Deck 43: Muscles, Bones, and Body Movements
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Premises:
high contraction intensity
high contraction intensity
high contraction intensity
high contraction intensity
high contraction intensity
many mitochondria
many mitochondria
many mitochondria
many mitochondria
many mitochondria
slow contraction speed
slow contraction speed
slow contraction speed
slow contraction speed
slow contraction speed
intermediate glycogen content
intermediate glycogen content
intermediate glycogen content
intermediate glycogen content
intermediate glycogen content
high myosin-ATPase activity
high myosin-ATPase activity
high myosin-ATPase activity
high myosin-ATPase activity
high myosin-ATPase activity
Responses:
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/87
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 43: Muscles, Bones, and Body Movements
1
Skeletal muscle contractions can be adjusted from gentle to strong because ____ are controlled by the axon branches of a single efferent neuron.
A) muscle fibers
B) sarcomeres
C) motor units
D) ATP molecules
E) neurotransmitters
A) muscle fibers
B) sarcomeres
C) motor units
D) ATP molecules
E) neurotransmitters
C
2
In skeletal muscle contraction, when ____ binds to Ca2+, it undergoes a conformational change that allows tropomyosin to move to the grooves in the actin double helix.
A) troponin
B) myosin
C) phosphate ions
D) ATP
E) acetylcholine
A) troponin
B) myosin
C) phosphate ions
D) ATP
E) acetylcholine
A
3
Which muscle type is found in the walls of body tubes and cavities of vertebrates, such as blood vessels and the intestines?
A) cardiac
B) smooth
C) skeletal
D) rough
E) epithelial
A) cardiac
B) smooth
C) skeletal
D) rough
E) epithelial
B
4
Individual skeletal muscle cells are packed with cylindrical contractile elements about 1 mm in diameter called ____.
A) muscle fibers
B) sarcomeres
C) tendons
D) ligaments
E) myofibrils
A) muscle fibers
B) sarcomeres
C) tendons
D) ligaments
E) myofibrils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The region between two adjacent "Z lines" is known as a ____.
A) muscle fiber
B) sarcomere
C) tendon
D) ligament
E) myofibril
A) muscle fiber
B) sarcomere
C) tendon
D) ligament
E) myofibril

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The binding of ____to ____ directly triggers the power stroke in skeletal muscle contraction.
A) myosin; actin
B) tropomyosin; myosin
C) myosin; troponin
D) tropomyosin; actin
E) troponin; tropomyosin
A) myosin; actin
B) tropomyosin; myosin
C) myosin; troponin
D) tropomyosin; actin
E) troponin; tropomyosin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The ____ is a system of vesicles that wraps around each A band and I band.
A) neuromuscular junction
B) Golgi apparatus
C) sheath
D) microvillus
E) sarcoplasmic reticulum
A) neuromuscular junction
B) Golgi apparatus
C) sheath
D) microvillus
E) sarcoplasmic reticulum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Skeletal muscle cells have ____ and are controlled by the ____ nervous system.
A) many nuclei; somatic
B) many nuclei; autonomic
C) one nucleus each; autonomic
D) one nucleus each; somatic
E) two nuclei each; somatic
A) many nuclei; somatic
B) many nuclei; autonomic
C) one nucleus each; autonomic
D) one nucleus each; somatic
E) two nuclei each; somatic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A typical human body has ____ skeletal muscles.
A) 78
B) 168
C) 206
D) 417
E) over 600
A) 78
B) 168
C) 206
D) 417
E) over 600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Thick filaments are parallel bundles of ____ molecules.
A) actin
B) tropomyosin
C) acetylcholine
D) myosin
E) troponin
A) actin
B) tropomyosin
C) acetylcholine
D) myosin
E) troponin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Skeletal muscles are made up of bundles of elongated, cylindrical cells called ____.
A) muscle fibers
B) sarcomeres
C) tendons
D) ligaments
E) myofibrils
A) muscle fibers
B) sarcomeres
C) tendons
D) ligaments
E) myofibrils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The Z lines in skeletal muscle are composed of ____.
A) discs to which thin filaments are anchored
B) stacked thick filaments along with the parts of thin filaments that overlap both ends
C) thin filaments but no thick filaments
D) thick filaments but no thin filaments
E) stacked thin filaments along with parts of thick filaments that overlap both ends
A) discs to which thin filaments are anchored
B) stacked thick filaments along with the parts of thin filaments that overlap both ends
C) thin filaments but no thick filaments
D) thick filaments but no thin filaments
E) stacked thin filaments along with parts of thick filaments that overlap both ends

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Skeletal muscle H zones are composed of ____.
A) discs to which thin filaments are anchored
B) stacked thick filaments along with the parts of thin filaments that overlap both ends
C) thin filaments but no thick filaments
D) thick filaments but no thin filaments
E) stacked thin filaments along with parts of thick filaments that overlap both ends
A) discs to which thin filaments are anchored
B) stacked thick filaments along with the parts of thin filaments that overlap both ends
C) thin filaments but no thick filaments
D) thick filaments but no thin filaments
E) stacked thin filaments along with parts of thick filaments that overlap both ends

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The I bands in skeletal muscle are composed of ____.
A) discs to which thin filaments are anchored
B) stacked thick filaments along with the parts of thin filaments that overlap both ends
C) thin filaments but no thick filaments
D) thick filaments but no thin filaments
E) stacked thin filaments along with parts of thick filaments that overlap both ends
A) discs to which thin filaments are anchored
B) stacked thick filaments along with the parts of thin filaments that overlap both ends
C) thin filaments but no thick filaments
D) thick filaments but no thin filaments
E) stacked thin filaments along with parts of thick filaments that overlap both ends

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The A bands in skeletal muscle are composed of ____.
A) discs to which thin filaments are anchored
B) stacked thick filaments along with the parts of thin filaments that overlap both ends
C) thin filaments but no thick filaments
D) thick filaments but no thin filaments
E) stacked thin filaments along with parts of thick filaments that overlap both ends
A) discs to which thin filaments are anchored
B) stacked thick filaments along with the parts of thin filaments that overlap both ends
C) thin filaments but no thick filaments
D) thick filaments but no thin filaments
E) stacked thin filaments along with parts of thick filaments that overlap both ends

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Skeletal muscles in vertebrates connect to ____.
A) tendons
B) sarcomeres
C) bones
D) ligaments
E) myofibrils
A) tendons
B) sarcomeres
C) bones
D) ligaments
E) myofibrils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In skeletal muscle contraction, an increase in ____in the cytosol triggers the crossbridge cycle.
A) troponin
B) Ca2+
C) tropomyosin
D) ATP
E) acetylcholine
A) troponin
B) Ca2+
C) tropomyosin
D) ATP
E) acetylcholine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Skeletal muscles attach to bones by ____.
A) ligaments
B) cartilage
C) smooth muscles
D) tendons
E) joints
A) ligaments
B) cartilage
C) smooth muscles
D) tendons
E) joints

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In skeletal muscle contraction, ____ directly fuels the movement of the myosin head.
A) glucose
B) fatty acids
C) GTP
D) ATP
E) an H+gradient
A) glucose
B) fatty acids
C) GTP
D) ATP
E) an H+gradient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In skeletal muscle contraction, the neurotransmitter ____ is released at the axon terminal of the neuromuscular junction to trigger an action potential in the muscle cell.
A) troponin
B) Ca2+
C) tropomyosin
D) ATP
E) acetylcholine
A) troponin
B) Ca2+
C) tropomyosin
D) ATP
E) acetylcholine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Exercising a muscle results in ____.
A) the expression of genes involved in energy metabolism, insulin response, and muscle inflammation
B) the expression of genes involved in metabolism only
C) no phenotypic or biochemical changes
D) no change in the expression of genes, but changes in phenotypes
E) changes in the expression of genes, but no changes in phenotypes
A) the expression of genes involved in energy metabolism, insulin response, and muscle inflammation
B) the expression of genes involved in metabolism only
C) no phenotypic or biochemical changes
D) no change in the expression of genes, but changes in phenotypes
E) changes in the expression of genes, but no changes in phenotypes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The main role of myoglobin in muscle fibers is to ____.
A) magnify responses to neurotransmitters
B) sequester ions
C) synthesize ATP
D) store oxygen
E) enhance the strength of the power stroke
A) magnify responses to neurotransmitters
B) sequester ions
C) synthesize ATP
D) store oxygen
E) enhance the strength of the power stroke

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Myoglobin content is high in ____.
A) fast anaerobic fibers only
B) slow muscle fibers only
C) slow muscle fibers and fast aerobic muscle fibers
D) fast aerobic and fast anaerobic muscle fibers
E) slow muscle fibers and fast anaerobic fibers
A) fast anaerobic fibers only
B) slow muscle fibers only
C) slow muscle fibers and fast aerobic muscle fibers
D) fast aerobic and fast anaerobic muscle fibers
E) slow muscle fibers and fast anaerobic fibers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Vertebrates such as ____ have both exo- and endoskeletons.
A) birds
B) humans
C) turtles
D) lobsters
E) fish
A) birds
B) humans
C) turtles
D) lobsters
E) fish

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The mechanism of muscle contraction was first studied in ____ muscle using high-resolution ____ microscopy.
A) skeletal; light
B) smooth; light
C) skeletal; electron
D) smooth; electron
E) cardiac; electron
A) skeletal; light
B) smooth; light
C) skeletal; electron
D) smooth; electron
E) cardiac; electron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A defect in the transport of ____ ions would have the most direct effect on muscle contraction.
A) Cl-
B) K+
C) Ca2+
D) Na+and Zn2+
E) Zn2+
A) Cl-
B) K+
C) Ca2+
D) Na+and Zn2+
E) Zn2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The frozen contraction of muscle cells called rigor mortis occurs after death because ____.
A) ions are not available in the cytoplasm of muscle cells
B) tropomyosin breaks down quickly
C) crossbridges become very rigid structures
D) ATP production stops
E) muscle cells are flooded with neurotransmitters
A) ions are not available in the cytoplasm of muscle cells
B) tropomyosin breaks down quickly
C) crossbridges become very rigid structures
D) ATP production stops
E) muscle cells are flooded with neurotransmitters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Tube feet of sea stars, erectile tissue of the penis in vertebrates, and the bodies of cnidarians are all supported by ____.
A) an exoskeleton
B) cardiac muscle
C) a hydrostatic skeleton
D) an endoskeleton
E) joined exo- and endoskeletons
A) an exoskeleton
B) cardiac muscle
C) a hydrostatic skeleton
D) an endoskeleton
E) joined exo- and endoskeletons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The bodies of arthropods are supported mainly by ____.
A) an exoskeleton
B) only nonskeletal structures
C) a hydrostatic skeleton
D) an endoskeleton
E) joined exo- and endoskeletons
A) an exoskeleton
B) only nonskeletal structures
C) a hydrostatic skeleton
D) an endoskeleton
E) joined exo- and endoskeletons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Clostridium botulinum produces a deadly toxin that stops muscle contractions by ____.
A) destroying cell membranes
B) killing mitochondria
C) disrupting the structure of actin filaments
D) preventing ATP synthesis
E) blocking acetylcholine release
A) destroying cell membranes
B) killing mitochondria
C) disrupting the structure of actin filaments
D) preventing ATP synthesis
E) blocking acetylcholine release

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The ribs and sternum are considered to be part of ____.
A) both the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton
B) the axial skeleton only
C) neither the axial skeleton nor the appendicular skeleton
D) the appendicular skeleton only
E) the axial or appendicular skeleton depending on the animal
A) both the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton
B) the axial skeleton only
C) neither the axial skeleton nor the appendicular skeleton
D) the appendicular skeleton only
E) the axial or appendicular skeleton depending on the animal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Unlike endurance training, weight lifting will convert ____.
A) slow muscle fibers to fast muscle fibers
B) fast muscle fibers to slow muscle fibers
C) fast muscle fibers from the anaerobic to the aerobic type
D) fast muscle fibers from the aerobic to the anaerobic type
E) fat to muscle fibers
A) slow muscle fibers to fast muscle fibers
B) fast muscle fibers to slow muscle fibers
C) fast muscle fibers from the anaerobic to the aerobic type
D) fast muscle fibers from the aerobic to the anaerobic type
E) fat to muscle fibers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A motor unit is a ____.
A) single muscle fiber activated individually
B) complete set of muscle fibers in a single muscle
C) single sarcomere
D) sequence of muscle fibers activated in order
E) group of muscle fibers activated as a block
A) single muscle fiber activated individually
B) complete set of muscle fibers in a single muscle
C) single sarcomere
D) sequence of muscle fibers activated in order
E) group of muscle fibers activated as a block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is caused by a mutation that ____.
A) weakens the cytoskeleton of the muscle fiber
B) weakens myofibrils
C) decreases the transmission of force
D) disrupts the sarcomere
E) increases the transmission of force
A) weakens the cytoskeleton of the muscle fiber
B) weakens myofibrils
C) decreases the transmission of force
D) disrupts the sarcomere
E) increases the transmission of force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
For humans and most vertebrates, the body is supported primarily by ____.
A) an exoskeleton
B) only nonskeletal structures
C) a hydrostatic skeleton
D) an endoskeleton
E) joined exo- and endoskeletons
A) an exoskeleton
B) only nonskeletal structures
C) a hydrostatic skeleton
D) an endoskeleton
E) joined exo- and endoskeletons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A muscle contraction during which fibers cannot relax between stimuli is called ____.
A) an action potential
B) a muscle twitch
C) fatigue
D) tetanus
E) constriction
A) an action potential
B) a muscle twitch
C) fatigue
D) tetanus
E) constriction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
By _____, researchers had established how actin and myosin arrangements changed during muscle ____.
A) 1924; relaxation
B) 1954; contraction
C) 1924; contraction
D) 1994; relaxation
E) 1904; stimulation
A) 1924; relaxation
B) 1954; contraction
C) 1924; contraction
D) 1994; relaxation
E) 1904; stimulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A rapid, powerful movement of short duration that could not be sustained very long would likely involve mainly ____.
A) fast anaerobic fibers
B) fast aerobic and fast anaerobic muscle fibers
C) slow muscle fibers and fast aerobic muscle fibers
D) slow muscle fibers
E) fast aerobic fibers
A) fast anaerobic fibers
B) fast aerobic and fast anaerobic muscle fibers
C) slow muscle fibers and fast aerobic muscle fibers
D) slow muscle fibers
E) fast aerobic fibers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The radius and ulna are considered to be part of ____.
A) both the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton
B) the axial skeleton only
C) neither the axial skeleton nor the appendicular skeleton
D) the appendicular skeleton only
E) the axial or appendicular skeleton depending on the animal
A) both the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton
B) the axial skeleton only
C) neither the axial skeleton nor the appendicular skeleton
D) the appendicular skeleton only
E) the axial or appendicular skeleton depending on the animal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A single, weak contraction of a muscle fiber is called ____.
A) an action potential
B) a muscle twitch
C) fatigue
D) tetanus
E) constriction
A) an action potential
B) a muscle twitch
C) fatigue
D) tetanus
E) constriction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
An animal that is evolved for rapid movement over the ground will have relatively ____ bones.
A) heavy and thick
B) heavy
C) light and thin
D) light
E) heavy and thin
A) heavy and thick
B) heavy
C) light and thin
D) light
E) heavy and thin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Bone plays a critical role in providing ____ for the blood.
A) sodium and calcium ions
B) magnesium and phosphate ions
C) carbon dioxide
D) phosphate and calcium ions
E) calcium ions and oxygen
A) sodium and calcium ions
B) magnesium and phosphate ions
C) carbon dioxide
D) phosphate and calcium ions
E) calcium ions and oxygen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A ____ joint can move rotate about its axis, providing maximum range of motion.
A) hinge
B) fulcrum
C) ball-and-socket
D) lever
E) ligament
A) hinge
B) fulcrum
C) ball-and-socket
D) lever
E) ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Synovial joints are held together by ____.
A) muscle fibers
B) sarcomeres
C) tendons
D) ligaments
E) myofibrils
A) muscle fibers
B) sarcomeres
C) tendons
D) ligaments
E) myofibrils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A muscle that decreases the angle between two bones at a joint is called a(n)____.
A) flexor
B) agonist
C) depressor
D) antagonist
E) extensor
A) flexor
B) agonist
C) depressor
D) antagonist
E) extensor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A promising means of improving conditions for patients with type-2 diabetes may be ____.
A) injections with myostatin
B) increasing muscle mass
C) ketoacidosis
D) injections with acetylcholine
E) increasing consumption of simple carbohydrates
A) injections with myostatin
B) increasing muscle mass
C) ketoacidosis
D) injections with acetylcholine
E) increasing consumption of simple carbohydrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Research indicates that compared to the genomes of bony fish, the elephant shark genome contains ____ the genes necessary for bone formation.
A) none of
B) half of
C) most of
D) all but one of
E) double
A) none of
B) half of
C) most of
D) all but one of
E) double

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Bone tissue is composed of ____ and ____ regions.
A) spongy; muscular
B) spongy; compact
C) compact; diffuse
D) aerobic; anaerobic
E) red; white
A) spongy; muscular
B) spongy; compact
C) compact; diffuse
D) aerobic; anaerobic
E) red; white

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A muscle that increases the angle between two bones at a joint is called a(n) ____.
A) flexor
B) agonist
C) depressor
D) antagonist
E) extensor
A) flexor
B) agonist
C) depressor
D) antagonist
E) extensor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A muscle that causes any type of movement in a joint when it contracts is called a(n) ____.
A) flexor
B) agonist
C) depressor
D) antagonist
E) extensor
A) flexor
B) agonist
C) depressor
D) antagonist
E) extensor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The primary source of new red blood cells in mammals is the ____.
A) liver
B) blood, itself
C) spleen
D) heart
E) bone marrow
A) liver
B) blood, itself
C) spleen
D) heart
E) bone marrow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The ____ joints, found in the vertebrae and some rib bones, have fibrous connective tissue covering the ends of the bones involved and are somewhat moveable.
A) synovial
B) cartilaginous
C) fibrous
D) agonist
E) antagonistic
A) synovial
B) cartilaginous
C) fibrous
D) agonist
E) antagonistic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The ____ muscles are an example of an antagonist muscle pair in humans.
A) calf and gluteus maximus
B) deltoid and pectoral
C) hamstring and biceps
D) calf and hamstring
E) biceps and triceps
A) calf and gluteus maximus
B) deltoid and pectoral
C) hamstring and biceps
D) calf and hamstring
E) biceps and triceps

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A ____ joint can move only in one direction, providing limited range of motion.
A) hinge
B) fulcrum
C) ball-and-socket
D) lever
E) ligament
A) hinge
B) fulcrum
C) ball-and-socket
D) lever
E) ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Human vertebrae are held together by ____ joints.
A) synovial
B) cartilaginous
C) fibrous
D) both fibrous and cartilaginous
E) both synovial and fibrous
A) synovial
B) cartilaginous
C) fibrous
D) both fibrous and cartilaginous
E) both synovial and fibrous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Skeletal muscle growth and development is inhibited by ____ produced in muscle cells.
A) erythropoietin
B) acetylcholine
C) epidermal growth factor
D) epinephrine
E) myostatin
A) erythropoietin
B) acetylcholine
C) epidermal growth factor
D) epinephrine
E) myostatin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The human elbow is an example of a ____ joint.
A) hinge
B) fulcrum
C) ball-and-socket
D) lever
E) ligament
A) hinge
B) fulcrum
C) ball-and-socket
D) lever
E) ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The ____ joints are usually highly moveable, with a fluid-filled capsule of connective tissue surrounding them.
A) synovial
B) cartilaginous
C) fibrous
D) agonist
E) antagonistic
A) synovial
B) cartilaginous
C) fibrous
D) agonist
E) antagonistic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
How are the muscle attachments optimized in animals evolved for movement through the soil?
A) The attachments produce levers that move relatively rapidly.
B) The attachments produce levers that need to apply large forces for movement.
C) The attachments produce levers that move relatively slowly, but need to apply only small forces for movement.
D) The attachments produce levers that move rapidly, but need to apply only small forces for movement.
E) The attachments produce levers that swing freely.
A) The attachments produce levers that move relatively rapidly.
B) The attachments produce levers that need to apply large forces for movement.
C) The attachments produce levers that move relatively slowly, but need to apply only small forces for movement.
D) The attachments produce levers that move rapidly, but need to apply only small forces for movement.
E) The attachments produce levers that swing freely.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Muscles that act as opposing pairs are____.
A) flexors
B) agonists
C) depressors
D) antagonists
E) extensors
A) flexors
B) agonists
C) depressors
D) antagonists
E) extensors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Each motor unit is composed of ____.
A) both slow and fast aerobic muscle fibers
B) both fast aerobic and anaerobic fibers
C) all types of muscle fibers mixed together
D) only one type muscle fiber
E) both slow and fast anaerobic muscle fibers
A) both slow and fast aerobic muscle fibers
B) both fast aerobic and anaerobic fibers
C) all types of muscle fibers mixed together
D) only one type muscle fiber
E) both slow and fast anaerobic muscle fibers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match between columns
Premises:
high contraction intensity
high contraction intensity
high contraction intensity
high contraction intensity
high contraction intensity
many mitochondria
many mitochondria
many mitochondria
many mitochondria
many mitochondria
slow contraction speed
slow contraction speed
slow contraction speed
slow contraction speed
slow contraction speed
intermediate glycogen content
intermediate glycogen content
intermediate glycogen content
intermediate glycogen content
intermediate glycogen content
high myosin-ATPase activity
high myosin-ATPase activity
high myosin-ATPase activity
high myosin-ATPase activity
high myosin-ATPase activity
Responses:
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic
fast aerobic
slow
fast anaerobic
both fast aerobic and fast anaerobic
both slow and fast aerobic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Muscles that can be controlled precisely and delicately have few muscle fibers in each motor unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A typical human body has ____ bones.
A) 78
B) 168
C) 206
D) 417
E) over 600
A) 78
B) 168
C) 206
D) 417
E) over 600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The most common type of lever system in the body has the force applied ____.
A) at the free end of the bone
B) at the attached end of the bone
C) at the fulcrum
D) between the fulcrum and the load
E) at the load end
A) at the free end of the bone
B) at the attached end of the bone
C) at the fulcrum
D) between the fulcrum and the load
E) at the load end

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Annelids must utilize ____ muscles in order to move.
A) only circular
B) only longitudinal
C) crosswise
D) circular and longitudinal
E) crosswise or longitudinal
A) only circular
B) only longitudinal
C) crosswise
D) circular and longitudinal
E) crosswise or longitudinal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The sliding filament model of muscle contraction depends on the dynamic interactions between myostatin and myoglobin proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The human finger contains ____ joints.
A) hinge
B) fulcrum
C) ball-and-socket
D) lever
E) ligament
A) hinge
B) fulcrum
C) ball-and-socket
D) lever
E) ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Answer the question using the accompanying figure. The muscle indicated by the letter 'B' is analogous to the ____ muscle in a human.
A) calf
B) deltoid
C) biceps
D) tongue
E) triceps
A) calf
B) deltoid
C) biceps
D) tongue
E) triceps

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Answer the question using the accompanying figure. Neurotransmitters and ____ are key components in the pathway for stimulating skeletal muscle contractions.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) A and B
E) B and C
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) A and B
E) B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Skeletal muscles are attached to bones by cords of connective tissue called tendons .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
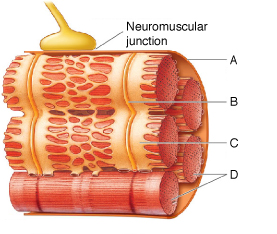 Figure 43.3 (questions 63, 64, and 65)
Figure 43.3 (questions 63, 64, and 65)A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Answer the question using the accompanying figure. The structure labeled "B" forms at the ____.
A) junctions of A bands and I bands
B) H zone
C) junctions of A bands and H zones
D) M line
E) junctions of I bands and M lines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The patterns by which muscles connect to bones are the same in all vertebrates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The striated muscles in most invertebrates have thick and thin filaments arranged in sarcomeres entirely similar to those of vertebrates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Describe the process by which botulinum toxin interrupts the crossbridge cycle. Provide other possible uses for this toxin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Recent research has shown that myostatin can negatively regulate cardiac muscle growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
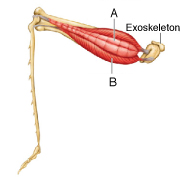 Figure 43.9 (questions 61 and 62)
Figure 43.9 (questions 61 and 62)A) A
B) B
Answer the question using the accompanying figure. The muscle indicated by the letter 'A' is a(n) ____ muscle.
A) flexor
B) agonist
C) depressor
D) antagonist
E) extensor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Answer the question using the accompanying figure. The structure labeled "C" is a modified form of the ____.
A) Golgi apparatus
B) plasma membrane
C) rough endoplasmic reticulum
D) smooth endoplasmic reticulum
E) nuclear membrane
A) Golgi apparatus
B) plasma membrane
C) rough endoplasmic reticulum
D) smooth endoplasmic reticulum
E) nuclear membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Describe the molecular activity that leads to muscle contractions, beginning at the neuromuscular junction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



