Deck 3: Working With Basic Schemas
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/91
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Working With Basic Schemas
1
When data values belong to a range rather than a set of values, you can create a list of possible values using the enumeration element.
False
2
XML Schema was created to replicate all DTD functionality in a schema; it does not support any data types beyond what can be found in DTDs.
False
3

The namespace prefix in the accompanying figure is xs .
True
4
When the mixed attribute is set to the value "true," XML Schema assumes that the element contains both text and child elements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
XML Schema supports a collection of built-in data types, but does not allow users to define their own.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A schema is an XML document that contains validation rules for an XML vocabulary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
User-derived data types fall into three categories: list, union, and restricted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A regular expression is a text string that defines a character pattern .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The choice compositor requires that child elements must appear either only once or not at all.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The xs:float data type is a double precision floating point number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
XML Schema allows for ample flexibility in the date and time format.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12

Given the accompanying figure, because the ID data type is built into the XML Schema, all elements and attributes from the XML Schema vocabulary must be identified using the xs namespace prefix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Schemas do not allow numeric data types.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
To specify the number of occurrences for a particular character or group of characters, a(n) quantifier can be appended to a character type or set .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15

The accompanying figure shows the xs:ID data type applied to the stuID attribute.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The code to specify the location of the schema file depends on whether the instance document has been placed in a namespace.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
XML Schema divides its user-derived data types into two classes: primitive and derived.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The root element in any XML Schema document is the main element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Unlike DTDs, schemas do not use a single standard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Attributes use the same collection of data types that simple type elements do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The _____ value of the use attribute means that the attribute cannot be used with the element.
A) forbid
B) preclude
C) prohibited
D) excluded
A) forbid
B) preclude
C) prohibited
D) excluded

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
To specify that an element contains both text and child elements, add the _____ attribute to the of an element.
A) double
B) multiple
C) aggregate
D) mixed
A) double
B) multiple
C) aggregate
D) mixed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
By convention, the namespace prefix _____ is assigned to the XML Schema namespace in order to identify elements and attributes that belong to the XML Schema vocabulary.
A) xsl
B) xst
C) xsm
D) xsd
A) xsl
B) xst
C) xsm
D) xsd

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
_____ is the most widely adopted schema standard.
A) DDML
B) RELAX
C) TREX
D) XML Schema
A) DDML
B) RELAX
C) TREX
D) XML Schema

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A file written in XML Schema typically ends with the _____ file extension.
A) )xsd
B) )xst
C) )xsl
D) )xs
A) )xsd
B) )xst
C) )xsl
D) )xs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Perhaps the most commonly used data type in XML Schema is _____ .
A) sequence
B) choice
C) empty
D) string
A) sequence
B) choice
C) empty
D) string

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
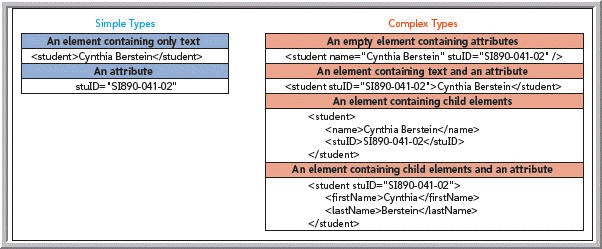
As shown in the accompanying figure, examples of a(n) _____ type of content are the value of an attribute or the textual content of an element.
A) aggregated
B) integrated
C) simple
D) complex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If both the maxOccurs and minOccurs attributes are missing, the element is assumed to occur _____.
A) zero times
B) once
C) twice
D) three times
A) zero times
B) once
C) twice
D) three times

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The _____ compositor allows any of the child elements to appear in any order in the instance document.
A) target
B) sequence
C) all
D) choice
A) target
B) sequence
C) all
D) choice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
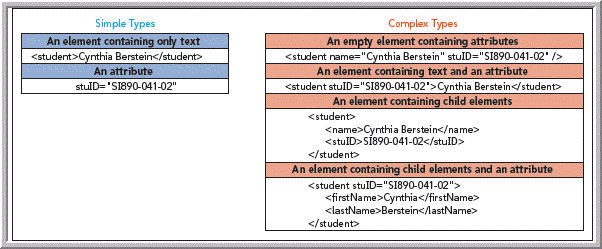
As shown in the accompanying figure, examples of a(n) _____ type of content are elements that contain attributes or elements that contain child elements.
A) simple
B) aggregated
C) complex
D) integrated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The _____ compositor defines a specific order for the child elements.
A) choice
B) all
C) target
D) sequence
A) choice
B) all
C) target
D) sequence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
DTDs employ a syntax called _____, which is different from the syntax used for XML.
A) SQL
B) EBNF
C) PHP
D) Perl
A) SQL
B) EBNF
C) PHP
D) Perl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An attribute is an example of a(n) _____ type.
A) simple
B) complex
C) integrated
D) aggregated
A) simple
B) complex
C) integrated
D) aggregated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The _____ and extension elements are important tools used by XML Schema to derive new data types and design complex content models.
A) additive
B) simpleContent
C) integrated
D) extensible
A) additive
B) simpleContent
C) integrated
D) extensible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The maxOccurs attribute can have a value of _____ for unlimited occurrences of the child element.
A) unlimited
B) max
C) 100
D) unbounded
A) unlimited
B) max
C) 100
D) unbounded

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If an element contains attributes, you have to extend the simple content model to include attributes through the use of the < ____ _ > tag.
A) extension
B) extensible
C) additive
D) integrated
A) extension
B) extensible
C) additive
D) integrated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

The item indicated with the arrow in the accompanying figure is the XML Schema namespace _____ .
A) URL
B) URC
C) URI
D) URR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The _____ data type allows an element to contain any text string.
A) pcdata
B) text
C) alpha
D) string
A) pcdata
B) text
C) alpha
D) string

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
To indicate whether an attribute is required, you add the _____ attribute to the element declaration or reference.
A) optional
B) require
C) use
D) attach
A) optional
B) require
C) use
D) attach

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
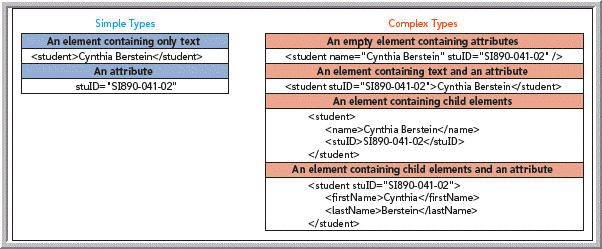
As shown in the accompanying figure, XML Schema supports _____ types of content.
A) two
B) three
C) four
D) six

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A base type is one of _____ fundamental data types not defined in terms of other types.
A) 15
B) 19
C) 25
D) 29
A) 15
B) 19
C) 25
D) 29

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The _____ character type is a word character.
A) \w
B) \W
C) \B
D) \b
A) \w
B) \W
C) \B
D) \b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Instead of a pattern involving specific characters, you usually want a more general pattern involving _____ types that represent different kinds of characters.
A) entity
B) character
C) decimal
D) facet
A) entity
B) character
C) decimal
D) facet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
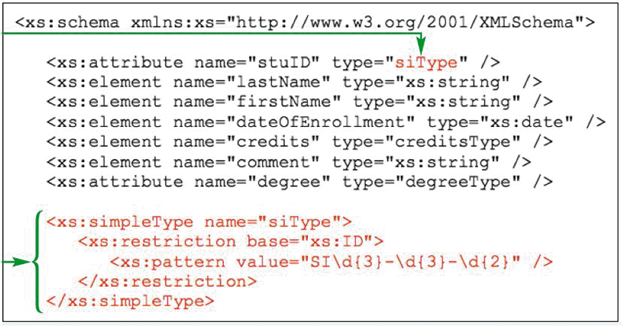
According to the accompanying figure, the stuID values must follow the rules of what data type?
A) degreeType
B) siType
C) simple
D) string

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A _____ can be appended to a character type or set to specify the number of occurrences for a particular character or group of characters.
A) certificate
B) quantifier
C) scope
D) model group
A) certificate
B) quantifier
C) scope
D) model group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A _____ expression is a text string that defines a character pattern.
A) stated
B) defined
C) regular
D) base
A) stated
B) defined
C) regular
D) base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The _____ facet specifies the maximum number of decimal places to the right of the decimal point in the data type's value.
A) pattern
B) enumeration
C) fractionDigits
D) length
A) pattern
B) enumeration
C) fractionDigits
D) length

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A _____ is a text string of word characters around a word.
A) pattern value
B) concatenation
C) precursor
D) boundary
A) pattern value
B) concatenation
C) precursor
D) boundary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following is a category of data type in XML Schema?
A) common
B) built-in
C) static
D) dynamic
A) common
B) built-in
C) static
D) dynamic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The _____ data type is a text string containing valid XML names with no white space.
A) xs:string
B) xs:token
C) xs:NMTOKEN
D) xs:IDREFS
A) xs:string
B) xs:token
C) xs:NMTOKEN
D) xs:IDREFS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Date values must be entered in the format _____.
A) yyyymmdd
B) yymmdd
C) yyyy-mm-dd
D) yy/mm/dd
A) yyyymmdd
B) yymmdd
C) yyyy-mm-dd
D) yy/mm/dd

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The _____ facet constrains the data type to a specified list of values.
A) length
B) enumeration
C) member
D) pattern
A) length
B) enumeration
C) member
D) pattern

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The _____ facet specifies the maximum number of decimals in the data type's value.
A) fractionDigits
B) totalDigits
C) whiteSpace
D) pattern
A) fractionDigits
B) totalDigits
C) whiteSpace
D) pattern

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
With the xs:float data type, non-numeric values can be represented by _____.
A) INF
B) NaN
C) BIN
D) 0
A) INF
B) NaN
C) BIN
D) 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A primitive data type is also known as a(n) _____ type.
A) main
B) base
C) key
D) indexed
A) main
B) base
C) key
D) indexed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
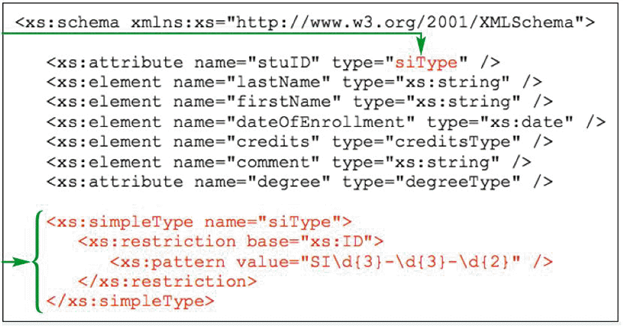
According to the data types defined in the accompanying figure, what is the form that the unique IDs must take?
A) SI###-###-###
B) AAA###-###-#
C) SI###-###-##
D) A###-###-#

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Derived data types share many of the same characteristics as the _____ data types they are derived from, but with one or two additional restrictions or modifications.
A) token
B) dynamic
C) string
D) primitive
A) token
B) dynamic
C) string
D) primitive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The _____ facet has three values: preserve , replace , and collapse .
A) whiteSpace
B) length
C) maxExclusive
D) pattern
A) whiteSpace
B) length
C) maxExclusive
D) pattern

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The _____ data type is a text string similar to the NMTOKEN data type, except that names must begin with a letter or the character " : " or " - ".
A) xs:token
B) xs:ENTITY
C) xs:Name
D) xs:NCName
A) xs:token
B) xs:ENTITY
C) xs:Name
D) xs:NCName

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A list data type uses _____ as the delimiter.
A) commas
B) tabs
C) white space
D) Any of the above.
A) commas
B) tabs
C) white space
D) Any of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 3-2
Judy has begun to apply the basic information that you have given her about schemas, and she would now like your help in mastering the details of how schemas work.
Judy has included the following element definition in her schema:
Judy would like to indicate that the ingredient element must appear at least once in a recipe, and that it cannot appear more than 20 times. Which of the following should she add to the element declaration to indicate these restrictions?
A) occurs="1:20"
B) occurs="[1:20]"
C) use="1:20"
D) minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="20"
Judy has begun to apply the basic information that you have given her about schemas, and she would now like your help in mastering the details of how schemas work.
Judy has included the following element definition in her schema:
Judy would like to indicate that the ingredient element must appear at least once in a recipe, and that it cannot appear more than 20 times. Which of the following should she add to the element declaration to indicate these restrictions?
A) occurs="1:20"
B) occurs="[1:20]"
C) use="1:20"
D) minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="20"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 3-1
Judy wants to be able to validate the XML documents that she uses for recipes. These documents include numeric elements that specify ingredient amounts and cooking times, so you recommend that she use a schema instead of a DTD, and you teach her some of the key facts about schemas.
Judy has an element called "recipeName" that she uses to record the name of a recipe. This element only contains text. Which of the following would be a valid XML Schema definition for this element?
A)recipeName
B)recipeName
C)
D)
Judy wants to be able to validate the XML documents that she uses for recipes. These documents include numeric elements that specify ingredient amounts and cooking times, so you recommend that she use a schema instead of a DTD, and you teach her some of the key facts about schemas.
Judy has an element called "recipeName" that she uses to record the name of a recipe. This element only contains text. Which of the following would be a valid XML Schema definition for this element?
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The _____ value of the use attribute means that the attribute must always appear with the element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A(n) _____ complex type has no name attribute used in the opening tag.
A) empty
B) named
C) anonymous
D) global scope
A) empty
B) named
C) anonymous
D) global scope

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A(n) _____ type contains a single value in XML Schema.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The _____ value of the use attribute means that the use of the attribute is optional with the element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 3-2
Judy has begun to apply the basic information that you have given her about schemas, and she would now like your help in mastering the details of how schemas work.
Judy has included the following element definition in her schema:
In this schema, w hat type of element is ingredient ?
A) an element containing only attributes
B) an element with nested children
C) an element with nested elements and attributes
D) a sequence element
Judy has begun to apply the basic information that you have given her about schemas, and she would now like your help in mastering the details of how schemas work.
Judy has included the following element definition in her schema:
In this schema, w hat type of element is ingredient ?
A) an element containing only attributes
B) an element with nested children
C) an element with nested elements and attributes
D) a sequence element

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The XML document to be validated is called the _____ document.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 3-2
Judy has begun to apply the basic information that you have given her about schemas, and she would now like your help in mastering the details of how schemas work.
Judy has included the following element definition in her schema:
Judy would like to indicate that the "substitution" attribute is a required attribute. Which of the following attribute definitions shows how to accomplish this?
A)
B)
C)
D)
Judy has begun to apply the basic information that you have given her about schemas, and she would now like your help in mastering the details of how schemas work.
Judy has included the following element definition in her schema:
Judy would like to indicate that the "substitution" attribute is a required attribute. Which of the following attribute definitions shows how to accomplish this?
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70

The arrow in the accompanying figure points to the XML Schema _____ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 3-1
Judy wants to be able to validate the XML documents that she uses for recipes. These documents include numeric elements that specify ingredient amounts and cooking times, so you recommend that she use a schema instead of a DTD, and you teach her some of the key facts about schemas.
You tell Judy that there are multiple vocabularies available for schema. Which of them is the most widely adopted?
A) XML Data
B) XML Schema
C) Regular Language for XML
D) Schematron
Judy wants to be able to validate the XML documents that she uses for recipes. These documents include numeric elements that specify ingredient amounts and cooking times, so you recommend that she use a schema instead of a DTD, and you teach her some of the key facts about schemas.
You tell Judy that there are multiple vocabularies available for schema. Which of them is the most widely adopted?
A) XML Data
B) XML Schema
C) Regular Language for XML
D) Schematron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 3-1
Judy wants to be able to validate the XML documents that she uses for recipes. These documents include numeric elements that specify ingredient amounts and cooking times, so you recommend that she use a schema instead of a DTD, and you teach her some of the key facts about schemas.
Which of the following is NOT an advantage of schemas over DTDs?
A) They are more flexible than DTDs in dealing with mixed content.
B) They support more data types than DTDs.
C) They provide better support for namespaces.
D) They are simpler to create and maintain.
Judy wants to be able to validate the XML documents that she uses for recipes. These documents include numeric elements that specify ingredient amounts and cooking times, so you recommend that she use a schema instead of a DTD, and you teach her some of the key facts about schemas.
Which of the following is NOT an advantage of schemas over DTDs?
A) They are more flexible than DTDs in dealing with mixed content.
B) They support more data types than DTDs.
C) They provide better support for namespaces.
D) They are simpler to create and maintain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A(n) _____ type contains two or more values placed within a defined structure in XML Schema.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
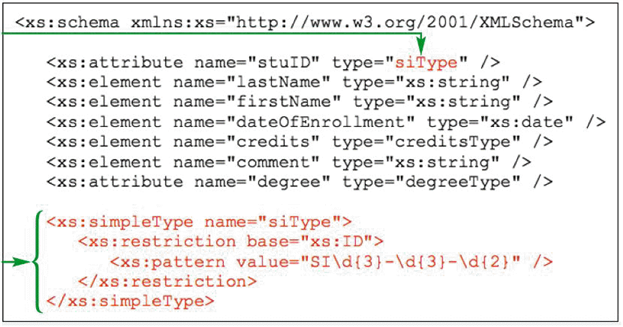
Which of the following is a valid ID according to the accompanying figure?
A) SI333-567-88
B) M97-56-344
C) SI789-456
D) Any of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 3-2
Judy has begun to apply the basic information that you have given her about schemas, and she would now like your help in mastering the details of how schemas work.
Judy has included the following element definition in her schema:
In her definition of the recipe element, Judy would like to reference the existing definition of the ingredient element. Which of the following element declarations accomplishes this?
A)
B)
C)
D)
Judy has begun to apply the basic information that you have given her about schemas, and she would now like your help in mastering the details of how schemas work.
Judy has included the following element definition in her schema:
In her definition of the recipe element, Judy would like to reference the existing definition of the ingredient element. Which of the following element declarations accomplishes this?
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 3-1
Judy wants to be able to validate the XML documents that she uses for recipes. These documents include numeric elements that specify ingredient amounts and cooking times, so you recommend that she use a schema instead of a DTD, and you teach her some of the key facts about schemas.
Judy has an attribute called "recipeType" that she uses to record whether the recipe is for an appetizer, entree, dessert, or other type of dish. This attribute only contains text. Which of the following would be a valid XML Schema definition for this attribute?
A)recipeType
B)
C)recipeType
D)
Judy wants to be able to validate the XML documents that she uses for recipes. These documents include numeric elements that specify ingredient amounts and cooking times, so you recommend that she use a schema instead of a DTD, and you teach her some of the key facts about schemas.
Judy has an attribute called "recipeType" that she uses to record whether the recipe is for an appetizer, entree, dessert, or other type of dish. This attribute only contains text. Which of the following would be a valid XML Schema definition for this attribute?
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
DTDs employ a syntax called _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 3-1
Judy wants to be able to validate the XML documents that she uses for recipes. These documents include numeric elements that specify ingredient amounts and cooking times, so you recommend that she use a schema instead of a DTD, and you teach her some of the key facts about schemas.
You teach Judy about the differences between simple and complex data types. Which of the following would NOT require a complex type?
A) an element containing only text
B) an empty element containing attributes
C) an element containing child elements
D) an element containing child elements and an attribute
Judy wants to be able to validate the XML documents that she uses for recipes. These documents include numeric elements that specify ingredient amounts and cooking times, so you recommend that she use a schema instead of a DTD, and you teach her some of the key facts about schemas.
You teach Judy about the differences between simple and complex data types. Which of the following would NOT require a complex type?
A) an element containing only text
B) an empty element containing attributes
C) an element containing child elements
D) an element containing child elements and an attribute

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 3-2
Judy has begun to apply the basic information that you have given her about schemas, and she would now like your help in mastering the details of how schemas work.
Judy has included the following element definition in her schema:
Judy would like to add a definition for an attribute called "substitution" to the element definition. It will indicate a possible substitution for the ingredient specified by the element. Where should the definition of this attribute appear in the element definition?
A) within the definition of the element
B) between the lines for and
C) between the lines for
D) between the lines for and
Judy has begun to apply the basic information that you have given her about schemas, and she would now like your help in mastering the details of how schemas work.
Judy has included the following element definition in her schema:
Judy would like to add a definition for an attribute called "substitution" to the element definition. It will indicate a possible substitution for the ingredient specified by the element. Where should the definition of this attribute appear in the element definition?
A) within the definition of the
B) between the lines for
C) between the lines for
D) between the lines for and

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The string data type is a(n) _____ data type, which is part of the XML Schema language.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



