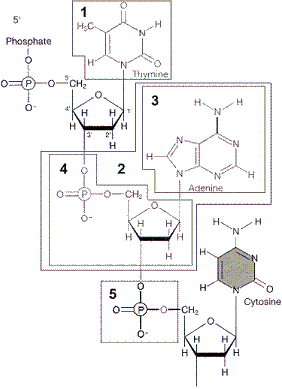 The chemical group box 1 in the accompanying figure is a:
The chemical group box 1 in the accompanying figure is a:
A) pyrimidine.
B) purine.
C) phosphate.
D) amino acid.
E) covalent bond.
 The chemical group box 1 in the accompanying figure is a:
The chemical group box 1 in the accompanying figure is a:A) pyrimidine.
B) purine.
C) phosphate.
D) amino acid.
E) covalent bond.
A
4
_____ bonds link the sugar and phosphate groups in the backbones of DNA molecules.
A) Covalent phosphodiester
B) Hydrogen
C) Weak
D) Ionic
E) Weak covalent
A) Covalent phosphodiester
B) Hydrogen
C) Weak
D) Ionic
E) Weak covalent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The two molecules that alternate to form the backbone of a polynucleotide chain are:
A) adenine and thymine.
B) cytosine and guanine.
C) sugar and phosphate.
D) base and sugar.
E) base and phosphate.
A) adenine and thymine.
B) cytosine and guanine.
C) sugar and phosphate.
D) base and sugar.
E) base and phosphate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The bacteriophages used in Alfred Hershey's and Martha Chase's experiments showed that:
A) DNA was injected into bacteria.
B) DNA and protein were injected into bacteria.
C) DNA remained on the outer coat of bacteria.
D) proteins were injected into bacteria.
E) proteins were responsible for the production of new viruses within the bacteria.
A) DNA was injected into bacteria.
B) DNA and protein were injected into bacteria.
C) DNA remained on the outer coat of bacteria.
D) proteins were injected into bacteria.
E) proteins were responsible for the production of new viruses within the bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following statements concerning DNA is FALSE?
A) The structure of DNA can be described as a double helix.
B) DNA is a polymer of nucleotides.
C) Purines and pyrimidines are complementary.
D) The sugar present in DNA is ribose.
E) The two chains of DNA are antiparallel.
A) The structure of DNA can be described as a double helix.
B) DNA is a polymer of nucleotides.
C) Purines and pyrimidines are complementary.
D) The sugar present in DNA is ribose.
E) The two chains of DNA are antiparallel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The information encoded by the DNA is specified by the:
A) sugar-phosphate backbone of the DNA molecule.
B) number of separate DNA strands.
C) size of a particular chromosome.
D) nucleotide sequence of the DNA molecule.
E) number of bases in a DNA molecule.
A) sugar-phosphate backbone of the DNA molecule.
B) number of separate DNA strands.
C) size of a particular chromosome.
D) nucleotide sequence of the DNA molecule.
E) number of bases in a DNA molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
X-ray diffraction images produced by ____ were used by Watson and Crick to infer the structure of DNA.
A) Wilkins
B) Griffith
C) Franklin
D) Hershey
E) Watson and Wilkins
A) Wilkins
B) Griffith
C) Franklin
D) Hershey
E) Watson and Wilkins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the experiments of Griffith, the conversion of nonlethal R-strain bacteria to lethal S-strain bacteria:
A) was due to genetic mutation.
B) was due to transformation.
C) proved that proteins are the genetic material.
D) could not be reproduced by other researchers.
E) was similar to experiments performed by Watson and Crick.
A) was due to genetic mutation.
B) was due to transformation.
C) proved that proteins are the genetic material.
D) could not be reproduced by other researchers.
E) was similar to experiments performed by Watson and Crick.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
According to Chargaff's rules:
A) the number of A-T base pairs is always equal to the number of G-C base pairs in all DNA molecules.
B) the adenine content in any DNA molecule is always equal to the thymine content.
C) the adenine content in any DNA molecule is always greater than the thymine content.
D) the guanine content in any DNA molecule is always less than the cytosine content.
E) there is no relationship between the ratio of purine and pyrimidine content in any DNA molecule.
A) the number of A-T base pairs is always equal to the number of G-C base pairs in all DNA molecules.
B) the adenine content in any DNA molecule is always equal to the thymine content.
C) the adenine content in any DNA molecule is always greater than the thymine content.
D) the guanine content in any DNA molecule is always less than the cytosine content.
E) there is no relationship between the ratio of purine and pyrimidine content in any DNA molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following nucleotide sequences represents the complement to the DNA strand 5 ′ − AGATCCG- 3 ′ ?
A) 5 ′ − AGATCCG- 3 ′
B) 3 ′ − AGATCCG- 5 ′
C) 5 ′ − CTCGAAT- 3 ′
D) 3 ′ − CTCGAAT- 5 ′
E) 3 ′ − TCTAGGC- 5 ′
A) 5 ′ − AGATCCG- 3 ′
B) 3 ′ − AGATCCG- 5 ′
C) 5 ′ − CTCGAAT- 3 ′
D) 3 ′ − CTCGAAT- 5 ′
E) 3 ′ − TCTAGGC- 5 ′

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Before the 1940s, scientists believed that proteins, rather than DNA, were the carriers of genetic material in the cell. Why?
A) Proteins are present within the nucleus.
B) Proteins are abundant within the cell.
C) Twenty different amino acids could produce a large number of unique combinations.
D) Proteins are able to self replicate.
E) Proteins are routinely exported from the cell.
A) Proteins are present within the nucleus.
B) Proteins are abundant within the cell.
C) Twenty different amino acids could produce a large number of unique combinations.
D) Proteins are able to self replicate.
E) Proteins are routinely exported from the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
From the DNA X-ray crystallography data, Franklin and Wilkins inferred that ____ while Watson and Crick determined that ____.
A) purines and pyrimidines exist in a 1:1 ratio; DNA is helical
B) phosphates are stacked liked rungs on a ladder; DNA is helical
C) DNA is helical; DNA is the genetic material
D) DNA is helical; the flat nucleotide bases are stacked upon each other
E) the flat nucleotide bases are stacked upon each other; DNA is helical.
A) purines and pyrimidines exist in a 1:1 ratio; DNA is helical
B) phosphates are stacked liked rungs on a ladder; DNA is helical
C) DNA is helical; DNA is the genetic material
D) DNA is helical; the flat nucleotide bases are stacked upon each other
E) the flat nucleotide bases are stacked upon each other; DNA is helical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Hydrogen bonds can form between guanine and ____, and between adenine and ____.
A) phosphate; sugar
B) thymine; cytosine
C) cytosine; thymine
D) sugar; phosphate
E) adenine; guanine
A) phosphate; sugar
B) thymine; cytosine
C) cytosine; thymine
D) sugar; phosphate
E) adenine; guanine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In order to fit the X-ray crystallographic data, the two DNA strands must be ____ to each other.
A) complementary
B) uncomplementary
C) parallel
D) antiparallel
E) semiconservative
A) complementary
B) uncomplementary
C) parallel
D) antiparallel
E) semiconservative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Chargaff determined that DNA from any source contains about the same amount of guanine as:
A) uracil.
B) thymine.
C) adenine.
D) cytosine.
E) guanine.
A) uracil.
B) thymine.
C) adenine.
D) cytosine.
E) guanine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The first scientists to use Griffith's transformation assay to identify genetic material were:
A) Meselson and Stahl.
B) Watson and Crick.
C) Franklin and Wilkins.
D) Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty.
E) Hershey and Chase.
A) Meselson and Stahl.
B) Watson and Crick.
C) Franklin and Wilkins.
D) Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty.
E) Hershey and Chase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Why is DNA able to store large amounts of information?
A) It is composed of 20 different nucleotides.
B) Its nucleotides can be arranged in a large number of possible sequences.
C) It is capable of assuming a wide variety of shapes.
D) Its sugars and phosphates can be arranged in many different sequences.
E) Its bases can be altered from purines to pyrimidines.
A) It is composed of 20 different nucleotides.
B) Its nucleotides can be arranged in a large number of possible sequences.
C) It is capable of assuming a wide variety of shapes.
D) Its sugars and phosphates can be arranged in many different sequences.
E) Its bases can be altered from purines to pyrimidines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
X-ray diffraction studies are used to determine the:
A) sequence of amino acids in protein molecules.
B) sequence of nucleotides in nucleic acid molecules.
C) distances between atoms of molecules.
D) identity of an unknown chemical.
E) wavelength of X-rays.
A) sequence of amino acids in protein molecules.
B) sequence of nucleotides in nucleic acid molecules.
C) distances between atoms of molecules.
D) identity of an unknown chemical.
E) wavelength of X-rays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What allows each strand of DNA to serve as a template for a new DNA strand during replication?
A) covalent bonding between nucleotide bases
B) hydrogen bonds between the deoxyribose and the phosphate groups
C) complementary base pairing between purines and purines on opposite strands
D) complementary base pairing between pyrimidines and pyrimidines on opposite strands
E) complementary base pairing between purines and pyrimidines on opposite strands
A) covalent bonding between nucleotide bases
B) hydrogen bonds between the deoxyribose and the phosphate groups
C) complementary base pairing between purines and purines on opposite strands
D) complementary base pairing between pyrimidines and pyrimidines on opposite strands
E) complementary base pairing between purines and pyrimidines on opposite strands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
DNA synthesis:
A) is unidirectional.
B) is facilitated by a phosphodiester linkage.
C) occurs only once during each cell generation.
D) has few mechanisms for fixing errors.
E) is proofread by DNA ligase.
A) is unidirectional.
B) is facilitated by a phosphodiester linkage.
C) occurs only once during each cell generation.
D) has few mechanisms for fixing errors.
E) is proofread by DNA ligase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following adds new nucleotides to a growing DNA chain?
A) DNA polymerase
B) DNA helicase
C) RNA primer
D) primase
E) RNA polymerase
A) DNA polymerase
B) DNA helicase
C) RNA primer
D) primase
E) RNA polymerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Because a newly synthesized DNA molecule contains ____, the replication process is said to be semiconservative.
A) two new strands
B) one parental strand and one new strand
C) two parental strands
D) half purines and half pyrimidines
E) nucleotides
A) two new strands
B) one parental strand and one new strand
C) two parental strands
D) half purines and half pyrimidines
E) nucleotides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following statements is FALSE with regard to DNA replication?
A) DNA synthesis proceeds in the 5'->3' direction.
B) The strand being copied is read in the 5'->3' direction.
C) Both strands replicate at the same time.
D) The position of the replication fork is constantly moving.
E) Two identical DNA polymerase molecules catalyze replication.
A) DNA synthesis proceeds in the 5'->3' direction.
B) The strand being copied is read in the 5'->3' direction.
C) Both strands replicate at the same time.
D) The position of the replication fork is constantly moving.
E) Two identical DNA polymerase molecules catalyze replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Individuals with mutations in excision repair enzymes may suffer from ____ due to unrepaired DNA damage caused by ____.
A) skin cancer; mutations inherited from their parents
B) colon cancer; the passing of DNA mutations to daughter cells
C) prostate cancer; telomerase
D) skin cancer; the sun's UV rays
E) skin cancer; complementary base pairing
A) skin cancer; mutations inherited from their parents
B) colon cancer; the passing of DNA mutations to daughter cells
C) prostate cancer; telomerase
D) skin cancer; the sun's UV rays
E) skin cancer; complementary base pairing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When a mutation occurs during DNA replication, ____ replaces the incorrect nucleotide with the correct one after the mismatched nucleotide has been removed.
A) mismatch repair enzymes
B) DNA ligase
C) DNA polymerase
D) telomerase
E) helicase
A) mismatch repair enzymes
B) DNA ligase
C) DNA polymerase
D) telomerase
E) helicase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following causes the unwinding of the DNA double helix?
A) DNA polymerase
B) DNA helicase
C) RNA primer
D) primosome
E) RNA polymerase
A) DNA polymerase
B) DNA helicase
C) RNA primer
D) primosome
E) RNA polymerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Why does DNA synthesis proceed in a 5 ′ to 3 ′ direction?
A) DNA polymerases can only add nucleotides to the 3 ′ end of a polynucleotide strand.
B) The 3 ′ end of the polynucleotide molecule contains more phosphates than the 5 ′ end.
C) DNA unzips in the 5' to 3' direction.
D) DNA strands are parallel to each other.
E) Chromosomes are aligned in the 5 ′ to 3 ′ direction in the nucleus.
A) DNA polymerases can only add nucleotides to the 3 ′ end of a polynucleotide strand.
B) The 3 ′ end of the polynucleotide molecule contains more phosphates than the 5 ′ end.
C) DNA unzips in the 5' to 3' direction.
D) DNA strands are parallel to each other.
E) Chromosomes are aligned in the 5 ′ to 3 ′ direction in the nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The ends of eukaryotic chromosomes can be lengthened by:
A) apoptosis.
B) mismatch repair enzymes.
C) primase.
D) telomerase.
E) DNA polymerase.
A) apoptosis.
B) mismatch repair enzymes.
C) primase.
D) telomerase.
E) DNA polymerase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
____, the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes, shorten with every cell division.
A) Centromeres
B) Telomeres
C) Kinetochores
D) Primosomes
E) Nucleosomes
A) Centromeres
B) Telomeres
C) Kinetochores
D) Primosomes
E) Nucleosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Errors in DNA replication can come from:
A) DNA polymerase.
B) DNA ligase.
C) complementary base pairing.
D) the sun's UV radiation.
E) Okazaki fragments.
A) DNA polymerase.
B) DNA ligase.
C) complementary base pairing.
D) the sun's UV radiation.
E) Okazaki fragments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Who first confirmed that the replication of DNA was semiconservative?
A) Chargaff and Hershey
B) Watson and Crick
C) Avery and Griffith
D) Meselson and Stahl
E) Watson, Crick, and Wilkins
A) Chargaff and Hershey
B) Watson and Crick
C) Avery and Griffith
D) Meselson and Stahl
E) Watson, Crick, and Wilkins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If DNA replication rejoined the two parental strands, it would be termed:
A) dispersive.
B) gradient.
C) semiconservative.
D) parental.
E) conservative.
A) dispersive.
B) gradient.
C) semiconservative.
D) parental.
E) conservative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The DNA strand that is replicated smoothly and continuously is called the:
A) primary strand.
B) template strand.
C) leading strand.
D) Okazaki fragment.
E) lagging strand.
A) primary strand.
B) template strand.
C) leading strand.
D) Okazaki fragment.
E) lagging strand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A replication fork is:
A) observed only in prokaryotic chromosomes.
B) observed only in nondividing cells..
C) a Y-shaped structure where parental DNA strands are separated by helicase.
D) a site where one DNA strand serves as a template, but the other strand is not replicated.
E) created by the action of the enzyme RNA polymerase.
A) observed only in prokaryotic chromosomes.
B) observed only in nondividing cells..
C) a Y-shaped structure where parental DNA strands are separated by helicase.
D) a site where one DNA strand serves as a template, but the other strand is not replicated.
E) created by the action of the enzyme RNA polymerase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Enzymes called ____ form breaks in the DNA molecules to prevent the formation of knots in the DNA helix during replication.
A) topoisomerases
B) single-strand binding proteins
C) DNA polymerases
D) RNA polymerases
E) DNA ligases
A) topoisomerases
B) single-strand binding proteins
C) DNA polymerases
D) RNA polymerases
E) DNA ligases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Primase is the enzyme responsible for:
A) unwinding the DNA double strand to allow DNA polymerase access to the template DNA.
B) introducing nicks into the DNA double strand in order to prevent the formation of knots.
C) hydrolyzing ATP to facilitate DNA unwinding.
D) making short strands of RNA at the site of replication initiation.
E) forming a replication fork in the DNA double helix.
A) unwinding the DNA double strand to allow DNA polymerase access to the template DNA.
B) introducing nicks into the DNA double strand in order to prevent the formation of knots.
C) hydrolyzing ATP to facilitate DNA unwinding.
D) making short strands of RNA at the site of replication initiation.
E) forming a replication fork in the DNA double helix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Unlike normal cells, cancerous cells:
A) have reduced levels of telomerase.
B) divide only a few times before succumbing to apoptosis.
C) have unusually short telomeres.
D) can maintain telomere length as they divide.
E) lack telomeres.
A) have reduced levels of telomerase.
B) divide only a few times before succumbing to apoptosis.
C) have unusually short telomeres.
D) can maintain telomere length as they divide.
E) lack telomeres.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In replication, once the DNA strands have been separated, reformation of the double helix is prevented by:
A) DNA helicase enzyme.
B) single-strand binding proteins.
C) DNA polymerases.
D) ATP.
E) DNA primase.
A) DNA helicase enzyme.
B) single-strand binding proteins.
C) DNA polymerases.
D) ATP.
E) DNA primase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Replication typically occurs at a single origin(s) of replication in eukaryotic chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Single-strand binding proteins prevent the hydrolysis of single-strand regions of DNA by nucleases.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Explain why proteins were initially hypothesized to be the genetic material instead of DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The two strands of a DNA double helix can be described as running parallel to each other.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Explain how apoptosis can protect the body against cancerous cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In one strand of a DNA molecule, adjacent nucleotides are joined by a(n) phosphodiester linkage.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
How is a bacterial chromosome replicated?
A) The linear DNA molecule is replicated from multiple origins of replication bidirectionally.
B) The linear DNA molecule is replicated from one origin of replication bidirectionally.
C) The circular DNA molecule is replicated from multiple origins of replication bidirectionally.
D) The circular DNA molecule is replicated from one origin of replication bidirectionally.
E) The circular DNA molecule is replicated from one origin of replication unidirectionally.
A) The linear DNA molecule is replicated from multiple origins of replication bidirectionally.
B) The linear DNA molecule is replicated from one origin of replication bidirectionally.
C) The circular DNA molecule is replicated from multiple origins of replication bidirectionally.
D) The circular DNA molecule is replicated from one origin of replication bidirectionally.
E) The circular DNA molecule is replicated from one origin of replication unidirectionally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The process of DNA replication is conservative .
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
List the steps and components involved in the process of DNA replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
One of the pyrimidine bases in a DNA molecule is adenine.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What happened in an experiment where normal cultured human cells were infected with a virus that carried DNA encoding for the telomerase catalytic subunit?
A) The cells underwent more cell divisions than normal.
B) The cells underwent fewer cell divisions than normal.
C) The cells died almost immediately.
D) The cells did not express the foreign telomerase gene.
E) The cell cycle shortened.
A) The cells underwent more cell divisions than normal.
B) The cells underwent fewer cell divisions than normal.
C) The cells died almost immediately.
D) The cells did not express the foreign telomerase gene.
E) The cell cycle shortened.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Compare and contrast DNA synthesis in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If you consider a DNA molecule to resemble a twisted ladder, the rungs of the ladder are paired nitrogen bases .
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Okazaki fragments are joined together by:
A) RNA polymerase.
B) DNA ligase.
C) DNA polymerase.
D) RNA ligase.
E) primase.
A) RNA polymerase.
B) DNA ligase.
C) DNA polymerase.
D) RNA ligase.
E) primase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Adenine and thymine are held together by two hydrogen bonds in a double stranded DNA molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
How are eukaryotic chromosomes replicated?
A) The linear DNA molecules are replicated from multiple origins of replication bidirectionally.
B) The linear DNA molecules are replicated from one origin of replication bidirectionally.
C) The circular DNA molecules are replicated from multiple origins of replication bidirectionally.
D) The circular DNA molecules are replicated from one origin of replication bidirectionally.
E) The linear DNA molecules are replicated from one origin of replication unidirectionally.
A) The linear DNA molecules are replicated from multiple origins of replication bidirectionally.
B) The linear DNA molecules are replicated from one origin of replication bidirectionally.
C) The circular DNA molecules are replicated from multiple origins of replication bidirectionally.
D) The circular DNA molecules are replicated from one origin of replication bidirectionally.
E) The linear DNA molecules are replicated from one origin of replication unidirectionally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What happens during nucleotide excision repair?
A) A mismatch mutation is repaired.
B) A nuclease removes the damaged DNA.
C) DNA polymerase joins the repaired DNA together.
D) DNA ligase adds new nucleotides to the repaired DNA strand.
E) DNA is damaged.
A) A mismatch mutation is repaired.
B) A nuclease removes the damaged DNA.
C) DNA polymerase joins the repaired DNA together.
D) DNA ligase adds new nucleotides to the repaired DNA strand.
E) DNA is damaged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In DNA replication, the lagging strand:
A) is synthesized as a series of Okazaki fragments.
B) is synthesized as a complementary copy of the leading strand.
C) pairs with the leading strand by complementary base pairing.
D) is made up entirely of RNA primers.
E) is not synthesized until the synthesis of the leading strand is completed.
A) is synthesized as a series of Okazaki fragments.
B) is synthesized as a complementary copy of the leading strand.
C) pairs with the leading strand by complementary base pairing.
D) is made up entirely of RNA primers.
E) is not synthesized until the synthesis of the leading strand is completed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
An RNA primer is synthesized by RNA primase .
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
DNA Pol III catalyzes the addition of successive nucleotides to the 5' end of a growing polynucleotide chain.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match between columns
Premises:
produces breaks in the DNA molecules and then rejoins the strands to prevent supercoiling
produces breaks in the DNA molecules and then rejoins the strands to prevent supercoiling
produces breaks in the DNA molecules and then rejoins the strands to prevent supercoiling
produces breaks in the DNA molecules and then rejoins the strands to prevent supercoiling
produces breaks in the DNA molecules and then rejoins the strands to prevent supercoiling
produces breaks in the DNA molecules and then rejoins the strands to prevent supercoiling
prevents formation of hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs
prevents formation of hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs
prevents formation of hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs
prevents formation of hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs
prevents formation of hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs
prevents formation of hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs
catalyzes formation of sugar-phosphate bonds in adjacent Okazaki fragments
catalyzes formation of sugar-phosphate bonds in adjacent Okazaki fragments
catalyzes formation of sugar-phosphate bonds in adjacent Okazaki fragments
catalyzes formation of sugar-phosphate bonds in adjacent Okazaki fragments
catalyzes formation of sugar-phosphate bonds in adjacent Okazaki fragments
catalyzes formation of sugar-phosphate bonds in adjacent Okazaki fragments
joins successive nucleotides to a growing polynucleotide strand, complementary to the template strand
joins successive nucleotides to a growing polynucleotide strand, complementary to the template strand
joins successive nucleotides to a growing polynucleotide strand, complementary to the template strand
joins successive nucleotides to a growing polynucleotide strand, complementary to the template strand
joins successive nucleotides to a growing polynucleotide strand, complementary to the template strand
joins successive nucleotides to a growing polynucleotide strand, complementary to the template strand
catalyzes the synthesis of an RNA primer at both leading and lagging strand
catalyzes the synthesis of an RNA primer at both leading and lagging strand
catalyzes the synthesis of an RNA primer at both leading and lagging strand
catalyzes the synthesis of an RNA primer at both leading and lagging strand
catalyzes the synthesis of an RNA primer at both leading and lagging strand
catalyzes the synthesis of an RNA primer at both leading and lagging strand
Responses:
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein
DNA ligase
DNA primase
topoisomerase
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
single-strand binding protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What is meant by the "directionality" of the strands of a DNA molecule? Explain how this directionality is ultimately responsible for Okazaki fragments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
How does the degradation of telomeres result in cellular aging?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Okazaki fragments are found in the leading strand of DNA.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Provide two lines of evidence that support the idea that DNA is the genetic material.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Short, noncoding, guanine-rich DNA sequences found at the ends of chromosomes are called telomeres .
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In mismatch repair , enzymes remove incorrectly-paired nucleotides.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



