Deck 8: Nuclear Chemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/73
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Nuclear Chemistry
1
Which of these scientists characterized and began to explain radioactivity?
A) Becquerel
B) Curie
C) Einstein
D) Rutherford
E) Thompson
A) Becquerel
B) Curie
C) Einstein
D) Rutherford
E) Thompson
Rutherford
2
Radioactivity results from the decay of unstable _____.
A) electrons
B) light nuclei
C) heavy nuclei
D) photons
E) bonds
A) electrons
B) light nuclei
C) heavy nuclei
D) photons
E) bonds
heavy nuclei
3
Uranium-238 decays via alpha emission to produce _____.
A)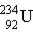
B)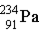
C)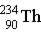
D)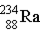
E)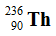
A)
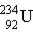
B)
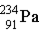
C)
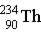
D)
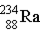
E)
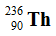
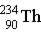
4
Which particle completes this equation?
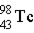
→ ____ +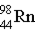
A) An alpha particle
B) A beta particle
C) A gamma particle
D) A positron
E) A proton
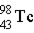
→ ____ +
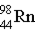
A) An alpha particle
B) A beta particle
C) A gamma particle
D) A positron
E) A proton

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which type of radioactive emission is analogous to an electron emission?
A) Positron
B) Neutron
C) Alpha particle
D) Gamma ray
E) Beta particle
A) Positron
B) Neutron
C) Alpha particle
D) Gamma ray
E) Beta particle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Identify the radioactive emission with the highest penetrating power.
A) Electrons
B) Beta particles
C) Alpha particles
D) Gamma rays
E) Neutrons
A) Electrons
B) Beta particles
C) Alpha particles
D) Gamma rays
E) Neutrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Thorium-234 decays via beta emission to produce _____.
A)
B)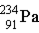
C)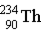
D)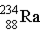
E)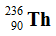
A)

B)
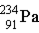
C)
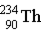
D)
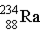
E)
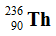

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following occurs during beta emission?
A) The mass number increases.
B) The mass number decreases.
C) The atomic number increases.
D) The atomic number decreases.
E) None of the above
A) The mass number increases.
B) The mass number decreases.
C) The atomic number increases.
D) The atomic number decreases.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following occurs during gamma emission?
A) The mass number increases.
B) The mass number decreases.
C) The atomic number increases.
D) The atomic number decreases.
E) The mass number and the atomic number remain the same.
A) The mass number increases.
B) The mass number decreases.
C) The atomic number increases.
D) The atomic number decreases.
E) The mass number and the atomic number remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which particle completes this equation? (Here, m means unstable Ba-137.)
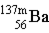
→ ____ +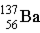
A) An alpha particle
B) A beta particle
C) A gamma particle
D) A positron
E) A proton
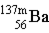
→ ____ +
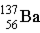
A) An alpha particle
B) A beta particle
C) A gamma particle
D) A positron
E) A proton

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following processes best describes a beta decay?
A) A proton is converted into a neutron and an electron.
B) A neutron is converted into a proton and an electron.
C) A proton and an electron are converted into a neutron.
D) A neutron and an electron are converted into a proton.
E) A neutron and a proton are converted into an electron.
A) A proton is converted into a neutron and an electron.
B) A neutron is converted into a proton and an electron.
C) A proton and an electron are converted into a neutron.
D) A neutron and an electron are converted into a proton.
E) A neutron and a proton are converted into an electron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which among the following scientists is responsible for coining the term "radioactivity" and is also the only person to receive two noble prizes in science?
A) Becquerel
B) Curie
C) Einstein
D) Rutherford
E) Thompson
A) Becquerel
B) Curie
C) Einstein
D) Rutherford
E) Thompson

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of these is the correct representation of a beta particle?
A)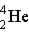
B)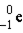
C)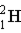
D)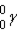
E)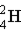
A)
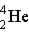
B)
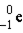
C)
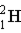
D)
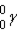
E)
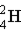

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which particle completes this equation?
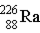
→ _____ +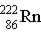
A) An alpha particle
B) A beta particle
C) A gamma particle
D) A positron
E) A proton
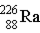
→ _____ +
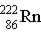
A) An alpha particle
B) A beta particle
C) A gamma particle
D) A positron
E) A proton

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following occurs during alpha emission?
A) The mass number increases.
B) The mass number remains the same.
C) The atomic number increases.
D) The atomic number decreases.
E) The atomic number remains the same.
A) The mass number increases.
B) The mass number remains the same.
C) The atomic number increases.
D) The atomic number decreases.
E) The atomic number remains the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of these is the correct representation of an alpha particle?
A)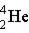
B)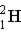
C)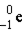
D)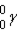
E)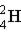
A)
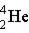
B)
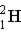
C)
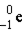
D)
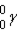
E)
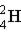

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which type of radioactive emission has the highest ionizing power?
A) Positron
B) Beta particle
C) Alpha particle
D) Gamma ray
E) Neutron
A) Positron
B) Beta particle
C) Alpha particle
D) Gamma ray
E) Neutron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which among the following scientists discovered radioactivity when a photographic plate was exposed to a piece of uranium?
A) Becquerel
B) Curie
C) Einstein
D) Rutherford
E) Thompson
A) Becquerel
B) Curie
C) Einstein
D) Rutherford
E) Thompson

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Krypton-85 decays via beta emission to produce _____.
A)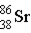
B)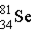
C)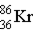
D)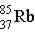
E)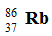
A)
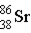
B)
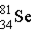
C)
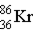
D)
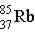
E)
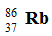

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Nuclear chemistry involves changes in the _____.
A) nucleus
B) valence electrons
C) bond number
D) inner electrons
E) photons
A) nucleus
B) valence electrons
C) bond number
D) inner electrons
E) photons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following terms describes the self-sustaining process of fission?
A) Binding energy
B) Chain reaction
C) Alpha emission
D) Gamma radiation
E) Radioactivity
A) Binding energy
B) Chain reaction
C) Alpha emission
D) Gamma radiation
E) Radioactivity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The _____ of a radioactive element is the time required for half the nuclei in a sample to decay.
A) half-life
B) mode of decay
C) emission series
D) decay constant
E) rate of decay
A) half-life
B) mode of decay
C) emission series
D) decay constant
E) rate of decay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A radioactive decay series will continue until _____.
A) an unstable nucleus disintegrates to produce radioactive decay particles
B) a stable nucleus is produced
C) the same number of alpha and beta emissions have taken place
D) the same number of beta and gamma emissions have taken place
E) none of these
A) an unstable nucleus disintegrates to produce radioactive decay particles
B) a stable nucleus is produced
C) the same number of alpha and beta emissions have taken place
D) the same number of beta and gamma emissions have taken place
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What percentage of a radioactive sample will remain after two half-lives?
A) 50%
B) 25%
C) 12.5%
D) 6.25%
E) 0%
A) 50%
B) 25%
C) 12.5%
D) 6.25%
E) 0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of these statements about fission reactions is incorrect ?
A) Fission reactions release a large amount of energy.
B) Two lighter nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus.
C) The fission of uranium-235 is initiated by the absorption of a neutron.
D) The first atomic bomb involved the fission of uranium-235 nuclei.
E) Fermi mistakenly discovered a fission reaction while synthesizing a new element.
A) Fission reactions release a large amount of energy.
B) Two lighter nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus.
C) The fission of uranium-235 is initiated by the absorption of a neutron.
D) The first atomic bomb involved the fission of uranium-235 nuclei.
E) Fermi mistakenly discovered a fission reaction while synthesizing a new element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The half-life of protactinium-231 is 3.25 × 10 4 years. How much time will 10.4 g of Pa-231 take to decay into 2.6 g?
A) 8.1 × 106 years
B) 4.0 × 105 years
C) 1.3 × 105 years
D) 6.5 × 104 years
E) 1.5 × 104 years
A) 8.1 × 106 years
B) 4.0 × 105 years
C) 1.3 × 105 years
D) 6.5 × 104 years
E) 1.5 × 104 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
There are no stable isotopes for elements with _____.
A) atomic number greater than 82
B) atomic number greater than 83
C) atomic number lower than 83
D) atomic number lower than 82
E) atomic number lower than 81
A) atomic number greater than 82
B) atomic number greater than 83
C) atomic number lower than 83
D) atomic number lower than 82
E) atomic number lower than 81

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The amount of fissile material necessary for a self-sustained fission reaction is known as _____.
A) radioactivity
B) tonnage
C) substantial mass
D) critical mass
E) chain reaction
A) radioactivity
B) tonnage
C) substantial mass
D) critical mass
E) chain reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The half-life of phosphorous-33 (P-33) is 25.3 days. How long will 64 g of P-33 take to decay to 1.0 g?
A) 10.67 days
B) 75 days
C) 100 days
D) 120 days
E) 151.8 days
A) 10.67 days
B) 75 days
C) 100 days
D) 120 days
E) 151.8 days

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following scientists discovered nuclear fission while attempting to create a synthetic element?
A) Fermi
B) Becquerel
C) Curie
D) Rutherford
E) Thompson
A) Fermi
B) Becquerel
C) Curie
D) Rutherford
E) Thompson

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following pairs of scientists built the first nuclear reactor?
A) Einstein and Rutherford
B) Hahn and Strassmann
C) Curie and Becquerel
D) Meitner and Fermi
E) Fermi and Szilard
A) Einstein and Rutherford
B) Hahn and Strassmann
C) Curie and Becquerel
D) Meitner and Fermi
E) Fermi and Szilard

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What was the secret code name for the building of the first atomic bomb?
A) Manhattan Project
B) Oralloy
C) Smiling Buddha
D) Project Albert
E) Site Y
A) Manhattan Project
B) Oralloy
C) Smiling Buddha
D) Project Albert
E) Site Y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Nitrogen-13 has a half-life of 10 minutes. What amount of a 16 mg sample would remain after 30 minutes?
A) 0.5 mg
B) 1 mg
C) 2 mg
D) 4 mg
E) 8 mg
A) 0.5 mg
B) 1 mg
C) 2 mg
D) 4 mg
E) 8 mg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following isotopes is naturally radioactive?
A)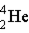
B)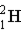
C)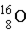
D)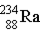
E)
A)
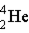
B)
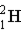
C)
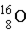
D)
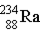
E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Radon-222 has a half-life of 3.82 days. How many alpha emissions would have occurred when a 10 g of radon-222 sample decays over 19.1 days?
A) 3.39 × 1020 emissions
B) 8.47 × 1020 emissions
C) 5.42 × 1021 emissions
D) 2.62 × 1022 emissions
E) 4.18 × 1025 emissions
A) 3.39 × 1020 emissions
B) 8.47 × 1020 emissions
C) 5.42 × 1021 emissions
D) 2.62 × 1022 emissions
E) 4.18 × 1025 emissions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following scientists did not participate in early research surrounding fission reactions?
A) Fermi
B) Strassmann
C) Curie
D) Meitner
E) Hahn
A) Fermi
B) Strassmann
C) Curie
D) Meitner
E) Hahn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What percentage of a radioactive sample will remain after one half-life?
A) 100%
B) 75%
C) 50%
D) 25%
E) 0%
A) 100%
B) 75%
C) 50%
D) 25%
E) 0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The half-life of Sr-83 is 32.4 hours. How many emissions would have occurred when 20 g of strontium-83 decays to 4.0 g?
A) 3.39 × 1020 emissions
B) 1.81 × 1022 emissions
C) 2.90 × 1022 emissions
D) 1.16 × 1023 emissions
E) 1.45 × 1023 emissions
A) 3.39 × 1020 emissions
B) 1.81 × 1022 emissions
C) 2.90 × 1022 emissions
D) 1.16 × 1023 emissions
E) 1.45 × 1023 emissions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following radioactive decays does not produce an atom of a different element?
A) Alpha
B) Beta
C) Gamma
D) Electron capture
E) Positron
A) Alpha
B) Beta
C) Gamma
D) Electron capture
E) Positron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What percentage of a radioactive sample will remain after three half-lives?
A) 50%
B) 25%
C) 12.5%
D) 6.25%
E) 0%
A) 50%
B) 25%
C) 12.5%
D) 6.25%
E) 0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Calculate the mass defect of 37 Cl if its mass is 36.9659 amu; the mass of proton is 1.0073 amu, and the mass of neutron is 1.0087 amu.
A) 2.693 amu
B) 0.388 amu
C) 0.341 amu
D) 0.332 amu
E) 0.263 amu
A) 2.693 amu
B) 0.388 amu
C) 0.341 amu
D) 0.332 amu
E) 0.263 amu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which among the following atoms has the most stable nuclei?
A) Ca
B) Fe
C) Mg
D) Ne
E) Xe
A) Ca
B) Fe
C) Mg
D) Ne
E) Xe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How many years old is a fossilized tree if it contains 25% of its original carbon-14? (Assume that the half-life of carbon-14 = 5,730 years.)
A) 1,433
B) 5,730
C) 11,460
D) 17,190
E) 22,920
A) 1,433
B) 5,730
C) 11,460
D) 17,190
E) 22,920

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of these radioactive dating methods is utilized in determining the age of the Earth?
A) Uranium dating
B) Carbon-14 dating
C) Nitrogen-14 dating
D) Oxygen-17 dating
E) Phosphorus dating
A) Uranium dating
B) Carbon-14 dating
C) Nitrogen-14 dating
D) Oxygen-17 dating
E) Phosphorus dating

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The energy that holds the nucleons together is known as the _____.
A) nuclear binding energy
B) mass defect
C) critical mass
D) fusion energy
E) substantial mass
A) nuclear binding energy
B) mass defect
C) critical mass
D) fusion energy
E) substantial mass

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of these equations gives the best explanation for mass defect?
A) E = h υ
B) c = λυ
C) Protons − neutrons
D) E = mc2
E) E = m/v
A) E = h υ
B) c = λυ
C) Protons − neutrons
D) E = mc2
E) E = m/v

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which among the following causes major problems for controlled energy generation by fission reaction?
A) Air pollution
B) Acid rain
C) Greenhouse gas emission
D) Waste disposal
E) Low energy yield per pound
A) Air pollution
B) Acid rain
C) Greenhouse gas emission
D) Waste disposal
E) Low energy yield per pound

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which among the following elements is the largest naturally occurring source of radiation?
A) Xenon
B) Argon
C) Neon
D) Radon
E) Krypton
A) Xenon
B) Argon
C) Neon
D) Radon
E) Krypton

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which among the following is the most significant problem in producing energy from fusion reactions?
A) Limited resources
B) Air pollution
C) Low-energy yield
D) Excessive radioactivity
E) Requirement of high temperature for fusion reactions
A) Limited resources
B) Air pollution
C) Low-energy yield
D) Excessive radioactivity
E) Requirement of high temperature for fusion reactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The difference between the experimentally determined mass and the sum of the masses of the protons and neutrons in an atom is known as the _____.
A) nuclear mass
B) molar mass
C) mass defect
D) decay mass
E) isotopic mass
A) nuclear mass
B) molar mass
C) mass defect
D) decay mass
E) isotopic mass

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Calculate the mass defect of 17 O if its mass is 16.9991 amu; the mass of proton is 1.0073 amu, and mass of neutron is 1.0087 amu.
A) 0.155 amu
B) 0.152 amu
C) 0.148 amu
D) 0.146 amu
E) 0.1376 amu
A) 0.155 amu
B) 0.152 amu
C) 0.148 amu
D) 0.146 amu
E) 0.1376 amu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which among the following radioactive exposures would be the most damaging if it occurs inside a human body?
A) Gamma radiation
B) Alpha emission
C) Beta emission
D) Positron emission
E) Electron emission
A) Gamma radiation
B) Alpha emission
C) Beta emission
D) Positron emission
E) Electron emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
How many half-lives has a fossilized tree undergone if it contains 12.5% of its original carbon-14?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 16
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Instantaneous exposure to radiation at a dosage of -____-_ rem or higher is lethal.
A) 40
B) 100
C) 200
D) 300
E) 500
A) 40
B) 100
C) 200
D) 300
E) 500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of these statements about fusion is correct ?
A) Two lighter nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus.
B) The fusion of uranium-238 nuclei was at the heart of the first atomic bomb.
C) Fusion waste products are typically more hazardous than fission materials.
D) Fusion reactions release a huge amount of energy but less than that of fission reactions.
E) All of these statements are correct.
A) Two lighter nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus.
B) The fusion of uranium-238 nuclei was at the heart of the first atomic bomb.
C) Fusion waste products are typically more hazardous than fission materials.
D) Fusion reactions release a huge amount of energy but less than that of fission reactions.
E) All of these statements are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The term used to describe the melting of an overheated nuclear reactor core is known as the _____.
A) Manhattan Project
B) chain reaction
C) China Syndrome
D) critical mass
E) nuclear binding energy
A) Manhattan Project
B) chain reaction
C) China Syndrome
D) critical mass
E) nuclear binding energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of these is the correct unit for measuring human radioactive exposure?
A) Roentgen
B) Curie
C) Rem
D) Sievert
E) Becquerel
A) Roentgen
B) Curie
C) Rem
D) Sievert
E) Becquerel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following nuclei has the highest binding energy?
A) Fe
B) Ar
C) U
D) Al
E) Na
A) Fe
B) Ar
C) U
D) Al
E) Na

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Instantaneous exposure to a radiation at a dosage of _____ or greater is may lead to radiation sickness.
A) 40 rem
B) 100 rem
C) 200 rem
D) 300 rem
E) 500 rem
A) 40 rem
B) 100 rem
C) 200 rem
D) 300 rem
E) 500 rem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The number of radioactive disintegrations per second is measured in units of ____.
A) Roentgen
B) Curie
C) Rem
D) Sievert
E) Becquerel
A) Roentgen
B) Curie
C) Rem
D) Sievert
E) Becquerel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of these is/are a possible effect of radiation exposure?
A) Death
B) Birth defects
C) Increased risk of cancer
D) Radiation sickness
E) All of these
A) Death
B) Birth defects
C) Increased risk of cancer
D) Radiation sickness
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The half-life of an element is 15 minutes. A sample contains 20,000 atoms of the element. How many atoms of the element will remain after 30 minutes?
A) 2,000
B) 5,000
C) 10,000
D) 2,500
E) 1,000
A) 2,000
B) 5,000
C) 10,000
D) 2,500
E) 1,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The SI unit of radiation exposure is _____.
A) Becquerel
B) Curie
C) Sievert
D) Rad
E) Roentgen
A) Becquerel
B) Curie
C) Sievert
D) Rad
E) Roentgen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of these is/are a common source of radiation exposure for humans?
A) X-rays
B) Cancer treatment
C) Radon gas
D) X-rays and cancer treatment
E) X-rays, cancer treatment, and radon gas
A) X-rays
B) Cancer treatment
C) Radon gas
D) X-rays and cancer treatment
E) X-rays, cancer treatment, and radon gas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What percentage of radiation exposure is a result of man-made sources?
A) 18%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 82%
E) 95%
A) 18%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 82%
E) 95%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A newly discovered rock formation contains fossils that are estimated to be 11,000 years old. Which radioactive dating method/methods would give the most accurate age of the fossils?
I. Uranium dating
II. Carbon-14 dating
III. Uranium-thorium dating
A) I only
B) II only
C) III
D) I and II
E) I and III
I. Uranium dating
II. Carbon-14 dating
III. Uranium-thorium dating
A) I only
B) II only
C) III
D) I and II
E) I and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
_____ contains the heaviest stable nucleus.
A) Bismuth
B) Uranium
C) Cobalt
D) Sodium
E) Potassium
A) Bismuth
B) Uranium
C) Cobalt
D) Sodium
E) Potassium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which among the following is not an application of nuclear chemistry?
A) Medicine
B) Energy
C) Radioactive dating
D) Warfare
E) All of these are applications of nuclear chemistry.
A) Medicine
B) Energy
C) Radioactive dating
D) Warfare
E) All of these are applications of nuclear chemistry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of these medical applications of nuclear chemistry is/are used in the treatment of cancerous tumors?
A) Tracers
B) Fission
C) Chemotherapy
D) Radiation therapy
E) Mass defect
A) Tracers
B) Fission
C) Chemotherapy
D) Radiation therapy
E) Mass defect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following radioactive elements was used in the Fat Man bomb?
A) Polonium
B) Thorium
C) Uranium
D) Plutonium
E) Radium
A) Polonium
B) Thorium
C) Uranium
D) Plutonium
E) Radium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The eruption of a volcano unearths rocks from deep within the Earth's crust. The rocks are estimated to be 9 × 10 9 years old. Which radioactive dating method/methods would give the most accurate age of the fossils?
I. Uranium dating
II. Carbon-14 dating
III. Sodium dating
A) I only
B) II only
C) III
D) I and III
E) II and III
I. Uranium dating
II. Carbon-14 dating
III. Sodium dating
A) I only
B) II only
C) III
D) I and III
E) II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of these health concerns is/are most common for higher radon exposure?
A) Thyroid cancer
B) Breast cancer
C) Lung cancer
D) Birth defects
E) Leukemia
A) Thyroid cancer
B) Breast cancer
C) Lung cancer
D) Birth defects
E) Leukemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Fermi and Szilard achieved a critical mass by using a pile of uranium and graphite that resulted in a self-sustaining fission reaction lasting _____ minutes.
A) 2.5
B) 5
C) 1.5
D) 4
E) 4.5
A) 2.5
B) 5
C) 1.5
D) 4
E) 4.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



