Deck 15: Advanced Gui Topics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/66
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Advanced Gui Topics
1
An additional layered pane exists above the root pane, but it is not often used explicitly by Java programmers.
True
2
Layout managers are interface classes that align components to prevent crowding or overlapping.
True
3
The FlowLayout class contains three constants you can use to align Component s with a ____ .
A) Border
B) Container
C) Button
D) Window
A) Border
B) Container
C) Button
D) Window
B
4
As you add new Components to a ____ , they are positioned in sequence from left to right across each row.
A) CardLayout
B) GridLayout
C) FlowLayout
D) BorderLayout
A) CardLayout
B) GridLayout
C) FlowLayout
D) BorderLayout

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A BorderLayout is arranged in north, south, east, west, and bottom positions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When you place a component on the screen, the vertical position is the x-axis and the horizontal position is the y-axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If you do not specify alignment, Component s are right-aligned in a FlowLayout Container by default.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Use the ____ layout manager when you add components to a maximum of five sections.
A) BorderLayout
B) GridLayout
C) GridBagLayout
D) CardLayout
A) BorderLayout
B) GridLayout
C) GridBagLayout
D) CardLayout

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Use the ____ layout manager when you need to add components that are displayed one at a time.
A) BorderLayout
B) GridLayout
C) GridBagLayout
D) CardLayout
A) BorderLayout
B) GridLayout
C) GridBagLayout
D) CardLayout

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The following statement produces a dark purple color that has green and blue components, but no red:
Color darkPurple = new Color(100, 0, 100);
Color darkPurple = new Color(100, 0, 100);

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The CardLayout manager generates a stack of containers, one on top of another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Java automatically converts the add() , remove() , and setLayoutManager() statements to more complete versions that include _____.
A) getContentPane()
B) glassPane()
C) getJFrame()
D) addAll()
A) getContentPane()
B) glassPane()
C) getJFrame()
D) addAll()

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A ____ is placed at the top of a container and contains user options.
A) glass pane
B) menu bar
C) content pane
D) containment hierarchy
A) glass pane
B) menu bar
C) content pane
D) containment hierarchy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The wildcard in the import java.awt.* statement imports all types in the java.awt package, including java.awt.Color and java.awt.Font .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When you create a simple scroll pane using the constructor that takes no arguments, horizontal and vertical scroll bars appear only if they are needed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the parent class of JPanel ?
A) Object
B) Component
C) JComponent
D) Container
A) Object
B) Component
C) JComponent
D) Container

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When you use BorderLayout , you are required to add components into each of the five regions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The Color class can be used with the setBackground() and setForeground() methods of the ____ class.
A) Container
B) JPanel
C) Component
D) JFrame
A) Container
B) JPanel
C) Component
D) JFrame

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When components in a Swing UI require more display area than they have been allocated, you can use a ____ container to hold the components and allow the user to display the components using scroll bars.
A) JScrollingPane
B) ScrollLayout
C) JPanel
D) JScrollPane
A) JScrollingPane
B) ScrollLayout
C) JPanel
D) JScrollPane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
With ____, a redrawn JPanel is displayed only when it is complete; this provides the viewer with updated screens that do not flicker while being redrawn.
A) single buffering
B) double buffering
C) auto filtering
D) double framing
A) single buffering
B) double buffering
C) auto filtering
D) double framing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The state of a JCheckBoxMenuItem or JRadioButtonMenuItem can be determined with the ____ method.
A) state()
B) getState()
C) getSelected()
D) isSelected()
A) state()
B) getState()
C) getSelected()
D) isSelected()

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When you type "A", two ____ key codes are generated: Shift and "a".
A) action
B) virtual
C) event
D) default
A) action
B) virtual
C) event
D) default

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A(n) ____ implements all methods in an interface and provides an empty body for each method.
A) action key
B) viewport
C) mnemonic
D) adapter class
A) action key
B) viewport
C) mnemonic
D) adapter class

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Each JMenu can contain options, called JMenuItem s, or can contain submenus that are ____ .
A) JMenuBar s
B) JMenuChild ren
C) JSubMenu s
D) JMenu s
A) JMenuBar s
B) JMenuChild ren
C) JSubMenu s
D) JMenu s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following statements will correctly add a JMenuBar named myBar to a JFrame ?
A) myBar = setJMenuBar
B) setJMenuBar(myBar)
C) JMenuBar.setJMenuBar(myBar)
D) JMenuBar = new JMenuBar(myBar)
A) myBar = setJMenuBar
B) setJMenuBar(myBar)
C) JMenuBar.setJMenuBar(myBar)
D) JMenuBar = new JMenuBar(myBar)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Clicking an item in a list box results in a(n) ____.
A) ItemEvent
B) WindowEvent
C) ActionEvent
D) MouseEvent
A) ItemEvent
B) WindowEvent
C) ActionEvent
D) MouseEvent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A(n) _________________________ is a tree of components that has a top-level container as its root (that is, at its uppermost level).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Clicking a component results in a(n) ____.
A) ItemEvent
B) WindowEvent
C) ActionEvent
D) MouseEvent
A) ItemEvent
B) WindowEvent
C) ActionEvent
D) MouseEvent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The ____________________ manager is the default manager class for all content panes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The parent class of MouseEvent is ____.
A) AWTEvent
B) EventObject
C) InputEvent
D) UserEvent
A) AWTEvent
B) EventObject
C) InputEvent
D) UserEvent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The focusGained(FocusEvent) handler is defined in the ____ interface.
A) FocusListener
B) ComponentListener
C) AdjustmentListener
D) ActionListener
A) FocusListener
B) ComponentListener
C) AdjustmentListener
D) ActionListener

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is NOT a method of the KeyListener interface?
A) keyTyped()
B) keyPressed()
C) keyClicked()
D) keyReleased()
A) keyTyped()
B) keyPressed()
C) keyClicked()
D) keyReleased()

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
You use the getModifiers() method with an InputEvent object, and you can assign the return value to a(n) ____ variable.
A) String
B) boolean
C) int
D) double
A) String
B) boolean
C) int
D) double

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The parent class for all event objects is named ____, which descends from the Object class.
A) EventObject
B) Event
C) ParentEvent
D) AWTEvent
A) EventObject
B) Event
C) ParentEvent
D) AWTEvent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The JMenu s are added to the JMenuBar using the ____ method.
A) addMenu()
B) add()
C) addNewMenu()
D) setMenu()
A) addMenu()
B) add()
C) addNewMenu()
D) setMenu()

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
You use the ____________________ interface when you are interested in actions the user initiates from the keyboard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
____________________ are lists of user options; they are commonly added features in GUI programs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following statements will set the background color of a button named stop to a color of red?
A) stop.setBackground(Color.RED);
B) stop.Backcolor = RED;
C) red.setBackground(Color.RED);
D) setBack.stop.Color.RED;
A) stop.setBackground(Color.RED);
B) stop.Backcolor = RED;
C) red.setBackground(Color.RED);
D) setBack.stop.Color.RED;

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If you wanted to see the x-coordinate of a user click, you would use the ____ method of the MouseEvent class.
A) getClick()
B) getX()
C) getY()
D) getHoriz()
A) getClick()
B) getX()
C) getY()
D) getHoriz()

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A(n) ____________________ is a plain, borderless surface that can hold lightweight GUI components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Describe the two CardLayout constructors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
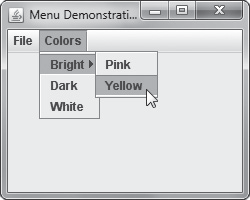 The above figure shows a JFrame with a horizontal JMenuBar named myMenu that holds two JMenu s: menu1 and menu2 . A submenu and JMenuItem s also exist with the Colors yellows , blues , and greens . Using the add() method, write the statements to add the JMenu s to the JMenuBar , and write the statements to add a submenu and JMenuItem s to the Colors menu.
The above figure shows a JFrame with a horizontal JMenuBar named myMenu that holds two JMenu s: menu1 and menu2 . A submenu and JMenuItem s also exist with the Colors yellows , blues , and greens . Using the add() method, write the statements to add the JMenu s to the JMenuBar , and write the statements to add a submenu and JMenuItem s to the Colors menu.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is a mnemonic? Provide an example of adding a mnemonic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is an adapter class?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Write the statement to set the background color of a button named goBtn to a color of green.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Describe the way in which components expand to fill their layout areas in FlowLayout and BorderLayout .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.Color;
public class JFrameWithColor extends JFrame
{
private final int SIZE = 180;
private Container con = getContentPane();
private JButton button =
new JButton("Press Me");
public JFrameWithColor()
{
super("Frame");
setSize(SIZE, SIZE);
con.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
con.add(button);
-----Code here-----
-----Code here-----
-----Code here-----
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
JFrameWithColor frame =
new JFrameWithColor();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
} In the first indicated line, write the statement to set the background color of the JFrame 's content pane to gray. Using the remaining two indicated lines, write the statements to set the JButton foreground color to white and the background color to blue.
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.Color;
public class JFrameWithColor extends JFrame
{
private final int SIZE = 180;
private Container con = getContentPane();
private JButton button =
new JButton("Press Me");
public JFrameWithColor()
{
super("Frame");
setSize(SIZE, SIZE);
con.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
con.add(button);
-----Code here-----
-----Code here-----
-----Code here-----
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
JFrameWithColor frame =
new JFrameWithColor();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
} In the first indicated line, write the statement to set the background color of the JFrame 's content pane to gray. Using the remaining two indicated lines, write the statements to set the JButton foreground color to white and the background color to blue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Write the statement to create a Color object named myGray with red, green, and blue values of 100 each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
To force the display of a scroll bar, you can use class variables defined in the ScrollPaneConstants class. What are they?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Write the code to create a scroll pane named myScroll that will display an image named scenery with a vertical scroll bar always present and a horizontal scroll bar as needed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
How do you find the red, green, and blue components of a color?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When do you need to worry about using the getContentPane() method?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class JDemoGridLayout extends JFrame
{
private JButton b1 = new JButton("Button 1");
private JButton b2 = new JButton("Button 2");
private JButton b3 = new JButton("Button 3");
private JButton b4 = new JButton("Button 4");
private JButton b5 = new JButton("Button 5");
-----Code here-----
private Container con = getContentPane();
public JDemoGridLayout()
{
con.setLayout(layout);
con.add(b1);
con.add(b2);
con.add(b3);
con.add(b4);
con.add(b5);
setSize(200, 200);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
JDemoGridLayout frame = new JDemoGridLayout();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Using the above code, write the statement in the indicated line to establish a GridLayout with three horizontal rows and two vertical columns, with horizontal and vertical gaps of five pixels each.
import java.awt.*;
public class JDemoGridLayout extends JFrame
{
private JButton b1 = new JButton("Button 1");
private JButton b2 = new JButton("Button 2");
private JButton b3 = new JButton("Button 3");
private JButton b4 = new JButton("Button 4");
private JButton b5 = new JButton("Button 5");
-----Code here-----
private Container con = getContentPane();
public JDemoGridLayout()
{
con.setLayout(layout);
con.add(b1);
con.add(b2);
con.add(b3);
con.add(b4);
con.add(b5);
setSize(200, 200);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
JDemoGridLayout frame = new JDemoGridLayout();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Using the above code, write the statement in the indicated line to establish a GridLayout with three horizontal rows and two vertical columns, with horizontal and vertical gaps of five pixels each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
How would you arrange columns into equal rows and columns? Provide an example.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Describe the difference between an ActionEvent and a MouseEvent .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57

Write the statement that will provide a shortcut menu key for a menu named myShortcutMenu . When a user presses Alt+F on the keyboard, the statement will set the F in File (shown in the above figure) as the mnemonic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What are the four methods defined in the Component class for adding event listeners?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class JMouseActionFrame extends JFrame implements MouseListener
{
private int x, y;
private JLabel label = new JLabel("Do something with the mouse");
String msg = "";
public JMouseActionFrame()
{
setTitle("Mouse Actions"); setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setLayout(new FlowLayout()); addMouseListener(this);
add(label);
}
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e)
{
int whichButton = e.getButton(); msg = "You pressed mouse ";
if(whichButton == MouseEvent.BUTTON1)
msg += "button 1.";
else
if(whichButton == MouseEvent.BUTTON2)
msg += "button 2.";
else
msg += "button 3.";
msg += " You are at position " +
e.getX() + ", " + e.getY() + ".";
if(e.getClickCount() == 2)
msg += " You double-clicked.";
else
msg += " You single-clicked.";
label.setText(msg);
}
@Override
public void mouseEntered(MouseEvent e)
{
msg = "You entered the frame.";
label.setText(msg);
}
@Override
public void mouseExited(MouseEvent e)
{
msg = "You exited the frame.";
label.setText(msg);
}
@Override
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e)
{
}
@Override
public void mouseReleased(MouseEvent e)
{
}
@Override
public static void main(String[] args)
{
JMouseActionFrame mFrame = new JMouseActionFrame();
final int WIDTH = 750; final int HEIGHT = 300; mFrame.setSize(WIDTH, HEIGHT); mFrame.setVisible(true);
}
}
The above code shows a JMouseActionFrame application that demonstrates several of the mouse listener and event methods. The constructor sets a frame title by passing it to the parent of JMouseActionFrame , sets a close operation, sets the layout manager, enables the frame to listen for mouse events, and adds the JLabel to the JFrame . However, most of the action occurs in the mouseClicked() method. Describe what actions occur in this method.
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class JMouseActionFrame extends JFrame implements MouseListener
{
private int x, y;
private JLabel label = new JLabel("Do something with the mouse");
String msg = "";
public JMouseActionFrame()
{
setTitle("Mouse Actions"); setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setLayout(new FlowLayout()); addMouseListener(this);
add(label);
}
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e)
{
int whichButton = e.getButton(); msg = "You pressed mouse ";
if(whichButton == MouseEvent.BUTTON1)
msg += "button 1.";
else
if(whichButton == MouseEvent.BUTTON2)
msg += "button 2.";
else
msg += "button 3.";
msg += " You are at position " +
e.getX() + ", " + e.getY() + ".";
if(e.getClickCount() == 2)
msg += " You double-clicked.";
else
msg += " You single-clicked.";
label.setText(msg);
}
@Override
public void mouseEntered(MouseEvent e)
{
msg = "You entered the frame.";
label.setText(msg);
}
@Override
public void mouseExited(MouseEvent e)
{
msg = "You exited the frame.";
label.setText(msg);
}
@Override
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e)
{
}
@Override
public void mouseReleased(MouseEvent e)
{
}
@Override
public static void main(String[] args)
{
JMouseActionFrame mFrame = new JMouseActionFrame();
final int WIDTH = 750; final int HEIGHT = 300; mFrame.setSize(WIDTH, HEIGHT); mFrame.setVisible(true);
}
}
The above code shows a JMouseActionFrame application that demonstrates several of the mouse listener and event methods. The constructor sets a frame title by passing it to the parent of JMouseActionFrame , sets a close operation, sets the layout manager, enables the frame to listen for mouse events, and adds the JLabel to the JFrame . However, most of the action occurs in the mouseClicked() method. Describe what actions occur in this method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
List and describe the four constructors that can be used when creating a JPanel object.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Write the statement to establish a GridLayout with three horizontal rows and six vertical columns in a Container named myGrid .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
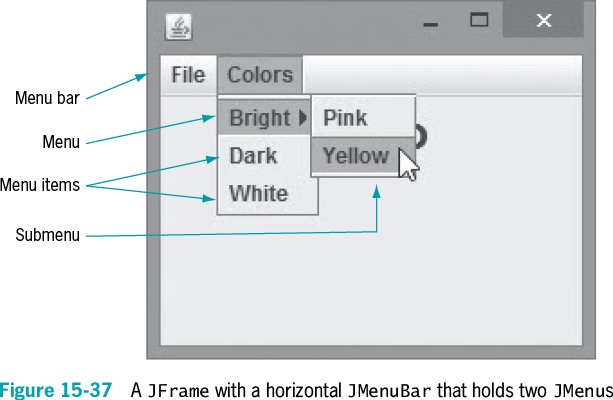 Using the figure above, write the statement to create a JMenuBar . Next, create the two JMenu s that are part of the JMenuBar , add the three components within the Colors JMenu , and add the two JMenuItem s that are part of the BrightJMenu . Finally, write the statement to add the JMenuBar to the JFrame using the setJMenuBar() method.
Using the figure above, write the statement to create a JMenuBar . Next, create the two JMenu s that are part of the JMenuBar , add the three components within the Colors JMenu , and add the two JMenuItem s that are part of the BrightJMenu . Finally, write the statement to add the JMenuBar to the JFrame using the setJMenuBar() method.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class JDemoBorderLayout extends JFrame
{
private JButton nb = new JButton("North Button");
private JButton sb = new JButton("South Button");
private JButton eb = new JButton("East Button");
private JButton wb = new JButton("West Button");
private JButton cb = new JButton("Center Button");
private Container con = getContentPane();
public JDemoBorderLayout()
{
con.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
-----Code here-----
-----Code here-----
-----Code here-----
-----Code here-----
-----Code here-----
setSize(400, 150);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
JDemoBorderLayout frame = new JDemoBorderLayout();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Using the above code, write the statements in the indicated lines to add components to each of the five regions (north, south, east, west and center).
import java.awt.*;
public class JDemoBorderLayout extends JFrame
{
private JButton nb = new JButton("North Button");
private JButton sb = new JButton("South Button");
private JButton eb = new JButton("East Button");
private JButton wb = new JButton("West Button");
private JButton cb = new JButton("Center Button");
private Container con = getContentPane();
public JDemoBorderLayout()
{
con.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
-----Code here-----
-----Code here-----
-----Code here-----
-----Code here-----
-----Code here-----
setSize(400, 150);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
JDemoBorderLayout frame = new JDemoBorderLayout();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Using the above code, write the statements in the indicated lines to add components to each of the five regions (north, south, east, west and center).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Using a FlowLayout object named myLayout , write the statement to set the layout of a content pane to left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Describe the purpose of an accelerator. Provide an example of an accelerator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.Color;
public class Checkerboard extends JFrame
{
private final int ROWS = 8;
private final int COLS = 8;
private final int GAP = 2;
private final int NUM = ROWS * COLS;
private int x;
private JPanel pane = new JPanel
(new GridLayout(ROWS, COLS, GAP, GAP));
private JPanel[] panel = new JPanel[NUM];
private Color color1 = Color.WHITE;
private Color color2 = Color.BLUE;
private Color tempColor;
public Checkerboard()
{
super("Checkerboard");
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
add(pane);
for(x = 0; x
{
panel[x] = new JPanel();
pane.add(panel[x]);
if(x % COLS == 0)
{
tempColor = color1;
color1 = color2;
color2 = tempColor;
}
if(x % 2 == 0)
panel[x].setBackground(color1);
else
panel[x].setBackground(color2);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Checkerboard frame = new Checkerboard();
final int SIZE = 300;
frame.setSize(SIZE, SIZE);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
The above code creates a loop to fill even-positioned squares with one color and odd-positioned squares with another color, resulting in a checkerboard pattern. Describe how JPanel s and a GridLayout are used to achieve this effect.
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.Color;
public class Checkerboard extends JFrame
{
private final int ROWS = 8;
private final int COLS = 8;
private final int GAP = 2;
private final int NUM = ROWS * COLS;
private int x;
private JPanel pane = new JPanel
(new GridLayout(ROWS, COLS, GAP, GAP));
private JPanel[] panel = new JPanel[NUM];
private Color color1 = Color.WHITE;
private Color color2 = Color.BLUE;
private Color tempColor;
public Checkerboard()
{
super("Checkerboard");
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
add(pane);
for(x = 0; x
{
panel[x] = new JPanel();
pane.add(panel[x]);
if(x % COLS == 0)
{
tempColor = color1;
color1 = color2;
color2 = tempColor;
}
if(x % 2 == 0)
panel[x].setBackground(color1);
else
panel[x].setBackground(color2);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Checkerboard frame = new Checkerboard();
final int SIZE = 300;
frame.setSize(SIZE, SIZE);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
The above code creates a loop to fill even-positioned squares with one color and odd-positioned squares with another color, resulting in a checkerboard pattern. Describe how JPanel s and a GridLayout are used to achieve this effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



