Deck 19: The Biosphere and Human Effects
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/73
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: The Biosphere and Human Effects
1
Global air circulation patterns are produced by ____ differences in the amount of solar radiation reaching Earth.
A) elevational
B) latitudinal
C) moisture
D) rotational
E) longitudinal
A) elevational
B) latitudinal
C) moisture
D) rotational
E) longitudinal
B
2
Which tree has needle-shaped leaves that are adaptations for minimizing water loss?
A) cacti
B) conifer
C) broadleaf evergreen
D) deciduous angiosperms
E) mesquite
A) cacti
B) conifer
C) broadleaf evergreen
D) deciduous angiosperms
E) mesquite
B
3
Which biome has a layered structure that will contain many vines and epiphytes?
A) chaparral
B) tundra
C) estuary
D) taiga
E) tropical rainforest
A) chaparral
B) tundra
C) estuary
D) taiga
E) tropical rainforest
E
4
Crater Lake in Oregon formed as a result of a(n) ____ about 7,700 years ago.
A) asteroid strike
B) collapsed volcano
C) massive earthquake
D) continental shift
E) shift in Earth's axis
A) asteroid strike
B) collapsed volcano
C) massive earthquake
D) continental shift
E) shift in Earth's axis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What happens to air as it is warmed?
A) It rises.
B) It sinks.
C) It moves toward higher latitudes.
D) It moves along a pressure gradient.
E) It moves toward lower latitudes.
A) It rises.
B) It sinks.
C) It moves toward higher latitudes.
D) It moves along a pressure gradient.
E) It moves toward lower latitudes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Unrelated species that live in ________ parts of a biome often have _______ traits because they face similar conditions.
A) widely separated; different
B) nearby; different
C) extreme; similar
D) widely separated; identical
E) widely separated; similar
A) widely separated; different
B) nearby; different
C) extreme; similar
D) widely separated; identical
E) widely separated; similar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What characterizes a biome?
A) its temperature and main type of vegetation
B) its climate and main type of vegetation
C) its climate and temperature
D) its humidity and temperature
E) its plant life and mountain ranges
A) its temperature and main type of vegetation
B) its climate and main type of vegetation
C) its climate and temperature
D) its humidity and temperature
E) its plant life and mountain ranges

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Evergreen broadleaf trees, along with abundant rain, warm temperatures, and consistent day length, characterize the ____ biome.
A) chaparral
B) tropical rain forest
C) temperate deciduous forest
D) temperate grassland
E) boreal forest
A) chaparral
B) tropical rain forest
C) temperate deciduous forest
D) temperate grassland
E) boreal forest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Logging of conifer forests in ________ threatens the butterflies' winter home.
A) Florida
B) Canada
C) Texas
D) California
E) Mexico
A) Florida
B) Canada
C) Texas
D) California
E) Mexico

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which biome is pictured here? 
A) temperate deciduous forest
B) chaparral
C) tropical rainforest
D) temperate grassland
E) boreal forest

A) temperate deciduous forest
B) chaparral
C) tropical rainforest
D) temperate grassland
E) boreal forest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What happens to air as it is cooled?
A) It rises.
B) It sinks.
C) It moves toward higher latitudes.
D) It moves along a pressure gradient.
E) It moves toward lower latitudes.
A) It rises.
B) It sinks.
C) It moves toward higher latitudes.
D) It moves along a pressure gradient.
E) It moves toward lower latitudes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Solar radiation that falls on high latitudes ____.
A) passes through about the same amount of atmosphere as that which falls at low latitudes
B) passes through less atmosphere than that which falls at low latitudes
C) passes through more atmosphere than that which falls near low latitudes
D) is spread out over less area than that which falls near low latitudes
E) covers about the same area as that which falls near low latitudes
A) passes through about the same amount of atmosphere as that which falls at low latitudes
B) passes through less atmosphere than that which falls at low latitudes
C) passes through more atmosphere than that which falls near low latitudes
D) is spread out over less area than that which falls near low latitudes
E) covers about the same area as that which falls near low latitudes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Climate is the ____.
A) average weather condition an area receives over a short interval
B) average weather condition an area receives over a long interval
C) annual amount of sunlight an area receives
D) annual amount of rainfall an area receives
E) annual amount of total precipitation that occurs in an area
A) average weather condition an area receives over a short interval
B) average weather condition an area receives over a long interval
C) annual amount of sunlight an area receives
D) annual amount of rainfall an area receives
E) annual amount of total precipitation that occurs in an area

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which form of the monarch butterfly makes it to Mexico?
A) migrant caterpillar
B) sexually dormant butterfly
C) sexually active butterfly
D) sexually active caterpillar
E) sexually dormant caterpillar
A) migrant caterpillar
B) sexually dormant butterfly
C) sexually active butterfly
D) sexually active caterpillar
E) sexually dormant caterpillar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The dark pink color at the top of this picture represents the ____ biome. 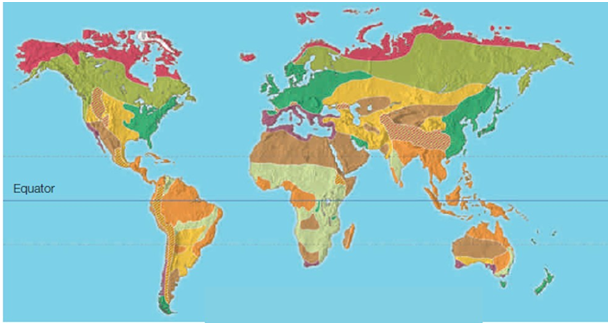
A) temperate deciduous forest
B) chaparral
C) tundra
D) temperate grassland
E) boreal forest

A) temperate deciduous forest
B) chaparral
C) tundra
D) temperate grassland
E) boreal forest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A characteristic of a temperate deciduous forest biome that differs from a tropical rainforest biome is that in a deciduous forest, ____.
A) there is greater biodiversity
B) there are more conifers
C) there are year-round warm temperatures
D) the trees shed their leaves
E) it is very similar to taiga
A) there is greater biodiversity
B) there are more conifers
C) there are year-round warm temperatures
D) the trees shed their leaves
E) it is very similar to taiga

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which way do ocean currents circulate in the northern hemisphere?
A) counterclockwise
B) clockwise
C) away from continents
D) toward the shore
E) parallel to the direction of the shore
A) counterclockwise
B) clockwise
C) away from continents
D) toward the shore
E) parallel to the direction of the shore

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Where are grassland biomes typically found?
A) in the middle of a continent
B) in the rain shadow of a mountain range
C) on the windward side of a mountain range
D) on the leeward side of a mountain range
E) adjacent to the shore of a continent
A) in the middle of a continent
B) in the rain shadow of a mountain range
C) on the windward side of a mountain range
D) on the leeward side of a mountain range
E) adjacent to the shore of a continent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Why is the monarch butterfly so sensitive to environmental changes?
A) It is preyed upon by many birds in a variety of ecosystems.
B) It eats a variety of foods in many ecosystems.
C) It competes for reproductive space with other butterflies in many ecosystems.
D) Its mimicry is sensitive to forests covers in many ecosystems.
E) It has a long-distance, multigenerational migration that crosses many ecosystems.
A) It is preyed upon by many birds in a variety of ecosystems.
B) It eats a variety of foods in many ecosystems.
C) It competes for reproductive space with other butterflies in many ecosystems.
D) Its mimicry is sensitive to forests covers in many ecosystems.
E) It has a long-distance, multigenerational migration that crosses many ecosystems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The most extensive of the biomes is the ____.
A) temperate deciduous forest
B) chaparral
C) tropical rainforest
D) temperate grassland
E) boreal forest
A) temperate deciduous forest
B) chaparral
C) tropical rainforest
D) temperate grassland
E) boreal forest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which primary succession event led to the formation of the tundra?
A) large tsunamis
B) glacial retreat
C) volcanic activity
D) the breaking up of Pangaea
E) large earthquakes
A) large tsunamis
B) glacial retreat
C) volcanic activity
D) the breaking up of Pangaea
E) large earthquakes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which event endangers far more species than the destruction of a comparable area elsewhere?
A) deforestation of temperate deciduous
B) desertification of grasslands
C) deforestation of taiga
D) desertification of savannah
E) deforestation in tropical rainforest biomes
A) deforestation of temperate deciduous
B) desertification of grasslands
C) deforestation of taiga
D) desertification of savannah
E) deforestation in tropical rainforest biomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What salt-tolerant woody plants have prop roots that help the plant stay upright in soft sediments?
A) wetlands
B) tide pools
C) cordgrass
D) mangroves
E) tidal flats
A) wetlands
B) tide pools
C) cordgrass
D) mangroves
E) tidal flats

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Permafrost is ____.
A) a temporary pool of water in an estuary
B) a permanent pool of water in the grasslands
C) permanently frozen ground in the polar icecap
D) temporary frozen ground in the polar icecap
E) permanently frozen layer of ground in the tundra
A) a temporary pool of water in an estuary
B) a permanent pool of water in the grasslands
C) permanently frozen ground in the polar icecap
D) temporary frozen ground in the polar icecap
E) permanently frozen layer of ground in the tundra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A clear lake is likely to be ____.
A) very old
B) well lit
C) shallow
D) recently formed
E) experiencing high primary productivity
A) very old
B) well lit
C) shallow
D) recently formed
E) experiencing high primary productivity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The distribution of major biomes is controlled mainly by ____.
A) ocean currents
B) climate
C) human manipulation
D) longitude
E) latitude
A) ocean currents
B) climate
C) human manipulation
D) longitude
E) latitude

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Seawater and freshwater mix in which coastal region?
A) hydrothermal vents
B) coral reefs
C) seamounts
D) tidal pools
E) estuary
A) hydrothermal vents
B) coral reefs
C) seamounts
D) tidal pools
E) estuary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The prime factor that drives coral bleaching is ____.
A) fungal infection
B) water levels changing
C) salinity levels changing
D) light levels changing
E) temperature changes
A) fungal infection
B) water levels changing
C) salinity levels changing
D) light levels changing
E) temperature changes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which biome is generally found between the polar ice cap and boreal forests?
A) desert
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) estuary
E) tundra
A) desert
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) estuary
E) tundra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The conversion of grasslands or woodlands to desertlike conditions is called ____.
A) desertification
B) bleaching
C) eutrophication
D) deforestation
E) intensive agriculture
A) desertification
B) bleaching
C) eutrophication
D) deforestation
E) intensive agriculture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is an undersea mountain called?
A) a seamount
B) a mangrove
C) a trench
D) an estuary
E) a coral reef
A) a seamount
B) a mangrove
C) a trench
D) an estuary
E) a coral reef

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Nutrient poor soils and dominant evergreen angiosperm trees dominate which biome?
A) boreal forests
B) chaparral
C) deserts
D) tropical rain forests
E) temperate deciduous forests
A) boreal forests
B) chaparral
C) deserts
D) tropical rain forests
E) temperate deciduous forests

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which North American biome has mostly disappeared because of extensive farming of wheat and corn?
A) chaparral
B) grasslands
C) boreal forest
D) desert
E) taiga
A) chaparral
B) grasslands
C) boreal forest
D) desert
E) taiga

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Concerning species survival, which status is of greatest concern?
A) threatened
B) endemic
C) critical
D) endangered
E) serious
A) threatened
B) endemic
C) critical
D) endangered
E) serious

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A(n) ____ species resides where it evolved and is found nowhere else on Earth.
A) invasive
B) endemic
C) endangered
D) exotic
E) persistent
A) invasive
B) endemic
C) endangered
D) exotic
E) persistent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In this freshwater aquatic ecosystem, species composition varies along its length based on rock types, depth, oxygen concentrations, and temperature.
A) streams
B) lakes
C) estuaries
D) coral reefs
E) hydrothermal vents
A) streams
B) lakes
C) estuaries
D) coral reefs
E) hydrothermal vents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The primary producers associated with hydrothermal vents are ____.
A) dinoflagellates
B) archaea
C) red algae
D) diatoms
E) sea kelp
A) dinoflagellates
B) archaea
C) red algae
D) diatoms
E) sea kelp

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
California's most extensive ecosystem, the ____ biome, is dominated by drought-resistant, fire-adapted shrubs with small, leathery leaves.
A) temperate deciduous forest
B) prairie
C) desert
D) chaparral
E) savannah
A) temperate deciduous forest
B) prairie
C) desert
D) chaparral
E) savannah

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An aquatic ecosystem that may include protists and bacteria as producers in a well-lit zone and detritus feeders in a deeper dark zone is a(n) ____.
A) estuary
B) stream
C) lake
D) coral reef
E) hydrothermal vent
A) estuary
B) stream
C) lake
D) coral reef
E) hydrothermal vent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In 2001, the ____ became the first invertebrate to be listed as endangered by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
A) dodo
B) white abalone
C) Texas blind salamander
D) harvester ant
E) coelacanth
A) dodo
B) white abalone
C) Texas blind salamander
D) harvester ant
E) coelacanth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A(n) ____ is an observed consequence of global climate change.
A) increase in earthquakes
B) acid rain
C) increase in the ozone hole
D) decrease in the ozone layer
E) rise in sea level
A) increase in earthquakes
B) acid rain
C) increase in the ozone hole
D) decrease in the ozone layer
E) rise in sea level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The increased concentration of plastics as they move up through the food chain is called ____.
A) biological magnification
B) eutrophication
C) biological accumulation
D) deposition
E) desertification
A) biological magnification
B) eutrophication
C) biological accumulation
D) deposition
E) desertification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The loss of mayflies from a stream suggests that the quality of water is declining; therefore, mayflies are a(n) ____ species.
A) degraded
B) endangered
C) threatened
D) keystone
E) indicator
A) degraded
B) endangered
C) threatened
D) keystone
E) indicator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The genetic diversity within a species of a given region is called the ____.
A) biodiversity
B) dominance hierarchy
C) biogeographic distribution
D) biome
E) community
A) biodiversity
B) dominance hierarchy
C) biogeographic distribution
D) biome
E) community

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which region experienced a desertification event called the Dust Bowl in the 1930s?
A) Europe
B) North America
C) South America
D) East Asia
E) Central Africa
A) Europe
B) North America
C) South America
D) East Asia
E) Central Africa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The only way to meet the resource needs of future generations is through ____.
A) sustainable resource use
B) biological magnification
C) creating conservation hotspots
D) clear cutting and mining
E) increasing use of nonrenewable resources
A) sustainable resource use
B) biological magnification
C) creating conservation hotspots
D) clear cutting and mining
E) increasing use of nonrenewable resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which term refers to the renewal of a natural ecosystem that has been degraded?
A) ecological balance
B) ecological restoration
C) eutrophication
D) biological magnification
E) bioremediation
A) ecological balance
B) ecological restoration
C) eutrophication
D) biological magnification
E) bioremediation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Plastic pollution has had serious ecological consequences in ____.
A) river ecosystems
B) the atmosphere over urban areas
C) oceans
D) temperate deciduous forests
E) desert biomes
A) river ecosystems
B) the atmosphere over urban areas
C) oceans
D) temperate deciduous forests
E) desert biomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Because all commercially produced energy has some kind of negative environmental impact, it is a good idea to simply use ____.
A) wind energy
B) solar energy
C) less energy
D) incandescent light bulbs
E) less water
A) wind energy
B) solar energy
C) less energy
D) incandescent light bulbs
E) less water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Renewable energy sources ____.
A) have no disadvantages
B) include coal-fired power plants
C) have by-products that increase acid rain
D) do not produce clean energy
E) do not produce greenhouse gases
A) have no disadvantages
B) include coal-fired power plants
C) have by-products that increase acid rain
D) do not produce clean energy
E) do not produce greenhouse gases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Due to biological magnification, which would have the highest concentration of a plastic?
A) grass-the dominant primary producer
B) cow-an herbivore
C) grasshoppers-an herbivore
D) mice-predators of butterflies
E) hawk-predators of mice
A) grass-the dominant primary producer
B) cow-an herbivore
C) grasshoppers-an herbivore
D) mice-predators of butterflies
E) hawk-predators of mice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Acid rain is the result of ____.
A) the burning of fossil fuels
B) the greenhouse effect
C) contamination with CFCs
D) desertification
E) deforestation
A) the burning of fossil fuels
B) the greenhouse effect
C) contamination with CFCs
D) desertification
E) deforestation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A plant pathologist, a scientist who studies plant diseases, examines a tree that has burnt leaves, is mineral deficient, and has several diseases. The plant pathologist concludes the tree's symptoms are most likely the direct result of ____.
A) biological magnification
B) desertification
C) ozone depletion
D) acid rain
E) deforestation
A) biological magnification
B) desertification
C) ozone depletion
D) acid rain
E) deforestation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What does the ozone layer absorb?
A) heat
B) pollution
C) ultraviolet radiation
D) infrared radiation
E) oxygen
A) heat
B) pollution
C) ultraviolet radiation
D) infrared radiation
E) oxygen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The Klamath-Siskiyou forest in southwestern Oregon and northwestern California is home to many rare conifers, two endangered birds, and the endangered Coho salmon. Because of this, it is considered to be a conservation _____.
A) hot spot
B) endangered region
C) national park
D) island
E) ecoregion
A) hot spot
B) endangered region
C) national park
D) island
E) ecoregion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
One disadvantage of hydroelectric energy as a renewable power source is that ____.
A) it causes disease-causing organisms to remain in the stream
B) it contributes to acid rain
C) it produces greenhouse gases
D) its dams block salmon from returning to streams to breed
E) it pollutes streams downriver from the dams
A) it causes disease-causing organisms to remain in the stream
B) it contributes to acid rain
C) it produces greenhouse gases
D) its dams block salmon from returning to streams to breed
E) it pollutes streams downriver from the dams

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What is the main function of the ozone layer?
A) to provide cloud cover for protection of polar regions
B) to provide a source of oxygen for photosynthesis
C) to filter toxins from acid rain
D) to block most of the sun's damaging rays from reaching Earth
E) to trap carbon dioxide and warm the planet
A) to provide cloud cover for protection of polar regions
B) to provide a source of oxygen for photosynthesis
C) to filter toxins from acid rain
D) to block most of the sun's damaging rays from reaching Earth
E) to trap carbon dioxide and warm the planet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In its use in conservation efforts, lichens are classified as an example of a(n) ____.
A) biological magnified species
B) endangered species
C) biodiverse species
D) indicator species
E) exotic species
A) biological magnified species
B) endangered species
C) biodiverse species
D) indicator species
E) exotic species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which was responsible for destruction of the ozone layer?
A) chlorofluorocarbons
B) carbon dioxide
C) methylmercury
D) methane
E) nitrogen
A) chlorofluorocarbons
B) carbon dioxide
C) methylmercury
D) methane
E) nitrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Protecting biodiversity can be problematic even for developed countries because ____.
A) it is politically incorrect
B) there are not enough endangered species in developed countries to make it worthwhile
C) there are more endangered species in undeveloped countries
D) people are afraid of nature
E) people fear economic consequences
A) it is politically incorrect
B) there are not enough endangered species in developed countries to make it worthwhile
C) there are more endangered species in undeveloped countries
D) people are afraid of nature
E) people fear economic consequences

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
For the monarch butterfly, farming has increased the use of ____ plants, which has further decreased the availability of nectar plants and ____.
A) crop; weeds
B) herbicide-resistant crop; trees
C) herbicide-resistant crop; milkweed
D) bioengineered; trees
E) drought-resistant; milkweed
A) crop; weeds
B) herbicide-resistant crop; trees
C) herbicide-resistant crop; milkweed
D) bioengineered; trees
E) drought-resistant; milkweed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Ultimately, what is the greatest threat to biodiversity?
A) plant pathogens
B) exotic species
C) unthinking humans
D) mineral and energy use
E) conservation efforts
A) plant pathogens
B) exotic species
C) unthinking humans
D) mineral and energy use
E) conservation efforts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The best way to reclaim an ecosystem that is extensively damaged is to ____.
A) allow natural succession to take over
B) remove all predators from the area
C) seed the area with a type of grass
D) bring in beneficial insects
E) implement ecological restoration
A) allow natural succession to take over
B) remove all predators from the area
C) seed the area with a type of grass
D) bring in beneficial insects
E) implement ecological restoration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Although extinction is a natural process and is ongoing, it is likely we are in a time of ____, an event in which many different kinds of organisms become extinct in a relatively short period.
A) mass extinction
B) genetic mutation
C) geologic catastrophe
D) loss of megafauna
E) birth of new species
A) mass extinction
B) genetic mutation
C) geologic catastrophe
D) loss of megafauna
E) birth of new species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Desertification is mainly caused by ____.
A) lack of rain
B) poor agricultural practices
C) too much precipitation
D) deforestation
E) erosion
A) lack of rain
B) poor agricultural practices
C) too much precipitation
D) deforestation
E) erosion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Very high concentrations of ____ accumulates in large predatory fishes such as swordfish, bluefin tuna, and albacore tuna, which may cause developmental abnormalities when consumed by pregnant women.
A) methylmercury
B) carbon dioxide
C) sulfur dioxide
D) chlorofluorocarbon (CFC)
E) ozone gas
A) methylmercury
B) carbon dioxide
C) sulfur dioxide
D) chlorofluorocarbon (CFC)
E) ozone gas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The Great Pacific Garbage Patch is a region of the north central Pacific where a high concentration of confetti-like plastic particles swirls slowly around an area as large as the state of ____.
A) Alaska
B) Idaho
C) Rhode Island
D) Texas
E) Pennsylvania
A) Alaska
B) Idaho
C) Rhode Island
D) Texas
E) Pennsylvania

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Pandas are an example of a(n) ____ species that is in danger of extinction because they are dependent on disappearing bamboo forests.
A) "extinct in the wild"
B) extinct
C) indicator
D) endemic
E) keystone
A) "extinct in the wild"
B) extinct
C) indicator
D) endemic
E) keystone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In a hydrothermal vent community pictured here, the typical consumer is a(n) ____. 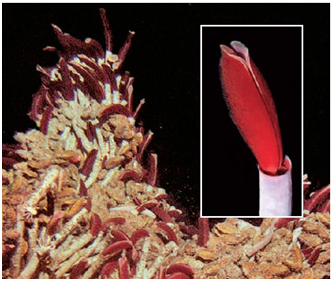
A) coral reef
B) bacteria
C) archaea
D) tube worm
E) algae

A) coral reef
B) bacteria
C) archaea
D) tube worm
E) algae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The photos of the Muir Glacier taken in 1941 (left) and 2004 (right) demonstrate the consequences of____. 
A) deforestation
B) biological magnification
C) acid rain
D) ozone destruction
E) global climate change

A) deforestation
B) biological magnification
C) acid rain
D) ozone destruction
E) global climate change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



