Deck 3: Understanding Structure
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Understanding Structure
1
In a selection structure, you perform an action or task, and then you perform the next action in order.
False
2
The following pseudocode is an example of a ____ structure. get firstNumber
Get secondNumber
Add firstNumber and secondNumber
Print result
A)sequence
B)decision
C)loop
D)nested
Get secondNumber
Add firstNumber and secondNumber
Print result
A)sequence
B)decision
C)loop
D)nested
A
3
In a structured program, any structure can be nested within another structure.
True
4
The case structure is a variation of the sequence structure and the do loop is a variation of the while loop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
No matter how complicated it is, any set of steps can always be reduced to combinations of the two basic structures of sequence and loop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Programs that use _____ code logic are unstructured programs that do not follow the rules of structured logic.
A)case
B)loop
C)spaghetti
D)nested
A)case
B)loop
C)spaghetti
D)nested

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
if-else examples can also be called ____ because they contain the action taken when the tested condition is true and the action taken when it is false.
A)do loops
B)single-alternative selections
C)repetition
D)dual-alternative selections
A)do loops
B)single-alternative selections
C)repetition
D)dual-alternative selections

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
With a(n)____, you perform an action or task, and then you perform the next action, in order.
A)ordered structure
B)sequence problem
C)sequence structure
D)loop sequence
A)ordered structure
B)sequence problem
C)sequence structure
D)loop sequence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The following pseudocode is an example of a ____ structure.
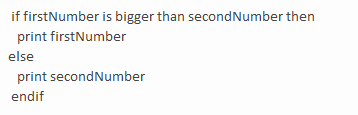
A)sequence
B)decision
C)loop
D)nested
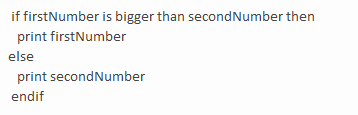
A)sequence
B)decision
C)loop
D)nested

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Fill in the blank in the following pseudocode: 
A)then
B)while
C)do
D)else

A)then
B)while
C)do
D)else

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Pseudocode uses the end-structure statement ____ to clearly show where the structure ends.
A)end
B)endstructure
C)endloop
D)endif
A)end
B)endstructure
C)endloop
D)endif

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
You may hear programmers refer to looping as ____.
A)execution
B)selection
C)iteration
D)case
A)execution
B)selection
C)iteration
D)case

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Structured programs use spaghetti code logic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The following pseudocode is an example of a ____ structure. 
A)sequence
B)decision
C)loop
D)nested

A)sequence
B)decision
C)loop
D)nested

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The action or actions that occur within a loop are known as a(n)____.
A)loop body
B)action body
C)loop internals
D)structure body
A)loop body
B)action body
C)loop internals
D)structure body

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
As a general rule, an eof question should always come immediately after an input statement because the end-of-file condition will be detected at input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Because you may stack and nest structures while retaining the overall structure, it might be difficult to determine whether a flowchart as a whole is structured.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Structured programming is sometimes called goto-less programming.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A structured program must contain a sequence, selection, and loop structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Repetition and sequence are alternate names for a loop structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The do loop is a variation of the ____ loop.
A)if-then-else
B)while
C)case
D)sequence
A)if-then-else
B)while
C)case
D)sequence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A ____ read is an added statement that gets the first input value in a program.
A)nested
B)stacked
C)posttest
D)priming
A)nested
B)stacked
C)posttest
D)priming

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A group of statements that execute as a single unit are called a(n)____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Attaching structures end to end is called ____ structures.
A)linking
B)stacking
C)nesting
D)building
A)linking
B)stacking
C)nesting
D)building

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The priming read is an example of a(n)____ task.
A)declaration
B)exit
C)housekeeping
D)selection
A)declaration
B)exit
C)housekeeping
D)selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Structured programming is sometimes called ____________________-less programming.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
One way to straighten out an unstructured flowchart segment is to use the ____ method.
A)spaghetti code
B)spaghetti bowl
C)restructuring
D)priming
A)spaghetti code
B)spaghetti bowl
C)restructuring
D)priming

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Some people call the selection structure a(n)____________________ statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A loop must return to the ____ question at some later point in a structure.
A)start loop
B)loop-controlling
C)master loop
D)continue loop
A)start loop
B)loop-controlling
C)master loop
D)continue loop

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Structured programs can be easily broken down into routines or ____ that can be assigned to any number of programmers.
A)segments
B)modules
C)units
D)sequences
A)segments
B)modules
C)units
D)sequences

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When you ____________________ structures, the statements that start and end a structure are always on the same level and always in pairs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A(n)____________________ can contain any number of tasks, but there is no option to branch off and skip any of the tasks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Structures can be stacked or connected to one another at their ____.
A)entry points only
B)exit points only
C)entry or exit points
D)entry or combination points
A)entry points only
B)exit points only
C)entry or exit points
D)entry or combination points

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The following pseudocode is an example of ____. 
A)nesting
B)stacking
C)single alternative structures
D)a posttest

A)nesting
B)stacking
C)single alternative structures
D)a posttest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Placing a structure within another structure is called ____ structures.
A)nesting
B)stacking
C)shelling
D)selecting
A)nesting
B)stacking
C)shelling
D)selecting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In older languages, you could leave a selection or loop before it was complete by using a ____ statement.
A)loop
B)go next
C)next
D)go to
A)loop
B)go next
C)next
D)go to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A structured program includes only combinations of the three basic structures: ____.
A)sequence, iteration, and loop
B)iteration, selection, and loop
C)sequence, selection, and loop
D)identification, selection, and loop
A)sequence, iteration, and loop
B)iteration, selection, and loop
C)sequence, selection, and loop
D)identification, selection, and loop

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The case structure is a variation of the ____ structure.
A)selection
B)while
C)sequence
D)do
A)selection
B)while
C)sequence
D)do

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The maximum number of entry points that any programming structure can have is ____.
A)zero
B)one
C)three
D)five
A)zero
B)one
C)three
D)five

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The following pseudocode is an example of ____. 
A)nesting
B)stacking
C)a posttest
D)a pretest

A)nesting
B)stacking
C)a posttest
D)a pretest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Describe how you can straighten out an unstructured flowchart segment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Explain the difference between the representation of a decision structure and a loop in a flowchart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Define the term structure as it relates to programming.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Describe a loop structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What are the characteristics of a structured program?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
All logic problems can be solved using only these three structures: sequence, selection, and loop. The three structures, of course, can be combined in an infinite number of ways. What are two general ways structures can be combined?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Why does spaghetti code have a shorter shelf life than structured code?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Why is it best to use only three programming structures?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What are the three basic structures and how can they be used?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Rewrite the following as a while loop:
do
pay bills
while more bills remain to be paid
do
pay bills
while more bills remain to be paid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



