Deck 17: Chemical Thermodynamics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/106
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Chemical Thermodynamics
1
For which of the following reactions is D H - D E > 0?
A) NaCl (aq) + AgNO3 (aq)→ AgCl (s) + NaNO3 (aq)
B) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g)→ 2 HCl (g)
C) 2 N2 (g) + O2 (g)→ 2 N2O (g)
D) NH4NO3 (s)→ N2O (g) + 2 H2O (g)
E) none of these
A) NaCl (aq) + AgNO3 (aq)→ AgCl (s) + NaNO3 (aq)
B) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g)→ 2 HCl (g)
C) 2 N2 (g) + O2 (g)→ 2 N2O (g)
D) NH4NO3 (s)→ N2O (g) + 2 H2O (g)
E) none of these
NH4NO3 (s)→ N2O (g) + 2 H2O (g)
2
The combustion of a 3.06 g sample of formic acid (H CO₂ H( 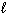 ), molar mass = 46.03 g/mol) in a bomb calorimeter with a heat capacity of 5.423 J/ C causes the temperature to rise from 23.27 C to 26.41 C. What is D E for the reaction?
), molar mass = 46.03 g/mol) in a bomb calorimeter with a heat capacity of 5.423 J/ C causes the temperature to rise from 23.27 C to 26.41 C. What is D E for the reaction?
2 H CO₂ H (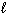 ) + O₂(g) 2 CO₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (
) + O₂(g) 2 CO₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O ( 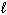 )
)
A) - 5.56 kJ
B) - 17.0 kJ
C) - 256 kJ
D) - 512 kJ
E) none of these
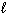 ), molar mass = 46.03 g/mol) in a bomb calorimeter with a heat capacity of 5.423 J/ C causes the temperature to rise from 23.27 C to 26.41 C. What is D E for the reaction?
), molar mass = 46.03 g/mol) in a bomb calorimeter with a heat capacity of 5.423 J/ C causes the temperature to rise from 23.27 C to 26.41 C. What is D E for the reaction?2 H CO₂ H (
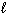 ) + O₂(g) 2 CO₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (
) + O₂(g) 2 CO₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O ( 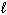 )
)A) - 5.56 kJ
B) - 17.0 kJ
C) - 256 kJ
D) - 512 kJ
E) none of these
- 512 kJ
3
From the D E given for 25 ° C, calculate D H at the same temperature for the reaction:
2 N2O (g)→2 N2 (g) + O2 (g) D E = - 161.62 kJ
A) - 159.14 kJ
B) - 161.62 kJ
C) - 164.10 kJ
D) - 166.58 kJ
E) none of these
2 N2O (g)→2 N2 (g) + O2 (g) D E = - 161.62 kJ
A) - 159.14 kJ
B) - 161.62 kJ
C) - 164.10 kJ
D) - 166.58 kJ
E) none of these
- 164.10 kJ
4
Which of the following units express(es) a quantity of energy?
I. joule
II. L × atm
III. kcal
A) I and III, but not II
B) I and II, but not III
C) I, II, and III
D) I only
E) none of them
I. joule
II. L × atm
III. kcal
A) I and III, but not II
B) I and II, but not III
C) I, II, and III
D) I only
E) none of them

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When a sample of an ideal gas is compressed at 25 ° C from 39.0 L to 15.0 L at a constant pressure of 1.90 atm, the work is
A) w = - 74.1 L × atm
B) w = - 45.6 L × atm
C) w = +28.5 L × atm
D) w = +45.6 L × atm
E) none of these
A) w = - 74.1 L × atm
B) w = - 45.6 L × atm
C) w = +28.5 L × atm
D) w = +45.6 L × atm
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements is incorrect ?
A) For any state function, X, D X = X(final) - X(initial).
B) State functions are path independent.
C) The variables T, V, and P are state functions.
D) The internal energy of a system (E) is a state function.
E) The heat absorbed by a system ( q ) is a state function.
A) For any state function, X, D X = X(final) - X(initial).
B) State functions are path independent.
C) The variables T, V, and P are state functions.
D) The internal energy of a system (E) is a state function.
E) The heat absorbed by a system ( q ) is a state function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following systems show(s) a decrease in entropy?
The system is underlined.
A) Molten iron solidifies.
B) Ice melts.
C) A jigsaw puzzle is solved.
D) More than one of these is correct.
E) None of these is correct.
The system is underlined.
A) Molten iron solidifies.
B) Ice melts.
C) A jigsaw puzzle is solved.
D) More than one of these is correct.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A sample of an ideal gas at 275 K occupies a volume oF42 L. The sample contracts to a volume of 15 L at a constant pressure of 1.50 atm, while heat of 2400 J is lost to the surroundings. What is D E for this process?
A) - 6.5 kJ
B) - 4.1 kJ
C) +1.7 kJ
D) +4.1 kJ
E) none of these
A) - 6.5 kJ
B) - 4.1 kJ
C) +1.7 kJ
D) +4.1 kJ
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The mathematical form of the first law of thermodynamics is:
A) P D V = D nRT
B) D E = q + w
C) D H rxn = D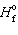 prod = D
prod = D 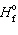 react
react
D) D G = D H + T D S
E) none of these
A) P D V = D nRT
B) D E = q + w
C) D H rxn = D
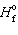 prod = D
prod = D 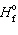 react
reactD) D G = D H + T D S
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
One mole of an ideal gas at 300 K expands from 2.0 L to 9.0 L against a constant external pressure of 1.8 atm. The work done by this expansion is (in L × atm):
A) 0
B)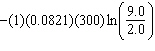
C) - (300)(4.5)(1.8)
D) - (1.8)(9.0 - 2.0)
E)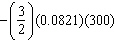
A) 0
B)
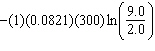
C) - (300)(4.5)(1.8)
D) - (1.8)(9.0 - 2.0)
E)
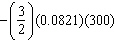

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
From the D E given for 25 ° C, calculate D H at the same temperature for the reaction:
2 HI (g)→H2 (g) + I2 (g) D E = +9.48 kJ
A) +7.00 kJ
B) +9.48 kJ
C) +11.96 kJ
D) +19.39 kJ
E) none of these
2 HI (g)→H2 (g) + I2 (g) D E = +9.48 kJ
A) +7.00 kJ
B) +9.48 kJ
C) +11.96 kJ
D) +19.39 kJ
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which thermodynamic parameter listed below measures the degree of disorder associated with a system?
A) Gibbs Free Energy
B) Enthalpy
C) Entropy
D) Internal energy
E) Work
A) Gibbs Free Energy
B) Enthalpy
C) Entropy
D) Internal energy
E) Work

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which substance listed below would be expected to have the greatest entropy value, S ° ?
Assume all substances are in the gas phase at the same temperature.
A) butane
B) ethane
C) methane
D) propane
E) pentane
Assume all substances are in the gas phase at the same temperature.
A) butane
B) ethane
C) methane
D) propane
E) pentane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If only work of expansion is done, the heat, q , for a change at constant temperature and volume is equal to what?
A) D E
B) D H
C) D G
D) w
E) none of these
A) D E
B) D H
C) D G
D) w
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When a 3.125 g sample of ammonium nitrate (NH ₄NO3 , molar mass = 80.05 g/mol) decomposes in a bomb calorimeter with a heat capacity oF4.116 kJ/ C, the temperature rises from 24.15 C to 25.35 C. What is D E for the decomposition of ammonium nitrate?
NH ₄NO3(s) N₂O (g) + 2 H₂ O ( )
)
A) - 126 kJ
B) - 69.5 kJ
C) - 4.94 kJ
D) - 1.58 kJ
E) none of these
NH ₄NO3(s) N₂O (g) + 2 H₂ O (
 )
)A) - 126 kJ
B) - 69.5 kJ
C) - 4.94 kJ
D) - 1.58 kJ
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The combustion of a 0.440 g sample of ethanol (C₂ H5 OH, molar mass = 46.07 g/mol) in a bomb calorimeter with a heat capacity of 5.278 kJ/ C causes the temperature to rise from 23.98 C to 26.45 C. What is D E for the reaction?
C₂ H5 OH (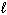 ) + 3 O₂(g) 2 CO₂ (g) + 3 H₂ O (
) + 3 O₂(g) 2 CO₂ (g) + 3 H₂ O ( 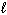 )
)
A) - 13.0 kJ
B) - 1.36×103 kJ
C) - 29.6 kJ
D) +13.0 kJ
E) none of these
C₂ H5 OH (
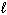 ) + 3 O₂(g) 2 CO₂ (g) + 3 H₂ O (
) + 3 O₂(g) 2 CO₂ (g) + 3 H₂ O ( 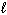 )
)A) - 13.0 kJ
B) - 1.36×103 kJ
C) - 29.6 kJ
D) +13.0 kJ
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which one of the following systems shows a positive entropy change?
The system is underlined.
A) A dormitory room is cleaned.
B) Ice melts.
C) Water freezes.
D) Silver ions react with chloride ions to form AgCl (s).
E) An egg grows into a chick.
The system is underlined.
A) A dormitory room is cleaned.
B) Ice melts.
C) Water freezes.
D) Silver ions react with chloride ions to form AgCl (s).
E) An egg grows into a chick.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If q of the system is negative:
A) the surroundings are heated by the system.
B) the bomb-calorimeter reaction is endothermic.
C) D S univ > 0.
D) PV work is zero.
E) w must also be negative.
A) the surroundings are heated by the system.
B) the bomb-calorimeter reaction is endothermic.
C) D S univ > 0.
D) PV work is zero.
E) w must also be negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
One mole of a gas, initially at 300 K and 1.00 atm, undergoes a change so the final conditions are T = 400 K and V = 50.0 liters. Which of the following cannot be calculated from this information?
A) q
B) D V
C) D P
D) D T
E) all of these can be found
A) q
B) D V
C) D P
D) D T
E) all of these can be found

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Calculate the work done by 1.00 mol of an ideal gas when it expands from a volume of 14.00 L to a volume of 18.00 L against a constant external pressure of 2.00 atm.
A) w = - 28.0 L × atm
B) w = - 8.00 L × atm
C) w = 0 L × atm
D) w = - 36.0 L × atm
E) w = +28.0 L × atm
A) w = - 28.0 L × atm
B) w = - 8.00 L × atm
C) w = 0 L × atm
D) w = - 36.0 L × atm
E) w = +28.0 L × atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following reactions has the largest positive entropy change?
A) PCl 3 (g) + Cl₂ (g)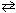 PCl5 (g)
PCl5 (g)
B) 2 N₂(g) + O₂(g)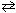 2 N₂O (g)
2 N₂O (g)
C) 2 NO2 (g)→ 2 NO (g) + O2 (g)
D) CO2 (g)→ O2 (g) + C (s)
E) H₂ O (g) H₂ O ( )
)
A) PCl 3 (g) + Cl₂ (g)
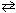 PCl5 (g)
PCl5 (g)B) 2 N₂(g) + O₂(g)
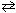 2 N₂O (g)
2 N₂O (g)C) 2 NO2 (g)→ 2 NO (g) + O2 (g)
D) CO2 (g)→ O2 (g) + C (s)
E) H₂ O (g) H₂ O (
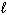 )
)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The following reduction of Fe2 O3 to Fe occurs in blast furnaces during the steel making process:
3 CO (g) + Fe2 O3(s) 2 Fe (s) + 3 CO₂ (g) Calculate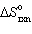 per mole of Fe2 O3 reacted, if the values of S for CO (g), Fe2 O3(s), Fe (s), and CO₂ (g) are 198, 87, 27, and 214 J/mol K, respectively (answer in units of J/K).
per mole of Fe2 O3 reacted, if the values of S for CO (g), Fe2 O3(s), Fe (s), and CO₂ (g) are 198, 87, 27, and 214 J/mol K, respectively (answer in units of J/K).
A) - 44 J/K
B) - 15 J/K
C) 15 J/K
D) 44 J/K
E) 411 J/K
3 CO (g) + Fe2 O3(s) 2 Fe (s) + 3 CO₂ (g) Calculate
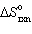 per mole of Fe2 O3 reacted, if the values of S for CO (g), Fe2 O3(s), Fe (s), and CO₂ (g) are 198, 87, 27, and 214 J/mol K, respectively (answer in units of J/K).
per mole of Fe2 O3 reacted, if the values of S for CO (g), Fe2 O3(s), Fe (s), and CO₂ (g) are 198, 87, 27, and 214 J/mol K, respectively (answer in units of J/K).A) - 44 J/K
B) - 15 J/K
C) 15 J/K
D) 44 J/K
E) 411 J/K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The third law of thermodynamics states that:
A) all spontaneous processes are accompanied by an increase in entropy.
B) the energy of the universe is constant when a physical or chemical change occurs.
C) the free energy change is positive for any spontaneous process.
D) the entropy of a pure crystalline solid is zero at 0 K.
E) heat and work are state functions.
A) all spontaneous processes are accompanied by an increase in entropy.
B) the energy of the universe is constant when a physical or chemical change occurs.
C) the free energy change is positive for any spontaneous process.
D) the entropy of a pure crystalline solid is zero at 0 K.
E) heat and work are state functions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
For which of the following processes will D S system be the most positive?
A) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g)→ 2 HCl (g)
B) 2 H₂ (g) + O₂(g) 2 H₂ O (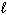 )
)
C) CaCO3 (s)→ CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
D) Ag+ (aq) + Cl - (aq)→ AgCl (s)
E) KClO4 (s)→ KCl (s) + 2 O2 (g)
A) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g)→ 2 HCl (g)
B) 2 H₂ (g) + O₂(g) 2 H₂ O (
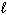 )
)C) CaCO3 (s)→ CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
D) Ag+ (aq) + Cl - (aq)→ AgCl (s)
E) KClO4 (s)→ KCl (s) + 2 O2 (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following physical changes would be expected to have a negative sign for D S system?
I. Dissolving oxygen gas, O2, in water.
II. Freezing ice cubes.
III. Breaking glass.
A) I only
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) All of these
I. Dissolving oxygen gas, O2, in water.
II. Freezing ice cubes.
III. Breaking glass.
A) I only
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
For the reaction 4 CuO (s)→2 Cu2O (s) + O2 (g), what is D S ° at 298 K (in J/K)?
S ° [CuO] = 43 J/mol × K; S ° [O2] = 205 J/mol × K; S ° [Cu2O] = 93.14 J/mol × K
A) 0.768 J/K
B) 219 J/K
C) 255 J/K
D) 348 J/K
E) 354 J/K
S ° [CuO] = 43 J/mol × K; S ° [O2] = 205 J/mol × K; S ° [Cu2O] = 93.14 J/mol × K
A) 0.768 J/K
B) 219 J/K
C) 255 J/K
D) 348 J/K
E) 354 J/K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following chemical equations would be expected to have a positive sign for D S system?
I. NaClO3 (s)→Na+ (aq) + ClO31 - (aq)
II. NH3 (g) + HBr (g)→NH4Br (s)
III. H2S (g) + 1/2 O 2 (g)→1/8 S8 (s) + H2O (g)
A) I only
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) All of these
I. NaClO3 (s)→Na+ (aq) + ClO31 - (aq)
II. NH3 (g) + HBr (g)→NH4Br (s)
III. H2S (g) + 1/2 O 2 (g)→1/8 S8 (s) + H2O (g)
A) I only
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which process below is accompanied by a decrease in entropy for the system ?
A) H₂ O (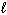 ) + SOCl₂ (
) + SOCl₂ ( 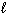 ) 2 HCl (g) + SO₂ (g)
) 2 HCl (g) + SO₂ (g)
B) CH4 (g) + 2 O₂(g) CO₂ (g) + H₂ O (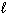 )
)
C) H2O (s)→ H2O (g)
D) H2O (g) (420 K)→ H2O (g) (450 K)
E) none of these
A) H₂ O (
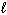 ) + SOCl₂ (
) + SOCl₂ ( 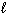 ) 2 HCl (g) + SO₂ (g)
) 2 HCl (g) + SO₂ (g)B) CH4 (g) + 2 O₂(g) CO₂ (g) + H₂ O (
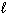 )
)C) H2O (s)→ H2O (g)
D) H2O (g) (420 K)→ H2O (g) (450 K)
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following reactions would be expected to have a positive entropy change , D S > 0?
I. 3 O2 (g)→2 O3 (g)
II. CaCO3 (s)→CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
III. C3H8 (g) + 5 O2 (g)→3 CO2 (g) + 4 H2O (g)
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) II and III
I. 3 O2 (g)→2 O3 (g)
II. CaCO3 (s)→CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
III. C3H8 (g) + 5 O2 (g)→3 CO2 (g) + 4 H2O (g)
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following physical changes would be expected to provide a positive change in entropy , D S > 0?
I. Compressing a gas until it liquefies.
II. Melting an ice-cube.
III. Heating a substance to a higher temperature.
A) I only
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) All of these
I. Compressing a gas until it liquefies.
II. Melting an ice-cube.
III. Heating a substance to a higher temperature.
A) I only
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Using the entropy values in the table below, what is the change in standard entropy, D S , for the following reaction?
2 CH₃ OH (g) + 3 O₂(g) 2 CO₂ (g) + 4 H₂ O (g) Substance S (J/mol K) CH₃ OH (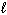 ) 126.8 CH₃ OH (g) 237.6 O₂(g) 205.0 CO₂ (g) 213.6 H₂ O (g) 188.83 H₂ O (
) 126.8 CH₃ OH (g) 237.6 O₂(g) 205.0 CO₂ (g) 213.6 H₂ O (g) 188.83 H₂ O ( 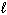 ) 69.91
) 69.91
A) D S ° = - 383.4 J/mol × K
B) D S ° = - 161.8 J/mol × K
C) D S ° = - 40.2 J/mol × K
D) D S ° = 92.3 J/mol × K
E) D S ° = 313.9 J/mol × K
2 CH₃ OH (g) + 3 O₂(g) 2 CO₂ (g) + 4 H₂ O (g) Substance S (J/mol K) CH₃ OH (
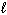 ) 126.8 CH₃ OH (g) 237.6 O₂(g) 205.0 CO₂ (g) 213.6 H₂ O (g) 188.83 H₂ O (
) 126.8 CH₃ OH (g) 237.6 O₂(g) 205.0 CO₂ (g) 213.6 H₂ O (g) 188.83 H₂ O ( 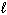 ) 69.91
) 69.91A) D S ° = - 383.4 J/mol × K
B) D S ° = - 161.8 J/mol × K
C) D S ° = - 40.2 J/mol × K
D) D S ° = 92.3 J/mol × K
E) D S ° = 313.9 J/mol × K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
"A spontaneous change is always accompanied by an increase in entropy." The entropy change referred to in this statement is:
A) D S system
B) D S universe
C) D S reversible
D) D S surroundings
E) none of these
A) D S system
B) D S universe
C) D S reversible
D) D S surroundings
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following chemical reactions would be expected to have a positive sign for D S reaction?
I. 2 N2 (g) + 3 F2 (g)→2 NF3 (g)
II. NaCl (aq) + AgNO3 (aq)→NaNO3 (aq) + AgCl (s)
III. CaCO3 (s)→CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
A) III only
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) All of these
I. 2 N2 (g) + 3 F2 (g)→2 NF3 (g)
II. NaCl (aq) + AgNO3 (aq)→NaNO3 (aq) + AgCl (s)
III. CaCO3 (s)→CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
A) III only
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following reactions would be expected to provide a negative change in entropy , D S
I. 2 K (s) + F2 (g)→2 KF (s)
II. 2 NO2 (g)→N2O4 (g)
III. NaClO3 (s)→Na+ (aq) + ClO31 - (aq)
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) All of these
I. 2 K (s) + F2 (g)→2 KF (s)
II. 2 NO2 (g)→N2O4 (g)
III. NaClO3 (s)→Na+ (aq) + ClO31 - (aq)
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following chemical reactions has the largest positive entropy change?
A) H2S (g)→ H2 (g) + S (s)
B) 2 CO2 (g)→ 2 CO (g) + O2 (g)
C) 2 Al (s) + 3 O2 (g)→ 2 Al2O3 (s)
D) N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g)→ 2 NH3 (g)
E) 6 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O (g)→ C6H12O6 (s) + 6 O2 (g)
A) H2S (g)→ H2 (g) + S (s)
B) 2 CO2 (g)→ 2 CO (g) + O2 (g)
C) 2 Al (s) + 3 O2 (g)→ 2 Al2O3 (s)
D) N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g)→ 2 NH3 (g)
E) 6 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O (g)→ C6H12O6 (s) + 6 O2 (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following processes would be expected to have a positive sign for D S system?
I. Hot air expanding.
II. A piece of wax melting.
III. Alcohol evaporating.
A) I only
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) All of these
I. Hot air expanding.
II. A piece of wax melting.
III. Alcohol evaporating.
A) I only
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The entropy change when one mole of acetone [(CH3)2CO] vaporizes at its boiling point (56 ° C) is D S vap = 97.16 J/mol × K. How much heat is absorbed when 58.0 grams of acetone vaporizes at 56 ° C?
A) 0.29 kJ
B) 5.44 kJ
C) 97.16 kJ
D) 234 J
E) 32.0 J
A) 0.29 kJ
B) 5.44 kJ
C) 97.16 kJ
D) 234 J
E) 32.0 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following reactions would be expected to have a positive entropy change, D S 0?
I. 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) 2 SO3(g)
II. Ba(OH) 2 (s) BaO (s) + H₂ O (g)
III. CO (g) + 2 H₂ (g) CH₃ OH (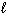 )
)
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) I and III
I. 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) 2 SO3(g)
II. Ba(OH) 2 (s) BaO (s) + H₂ O (g)
III. CO (g) + 2 H₂ (g) CH₃ OH (
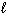 )
)A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) I and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following processes results in a negative entropy change?
A) HCN(g, V = 10 L, P = 4 atm) HCN (g, V = 20 L, P = 2 atm)
HCN (g, V = 20 L, P = 2 atm)
B) 2 HI (g) H₂ (g) + I2 (s)
H₂ (g) + I2 (s)
C) NaI (s)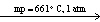 NaI (
NaI ( 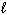 )
)
D) CaCO3(s)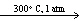 CaO (s) + CO₂ (g)
CaO (s) + CO₂ (g)
E) Bi (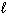 ) + Sn (
) + Sn ( 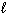 ) + Pb (
) + Pb ( 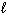 )
) 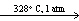 Soft Solder (
Soft Solder ( 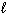 )
)
A) HCN(g, V = 10 L, P = 4 atm)
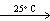 HCN (g, V = 20 L, P = 2 atm)
HCN (g, V = 20 L, P = 2 atm)B) 2 HI (g)
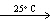 H₂ (g) + I2 (s)
H₂ (g) + I2 (s)C) NaI (s)
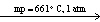 NaI (
NaI ( 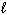 )
)D) CaCO3(s)
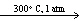 CaO (s) + CO₂ (g)
CaO (s) + CO₂ (g)E) Bi (
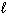 ) + Sn (
) + Sn ( 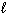 ) + Pb (
) + Pb ( 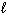 )
) 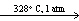 Soft Solder (
Soft Solder ( 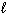 )
)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Estimate the normal boiling point of mercury, given that for Hg ( 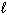 ),
), 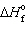 = 0 kJ/mol and D S = 76.02 J/mol K and for Hg (g),
= 0 kJ/mol and D S = 76.02 J/mol K and for Hg (g), 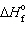 = 61.32 kJ/mol and D S = 174.85 J/mol K. The change is:
= 61.32 kJ/mol and D S = 174.85 J/mol K. The change is:
Hg (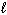 )
) 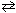 Hg (g)
Hg (g)
A) 0.62 K
B) 620 K
C) 1.6 K
D) 160 K
E) 1612 K
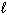 ),
), 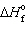 = 0 kJ/mol and D S = 76.02 J/mol K and for Hg (g),
= 0 kJ/mol and D S = 76.02 J/mol K and for Hg (g), 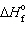 = 61.32 kJ/mol and D S = 174.85 J/mol K. The change is:
= 61.32 kJ/mol and D S = 174.85 J/mol K. The change is:Hg (
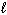 )
)  Hg (g)
Hg (g)A) 0.62 K
B) 620 K
C) 1.6 K
D) 160 K
E) 1612 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following processes is(are) considered spontaneous ?
I. Melting ice cubes at - 5 ° C and 1 atm.
II. Alignment of iron fillings in a magnetic field.
III. Formation of CH4 and O2 from CO2 and H2O at 1 atm and 25 ° C.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) All of these.
I. Melting ice cubes at - 5 ° C and 1 atm.
II. Alignment of iron fillings in a magnetic field.
III. Formation of CH4 and O2 from CO2 and H2O at 1 atm and 25 ° C.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The reaction PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)→PCl5 (g) is exothermic. The reaction is:
A) spontaneous at all temperatures.
B) nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
C) spontaneous at low temperatures.
D) spontaneous at high temperatures.
E) spontaneous if D G rxn is positive.
A) spontaneous at all temperatures.
B) nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
C) spontaneous at low temperatures.
D) spontaneous at high temperatures.
E) spontaneous if D G rxn is positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which thermodynamic statement listed below would confirm that a chemical reaction is spontaneous as written?
A) D G < 0
B) D G > 0
C) D S < 0
D) D H > 0
E) D H > 0 and D S < 0
A) D G < 0
B) D G > 0
C) D S < 0
D) D H > 0
E) D H > 0 and D S < 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the criterion for a reaction to be considered spontaneous?
A) D H < 0
B) D H > 0
C) D S > 0
D) D G > 0
E) D G < 0
A) D H < 0
B) D H > 0
C) D S > 0
D) D G > 0
E) D G < 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Given the abbreviated table for selected standard molar entropy values of each substance in the reaction below, what is the standard molar change in entropy, D S ° rxn, for the following reaction?
C6H12O6 (s) + 6 O2 (g)→6 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O (g) Substance S ° (Jmol - 1K - 1) C6H12O6 (s) 212.1 O2 (g) 205.0 CO2 (g) 213.7 H2O (g) 188.7
A) D S ° rxn = - 14.7 Jmol - 1K - 1
B) D S ° rxn = 972.3 Jmol - 1K - 1
C) D S ° rxn = 1396.5 Jmol - 1K - 1
D) D S ° rxn = 3432.3 Jmol - 1K - 1
E) D S ° rxn = 3856.5 Jmol - 1K - 1
C6H12O6 (s) + 6 O2 (g)→6 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O (g) Substance S ° (Jmol - 1K - 1) C6H12O6 (s) 212.1 O2 (g) 205.0 CO2 (g) 213.7 H2O (g) 188.7
A) D S ° rxn = - 14.7 Jmol - 1K - 1
B) D S ° rxn = 972.3 Jmol - 1K - 1
C) D S ° rxn = 1396.5 Jmol - 1K - 1
D) D S ° rxn = 3432.3 Jmol - 1K - 1
E) D S ° rxn = 3856.5 Jmol - 1K - 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Given the following data:
2 Cr (s) + 3/2 O2 (g)→Cr2O3 (s) D G ° = - 100 kJ 2 CrO (s) + O2 (g)→CrO3 (s) D G ° = - 50 kJ 2 CrO (s) + 1/2 O2 (g)→Cr2O3 (s) D G ° = - 250 kJ Calculate D G ° for:
Cr (s) + 3/2 O2 (g)→CrO3 (s)
A) 50 kJ
B) 25 kJ
C) - 100 kJ
D) - 300 kJ
E) - 400 kJ
2 Cr (s) + 3/2 O2 (g)→Cr2O3 (s) D G ° = - 100 kJ 2 CrO (s) + O2 (g)→CrO3 (s) D G ° = - 50 kJ 2 CrO (s) + 1/2 O2 (g)→Cr2O3 (s) D G ° = - 250 kJ Calculate D G ° for:
Cr (s) + 3/2 O2 (g)→CrO3 (s)
A) 50 kJ
B) 25 kJ
C) - 100 kJ
D) - 300 kJ
E) - 400 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Exhibit 17-1 Consider the reaction of carbon monoxide and chlorine gas to form phosgene as shown below to answer the following question(s). CO (g) + Cl2 (g)→ClC(O)Cl (g)
Refer to Exhibit 17-1. What is the standard change in entropy, D S ° rxn, at 298 K for this reaction given that D G ° rxn = - 206 kJ/mol and D H ° rxn = - 220 kJ/mol?
A) D S ° rxn = - 4.17×103 Jmol - 1K - 1
B) D S ° rxn = - 1.43×103 Jmol - 1K - 1
C) D S ° rxn = - 47.0 Jmol - 1K - 1
D) D S ° rxn = - 21.3 Jmol - 1K - 1
E) D S ° rxn = 47.0 Jmol - 1K - 1
Refer to Exhibit 17-1. What is the standard change in entropy, D S ° rxn, at 298 K for this reaction given that D G ° rxn = - 206 kJ/mol and D H ° rxn = - 220 kJ/mol?
A) D S ° rxn = - 4.17×103 Jmol - 1K - 1
B) D S ° rxn = - 1.43×103 Jmol - 1K - 1
C) D S ° rxn = - 47.0 Jmol - 1K - 1
D) D S ° rxn = - 21.3 Jmol - 1K - 1
E) D S ° rxn = 47.0 Jmol - 1K - 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which substance(s) listed below has(have) a standard molar Gibbs Free Energy of formation, D G f , value equal to 0 kJ/mol?
I. H₂ (g)
II. N₂(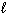 )
)
III. H₂ O (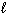 )
)
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) All of these
I. H₂ (g)
II. N₂(
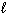 )
)III. H₂ O (
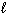 )
)A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Given the abbreviated table for selected standard state entropy values of each substance in the reaction below, what is the value of the standard change in entropy, D S ° , for the following chemical reaction?
3 H2 (g) + Fe2O3 (s)→2 Fe (s) + 3 H2O (g) Substance S ° (Jmol - 1K - 1) H2 (g) 130.6 Fe (s) 27.3 Fe2O3 (s) 87.4 H2O (g) 188.7
A) D S ° = - 32.5 Jmol - 1K - 1
B) D S ° = - 2.0 Jmol - 1K - 1
C) D S ° = 141.5 Jmol - 1K - 1
D) D S ° = 316.3 Jmol - 1K - 1
E) D S ° = 925.1 Jmol - 1K - 1
3 H2 (g) + Fe2O3 (s)→2 Fe (s) + 3 H2O (g) Substance S ° (Jmol - 1K - 1) H2 (g) 130.6 Fe (s) 27.3 Fe2O3 (s) 87.4 H2O (g) 188.7
A) D S ° = - 32.5 Jmol - 1K - 1
B) D S ° = - 2.0 Jmol - 1K - 1
C) D S ° = 141.5 Jmol - 1K - 1
D) D S ° = 316.3 Jmol - 1K - 1
E) D S ° = 925.1 Jmol - 1K - 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Given D 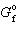 = - 371.1 kJ/mol for SO3 and D
= - 371.1 kJ/mol for SO3 and D 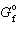 = - 300.3 kJ/mol for SO₂ , what is D G for the following reaction?
= - 300.3 kJ/mol for SO₂ , what is D G for the following reaction?
2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) 2 SO3(g)
A) +141.6 kJ
B) +70.8 kJ
C) - 70.8 kJ
D) - 141.6 kJ
E) not enough information
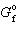 = - 371.1 kJ/mol for SO3 and D
= - 371.1 kJ/mol for SO3 and D 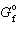 = - 300.3 kJ/mol for SO₂ , what is D G for the following reaction?
= - 300.3 kJ/mol for SO₂ , what is D G for the following reaction?2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) 2 SO3(g)
A) +141.6 kJ
B) +70.8 kJ
C) - 70.8 kJ
D) - 141.6 kJ
E) not enough information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which substance(s) listed below would be expected to have a standard molar Gibbs Free-Energy of formation equal to zero, D G f = 0?
I. Na + (aq)
II. O₂(g)
III. H₂ O (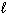 )
)
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) All of these
I. Na + (aq)
II. O₂(g)
III. H₂ O (
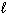 )
)A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Exhibit 17-1 Consider the reaction of carbon monoxide and chlorine gas to form phosgene as shown below to answer the following question(s). CO (g) + Cl2 (g)→ClC(O)Cl (g)
Refer to Exhibit 17-1. Given that D S ° rxn = - 47.0 Jmol - 1K - 1 and D H ° rxn = - 220. kJ/mol for this reaction, what is the standard Gibbs Free Energy, D G ° rxn, for this reaction at 500 K?
A) D G ° rxn = - 2.37×104 kJ/mol
B) D G ° rxn = - 243.5 kJ/mol
C) D G ° rxn = - 196.5 kJ/mol
D) D G ° rxn = 63.0 kJ/mol
E) D G ° rxn = 2.33×104 kJ/mol
Refer to Exhibit 17-1. Given that D S ° rxn = - 47.0 Jmol - 1K - 1 and D H ° rxn = - 220. kJ/mol for this reaction, what is the standard Gibbs Free Energy, D G ° rxn, for this reaction at 500 K?
A) D G ° rxn = - 2.37×104 kJ/mol
B) D G ° rxn = - 243.5 kJ/mol
C) D G ° rxn = - 196.5 kJ/mol
D) D G ° rxn = 63.0 kJ/mol
E) D G ° rxn = 2.33×104 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The best measure of the spontaneity of a process is:
A) the change in the number of moles of gaseous species.
B) the change in internal energy of the process.
C) the change in free energy of the process.
D) the change in enthalpy of the process.
E) the change in entropy of the process.
A) the change in the number of moles of gaseous species.
B) the change in internal energy of the process.
C) the change in free energy of the process.
D) the change in enthalpy of the process.
E) the change in entropy of the process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following processes is(are) considered spontaneous ?
I. Melting ice cubes at 5 C and 1 atm.
II. Rust, Fe2 O3 , is converted to iron, Fe, and oxygen, O₂.
III. Forming additional NH₃from the following reaction that has previously reached a state of dynamic equilibrium:
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g)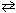 2 NH₃(g)
2 NH₃(g)
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) All of these.
I. Melting ice cubes at 5 C and 1 atm.
II. Rust, Fe2 O3 , is converted to iron, Fe, and oxygen, O₂.
III. Forming additional NH₃from the following reaction that has previously reached a state of dynamic equilibrium:
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g)
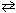 2 NH₃(g)
2 NH₃(g)A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
For a given chemical reaction, the value of D H is negative and the value of D S is positive. The value of D G for this reaction indicates that the reaction is:
A) always nonspontaneous.
B) spontaneous only at high temperatures.
C) spontaneous only at low temperatures.
D) spontaneous at all temperatures.
E) nonspontaneous only at high temperatures.
A) always nonspontaneous.
B) spontaneous only at high temperatures.
C) spontaneous only at low temperatures.
D) spontaneous at all temperatures.
E) nonspontaneous only at high temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is true?
A) D E = q - w
B) D G = D E - P D V - T D S
C) D H = D G - T D S
D) D G ° = 0 at 0 K
E) The entropy of the universe is increasing.
A) D E = q - w
B) D G = D E - P D V - T D S
C) D H = D G - T D S
D) D G ° = 0 at 0 K
E) The entropy of the universe is increasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Given D 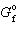 CuO = - 130 kJ/mol and D
CuO = - 130 kJ/mol and D 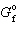 Cu 2 O = - 146 kJ/mol, what is D G for the following reaction?
Cu 2 O = - 146 kJ/mol, what is D G for the following reaction?
4 CuO (s) 2 Cu 2 O (s) + O₂(g)
A) +298 kJ
B) +228 kJ
C) - 7 kJ
D) - 4 kJ
E) not enough information
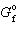 CuO = - 130 kJ/mol and D
CuO = - 130 kJ/mol and D 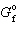 Cu 2 O = - 146 kJ/mol, what is D G for the following reaction?
Cu 2 O = - 146 kJ/mol, what is D G for the following reaction?4 CuO (s) 2 Cu 2 O (s) + O₂(g)
A) +298 kJ
B) +228 kJ
C) - 7 kJ
D) - 4 kJ
E) not enough information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which substance(s) listed below would be expected to have a standard Molar Gibbs Free Energy of formation value equal to zero, D G ° f = 0?
(Pay careful attention to the phase indicators.)
A) H2 (g)
B) CO2 (g)
C) NaCl (s)
D) H₂ O (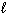 )
)
E) All of these.
(Pay careful attention to the phase indicators.)
A) H2 (g)
B) CO2 (g)
C) NaCl (s)
D) H₂ O (
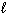 )
)E) All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A positive value of D G ° for a reaction indicates that:
A) the reaction favors formation of products.
B) the reaction is spontaneous.
C) the reaction is nonspontaneous.
D) the reaction is at equilibrium.
E) the reaction cannot reach equilibrium.
A) the reaction favors formation of products.
B) the reaction is spontaneous.
C) the reaction is nonspontaneous.
D) the reaction is at equilibrium.
E) the reaction cannot reach equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Given the abbreviated table for selected standard molar entropy values of each substance in the reaction below, what is the standard molar change in entropy, D S rxn , for the following reaction?
3 NO₂ (g) + H₂ O (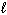 ) 2 HNO3(
) 2 HNO3( 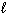 ) + NO (g) Substance S (Jmol - 1 K - 1 ) NO₂ (g) 239.9 H₂ O (
) + NO (g) Substance S (Jmol - 1 K - 1 ) NO₂ (g) 239.9 H₂ O ( 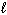 ) 69.94 HNO3(
) 69.94 HNO3( 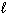 ) 155.6 NO (g) 210.65
) 155.6 NO (g) 210.65
A) D S ° rxn = - 267.8 Jmol - 1K - 1
B) D S ° rxn = - 127.9 Jmol - 1K - 1
C) D S ° rxn = 56.4 Jmol - 1K - 1
D) D S ° rxn = 1171.6 Jmol - 1K - 1
E) D S ° rxn = 1311.5 Jmol - 1K - 1
3 NO₂ (g) + H₂ O (
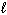 ) 2 HNO3(
) 2 HNO3( 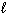 ) + NO (g) Substance S (Jmol - 1 K - 1 ) NO₂ (g) 239.9 H₂ O (
) + NO (g) Substance S (Jmol - 1 K - 1 ) NO₂ (g) 239.9 H₂ O ( 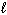 ) 69.94 HNO3(
) 69.94 HNO3( 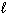 ) 155.6 NO (g) 210.65
) 155.6 NO (g) 210.65A) D S ° rxn = - 267.8 Jmol - 1K - 1
B) D S ° rxn = - 127.9 Jmol - 1K - 1
C) D S ° rxn = 56.4 Jmol - 1K - 1
D) D S ° rxn = 1171.6 Jmol - 1K - 1
E) D S ° rxn = 1311.5 Jmol - 1K - 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If D H is positive and D S is negative for a particular reaction:
A) the reaction proceeds forward at all temperatures.
B) the reaction proceeds forward at low temperatures.
C) the reaction proceeds forward at high temperatures.
D) the reaction doesn't proceed forward at any temperature.
E) none of these.
A) the reaction proceeds forward at all temperatures.
B) the reaction proceeds forward at low temperatures.
C) the reaction proceeds forward at high temperatures.
D) the reaction doesn't proceed forward at any temperature.
E) none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Consider the following reaction and its corresponding thermodynamic data:
4 KClO3 (s)→3 KClO4 (s) + KCl (s) D H ° = - 140 kJ/mol and D S ° = - 45 Jmol - 1K - 1 At what approximate temperature does this reaction cross-over from being considered spontaneous to being non-spontaneous?
A) It won't cross over. It will always be spontaneous.
B) It won't cross over. It will always be non-spontaneous.
C) 321 K
D) 3111 K
E) 6300 K
4 KClO3 (s)→3 KClO4 (s) + KCl (s) D H ° = - 140 kJ/mol and D S ° = - 45 Jmol - 1K - 1 At what approximate temperature does this reaction cross-over from being considered spontaneous to being non-spontaneous?
A) It won't cross over. It will always be spontaneous.
B) It won't cross over. It will always be non-spontaneous.
C) 321 K
D) 3111 K
E) 6300 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Exhibit 17-3 Consider the reaction below and its corresponding thermodynamic data to answer the following problem(s). NH3 (g) + HCl (s)→NH4Cl (s) D H ° = - 175.9 kJ/mol and D S ° = - 284.6 J/mol × K
Refer to Exhibit 17-3. What is the Standard Gibbs Free Energy change, D G ° , for this reaction at 25 ° C?
A) D G ° = - 261 kJ/mol
B) D G ° = - 183 kJ/mol
C) D G ° = - 169 kJ/mol
D) D G ° = - 91.1 kJ/mol
E) D G ° = 6.94×103 kJ/mol
Refer to Exhibit 17-3. What is the Standard Gibbs Free Energy change, D G ° , for this reaction at 25 ° C?
A) D G ° = - 261 kJ/mol
B) D G ° = - 183 kJ/mol
C) D G ° = - 169 kJ/mol
D) D G ° = - 91.1 kJ/mol
E) D G ° = 6.94×103 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Consider the following reaction and its corresponding thermodynamic data:
NH3 (g) + HCl (s)→NH4Cl (s) D H ° = - 175.9 kJ/mol and D S ° = - 284.6 J/mol × K At what approximate temperature does this reaction cross over from being considered spontaneous to being non-spontaneous?
A) It won't cross over. It will always be spontaneous.
B) It won't cross over. It will always be non-spontaneous.
C) 50.1 K
D) 618 K
E) 1618 K
NH3 (g) + HCl (s)→NH4Cl (s) D H ° = - 175.9 kJ/mol and D S ° = - 284.6 J/mol × K At what approximate temperature does this reaction cross over from being considered spontaneous to being non-spontaneous?
A) It won't cross over. It will always be spontaneous.
B) It won't cross over. It will always be non-spontaneous.
C) 50.1 K
D) 618 K
E) 1618 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Exhibit 17-5 Consider the reaction of Barium oxide with carbon dioxide to form Barium Carbonate as shown below to answer the following question(s). BaO (s) + CO2 (g)→BaCO3 (s) D S ° rxn = - 174 J/mol × K and D H ° rxn = - 277 kJ/mol
Refer to Exhibit 17-5. Which statement below is true?
A) This reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
B) This reaction is non-spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively lower temperatures and non-spontaneous at higher temperatures.
D) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively higher temperatures and non-spontaneous at lower temperatures.
E) There is not enough information to make an assessment.
Refer to Exhibit 17-5. Which statement below is true?
A) This reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
B) This reaction is non-spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively lower temperatures and non-spontaneous at higher temperatures.
D) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively higher temperatures and non-spontaneous at lower temperatures.
E) There is not enough information to make an assessment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following conditions describe a reaction that is spontaneous at "high" temperatures and nonspontaneous at low temperatures?
A) D H is ( - ), D S is (+)
B) D H is (+), D S is ( - )
C) D H is (+), D S is (+)
D) D H is ( - ), D S is ( - )
E) All reactions are spontaneous at high temperatures.
A) D H is ( - ), D S is (+)
B) D H is (+), D S is ( - )
C) D H is (+), D S is (+)
D) D H is ( - ), D S is ( - )
E) All reactions are spontaneous at high temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Exhibit 17-4 Consider the reaction of nitrogen monoxide and oxygen gas to form nitrogen dioxide as shown below to answer the following question(s). NO (g) + O2 (g)→2 NO2 (g)
Refer to Exhibit 17-4. Which statement below is correct about the reaction above?
A) This reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
B) This reaction is non-spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively lower temperatures and non-spontaneous at higher temperatures.
D) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively higher temperatures and non-spontaneous at lower temperatures.
E) There is not enough information to make an assessment.
Refer to Exhibit 17-4. Which statement below is correct about the reaction above?
A) This reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
B) This reaction is non-spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively lower temperatures and non-spontaneous at higher temperatures.
D) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively higher temperatures and non-spontaneous at lower temperatures.
E) There is not enough information to make an assessment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The reaction PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)→PCl5 (g) is exothermic. The reaction is:
A) spontaneous at all temperatures.
B) nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
C) spontaneous at low temperatures.
D) spontaneous at high temperatures.
E) spontaneous if D G rxn is positive.
A) spontaneous at all temperatures.
B) nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
C) spontaneous at low temperatures.
D) spontaneous at high temperatures.
E) spontaneous if D G rxn is positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Consider splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen gas and its corresponding thermodynamic data as shown below:
2 H₂ O (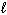 ) 2 H₂ (g) + O₂(g) D S rxn = 326 J/mol K and D H rxn = 572 kJ/mol At what approximate temperature does this reaction cross-over from being considered non-spontaneous to being spontaneous?
) 2 H₂ (g) + O₂(g) D S rxn = 326 J/mol K and D H rxn = 572 kJ/mol At what approximate temperature does this reaction cross-over from being considered non-spontaneous to being spontaneous?
A) It won't cross over. It is spontaneous at all temperatures.
B) It won't cross over. It is non-spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) 186 K
D) 570 K
E) 1.75×103 K
2 H₂ O (
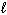 ) 2 H₂ (g) + O₂(g) D S rxn = 326 J/mol K and D H rxn = 572 kJ/mol At what approximate temperature does this reaction cross-over from being considered non-spontaneous to being spontaneous?
) 2 H₂ (g) + O₂(g) D S rxn = 326 J/mol K and D H rxn = 572 kJ/mol At what approximate temperature does this reaction cross-over from being considered non-spontaneous to being spontaneous?A) It won't cross over. It is spontaneous at all temperatures.
B) It won't cross over. It is non-spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) 186 K
D) 570 K
E) 1.75×103 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Exhibit 17-2 Consider the reaction below and its corresponding thermodynamic data to answer the following problem(s). 3 O2 (g)→2 O3 (g) D H ° = 284.6 kJ/mol and D S ° = - 139.8 J/mol × K
Refer to Exhibit 17-2. Which statement below is true regarding this reaction?
A) This reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
B) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively lower temperatures and non-spontaneous at higher temperatures.
C) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively higher temperatures and non-spontaneous at lower temperatures.
D) This reaction is non-spontaneous at all temperatures.
E) There is not enough information to make an assessment.
Refer to Exhibit 17-2. Which statement below is true regarding this reaction?
A) This reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
B) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively lower temperatures and non-spontaneous at higher temperatures.
C) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively higher temperatures and non-spontaneous at lower temperatures.
D) This reaction is non-spontaneous at all temperatures.
E) There is not enough information to make an assessment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The reaction of carbon and water to produce water gas , a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, is an important industrial reaction. If  = +131.3 kJ and
= +131.3 kJ and 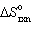 = +0.1336 kJ/K for C (s) + H₂ O (g)
= +0.1336 kJ/K for C (s) + H₂ O (g) 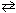 CO (g) + H₂ (g), determine the temperatures at which this reaction is spontaneous under standard conditions.
CO (g) + H₂ (g), determine the temperatures at which this reaction is spontaneous under standard conditions.
A) T > 1.02×10 - 3 K
B) T < 298 K
C) T < 983 K
D) T < 710 K
E) T > 983 K
 = +131.3 kJ and
= +131.3 kJ and 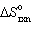 = +0.1336 kJ/K for C (s) + H₂ O (g)
= +0.1336 kJ/K for C (s) + H₂ O (g) 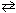 CO (g) + H₂ (g), determine the temperatures at which this reaction is spontaneous under standard conditions.
CO (g) + H₂ (g), determine the temperatures at which this reaction is spontaneous under standard conditions.A) T > 1.02×10 - 3 K
B) T < 298 K
C) T < 983 K
D) T < 710 K
E) T > 983 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A reaction will proceed spontaneously at any temperature when all reactants and products are present at 1 atm pressure if:
A) D H ° > 0 and D S ° > 0
B) D H ° > 0 and D S ° < 0
C) D H ° D S ° < 0
D) D H ° D S ° > 0
E) none of these
A) D H ° > 0 and D S ° > 0
B) D H ° > 0 and D S ° < 0
C) D H ° D S ° < 0
D) D H ° D S ° > 0
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
For the reaction, PCl5 (g) 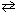 PCl 3 (g) + Cl₂ (g), D H = +92.5 kJ and D S = +182 J/K at 25 C. If D H and D S do not change with temperature, this reaction is spontaneous:
PCl 3 (g) + Cl₂ (g), D H = +92.5 kJ and D S = +182 J/K at 25 C. If D H and D S do not change with temperature, this reaction is spontaneous:
A) if T > 0.508 K
B) if T > 508 K
C) if T > 1.93 K
D) if T > 274 K
E) if T < 274 K
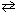 PCl 3 (g) + Cl₂ (g), D H = +92.5 kJ and D S = +182 J/K at 25 C. If D H and D S do not change with temperature, this reaction is spontaneous:
PCl 3 (g) + Cl₂ (g), D H = +92.5 kJ and D S = +182 J/K at 25 C. If D H and D S do not change with temperature, this reaction is spontaneous:A) if T > 0.508 K
B) if T > 508 K
C) if T > 1.93 K
D) if T > 274 K
E) if T < 274 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Exhibit 17-2 Consider the reaction below and its corresponding thermodynamic data to answer the following problem(s). 3 O2 (g)→2 O3 (g) D H ° = 284.6 kJ/mol and D S ° = - 139.8 J/mol × K
Refer to Exhibit 17-2. What is the Standard Gibbs Free Energy change, D G ° , for this reaction at 25 ° C?
A) D G ° = 242.9 kJ/mol
B) D G ° = 281.1 kJ/mol
C) D G ° = 288.1 kJ/mol
D) D G ° = 326.3 kJ/mol
E) D G ° = 4.195×104 kJ/mol
Refer to Exhibit 17-2. What is the Standard Gibbs Free Energy change, D G ° , for this reaction at 25 ° C?
A) D G ° = 242.9 kJ/mol
B) D G ° = 281.1 kJ/mol
C) D G ° = 288.1 kJ/mol
D) D G ° = 326.3 kJ/mol
E) D G ° = 4.195×104 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Exhibit 17-3 Consider the reaction below and its corresponding thermodynamic data to answer the following problem(s). NH3 (g) + HCl (s)→NH4Cl (s) D H ° = - 175.9 kJ/mol and D S ° = - 284.6 J/mol × K
Refer to Exhibit 17-3. Which statement below is true regarding this reaction?
A) This reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
B) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively lower temperatures and non-spontaneous at higher temperatures.
C) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively higher temperatures and non-spontaneous at lower temperatures.
D) This reaction is non-spontaneous at all temperatures.
E) There is not enough information to make an assessment.
Refer to Exhibit 17-3. Which statement below is true regarding this reaction?
A) This reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
B) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively lower temperatures and non-spontaneous at higher temperatures.
C) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively higher temperatures and non-spontaneous at lower temperatures.
D) This reaction is non-spontaneous at all temperatures.
E) There is not enough information to make an assessment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Exhibit 17-4 Consider the reaction of nitrogen monoxide and oxygen gas to form nitrogen dioxide as shown below to answer the following question(s). NO (g) + O2 (g)→2 NO2 (g)
Refer to Exhibit 17-4. Given that D S ° rxn = - 146.5 Jmol - 1K - 1 and D H ° rxn = - 114.2. kJ/mol for this reaction, what is the standard Gibbs Free Energy, D G ° rxn, for this reaction at 500 K?
A) D G ° rxn = 7.31×104 kJ/mol
B) D G ° rxn = - 41.0 kJ/mol
C) D G ° rxn = - 89.4 kJ/mol
D) D G ° rxn = - 187.5 kJ/mol
E) D G ° rxn = - 203.6 kJ/mol
Refer to Exhibit 17-4. Given that D S ° rxn = - 146.5 Jmol - 1K - 1 and D H ° rxn = - 114.2. kJ/mol for this reaction, what is the standard Gibbs Free Energy, D G ° rxn, for this reaction at 500 K?
A) D G ° rxn = 7.31×104 kJ/mol
B) D G ° rxn = - 41.0 kJ/mol
C) D G ° rxn = - 89.4 kJ/mol
D) D G ° rxn = - 187.5 kJ/mol
E) D G ° rxn = - 203.6 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The calculated value of D S is 314.1 J/K for the exothermic reaction:
2 CH₃ OH (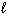 ) + 3 O₂(g) 2 CO₂ (g) + 4 H₂ O (g) Therefore this reaction is:
) + 3 O₂(g) 2 CO₂ (g) + 4 H₂ O (g) Therefore this reaction is:
A) spontaneous only at high temperatures.
B) nonspontaneous only at high temperatures.
C) spontaneous only at low temperatures.
D) nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
E) spontaneous at all temperatures.
2 CH₃ OH (
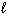 ) + 3 O₂(g) 2 CO₂ (g) + 4 H₂ O (g) Therefore this reaction is:
) + 3 O₂(g) 2 CO₂ (g) + 4 H₂ O (g) Therefore this reaction is:A) spontaneous only at high temperatures.
B) nonspontaneous only at high temperatures.
C) spontaneous only at low temperatures.
D) nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
E) spontaneous at all temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The reaction of ammonia and hydrogen chloride produces ammonium chloride as shown:
NH3 (g) + HCl (g)→NH4Cl (s) If D H D S < O, then what can be stated about this reaction?
A) This reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
B) This reaction is non-spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively lower temperatures and non-spontaneous at relatively higher temperatures.
D) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively higher temperatures and non-spontaneous at relatively lower temperatures.
NH3 (g) + HCl (g)→NH4Cl (s) If D H D S < O, then what can be stated about this reaction?
A) This reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
B) This reaction is non-spontaneous at all temperatures.
C) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively lower temperatures and non-spontaneous at relatively higher temperatures.
D) This reaction is spontaneous at relatively higher temperatures and non-spontaneous at relatively lower temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Consider the conversion of ozone, O3, to oxygen, O2, and this reaction's corresponding thermodynamic data:
2 O3 (g)→3 O2 (g) D H ° = - 286 kJ/mol and D S ° = 137 Jmol - 1K - 1 At what approximate temperature does this reaction cross-over from being considered spontaneous to being non-spontaneous?
A) It won't cross over. It will always be spontaneous.
B) It won't cross over. It will always be non-spontaneous.
C) 149 K
D) 208 K
E) 479 K
2 O3 (g)→3 O2 (g) D H ° = - 286 kJ/mol and D S ° = 137 Jmol - 1K - 1 At what approximate temperature does this reaction cross-over from being considered spontaneous to being non-spontaneous?
A) It won't cross over. It will always be spontaneous.
B) It won't cross over. It will always be non-spontaneous.
C) 149 K
D) 208 K
E) 479 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Exhibit 17-5 Consider the reaction of Barium oxide with carbon dioxide to form Barium Carbonate as shown below to answer the following question(s). BaO (s) + CO2 (g)→BaCO3 (s) D S ° rxn = - 174 J/mol × K and D H ° rxn = - 277 kJ/mol
Refer to Exhibit 17-5. What is the standard molar Gibbs Free Energy, D G ° rxn, for this reaction at 500 K?
A) D G ° rxn = - 365 KJ/mol
B) D G ° rxn = - 313 KJ/mol
C) D G ° rxn = - 226 KJ/mol
D) D G ° rxn = - 190 KJ/mol
E) D G ° rxn = - 35 KJ/mol
Refer to Exhibit 17-5. What is the standard molar Gibbs Free Energy, D G ° rxn, for this reaction at 500 K?
A) D G ° rxn = - 365 KJ/mol
B) D G ° rxn = - 313 KJ/mol
C) D G ° rxn = - 226 KJ/mol
D) D G ° rxn = - 190 KJ/mol
E) D G ° rxn = - 35 KJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



