Deck 6: Elasticity
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/204
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Elasticity
1
When the price of a good rises, total revenue will fall if the good is elastic in demand.
True
2
The cross elasticity of demand coefficient between Coca-Cola and Pepsi Cola would be expected to be negative.
False
3
Income elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity supplied to changes in price.
False
4
Cross elasticity of demand measures consumer responsiveness to a change in the price of one good, in terms of the quantity demanded of some other good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Price elasticity of demand is the ratio of the percentage change in price of one good to the percentage change in quantity demanded of another good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When a good is perfectly inelastic in demand, or perfectly elastic in supply, the buyers will pay the full tax that is placed on the sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A good is unit elastic in demand if as the price changes there is no resulting change in total revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
It is very important for the seller of a good to know whether the good is elastic, unit elastic, or inelastic in demand so that she will know what will happen to total revenue when she changes the price of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The more narrowly defined a good is, the more elastic the demand for the good will tend to be, ceteris paribus .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If the demand for cocaine is inelastic and people commit crimes to buy drugs, then a drug bust can increase the amount of drug-related crime.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Ford Mustangs would tend to be more elastic in demand than all cars because there are more substitutes for Ford Mustangs than for cars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
As the price of a product rises the product will become more elastic in demand, assuming that the demand curve for the product is a downward-sloping straight line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
From the sellers' perspective, it is most desirable for a product to be perfectly elastic in demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The existence of substitutes for a good and the percentage of one's budget spent on the good are among the factors that determine how elastic the demand for the good will be.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If the supply curve for good X is vertical, then the demand for good X must be perfectly inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If a good is a normal good, it can not also be income inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If the percentage change in quantity supplied is greater than the percentage change in price, then supply is elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When the price of a good rises, the total revenue received by the seller of that good always rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
It is impossible for a given good to be both elastic in demand and inelastic in supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If a good is perfectly inelastic in a given price range, it will be perfectly inelastic at all prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If quantity demanded is completely unresponsive to changes in the price of good XYZ, then demand for good XYZ is
A)inelastic.
B)unit elastic.
C)elastic.
D)perfectly elastic.
E)perfectly inelastic.
A)inelastic.
B)unit elastic.
C)elastic.
D)perfectly elastic.
E)perfectly inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If the percentage change in quantity demanded is equal to the percentage change in price for good Z, then demand for good Z is
A)inelastic.
B)unit elastic.
C)elastic.
D)perfectly elastic.
E)perfectly inelastic.
A)inelastic.
B)unit elastic.
C)elastic.
D)perfectly elastic.
E)perfectly inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If the price of good X falls and the demand for good X is unit elastic, then the percentage rise in quantity demanded is __________ the percentage fall in price, and total revenue __________.
A)greater than; rises
B)less than; falls
C)equal to; remains constant
D)greater than; falls
E)less than; rises
A)greater than; rises
B)less than; falls
C)equal to; remains constant
D)greater than; falls
E)less than; rises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following statements is false ?
A)Ham has a higher price elasticity of demand than meat.
B)Peaches have a higher price elasticity of demand than fruit.
C)Soap has a higher price elasticity of demand than Ivory brand soap.
D)Carrots have a higher price elasticity of demand than vegetables.
A)Ham has a higher price elasticity of demand than meat.
B)Peaches have a higher price elasticity of demand than fruit.
C)Soap has a higher price elasticity of demand than Ivory brand soap.
D)Carrots have a higher price elasticity of demand than vegetables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The fewer substitutes for a good,
A)the lower its income elasticity of demand.
B)the higher its income elasticity of demand.
C)the lower its price elasticity of demand.
D)the higher its price elasticity of demand.
A)the lower its income elasticity of demand.
B)the higher its income elasticity of demand.
C)the lower its price elasticity of demand.
D)the higher its price elasticity of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose that the quantity demanded of good X rises by 8 percent when the price of good X falls by 2 percent. This information indicates that the price elasticity of demand equals
A)4.
B)2.50.
C)0.25.
D)10.
E)There is not enough information provided to answer this question.
A)4.
B)2.50.
C)0.25.
D)10.
E)There is not enough information provided to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Suppose at a price of $4 and at a price of $6, John purchases 40 units of good X. Given this information, we know that
A)John's entire demand curve for good X is perfectly elastic.
B)John's entire demand curve for good X is inelastic.
C)John's demand for good X is perfectly inelastic between the prices of $4 and $6.
D)John's demand for good X is perfectly elastic between the prices of $4 and $6.
E)John's entire demand curve for good X is unit elastic.
A)John's entire demand curve for good X is perfectly elastic.
B)John's entire demand curve for good X is inelastic.
C)John's demand for good X is perfectly inelastic between the prices of $4 and $6.
D)John's demand for good X is perfectly elastic between the prices of $4 and $6.
E)John's entire demand curve for good X is unit elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Price elasticity of demand is the ratio of the
A)absolute change in quantity demanded to the absolute change in price.
B)absolute change in price to the absolute change in quantity demanded.
C)percentage change in quantity demanded to the percentage change in price.
D)percentage change in price to the percentage change in quantity demanded.
A)absolute change in quantity demanded to the absolute change in price.
B)absolute change in price to the absolute change in quantity demanded.
C)percentage change in quantity demanded to the percentage change in price.
D)percentage change in price to the percentage change in quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Suppose that when the price of a good rises from $12 to $14, the quantity demanded of that good falls from 220 units to 180 units. What is the approximate price elasticity of demand between these two prices?
A)1.30
B)0.77
C)1.73
D)0.27
A)1.30
B)0.77
C)1.73
D)0.27

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following would result in higher price elasticity of good X?
A)more substitutes for good X
B)a shorter period of time has passed since the change in the price of good X
C)lower costs of labor in the production of good X
D)good X is more of a necessity than a luxury
A)more substitutes for good X
B)a shorter period of time has passed since the change in the price of good X
C)lower costs of labor in the production of good X
D)good X is more of a necessity than a luxury

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the price elasticity of demand for a given product is 0.7, this means that
A)the percentage change in quantity demanded is 0.7 times the percentage change in price.
B)if quantity demanded fell by 1 percent, price would fall by 7 percent.
C)if price was raised 7 percent, quantity demanded would fall by 0.7 percent.
D)if price was raised 7 percent, quantity demanded would rise 0.7 percent.
E)the percentage change in price is 0.7 times the percentage change in quantity demanded.
A)the percentage change in quantity demanded is 0.7 times the percentage change in price.
B)if quantity demanded fell by 1 percent, price would fall by 7 percent.
C)if price was raised 7 percent, quantity demanded would fall by 0.7 percent.
D)if price was raised 7 percent, quantity demanded would rise 0.7 percent.
E)the percentage change in price is 0.7 times the percentage change in quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If the percentage change in quantity demanded is less than the percentage change in price for good Y, then the demand for good Y is
A)inelastic.
B)unit elastic.
C)elastic.
D)perfectly elastic.
A)inelastic.
B)unit elastic.
C)elastic.
D)perfectly elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Price elasticity of demand is a measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in
A)interest rates.
B)price.
C)supply.
D)demand.
A)interest rates.
B)price.
C)supply.
D)demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the price of good X rises and the demand for good X is inelastic, then the percentage fall in quantity demanded is __________ the percentage rise in price, and total revenue __________.
A)greater than; rises
B)less than; falls
C)equal to; remains constant
D)greater than; falls
E)less than; rises
A)greater than; rises
B)less than; falls
C)equal to; remains constant
D)greater than; falls
E)less than; rises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Suppose that when the price of a good falls from $12 to $9, the quantity demanded of that good rises from 310 units to 350 units. What is the approximate price elasticity of demand between these two prices?
A)0.42
B)2.36
C)0.68
D)3.80
E)1.12
A)0.42
B)2.36
C)0.68
D)3.80
E)1.12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the price of good X rises and the demand for good X is elastic, then the percentage __________ in quantity demanded is __________ the percentage rise in price, and total revenue __________.
A)fall; greater than; rises
B)fall; less than; falls
C)fall; equal to; remains constant
D)rise; greater than; falls
E)fall; greater than; falls
A)fall; greater than; rises
B)fall; less than; falls
C)fall; equal to; remains constant
D)rise; greater than; falls
E)fall; greater than; falls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The price elasticity of demand would most likely be highest for which of the following goods?
A)food (in general)
B)cars (in general)
C)clothing (in general)
D)Ford cars
A)food (in general)
B)cars (in general)
C)clothing (in general)
D)Ford cars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
For a certain good, when price rises from $90 to $98, quantity demanded falls from 7,400 to 6,500. The price elasticity of demand here is approximately _____________, making the demand for this good ____________ in the price range between $90 and $98.
A)1.52; inelastic
B)1.52; elastic
C)1.86; elastic
D)0.66; elastic
E)0.66; inelastic
A)1.52; inelastic
B)1.52; elastic
C)1.86; elastic
D)0.66; elastic
E)0.66; inelastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
For a certain good, when the good's price falls from $22 to $20, its quantity demanded rises from 2,000 to 2,200 units. Given this information, the price elasticity of demand for this good is approximately
A)2.55.
B)0.66.
C)0.39.
D)0.20.
E)1.00
A)2.55.
B)0.66.
C)0.39.
D)0.20.
E)1.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If the percentage change in quantity demanded is greater than the percentage change in price for good X, then the demand for good X is
A)inelastic.
B)unit elastic.
C)elastic.
D)perfectly inelastic.
A)inelastic.
B)unit elastic.
C)elastic.
D)perfectly inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If the price of good A decreases by 10 percent and the quantity demanded of good B decreases by 10 percent, this is evidence that goods A and B are
A)substitutes for one another.
B)complement goods to one another.
C)both inferior goods.
D)both normal goods.
E)not related.
A)substitutes for one another.
B)complement goods to one another.
C)both inferior goods.
D)both normal goods.
E)not related.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If Jack bought 18 CDs last year when his income was $20,000 and he buys 19 CDs this year when his income is $25,000, then for Jack CDs are
A)an inferior good.
B)a normal good.
C)a substitute good.
D)a complementary good.
E)There is not enough information to answer this question.
A)an inferior good.
B)a normal good.
C)a substitute good.
D)a complementary good.
E)There is not enough information to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If two goods are substitute goods,
A)an increase in the price of one will cause a decrease in the demand for the other.
B)an increase in the price of one will cause an increase in the demand for the other.
C)the price elasticity of demand for both goods will be greater than 1.
D)the price elasticity of demand for both goods will be less than 1.
A)an increase in the price of one will cause a decrease in the demand for the other.
B)an increase in the price of one will cause an increase in the demand for the other.
C)the price elasticity of demand for both goods will be greater than 1.
D)the price elasticity of demand for both goods will be less than 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If Cassandra bought 12 blouses last year when her income was $46,000 and she buys 14 blouses this year when her income is $52,000, then her income elasticity of demand for blouses is approximately
A)-1.26.
B)+1.26.
C)-0.80.
D)+0.80.
E)-2.52.
A)-1.26.
B)+1.26.
C)-0.80.
D)+0.80.
E)-2.52.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If Jack bought 12 DVDs last year when his income was $40,000 and he buys 14 DVDs this year when his income is $43,000, then his income elasticity of demand is ______________ which means that DVDs are a(n)______________ good for Jack.
A)+0.41 ; normal
B)-0.47; inferior
C)+2.13; normal
D)+0.59; inferior
E)-2.13; inferior
A)+0.41 ; normal
B)-0.47; inferior
C)+2.13; normal
D)+0.59; inferior
E)-2.13; inferior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the price of a good rises and as a result total revenue falls, then it must be true that
A)cross elasticity of demand for the good is negative.
B)price elasticity of demand for the good is less than 1.
C)income elasticity of demand for the good is positive.
D)income elasticity of demand for the good is negative.
E)price elasticity of demand for the good is greater than 1.
A)cross elasticity of demand for the good is negative.
B)price elasticity of demand for the good is less than 1.
C)income elasticity of demand for the good is positive.
D)income elasticity of demand for the good is negative.
E)price elasticity of demand for the good is greater than 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following statements is false ?
A)If the income elasticity of demand for a good is less than 1, the demand for the good is income inelastic.
B)If the income elasticity of demand for a good is greater than 1, the demand for the good is income elastic.
C)If the income elasticity of demand for a good is equal to 1, the demand for the good is income unit elastic.
D)If the income elasticity of demand for a good is less than zero, the good is a normal good.
E)A good can be both a normal good and income inelastic.
A)If the income elasticity of demand for a good is less than 1, the demand for the good is income inelastic.
B)If the income elasticity of demand for a good is greater than 1, the demand for the good is income elastic.
C)If the income elasticity of demand for a good is equal to 1, the demand for the good is income unit elastic.
D)If the income elasticity of demand for a good is less than zero, the good is a normal good.
E)A good can be both a normal good and income inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If goods A and B have a cross elasticity of demand that is positive, this is evidence that goods A and B are __________ goods.
A)complementary
B)substitute
C)normal
D)inferior
A)complementary
B)substitute
C)normal
D)inferior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Vernon spends the following percentages of his budget on the goods A, B, C, and D: 23 percent on good A, 11 percent on good B, 1 percent on good C, and 3 percent on good D. For which good is price elasticity of demand the highest, ceteris paribus ?
A)good A
B)good B
C)good C
D)good D
A)good A
B)good B
C)good C
D)good D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If the price of good A decreases by 10 percent and the quantity demanded of good B increases by 10 percent, this is evidence that goods A and B are
A)substitute for one another.
B)complement goods to one another.
C)both inferior goods.
D)both normal goods.
E)not related.
A)substitute for one another.
B)complement goods to one another.
C)both inferior goods.
D)both normal goods.
E)not related.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If Casey bought 16 cotton t-shirts last year when her income was $40,000 and she buys 14 cotton t-shirts this year when her income is $45,000, then for Casey cotton t-shirts are
A)an inferior good.
B)a normal good.
C)a substitute good.
D)a complementary good.
E)There is not enough information to answer this question.
A)an inferior good.
B)a normal good.
C)a substitute good.
D)a complementary good.
E)There is not enough information to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A good will tend to have a low price elasticity of demand if
A)the good has few substitutes.
B)a person spends a high percentage of his or her budget on the good.
C)a person has a long period of time to adjust to price changes.
D)the good is a luxury.
A)the good has few substitutes.
B)a person spends a high percentage of his or her budget on the good.
C)a person has a long period of time to adjust to price changes.
D)the good is a luxury.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Cross elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of changes in the quantity __________ of one good to changes in __________.
A)demanded; the price of the same good
B)demanded; income
C)demanded; the price of another good
D)supplied; the price of the same good
A)demanded; the price of the same good
B)demanded; income
C)demanded; the price of another good
D)supplied; the price of the same good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Income elasticity of demand for a normal good is always
A)less than zero.
B)greater than zero.
C)equal to zero.
D)less than one.
A)less than zero.
B)greater than zero.
C)equal to zero.
D)less than one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If the cross elasticity of demand for good A with respect to good B is +2.7, then good A is
A)an inferior good.
B)a normal good.
C)a substitute for good B.
D)a complement to good B.
A)an inferior good.
B)a normal good.
C)a substitute for good B.
D)a complement to good B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The shorter the period of time consumers have to adjust to price changes, the __________ the __________ elasticity of demand.
A)lower; income
B)lower; price
C)higher; income
D)higher; price
A)lower; income
B)lower; price
C)higher; income
D)higher; price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If the cross elasticity of demand for two goods is negative,
A)one of the goods is necessarily a normal good, and the other good is necessarily an inferior good.
B)both goods are normal goods.
C)the goods are substitutes.
D)the goods are complements.
A)one of the goods is necessarily a normal good, and the other good is necessarily an inferior good.
B)both goods are normal goods.
C)the goods are substitutes.
D)the goods are complements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If the cross elasticity of demand for good A with respect to good B is -0.87, then good A is
A)an inferior good.
B)a normal good.
C)a substitute for good B.
D)a complement to good B.
A)an inferior good.
B)a normal good.
C)a substitute for good B.
D)a complement to good B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The longer the period of time consumers have to adjust to price changes, the __________ the __________ elasticity of demand.
A)lower, price
B)lower, income
C)higher, price
D)higher, income
A)lower, price
B)lower, income
C)higher, price
D)higher, income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Cross elasticity of demand is the percentage change in the quantity __________ of a good divided by the percentage change in __________.
A)demanded; the price of the good
B)supplied; the price of the good
C)demanded; the price of another good
D)supplied; the price of another good
E)demanded; income
A)demanded; the price of the good
B)supplied; the price of the good
C)demanded; the price of another good
D)supplied; the price of another good
E)demanded; income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A normal good is
A)any good that consumers normally buy.
B)any good for which other goods can substitute.
C)a good for which the demand rises as income falls.
D)a good for which the demand rises as income rises.
E)a good for which the quantity demanded rises as its price falls.
A)any good that consumers normally buy.
B)any good for which other goods can substitute.
C)a good for which the demand rises as income falls.
D)a good for which the demand rises as income rises.
E)a good for which the quantity demanded rises as its price falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Suppose the demand for a particular good is perfectly inelastic and the government decides to impose a tax on the production of this good. Who will pay the greater share of such a tax?
A)The buyers will pay the entire share.
B)The sellers will pay the entire share.
C)The buyers and the sellers will pay equal shares.
D)The sellers will bear the greater share of the tax.
A)The buyers will pay the entire share.
B)The sellers will pay the entire share.
C)The buyers and the sellers will pay equal shares.
D)The sellers will bear the greater share of the tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
An inferior good is
A)any good that consumers think is of low quality.
B)a good for which the quantity demanded increases as its price decreases.
C)a good for which the demand rises as income falls.
D)a good for which the demand rises as income rises.
E)any good that a producer cannot sell a large quantity of, even at a low price.
A)any good that consumers think is of low quality.
B)a good for which the quantity demanded increases as its price decreases.
C)a good for which the demand rises as income falls.
D)a good for which the demand rises as income rises.
E)any good that a producer cannot sell a large quantity of, even at a low price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Exhibit 19-1
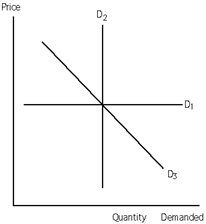
Refer to Exhibit 19-l. The demand for the good represented by demand curve D3 is
A)inelastic.
B)elastic.
C)unit elastic.
D)perfectly elastic.
E)more elastic at higher prices than at lower prices.

Refer to Exhibit 19-l. The demand for the good represented by demand curve D3 is
A)inelastic.
B)elastic.
C)unit elastic.
D)perfectly elastic.
E)more elastic at higher prices than at lower prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Exhibit 19-2
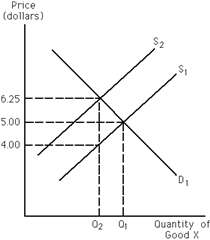
Refer to Exhibit 19-2. The market for good X is initially in equilibrium at $5. The government then places a tax on the producers of good X, taxing them on each unit of good X they sell. As a result, the supply curve
A)shifts (down and)rightward from S2 to S1.
B)shifts (up and)leftward from S1 to S2.
C)does not shift from S1.
D)There is not enough information to answer the question.

Refer to Exhibit 19-2. The market for good X is initially in equilibrium at $5. The government then places a tax on the producers of good X, taxing them on each unit of good X they sell. As a result, the supply curve
A)shifts (down and)rightward from S2 to S1.
B)shifts (up and)leftward from S1 to S2.
C)does not shift from S1.
D)There is not enough information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If for good Z income elasticity is less than 1 but greater than zero, then demand for good Z is income __________, and good Z is a(n)__________ good.
A)inelastic; normal
B)inelastic; inferior
C)elastic; normal
D)elastic; an inferior
E)unit elastic; normal
A)inelastic; normal
B)inelastic; inferior
C)elastic; normal
D)elastic; an inferior
E)unit elastic; normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose a producer decides that if the price of his or her product is $10, the quantity supplied will be 1,000 units, and if the price is $11, the quantity supplied will be 1,100. The supply of the good is
A)elastic.
B)inelastic.
C)perfectly elastic.
D)unit elastic.
E)perfectly inelastic.
A)elastic.
B)inelastic.
C)perfectly elastic.
D)unit elastic.
E)perfectly inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Exhibit 19-1
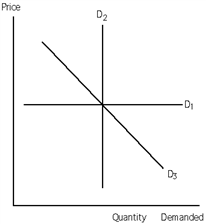
Refer to Exhibit 19-l. The demand for the good represented by demand curve D2 is
A)inelastic.
B)elastic.
C)unit elastic.
D)perfectly elastic.
E)perfectly inelastic.

Refer to Exhibit 19-l. The demand for the good represented by demand curve D2 is
A)inelastic.
B)elastic.
C)unit elastic.
D)perfectly elastic.
E)perfectly inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The quantity supplied of land is constant regardless of price. Suppose a tax is imposed on the rental price of land. Who will pay the greater share of such a tax?
A)The buyers will pay the entire share.
B)The sellers will pay the entire share.
C)The buyers and the sellers will pay equal shares.
D)The buyers will bear the greater share of the tax.
A)The buyers will pay the entire share.
B)The sellers will pay the entire share.
C)The buyers and the sellers will pay equal shares.
D)The buyers will bear the greater share of the tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Price elasticity of supply is perfectly inelastic if the coefficient of price elasticity of supply is
A)infinity.
B)1.
C)0.
D)-1.
A)infinity.
B)1.
C)0.
D)-1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The longer the period of time allowed for the ___________ of a good to adjust to a change in the price of the good, the ___________ the price elasticity of supply will be. This statement assumes that the quantity supplied __________ be altered with time.
A)producer; higher; can
B)consumer; higher; can
C)producer; lower; can
D)producer; lower; cannot
A)producer; higher; can
B)consumer; higher; can
C)producer; lower; can
D)producer; lower; cannot

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose a producer decides that if the price of her product is $42, the quantity supplied will be 1,000 units, and if the price is $45, the quantity supplied will be 1,300. The price elasticity of supply for the good is approximately
A)+1.9.
B)-0.26.
C)+0.26.
D)-3.8.
E)+3.8.
A)+1.9.
B)-0.26.
C)+0.26.
D)-3.8.
E)+3.8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If good Z has an income elasticity of 1.0, then demand for good Z is income __________ and the good is __________.
A)inelastic, normal
B)inelastic, inferior
C)elastic, normal
D)elastic, inferior
E)unit elastic, normal
A)inelastic, normal
B)inelastic, inferior
C)elastic, normal
D)elastic, inferior
E)unit elastic, normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If for good Z income elasticity is greater than 1, then demand for good Z is income __________, and good Z is a(n)__________ good.
A)inelastic; normal
B)inelastic; inferior
C)elastic; normal
D)elastic; inferior
E)unit elastic; normal
A)inelastic; normal
B)inelastic; inferior
C)elastic; normal
D)elastic; inferior
E)unit elastic; normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Exhibit 19-2
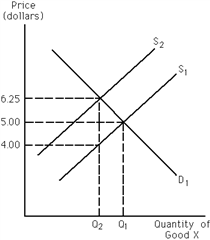
Refer to Exhibit 19-2. The market for good X is initially in equilibrium at $5. The government then places a per-unit tax on good X, as shown by the shift of S1 to S2. As a result, the equilibrium price
A)rises from $5.00 to $6.25.
B)falls from $5.00 to $4.00.
C)remains constant at $5.00.
D)falls from $6.25 to $5.00.

Refer to Exhibit 19-2. The market for good X is initially in equilibrium at $5. The government then places a per-unit tax on good X, as shown by the shift of S1 to S2. As a result, the equilibrium price
A)rises from $5.00 to $6.25.
B)falls from $5.00 to $4.00.
C)remains constant at $5.00.
D)falls from $6.25 to $5.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If the percentage change in quantity demanded of a good is less than the percentage change in buyer's income, then the good is said to be
A)income elastic.
B)income inelastic.
C)income unit elastic.
D)price elastic.
E)price inelastic.
A)income elastic.
B)income inelastic.
C)income unit elastic.
D)price elastic.
E)price inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Exhibit 19-1
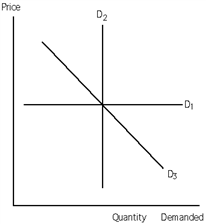
Refer to Exhibit 19-1. The demand for the good represented by demand curve D1 is
A)inelastic.
B)elastic.
C)unit elastic.
D)perfectly elastic.
E)perfectly inelastic.

Refer to Exhibit 19-1. The demand for the good represented by demand curve D1 is
A)inelastic.
B)elastic.
C)unit elastic.
D)perfectly elastic.
E)perfectly inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Price elasticity of supply is the percentage change in the quantity __________ of a good divided by the percentage change in __________.
A)demanded; the price of the good
B)supplied; the price of the good
C)demanded; the price of another good
D)supplied; the price of another good
E)demanded; income
A)demanded; the price of the good
B)supplied; the price of the good
C)demanded; the price of another good
D)supplied; the price of another good
E)demanded; income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The demand curve for good X is generally highly inelastic at and around the current price. If we assume that the supply curve is neither perfectly elastic nor perfectly inelastic, then who will pay the greater share of a tax placed on the production of good X?
A)The buyers will pay the greater share.
B)The sellers will pay the greater share.
C)The buyers and the sellers will pay equal shares.
D)There is not enough information to answer the question.
A)The buyers will pay the greater share.
B)The sellers will pay the greater share.
C)The buyers and the sellers will pay equal shares.
D)There is not enough information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If the percentage change in quantity demanded of a good is equal to the percentage change in buyer's income, then the good is said to be
A)income elastic.
B)income inelastic.
C)income unit elastic.
D)price unit elastic.
E)price inelastic.
A)income elastic.
B)income inelastic.
C)income unit elastic.
D)price unit elastic.
E)price inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



