Deck 20: Chromosomes and Human Genetics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/85
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Chromosomes and Human Genetics
1
How many genes does a Y chromosome carry?
A)100
B)1,400
C)2,800
D)14,000
E)28,000
A)100
B)1,400
C)2,800
D)14,000
E)28,000
A
2
During meiosis homologous pairs of chromosomes ____.
A)move together to the newly formed cells
B)ultimately create diploid cells
C)are sorted in a dependent fashion
D)may exchange corresponding segments
E)stay in the cytoplasm
A)move together to the newly formed cells
B)ultimately create diploid cells
C)are sorted in a dependent fashion
D)may exchange corresponding segments
E)stay in the cytoplasm
D
3
Karyotype analysis ____.
A)is a means of detecting and reducing mutagenic agents.
B)is a surgical technique that separates chromosomes that have failed to segregate properly during meiosis II.
C)can be used in prenatal diagnosis to detect chromosomal mutations and genetic disorders in embryos.
D)replaces defective alleles with normal ones.
E)is used in DNA analysis for paternity.
A)is a means of detecting and reducing mutagenic agents.
B)is a surgical technique that separates chromosomes that have failed to segregate properly during meiosis II.
C)can be used in prenatal diagnosis to detect chromosomal mutations and genetic disorders in embryos.
D)replaces defective alleles with normal ones.
E)is used in DNA analysis for paternity.
C
4
What explains why even close relatives have a varied mix of genetic traits?
A)heterozygous
B)allele variation
C)co-dominance
D)independent assortment
E)gene exchange
A)heterozygous
B)allele variation
C)co-dominance
D)independent assortment
E)gene exchange

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which cell type is most often used in karyotyping?
A)bone
B)nerve
C)epithelial
D)blood
E)cartilage
A)bone
B)nerve
C)epithelial
D)blood
E)cartilage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A female haploid cell has which sex chromosome combination?
A)XX
B)XY
C)YY
D)X
E)Y
A)XX
B)XY
C)YY
D)X
E)Y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Chromosomes are most easily identified in which mitotic stage?
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)anaphase
D)telophase
E)cytokinesis
A)prophase
B)metaphase
C)anaphase
D)telophase
E)cytokinesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A male diploid cell has which sex chromosome combination?
A)XX
B)XY
C)YY
D)X
E)Y
A)XX
B)XY
C)YY
D)X
E)Y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
How many genes does an X chromosome carry?
A)100
B)1,400
C)2,800
D)14,000
E)28,000
A)100
B)1,400
C)2,800
D)14,000
E)28,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which chemical is used to stop mitosis in metaphase?
A)AZT
B)histamine
C)UV light
D)eosin
E)colchicine
A)AZT
B)histamine
C)UV light
D)eosin
E)colchicine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Closely linked genes nearly always end up ____.
A)crossing over
B)assorting independently
C)in the same gamete
D)segregated during meiosis
E)inverted
A)crossing over
B)assorting independently
C)in the same gamete
D)segregated during meiosis
E)inverted

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A gene's location on a chromosome is its ____.
A)genotype
B)phenotype
C)diploid number
D)haploid number
E)locus
A)genotype
B)phenotype
C)diploid number
D)haploid number
E)locus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A diploid cell has ____.
A)23 chromosomes
B)n sets of chromosomes
C)only the X or Y chromosome
D)23 pairs of homologous chromosomes
E)46 different chromosomes
A)23 chromosomes
B)n sets of chromosomes
C)only the X or Y chromosome
D)23 pairs of homologous chromosomes
E)46 different chromosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What explains why two genes have a high percentage of ending up in the same gamete?
A)heterozygous
B)allele variation
C)co-dominance
D)independent assortment
E)linkage
A)heterozygous
B)allele variation
C)co-dominance
D)independent assortment
E)linkage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A haploid cell has how many versions of each allele?
A)1
B)2
C)4
D)8
E)16
A)1
B)2
C)4
D)8
E)16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is NOT true concerning homologous chromosomes?
A)There are two of each kind.
B)Each parent contributes one of each homologous pair.
C)Most homologous chromosomes carry the same genes for the same traits.
D)The number of homologous chromosomes is doubled in each generation.
E)Homologous chromosomes pair up during early meiosis.
A)There are two of each kind.
B)Each parent contributes one of each homologous pair.
C)Most homologous chromosomes carry the same genes for the same traits.
D)The number of homologous chromosomes is doubled in each generation.
E)Homologous chromosomes pair up during early meiosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A female diploid cell has which sex chromosome combination?
A)XX
B)XY
C)YY
D)X
E)Y
A)XX
B)XY
C)YY
D)X
E)Y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A diploid cell has how many versions of each allele?
A)1
B)2
C)4
D)8
E)16
A)1
B)2
C)4
D)8
E)16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements is false?
A)Crossing over tends to reduce the frequency that two linked genes are inherited together.
B)Independent assortment of homologous chromosomes during meiosis increases variation.
C)Crossing over leads to variation.
D)An abnormal number or structure of chromosomes may influence the course of evolution.
E)The closer together genes are found on a chromosome, the greater the chance that crossing over will occur between them.
A)Crossing over tends to reduce the frequency that two linked genes are inherited together.
B)Independent assortment of homologous chromosomes during meiosis increases variation.
C)Crossing over leads to variation.
D)An abnormal number or structure of chromosomes may influence the course of evolution.
E)The closer together genes are found on a chromosome, the greater the chance that crossing over will occur between them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When producing a karyotype homologous the pairs of chromosomes ____.
A)are arranged largest to smallest
B)are arranged in alphabetical order
C)are arranged with the X and Y first
D)are aligned horizontally by their centromeres
E)are arranged randomly
A)are arranged largest to smallest
B)are arranged in alphabetical order
C)are arranged with the X and Y first
D)are aligned horizontally by their centromeres
E)are arranged randomly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If a pregnancy has a 1/4 changes of producing a child with a genetic disorder, what are the odds that the next child will also be born with the same disorder?
A)1/4
B)1/8
C)1/12
D)1/16
E)1/1
A)1/4
B)1/8
C)1/12
D)1/16
E)1/1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
For a woman to get pattern baldness she must ____.
A)have the SRY gene
B)be younger than 40 years old
C)possess two copies of the allele
D)have a sex-limited chromosome arrangement
E)have Y inactivation
A)have the SRY gene
B)be younger than 40 years old
C)possess two copies of the allele
D)have a sex-limited chromosome arrangement
E)have Y inactivation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A carrier for a genetic disorder ____.
A)is homozygous recessive
B)shows the recessive phenotype
C)shows no symptoms
D)is homozygous dominant
E)is always male
A)is homozygous recessive
B)shows the recessive phenotype
C)shows no symptoms
D)is homozygous dominant
E)is always male

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which chromosome event occurs in females but not males?
A)linkage
B)SRY activation
C)homologous pair crossover
D)X inactivation
E)X Y crossover
A)linkage
B)SRY activation
C)homologous pair crossover
D)X inactivation
E)X Y crossover

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following conditions is a sex-influenced trait?
A)pattern baldness
B)incontinentia pigmenti
C)ectoderm pigmentation syndrome
D)epithelial aggregate syndrome
E)albinism
A)pattern baldness
B)incontinentia pigmenti
C)ectoderm pigmentation syndrome
D)epithelial aggregate syndrome
E)albinism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In a pedigree chart, a male who does not demonstrate the trait being studied is represented by a ____.
A)darkened square
B)darkened circle
C)clear square
D)clear circle
E)clear diamond
A)darkened square
B)darkened circle
C)clear square
D)clear circle
E)clear diamond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Growth of a man's beard and a woman's breasts are governed by ___
A)sex-linked genes
B)sex-influenced genes
C)sex-exclusive genes
D)sex-limited genes
E)sex-independent genes
A)sex-linked genes
B)sex-influenced genes
C)sex-exclusive genes
D)sex-limited genes
E)sex-independent genes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An inactivated X chromosome is called a ____.
A)Barr body
B)polar body
C)SRY body
D)linked chromosome
E)linked body
A)Barr body
B)polar body
C)SRY body
D)linked chromosome
E)linked body

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In which condition is the mosaic tissue pattern of females easily observed?
A)psoriasis
B)incontinentia pigmenti
C)ectoderm pigmentation syndrome
D)epithelial aggregate syndrome
E)albinism
A)psoriasis
B)incontinentia pigmenti
C)ectoderm pigmentation syndrome
D)epithelial aggregate syndrome
E)albinism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In a pedigree chart, a female who demonstrates the trait being studied is represented by a ____.
A)darkened square
B)darkened circle
C)clear square
D)clear circle
E)clear diamond
A)darkened square
B)darkened circle
C)clear square
D)clear circle
E)clear diamond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Sex chromosomes do all of the following EXCEPT ____.
A)determine gender
B)vary from one sex to another
C)carry some genes that have nothing to do with sex
D)appear in a diploid cell as either XX or XY
E)appear in a haploid cell as either XX or XY
A)determine gender
B)vary from one sex to another
C)carry some genes that have nothing to do with sex
D)appear in a diploid cell as either XX or XY
E)appear in a haploid cell as either XX or XY

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Sex influenced traits are influenced by the presence of ____.
A)cortisol
B)estrogen
C)testosterone
D)thyroid hormone
E)both estrogen and testosterone
A)cortisol
B)estrogen
C)testosterone
D)thyroid hormone
E)both estrogen and testosterone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A deviation like having an extra toe is considered a ____.
A)genetic abnormality
B)genetic disorder
C)syndrome
D)pedigree
E)carrier
A)genetic abnormality
B)genetic disorder
C)syndrome
D)pedigree
E)carrier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A genetic condition causing mild to severe medical problems is a ____.
A)genetic abnormality
B)genetic disorder
C)syndrome
D)pedigree
E)carrier
A)genetic abnormality
B)genetic disorder
C)syndrome
D)pedigree
E)carrier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In a pedigree chart, a male who demonstrates the trait being studied is represented by a ____.
A)darkened square
B)darkened circle
C)clear square
D)clear circle
E)clear diamond
A)darkened square
B)darkened circle
C)clear square
D)clear circle
E)clear diamond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What term describes the set of symptoms associated with a medical issue?
A)genetic abnormality
B)genetic disorder
C)syndrome
D)disease
E)carrier
A)genetic abnormality
B)genetic disorder
C)syndrome
D)disease
E)carrier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In a pedigree chart what represent marriage/mating between two individuals?
A)> sign
B)vertical dashed line
C)horizontal dashed line
D)horizontal solid line
E)vertical solid line
A)> sign
B)vertical dashed line
C)horizontal dashed line
D)horizontal solid line
E)vertical solid line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A detailed analysis that tracks several generations of a family history is a ____.
A)carrier chart
B)pedigree
C)syndrome chart
D)genetic chart
E)karyotype
A)carrier chart
B)pedigree
C)syndrome chart
D)genetic chart
E)karyotype

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
X chromosome inactivation occurs ____.
A)fertilization but before cell division begins
B)just after cleavage begins
C)at implantation
D)gestational week 1
E)just after birth
A)fertilization but before cell division begins
B)just after cleavage begins
C)at implantation
D)gestational week 1
E)just after birth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What determines the gender of a fetus?
A)presence of an SRYgene
B)presence of X and Y chromosomes
C)absence of an X chromosome
D)the sex chromosomes in the egg
E)the presence of estrogen
A)presence of an SRYgene
B)presence of X and Y chromosomes
C)absence of an X chromosome
D)the sex chromosomes in the egg
E)the presence of estrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A chromosome region may be deleted by all of the following means EXCEPT ____.
A)bacteria
B)virus
C)chemical
D)irradiation
E)environmental factor
A)bacteria
B)virus
C)chemical
D)irradiation
E)environmental factor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What disease was studied in a famous pedigree analysis that included thousands of people?
A)Alzheimer's disease
B)Huntington's disease
C)cystic fibrosis
D)sickle-cell anemia
E)Turner's syndrome
A)Alzheimer's disease
B)Huntington's disease
C)cystic fibrosis
D)sickle-cell anemia
E)Turner's syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A human X-linked gene is ____.
A)found only in males
B)more frequently expressed in females
C)found on the Y chromosome
D)transmitted from father to son
E)found on the X chromosome
A)found only in males
B)more frequently expressed in females
C)found on the Y chromosome
D)transmitted from father to son
E)found on the X chromosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A female who is heterozygous for hemophilia will ____.
A)exhibit the condition throughout her life
B)suffer from bleeding when severely stressed
C)show no signs of the disease at all
D)pass the gene on to all of her children
E)pass the gene on to only her sons
A)exhibit the condition throughout her life
B)suffer from bleeding when severely stressed
C)show no signs of the disease at all
D)pass the gene on to all of her children
E)pass the gene on to only her sons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which autosomal dominant condition can be controlled by dietary means?
A)cystic fibrosis
B)PKU
C)Tay-Sachs disease
D)Marfan syndrome
E)achondroplasia
A)cystic fibrosis
B)PKU
C)Tay-Sachs disease
D)Marfan syndrome
E)achondroplasia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In an autosomal recessive disorder ____.
A)if one parent is homozygous dominant, none of the children will be affected
B)heterozygous dominant genotypes do not survive birth
C)the trait is only expressed in adults
D)a carrier rarely lives long enough to have children
E)the heterozygote condition expresses the trait
A)if one parent is homozygous dominant, none of the children will be affected
B)heterozygous dominant genotypes do not survive birth
C)the trait is only expressed in adults
D)a carrier rarely lives long enough to have children
E)the heterozygote condition expresses the trait

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which X-linked trait is caused by a dominant mutant allele?
A)hemophilia A
B)Duchenne muscular dystrophy
C)red-green color blindness
D)amelogenesis imperfecta
E)testicular feminizing syndrome
A)hemophilia A
B)Duchenne muscular dystrophy
C)red-green color blindness
D)amelogenesis imperfecta
E)testicular feminizing syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A color-blind man and a woman with normal vision whose father was color blind have a son. Color blindness, in this case, is caused by an X-linked recessive gene. If only the male offspring are considered, the probability that their son is color-blind is ____.
A)25 percent
B)50 percent
C)75 percent
D)100 percent
E)0 percent
A)25 percent
B)50 percent
C)75 percent
D)100 percent
E)0 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which autosomal dominant condition results in defective connective tissue production affecting blood vessels like the aorta?
A)cystic fibrosis
B)PKU
C)Tay-Sachs disease
D)Marfan syndrome
E)achondroplasia
A)cystic fibrosis
B)PKU
C)Tay-Sachs disease
D)Marfan syndrome
E)achondroplasia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Because of genetic differences in people's responses to medications, there are over 100 different types of ____.
A)antibiotics
B)muscle relaxers
C)tranquilizers
D)blood pressure medications
E)stimulants
A)antibiotics
B)muscle relaxers
C)tranquilizers
D)blood pressure medications
E)stimulants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Queen Victoria ____.
A)was a carrier of hemophilia
B)had a hemophilic parent
C)had hemophilia
D)married a man with hemophilia
E)both had a hemophilic parent and married a man with hemophilia
A)was a carrier of hemophilia
B)had a hemophilic parent
C)had hemophilia
D)married a man with hemophilia
E)both had a hemophilic parent and married a man with hemophilia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which autosomal recessive condition results in accumulation of phenylalanine?
A)cystic fibrosis
B)PKU
C)Tay-Sachs disease
D)Marfan syndrome
E)achondroplasia
A)cystic fibrosis
B)PKU
C)Tay-Sachs disease
D)Marfan syndrome
E)achondroplasia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If a daughter expresses an X-linked recessive gene, she inherited the trait from ____.
A)her mother
B)her father
C)both parents
D)neither parent
E)her grandmother
A)her mother
B)her father
C)both parents
D)neither parent
E)her grandmother

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The disorder cri-du-chat is caused by a ____.
A)deletion on chromosome 5
B)deletion on chromosome 11
C)translocation between chromosome 8 and 14
D)deletion of one nucleotide
E)third copy of chromosome 21
A)deletion on chromosome 5
B)deletion on chromosome 11
C)translocation between chromosome 8 and 14
D)deletion of one nucleotide
E)third copy of chromosome 21

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The field of study that focuses on how genes determine an individual's response to a medication is ____.
A)pharmacokinetics
B)pharmacodynamics
C)pharmacogenetics
D)pharmacotherapeutics
E)pharmacoeugenics
A)pharmacokinetics
B)pharmacodynamics
C)pharmacogenetics
D)pharmacotherapeutics
E)pharmacoeugenics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following points to a recessive X-linked trait?
A)it is common in both men and woman
B)a carrier mother has the trait on both X chromosomes
C)a carrier father carries two copies of the gene
D)only a daughter can inherit a recessive allele from an affected father
E)an affected daughter has the trait on one X chromosome
A)it is common in both men and woman
B)a carrier mother has the trait on both X chromosomes
C)a carrier father carries two copies of the gene
D)only a daughter can inherit a recessive allele from an affected father
E)an affected daughter has the trait on one X chromosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If a son expresses an X-linked recessive gene, he inherited the trait from ____.
A)his mother
B)his father
C)both parents
D)neither parent
E)his grandmother
A)his mother
B)his father
C)both parents
D)neither parent
E)his grandmother

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In an autosomal dominant disorder ____.
A)both parents must be carriers in order for the child to inherit the disorder
B)homozygous recessive genotypes do not survive birth
C)the trait is always expressed at birth
D)a carrier rarely lives long enough to have children
E)the heterozygote condition expresses the trait
A)both parents must be carriers in order for the child to inherit the disorder
B)homozygous recessive genotypes do not survive birth
C)the trait is always expressed at birth
D)a carrier rarely lives long enough to have children
E)the heterozygote condition expresses the trait

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which protein is defective in cases of Duchenne muscular dystrophy?
A)dystrophin
B)albumin
C)fibrillin
D)fibrinogen
E)fibrin
A)dystrophin
B)albumin
C)fibrillin
D)fibrinogen
E)fibrin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In the disease hemophilia A, a male with a recessive allele ____.
A)is classified as a carrier
B)is always affected
C)has normal clotting unless the situation is severe
D)carries the trait on two chromosomes
E)has a 100% chance of passing the trait to his son
A)is classified as a carrier
B)is always affected
C)has normal clotting unless the situation is severe
D)carries the trait on two chromosomes
E)has a 100% chance of passing the trait to his son

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Fertilization resulting in a chromosome number of 2n + 1 is ____.
A)monosomy
B)trisomy
C)haploid
D)diploid
E)triploid
A)monosomy
B)trisomy
C)haploid
D)diploid
E)triploid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Fertilization resulting in three or more complete haploid chromosome sets is ____.
A)monosomy
B)trisomy
C)haploid
D)diploid
E)polyploidy
A)monosomy
B)trisomy
C)haploid
D)diploid
E)polyploidy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Down's syndrome individuals have how many chromosomes?
A)23
B)24
C)45
D)46
E)47
A)23
B)24
C)45
D)46
E)47

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In nondisjunction one or more pairs of chromosomes ____.
A)are deleted
B)are duplicated
C)undergo translocation
D)undergo random mutations
E)fail to separate
A)are deleted
B)are duplicated
C)undergo translocation
D)undergo random mutations
E)fail to separate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Patients with an abnormally long chromosome 9 have ____.
A)the Philadelphia chromosome
B)a rare form of eye development
C)hemophilia
D)Down's syndrome
E)a deletion mutation
A)the Philadelphia chromosome
B)a rare form of eye development
C)hemophilia
D)Down's syndrome
E)a deletion mutation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following represents a normal female phenotype?
A)XX
B)XO
C)YY
D)XXX
E)YYY
A)XX
B)XO
C)YY
D)XXX
E)YYY

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Males that tend to be taller than normal with an otherwise normal phenotype have which chromosomal makeup?
A)XX
B)XO
C)YY
D)XXX
E)YYY
A)XX
B)XO
C)YY
D)XXX
E)YYY

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Compare and contrast autosomal recessive and dominant inheritance. Use a Punnett square to support your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
About half the fertilized eggs have a lethal condition called ____.
A)polyploidy
B)aneuploidy
C)translocation syndrome
D)nondisjunction
E)euploidy
A)polyploidy
B)aneuploidy
C)translocation syndrome
D)nondisjunction
E)euploidy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Turner's syndrome individuals have how many chromosomes?
A)23
B)24
C)45
D)46
E)47
A)23
B)24
C)45
D)46
E)47

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If a chromosome's gene sequence is represented by the letters A - B - C - D - E - F - G before modification and A - B - C - D - L - M - N - O - P afterward, this would be an example of ____.
A)inversion
B)deletion
C)duplication
D)translocation
E)cross over
A)inversion
B)deletion
C)duplication
D)translocation
E)cross over

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Down's syndrome individuals have trisomy of chromosome number ____.
A)1
B)21
C)45
D)X
E)Y
A)1
B)21
C)45
D)X
E)Y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Klinefelter's syndrome individuals have which chromosome makeup?
A)XX
B)XO
C)YY
D)XXX
E)YYY
A)XX
B)XO
C)YY
D)XXX
E)YYY

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Fertilization resulting in a chromosome number of 45 is ____.
A)monosomy
B)trisomy
C)haploid
D)diploid
E)triploid
A)monosomy
B)trisomy
C)haploid
D)diploid
E)triploid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A chromosome's gene sequence that was A - B - C - D - E - F - G before damage and A - B - C - F - G after is an example of ____.
A)inversion
B)deletion
C)duplication
D)translocation
E)cross over
A)inversion
B)deletion
C)duplication
D)translocation
E)cross over

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Turner's syndrome individuals ____.
A)are missing an X chromosome
B)have an extra Y chromosome
C)have 47 chromosomes
D)are always male
E)have XXX sex chromosome variation
A)are missing an X chromosome
B)have an extra Y chromosome
C)have 47 chromosomes
D)are always male
E)have XXX sex chromosome variation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The condition known as "Philadelphia chromosome" is an example of ____.
A)inversion
B)deletion
C)duplication
D)translocation
E)cross over
A)inversion
B)deletion
C)duplication
D)translocation
E)cross over

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Match the form of inheritance to the statements below.
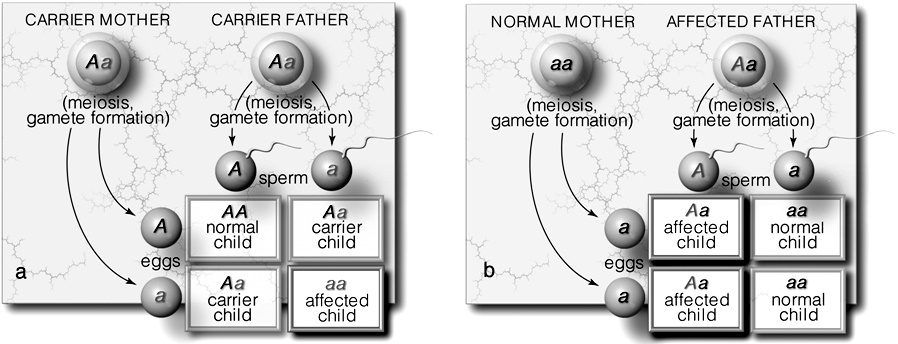
pattern associated with Tay-Sachs disease

pattern associated with Tay-Sachs disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



