Deck 9: Optics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/143
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Optics
1
Light is a transverse wave.
True
2
The path of a light ray through a refracting surface is reversible.
True
3
Light goes slower through glass than through air.
True
4
When light passes through two or more narrow slits, an alternating dark and bright pattern is observed on a screen because of interference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A light ray bends when it goes from one medium to another because of diffraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The colors you see with a prism result because the light is diffracted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Optical fibers work because of dispersion of light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Liquid crystal displays make use of interference of light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Blue light travels more slowly through glass than red light does.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Certain types of sunglasses are very effective at diminishing light reflected from surfaces because of polarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Your eye's iris changes the size of your pupil to adjust the amount of light that enters your eye.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Astigmatism is due to too flat a cornea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
You can see your image in a mirror because of diffuse reflection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Light spreads out when it passes through a narrow slit because of interference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
You see colors in a rainbow because of diffraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Dispersion results because the speed of light in a transparent medium varies with frequency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A light ray can pass through a diverging lens without being deflected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
You do not see your image when you look at a flat rough aluminum surface because of specular reflection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When you look into a pool of water, the depth looks less than it actually is because the light is dispersed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The lens in your eye and the cornea both contribute to image formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Halos are caused by hexagonal ice crystals in the upper atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A converging lens always forms an object's image at the focal point of the lens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The Hubble Space Telescope has been repaired.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
LCDs operate on the principle of refraction through glass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The speed of light in any transparent medium is the same as the speed of light in a vacuum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
An EM wave with a wavelength of 500 nm will be visible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
You look at yourself in a plane mirror. If you move away from the mirror and look at yourself again, you now see more of yourself.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A diverging lens is thicker at the center than the edges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A person looking through eyeglasses sees real images.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A magnifying glass with focal length 15 cm is placed 10 cm above a stamp. The image of the stamp is located 30 cm above the magnifying glass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The lens formula relating the image distance, p , to the focal length, f , and object distance, s , is 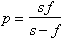
The magnification of a lens is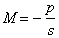
A movie projector is equipped with a 0.5-m focal length lens that is positioned 0.505 m in front of the film. The distance in front of the lens that a screen must be placed for an image to be in focus is 50.5 m.
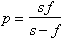
The magnification of a lens is
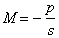
A movie projector is equipped with a 0.5-m focal length lens that is positioned 0.505 m in front of the film. The distance in front of the lens that a screen must be placed for an image to be in focus is 50.5 m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The lens formula relating the image distance, p , to the focal length, f , and object distance, s , is 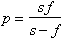
The magnification of a lens is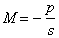
The magnification of the magnifying glass in the previous problem is -3.
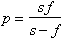
The magnification of a lens is
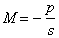
The magnification of the magnifying glass in the previous problem is -3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The ideal shape for the primary mirror of a telescope is concave parabolic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A one-way mirror works because its surfaces are half-silvered.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A convex mirror will allow you to see large areas normally hidden from your view.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An image seen projected on a screen by a single lens is always inverted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The lens formula relating the image distance, p , to the focal length, f , and object distance, s , is 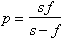
The magnification of a lens is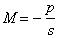
For the projector in the previous problem, the image is 10 times as large as the object.
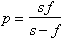
The magnification of a lens is
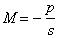
For the projector in the previous problem, the image is 10 times as large as the object.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Diverging lenses have negative focal lengths.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In the atmosphere, the intensity of scattered sunlight of longer wavelength is greater than that of shorter wavelength.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A curved mirror that produces an enlarged image will also have a greater field of view than a plane mirror.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In order to see a rainbow, the Sun must be directly in front of you.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If you see a rainbow near the time of sunset, where in the sky will the rainbow be?
A) overhead
B) toward the eastern horizon
C) toward the western horizon
D) toward the northern horizon
E) toward the southern horizon
A) overhead
B) toward the eastern horizon
C) toward the western horizon
D) toward the northern horizon
E) toward the southern horizon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is not involved in the formation of a rainbow?
A) interference
B) dispersion
C) internal reflection
D) refraction
A) interference
B) dispersion
C) internal reflection
D) refraction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
You see colors in a rainbow because of
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) dispersion.
E) polarization.
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) dispersion.
E) polarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Light spreads out when it passes through a narrow slit because of
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) diffuse reflection.
E) polarization.
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) diffuse reflection.
E) polarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When light passes through two or more narrow slits, an alternating dark and bright pattern is observed on a screen because of
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) diffuse reflection.
E) polarization.
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) diffuse reflection.
E) polarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
You can see your image in a mirror because of
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) diffuse reflection.
E) polarization.
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) diffuse reflection.
E) polarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Optical fibers work because of
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) total internal reflection.
D) diffuse reflection.
E) polarization.
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) total internal reflection.
D) diffuse reflection.
E) polarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is meant by the "normal" to a surface?
A) a line perpendicular to the surface at a given point
B) the angle between the surface and the light ray
C) a line parallel to the surface at a given point
D) the direction of a reflected ray
A) a line perpendicular to the surface at a given point
B) the angle between the surface and the light ray
C) a line parallel to the surface at a given point
D) the direction of a reflected ray

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the lines in the figure represents the normal to the surface at point P? 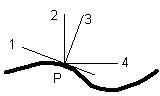
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) none of the above

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Why are optical fibers important for communication?
A) They can carry thousands of times the information that wires can.
B) Light goes faster than electricity.
C) They carry digital information. Wires can't carry digital information.
D) all of the above
A) They can carry thousands of times the information that wires can.
B) Light goes faster than electricity.
C) They carry digital information. Wires can't carry digital information.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Thin film interference is responsible for the colors of
A) bird feathers.
B) gasoline spills.
C) soap bubbles.
D) all of the above.
A) bird feathers.
B) gasoline spills.
C) soap bubbles.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The colors of objects we see by reflected light are due to
A) interference.
B) selective absorption.
C) specular reflection.
D) diffuse reflection.
A) interference.
B) selective absorption.
C) specular reflection.
D) diffuse reflection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which angle is the angle of incidence for the light ray shown approaching the plane mirror? 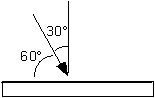
A) 60°
B) 30°
C) neither
D) either

A) 60°
B) 30°
C) neither
D) either

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
You do not see your image when you look at a flat rough aluminum surface because of
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) diffuse reflection.
E) polarization.
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) diffuse reflection.
E) polarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A helium neon laser generates light of 632.8-nm wavelength. What color is that?
A) blue
B) yellow
C) red
D) green
A) blue
B) yellow
C) red
D) green

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Certain types of sunglasses are very effective at diminishing light reflected from surfaces because of
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) diffuse reflection.
E) polarization.
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) diffuse reflection.
E) polarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Liquid crystal displays make use of
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) diffuse reflection.
E) polarization.
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) diffuse reflection.
E) polarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
According to the law of reflection, a light ray striking a mirror at an angle of incidence of 30 degrees will leaves the mirror at an angle of
A) 60 degrees.
B) 30 degrees.
C) less than 30 degrees.
D) none of the above.
A) 60 degrees.
B) 30 degrees.
C) less than 30 degrees.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The sky is blue due to air molecules scattering sunlight in all directions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The ideal shape for the primary mirror of a telescope is
A) concave circular.
B) convex circular.
C) concave parabolic.
D) convex parabolic.
E) plane.
A) concave circular.
B) convex circular.
C) concave parabolic.
D) convex parabolic.
E) plane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The variation of the speed of light in a transparent medium with frequency results in
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) dispersion.
D) diffuse reflection.
E) polarization.
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) dispersion.
D) diffuse reflection.
E) polarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In optics, what is meant by an "interface?"
A) optically connecting one computer to another
B) using the image created by one lens as the object for another lens
C) when the crest of one wave lines up with the trough of another wave
D) none of the above
A) optically connecting one computer to another
B) using the image created by one lens as the object for another lens
C) when the crest of one wave lines up with the trough of another wave
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In this figure a light ray travels between air and glass. Which way did the light ray go? 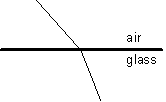
A) from the air into the glass
B) from the glass into the air
C) either A or B.
D) None of the above-this depicts an impossible situation.
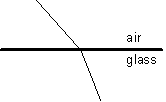
A) from the air into the glass
B) from the glass into the air
C) either A or B.
D) None of the above-this depicts an impossible situation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
An object is 50 cm in front of a plane mirror. Its image will be located
A) 50 cm in front of the mirror.
B) at the mirror's surface.
C) 50 cm behind the mirror.
D) 25 cm in front of the mirror.
E) 25 cm behind the mirror.
A) 50 cm in front of the mirror.
B) at the mirror's surface.
C) 50 cm behind the mirror.
D) 25 cm in front of the mirror.
E) 25 cm behind the mirror.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A light ray bends when it goes from one medium to another because of
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) refraction.
E) polarization.
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) refraction.
E) polarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What is meant by the term "plane mirror?"
A) not an unusual mirror
B) a flat mirror
C) a horizontal mirror
D) none of the above
A) not an unusual mirror
B) a flat mirror
C) a horizontal mirror
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Upon entering a medium in which the speed of light is 1.5 × 108 m/s from a medium in which the speed of light is 2 × 108 m/s, an oblique light ray will be _____________ the normal to the interface between the two media.
A) bent away from
B) bent toward
C) travel along
D) remain undeviated with respect to
A) bent away from
B) bent toward
C) travel along
D) remain undeviated with respect to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In air a light source emits a wavelength of 630 nm. Under water the wavelength of this light will be
A) 630 nm.
B) less than 630 nm.
C) more than 630 nm.
D) unpredictable.
A) 630 nm.
B) less than 630 nm.
C) more than 630 nm.
D) unpredictable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What makes pink ink pink?
A) refraction
B) selective absorption
C) dispersion
D) none of the above
A) refraction
B) selective absorption
C) dispersion
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The type of mirror that will allow you to see large areas normally hidden from your view is
A) concave.
B) convex.
C) plane.
D) half-silvered.
E) Polaroid.
A) concave.
B) convex.
C) plane.
D) half-silvered.
E) Polaroid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A one-way mirror works because of
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) its surfaces being half-silvered.
D) dispersion.
E) polarization.
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) its surfaces being half-silvered.
D) dispersion.
E) polarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
New telescopes are using "adaptive optics." What is that?
A) using parabolic instead of spherical mirrors
B) using computer image processing to enhance images
C) building mirrors in hexagonal segments
D) continually adjusting the mirror's shape during observations
A) using parabolic instead of spherical mirrors
B) using computer image processing to enhance images
C) building mirrors in hexagonal segments
D) continually adjusting the mirror's shape during observations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The sky is blue because of
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) scattering.
D) dispersion.
E) polarization.
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) scattering.
D) dispersion.
E) polarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Parallel light rays from a distant object strike the surface of a concave mirror. After reflecting from the mirror's surface, the rays will converge at
A) the mirror's focal point.
B) a point beyond the mirror's focal point.
C) a point nearer than the mirror's focal point.
D) none of the above.
A) the mirror's focal point.
B) a point beyond the mirror's focal point.
C) a point nearer than the mirror's focal point.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Diverging light rays from a nearby object (a few focal lengths away from the mirror) strike the surface of a concave mirror. After reflecting from the mirror's surface, the rays will converge at
A) the mirror's focal point.
B) a point beyond the mirror's focal point.
C) a point nearer than the mirror's focal point.
D) none of the above.
A) the mirror's focal point.
B) a point beyond the mirror's focal point.
C) a point nearer than the mirror's focal point.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
When you look into a pool of water, the depth looks less than it actually is because of
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) refraction.
E) polarization.
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) refraction.
E) polarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Rank the following media in order according to the speed of light in them, from slowest to fastest: vacuum, air, water and glass.
A) air, water, glass, vacuum
B) glass, air, water, vacuum
C) water, glass, air, vacuum
D) glass, water, air, vacuum
E) none of the above
A) air, water, glass, vacuum
B) glass, air, water, vacuum
C) water, glass, air, vacuum
D) glass, water, air, vacuum
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The primary mirror in an astronomical telescope must be a
A) half-silvered mirror.
B) convex mirror.
C) concave mirror.
D) plane mirror.
A) half-silvered mirror.
B) convex mirror.
C) concave mirror.
D) plane mirror.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
You see colors with a prism because of
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) dispersion.
E) polarization.
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) specular reflection.
D) dispersion.
E) polarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



