Deck 46: Gas Exchange
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/93
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 46: Gas Exchange
1
The process of gas exchange in parabronchi is similar to:
A) osmosis in spiracles.
B) respiration in tracheal tubes.
C) concurrent exchange in gills.
D) diffusion in small animals.
E) countercurrent exchange in gills.
A) osmosis in spiracles.
B) respiration in tracheal tubes.
C) concurrent exchange in gills.
D) diffusion in small animals.
E) countercurrent exchange in gills.
E
2
The countercurrent exchange system found in fish gills maximizes gas exchange efficiency by:
A) producing rapid water flows across the gill surface.
B) allowing water and blood to come in direct contact to maximize oxygen exchange.
C) having a high concentration gradient of oxygen at the start of the capillaries.
D) maintaining a high concentration gradient of oxygen along the entire length of capillaries.
E) decreasing the oxygen content of the blood leaving the gill filaments.
A) producing rapid water flows across the gill surface.
B) allowing water and blood to come in direct contact to maximize oxygen exchange.
C) having a high concentration gradient of oxygen at the start of the capillaries.
D) maintaining a high concentration gradient of oxygen along the entire length of capillaries.
E) decreasing the oxygen content of the blood leaving the gill filaments.
D
3
The ventilation of insect tracheal tubes is dependent upon the presence of:
A) pores.
B) alveoli.
C) gills.
D) spiracles.
E) opercula.
A) pores.
B) alveoli.
C) gills.
D) spiracles.
E) opercula.
D
4
A respiratory system is needed if an organism is too ____ to rely on the diffusion of gases through the body's tissues.
A) small
B) long
C) thick
D) thin
E) round
A) small
B) long
C) thick
D) thin
E) round

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Mitochondria use respired oxygen as an electron acceptor in the process known as:
A) pulmonary ventilation.
B) cellular respiration.
C) external respiration.
D) internal respiration.
E) anaerobic respiration.
A) pulmonary ventilation.
B) cellular respiration.
C) external respiration.
D) internal respiration.
E) anaerobic respiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Why do land dwelling insects drown when they are in water?
A) Their lungs fill with water.
B) Their lungs are functioning too fast to sustain life.
C) They cannot respire across their body surface.
D) They are unable to ventilate because their spiracles are underwater.
E) Their gills are too moist.
A) Their lungs fill with water.
B) Their lungs are functioning too fast to sustain life.
C) They cannot respire across their body surface.
D) They are unable to ventilate because their spiracles are underwater.
E) Their gills are too moist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the process of organismic respiration:
A) oxygen is extracted from the environment by the organism and delivered to its cells.
B) the citric acid cycle takes place in the cells.
C) carbohydrates are broken down and electrons are transferred to oxygen.
D) there is an accumulation of lactic acid in the tissues due to the absence of oxygen.
E) carbon dioxide is produced in the Krebs cycle.
A) oxygen is extracted from the environment by the organism and delivered to its cells.
B) the citric acid cycle takes place in the cells.
C) carbohydrates are broken down and electrons are transferred to oxygen.
D) there is an accumulation of lactic acid in the tissues due to the absence of oxygen.
E) carbon dioxide is produced in the Krebs cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In fish, blood flows in a direction opposite to the flow of water over the gills in a process known as:
A) concurrent exchange.
B) countercurrent exchange.
C) crosscurrent exchange.
D) exhalation.
E) diffusion.
A) concurrent exchange.
B) countercurrent exchange.
C) crosscurrent exchange.
D) exhalation.
E) diffusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Clams and other bivalves typically have:
A) dermal gills.
B) gills adapted for trapping food.
C) an operculum.
D) book lungs.
E) swim bladders.
A) dermal gills.
B) gills adapted for trapping food.
C) an operculum.
D) book lungs.
E) swim bladders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
____ have the most efficient respiratory system of any living vertebrate.
A) Amphibians
B) Birds
C) Mammals
D) Fish
E) Nonavian reptiles
A) Amphibians
B) Birds
C) Mammals
D) Fish
E) Nonavian reptiles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
To facilitate respiration, birds have extensions of their lungs called ____, which reach into all parts of their bodies.
A) tracheal tubes
B) spiracles
C) air bladders
D) parabronchi
E) air sacs
A) tracheal tubes
B) spiracles
C) air bladders
D) parabronchi
E) air sacs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If mitochondria were deprived of oxygen:
A) cellular respiration would cease.
B) ATP synthesis would cease.
C) cells would eventually die.
D) cellular respiration and ATP synthesis would cease.
E) cellular respiration and ATP synthesis would cease and the cells would eventually die.
A) cellular respiration would cease.
B) ATP synthesis would cease.
C) cells would eventually die.
D) cellular respiration and ATP synthesis would cease.
E) cellular respiration and ATP synthesis would cease and the cells would eventually die.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following sequences correctly describes the movement of air in a bird's respiratory system?
A) lungs; anterior air sacs; posterior air sacs
B) anterior air sacs; posterior air sac; lungs
C) posterior air sacs; lungs; anterior air sacs
D) lungs; posterior air sacs; anterior air sacs
E) anterior air sacs; lungs; posterior air sacs
A) lungs; anterior air sacs; posterior air sacs
B) anterior air sacs; posterior air sac; lungs
C) posterior air sacs; lungs; anterior air sacs
D) lungs; posterior air sacs; anterior air sacs
E) anterior air sacs; lungs; posterior air sacs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Some amphibians:
A) may exchange gases across their body surfaces.
B) all have fairly simple, book lungs.
C) all have gills and swim bladders, homologous to those found in fishes.
D) are characterized by having parabronchi across which most of the gas exchange occurs.
E) have a large oxygen demand that is met by using a countercurrent gas exchange mechanism.
A) may exchange gases across their body surfaces.
B) all have fairly simple, book lungs.
C) all have gills and swim bladders, homologous to those found in fishes.
D) are characterized by having parabronchi across which most of the gas exchange occurs.
E) have a large oxygen demand that is met by using a countercurrent gas exchange mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Figure 46-1  Refer to the accompanying figure. Which two figures in the accompanying illustration represent inhalation steps of the respiratory cycle?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which two figures in the accompanying illustration represent inhalation steps of the respiratory cycle?
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 2
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
E) 3 and 4
 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which two figures in the accompanying illustration represent inhalation steps of the respiratory cycle?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which two figures in the accompanying illustration represent inhalation steps of the respiratory cycle?A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 2
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
E) 3 and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Fish can control buoyancy by:
A) holding air in their lungs.
B) expelling air from their lungs.
C) facilitating swift operculum movement.
D) adjusting the amount of gas in their swim bladders.
E) inflating the chambers of their tracheae.
A) holding air in their lungs.
B) expelling air from their lungs.
C) facilitating swift operculum movement.
D) adjusting the amount of gas in their swim bladders.
E) inflating the chambers of their tracheae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The exchange of gases between an organism and its environment is known as:
A) exhalation.
B) aeration.
C) inhalation.
D) respiration.
E) ventilation.
A) exhalation.
B) aeration.
C) inhalation.
D) respiration.
E) ventilation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Figure 46-1 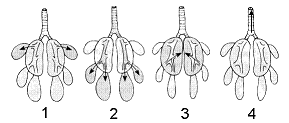 Refer to the accompanying figure. Place figures 1-4 in the correct order to represent the two-cycle breathing process of birds.
Refer to the accompanying figure. Place figures 1-4 in the correct order to represent the two-cycle breathing process of birds.
A) 1 → 2 → 3 → 4
B) 2 → 3 → 4 → 1
C) 2 → 3 → 1 → 4
D) 3 → 2 → 1 → 4
E) 4 → 3 → 2 → 1
 Refer to the accompanying figure. Place figures 1-4 in the correct order to represent the two-cycle breathing process of birds.
Refer to the accompanying figure. Place figures 1-4 in the correct order to represent the two-cycle breathing process of birds.A) 1 → 2 → 3 → 4
B) 2 → 3 → 4 → 1
C) 2 → 3 → 1 → 4
D) 3 → 2 → 1 → 4
E) 4 → 3 → 2 → 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Parabronchi are characteristic of:
A) insects.
B) spiders.
C) mollusks.
D) birds.
E) mammals.
A) insects.
B) spiders.
C) mollusks.
D) birds.
E) mammals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is a disadvantage of gas exchange in water, as compared to gas exchange in air?
A) Air is less dense than water.
B) Air contains a higher concentration of oxygen.
C) Less energy is needed to move air over a gas exchange surface.
D) Oxygen diffuses more slowly through air than water.
E) Air is less viscous than water.
A) Air is less dense than water.
B) Air contains a higher concentration of oxygen.
C) Less energy is needed to move air over a gas exchange surface.
D) Oxygen diffuses more slowly through air than water.
E) Air is less viscous than water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The volume of air remaining in the lungs after maximal expiration is the:
A) vital capacity.
B) tidal volume.
C) tidal capacity.
D) residual capacity.
E) residual volume.
A) vital capacity.
B) tidal volume.
C) tidal capacity.
D) residual capacity.
E) residual volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Hemocyanin:
A) combines irreversibly with oxygen for transport within the body of various organisms.
B) is bright red in color when combined with oxygen.
C) has an iron-porphyrin group that is responsible for oxygen transport.
D) is a respiratory pigment found in the blood of some invertebrate and vertebrate species.
E) is a respiratory pigment that is colorless when deoxygenated.
A) combines irreversibly with oxygen for transport within the body of various organisms.
B) is bright red in color when combined with oxygen.
C) has an iron-porphyrin group that is responsible for oxygen transport.
D) is a respiratory pigment found in the blood of some invertebrate and vertebrate species.
E) is a respiratory pigment that is colorless when deoxygenated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The percent oxygen saturation of hemoglobin is highest in the:
A) tissues where oxygen concentration is lowest.
B) tissues where oxygen concentration is highest.
C) venules where oxygen concentration is lowest.
D) pulmonary capillaries where oxygen concentration is lowest.
E) pulmonary capillaries where oxygen concentration is highest.
A) tissues where oxygen concentration is lowest.
B) tissues where oxygen concentration is highest.
C) venules where oxygen concentration is lowest.
D) pulmonary capillaries where oxygen concentration is lowest.
E) pulmonary capillaries where oxygen concentration is highest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Figure 46-4 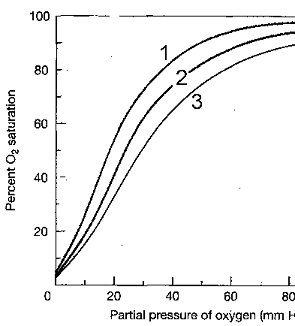 Oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curves at three different pH levels
Oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curves at three different pH levels
The phenomenon illustrated in the accompanying figure is known as:
A) carbon dioxide unloading.
B) the Bohr effect.
C) hemoglobin transportation.
D) chloride shift.
E) residual capacity.
 Oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curves at three different pH levels
Oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curves at three different pH levelsThe phenomenon illustrated in the accompanying figure is known as:
A) carbon dioxide unloading.
B) the Bohr effect.
C) hemoglobin transportation.
D) chloride shift.
E) residual capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Figure 46-3 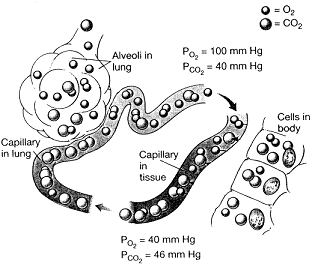 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which statement is accurate?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which statement is accurate?
A) CO2 will diffuse from the alveoli into the capillaries.
B) CO2 will diffuse from the capillaries into the tissues.
C) O2 will diffuse from the capillaries in the tissues to the capillaries in the lung.
D) O2 will diffuse from the alveoli into the capillaries.
E) O2 will diffuse from the tissues into the capillaries.
 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which statement is accurate?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which statement is accurate?A) CO2 will diffuse from the alveoli into the capillaries.
B) CO2 will diffuse from the capillaries into the tissues.
C) O2 will diffuse from the capillaries in the tissues to the capillaries in the lung.
D) O2 will diffuse from the alveoli into the capillaries.
E) O2 will diffuse from the tissues into the capillaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Figure 46-2 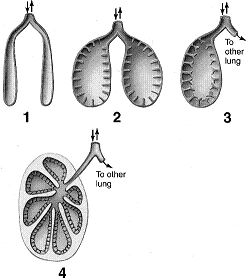 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of these lungs would be found in reptiles?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of these lungs would be found in reptiles?
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 4 only
E) both 1 and 2
 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of these lungs would be found in reptiles?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of these lungs would be found in reptiles?A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 4 only
E) both 1 and 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following occurs during forced expiration?
A) The alveoli inflate.
B) The ribs move upward.
C) The internal intercostal muscles contract.
D) The floor of the thoracic cavity moves downward.
E) The pressure increases in the thoracic cavity.
A) The alveoli inflate.
B) The ribs move upward.
C) The internal intercostal muscles contract.
D) The floor of the thoracic cavity moves downward.
E) The pressure increases in the thoracic cavity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The maximum amount of air a person can exhale is called:
A) vital capacity.
B) tidal volume.
C) tidal capacity
D) residual capacity.
E) residual volume
A) vital capacity.
B) tidal volume.
C) tidal capacity
D) residual capacity.
E) residual volume

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The amount of air being moved with each ventilation is referred to as:
A) vital capacity.
B) tidal volume.
C) residual capacity.
D) the Bohr effect.
E) hyperventilation.
A) vital capacity.
B) tidal volume.
C) residual capacity.
D) the Bohr effect.
E) hyperventilation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Figure 46-2 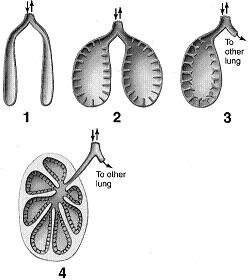 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of these lungs would be best for an animal that is fairly active?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of these lungs would be best for an animal that is fairly active?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) Any of these.
 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of these lungs would be best for an animal that is fairly active?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of these lungs would be best for an animal that is fairly active?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) Any of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Fick's law states that:
A) the amount of gas diffusing across a membrane depends on differences in partial pressure.
B) the total pressure of a mixture of gases is the sum of the pressures of the individual gases.
C) the dissociation of oxygen from hemoglobin depends on the pH of the environment.
D) as oxygen concentration increases, there is an increase in the amount of hemoglobin produced.
E) the size of an animal varies inversely to the amount of diffusion across its respiratory membranes.
A) the amount of gas diffusing across a membrane depends on differences in partial pressure.
B) the total pressure of a mixture of gases is the sum of the pressures of the individual gases.
C) the dissociation of oxygen from hemoglobin depends on the pH of the environment.
D) as oxygen concentration increases, there is an increase in the amount of hemoglobin produced.
E) the size of an animal varies inversely to the amount of diffusion across its respiratory membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Figure 46-1 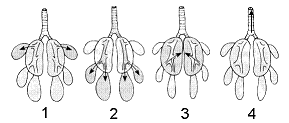 Refer to the accompanying figure. The structures receiving air in figure 1 are known as:
Refer to the accompanying figure. The structures receiving air in figure 1 are known as:
A) anterior air sacs.
B) parabronchi.
C) spiracles.
D) alveoli.
E) tracheae.
 Refer to the accompanying figure. The structures receiving air in figure 1 are known as:
Refer to the accompanying figure. The structures receiving air in figure 1 are known as:A) anterior air sacs.
B) parabronchi.
C) spiracles.
D) alveoli.
E) tracheae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is typically used to measure the functional capacity of the lungs?
A) vital capacity
B) tidal volume
C) tidal capacity
D) residual capacity
E) residual volume
A) vital capacity
B) tidal volume
C) tidal capacity
D) residual capacity
E) residual volume

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Both aquatic and terrestrial organisms must have ____ across which gas exchange can take place.
A) a respiratory system
B) tracheal tubes
C) gills and lungs
D) stratified squamous epithelial tissue
E) a moist surface
A) a respiratory system
B) tracheal tubes
C) gills and lungs
D) stratified squamous epithelial tissue
E) a moist surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The most common respiratory pigments in animals are:
A) myoglobin and hemocyanin.
B) myoglobin and hemoglobin.
C) hemocyanin and hemoglobin.
D) mucus and hemoglobin.
E) pulmonary surfactant and myoglobin.
A) myoglobin and hemocyanin.
B) myoglobin and hemoglobin.
C) hemocyanin and hemoglobin.
D) mucus and hemoglobin.
E) pulmonary surfactant and myoglobin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
During respiratory exchange, carbon dioxide moves from the blood into the alveoli due to:
A) the presence of a permease, which removes carbon dioxide from the capillaries.
B) potassium cotransport.
C) diffusion down a concentration gradient.
D) the air pressure of dissolved oxygen, which forces it out.
E) the contraction of the diaphragm, which creates a vacuum that pulls it out.
A) the presence of a permease, which removes carbon dioxide from the capillaries.
B) potassium cotransport.
C) diffusion down a concentration gradient.
D) the air pressure of dissolved oxygen, which forces it out.
E) the contraction of the diaphragm, which creates a vacuum that pulls it out.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following best defines the Bohr effect?
A) The amount of a gas that diffuses across a membrane depends on the differences in the gas' partial pressure.
B) The ability of hemoglobin to bind oxygen depends on the partial pressure of oxygen.
C) In a mixture of gases, the total pressure of the mixture is the sum of the pressures of the individual gases.
D) pH causes a displacement of the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve.
E) As the concentration of chloride ions increases, the ability of hemoglobin to bind carbon dioxide decreases.
A) The amount of a gas that diffuses across a membrane depends on the differences in the gas' partial pressure.
B) The ability of hemoglobin to bind oxygen depends on the partial pressure of oxygen.
C) In a mixture of gases, the total pressure of the mixture is the sum of the pressures of the individual gases.
D) pH causes a displacement of the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve.
E) As the concentration of chloride ions increases, the ability of hemoglobin to bind carbon dioxide decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Dalton's Law states that:
A) the amount of a gas that diffuses across a membrane depends on the differences in the gas' partial pressure.
B) the ability of hemoglobin to bind oxygen depends on the partial pressure of oxygen.
C) in a mixture of gases, the total pressure of the mixture is the sum of the pressures of the individual gases.
D) pH causes a displacement of the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve.
E) as the concentration of chloride ions increases, the ability of hemoglobin to bind carbon dioxide decreases.
A) the amount of a gas that diffuses across a membrane depends on the differences in the gas' partial pressure.
B) the ability of hemoglobin to bind oxygen depends on the partial pressure of oxygen.
C) in a mixture of gases, the total pressure of the mixture is the sum of the pressures of the individual gases.
D) pH causes a displacement of the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve.
E) as the concentration of chloride ions increases, the ability of hemoglobin to bind carbon dioxide decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Figure 46-2  Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of these lungs would have the greatest surface area?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of these lungs would have the greatest surface area?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) All have equal surface area.
 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of these lungs would have the greatest surface area?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of these lungs would have the greatest surface area?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) All have equal surface area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Figure 46-3 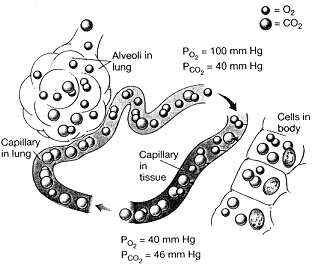 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which statement is FALSE?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which statement is FALSE?
A) The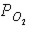 of the air in the alveoli must be greater than 100 mm Hg.
of the air in the alveoli must be greater than 100 mm Hg.
B) The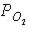 in the tissues must be less than 100 mm Hg.
in the tissues must be less than 100 mm Hg.
C) The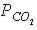 of the air in the alveoli must be less than 40 mm Hg.
of the air in the alveoli must be less than 40 mm Hg.
D) The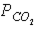 in the tissues must be greater than 40 mm Hg.
in the tissues must be greater than 40 mm Hg.
E) The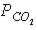 in the tissues must be equal to the
in the tissues must be equal to the 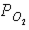 in the tissues.
in the tissues.
 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which statement is FALSE?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which statement is FALSE?A) The
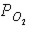 of the air in the alveoli must be greater than 100 mm Hg.
of the air in the alveoli must be greater than 100 mm Hg.B) The
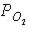 in the tissues must be less than 100 mm Hg.
in the tissues must be less than 100 mm Hg.C) The
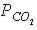 of the air in the alveoli must be less than 40 mm Hg.
of the air in the alveoli must be less than 40 mm Hg.D) The
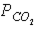 in the tissues must be greater than 40 mm Hg.
in the tissues must be greater than 40 mm Hg.E) The
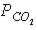 in the tissues must be equal to the
in the tissues must be equal to the 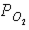 in the tissues.
in the tissues.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following areas of the respiratory tract is lined with a single layer of epithelial cells?
A) nasal cavity
B) larynx
C) trachea
D) bronchi
E) alveoli
A) nasal cavity
B) larynx
C) trachea
D) bronchi
E) alveoli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which statement about the regulation of respiration is FALSE?
A) Respiratory centers in the medulla control the transition from inspiration to expiration.
B) Carbon dioxide concentration is the most important chemical stimulus for regulating respiratory rate.
C) Chemoreceptors in the walls of various arteries are sensitive to carbon dioxide levels in the blood.
D) A group of neurons in the ventral medulla only become active when we need to breathe forcefully.
E) Chemoreceptors may be sensitive to oxygen, carbon dioxide, and/or hydrogen ion concentration.
A) Respiratory centers in the medulla control the transition from inspiration to expiration.
B) Carbon dioxide concentration is the most important chemical stimulus for regulating respiratory rate.
C) Chemoreceptors in the walls of various arteries are sensitive to carbon dioxide levels in the blood.
D) A group of neurons in the ventral medulla only become active when we need to breathe forcefully.
E) Chemoreceptors may be sensitive to oxygen, carbon dioxide, and/or hydrogen ion concentration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The smallest branches of the respiratory tree are the:
A) pharynx.
B) tracheae.
C) bronchial tubes.
D) bronchioles.
E) bronchi.
A) pharynx.
B) tracheae.
C) bronchial tubes.
D) bronchioles.
E) bronchi.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The ability of oxygen to combine with and detach from hemoglobin is influenced by which of the following factors?
A) percent oxygen saturation
B) humidity
C) oxygen concentration
D) tidal volume
E) partial pressure
A) percent oxygen saturation
B) humidity
C) oxygen concentration
D) tidal volume
E) partial pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Cilia lining the respiratory tubes beat mucus upward in order to:
A) moisten the bronchioles.
B) conduct the mucus that contains particles to the pharynx and away from the lungs.
C) provide mucus to the lungs to prevent them from dehydrating.
D) lubricate the throat for easier swallowing.
E) promote gas exchange by providing mucus for the respiratory surfaces.
A) moisten the bronchioles.
B) conduct the mucus that contains particles to the pharynx and away from the lungs.
C) provide mucus to the lungs to prevent them from dehydrating.
D) lubricate the throat for easier swallowing.
E) promote gas exchange by providing mucus for the respiratory surfaces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The film of fluid in the pleural cavity functions to:
A) nourish the lungs.
B) rehydrate the lungs.
C) provide lubrication between the lungs and thoracic wall.
D) trap bacteria that may enter the lungs.
E) inflate the lungs.
A) nourish the lungs.
B) rehydrate the lungs.
C) provide lubrication between the lungs and thoracic wall.
D) trap bacteria that may enter the lungs.
E) inflate the lungs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the chloride shift, ____ move into RBCs to replace the ____ that move out.
A) oxygen molecules; chloride ions
B) carbon dioxide molecules; chloride ions
C) bicarbonate ions; chloride ions
D) chloride ions; oxygen molecules
E) chloride ions; bicarbonate ions
A) oxygen molecules; chloride ions
B) carbon dioxide molecules; chloride ions
C) bicarbonate ions; chloride ions
D) chloride ions; oxygen molecules
E) chloride ions; bicarbonate ions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Decompression sickness is caused by:
A) dissolved gases coming out of solution and forming gas bubbles.
B) the concentration of hemoglobin dropping markedly.
C) chloride ions precipitating from solution.
D) the pH of the blood rising too rapidly.
E) carbonic anhydrase being inhibited.
A) dissolved gases coming out of solution and forming gas bubbles.
B) the concentration of hemoglobin dropping markedly.
C) chloride ions precipitating from solution.
D) the pH of the blood rising too rapidly.
E) carbonic anhydrase being inhibited.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Oxygen concentration generally plays an important role in regulating respiration:
A) all the time.
B) never.
C) only when the carbon dioxide concentration falls markedly.
D) only when the oxygen concentration falls markedly.
E) only when the pH falls markedly.
A) all the time.
B) never.
C) only when the carbon dioxide concentration falls markedly.
D) only when the oxygen concentration falls markedly.
E) only when the pH falls markedly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The voice box is also referred to as the:
A) larynx.
B) nasal cavity.
C) epiglottis.
D) pharynx.
E) trachea.
A) larynx.
B) nasal cavity.
C) epiglottis.
D) pharynx.
E) trachea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
During swallowing, ____ closes off the ____ so food cannot enter the lower airway.
A) the pleural membrane; trachea
B) cartilage; larynx
C) the pharynx; esophagus
D) the Adam's apple; trachea
E) the epiglottis; larynx
A) the pleural membrane; trachea
B) cartilage; larynx
C) the pharynx; esophagus
D) the Adam's apple; trachea
E) the epiglottis; larynx

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The pleural cavity is located:
A) between the pleural membranes.
B) inside the innermost pleural membrane.
C) outside the outermost pleural membrane.
D) between the right lung and the left lung.
E) within the bronchioles.
A) between the pleural membranes.
B) inside the innermost pleural membrane.
C) outside the outermost pleural membrane.
D) between the right lung and the left lung.
E) within the bronchioles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When drinking water at a party you sneeze and water comes out of your nose. Why did this happen?
A) The epiglottis did not close.
B) The glottis did not close.
C) The pharynx and nasal cavity were connected.
D) The tongue blocked the pharynx.
E) The water was carbonated.
A) The epiglottis did not close.
B) The glottis did not close.
C) The pharynx and nasal cavity were connected.
D) The tongue blocked the pharynx.
E) The water was carbonated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Asian pearl divers hyperventilate in order to reduce the ____ concentration in the blood.
A) oxygen
B) hydrogen ion
C) carbon dioxide
D) chloride ion
E) hemoglobin
A) oxygen
B) hydrogen ion
C) carbon dioxide
D) chloride ion
E) hemoglobin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Respiratory acidosis results when ____ are produced more rapidly than they are removed.
A) oxygen molecules
B) carbon dioxide molecules
C) chloride ions
D) hydrogen ions
E) carbonic anhydrase molecules
A) oxygen molecules
B) carbon dioxide molecules
C) chloride ions
D) hydrogen ions
E) carbonic anhydrase molecules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Most of the carbon dioxide in the blood is transported:
A) by being dissolved in plasma.
B) as bicarbonate ions.
C) by hemoglobin.
D) as carbonic anhydrase.
E) as carbonic acid.
A) by being dissolved in plasma.
B) as bicarbonate ions.
C) by hemoglobin.
D) as carbonic anhydrase.
E) as carbonic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
When chemoreceptors detect a slight decrease in pH, this means that ____ concentrations have increased, and the breathing rate must ____.
A) carbon dioxide; increase
B) carbon dioxide; decrease
C) oxygen; increase
D) oxygen; decrease
E) chloride; decrease
A) carbon dioxide; increase
B) carbon dioxide; decrease
C) oxygen; increase
D) oxygen; decrease
E) chloride; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Carbonic anhydrase in red blood cells:
A) removes oxygen from the erythrocyte.
B) carries carbon dioxide in the erythrocyte.
C) converts carbon dioxide to carbonic acid.
D) increases the pH of the blood.
E) increases the permeability of the capillary to carbon dioxide.
A) removes oxygen from the erythrocyte.
B) carries carbon dioxide in the erythrocyte.
C) converts carbon dioxide to carbonic acid.
D) increases the pH of the blood.
E) increases the permeability of the capillary to carbon dioxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What will happen if a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor is added to blood?
A) The level of CO2 in the blood will increase.
B) The level of CO2 in the blood will decrease.
C) The level of CO2 in the blood will remain the same.
D) The pH of the blood will remain the same.
E) The pH of the blood will decrease.
A) The level of CO2 in the blood will increase.
B) The level of CO2 in the blood will decrease.
C) The level of CO2 in the blood will remain the same.
D) The pH of the blood will remain the same.
E) The pH of the blood will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What happens at higher altitudes?
A) The concentration of oxygen decreases.
B) The concentration of carbon dioxide increases.
C) The partial pressure of oxygen decreases.
D) The partial pressure of carbon dioxide increases.
E) There is no change in the concentration or partial pressures of atmospheric gases.
A) The concentration of oxygen decreases.
B) The concentration of carbon dioxide increases.
C) The partial pressure of oxygen decreases.
D) The partial pressure of carbon dioxide increases.
E) There is no change in the concentration or partial pressures of atmospheric gases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The efficient exchange of gases in gills is an example of countercurrent exchange .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
You have a significant reduction in the amount of pulmonary surfactant. What is the likely effect?
A) The risk of bacterial infection will increase.
B) The risk of having chronic obstructive pulmonary disease will increase.
C) The bronchioles will constrict, which will increase airway resistance.
D) The lungs will be difficult to inflate.
E) Gas exchange cannot occur.
A) The risk of bacterial infection will increase.
B) The risk of having chronic obstructive pulmonary disease will increase.
C) The bronchioles will constrict, which will increase airway resistance.
D) The lungs will be difficult to inflate.
E) Gas exchange cannot occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
During forced inhalation, the ____ intercostal muscles contract, moving ____ upward.
A) internal; the diaphragm
B) internal; the ribs
C) external; the diaphragm
D) external; the ribs
E) external; both the diaphragm and the ribs
A) internal; the diaphragm
B) internal; the ribs
C) external; the diaphragm
D) external; the ribs
E) external; both the diaphragm and the ribs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Arrange the structures through which air passes upon entering the body in the proper sequence.
1) alveoli
2) bronchi
3) larynx
4) bronchioles
5) pharynx
6) trachea
A) 5 → 3 → 6 → 2 → 4 → 1
B) 3 → 5 → 2 → 6 → 1 → 4
C) 2 → 4 → 3 → 5 → 6 → 1
D) 3 → 6 → 5 → 2 → 4 → 1
E) 5 → 6 → 3 → 4 → 2 → 1
1) alveoli
2) bronchi
3) larynx
4) bronchioles
5) pharynx
6) trachea
A) 5 → 3 → 6 → 2 → 4 → 1
B) 3 → 5 → 2 → 6 → 1 → 4
C) 2 → 4 → 3 → 5 → 6 → 1
D) 3 → 6 → 5 → 2 → 4 → 1
E) 5 → 6 → 3 → 4 → 2 → 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
During exhalation, air moves from the bronchi directly into the alveoli .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The parabronchi of birds are open at both ends .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
During inspiration, the diaphragm ____ and ____ the volume of the thoracic cavity, causing air to flow ____.
A) relaxes; increases; inward
B) contracts; increases; inward
C) relaxes; decreases; outward
D) relaxes; decreases; inward
E) contracts; decreases; inward
A) relaxes; increases; inward
B) contracts; increases; inward
C) relaxes; decreases; outward
D) relaxes; decreases; inward
E) contracts; decreases; inward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Dalton's law of partial pressures states that the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the pressures of the individual gases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following occurs in pulmonary emphysema?
A) The alveoli lose their elasticity.
B) The surface area of the lung is greatly decreased.
C) Walls between adjacent alveoli become reinforced.
D) The heart becomes enlarged from pressure.
E) Fresh air accumulates in the lungs because it cannot be properly inhaled.
A) The alveoli lose their elasticity.
B) The surface area of the lung is greatly decreased.
C) Walls between adjacent alveoli become reinforced.
D) The heart becomes enlarged from pressure.
E) Fresh air accumulates in the lungs because it cannot be properly inhaled.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Identify a respiratory pigment, and then describe its structure and how this relates to its function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of gas exchange in terrestrial and aquatic environments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Tracheal tubes and spiracles are characteristically found in annelids .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The single most preventable cause of disease in the United States is:
A) alcohol use.
B) tobacco use.
C) automobile accidents.
D) suicide.
E) homicide.
A) alcohol use.
B) tobacco use.
C) automobile accidents.
D) suicide.
E) homicide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Gases move freely across the walls of the bronchioles into the capillaries that surround them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
During inhalation, the diaphragm moves upward .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The swim bladders of fishes function primarily in ventilation .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Vocal cords are located in the larynx.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
During inhalation, air moves from the pharynx directly into the trachea .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Pulmonary surfactant functions by:
A) increasing the cohesive forces of water molecules.
B) increasing the surface tension of water.
C) moving water across respiratory surfaces.
D) preventing the alveoli from expanding.
E) increasing the energy required to stretch the lungs.
A) increasing the cohesive forces of water molecules.
B) increasing the surface tension of water.
C) moving water across respiratory surfaces.
D) preventing the alveoli from expanding.
E) increasing the energy required to stretch the lungs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Identify and briefly explain two adaptations of diving marine mammals, such as seals and dolphins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



