Deck 6: Waves and Sound
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/142
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Waves and Sound
1
When the frequency of the source of a water wave increases, the distance between successive peaks in the wave increases.
False
2
The maximum displacement of points on a wave from the equilibrium position is the wave's wavelength.
False
3
The wavelength of a wave divided by the frequency of the wave is the wave's speed.
False
4
The distance between two successive 'like' points on a wave is the wave's wavelength.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A sound wave in a metal bar is an example of a longitudinal wave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A source emits sound at a fixed constant frequency f .
If the source moves away from you, and at the same time you run away from the source, the frequency you hear is the same as f .
If the source moves away from you, and at the same time you run away from the source, the frequency you hear is the same as f .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A source emits sound at a fixed constant frequency f .
If the source moves away from you, the frequency you hear is lower than f .
If the source moves away from you, the frequency you hear is lower than f .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When a force F stretches a rope of mass per unit length ρ , the velocity of a wave in the rope is given by 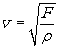
You pull on a rope with a certain force, and a wave travels in the rope with a certain velocity. If you double your force, the velocity of a wave in the rope is now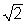 times the original velocity.
times the original velocity.
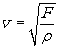
You pull on a rope with a certain force, and a wave travels in the rope with a certain velocity. If you double your force, the velocity of a wave in the rope is now
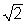 times the original velocity.
times the original velocity.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Regions of a longitudinal wave where the particles of the medium are squeezed together are called compressions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Sound in a vacuum is impossible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When a force F stretches a rope of mass per unit length ρ , the velocity of a wave in the rope is given by 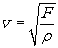
You have two identical ropes stretched with the same force between two different sets of posts. The second rope is twice as long as the first rope. The velocity of a wave in the second rope is half the velocity of a wave in the first rope.
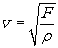
You have two identical ropes stretched with the same force between two different sets of posts. The second rope is twice as long as the first rope. The velocity of a wave in the second rope is half the velocity of a wave in the first rope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A source emits sound at a fixed constant frequency f .
If you run towards the source, the frequency you hear is lower than f .
If you run towards the source, the frequency you hear is lower than f .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Waves carry energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The speed of a wave is the same as the speed of the particles displaced by the wave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A water wave is an example of a transverse wave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When a force F stretches a rope of mass per unit length ρ , the velocity of a wave in the rope is given by 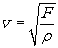
You have two ropes of the same length. The mass of the second rope is twice the mass of the first rope. The velocity of a wave in the second rope is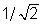 times the velocity of a wave in the first rope.
times the velocity of a wave in the first rope.
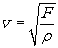
You have two ropes of the same length. The mass of the second rope is twice the mass of the first rope. The velocity of a wave in the second rope is
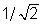 times the velocity of a wave in the first rope.
times the velocity of a wave in the first rope.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The number of cycles of a wave passing a point per unit time is the wave's period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The flash from a camera is an example of a continuous wave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When the frequency of the source of a water wave increases, the speed of the waves traveling in the water increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A wave moves in a rope with a certain wavelength. A second wave is made to move in the same rope with twice the wavelength of the first wave. The frequency of the second wave is half the frequency of the first wave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Two identical sound producers will sound twice as loud as just one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Telephones don't transmit frequencies above 3,400 Hz. Musical notes should sound normal over the telephone as long as they are below 3,400 Hz.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Combining two sounds of equal intensity will give a sound level 3 dB higher than the sound level due to just one of them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A source emits sound at a fixed constant frequency f .
If the source moves away from you faster than the speed of sound in air, you do not hear any frequency but instead a 'sonic boom.'
If the source moves away from you faster than the speed of sound in air, you do not hear any frequency but instead a 'sonic boom.'

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
As you move farther away from a source emitting a pure tone, the frequency of the sound you hear decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A source emits sound at a fixed constant frequency f .
If the temperature of the air rises, the frequency you hear is higher than f .
If the temperature of the air rises, the frequency you hear is higher than f .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Two uses of ultrasound are navigation by bats and controlling insects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A sound level of 80 dB has twenty times the amplitude of a 60 dB sound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Reverberation can both inhibit conversation and enhance music.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Your vocal cords are used to produce all the sounds you make while speaking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Reverberation time of a room can be increased by covering the walls with better reflectors of sound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A sound with ten times the amplitude of another sound is judged to be ten times as loud.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Two speakers in a stereo emit identical pure tones. As you move around in front of the speakers, you hear the sound alternating between loud and zero. This occurs because of diffraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A zero decibel sound level has zero amplitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
You can hear sound through an open window from sources that are not in your line of sight because of diffraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In order for two waves to interfere completely destructively, they must have the same amplitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In ultrasound the wavelength of the sound is much smaller than in normal sound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Sound cannot travel through solid steel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the source moves, the wavelength of the sound in front of the direction of motion is smaller than the wavelength behind the direction of motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When two identical waves arrive at the same place in phase, there is destructive interference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following can change the frequency of a wave?
A) interference
B) the Doppler effect
C) diffraction
D) all of the above
A) interference
B) the Doppler effect
C) diffraction
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
For waves moving through the atmosphere at a constant velocity, higher frequency waves must have proportionally longer wavelengths.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The distance between two successive 'like' points on a wave is the wave's
A) speed.
B) frequency.
C) wavelength.
D) amplitude.
E) loudness.
A) speed.
B) frequency.
C) wavelength.
D) amplitude.
E) loudness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When a force F stretches a rope of mass per unit length ρ , the velocity of a wave in the rope is given by 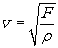 You pull on a rope with a certain force, and a wave travels in the rope with a certain velocity. If you double your force, the velocity of a wave in the rope is now ____________ the original velocity.
You pull on a rope with a certain force, and a wave travels in the rope with a certain velocity. If you double your force, the velocity of a wave in the rope is now ____________ the original velocity.
A) 1/2
B)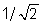 times
times
C) the same as
D)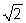 times
times
E) 2 times
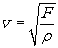 You pull on a rope with a certain force, and a wave travels in the rope with a certain velocity. If you double your force, the velocity of a wave in the rope is now ____________ the original velocity.
You pull on a rope with a certain force, and a wave travels in the rope with a certain velocity. If you double your force, the velocity of a wave in the rope is now ____________ the original velocity.A) 1/2
B)
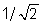 times
timesC) the same as
D)
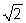 times
timesE) 2 times

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Sound waves propagate in two dimensions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
You drop a rock in a pond, and the water waves travel away from the rock with a certain speed. You drop a heavier rock in the water. The speed of the waves in the water from the heavier rock
A) remains unchanged.
B) increases.
C) decreases.
D) cannot be determined.
A) remains unchanged.
B) increases.
C) decreases.
D) cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When a force F stretches a rope of mass per unit length ρ , the velocity of a wave in the rope is given by 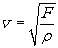 You have two identical ropes stretched with the same force between two different sets of posts. The second rope is twice as long as the first rope. The velocity of a wave in the second rope is ____________ the velocity of a wave in the first rope.
You have two identical ropes stretched with the same force between two different sets of posts. The second rope is twice as long as the first rope. The velocity of a wave in the second rope is ____________ the velocity of a wave in the first rope.
A) 1/2
B)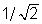 times
times
C) the same as
D)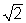 times
times
E) 2 times
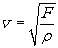 You have two identical ropes stretched with the same force between two different sets of posts. The second rope is twice as long as the first rope. The velocity of a wave in the second rope is ____________ the velocity of a wave in the first rope.
You have two identical ropes stretched with the same force between two different sets of posts. The second rope is twice as long as the first rope. The velocity of a wave in the second rope is ____________ the velocity of a wave in the first rope.A) 1/2
B)
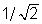 times
timesC) the same as
D)
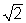 times
timesE) 2 times

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When a force F stretches a rope of mass per unit length ρ , the velocity of a wave in the rope is given by 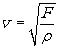 You have two ropes of the same length. The mass of the second rope is twice the mass of the first rope. The velocity of a wave in the second rope is ___________ the velocity of a wave in the first rope.
You have two ropes of the same length. The mass of the second rope is twice the mass of the first rope. The velocity of a wave in the second rope is ___________ the velocity of a wave in the first rope.
A) 1/2
B)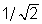 times
times
C) the same as
D)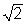 times
times
E) 2 times
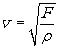 You have two ropes of the same length. The mass of the second rope is twice the mass of the first rope. The velocity of a wave in the second rope is ___________ the velocity of a wave in the first rope.
You have two ropes of the same length. The mass of the second rope is twice the mass of the first rope. The velocity of a wave in the second rope is ___________ the velocity of a wave in the first rope.A) 1/2
B)
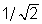 times
timesC) the same as
D)
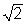 times
timesE) 2 times

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The distance between peaks on a wave divided by the time for the wave to travel this distance is the wave's
A) speed.
B) frequency.
C) wavelength.
D) amplitude.
E) loudness.
A) speed.
B) frequency.
C) wavelength.
D) amplitude.
E) loudness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The wavelength of a wave multiplied by the frequency of the wave is the wave's
A) speed.
B) frequency.
C) wavelength.
D) amplitude.
E) loudness.
A) speed.
B) frequency.
C) wavelength.
D) amplitude.
E) loudness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The number of cycles of a wave passing a point per unit time is the wave's
A) speed.
B) frequency.
C) wavelength.
D) amplitude.
E) loudness.
A) speed.
B) frequency.
C) wavelength.
D) amplitude.
E) loudness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If a source of sound is traveling toward you, the speed of the sound waves reaching you is _______________ the speed the sound waves would have had if the source were stationary.
A) faster than
B) slower than
C) the same as
A) faster than
B) slower than
C) the same as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If you increase the linear mass density of a rope, the speed of a wave on the rope also increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When the frequency of the source of a water wave increases, the distance between successive peaks in the wave
A) remains unchanged.
B) increases.
C) decreases.
D) cannot be determined.
A) remains unchanged.
B) increases.
C) decreases.
D) cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When the frequency of the source of a water wave increases, the speed of the waves traveling in the water
A) remains unchanged.
B) increases.
C) decreases.
D) cannot be determined.
A) remains unchanged.
B) increases.
C) decreases.
D) cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The maximum displacement of points on a wave from the equilibrium position is the wave's
A) speed.
B) frequency.
C) wavelength.
D) amplitude.
E) loudness.
A) speed.
B) frequency.
C) wavelength.
D) amplitude.
E) loudness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What is meant by a wave medium ?
A) a wave of moderate amplitude
B) water
C) air
D) any material through which a wave travels
A) a wave of moderate amplitude
B) water
C) air
D) any material through which a wave travels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Two sound waves traveling through the air have different frequencies. Consequently, they must also have different
A) amplitudes.
B) speeds.
C) wavelengths.
D) all of the above
A) amplitudes.
B) speeds.
C) wavelengths.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In the troposphere segment of the Earth's atmosphere, as you increase in altitude the temperature decreases. This means the speed of sound decreases as you increase in altitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the symbol traditionally used to represent wavelength?
A) wl
B) y
C) μ
D) λ
A) wl
B) y
C) μ
D) λ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The wavelength of ultrasound at 1 million Hz in air where the speed of sound is 340 m/s is
A) 0.00000034 m.
B) 0.0000034 m.
C) 0.00034 m.
D) 0.34 m.
E) 340,000,000 m.
A) 0.00000034 m.
B) 0.0000034 m.
C) 0.00034 m.
D) 0.34 m.
E) 340,000,000 m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A source emits sound at a fixed constant frequency f . If the source moves away from you faster than the speed of sound in air, the frequency that you hear is
A) the same as f.
B) higher than f.
C) lower than f.
D) unrelated to f.
A) the same as f.
B) higher than f.
C) lower than f.
D) unrelated to f.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A source emits sound at a fixed constant frequency f . If you run towards the source, the frequency you hear is
A) the same as f.
B) higher than f.
C) lower than f.
D) unrelated to f.
A) the same as f.
B) higher than f.
C) lower than f.
D) unrelated to f.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A source emits sound at a fixed constant frequency f . If the source moves away from you, and at the same time you run away from the source, the frequency you hear is
A) the same as f.
B) higher than f.
C) lower than f.
D) unrelated to f.
A) the same as f.
B) higher than f.
C) lower than f.
D) unrelated to f.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following is not one of the ways sound can be used?
A) to circulate the refrigerant in a refrigerator
B) to relay information to orbiting satellites
C) to form images of internal organs
D) to measure the air temperature aloft
E) to make a bubble in water produce light
A) to circulate the refrigerant in a refrigerator
B) to relay information to orbiting satellites
C) to form images of internal organs
D) to measure the air temperature aloft
E) to make a bubble in water produce light

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Choose the correct statement.
A) The perceived pitch of a sound usually doesn't depend on the sound's frequency.
B) The frequency of each musical note is 10 Hz higher than that of the next lower note.
C) The decibel is the standard measure of tone quality.
D) The perceived loudness of a sound depends somewhat on frequency.
A) The perceived pitch of a sound usually doesn't depend on the sound's frequency.
B) The frequency of each musical note is 10 Hz higher than that of the next lower note.
C) The decibel is the standard measure of tone quality.
D) The perceived loudness of a sound depends somewhat on frequency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
As you move farther away from a source emitting a pure tone, the ___________ of the sound you hear decreases.
A) frequency
B) period
C) wavelength
D) amplitude
E) none of the above
A) frequency
B) period
C) wavelength
D) amplitude
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
You listen to a live orchestra concert from a cheap seat far away, high up in the balcony. The music seems to be a little out of sync with the conductor's beat. Why?
A) The musicians are paying no attention to the conductor.
B) You are noticing a time lag due to the finite speed of sound.
C) The orchestra is not very good.
D) The viola section is dragging.
A) The musicians are paying no attention to the conductor.
B) You are noticing a time lag due to the finite speed of sound.
C) The orchestra is not very good.
D) The viola section is dragging.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The figure shows a 'snapshot' of four different waves in identical ropes stretched with the same force. 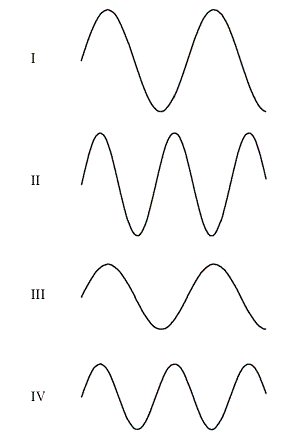 The wave where the speed is greatest is
The wave where the speed is greatest is
A) I.
B) II.
C) III.
D) IV.
E) all of the above.
 The wave where the speed is greatest is
The wave where the speed is greatest isA) I.
B) II.
C) III.
D) IV.
E) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A source emits sound at a fixed constant frequency f . If the source moves away from you, the frequency you hear is
A) the same as f.
B) higher than f.
C) lower than f.
D) unrelated to f.
A) the same as f.
B) higher than f.
C) lower than f.
D) unrelated to f.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In ultrasound the _____________ of the sound is much greater than in normal sound.
A) frequency
B) period
C) wavelength
D) amplitude
E) speed
A) frequency
B) period
C) wavelength
D) amplitude
E) speed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Two speakers in a stereo emit identical pure tones. As you move around in front of the speakers, you hear the sound alternating between loud and zero. This occurs because of
A) interference.
B) changing sound level.
C) diffraction.
D) the Doppler effect.
E) shock waves.
A) interference.
B) changing sound level.
C) diffraction.
D) the Doppler effect.
E) shock waves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
You can hear sound through an open window from sources that are not in your line of sight because of
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) the sound level.
D) the Doppler effect.
E) none of the above.
A) interference.
B) diffraction.
C) the sound level.
D) the Doppler effect.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A source emits sound at a fixed constant frequency f . If the temperature of the air rises, the frequency you hear is
A) the same as f.
B) higher than f.
C) lower than f.
D) unrelated to f.
A) the same as f.
B) higher than f.
C) lower than f.
D) unrelated to f.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of these waves will diffract the most when passing through a 20 cm wide opening in a barrier?
A) a wave with a wavelength of 25 cm
B) a wave with a wavelength of 2 cm
C) a wave with a wavelength of 0.05 cm
D) none of these waves will diffract at all
A) a wave with a wavelength of 25 cm
B) a wave with a wavelength of 2 cm
C) a wave with a wavelength of 0.05 cm
D) none of these waves will diffract at all

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A wave moves in a rope with a certain wavelength. A second wave is made to move in the same rope with twice the wavelength of the first wave. The frequency of the second wave is _______________ the frequency of the first wave.
A) 1/2
B) the same as
C) 2 times
D) unrelated to
A) 1/2
B) the same as
C) 2 times
D) unrelated to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
When two identical waves arrive at the same place in phase, there is
A) constructive interference.
B) destructive interference.
C) diffraction.
D) a Doppler effect.
E) a shock wave.
A) constructive interference.
B) destructive interference.
C) diffraction.
D) a Doppler effect.
E) a shock wave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Ultrasound is used
A) to form images of internal organs.
B) by bats to navigate.
C) in automatic focus cameras.
D) to control insects.
E) all of the above
A) to form images of internal organs.
B) by bats to navigate.
C) in automatic focus cameras.
D) to control insects.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A source emits sound at a fixed constant frequency f . If the source moves, the wavelength of the sound in front of the direction of motion is ____________ the wavelength behind the direction of motion.
A) the same as
B) larger than
C) smaller than
D) unrelated to
A) the same as
B) larger than
C) smaller than
D) unrelated to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
You shout at a cliff, and hear your echo in 2 seconds. If the speed of sound in the air is 340 m/s, the distance of the cliff from you is
A) 85 m.
B) 170 m.
C) 340 m.
D) 680 m.
E) none of the above.
A) 85 m.
B) 170 m.
C) 340 m.
D) 680 m.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



