Deck 15: Gross Domestic Product
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/109
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Gross Domestic Product
1
Which of the following purchases would be counted as a final good in the GDP calculation?
A) A family's purchase of a used car.
B) A speculator's purchase of 100 shares of Apple Computer stock.
C) A deli's purchase of bread for making its sandwiches.
D) A business's purchase of new office equipment.
A) A family's purchase of a used car.
B) A speculator's purchase of 100 shares of Apple Computer stock.
C) A deli's purchase of bread for making its sandwiches.
D) A business's purchase of new office equipment.
D
2
Payments to households not in exchange for goods and services currently produced are:
A) transfer payments.
B) government purchases.
C) consumption expenditures.
D) investment expenditures.
A) transfer payments.
B) government purchases.
C) consumption expenditures.
D) investment expenditures.
A
3
GDP is a measure of:
A) domestic production.
B) changes in the general level of prices.
C) material well-being.
D) social welfare.
A) domestic production.
B) changes in the general level of prices.
C) material well-being.
D) social welfare.
A
4
Based on the circular flow model, goods and services flow from:
A) households to businesses in product markets.
B) businesses to households in product markets.
C) households to businesses in factor markets.
D) businesses to households in factor markets.
A) households to businesses in product markets.
B) businesses to households in product markets.
C) households to businesses in factor markets.
D) businesses to households in factor markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The circular flow model assumes:
A) businesses and households own the factors of production.
B) businesses own the factors of production.
C) government owns the factors of production.
D) households own the factors of production.
A) businesses and households own the factors of production.
B) businesses own the factors of production.
C) government owns the factors of production.
D) households own the factors of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
GDP:
A) is the dollar value of all the final goods and services produced within the borders of a nation.
B) includes intermediate and final goods and services.
C) minus an allowance for depreciation of fixed capital equals GNP.
D) is a less-than-perfect measure of social well-being because it does not include exports and imports.
A) is the dollar value of all the final goods and services produced within the borders of a nation.
B) includes intermediate and final goods and services.
C) minus an allowance for depreciation of fixed capital equals GNP.
D) is a less-than-perfect measure of social well-being because it does not include exports and imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The circular flow of economic activity is a model of the:
A) flow of goods, resources, payments, and expenditures between the sectors of the economy.
B) influence of government on business behavior.
C) influence of business on consumers.
D) role of unions and government in the economy.
A) flow of goods, resources, payments, and expenditures between the sectors of the economy.
B) influence of government on business behavior.
C) influence of business on consumers.
D) role of unions and government in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which one of the following transactions would be included in GDP?
A) Ms. Kim pays $50 for a used picture frame at a neighborhood garage sale.
B) Mr. Doe donates $500 to his town's junior college scholarship fund.
C) Ms. Bartolini pays $500 to fix the front end of her car damaged in a recent accident.
D) Ms. Smith pays $5,000 to purchase 100 shares of Microsoft stock.
A) Ms. Kim pays $50 for a used picture frame at a neighborhood garage sale.
B) Mr. Doe donates $500 to his town's junior college scholarship fund.
C) Ms. Bartolini pays $500 to fix the front end of her car damaged in a recent accident.
D) Ms. Smith pays $5,000 to purchase 100 shares of Microsoft stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following expenditures would be included in GDP for this year?
A) The purchase of a new car.
B) The purchase of a new tire by General Motors for a new car.
C) The purchase of a used car.
D) The purchase of an intermediate good.
A) The purchase of a new car.
B) The purchase of a new tire by General Motors for a new car.
C) The purchase of a used car.
D) The purchase of an intermediate good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following market transactions of final goods and services are excluded from the computation of U.S. GDP?
A) Purchases of products such as wine, beer, hard liquor, and cigarettes.
B) Secondhand transactions, such as when a used car is sold.
C) New purchase that a resident of one state makes in a different state.
D) Purchases of necessities such as groceries and rent.
A) Purchases of products such as wine, beer, hard liquor, and cigarettes.
B) Secondhand transactions, such as when a used car is sold.
C) New purchase that a resident of one state makes in a different state.
D) Purchases of necessities such as groceries and rent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Economic values that are measured in units per period of time are referred to as:
A) stocks.
B) flows.
C) unit values.
D) dollars.
A) stocks.
B) flows.
C) unit values.
D) dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Gross domestic product (GDP) includes:
A) intermediate as well as final goods.
B) foreign goods as well as domestically produced goods.
C) used goods sold in the current time period.
D) only final goods and services.
A) intermediate as well as final goods.
B) foreign goods as well as domestically produced goods.
C) used goods sold in the current time period.
D) only final goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Activities that are directly included in GDP accounts include:
A) the value of housework done by householders.
B) the selling of illegal drugs.
C) unreported labor in sweatshops.
D) buying a ticket to a Yankees-Red Sox game on your day off.
A) the value of housework done by householders.
B) the selling of illegal drugs.
C) unreported labor in sweatshops.
D) buying a ticket to a Yankees-Red Sox game on your day off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following expenditures would not be included in GDP?
A) Purchase of a new lawnmower.
B) Purchase of a silver cup previously sold new in 1950.
C) Purchase of a ticket to the latest movie.
D) Purchase of a landscaping service.
A) Purchase of a new lawnmower.
B) Purchase of a silver cup previously sold new in 1950.
C) Purchase of a ticket to the latest movie.
D) Purchase of a landscaping service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The lower portion of the circular flow model contains factor markets in which households receive:
A) output of all final goods and services produced.
B) savings, spending, and investment.
C) goods and services.
D) wages, rents, interest, and profits.
A) output of all final goods and services produced.
B) savings, spending, and investment.
C) goods and services.
D) wages, rents, interest, and profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The lower portion of the circular flow model contains factor markets in which households provide:
A) goods and services.
B) savings, spending, and investment.
C) natural resources, labor, and capital.
D) output of all final goods and services produced.
A) goods and services.
B) savings, spending, and investment.
C) natural resources, labor, and capital.
D) output of all final goods and services produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Based on the circular flow model, money flows from households to businesses in:
A) factor markets.
B) product markets.
C) neither factor nor product markets.
D) both factor and product markets.
A) factor markets.
B) product markets.
C) neither factor nor product markets.
D) both factor and product markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following activities would be calculated as part of GDP accounts?
A) Drug trafficking.
B) Money laundry.
C) Prostitution.
D) Purchasing plastic surgery.
A) Drug trafficking.
B) Money laundry.
C) Prostitution.
D) Purchasing plastic surgery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Intermediate goods are goods and services used:
A) by the ultimate user.
B) by state and local governments.
C) as inputs.
D) both as inputs and final goods.
A) by the ultimate user.
B) by state and local governments.
C) as inputs.
D) both as inputs and final goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is an example of a stock rather than a flow?
A) Ana collects $5,000 per month rent on her property that she leases.
B) Brant mows 25 lawns per week.
C) Connie earns $75,000 per year.
D) Derek has $2,568 in his checking account.
A) Ana collects $5,000 per month rent on her property that she leases.
B) Brant mows 25 lawns per week.
C) Connie earns $75,000 per year.
D) Derek has $2,568 in his checking account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The largest component of GDP is:
A) personal consumption expenditures.
B) government spending.
C) durable goods.
D) net exports.
A) personal consumption expenditures.
B) government spending.
C) durable goods.
D) net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If you buy a book of U.S. postage stamps to use to mail love letters to your sweetheart, the purchase is considered part of:
A) C.
B) I.
C) G.
D) X.
A) C.
B) I.
C) G.
D) X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Exhibit 5-1 Use the information below to answer the following question(s).

Refer to Exhibit 5-1. What is this country's gross domestic product?
A) $1,225.
B) $1,305.
C) $1,365.
D) $1,440.

Refer to Exhibit 5-1. What is this country's gross domestic product?
A) $1,225.
B) $1,305.
C) $1,365.
D) $1,440.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Exhibit 5-7 GDP data (billions of dollars)
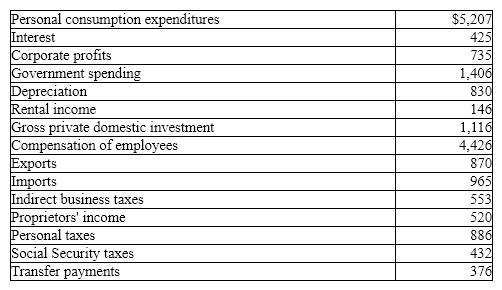
In Exhibit 5-7, and using the expenditures approach, gross domestic product (GDP) is:
A) $6,807 billion.
B) $7,082 billion.
C) $7,634 billion.
D) $7,637 billion.

In Exhibit 5-7, and using the expenditures approach, gross domestic product (GDP) is:
A) $6,807 billion.
B) $7,082 billion.
C) $7,634 billion.
D) $7,637 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which one of the following would count as investment in the GDP accounts?
A) Purchase of a new airplane by an airline.
B) Purchase of a U.S. government bond.
C) Purchase of 100 shares of Wal-Mart stock.
D) Purchase of an existing house.
A) Purchase of a new airplane by an airline.
B) Purchase of a U.S. government bond.
C) Purchase of 100 shares of Wal-Mart stock.
D) Purchase of an existing house.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Gross private domestic investment does not include:
A) spending for new houses.
B) spending to build up inventories.
C) unintentional inventory investment.
D) spending on employee salaries.
A) spending for new houses.
B) spending to build up inventories.
C) unintentional inventory investment.
D) spending on employee salaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Gross private domestic investment includes business:
A) purchases of capital goods, all new construction, and purchases of consumer durable goods.
B) purchases of capital goods, all new construction, and inventory investment.
C) purchases of capital goods, all new commercial construction, and inventory investment.
D) purchases of all types of durable goods, all new construction, and inventory investment.
A) purchases of capital goods, all new construction, and purchases of consumer durable goods.
B) purchases of capital goods, all new construction, and inventory investment.
C) purchases of capital goods, all new commercial construction, and inventory investment.
D) purchases of all types of durable goods, all new construction, and inventory investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which one of the following is an example of the circular flow model and shows the interdependence of households and firms?
A) Households demand their resources from the firms in the factor markets and, in turn, supply in the product market the goods and services produced by firms.
B) The firms go to the resource market to supply resources that households demand and, in turn, provide households with the goods and services produced for the product markets.
C) Households supply their resources to the firms in the factor markets and, in turn, demand in the product market the goods and services produced by the firms.
D) The firms in the factor markets pay to households in the form of wages, interest, rent and profit ⎯ for resources demanded.
A) Households demand their resources from the firms in the factor markets and, in turn, supply in the product market the goods and services produced by firms.
B) The firms go to the resource market to supply resources that households demand and, in turn, provide households with the goods and services produced for the product markets.
C) Households supply their resources to the firms in the factor markets and, in turn, demand in the product market the goods and services produced by the firms.
D) The firms in the factor markets pay to households in the form of wages, interest, rent and profit ⎯ for resources demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Durable and nondurable goods and services lumped together in the expenditure approach to measuring GDP are called:
A) Personal consumption.
B) Gross private domestic investment.
C) Government spending.
D) Inventory.
A) Personal consumption.
B) Gross private domestic investment.
C) Government spending.
D) Inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which one of the following statements is true ?
A) Money flows from households to firms for resources.
B) Money flows from households to foreign economies for exports.
C) Money flows from government to firms for resources.
D) Money flows from firms to households for resources.
A) Money flows from households to firms for resources.
B) Money flows from households to foreign economies for exports.
C) Money flows from government to firms for resources.
D) Money flows from firms to households for resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following would be included in the government expenditures component of GDP?
A) The export of 100 fighter jets to Japan
B) Construction costs of a new public school building
C) Food stamps used by the Smith family
D) A $1,000 check issued by the federal government as part of the Pell Grant program to help college students pay for school
A) The export of 100 fighter jets to Japan
B) Construction costs of a new public school building
C) Food stamps used by the Smith family
D) A $1,000 check issued by the federal government as part of the Pell Grant program to help college students pay for school

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If net exports are a negative number, then:
A) we are not buying enough exports.
B) we are exporting less than we are importing.
C) GDP will underestimated when measured using the expenditure approach.
D) we are exporting more than we are importing.
A) we are not buying enough exports.
B) we are exporting less than we are importing.
C) GDP will underestimated when measured using the expenditure approach.
D) we are exporting more than we are importing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which one of the following is not a component of GDP, as measured using the expenditure approach?
A) personal consumption
B) exports
C) interest
D) government spending
A) personal consumption
B) exports
C) interest
D) government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following would not be included in the government consumption expenditures and gross investment (G) category of GDP?
A) The payments made to Social Security recipients.
B) The expenditures made to repair a highway.
C) The spending for professors at state universities.
D) The purchase of new china for White House functions.
A) The payments made to Social Security recipients.
B) The expenditures made to repair a highway.
C) The spending for professors at state universities.
D) The purchase of new china for White House functions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If exports rise and imports fall, then:
A) GDP will increase.
B) GDP will decrease.
C) GDP may remain unchanged.
D) net exports will fall.
A) GDP will increase.
B) GDP will decrease.
C) GDP may remain unchanged.
D) net exports will fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Your purchase of a Gucci purse made in Italy would be classified as:
A) an export.
B) an investment good.
C) a durable good.
D) an import.
A) an export.
B) an investment good.
C) a durable good.
D) an import.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
New residential housing is counted in GDP as a(n):
A) durable consumption good.
B) household durable good.
C) investment good.
D) inventory expansion.
A) durable consumption good.
B) household durable good.
C) investment good.
D) inventory expansion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Resources that flow through the circular flow model include all of the following except :
A) land.
B) labor.
C) capital.
D) final goods.
A) land.
B) labor.
C) capital.
D) final goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Using the expenditure approach, GDP equals:
A) C + I + G + (X − M).
B) C + I + G + (X + M).
C) C + I − G + (X − M).
D) C + I + G − (X − M).
A) C + I + G + (X − M).
B) C + I + G + (X + M).
C) C + I − G + (X − M).
D) C + I + G − (X − M).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following would be classified as a personal consumption expenditure?
A) Your purchase of this economics course.
B) Your purchase of a newly constructed house
C) Your purchase of a preowned house.
D) Your purchase of one share of Microsoft stock.
A) Your purchase of this economics course.
B) Your purchase of a newly constructed house
C) Your purchase of a preowned house.
D) Your purchase of one share of Microsoft stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which approach to calculating GDP is computed using compensation of employees, rental income, profits, net interest, indirect business taxes, and depreciation?
A) The expenditure approach.
B) The income approach.
C) The product-market approach.
D) The circular-flow approach.
A) The expenditure approach.
B) The income approach.
C) The product-market approach.
D) The circular-flow approach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Exhibit 5-8 GDP data (billions of dollars)
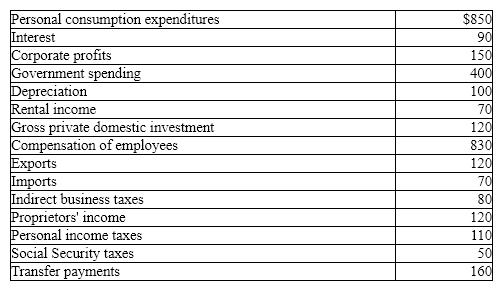
In Exhibit 5-8, and using the expenditures approach, gross domestic product (GDP) equals:
A) $1,420 billion.
B) $2,460 billion.
C) $2,430 billion.
D) $1,450 billion.

In Exhibit 5-8, and using the expenditures approach, gross domestic product (GDP) equals:
A) $1,420 billion.
B) $2,460 billion.
C) $2,430 billion.
D) $1,450 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Using the income approach, net interest is included because
A) households both receive and pay interest.
B) households pay but do not receive interest and firms receive but do not pay interest.
C) firms pay but do not receive interest and households receive but do not pay interest.
D) it is income to the government but not to households nor firms.
A) households both receive and pay interest.
B) households pay but do not receive interest and firms receive but do not pay interest.
C) firms pay but do not receive interest and households receive but do not pay interest.
D) it is income to the government but not to households nor firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Using the income approach, the largest component in the calculation of GDP is:
A) net interest.
B) rental income.
C) profits.
D) compensation of employees.
A) net interest.
B) rental income.
C) profits.
D) compensation of employees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Using the income approach, the smallest component in the calculation of GDP is:
A) net interest.
B) rental income.
C) profits.
D) compensation of employees.
A) net interest.
B) rental income.
C) profits.
D) compensation of employees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Exhibit 5-10 GDP data (billions of dollars)
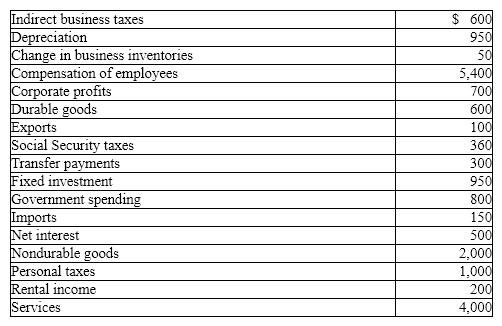
In Exhibit 5-10, GDP calculated using the income approach,
A) is greater than GDP calculated using the expenditure approach.
B) is equal to GDP calculated using the expenditure approach.
C) is less than GDP calculated using the expenditure approach.
D) is unrelated to GDP calculated using the expenditure approach.

In Exhibit 5-10, GDP calculated using the income approach,
A) is greater than GDP calculated using the expenditure approach.
B) is equal to GDP calculated using the expenditure approach.
C) is less than GDP calculated using the expenditure approach.
D) is unrelated to GDP calculated using the expenditure approach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Dividends, retained earnings, and corporate income taxes sum to which of the income categories in the income approach to computing GDP?
A) corporate profits
B) net interest
C) indirect business taxes
D) compensation of employees
A) corporate profits
B) net interest
C) indirect business taxes
D) compensation of employees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Using the income approach, an estimate of the value of capital worn out producing GDP is:
A) indirect business taxes.
B) capital consumption allowance or depreciation.
C) gross private domestic investment.
D) capital erosion estimate.
A) indirect business taxes.
B) capital consumption allowance or depreciation.
C) gross private domestic investment.
D) capital erosion estimate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Exhibit 5-10 GDP data (billions of dollars)
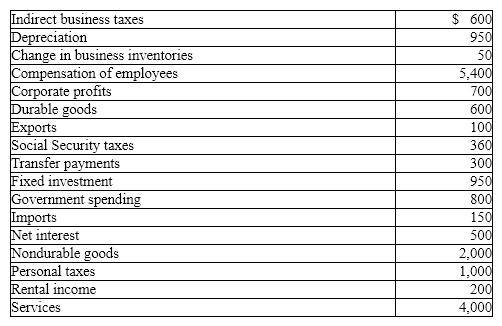
In Exhibit 5-10, and using the expenditures approach, compute net exports (X-M). Which of the following is correct ?
A) $500 billion.
B) $150 billion.
C) $100 billion.
D) -$50 billion.

In Exhibit 5-10, and using the expenditures approach, compute net exports (X-M). Which of the following is correct ?
A) $500 billion.
B) $150 billion.
C) $100 billion.
D) -$50 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Exhibit 5-11 GDP data (billions of dollars)
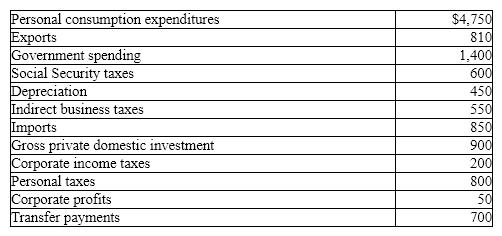
In Exhibit 5-11, and using the expenditures approach, gross domestic product (GDP) equals:
A) $7,010 billion.
B) $10,360 billion.
C) $9,660 billion.
D) $7,860 billion.

In Exhibit 5-11, and using the expenditures approach, gross domestic product (GDP) equals:
A) $7,010 billion.
B) $10,360 billion.
C) $9,660 billion.
D) $7,860 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Discuss the components of GDP using the expenditure approach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Brady pays $37,450 for a new car, including a federal excise tax of $700 and a state sales tax of $1,750. The indirect business tax value added to GDP under the income approach for this purchase is
A) $2,450 because this is income for the government.
B) $2,450 because this is profit for the firm.
C) $700 because only federal taxes are included in indirect business taxes; state taxes are excluded.
D) $1,750 because only state taxes are included in indirect business taxes; federal taxes are excluded.
A) $2,450 because this is income for the government.
B) $2,450 because this is profit for the firm.
C) $700 because only federal taxes are included in indirect business taxes; state taxes are excluded.
D) $1,750 because only state taxes are included in indirect business taxes; federal taxes are excluded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Exhibit 5-5 Gross domestic product data

As shown in Exhibit 5-5, using the income approach, gross domestic product (GDP) is:
A) $8,000 billion.
B) $8,800 billion.
C) $9,400 billion.
D) $11,000 billion.

As shown in Exhibit 5-5, using the income approach, gross domestic product (GDP) is:
A) $8,000 billion.
B) $8,800 billion.
C) $9,400 billion.
D) $11,000 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Victor works as a manager of a clothing store. He is paid an annual salary of $55,000. As part of his employee benefits, he receives private health insurance and his company contributes a small amount each month to a pension plan in his name. The company also pays taxes for Social Security and unemployment insurance. When considering the compensation of employees category of the income approach to GDP, which of the following lists includes the correct components of Victor's compensation?
A) salary and pension plan contribution only
B) salary, health insurance, and pension plan contribution only
C) Social Security taxes and unemployment insurance taxes only
D) salary, health insurance, pension plan contribution, Social Security taxes, unemployment insurance taxes
A) salary and pension plan contribution only
B) salary, health insurance, and pension plan contribution only
C) Social Security taxes and unemployment insurance taxes only
D) salary, health insurance, pension plan contribution, Social Security taxes, unemployment insurance taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Exhibit 5-10 GDP data (billions of dollars)
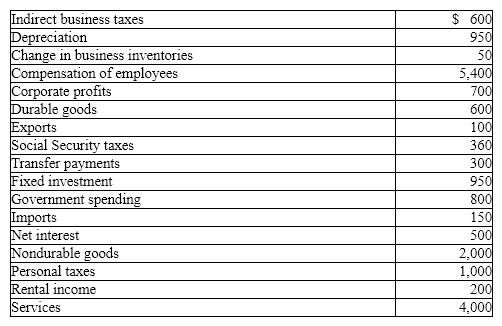
In Exhibit 5-10, and using the income approach, GDP equals
A) $8,350 billion.
B) $9,710 billion.
C) $5,400 billion.
D) $8,400 billion.

In Exhibit 5-10, and using the income approach, GDP equals
A) $8,350 billion.
B) $9,710 billion.
C) $5,400 billion.
D) $8,400 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The unreported or illegal production of goods and services in the economy that is not counted in GDP is termed:
A) money laundering.
B) the underground economy.
C) disposable personal income.
D) indirect national income.
A) money laundering.
B) the underground economy.
C) disposable personal income.
D) indirect national income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Depreciation or consumption of fixed capital measures:
A) the decline in the value of inventories caused by inflation.
B) the loss of productive ability due to capital intensive production.
C) capital that is wasted in the production process.
D) the value of existing capital stock used up in the production process.
A) the decline in the value of inventories caused by inflation.
B) the loss of productive ability due to capital intensive production.
C) capital that is wasted in the production process.
D) the value of existing capital stock used up in the production process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Exhibit 5-4 Gross domestic product data

As shown in Exhibit 5-4, using the income approach, gross domestic product (GDP) is:
A) $9,000 billion.
B) $6,600 billion.
C) $7,400 billion.
D) $8,000 billion.

As shown in Exhibit 5-4, using the income approach, gross domestic product (GDP) is:
A) $9,000 billion.
B) $6,600 billion.
C) $7,400 billion.
D) $8,000 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Why do national income accountants include indirect business taxes in the income approach to GDP computation?
A) Indirect business taxes are the allowances for the portion of capital worn out by producing GDP.
B) Indirect business taxes are part of firms' profits.
C) Indirect taxes are income payments to suppliers of resources.
D) Indirect business taxes are income for the government received through collection by firms.
A) Indirect business taxes are the allowances for the portion of capital worn out by producing GDP.
B) Indirect business taxes are part of firms' profits.
C) Indirect taxes are income payments to suppliers of resources.
D) Indirect business taxes are income for the government received through collection by firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The Department of Commerce sums the payments made to resources to arrive at GDP in the form of compensation of employees, rents, profits, net interest, indirect taxes, and depreciation. This method of deriving GDP is called the:
A) opportunity cost approach.
B) income approach.
C) expenditure approach.
D) monetarist approach.
A) opportunity cost approach.
B) income approach.
C) expenditure approach.
D) monetarist approach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following is a shortcoming of GDP?
A) GDP measures nonmarket transactions.
B) GDP includes an estimate of illegal transactions.
C) GDP includes an estimate of the value of household services.
D) GDP does not account for the distribution of consumption across a country's population.
A) GDP measures nonmarket transactions.
B) GDP includes an estimate of illegal transactions.
C) GDP includes an estimate of the value of household services.
D) GDP does not account for the distribution of consumption across a country's population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
National income (NI) is calculated by adjusting GDP for:
A) depreciation.
B) investment and net exports.
C) Social Security insurance contributions and transfer payments.
D) corporate and personal income taxes.
A) depreciation.
B) investment and net exports.
C) Social Security insurance contributions and transfer payments.
D) corporate and personal income taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Because of transactions which take place in the underground economy, the:
A) GDP calculation tends to overstate the actual value of goods sold in the economy.
B) value of the GDP calculation through the expenditure approach will be greater than the value calculated through the income approach.
C) GDP calculation tends to understate the actual value of goods sold in the economy.
D) value of the GDP calculation will be equal to the value of the national income calculation.
A) GDP calculation tends to overstate the actual value of goods sold in the economy.
B) value of the GDP calculation through the expenditure approach will be greater than the value calculated through the income approach.
C) GDP calculation tends to understate the actual value of goods sold in the economy.
D) value of the GDP calculation will be equal to the value of the national income calculation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Explain why GDP was never intended to be a measure of social well being.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following is a shortcoming of GDP?
A) GDP excludes changes in inventories.
B) GDP includes an estimate of illegal transactions.
C) GDP excludes nonmarket transactions.
D) GDP excludes business investment spending.
A) GDP excludes changes in inventories.
B) GDP includes an estimate of illegal transactions.
C) GDP excludes nonmarket transactions.
D) GDP excludes business investment spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If an artisan sells handmade jewelry at a craft fair
A) and does not report the income earned to the Internal Revenue Service, GDP is understated.
B) and does not report the income earned to the Internal Revenue Service, GDP is overstated.
C) and reports the income earned to the Internal Revenue Service, GDP is understated.
D) and reports the income earned to the Internal Revenue Service, GDP is overstated.
A) and does not report the income earned to the Internal Revenue Service, GDP is understated.
B) and does not report the income earned to the Internal Revenue Service, GDP is overstated.
C) and reports the income earned to the Internal Revenue Service, GDP is understated.
D) and reports the income earned to the Internal Revenue Service, GDP is overstated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
GDP underestimates our economic well-being:
A) because it includes the value of work done by illegal immigrants.
B) because it includes the value of work done by nannies.
C) because it ignores leisure.
D) because it includes the value of work done by householders.
A) because it includes the value of work done by illegal immigrants.
B) because it includes the value of work done by nannies.
C) because it ignores leisure.
D) because it includes the value of work done by householders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Because GDP does not account for improvements in the quality of goods, the GDP calculation:
A) tends to overstate the true value of output in the United States.
B) tends to understate the true value of output in the United States.
C) provides an accurate value of output in the United States.
D) provides the best measure of output in the United States.
A) tends to overstate the true value of output in the United States.
B) tends to understate the true value of output in the United States.
C) provides an accurate value of output in the United States.
D) provides the best measure of output in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
GDP includes:
A) the negative attributes from erosion and deforested landscape.
B) all quality improvements resulting from higher quality goods replacing inferior goods.
C) the cleaning-up expenses associated with pollution.
D) the value of leisure time.
A) the negative attributes from erosion and deforested landscape.
B) all quality improvements resulting from higher quality goods replacing inferior goods.
C) the cleaning-up expenses associated with pollution.
D) the value of leisure time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If the underground economy is sizable, then GDP will:
A) understate the economy's performance.
B) overstate the economy's performance.
C) fluctuate unpredictably.
D) accurately reflect this subterranean activity.
A) understate the economy's performance.
B) overstate the economy's performance.
C) fluctuate unpredictably.
D) accurately reflect this subterranean activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is a shortcoming of GDP?
A) GDP measures used goods and services.
B) GDP includes changes in inventories.
C) GDP includes the value of net exports.
D) GDP does not make an allowance for leisure time.
A) GDP measures used goods and services.
B) GDP includes changes in inventories.
C) GDP includes the value of net exports.
D) GDP does not make an allowance for leisure time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In recent years, people have benefited from greater amounts of leisure time. This trend:
A) has caused GDP to rise.
B) has caused GDP to fall.
C) made GDP fluctuate randomly.
D) is not accounted for in GDP.
A) has caused GDP to rise.
B) has caused GDP to fall.
C) made GDP fluctuate randomly.
D) is not accounted for in GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Exhibit 5-4 Gross domestic product data

As shown in Exhibit 5-4, national income (NI) is:
A) $6,000 billion.
B) $6,600 billion.
C) $7,200 billion.
D) $8,000 billion.

As shown in Exhibit 5-4, national income (NI) is:
A) $6,000 billion.
B) $6,600 billion.
C) $7,200 billion.
D) $8,000 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
GDP does not count:
A) the estimated value of homemaker production.
B) state and local government purchases.
C) spending for new homes.
D) changes in inventories.
A) the estimated value of homemaker production.
B) state and local government purchases.
C) spending for new homes.
D) changes in inventories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
National income is calculated as GDP:
A) plus depreciation.
B) plus exports.
C) minus imports.
D) minus depreciation.
A) plus depreciation.
B) plus exports.
C) minus imports.
D) minus depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If GDP is $9,560 billion and depreciation is $50 billion, then national income is
A) $9,610 billion.
B) $9,560 billion.
C) $9,510 billion.
D) $9,500 billion.
A) $9,610 billion.
B) $9,560 billion.
C) $9,510 billion.
D) $9,500 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Exhibit 5-5 Gross domestic product data

As shown in Exhibit 5-5, national income (NI) is:
A) $9,000 billion.
B) $9,900 billion.
C) $10,500 billion.
D) $11,000 billion.

As shown in Exhibit 5-5, national income (NI) is:
A) $9,000 billion.
B) $9,900 billion.
C) $10,500 billion.
D) $11,000 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If a homeowner sells a kitchen table and chairs that she no longer wants to use and does not report the income earned from the sale to the Internal Revenue Service, the value of GDP is
A) understated because this transaction took place in the underground economy.
B) overstated because the sale of the furniture is counted twice in GDP calculations.
C) unaffected by this transaction because the table and chairs were already counted in GDP as final goods when the homeowner bought them new.
D) understated because this purchase was a nonmarket transaction.
A) understated because this transaction took place in the underground economy.
B) overstated because the sale of the furniture is counted twice in GDP calculations.
C) unaffected by this transaction because the table and chairs were already counted in GDP as final goods when the homeowner bought them new.
D) understated because this purchase was a nonmarket transaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following is the most likely side effect of an increase in the relative size of the underground economy with the passage of time?
A) The growth rate of real GDP will tend to understate the growth rate of total output.
B) The growth rate of real GDP will tend to overstate the growth rate of total output.
C) The GDP deflator will tend to overstate any increase in inflation.
D) The GDP deflator will tend to understate any increase in inflation.
A) The growth rate of real GDP will tend to understate the growth rate of total output.
B) The growth rate of real GDP will tend to overstate the growth rate of total output.
C) The GDP deflator will tend to overstate any increase in inflation.
D) The GDP deflator will tend to understate any increase in inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
GDP overstates the productive capacity of a country when:
A) economic bads like pollution are produced and then must be cleaned up.
B) there is a sizable underground economy.
C) nonmarket production represents a large portion of the economy.
D) working conditions improve, allowing jobs to be completed safer and faster.
A) economic bads like pollution are produced and then must be cleaned up.
B) there is a sizable underground economy.
C) nonmarket production represents a large portion of the economy.
D) working conditions improve, allowing jobs to be completed safer and faster.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



