Deck 12: Chemical Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/45
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Chemical Equilibrium
1
If the equilibrium constant of a reaction is greater than zero, it indicates that the reaction tends to favor the forward direction and the formation of products.
True
2
In the context of equilibrium constants of chemical reactions, which "K" value indicates a reaction that favors the formation of products the most?
A)K = 5.31 × 103
B)K = 4.99 × 106
C)K = 8.2 × 10 − 3
D)K = 1.7 × 10 − 6
A)K = 5.31 × 103
B)K = 4.99 × 106
C)K = 8.2 × 10 − 3
D)K = 1.7 × 10 − 6
K = 4.99 × 106
3
Which of the following chemical species is a Brønsted Lowry base?
A)NaOH
B)C4H10
C)CaCl2
D)H2SO4
A)NaOH
B)C4H10
C)CaCl2
D)H2SO4
NaOH
4
Concrete structures with many small cracks are more likely to fail than similar structures with fewer, larger cracks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In a dynamic equilibrium, _____.
A)the rate of the forward reaction goes to zero
B)the rate of the reverse reaction goes to zero
C)the rates of the forward and reverse reactions become equal
D)the reaction begins to favor the reverse direction
A)the rate of the forward reaction goes to zero
B)the rate of the reverse reaction goes to zero
C)the rates of the forward and reverse reactions become equal
D)the reaction begins to favor the reverse direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Hydrogen is industrially produced by the following reaction between propane and liquid water:
C3H8( g )+ 3H2O( l )→ 3CO( g )+ 7H2( g ).
If the denominator of the equilibrium expression is expressed as [C 3 H 8 ] m [ H 2 O] n , what are the values of "m" and "n"?
A)3 and 7
B)1 and 0
C)1 and 3
D)7 and 3
C3H8( g )+ 3H2O( l )→ 3CO( g )+ 7H2( g ).
If the denominator of the equilibrium expression is expressed as [C 3 H 8 ] m [ H 2 O] n , what are the values of "m" and "n"?
A)3 and 7
B)1 and 0
C)1 and 3
D)7 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In a dynamic equilibrium, the rates of the forward and reverse reactions go to zero once the equilibrium is reached.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The reaction 2A( s )+ B( g ) 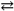 2C( s )represents a(n) _____.
2C( s )represents a(n) _____.
A)homogeneous equilibrium
B)heterogeneous equilibrium
C)instantaneous equilibrium
D)reaction that will not come to an equilibrium
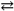 2C( s )represents a(n) _____.
2C( s )represents a(n) _____.A)homogeneous equilibrium
B)heterogeneous equilibrium
C)instantaneous equilibrium
D)reaction that will not come to an equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following chemical species is a Brønsted-Lowry acid?
A)NaOH
B)C4H10
C)CaCl2
D)H2SO4
A)NaOH
B)C4H10
C)CaCl2
D)H2SO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
"Insoluble" salts are actually "sparingly" soluble at equilibrium conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The term "strong acid" refers to any acid of 0.100 M concentration or higher.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the context of exothermic reactions in equilibrium, when the temperature is lowered, heat flows out from the system and the system responds by generating additional heat-moving the equilibrium toward products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a reaction is in a state where the reaction quotient is more than the equilibrium constant, _____.
A)the rate of the reaction will always double
B)more products will form
C)more reactants will form
D)the reaction will remain in a steady state
A)the rate of the reaction will always double
B)more products will form
C)more reactants will form
D)the reaction will remain in a steady state

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The higher the K sp of a salt, the less soluble the salt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The production of ammonia N2( g )+ 3H2( g ) 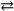 2NH3( g )represents a(n) _____.
2NH3( g )represents a(n) _____.
A)homogeneous equilibrium
B)heterogeneous equilibrium
C)instantaneous equilibrium
D)reaction that will not come to an equilibrium
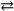 2NH3( g )represents a(n) _____.
2NH3( g )represents a(n) _____.A)homogeneous equilibrium
B)heterogeneous equilibrium
C)instantaneous equilibrium
D)reaction that will not come to an equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
According to the Brønsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases, acids are proton (hydronium)acceptors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Unlike traditional concrete, engineered cementitious composites (ECC)do not contain gravel but instead contain fly ash.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If NaCl is added to a saturated solution of AgCl, the equilibrium will shift back toward the reactants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A catalyst will increase the rate of the forward and reverse reactions equally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Products appear in the numerator of the reaction quotient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
At equilibrium, Δ G _____.
A)= 0
B)> 0
C)< 0
D)cannot be determined
A)= 0
B)> 0
C)< 0
D)cannot be determined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the molar solubility of AgCl (Ksp= 1.8 × 10 − 10)?
A)7.31 × 10 − 5M
B)5.13 × 10 − 6M
C)3.84 × 10 − 5M
D)1.34 × 10 − 5M
A)7.31 × 10 − 5M
B)5.13 × 10 − 6M
C)3.84 × 10 − 5M
D)1.34 × 10 − 5M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The conjugate acid of sodium acetate (Na+CH3COO − )is _____.
A)NaOH
B)CH3COOH
C)HCl
D)K+CH3COO −
A)NaOH
B)CH3COOH
C)HCl
D)K+CH3COO −

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the pH of a 0.1055 M CH3COOH solution (Ka= 1.75 × 10 − 5)?
A)2.770
B)2.867
C)3.188
D)8.474
A)2.770
B)2.867
C)3.188
D)8.474

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is a strong base?
A)HClO4
B)HNO2
C)HCl
D)KOH
A)HClO4
B)HNO2
C)HCl
D)KOH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHP)concentrations can be determined through titrating samples of KHP (a monoprotic acid)with bases such as NaOH in the presence of an indicator such as phenolphthalein. The indicator is colorless in an acidic solution and turns pink in an alkaline solution. Thus, we can establish an equilibrium for the phenolphthalein with the following reaction.
HIn + H2O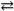 In − + H3O+
In − + H3O+
If the HIn species is "acid color" or colorless for the phenolphthalein, and the In − species is "base color" or pink for this particular indicator, what color will appear in a flask in which a 0.2993 gram sample of KHP is completely neutralized with an excess of NaOH?
A)The flask will be colorless.
B)The flask will be pink.
C)The flask will be white from KCl precipitation.
D)There is insufficient information to solve this problem.
HIn + H2O
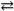 In − + H3O+
In − + H3O+
If the HIn species is "acid color" or colorless for the phenolphthalein, and the In − species is "base color" or pink for this particular indicator, what color will appear in a flask in which a 0.2993 gram sample of KHP is completely neutralized with an excess of NaOH?
A)The flask will be colorless.
B)The flask will be pink.
C)The flask will be white from KCl precipitation.
D)There is insufficient information to solve this problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The synthesis of the pesticide thionyl chloride (OSCl2)proceeds according to the following reaction:
SO3( g )+ SCl2( l )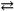 OSCl2( l )+ SO2( g )
OSCl2( l )+ SO2( g )
If Δ G0 is − 106 kJ\mol for this reaction at 298K, what is the Keqat this temperature? Recall that R is 8.314 J mol − 1K − 1.
A)7.21 × 1012
B)3.50 × 1014
C)3.81 × 1018
D)1.19 × 1020
SO3( g )+ SCl2( l )
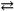 OSCl2( l )+ SO2( g )
OSCl2( l )+ SO2( g )
If Δ G0 is − 106 kJ\mol for this reaction at 298K, what is the Keqat this temperature? Recall that R is 8.314 J mol − 1K − 1.
A)7.21 × 1012
B)3.50 × 1014
C)3.81 × 1018
D)1.19 × 1020

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The conjugate base of ammonium ion is _____.
A)NH3
B)HNO2
C)HCl
D)HNO3
A)NH3
B)HNO2
C)HCl
D)HNO3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following chemical species is amphoteric?
A)NaOH
B)C4H10
C)H2O
D)H2SO4
A)NaOH
B)C4H10
C)H2O
D)H2SO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Consider the following reaction of a weak base with water :
ClO − + H2O![<strong>Consider the following reaction of a weak base with water : ClO<sup> − </sup>+ H<sub>2</sub>O HClO + OH<sup> − </sup> If a dilute HCl sample is slowly titrated into a sample of ClO <sup> − </sup>, the [ClO <sup> − </sup>] concentration:</strong> A)decreases. B)remains constant. C)increases in a linear fashion. D)increases exponentially.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8710/11ebeecb_bed8_4c28_b31f_61403dcaa607_TBX8710_11.jpg) HClO + OH −
HClO + OH −
If a dilute HCl sample is slowly titrated into a sample of ClO − , the [ClO − ] concentration:
A)decreases.
B)remains constant.
C)increases in a linear fashion.
D)increases exponentially.
ClO − + H2O
![<strong>Consider the following reaction of a weak base with water : ClO<sup> − </sup>+ H<sub>2</sub>O HClO + OH<sup> − </sup> If a dilute HCl sample is slowly titrated into a sample of ClO <sup> − </sup>, the [ClO <sup> − </sup>] concentration:</strong> A)decreases. B)remains constant. C)increases in a linear fashion. D)increases exponentially.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8710/11ebeecb_bed8_4c28_b31f_61403dcaa607_TBX8710_11.jpg) HClO + OH −
HClO + OH −
If a dilute HCl sample is slowly titrated into a sample of ClO − , the [ClO − ] concentration:
A)decreases.
B)remains constant.
C)increases in a linear fashion.
D)increases exponentially.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What change in the reaction direction occurs if dilute NaOH is added to a H 2 PO 4 − solution?
H2PO4 − + H2O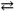 HPO42 − + H3O+
HPO42 − + H3O+
A)The reaction shifts to the right.
B)The reaction shifts to the left.
C)There is no change in the reaction.
D)There is insufficient information to solve this problem.
H2PO4 − + H2O
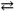 HPO42 − + H3O+
HPO42 − + H3O+
A)The reaction shifts to the right.
B)The reaction shifts to the left.
C)There is no change in the reaction.
D)There is insufficient information to solve this problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is a weak acid?
A)NH3
B)HCN
C)HCl
D)HNO3
A)NH3
B)HCN
C)HCl
D)HNO3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What change in reaction direction occurs if dilute HCl is added to a H2PO4 − solution?
H2PO4 − + H2O HPO42 − + H3O+
HPO42 − + H3O+
A)The reaction shifts to the right.
B)The reaction shifts to the left.
C)There is no change in the reaction.
D)There is insufficient information to solve this problem.
H2PO4 − + H2O
 HPO42 − + H3O+
HPO42 − + H3O+
A)The reaction shifts to the right.
B)The reaction shifts to the left.
C)There is no change in the reaction.
D)There is insufficient information to solve this problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the molar solubility of CaF2(Ksp= 3.9 × 10 − 11)?
A)6.24 × 10 − 6M
B)4.41 × 10 − 6M
C)2.14 × 10 − 4M
D)9.27 × 10 − 5M
A)6.24 × 10 − 6M
B)4.41 × 10 − 6M
C)2.14 × 10 − 4M
D)9.27 × 10 − 5M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the pH of a 0.150 M NaOH solution?
A)0.82
B)3.05
C)11.66
D)13.18
A)0.82
B)3.05
C)11.66
D)13.18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the pH of a 0.0250 M pyridine (C 5 H 5 N) solution? (Kb= 1.5 × 10 − 9)
A)8.79
B)5.21
C)13.1
D)4.72
A)8.79
B)5.21
C)13.1
D)4.72

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The lower the pH of a weak acid, the:
A)higher the concentration of the weak acid.
B)higher the dissolved H2(g)concentration.
C)higher the acid ionization constant of the acid.
D)higher the concentration of its conjugate base.
A)higher the concentration of the weak acid.
B)higher the dissolved H2(g)concentration.
C)higher the acid ionization constant of the acid.
D)higher the concentration of its conjugate base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Consider the solubility of BaSO4. If Ba(NO3)2is added to the solution, the solubility of the barium sulfate _____.
A)is unaffected
B)is unchanged as barium sulfate is a strong electrolyte
C)decreases
D)increases
A)is unaffected
B)is unchanged as barium sulfate is a strong electrolyte
C)decreases
D)increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is the pH of a 0.200 M solution of HNO3?
A)0.70
B)1.31
C)6.18
D)8.53
A)0.70
B)1.31
C)6.18
D)8.53

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following solids will provide the greatest concentration of Cl − ions if one mole of salt is placed in one liter of deionized water?
A)AgCl( s )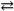 Ag1+( aq )+ Cl1 − ( aq )Ksp= 1.8 × 10 − 10
Ag1+( aq )+ Cl1 − ( aq )Ksp= 1.8 × 10 − 10
B)NH 4 Cl ( s )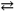 NH 4 + ( aq )+ Cl 1 − ( aq )K sp = 30.9
NH 4 + ( aq )+ Cl 1 − ( aq )K sp = 30.9
C)Hg2Cl2( s )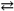 2Hg1+( aq )+ 2Cl1 − ( aq )Ksp= 1.1 × 10 − 18
2Hg1+( aq )+ 2Cl1 − ( aq )Ksp= 1.1 × 10 − 18
D)NaCl( s )→ Na 1+ ( aq )+ Cl 1 − ( aq )K sp = 36
A)AgCl( s )
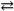 Ag1+( aq )+ Cl1 − ( aq )Ksp= 1.8 × 10 − 10
Ag1+( aq )+ Cl1 − ( aq )Ksp= 1.8 × 10 − 10B)NH 4 Cl ( s )
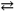 NH 4 + ( aq )+ Cl 1 − ( aq )K sp = 30.9
NH 4 + ( aq )+ Cl 1 − ( aq )K sp = 30.9C)Hg2Cl2( s )
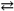 2Hg1+( aq )+ 2Cl1 − ( aq )Ksp= 1.1 × 10 − 18
2Hg1+( aq )+ 2Cl1 − ( aq )Ksp= 1.1 × 10 − 18D)NaCl( s )→ Na 1+ ( aq )+ Cl 1 − ( aq )K sp = 36

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
According to LeChatelier's principle, when a system at equilibrium is stressed, it responds by reestablishing equilibrium to reduce the applied stress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In any chemical system at equilibrium, the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Consider the following reaction:
SO3( g )+ CaO( s )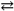 CaSO4( s ).
CaSO4( s ).
If Δ G 0 is − 345 kJ\mol for this reaction at 298K, what is the K eq at this temperature? Recall that R is 8.314 J mol − 1 K − 1 .
A)3.1 × 10 40
B)3.50 × 10 50
C)2.96 × 10 60
D)2.23 × 10 70
SO3( g )+ CaO( s )
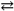 CaSO4( s ).
CaSO4( s ).If Δ G 0 is − 345 kJ\mol for this reaction at 298K, what is the K eq at this temperature? Recall that R is 8.314 J mol − 1 K − 1 .
A)3.1 × 10 40
B)3.50 × 10 50
C)2.96 × 10 60
D)2.23 × 10 70

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In heterogeneous equilibria, reactants and products are all in the same phase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
According to LeChatelier's principle, when the reaction quotient is less than the equilibrium constant of a reaction, the reaction:
A)must shift toward products to reach equilibrium.
B)must shift toward reactants to reach equilibrium.
C)results in an increase in standard enthalpy of formation of reactants.
D)results in an increase in standard enthalpy of formation of products.
A)must shift toward products to reach equilibrium.
B)must shift toward reactants to reach equilibrium.
C)results in an increase in standard enthalpy of formation of reactants.
D)results in an increase in standard enthalpy of formation of products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



