Deck 56: Ecology and the Geography of Life
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/81
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 56: Ecology and the Geography of Life
1
Which of the following characteristics applies to biomes?
A) They are usually confined to a relatively small geographical area.
B) They encompass interacting landscapes.
C) Their distribution is largely the result of differences in population.
D) Their boundaries extend beyond climate barriers.
E) They include regions with similar climate, but different plants, animals, and soil.
A) They are usually confined to a relatively small geographical area.
B) They encompass interacting landscapes.
C) Their distribution is largely the result of differences in population.
D) Their boundaries extend beyond climate barriers.
E) They include regions with similar climate, but different plants, animals, and soil.
B
2
Which biome is characterized by weasels, gray wolves, ptarmigan, musk oxen, and lemmings?
A) tundra
B) desert
C) tropical rain forest
D) savanna
E) temperate deciduous forest
A) tundra
B) desert
C) tropical rain forest
D) savanna
E) temperate deciduous forest
A
3
Figure 56-1  Based on the temperature range and precipitation, the area on the accompanying figure labeled as 3 represents which of the following biomes?
Based on the temperature range and precipitation, the area on the accompanying figure labeled as 3 represents which of the following biomes?
A) savanna
B) temperate deciduous forest
C) temperate rain forest
D) taiga
E) tundra
 Based on the temperature range and precipitation, the area on the accompanying figure labeled as 3 represents which of the following biomes?
Based on the temperature range and precipitation, the area on the accompanying figure labeled as 3 represents which of the following biomes?A) savanna
B) temperate deciduous forest
C) temperate rain forest
D) taiga
E) tundra
A
4
Which biome has the shortest growing season?
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) desert
E) tropical rain forest
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) desert
E) tropical rain forest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Near the poles, what is generally the overriding climate factor?
A) temperature
B) precipitation
C) latitude
D) altitude
E) pH
A) temperature
B) precipitation
C) latitude
D) altitude
E) pH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Tundra soils are usually ____ and have ____ in the uppermost layer of soil.
A) nutrient poor; little organic litter
B) nutrient rich; much organic litter
C) frozen; nutrients
D) moist; dead plant material
E) sandy; high pH
A) nutrient poor; little organic litter
B) nutrient rich; much organic litter
C) frozen; nutrients
D) moist; dead plant material
E) sandy; high pH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
There are no trees in the tundra because:
A) of the short growing season.
B) of the limited supply of nutrients in the soil.
C) of limited root penetration due to permafrost.
D) of limited precipitation.
E) of low temperatures.
A) of the short growing season.
B) of the limited supply of nutrients in the soil.
C) of limited root penetration due to permafrost.
D) of limited precipitation.
E) of low temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Figure 56-1 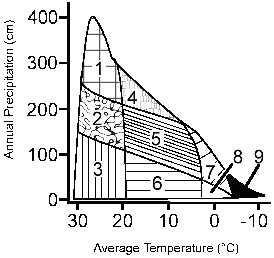 Based on the temperature range and precipitation, the area on the accompanying figure labeled as 5 represents which of the following biomes?
Based on the temperature range and precipitation, the area on the accompanying figure labeled as 5 represents which of the following biomes?
A) savanna
B) temperate deciduous forest
C) temperate rain forest
D) taiga
E) tundra
 Based on the temperature range and precipitation, the area on the accompanying figure labeled as 5 represents which of the following biomes?
Based on the temperature range and precipitation, the area on the accompanying figure labeled as 5 represents which of the following biomes?A) savanna
B) temperate deciduous forest
C) temperate rain forest
D) taiga
E) tundra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Glacier ice occupied about ____% of Earth's land during the last Ice Age, then began retreating about 17,000 years ago. Today, glacier ice occupies about ____% of the land surface.
A) 30; 10.
B) 50; 10
C) 73; 50
D) 80; 50
E) 15; 1
A) 30; 10.
B) 50; 10
C) 73; 50
D) 80; 50
E) 15; 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
____ is characterized by cold temperatures, little precipitation, and few or no trees.
A) Taiga
B) Chaparral
C) Savanna
D) Tundra
E) Desert
A) Taiga
B) Chaparral
C) Savanna
D) Tundra
E) Desert

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which biome has the least primary productivity?
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) desert
E) tropical rain forest
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) desert
E) tropical rain forest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Soils of the tundra are very ____ due to ____.
A) old; lack of precipitation
B) young; lack of precipitation
C) old; glaciation
D) young; glaciation
E) thick; high precipitation
A) old; lack of precipitation
B) young; lack of precipitation
C) old; glaciation
D) young; glaciation
E) thick; high precipitation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which biome has the fewest types of species?
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) desert
E) It is not possible to determine this based on the information provided.
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) desert
E) It is not possible to determine this based on the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Based on the temperature range and precipitation, which area in the accompanying figure is dominated by pine trees?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Figure 56-1 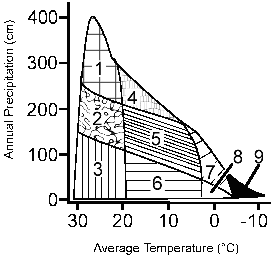 Based on the accompanying figure, what is the annual precipitation and temperature range for a temperate rain forest?
Based on the accompanying figure, what is the annual precipitation and temperature range for a temperate rain forest?
A) 300 − 400 cm/yr precipitation and 20 − 30 ° C
B) 200 − 300 cm/yr precipitation and 20 − 30 ° C
C) 200 − 300 cm/yr precipitation and 10 − 20 ° C
D) 150 − 250 cm/yr precipitation and 10 − 20 ° C
E) 150 − 250 cm/yr precipitation and 20 − 30 ° C
 Based on the accompanying figure, what is the annual precipitation and temperature range for a temperate rain forest?
Based on the accompanying figure, what is the annual precipitation and temperature range for a temperate rain forest?A) 300 − 400 cm/yr precipitation and 20 − 30 ° C
B) 200 − 300 cm/yr precipitation and 20 − 30 ° C
C) 200 − 300 cm/yr precipitation and 10 − 20 ° C
D) 150 − 250 cm/yr precipitation and 10 − 20 ° C
E) 150 − 250 cm/yr precipitation and 20 − 30 ° C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The Southern Hemisphere has no equivalent of the boreal forest of the north. Why?
A) It has no latitudes near the poles.
B) It has insufficient altitudes.
C) It has no land in the corresponding latitudes.
D) It is too close to the sun during the winter.
E) It has an inhospitable temperature.
A) It has no latitudes near the poles.
B) It has insufficient altitudes.
C) It has no land in the corresponding latitudes.
D) It is too close to the sun during the winter.
E) It has an inhospitable temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Currently, much commercial lumber and wood products come from which biome?
A) tundra
B) temperate rain forest
C) savanna
D) tropical rain forest
E) temperate deciduous forest
A) tundra
B) temperate rain forest
C) savanna
D) tropical rain forest
E) temperate deciduous forest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which statement about Earth's biomes is FALSE?
A) Biomes near the poles have less rainfall than biomes on the equator.
B) Altitude can result in biomes that are not characteristic for a particular latitude.
C) Deserts have less rainfall due to their distance from the ocean.
D) Rainforests occur in both the Northern and Southern Hemisphere.
E) Deserts occur in both the Northern and Southern Hemisphere.
A) Biomes near the poles have less rainfall than biomes on the equator.
B) Altitude can result in biomes that are not characteristic for a particular latitude.
C) Deserts have less rainfall due to their distance from the ocean.
D) Rainforests occur in both the Northern and Southern Hemisphere.
E) Deserts occur in both the Northern and Southern Hemisphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In tropical and temperate regions, ____ becomes more significant than temperature.
A) altitude
B) precipitation
C) latitude
D) migration
E) pH
A) altitude
B) precipitation
C) latitude
D) migration
E) pH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is an adaptation of black-tailed prairie dogs?
A) modified digestive tracts to easily digest seeds and leaves of grasses
B) transition to a carnivore lifestyle
C) movement towards above ground living
D) hibernation throughout the spring
E) movement towards living in small social groups
A) modified digestive tracts to easily digest seeds and leaves of grasses
B) transition to a carnivore lifestyle
C) movement towards above ground living
D) hibernation throughout the spring
E) movement towards living in small social groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The ____ biome is characterized by plants that are particularly well adapted to periodic fires.
A) taiga
B) temperate rain forest
C) tundra
D) chaparral
E) tropical rain forest
A) taiga
B) temperate rain forest
C) tundra
D) chaparral
E) tropical rain forest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Figure 56-2 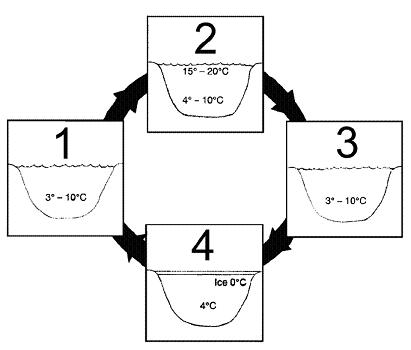 Which of the lakes in the accompanying figure may have a thermocline?
Which of the lakes in the accompanying figure may have a thermocline?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 1 and 3
E) 2 and 4
 Which of the lakes in the accompanying figure may have a thermocline?
Which of the lakes in the accompanying figure may have a thermocline?A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 1 and 3
E) 2 and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Lianas and epiphytes are especially common in the:
A) tropical rain forest.
B) savanna.
C) temperate grassland.
D) chaparral.
E) taiga.
A) tropical rain forest.
B) savanna.
C) temperate grassland.
D) chaparral.
E) taiga.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which biome has the greatest number of distinct layers of vegetation?
A) savanna
B) tropical rain forest
C) desert
D) chaparral
E) grassland
A) savanna
B) tropical rain forest
C) desert
D) chaparral
E) grassland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The ____ covers approximately 11% of Earth's land and contains numerous lakes and ponds.
A) boreal forest
B) tropical rain forest
C) temperate rain forest
D) temperate deciduous forest
E) tropical dry forest
A) boreal forest
B) tropical rain forest
C) temperate rain forest
D) temperate deciduous forest
E) tropical dry forest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Figure 56-2 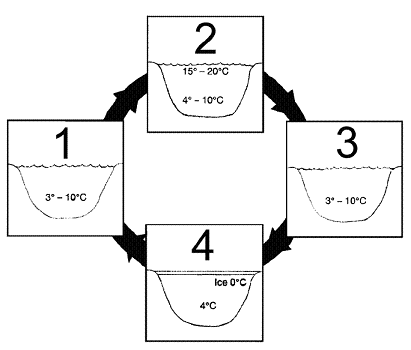 Which of the lakes in the accompanying figure may experience turnover?
Which of the lakes in the accompanying figure may experience turnover?
A) 2 and 4
B) 2 and 3
C) 3 and 4
D) 1 and 2
E) 1 and 3
 Which of the lakes in the accompanying figure may experience turnover?
Which of the lakes in the accompanying figure may experience turnover?A) 2 and 4
B) 2 and 3
C) 3 and 4
D) 1 and 2
E) 1 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Much precipitation in the tropical rain forest is derived from:
A) evaporation from lakes.
B) evaporation from rivers.
C) groundwater.
D) transpiration.
E) translocation.
A) evaporation from lakes.
B) evaporation from rivers.
C) groundwater.
D) transpiration.
E) translocation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The tropical rain forest biome is characterized by:
A) high density of plants, but nutrient poor soil.
B) high density of plants and nutrient rich soil.
C) low density of plants due to nutrient poor soil.
D) low density of plants, yet nutrient rich soil.
E) intermediate density of plants and intermediate nutrient supply.
A) high density of plants, but nutrient poor soil.
B) high density of plants and nutrient rich soil.
C) low density of plants due to nutrient poor soil.
D) low density of plants, yet nutrient rich soil.
E) intermediate density of plants and intermediate nutrient supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The ____ biome is found in states such as Iowa, Minnesota, Nebraska, and other Midwestern states, and is characterized by thick, rich soils, and a thick mat of sod.
A) savannah
B) tallgrass prairie
C) taiga
D) temperate deciduous forest
E) chaparral
A) savannah
B) tallgrass prairie
C) taiga
D) temperate deciduous forest
E) chaparral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is most characteristic of desert animals?
A) They tend to be quite large in size.
B) They estivate during the rainy season.
C) They mostly only come out at night.
D) They do not include mammals except for rodents.
E) They do not include insects.
A) They tend to be quite large in size.
B) They estivate during the rainy season.
C) They mostly only come out at night.
D) They do not include mammals except for rodents.
E) They do not include insects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The ____ biome has the greatest species richness of the terrestrial biomes.
A) tropical rain forest
B) savanna
C) grassland
D) chaparral
E) temperate deciduous forest
A) tropical rain forest
B) savanna
C) grassland
D) chaparral
E) temperate deciduous forest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The greatest proportion of which two biomes have been converted to agriculture?
A) taiga and tropical rain forest
B) tropical rain forest and temperate rain forest
C) temperate deciduous forest and temperate grassland
D) chaparral and tropical rain forest
E) temperate grassland and savanna
A) taiga and tropical rain forest
B) tropical rain forest and temperate rain forest
C) temperate deciduous forest and temperate grassland
D) chaparral and tropical rain forest
E) temperate grassland and savanna

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Figure 56-2 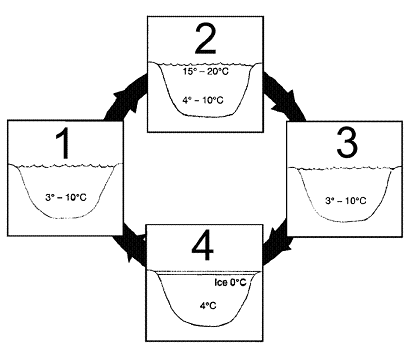 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the following represents the fall turnover?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the following represents the fall turnover?
A) 1 going to 2
B) 2 going to 3
C) 3 going to 4
D) 4 going to 1
E) 4 going to 2
 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the following represents the fall turnover?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the following represents the fall turnover?A) 1 going to 2
B) 2 going to 3
C) 3 going to 4
D) 4 going to 1
E) 4 going to 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The exact elevation at which the treeline occurs depends on the ____ and ____.
A) temperature; distance from the sun
B) altitude; distance from the sun
C) elevation; annual precipitation
D) latitude; distance from the ocean
E) longitude; distance from the equator
A) temperature; distance from the sun
B) altitude; distance from the sun
C) elevation; annual precipitation
D) latitude; distance from the ocean
E) longitude; distance from the equator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Overgrazing in savannas by domestic animals has contributed to its conversion into:
A) chaparral.
B) grassland.
C) desert.
D) taiga.
E) ecotones.
A) chaparral.
B) grassland.
C) desert.
D) taiga.
E) ecotones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which biome has the longest growing season?
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) temperate deciduous forest
E) tropical rain forest
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) temperate deciduous forest
E) tropical rain forest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The dominant vegetation of the temperate rain forest includes which of the following?
A) Sitka spruce
B) western red oak
C) beech
D) bamboo
E) Southern pine
A) Sitka spruce
B) western red oak
C) beech
D) bamboo
E) Southern pine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Climates characteristic of the Mediterranean region are also common in:
A) Nebraska.
B) New York.
C) Florida.
D) Hawaii.
E) California.
A) Nebraska.
B) New York.
C) Florida.
D) Hawaii.
E) California.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is a characteristic of desert plants?
A) common annuals
B) enlarged leaf size
C) lianas with extensive epiphytes
D) adaptations that conserve water
E) adaptations to stable temperatures
A) common annuals
B) enlarged leaf size
C) lianas with extensive epiphytes
D) adaptations that conserve water
E) adaptations to stable temperatures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Compared to soils of other ecosystems, desert soils are characterized as having:
A) high amounts of organic material and low mineral content.
B) low amounts of organic material and low mineral content.
C) high amounts of organic material and high mineral content.
D) low amounts of organic material and high mineral content.
E) moderate levels of both organic material and minerals.
A) high amounts of organic material and low mineral content.
B) low amounts of organic material and low mineral content.
C) high amounts of organic material and high mineral content.
D) low amounts of organic material and high mineral content.
E) moderate levels of both organic material and minerals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The marine euphotic zone is comparable to the ____ zone of lakes.
A) profundal
B) intertidal
C) abyssal
D) littoral
E) limnetic
A) profundal
B) intertidal
C) abyssal
D) littoral
E) limnetic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which factor is most important in determining the distribution of organisms in aquatic biomes?
A) interspecies composition
B) dominant vegetation
C) distance from shore
D) salinity
E) intraspecies composition
A) interspecies composition
B) dominant vegetation
C) distance from shore
D) salinity
E) intraspecies composition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Sponges and brittle stars are members of the ____ category of organisms:
A) nekton
B) phytoplankton
C) zooplankton
D) benthos
E) profundal zone
A) nekton
B) phytoplankton
C) zooplankton
D) benthos
E) profundal zone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which organism would be found exclusively in the benthic environment?
A) painted turtles
B) pond snail
C) bur-reeds
D) cattails
E) bloodworms
A) painted turtles
B) pond snail
C) bur-reeds
D) cattails
E) bloodworms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The Southern Hemisphere has no alpine tundra.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What environment is characterized by high nutrient inputs and by relatively great fluctuations in salinity and temperature?
A) A river
B) An estuary
C) A freshwater wetland
D) Aa large lake
E) The oceanic province
A) A river
B) An estuary
C) A freshwater wetland
D) Aa large lake
E) The oceanic province

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Describe the climate, soil, and representative organisms for two of the following terrestrial biomes: savanna, temperate rain forest, chaparral, or taiga.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following applies to the deepest zone of a large lake?
A) effective recycling of minerals
B) anaerobic conditions
C) a mineral-poor zone
D) plentiful light penetration
E) numerous organisms
A) effective recycling of minerals
B) anaerobic conditions
C) a mineral-poor zone
D) plentiful light penetration
E) numerous organisms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
For coral reefs to form in tropical waters, it is necessary for the coral animals to live in symbiosis with:
A) bacteria.
B) parrot fish.
C) zooxanthellae.
D) sea urchins.
E) kelp.
A) bacteria.
B) parrot fish.
C) zooxanthellae.
D) sea urchins.
E) kelp.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The ____ contains the greatest volume of ocean water.
A) oceanic province
B) intertidal zone
C) euphotic zone
D) neritic province
E) limnetic zone
A) oceanic province
B) intertidal zone
C) euphotic zone
D) neritic province
E) limnetic zone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The most productive region of a lake is the ____ zone.
A) neritic
B) limnetic
C) profundal
D) littoral
E) oceanic
A) neritic
B) limnetic
C) profundal
D) littoral
E) oceanic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Characteristics of headwaters include:
A) fast flow, high oxygen, and free-floating vegetation.
B) fast flow, low oxygen, and free-floating vegetation.
C) fast flow, high oxygen, and streamlined animal bodies.
D) fast flow, high oxygen, and free-floating vegetation.
E) slow flow, high oxygen, and free-floating vegetation.
A) fast flow, high oxygen, and free-floating vegetation.
B) fast flow, low oxygen, and free-floating vegetation.
C) fast flow, high oxygen, and streamlined animal bodies.
D) fast flow, high oxygen, and free-floating vegetation.
E) slow flow, high oxygen, and free-floating vegetation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Marine snow is a major source of energy for the ____ region of the ocean.
A) littoral
B) aphotic
C) euphotic
D) intertidal
E) neustonic
A) littoral
B) aphotic
C) euphotic
D) intertidal
E) neustonic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Explain the changes in vegetation observed with increasing elevation. BONUS: Compare this to changes in vegetation with latitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A(n) ____ is the transition zone where two ecosystems meet and intergrade.
A) intertidal zone
B) ecotone
C) range
D) biome
E) thermocline
A) intertidal zone
B) ecotone
C) range
D) biome
E) thermocline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Identify and briefly describe three biogeographical realms as described by Wallace.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The ____ realm has long been separated from other land masses and is the area in which marsupials are particularly common.
A) Ethiopian
B) Palearctic
C) Nearctic
D) Oriental
E) Australian
A) Ethiopian
B) Palearctic
C) Nearctic
D) Oriental
E) Australian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Headwater streams depend primarily on ____ as an energy input.
A) photosynthesis
B) detritus
C) phytoplankton
D) zooplankton
E) nekton
A) photosynthesis
B) detritus
C) phytoplankton
D) zooplankton
E) nekton

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Adaptations found in inhabitants of the rocky intertidal zone include:
A) soft bodies.
B) an anchor or some other means of attachment.
C) strong swimming abilities.
D) active burrowing.
E) delicate outer coverings or bodies.
A) soft bodies.
B) an anchor or some other means of attachment.
C) strong swimming abilities.
D) active burrowing.
E) delicate outer coverings or bodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Microscopic algae typically fall under the classification of:
A) nekton.
B) phytoplankton.
C) zooplankton.
D) benthos.
E) profundal microorganisms.
A) nekton.
B) phytoplankton.
C) zooplankton.
D) benthos.
E) profundal microorganisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Describe the human impact on at least two aquatic ecosystems discussed. How have these alterations impacted these ecosystems?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The upper part of the neritic province is called the euphotic zone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Describe and diagram the various zones and provinces in the ocean. What adaptations to these variable conditions are seen in the biota that inhabit these regions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The hadal zone is that part of the benthic environment deeper than 6000 m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The American kangaroo rat is characteristic of the desert biome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Describe the alteration of five selected biomes by humans. How have different biomes been converted for commercial or agricultural use? Of those selected, which has undergone the most extensive change?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A layer of permanently frozen ground is called permafrost .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Describe the physical processes that result in the summer and winter stratification in temperate zone lakes. What causes the mixing in the spring and fall? What are major consequences of the winter stratification on the biota of the lake?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The United States is part of the Palearctic realm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The boreal forest biome does not contain deciduous trees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Dense coastal fog is characteristic of the temperate deciduous forest biome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The term nekton refers to bottom-dwelling organisms in an aquatic ecosystem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The oceanic province is that part of the ocean that overlies the continental shelf.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The chaparral biome is characterized by grasses as high as two meters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The transition zone between biomes is called a(n) ecotone .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The limnetic zone is the shallow-water area along the shore of a lake or pond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Small lakes and ponds usually lack a profundal zone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Extensive epiphytes are found in the tropical dry forests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
An example of a freshwater wetland is a(n) estuary .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



