Deck 56: Animal Behavior
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/87
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 56: Animal Behavior
1
Research of knockout mice with no active copies of the Dvl1 gene can be used to study ____ in humans.
A) schizophrenia only
B) obsessive compulsive disorder only
C) Huntington disease only
D) prostate cancer only
E) schizophrenia, obsessive compulsive disorder, and Huntington disease
A) schizophrenia only
B) obsessive compulsive disorder only
C) Huntington disease only
D) prostate cancer only
E) schizophrenia, obsessive compulsive disorder, and Huntington disease
E
2
What are the proximate causes that underlie an animal's ability to detect and respond to stimuli?
A) only physiological mechanisms
B) only genetic mechanisms
C) genetic and physiological mechanisms
D) genetic, cellular, physiological, and anatomical mechanisms
E) genetic, physiological, and anatomical mechanisms
A) only physiological mechanisms
B) only genetic mechanisms
C) genetic and physiological mechanisms
D) genetic, cellular, physiological, and anatomical mechanisms
E) genetic, physiological, and anatomical mechanisms
D
3
Questions about ultimate causes of behavior are ____ questions, while proximate questions about behavior are ____ questions.
A) how; why
B) what; how
C) how; when
D) what; who
E) why; how
A) how; why
B) what; how
C) how; when
D) what; who
E) why; how
E
4
Experiments on the feeding preferences of newborn garter snakes born to coastal vs. inland California revealed that even in the same species, differential instinctive responses can be ____.
A) learned
B) genetic
C) forgotten
D) homozygous
E) sex-linked
A) learned
B) genetic
C) forgotten
D) homozygous
E) sex-linked

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A male zebra finch can discriminate between the songs of strangers and the songs of established neighbors on adjacent territories through a cluster of neurons in the ____.
A) cerebellum
B) brainstem
C) midbrain
D) forebrain
E) hindbrain
A) cerebellum
B) brainstem
C) midbrain
D) forebrain
E) hindbrain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Instinctive behaviors are ____, while learned behaviors are ____.
A) acquired from observation; acquired from practice
B) taught by parents; acquired from trial and error
C) incomplete the first few times they are displayed; apparently a product of reason
D) genetically programmed responses; dependent upon experience
E) dependent upon experience; genetically programmed responses
A) acquired from observation; acquired from practice
B) taught by parents; acquired from trial and error
C) incomplete the first few times they are displayed; apparently a product of reason
D) genetically programmed responses; dependent upon experience
E) dependent upon experience; genetically programmed responses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Male zebra finches behave differently toward familiar neighbors, whom they largely ignore, and unfamiliar singers, whom they attack and drive away. This behavior is a result of ____.
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) cognition
D) imprinting
E) habituation
A) operant conditioning
B) classical conditioning
C) cognition
D) imprinting
E) habituation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When researchers studied knockout mice with no active copies of the Dvl1 gene, they found these mice were____.
A) physically abnormal
B) socially normal
C) not easily startled
D) physically and socially normal
E) physically normal, but socially abnormal
A) physically abnormal
B) socially normal
C) not easily startled
D) physically and socially normal
E) physically normal, but socially abnormal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When geese or ducks are imprinted, this means that they ____.
A) will return to the place they were born to breed and raise their own young
B) have become habituated to harmless stimuli
C) have been experimentally trained by operant conditioning
D) learned the features of a suitable mate during a critical period
E) have two nonfunctional copies of a particular gene
A) will return to the place they were born to breed and raise their own young
B) have become habituated to harmless stimuli
C) have been experimentally trained by operant conditioning
D) learned the features of a suitable mate during a critical period
E) have two nonfunctional copies of a particular gene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Young male white-crowned sparrows that were experimentally raised without ever hearing the song of their species ____.
A) instinctively performed the song perfectly
B) never sang at all
C) sang a poorly developed, but similar, version of their species' song
D) sang a recognizable version of an ancestral species' song
E) never sang the way wild males do
A) instinctively performed the song perfectly
B) never sang at all
C) sang a poorly developed, but similar, version of their species' song
D) sang a recognizable version of an ancestral species' song
E) never sang the way wild males do

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is an example of an ultimate cause of animal behavior?
A) physiological
B) cellular
C) genetic
D) anatomical
E) adaptive
A) physiological
B) cellular
C) genetic
D) anatomical
E) adaptive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An animal that is apparently aware of its circumstances and uses reasoning to achieve a goal is said to have ____.
A) conditioning
B) habituation
C) cognition
D) imprinting
E) learning
A) conditioning
B) habituation
C) cognition
D) imprinting
E) learning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The pecking behavior in young herring gulls is triggered primarily by a red spot on the bill of the parent, and is performed repeatedly in the same way; therefore, it is an example of ____.
A) imprinting
B) a learned response
C) a fixed action pattern
D) operant conditioning
E) classical conditioning
A) imprinting
B) a learned response
C) a fixed action pattern
D) operant conditioning
E) classical conditioning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Ethology is the study of ____.
A) the genetic mechanisms that underlie behavior
B) how evolution shaped animal behavior
C) how humans influence animal behavior
D) the physiological mechanisms that underlie behavior
E) how animals process information
A) the genetic mechanisms that underlie behavior
B) how evolution shaped animal behavior
C) how humans influence animal behavior
D) the physiological mechanisms that underlie behavior
E) how animals process information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
According to Niko Tinbergen, which question is least likely to be addressed by basic studies of animal behavior?
A) What is the behavior's ecological function and how does it increase an animal's chances of surviving and reproducing?
B) How did the behavior evolve?
C) Which mechanisms trigger a specific behavioral response?
D) How does the expression of a behavior develop as an animal matures?
E) How will the behavior be displayed after future evolutionary processes occur?
A) What is the behavior's ecological function and how does it increase an animal's chances of surviving and reproducing?
B) How did the behavior evolve?
C) Which mechanisms trigger a specific behavioral response?
D) How does the expression of a behavior develop as an animal matures?
E) How will the behavior be displayed after future evolutionary processes occur?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Instinctive behaviors that are performed in exactly the same way every time they are triggered are defined as ____.
A) habitual behaviors
B) sign stimuli
C) conditioned behaviors
D) imprinted responses
E) fixed action patterns
A) habitual behaviors
B) sign stimuli
C) conditioned behaviors
D) imprinted responses
E) fixed action patterns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When behavioral biologists look at the ultimate evolutionary benefit of animal communication, they are primarily focusing on the effects of the communication on the individual's ability to ____.
A) secure food resources
B) intimidate other animals
C) form alliances with other animals
D) produce surviving offspring
E) maintain a favorable position in the dominance hierarchy
A) secure food resources
B) intimidate other animals
C) form alliances with other animals
D) produce surviving offspring
E) maintain a favorable position in the dominance hierarchy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When young male white-crowned sparrows first begin to sing, they match their vocal output to ____.
A) any birdsong they hear during their initial days of singing
B) an instinctive blueprint of their species' song
C) the memory of their species' song heard months earlier
D) the memory of whatever song they heard during an early critical period
E) the songs of male relatives heard during their initial days of singing
A) any birdsong they hear during their initial days of singing
B) an instinctive blueprint of their species' song
C) the memory of their species' song heard months earlier
D) the memory of whatever song they heard during an early critical period
E) the songs of male relatives heard during their initial days of singing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Biologists categorize the cue that stimulates young herring gulls to peck as a sign stimulus because the pecking behavior ____.
A) requires learning to perfect
B) is a cue released by the baby gulls to their parents
C) is triggered by presentation of the cue
D) is only triggered by the cue if it is accompanied by species-specific behaviors
E) appears both in the presence and absence of the cue
A) requires learning to perfect
B) is a cue released by the baby gulls to their parents
C) is triggered by presentation of the cue
D) is only triggered by the cue if it is accompanied by species-specific behaviors
E) appears both in the presence and absence of the cue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Classical conditioning associates ____, while operant conditioning links ____.
A) two phenomena that are usually unrelated; a voluntary activity with a reward
B) a response with a punishment; a response with a reward
C) instinctive behaviors with punishments; learned behaviors with rewards
D) a voluntary activity with a reward; two phenomena that are usually unrelated
E) learned behaviors with rewards; instinctive behaviors with rewards
A) two phenomena that are usually unrelated; a voluntary activity with a reward
B) a response with a punishment; a response with a reward
C) instinctive behaviors with punishments; learned behaviors with rewards
D) a voluntary activity with a reward; two phenomena that are usually unrelated
E) learned behaviors with rewards; instinctive behaviors with rewards

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
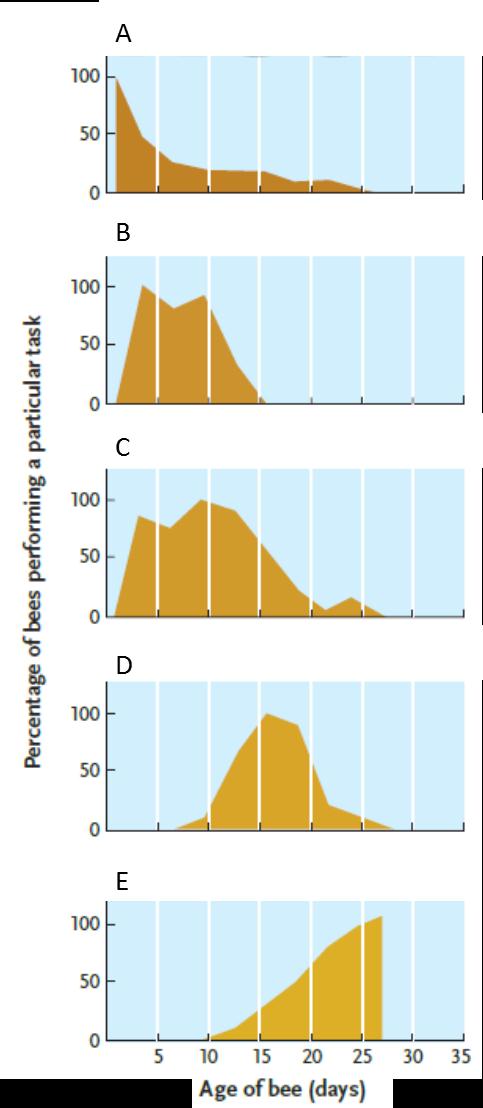 Answer the question using the accompanying figure. Which graph represents the age span of worker bees primarily involved in feeding the brood?
Answer the question using the accompanying figure. Which graph represents the age span of worker bees primarily involved in feeding the brood?A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A worker bee that is a day old is most likely to perform which function?
A) cleaning cells
B) feeding nestmates
C) packing pollen
D) feeding brood
E) foraging
A) cleaning cells
B) feeding nestmates
C) packing pollen
D) feeding brood
E) foraging

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The Arctic tern makes an annual migration of up to ____.
A) 700,000 km
B) 70,000 km
C) 7,000 km
D) 700 km
E) 70 km
A) 700,000 km
B) 70,000 km
C) 7,000 km
D) 700 km
E) 70 km

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which hormone results in the production of more neurons in the higher vocal center of the brains of male, but not female, zebra finches?
A) testosterone
B) estrogen
C) octopamine
D) epinephrine
E) androgen
A) testosterone
B) estrogen
C) octopamine
D) epinephrine
E) androgen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
As a result of the hormonal and neuroanatomical differences between the male and female brains of zebra finches, ____.
A) only males sing their species' songs
B) only females sing their species' songs
C) males sing their species' songs at earlier ages than females
D) females sing their species' songs at earlier ages than males
E) females only sing their species' songs later in their lives
A) only males sing their species' songs
B) only females sing their species' songs
C) males sing their species' songs at earlier ages than females
D) females sing their species' songs at earlier ages than males
E) females only sing their species' songs later in their lives

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
An animal that finds its way by the mechanism known as piloting is using ____.
A) familiar landmarks to guide his journey
B) the sun's position in the sky to orient himself
C) both the sun's position and a mental map
D) the Earth's magnetic field to orient himself
E) another animal to lead the way as he learns the route
A) familiar landmarks to guide his journey
B) the sun's position in the sky to orient himself
C) both the sun's position and a mental map
D) the Earth's magnetic field to orient himself
E) another animal to lead the way as he learns the route

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
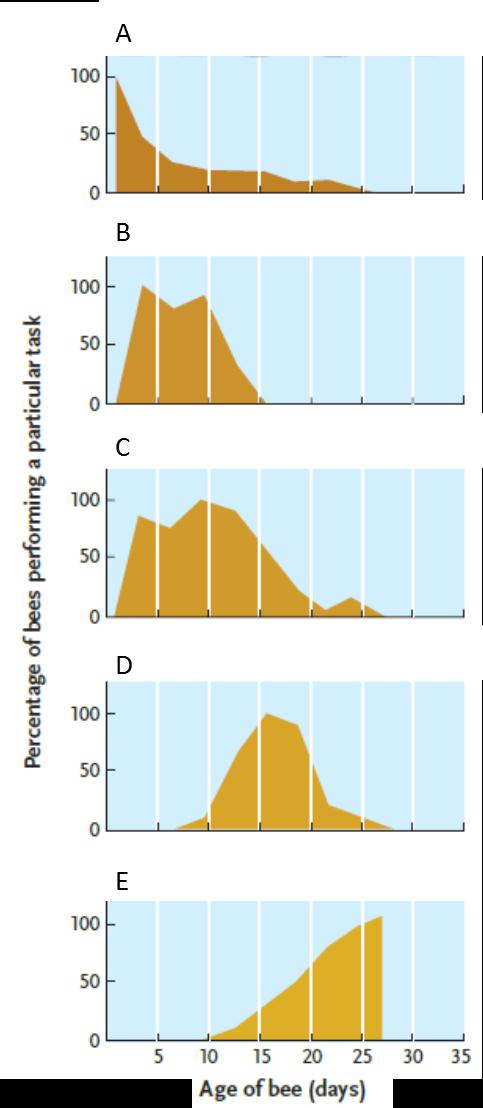 Answer the question using the accompanying figure. Which graph represents the age span of worker bees primarily involved in foraging?
Answer the question using the accompanying figure. Which graph represents the age span of worker bees primarily involved in foraging?A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
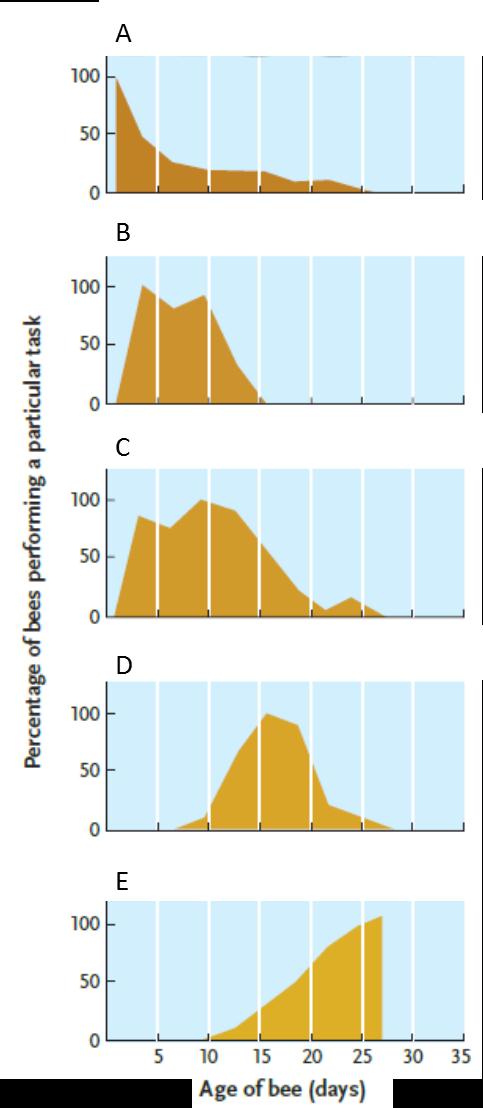 Answer the question using the accompanying figure. Which graph represents the age span of worker bees primarily involved in packing pollen?
Answer the question using the accompanying figure. Which graph represents the age span of worker bees primarily involved in packing pollen?A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In African cichlid fish, ____ regulates neurons that control sexual and aggressive behavior.
A) testosterone
B) estrogen
C) androgen
D) gonadotropin-releasing hormone
E) follicle-stimulating hormone
A) testosterone
B) estrogen
C) androgen
D) gonadotropin-releasing hormone
E) follicle-stimulating hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which chemical exerts its effect on honeybee behavior by stimulating neural transmissions and reinforcing memories?
A) estrogen
B) octopamine
C) testosterone
D) androgen
E) epinephrine
A) estrogen
B) octopamine
C) testosterone
D) androgen
E) epinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The brains of female zebra finches lack the hormonal influences that occur in the brains of males. As a result, what changes are seen in the female brains?
A) Auditory processing centers are especially well-developed in females.
B) More neurons are produced in the higher vocal center.
C) There is increased transcription of genes whose products are involved in memory retention.
D) The number of neurons in the higher vocal center declines.
E) Octopamine levels increase, stimulating neural transmissions.
A) Auditory processing centers are especially well-developed in females.
B) More neurons are produced in the higher vocal center.
C) There is increased transcription of genes whose products are involved in memory retention.
D) The number of neurons in the higher vocal center declines.
E) Octopamine levels increase, stimulating neural transmissions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Altruism involves ____, but reciprocal altruism involves ____.
A) the sacrifice of an individual's reproductive success to help others; the expectation of a future favor in return for present aid
B) aid given to nonrelatives; benefits given to close relatives only
C) the expectation of a future favor in return for present aid; close relatives helping each other
D) low-risk behavior that provides minor benefits to others; high-risk behavior providing major benefits to others
E) aid given to relatives; benefits given to nonrelatives only
A) the sacrifice of an individual's reproductive success to help others; the expectation of a future favor in return for present aid
B) aid given to nonrelatives; benefits given to close relatives only
C) the expectation of a future favor in return for present aid; close relatives helping each other
D) low-risk behavior that provides minor benefits to others; high-risk behavior providing major benefits to others
E) aid given to relatives; benefits given to nonrelatives only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The process of song learning by white-crowned sparrows is similar to the process of territory-holding by African cichlid fishes because brain cells in both animals can change ____ in response to well-defined social stimuli.
A) only their biochemistry
B) only their structure
C) only their function
D) only their structure and function
E) their biochemistry, structure, and function
A) only their biochemistry
B) only their structure
C) only their function
D) only their structure and function
E) their biochemistry, structure, and function

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The most complex wayfinding mechanism is ____, in which animals use both a compass and a mental map of the area.
A) piloting
B) orienteering
C) compass orientation
D) migration
E) navigation
A) piloting
B) orienteering
C) compass orientation
D) migration
E) navigation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When extra juvenile hormone is experimentally administered to worker bees ( Apis mellifera ), they ____.
A) revert to performing duties of younger bees
B) live longer and produce more offspring
C) begin to mate and lay eggs
D) produce more chemicals that reinforce memory
E) develop impaired memories
A) revert to performing duties of younger bees
B) live longer and produce more offspring
C) begin to mate and lay eggs
D) produce more chemicals that reinforce memory
E) develop impaired memories

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Place the events illustrating how genes and hormones interact in the development of behavior in the correct order.
1) target neurons change intracellularly
2) hormones change genetic activity and enzymatic biochemistry in their target neurons
3) genes code for hormone production
4) animal's behavior changes
A) 1, 2, 3, 4
B) 3, 2, 1, 4
C) 2, 3, 1, 4
D) 2, 1, 3, 4
E) 3, 1, 2, 4
1) target neurons change intracellularly
2) hormones change genetic activity and enzymatic biochemistry in their target neurons
3) genes code for hormone production
4) animal's behavior changes
A) 1, 2, 3, 4
B) 3, 2, 1, 4
C) 2, 3, 1, 4
D) 2, 1, 3, 4
E) 3, 1, 2, 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When Tinbergen arranged pinecones around the nest of a female digger wasp, then moved them when the wasp was gone, the wasp ____.
A) did not find the nest unless the pinecones were returned
B) dug a new nest in the center of the repositioned circle of pinecones
C) found the nest immediately demonstrating pinecone placement was irrelevant
D) abandoned the nest entirely
E) took longer to find the nest
A) did not find the nest unless the pinecones were returned
B) dug a new nest in the center of the repositioned circle of pinecones
C) found the nest immediately demonstrating pinecone placement was irrelevant
D) abandoned the nest entirely
E) took longer to find the nest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is a proximate cause of the non-combative behavior of male African cichlids that do not hold territories?
A) Cichlids can detect and store information about aggressive encounters.
B) The GnRH-producing neurons in the hypothalamus are small.
C) The testes do not produce testosterone.
D) GnRH production is high.
E) Non-combative behavior allows the male to build his strength for a takeover attempt of territory.
A) Cichlids can detect and store information about aggressive encounters.
B) The GnRH-producing neurons in the hypothalamus are small.
C) The testes do not produce testosterone.
D) GnRH production is high.
E) Non-combative behavior allows the male to build his strength for a takeover attempt of territory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
How does losing or acquiring territory affect the brain anatomy and chemistry of an African cichlid fish?
A) Only the size of the brain is changed.
B) Only the shape of brain is changed.
C) Both the size and shape of the brain are changed.
D) The size of brain cells producing sex hormones are changed.
E) The size of brain cells producing territorial hormone are changed.
A) Only the size of the brain is changed.
B) Only the shape of brain is changed.
C) Both the size and shape of the brain are changed.
D) The size of brain cells producing sex hormones are changed.
E) The size of brain cells producing territorial hormone are changed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Tinbergen's wasp experiments demonstrated that wasps find their nests by ____ cues.
A) olfactory
B) auditory
C) visual
D) both olfactory and visual
E) both magnetic and auditory
A) olfactory
B) auditory
C) visual
D) both olfactory and visual
E) both magnetic and auditory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In an experiment on wayfinding, indigo buntings were housed in outdoor cages with blotting paper walls and inkpads on the floors. Which line of evidence demonstrated to researchers that the indigo bunting uses the positions of stars to orient its migration?
A) The birds' inky feet made prints indicating the direction in which they attempted to fly.
B) In spring, the inky footprints were mostly on the northern side of the cage.
C) In fall, the inky footprints were mostly on the south side of the cage.
D) On cloudy nights, the inky footprint patterns were evenly distributed in all directions.
E) In spring, the birds' anterior pituitary gland generated a series of hormonal changes.
A) The birds' inky feet made prints indicating the direction in which they attempted to fly.
B) In spring, the inky footprints were mostly on the northern side of the cage.
C) In fall, the inky footprints were mostly on the south side of the cage.
D) On cloudy nights, the inky footprint patterns were evenly distributed in all directions.
E) In spring, the birds' anterior pituitary gland generated a series of hormonal changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Some migratory birds that fly during the day position themselves using the location of the Sun in conjunction with an internal biological clock. This wayfinding mechanism is called ____.
A) solar migration
B) landmark migration
C) piloting
D) navigation
E) compass orientation
A) solar migration
B) landmark migration
C) piloting
D) navigation
E) compass orientation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which type of signal only operates over very short distances?
A) chemical
B) tactile
C) electrical
D) visual
E) acoustical
A) chemical
B) tactile
C) electrical
D) visual
E) acoustical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Migratory birds in the Northern Hemisphere most likely head to tropical overwintering grounds because ____.
A) they are looking for appropriate sites for egg-laying
B) of seasonal changes in the abundance of predators
C) they are looking for appropriate breeding sites
D) of seasonal changes in food supplies
E) they are ectotherms and cannot withstand cold temperatures
A) they are looking for appropriate sites for egg-laying
B) of seasonal changes in the abundance of predators
C) they are looking for appropriate breeding sites
D) of seasonal changes in food supplies
E) they are ectotherms and cannot withstand cold temperatures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In studying the dance of the honeybees, Karl von Frisch determined that the duration of the dance conveyed the ____ of the food and the angle of the dance conveyed the ____ of the food.
A) direction; distance
B) distance; direction
C) type; direction
D) direction; type
E) distance; type
A) direction; distance
B) distance; direction
C) type; direction
D) direction; type
E) distance; type

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Female silkworm moths produce a ____ signal referred to as bombykol, which generates a message in specialized receptors on the antennae of any male silkworm moth that is downwind.
A) chemical
B) visual
C) electrical
D) acoustical
E) tactile
A) chemical
B) visual
C) electrical
D) acoustical
E) tactile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The courtship display of the wandering albatross is primarily a(n) ____display.
A) acoustical
B) visual
C) chemical
D) electrical
E) tactile
A) acoustical
B) visual
C) chemical
D) electrical
E) tactile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Polyandry is the mating system in which ____.
A) one male and one female form a long-term association
B) both males and females mate with multiple partners
C) one male mates with many females
D) one female mates with many males
E) both males and females provide care to offspring
A) one male and one female form a long-term association
B) both males and females mate with multiple partners
C) one male mates with many females
D) one female mates with many males
E) both males and females provide care to offspring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Animals establish and defend territories only when ____.
A) the effort does not endanger the life of the individual
B) males compete for females by fighting
C) some critical resource is in short supply
D) females choose among displaying males
E) territorial defense is not energetically costly
A) the effort does not endanger the life of the individual
B) males compete for females by fighting
C) some critical resource is in short supply
D) females choose among displaying males
E) territorial defense is not energetically costly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Recent research suggests that a homing pigeon can navigate to its home coop from any direction by using ____ as their compass and ____ as their map.
A) the position of the Sun; olfactory cues
B) the position of the stars; other visual cues
C) olfactory cues; the position of the stars
D) olfactory cues; the position of the Sun
E) landmarks; olfactory cues
A) the position of the Sun; olfactory cues
B) the position of the stars; other visual cues
C) olfactory cues; the position of the stars
D) olfactory cues; the position of the Sun
E) landmarks; olfactory cues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Territorial behavior provides a specific example of ____, the conveyance of information to other individuals.
A) taxis
B) kinesis
C) habituation
D) communication
E) imprinting
A) taxis
B) kinesis
C) habituation
D) communication
E) imprinting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Males and females often differ in their reproductive strategies due to the fact that males can increase the number of offspring they produce by ____ while females reproduce most successfully by ____.
A) mating with a high-quality female; mating with a high-quality male
B) driving off other males; defending a productive territory
C) defending a productive territory; enlisting multiple males to aid in raising her offspring
D) mating with multiple females; mating with a high-quality male
E) mating with multiple females; mating with multiple males
A) mating with a high-quality female; mating with a high-quality male
B) driving off other males; defending a productive territory
C) defending a productive territory; enlisting multiple males to aid in raising her offspring
D) mating with multiple females; mating with a high-quality male
E) mating with multiple females; mating with multiple males

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A taxis is ____ movement, while a kinesis is ____ movement.
A) ordered; a change in the rate of
B) disordered; ordered
C) random; uniform
D) a group; an individual
E) a change in the rate of; disordered
A) ordered; a change in the rate of
B) disordered; ordered
C) random; uniform
D) a group; an individual
E) a change in the rate of; disordered

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Upon finding a carcass, a raven will only call and attract other ravens to the food source if the ____.
A) nearby ravens are relatives
B) food source is large and plentiful
C) food is found in a resident pair's territory
D) food is found in his own territory
E) food is being consumed by an animal of another species
A) nearby ravens are relatives
B) food source is large and plentiful
C) food is found in a resident pair's territory
D) food is found in his own territory
E) food is being consumed by an animal of another species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Pheromones are ____ signals.
A) tactile
B) electrical
C) acoustical
D) visual
E) chemical
A) tactile
B) electrical
C) acoustical
D) visual
E) chemical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Bioluminescent signals that fireflies and certain fishes send to distant receivers in the dark are classified as ____ signals.
A) tactile
B) visual
C) chemical
D) electrical
E) mechanical
A) tactile
B) visual
C) chemical
D) electrical
E) mechanical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Male Jarrow's spiny lizards ordinarily exhibit strong territoriality only during the ____ mating season, when elevated blood levels of ____ stimulate their aggressive behavior.
A) summer; estrogen
B) summer; testosterone
C) autumn; octopamine
D) autumn; estrogen
E) autumn; testosterone
A) summer; estrogen
B) summer; testosterone
C) autumn; octopamine
D) autumn; estrogen
E) autumn; testosterone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which trait is least consistent with evolution by sexual selection?
A) males are larger than females
B) females actively choose superior males
C) males often bear showy or defensive structures
D) males gather and defend harems of females
E) female queen bees are responsible for reproducing
A) males are larger than females
B) females actively choose superior males
C) males often bear showy or defensive structures
D) males gather and defend harems of females
E) female queen bees are responsible for reproducing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When a foraging honeybee discovers pollen or nectar, it returns to its colony and performs a dance involving ____ signals in the complete darkness of the hive.
A) visual and acoustical
B) visual and chemical
C) tactile, acoustical, and chemical
D) tactile, acoustical, chemical, and electrical
E) visual, tactile, acoustical, chemical, and electrical
A) visual and acoustical
B) visual and chemical
C) tactile, acoustical, and chemical
D) tactile, acoustical, chemical, and electrical
E) visual, tactile, acoustical, chemical, and electrical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In many animals, visual signals are ____, meaning they have become exaggerated and stereotyped over evolutionary time, forming an easily recognized visual display.
A) tactile
B) conditioned
C) ritualized
D) habituated
E) operants
A) tactile
B) conditioned
C) ritualized
D) habituated
E) operants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Answer the question using the accompanying figure. The male bee represented by letter A is ____ and the queen bee represented by letter B is ____.
A) diploid; triploid
B) haploid; triploid
C) triploid; diploid
D) diploid; haploid
E) haploid; diploid
A) diploid; triploid
B) haploid; triploid
C) triploid; diploid
D) diploid; haploid
E) haploid; diploid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Answer the question using the accompanying figure. The worker bees represented by letters C and F, which receive different alleles from the queen, are related to each other by ____.
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 75%
E) 100%
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 75%
E) 100%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If a species of animal defends territories primarily to secure sufficient food supply for reproduction, we would expect the size of territories to be most closely related to ____.
A) the intensity of competition for nesting sites
B) the density of food resources in the territory
C) the habitat in which the territory exists
D) the amount of parental care invested by the species
E) the mating system used by the species
A) the intensity of competition for nesting sites
B) the density of food resources in the territory
C) the habitat in which the territory exists
D) the amount of parental care invested by the species
E) the mating system used by the species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When individuals of a species do not form close pair bonds, and both males and females mate with multiple partners, the species' mating system is described as promiscuous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Kin selection is a form of natural selection in which ____.
A) dominant individuals share resources disproportionately with their close relatives
B) individuals help relatives only if they are likely to return the favor in the future
C) group members sacrifice their own reproductive success to help individuals who are not their direct descendants
D) shared alleles for altruism are perpetuated if the assisted animals produce more offspring than the helper could have produced if he had not helped
E) shared alleles for altruism are perpetuated if the helper produces more offspring than the relatives that he aids
A) dominant individuals share resources disproportionately with their close relatives
B) individuals help relatives only if they are likely to return the favor in the future
C) group members sacrifice their own reproductive success to help individuals who are not their direct descendants
D) shared alleles for altruism are perpetuated if the assisted animals produce more offspring than the helper could have produced if he had not helped
E) shared alleles for altruism are perpetuated if the helper produces more offspring than the relatives that he aids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Winkler and Sheldon used the _____ to study _____ in swallows and martins.
A) coefficient of relatedness; kin selection
B) coefficient of relatedness; nest building behavior
C) comparative method; mating systems
D) comparative method; nest building behavior
E) reproductive method; kin selection
A) coefficient of relatedness; kin selection
B) coefficient of relatedness; nest building behavior
C) comparative method; mating systems
D) comparative method; nest building behavior
E) reproductive method; kin selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
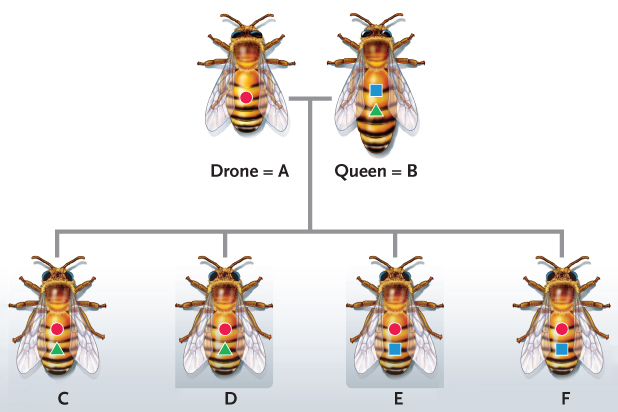 Figure 56.29 (questions 66-69).
Figure 56.29 (questions 66-69).Answer the question based on the accompanying figure. The worker bees represented by letters E and F, which received the same alleles from the queen, are related to each other by ____.
A) 50%
B) 75%
C) 0%
D) 100%
E) 25%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The zenk gene in the zebra finch brain is activated by tactile stimuli.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Neurons in the higher vocal center of a male zebra finch's brain are stimulated to proliferate by testosterone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A subordinate animal in a dominance hierarchy has limited access to food and mates. The most likely reason he remains in a social group that dominates him is because ____.
A) he is exhibiting altruistic behavior
B) his chances of survival and reproduction are better in the group than alone
C) he expects to become dominant in the future
D) he does not know that it would be an advantage for him to leave
E) dominant group members will not allow him to leave
A) he is exhibiting altruistic behavior
B) his chances of survival and reproduction are better in the group than alone
C) he expects to become dominant in the future
D) he does not know that it would be an advantage for him to leave
E) dominant group members will not allow him to leave

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
When one male and one female form a long-term association, the mating system is referred to as ____.
A) promiscuous
B) polygamous
C) monogamous
D) polygynous
E) polyandrous
A) promiscuous
B) polygamous
C) monogamous
D) polygynous
E) polyandrous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In honeybees, queen bees are haploid organisms while male drones are diploid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Why do peahens choose peacocks with the longest, showiest tails, when a long tail might be easily grabbed by a predator?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Half siblings share on average 50% of their alleles by inheritance from their shared parent, making their degree of relatedness 0.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
What is haplodiploidy, and how is it related to altruism in honeybees?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The red spot on the beak of a herring gull parent is a sign stimulus received by baby gulls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The degree of relatedness between a niece and an uncle is ____, and the degree of relatedness between first cousins is ____.
A) 0.75; 0.50
B) 0.50; 0.25
C) 0.25; 0.125
D) 0.125; 0.0625
E) 0.0625; 0.03125
A) 0.75; 0.50
B) 0.50; 0.25
C) 0.25; 0.125
D) 0.125; 0.0625
E) 0.0625; 0.03125

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Answer the question using the accompanying figure. Bees C and D ____.
A) had a different father than bees E and F
B) had a different mother than bees E and F
C) inherited different alleles than bees E and F from their mother
D) inherited different alleles than bees E and F from their father
E) are haploid drones, while bees E and F are diploid female workers
A) had a different father than bees E and F
B) had a different mother than bees E and F
C) inherited different alleles than bees E and F from their mother
D) inherited different alleles than bees E and F from their father
E) are haploid drones, while bees E and F are diploid female workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



