Deck 12: Exception Handling
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/66
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Exception Handling
1
Some programmers refer to a catch block as a catch ____.
A) method
B) phrase
C) statement
D) clause
A) method
B) phrase
C) statement
D) clause
D
2
Placing data conversion attempts in a try block allows you to handle potential data conversion errors caused by careless user entry.
True
3
To create your own throwable Exception class, you must extend a subclass of Catchable .
False
4
Unplanned exceptions that occur during a program's execution are also called execution exceptions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Although a method can throw any number of ____ types, many developers believe that it is poor style for a method to throw and catch more than three or four types.
A) Error
B) Clause
C) Exception
D) Catch
A) Error
B) Clause
C) Exception
D) Catch

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
____ represents the degree to which a system is resilient to stress, maintaining correct functioning.
A) Endurance
B) Robustness
C) Fault-tolerant
D) Strength
A) Endurance
B) Robustness
C) Fault-tolerant
D) Strength

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
To use a method to its full potential, you must know the method name, return type, type and number of arguments required, and type and number of exceptions the method throws.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A(n) ____ statement is one that sends an Exception object to a catch block.
A) throw
B) catch
C) optional
D) assert
A) throw
B) catch
C) optional
D) assert

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
You can place as many statements as you need within a try block, and you can catch as many exceptions as you want.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Since variables declared within a try or catch block are local to that block, the variable goes out of scope when the try or catch block ends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A variable declared within a try or catch block is ____ to that block.
A) local
B) universal
C) public
D) unique
A) local
B) universal
C) public
D) unique

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
____ statements are program statements that can never execute under any circumstances.
A) Stagnant
B) Error
C) Unreachable
D) Exception
A) Stagnant
B) Error
C) Unreachable
D) Exception

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A catch block is a method that can be called directly and takes an argument that is some type of exception.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The ____ class represents more serious errors from which your program usually cannot recover.
A) Error
B) Throwable
C) Exception
D) Menu
A) Error
B) Throwable
C) Exception
D) Menu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When you have actions you must perform at the end of a try…catch sequence, you can use a ____ block.
A) finally
B) catch
C) throw
D) try
A) finally
B) catch
C) throw
D) try

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The keyword catch followed by an Exception type in the method header is used when a method throws an exception that it will not catch but that will be caught by a different method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The code within a finally block cannot execute if the preceding try block identifies an exception.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When a program contains multiple ____ blocks, they are examined in sequence until a match is found for the type of exception that occurred.
A) throw
B) finally
C) catch
D) try
A) throw
B) finally
C) catch
D) try

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When an exception is a checked exception, client programmers are forced to deal with the possibility that an exception will be thrown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The parent class of Error is ____.
A) Object
B) Exception
C) RuntimeError
D) RuntimeException
A) Object
B) Exception
C) RuntimeError
D) RuntimeException

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the correct syntax of an assert statement?
A) assert AssertionError : optionalErrorMessage
B) assert booleanExpression : optionalErrorMessage
C) assert stringExpression : optionalErrorMessage
D) assert booleanExpression = optionalErrorMessage
A) assert AssertionError : optionalErrorMessage
B) assert booleanExpression : optionalErrorMessage
C) assert stringExpression : optionalErrorMessage
D) assert booleanExpression = optionalErrorMessage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A(n) ____ clause is used in the method header so that applications that use your methods are notified of the potential for an exception.
A) throws
B) return
C) stack
D) exception
A) throws
B) return
C) stack
D) exception

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The memory location known as the ____________________ is where the computer stores the list of method locations to which the system must return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which method constructor constructs a new exception with the specified detail message and cause?
A) Exception()
B) Exception(String message)
C) Exception(String message, Throwable cause)
D) Exception(Throwable cause)
A) Exception()
B) Exception(String message)
C) Exception(String message, Throwable cause)
D) Exception(Throwable cause)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Any ____________________ block might throw an Exception for which you did not provide a catch block.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If a method throws an exception that it will not catch but that will be caught by a different method, you must also use the keyword ____ followed by an Exception type in the method header.
A) finally
B) try
C) catch
D) throws
A) finally
B) try
C) catch
D) throws

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is NOT a component of a try block?
A) a closing curly brace
B) the keyword try
C) executable statements
D) a throw statement
A) a closing curly brace
B) the keyword try
C) executable statements
D) a throw statement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Assertions are meant to be helpful in the ____ stage of a program.
A) development
B) testing
C) production
D) modeling
A) development
B) testing
C) production
D) modeling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Programs would be less clear if you had to account for ____ exceptions in every method declaration.
A) unthrown
B) thrown
C) runtime
D) checked
A) unthrown
B) thrown
C) runtime
D) checked

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When you catch an Exception object, you can call ____________________ to display a list of methods in the call stack so you can determine the location of the statement that caused the exception.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The ____ option must be used when running a program in order to see the results of assert statements.
A) -db
B) -ea
C) -debug
D) -assert
A) -db
B) -ea
C) -debug
D) -assert

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When you use a(n) ____ statement, you state a condition that should be true , and Java throws an AssertionError when it is not.
A) if
B) boolean
C) assert
D) exception
A) if
B) boolean
C) assert
D) exception

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
____ exceptions are the type that programmers should anticipate and from which programs should be able to recover.
A) Unchecked
B) Runtime
C) Checked
D) Thrown
A) Unchecked
B) Runtime
C) Checked
D) Thrown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If you create an object using Java's BigDecimal class, and then perform a division that results in a non-terminating decimal division such as 1/3, but specify that an exact result is needed, a(n) ____________________ is thrown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In order to use a variable both with a try or catch block and afterward, you must declare the variable before the ____ block begins.
A) catch
B) try
C) main
D) finally
A) catch
B) try
C) main
D) finally

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In the case where a method might throw more than one exception type, you specify a list of potential exceptions in the method header by separating them with ____.
A) spaces
B) semicolons
C) commas
D) periods
A) spaces
B) semicolons
C) commas
D) periods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The Java compiler does not require that you catch or specify ____ exceptions.
A) checked
B) runtime
C) return
D) optional
A) checked
B) runtime
C) return
D) optional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The ____________________ class comprises less serious errors that represent unusual conditions that arise while a program is running and from which the program can recover.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A(n) ____ is a Java language feature that can help you detect logic errors that do not cause a program to terminate, but nevertheless produce incorrect results.
A) error checker
B) thread
C) assertion
D) throw statement
A) error checker
B) thread
C) assertion
D) throw statement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If you want to ensure that a user enters numeric data, you should use ____ techniques that provide the means for your program to recover from the mistake.
A) error-handling
B) looping
C) exception-handling
D) decision
A) error-handling
B) looping
C) exception-handling
D) decision

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What advantage to programmers does the technique of cycling through the methods in the stack offer? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is an Exception class? Give an example.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What advantages does object-oriented exception handling provide?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An alternative to hard coding error messages into your Exception classes is creating a catalog of possible messages to use. What are the advantages of doing so?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AssertTest
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
Scanner input = new Scanner( System.in );
System.out.print( "Enter a number between 0 and 10: " );
int number = input.nextInt();
assert ( number >= 0 && number
System.out.printf( "You entered %d\n", number );
}
}
The above code demonstrates the functionality of the assert statement. Explain what happens when an entered number is valid and when an entered number is out of range.
public class AssertTest
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
Scanner input = new Scanner( System.in );
System.out.print( "Enter a number between 0 and 10: " );
int number = input.nextInt();
assert ( number >= 0 && number
System.out.printf( "You entered %d\n", number );
}
}
The above code demonstrates the functionality of the assert statement. Explain what happens when an entered number is valid and when an entered number is out of range.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47

Using the example code above, complete the statement of the catch block to generate the message that comes with the caught ArithmeticException .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is unreachable code and how might using multiple catch blocks cause this? Provide an example.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
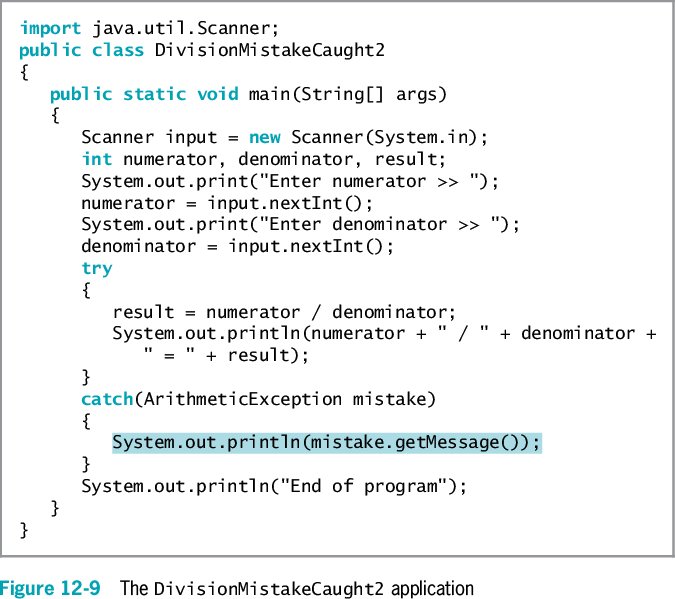
The example code above uses the getMessage() method. Explain how the getMessage() method makes error message generation more specific to the error encountered.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When a program contains multiple catch blocks, how are they handled?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What are unchecked exceptions? Give an example.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
public class exceptions
{
public static void main(String Args[])
{
int[] array = new int[3];
try
{
for(int a=0;a
{
array[a] = a;
}
System.out.println(array);
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println("Out of bounds");
}
}
}
In the above code, the line System.out.println(array); gets skipped when an exception occurs. Write a finally block that will execute, and will execute a System.out.println(array); if there is an exception.
{
public static void main(String Args[])
{
int[] array = new int[3];
try
{
for(int a=0;a
{
array[a] = a;
}
System.out.println(array);
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println("Out of bounds");
}
}
}
In the above code, the line System.out.println(array); gets skipped when an exception occurs. Write a finally block that will execute, and will execute a System.out.println(array); if there is an exception.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
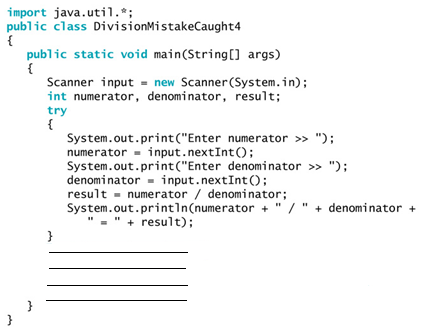
Using the above code, fill in the blank lines to create a catch block that will catch any type of Exception object and display the message "Invalid operation".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AssertionExample
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner( System.in );
System.out.print( "Enter a number between 0 and 20: " );
int value = scanner.nextInt();
---Code here---
"Invalid number: " + value;
System.out.printf( "You have entered %d\n", value );
}
}
In the code above, when the user enters the number, the scanner.nextInt() method reads the number from the command line. In the blank line provided, create an assert statement that determines whether the entered number is within the valid range (between 0 and 20). If the user entered a number that is out of range, then the "Invalid number" error should occur.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AssertionExample
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner( System.in );
System.out.print( "Enter a number between 0 and 20: " );
int value = scanner.nextInt();
---Code here---
"Invalid number: " + value;
System.out.printf( "You have entered %d\n", value );
}
}
In the code above, when the user enters the number, the scanner.nextInt() method reads the number from the command line. In the blank line provided, create an assert statement that determines whether the entered number is within the valid range (between 0 and 20). If the user entered a number that is out of range, then the "Invalid number" error should occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55

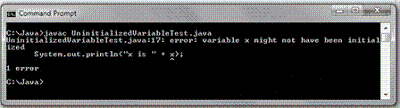
In the example above, the user might not enter an integer, the conversion to an integer might fail, and an exception might be thrown. Why is this a problem and what are some possible options for fixing these types of errors?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What things might a programmer do to cause a potential exception in a program?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57

In the above code, explain the importance of the shaded statement. What occurs if the statement is commented out of the program?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What are the elements that make up a try block?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
How is an Error class different from an Exception class?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is a finally block and how would a programmer use it?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
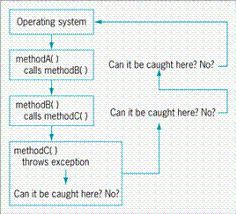
The figure above shows a call stack. Explain how a call stack works.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62

The figure above represents code that executes in the try block any statements that might throw exceptions, along with a catch and finally block. Explain three different outcomes of the try block that would cause the code in the finally block to execute.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
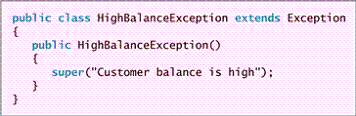
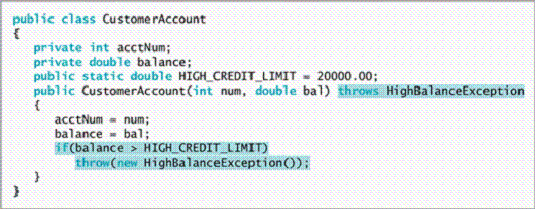
The figures above show the HighBalanceException and CustomerAccount classes. Explain what is involved in creating your own throwable Exception s. Explain what will happen if the CustomerAccount throws a HighBalanceException .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a, b;
try
{
a = 0;
b = 42 / a;
System.out.println("This will not be printed.");
}
catch (ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println("Division by zero.");
}
System.out.println("After catch statement.");
}
The program above includes a try block and a catch clause that processes the ArithmeticException generated by the division-by-zero error. Explain how the try and catch blocks operate, and what the output will be following program execution.
{
int a, b;
try
{
a = 0;
b = 42 / a;
System.out.println("This will not be printed.");
}
catch (ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println("Division by zero.");
}
System.out.println("After catch statement.");
}
The program above includes a try block and a catch clause that processes the ArithmeticException generated by the division-by-zero error. Explain how the try and catch blocks operate, and what the output will be following program execution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
import java.util.*;
public class DivisionMistakeCaught3
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int numerator, denominator, result;
try
{
System.out.print("Enter numerator >> ");
numerator = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter denominator >> ");
denominator = input.nextInt();
result = numerator / denominator;
System.out.println(numerator + " / " + denominator + " = " + result);
}
catch(ArithmeticException mistake)
{
System.out.println(mistake.getMessage());
}
catch(InputMismatchException mistake)
{
System.out.println("Wrong data type");
}
}
}
Using the above code, describe what will happen if a user enters two usable integers. What will happen if a user enters an invalid noninteger value? What will happen if the user enters 0 for the denominator?
public class DivisionMistakeCaught3
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int numerator, denominator, result;
try
{
System.out.print("Enter numerator >> ");
numerator = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter denominator >> ");
denominator = input.nextInt();
result = numerator / denominator;
System.out.println(numerator + " / " + denominator + " = " + result);
}
catch(ArithmeticException mistake)
{
System.out.println(mistake.getMessage());
}
catch(InputMismatchException mistake)
{
System.out.println("Wrong data type");
}
}
}
Using the above code, describe what will happen if a user enters two usable integers. What will happen if a user enters an invalid noninteger value? What will happen if the user enters 0 for the denominator?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
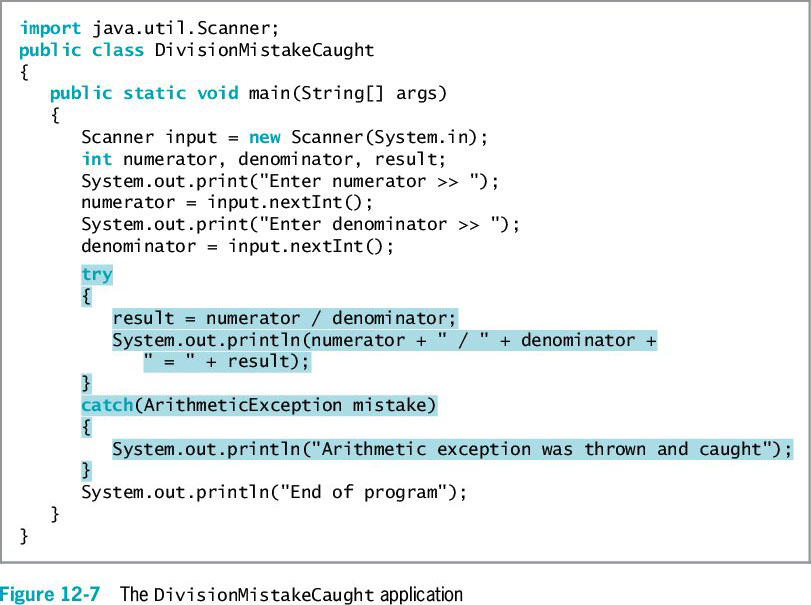
The example code above depicts a try block and a catch block. Describe how the try and catch blocks operate when illegal integer division is attempted. Describe what will happen if valid values are entered.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



