Deck 14: Electron Flow in Organotrophy, Lithotrophy, and Phototrophy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/73
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Electron Flow in Organotrophy, Lithotrophy, and Phototrophy
1
In a redox reaction, the reduction potential E depends on the ratio of product concentrations ([C] and [D]) to reactant concentrations ([A] and [B]), as per equation E = E°' - 60 (mV/n) log [C][D]/[A][B]. What would be the effect of increasing the ratio of products to reactants by a factor of 10?
A) No effect: E°' assumes 1-M concentrations of reactants and products.
B) A change of -60 mV will not modify the estimate of E.
C) The value of E will decrease by 60 mV, decreasing energy yield.
D) The value of E will increase by 60 mV, increasing energy yield.
E) The E°' term is unaffected by changes in concentrations of products or reactants.
A) No effect: E°' assumes 1-M concentrations of reactants and products.
B) A change of -60 mV will not modify the estimate of E.
C) The value of E will decrease by 60 mV, decreasing energy yield.
D) The value of E will increase by 60 mV, increasing energy yield.
E) The E°' term is unaffected by changes in concentrations of products or reactants.
C
2
How are drug efflux pumps spread among virulent bacterial strains?
A) They are spread through generalized transduction.
B) Their genes are contained in plasmids that are transmitted among bacterial cells.
C) They are spread through conjugation between two virulent strains.
D) They are spread through transformation with Hfr plasmids.
E) DNA is released from bacterial cells previously infected with bacteriophages.
A) They are spread through generalized transduction.
B) Their genes are contained in plasmids that are transmitted among bacterial cells.
C) They are spread through conjugation between two virulent strains.
D) They are spread through transformation with Hfr plasmids.
E) DNA is released from bacterial cells previously infected with bacteriophages.
B
3
Which of the following is FALSE regarding the ETS in Escherichia coli?
A) NDH-1 is the main initial substrate oxydoreductase; NDH-2 is an alternative NADH dehydrogenase.
B) It pumps 10-12 protons per NADH.
C) It pumps 2-8 protons per NADH.
D) The main terminal oxidase is the cytochrome bo quinol oxidase, which contains heme b, heme O3, and Cu.
E) An alternative cytochrome bd quinol oxidase has a higher affinity for oxygen than other terminal oxidases and allows E. coli growth in low-O2 habitats.
A) NDH-1 is the main initial substrate oxydoreductase; NDH-2 is an alternative NADH dehydrogenase.
B) It pumps 10-12 protons per NADH.
C) It pumps 2-8 protons per NADH.
D) The main terminal oxidase is the cytochrome bo quinol oxidase, which contains heme b, heme O3, and Cu.
E) An alternative cytochrome bd quinol oxidase has a higher affinity for oxygen than other terminal oxidases and allows E. coli growth in low-O2 habitats.
B
4
The chemiosmotic theory states that the proton potential is composed of
A) [ATP] and [ADP]+[Pi].
B) a pH gradient and [Na+] gradient.
C) pH and pNa+.
D) pH and
E) a pH gradient and a [Ca2+] wave.
A) [ATP] and [ADP]+[Pi].
B) a pH gradient and [Na+] gradient.
C) pH and pNa+.
D) pH and
E) a pH gradient and a [Ca2+] wave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following substrates is an electron donor in organotrophy?
A) Fe2+
B) succinate
C) NO2
D) H2
E) H2O
A) Fe2+
B) succinate
C) NO2
D) H2
E) H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is lithotrophy?
A) breakdown of molecules using light energy
B) oxidation of organic electron donors to CO2 and H2O
C) photolysis of H2S or H2O coupled to CO2 fixation
D) oxidation of inorganic electron donors such as Fe2+ using O2 or anaerobic electronic acceptors
E) physical breakdown of food particles to facilitate ingestion
A) breakdown of molecules using light energy
B) oxidation of organic electron donors to CO2 and H2O
C) photolysis of H2S or H2O coupled to CO2 fixation
D) oxidation of inorganic electron donors such as Fe2+ using O2 or anaerobic electronic acceptors
E) physical breakdown of food particles to facilitate ingestion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The following groups or molecules are components of electron transport systems, EXCEPT



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
While testing the chemiosmotic theory across the domains of life, researchers prepared "inside-out" vesicles from bacterial plasma membranes, mitochondrial internal membranes, and chloroplast thylakoids. An inside-out vesicle is a
A) vesicle in which the F1 subunit of the proton-ATPase faces outward.
B) membrane in which the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids face outward.
C) cell that has been enzymatically stripped of its cell wall.
D) preparation of outer membranes in Gram-negative bacteria, chloroplast envelopes, and mitochondria outer membranes.
E) preparation from bacterial cytoplasm, chloroplast stroma, and mitochondrial matrix.
A) vesicle in which the F1 subunit of the proton-ATPase faces outward.
B) membrane in which the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids face outward.
C) cell that has been enzymatically stripped of its cell wall.
D) preparation of outer membranes in Gram-negative bacteria, chloroplast envelopes, and mitochondria outer membranes.
E) preparation from bacterial cytoplasm, chloroplast stroma, and mitochondrial matrix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Reduction potential is defined as
A) the tendency for a compound to release H+ in solution.
B) the tendency for a compound to release OH- in solution.
C) the tendency of a compound to accept electrons.
D) the tendency of a compound to donate electrons.
E) a synonym for chemical valence.
A) the tendency for a compound to release H+ in solution.
B) the tendency for a compound to release OH- in solution.
C) the tendency of a compound to accept electrons.
D) the tendency of a compound to donate electrons.
E) a synonym for chemical valence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In cytochromes, the heme group plays a key role in acquiring and transferring electrons with a(n) __________ transition.
A) Mg0/Mg2+
B) S0/S2-
C) Cu+/Cu2+
D) Fe3+/Fe2+
E) Mn0/Mn2+
A) Mg0/Mg2+
B) S0/S2-
C) Cu+/Cu2+
D) Fe3+/Fe2+
E) Mn0/Mn2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Electron transport systems are embedded in all of the following membrane systems EXCEPT
A) the mitochondrial inner membrane.
B) thylakoids.
C) the inner membrane of Gram-negative bacteria.
D) the eukaryotic plasma membrane.
E) the archaeal plasma membrane.
A) the mitochondrial inner membrane.
B) thylakoids.
C) the inner membrane of Gram-negative bacteria.
D) the eukaryotic plasma membrane.
E) the archaeal plasma membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The following are cellular processes that can be directly powered by the proton motivo force ( 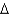 p), EXCEPT
p), EXCEPT
A) ATP biosynthesis from ADP and Pi.
B) flagellar rotation.
C) nutrient uptake.
D) drug efflux in some pathogens.
E) protein biosynthesis.
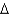 p), EXCEPT
p), EXCEPTA) ATP biosynthesis from ADP and Pi.
B) flagellar rotation.
C) nutrient uptake.
D) drug efflux in some pathogens.
E) protein biosynthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Enzymes transferring electrons at the start of the ETS are referred to as __________, whereas enzymes transferring electrons to the terminal electron acceptor are designated as __________.
A) dehydrogenases; oxidases
B) oxidases; dehydrogenases
C) sulfatases; nitrogenases
D) permeases; proton pumps
E) lyases; hydrolases
A) dehydrogenases; oxidases
B) oxidases; dehydrogenases
C) sulfatases; nitrogenases
D) permeases; proton pumps
E) lyases; hydrolases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is NOT a redox pair?
A) fumarate/succinate
B) NADH + H+/NAD
C) H2S/H2O
D) quinone/quinol (Q/QH2)
E) FAD/FADH2
A) fumarate/succinate
B) NADH + H+/NAD
C) H2S/H2O
D) quinone/quinol (Q/QH2)
E) FAD/FADH2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is NOT true of 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP)?
A) It is an uncoupler.
B) It can be used to measure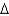 pH.
pH.
C) Unprotonated DNP can cross the membrane.
D) Protonated DNP can cross the membrane.
E)It dissipates the proton motive force.
A) It is an uncoupler.
B) It can be used to measure
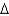 pH.
pH.C) Unprotonated DNP can cross the membrane.
D) Protonated DNP can cross the membrane.
E)It dissipates the proton motive force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the reactions below is written in the direction "electron acceptor  electron donor"?
electron donor"?

 electron donor"?
electron donor"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Although embedded in the membrane as an ETS component, the enzyme __________ does not pump protons.
A) pyruvate dehydrogenase
B) 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase
C) succinate dehydrogenase
D) malate dehydrogenase
E) glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase
A) pyruvate dehydrogenase
B) 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase
C) succinate dehydrogenase
D) malate dehydrogenase
E) glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The molecule shown below, __________, is a cofactor for electron transport. 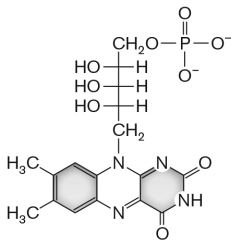
A) a cytochrome
B) ubiquinone
C) flavin mononucleotide
D) nicotine amide dinucleotide
E) heme b

A) a cytochrome
B) ubiquinone
C) flavin mononucleotide
D) nicotine amide dinucleotide
E) heme b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is FALSE regarding the electron transfer system in mitochondria?
A) The subunits of cytochrome c oxidoreductase (complex IV) are associated to eukaryotic proteins.
B) Oxidation of NADH + H+ contributes to the formation of a larger p.
C) The initial oxidoreductase, the NADH dehydrogenase (complex I), pumps more protons than the NDH-1 in Escherichia coli.
D) The succinate dehydrogenase (complex II) contributes to p by pumping protons onto the intermembrane space.
E) The ETS of some bacteria, such as Paracoccus denitrificans, are organized in a manner similar to that of mitochondria.
A) The subunits of cytochrome c oxidoreductase (complex IV) are associated to eukaryotic proteins.
B) Oxidation of NADH + H+ contributes to the formation of a larger p.
C) The initial oxidoreductase, the NADH dehydrogenase (complex I), pumps more protons than the NDH-1 in Escherichia coli.
D) The succinate dehydrogenase (complex II) contributes to p by pumping protons onto the intermembrane space.
E) The ETS of some bacteria, such as Paracoccus denitrificans, are organized in a manner similar to that of mitochondria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Protons can have different fates in bacterial ETS. Which of the following processes does NOT affect the proton motive force (  p)?
p)?
A) Protons are pumped across the membrane (H+) by oxidoreductase complexes.
B) Protons are consumed from the cytoplasm by the quinone/quinol pool.
C) Protons are released outside the membrane from the quinone/quinol pool.
D) Protons are consumed by combining with terminal electron acceptors such as O2.
E) Protons combining with O2, used as a terminal acceptor, compensate protons released by catabolic pathways.
 p)?
p)?A) Protons are pumped across the membrane (H+) by oxidoreductase complexes.
B) Protons are consumed from the cytoplasm by the quinone/quinol pool.
C) Protons are released outside the membrane from the quinone/quinol pool.
D) Protons are consumed by combining with terminal electron acceptors such as O2.
E) Protons combining with O2, used as a terminal acceptor, compensate protons released by catabolic pathways.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the chromophore group in bacteriorhodopsin?
A) tocopherol
B) b-carotene
C) folic acid
D) retinal
E) chlorophyll
A) tocopherol
B) b-carotene
C) folic acid
D) retinal
E) chlorophyll

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is NOT a terminal electron acceptor in anaerobic respirations?
A) nitrate
B) nitrite
C) hydrogen sulfide
D) carbon dioxide
E) sulfate
A) nitrate
B) nitrite
C) hydrogen sulfide
D) carbon dioxide
E) sulfate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Nitrifiers are bacteria
A) that generate nitrites or nitrates.
B) that convert N2 to NH3.
C) capable of oxidizing NH3 using NO.
D) capable of living in symbiosis in the roots of some plants.
E) capable of using NH3 as an electron donor.
A) that generate nitrites or nitrates.
B) that convert N2 to NH3.
C) capable of oxidizing NH3 using NO.
D) capable of living in symbiosis in the roots of some plants.
E) capable of using NH3 as an electron donor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In marine sediments, CO₂ is reduced to CH₄ by
A) bacteria containing proteorhodopsin.
B) oxygenic cyanobacteria.
C) methanotrophic archaea.
D) methanogenic archaea.
E) nonpurple sulfur bacteria.
A) bacteria containing proteorhodopsin.
B) oxygenic cyanobacteria.
C) methanotrophic archaea.
D) methanogenic archaea.
E) nonpurple sulfur bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In dehalorespiration of chlorinated pollutants, the chlorine is removed and replaced by
A) hydrogen.
B) oxygen.
C) nitrogen.
D) sulfur.
E) ammonia.
A) hydrogen.
B) oxygen.
C) nitrogen.
D) sulfur.
E) ammonia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Extreme halophilic archaea exclusively utilize which kind of ion gradient?
A) H+
B) Na+
C) Ca2+
D) K+
E) Mg2+
A) H+
B) Na+
C) Ca2+
D) K+
E) Mg2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which species can be utilized in biomining because it oxidizes copper and iron sulfides?
A) Geobacter metallireducens
B) Sulfurospirillum barnesii
C) Haloferax volcanii
D) Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans
E) Bacillus subtilis
A) Geobacter metallireducens
B) Sulfurospirillum barnesii
C) Haloferax volcanii
D) Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans
E) Bacillus subtilis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Ferroplasma acidarmanus produces large amounts of sulfuric acid through
A) oxidation of Cu+ with Cu(NO3)2.
B) oxidation of FeS2 with Fe3+ and H2O.
C) oxidation of Fe3O2 with Fe2+.
D) oxidation of H2S with H2O.
E) reduction of SO with H2.
A) oxidation of Cu+ with Cu(NO3)2.
B) oxidation of FeS2 with Fe3+ and H2O.
C) oxidation of Fe3O2 with Fe2+.
D) oxidation of H2S with H2O.
E) reduction of SO with H2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The reduction of U⁶⁺ to U⁴⁺ by Geobacter metallireducens is an example of
A) assimilatory metal reduction.
B) fermentation.
C) dissimilatory metal reduction.
D) organotrophy.
E) lithotrophy.
A) assimilatory metal reduction.
B) fermentation.
C) dissimilatory metal reduction.
D) organotrophy.
E) lithotrophy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is NOT correct about the process of methanogenesis?
A) CO2 and H2O are weak electron acceptors, whereas CH4 and H2 are strong electron donors.
B) CH4 synthesis from CO2 releases energy for growth.
C) CH4 and water can be formed from CO2 and 4H2 from a hydrogen donor.
D) Oxygen atoms in CO2 are reduced one at a time.
E) Oxygen atoms in CO2 are reduced to water at the same time.
A) CO2 and H2O are weak electron acceptors, whereas CH4 and H2 are strong electron donors.
B) CH4 synthesis from CO2 releases energy for growth.
C) CH4 and water can be formed from CO2 and 4H2 from a hydrogen donor.
D) Oxygen atoms in CO2 are reduced one at a time.
E) Oxygen atoms in CO2 are reduced to water at the same time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The Fₒ portion of Escherichia coli ATP synthase that rotates while translocating protons is
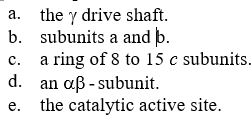

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The figure below shows anaerobic corrosion of a piece of steel accelerated by the action of anaerobic microorganisms. What should be on label 2? 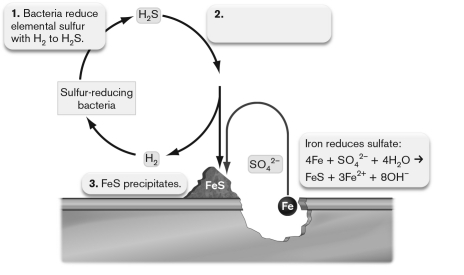


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following reactions is possible by reverse electron flow?
A) reduction of Fe3+ to Fe2+
B) NADP+ reduction to NADPH
C) protein biosynthesis
D) reduction of oxygen by Fe2+ to form H2O and Fe3+
E) anammox
A) reduction of Fe3+ to Fe2+
B) NADP+ reduction to NADPH
C) protein biosynthesis
D) reduction of oxygen by Fe2+ to form H2O and Fe3+
E) anammox

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Neisseria species use dissimilatory reduction of nitrate to ammonium. How can this reaction be used to distinguish Neisseria gonorrhoeae from other related species?
A) N. gonorrhoeae will test negative for terminal NO reductase.
B) N. gonorrhoeae will test positive for terminal NO reductase.
C) All Neisseria species test negative for terminal NO reductase.
D) All Neisseria species test positive for terminal NO reductase.
E) None of the enzymes involved in dissimilatory reduction of nitrate are known from species of Neisseria.
A) N. gonorrhoeae will test negative for terminal NO reductase.
B) N. gonorrhoeae will test positive for terminal NO reductase.
C) All Neisseria species test negative for terminal NO reductase.
D) All Neisseria species test positive for terminal NO reductase.
E) None of the enzymes involved in dissimilatory reduction of nitrate are known from species of Neisseria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is FALSE with respect to the use of sulfate by marine archaeal and bacterial groups?
A) Oxidized sulfur-containing molecules have redox potentials lower than those of the nitrogen series.
B) Oxidized sulfur molecules such as sulfate and sulfite serve as electron acceptors.
C) Sulfate and sulfite can receive electrons from hydrocarbons.
D) Sulfate-reducing archaea and bacteria are widespread in the ocean.
E) Sulfate is more abundant than chloride in the ocean.
A) Oxidized sulfur-containing molecules have redox potentials lower than those of the nitrogen series.
B) Oxidized sulfur molecules such as sulfate and sulfite serve as electron acceptors.
C) Sulfate and sulfite can receive electrons from hydrocarbons.
D) Sulfate-reducing archaea and bacteria are widespread in the ocean.
E) Sulfate is more abundant than chloride in the ocean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Sulfolobus species produce __________; as a result, their immediate environment has a pH __________.
A) H2SO4; as low as 2
B) H3PO4; as low as 3
C) HCl; of 1
D) CH3COOH; of 4
E) HCOOH; of 3
A) H2SO4; as low as 2
B) H3PO4; as low as 3
C) HCl; of 1
D) CH3COOH; of 4
E) HCOOH; of 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In anaerobic soils, some yeasts and filamentous fungi can reduce nitrate to nitrite and nitrite to
A) ammonia (NH3).
B) nitric oxide (NO).
C) urea.
D) nitrogen gas (N2).
E) ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH).
A) ammonia (NH3).
B) nitric oxide (NO).
C) urea.
D) nitrogen gas (N2).
E) ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is FALSE regarding dehalorespiration?
A) It is a type of hydrogenotrophy.
B) Cl- can be removed from toxic compounds by dehalorespiration.
C) Nitrogen (N2) is a by-product of dehalorespiration.
D) Halogenated organic molecules serve as electron acceptors for H2.
E) Hydrogenotrophs can be used in bioremediation.
A) It is a type of hydrogenotrophy.
B) Cl- can be removed from toxic compounds by dehalorespiration.
C) Nitrogen (N2) is a by-product of dehalorespiration.
D) Halogenated organic molecules serve as electron acceptors for H2.
E) Hydrogenotrophs can be used in bioremediation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The diagram below shows the structure of the universal FₒF₁ synthase. Which of the following FALSELY labels the figure? 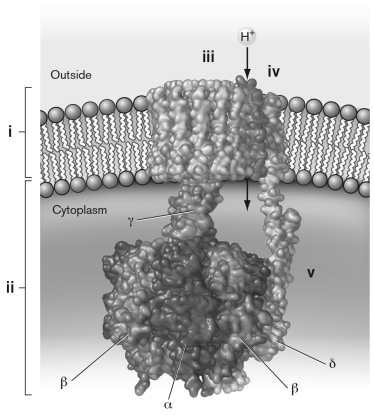
A) i) Fo subunit
B) ii) F1 subunit
C) iii) catalytic subunit
D) iv) subunit a
E) v) subunit b

A) i) Fo subunit
B) ii) F1 subunit
C) iii) catalytic subunit
D) iv) subunit a
E) v) subunit b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The anammox reaction consists of __________ and, as a consequence, __________.
A) reduction of sulfate by ammonia; sulfur and nitrogen are incorporated into amino acids
B) reduction of ammonium to form nitrite; plants can absorb nitrite
C) anaerobic ammonium oxidation by nitrite; large amounts of N2 are released into the atmosphere
D) reduction of ammonium by water; ammonium becomes ammonia
E) reduction of N2 to ammonium; nitrogen atoms are incorporated into amino acids
A) reduction of sulfate by ammonia; sulfur and nitrogen are incorporated into amino acids
B) reduction of ammonium to form nitrite; plants can absorb nitrite
C) anaerobic ammonium oxidation by nitrite; large amounts of N2 are released into the atmosphere
D) reduction of ammonium by water; ammonium becomes ammonia
E) reduction of N2 to ammonium; nitrogen atoms are incorporated into amino acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In photosystem II of purple bacteria, electrons flow through cytochrome bc, coupled to pumping of protons and the proton potential drives synthesis of ATP. The cytochrome bc complex transfers the electrons back to bacteriochlorophyll P870. This type of ATP synthesis is called
A) reverse electron flow.
B) membrane potential.
C) noncyclic photophosphorylation.
D) cyclic photophosphorylation.
E) proton motive force.
A) reverse electron flow.
B) membrane potential.
C) noncyclic photophosphorylation.
D) cyclic photophosphorylation.
E) proton motive force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Standard reduction potentials 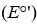 and standard free energy change
and standard free energy change 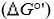 are related by the
are related by the
equation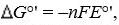 , where F is the Faraday’s constant and n is the number of electrons
, where F is the Faraday’s constant and n is the number of electrons
transferred from donor to acceptor.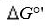 has units of kJ/mol. Which of the following redox pairs
has units of kJ/mol. Which of the following redox pairs
will have the highest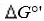 value?
value?
(1)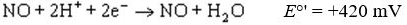
(2)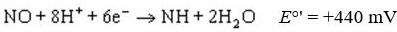
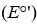 and standard free energy change
and standard free energy change 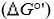 are related by the
are related by theequation
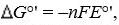 , where F is the Faraday’s constant and n is the number of electrons
, where F is the Faraday’s constant and n is the number of electronstransferred from donor to acceptor.
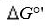 has units of kJ/mol. Which of the following redox pairs
has units of kJ/mol. Which of the following redox pairswill have the highest
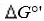 value?
value?(1)
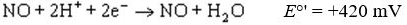
(2)
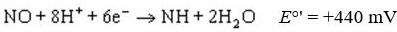

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What factors may affect ∆p in metabolically active bacterial cells?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Some Escherichia coli mutants can use nitrate (NO) as an electron acceptor under anaerobic conditions. A researcher wants to test the hypothesis that such a mutant obtained in a laboratory can obtain energy from succinate as an electron donor. Her proposed hypothesis is based on energy production from the redox pairs succinate/fumarate and nitrate/nitrite. Predict her calculations and determine if succinate oxidation to fumarate coupled to nitrite (NO) formation can yield some energy for growth as evidenced by an overall - 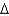 G°' of the coupled reactions.
G°' of the coupled reactions.
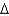 G°' of the coupled reactions.
G°' of the coupled reactions.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
How does Shewanella oneidensis donate electrons to oxidized minerals in marine sediments?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Electron donors for anaerobic photosystem I in green sulfur bacteria and chloroflexi include the following, EXCEPT
A) H2S.
B) HS.-
C) H2.
D) H2O.
E) Fe2+.
A) H2S.
B) HS.-
C) H2.
D) H2O.
E) Fe2+.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Cyanobacteria have __________-based photosynthesis and are the only __________-producing bacteria.
A) H2S; S0
B) Mg2+; NO
C) H2O; O2
D) succinate; O2
E) fumarate; O2
A) H2S; S0
B) Mg2+; NO
C) H2O; O2
D) succinate; O2
E) fumarate; O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The chlorophyll chromophore consists of a heteroaromatic ring complexed to a __________ ion.
A) calcium
B) chloride
C) magnesium
D) manganese
E) potassium
A) calcium
B) chloride
C) magnesium
D) manganese
E) potassium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Phototrophy is
A) photolysis.
B) use of photoexcited electrons to power cell growth.
C) chlorophyll photoexcitation.
D) photoionization.
E) a charge-separating photopigment.
A) photolysis.
B) use of photoexcited electrons to power cell growth.
C) chlorophyll photoexcitation.
D) photoionization.
E) a charge-separating photopigment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In purple bacteria, bacteriochlorophylls are supplemented by accessory pigments called
A) antenna complexes.
B) bacteriorhodopsin.
C) carotenoids.
D) chlorophylls.
E) thylakoids.
A) antenna complexes.
B) bacteriorhodopsin.
C) carotenoids.
D) chlorophylls.
E) thylakoids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
While testing the chemiosmotic theory, researchers prepared "inside-out" vesicles from bacterial cells, mitochondrial internal membranes, and chloroplast thylakoids. In an inside-out vesicle, the F₁ subunit of the proton-ATPase faces outward. Using the figure below, briefly discuss how the use of inside-out vesicles helped to study the relative contributions of the proton gradient (∆pH) and the membrane potential ( 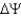 ) to∆ p.
) to∆ p.
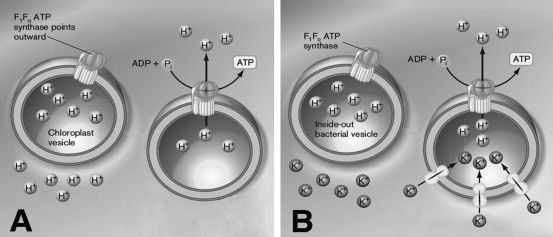
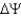 ) to∆ p.
) to∆ p.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Some respiratory bacteria, such as the nitrate oxidizer, nitospira, pack their ETS within intracytoplasmic pockets called
A) insoluable particles.
B) mitochondrial inner membrane.
C) inner membrane space.
D) cristae.
E) lamellae.
A) insoluable particles.
B) mitochondrial inner membrane.
C) inner membrane space.
D) cristae.
E) lamellae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The direction of the proton current in the chloroplast F₁Fₒ ATP synthase during ATP synthesis is from
A) stroma to cytoplasm.
B) cytoplasm to stroma.
C) lumen to stroma.
D) stroma to lumen.
E) one thylakoid to another through their lumen.
A) stroma to cytoplasm.
B) cytoplasm to stroma.
C) lumen to stroma.
D) stroma to lumen.
E) one thylakoid to another through their lumen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Use the figure below to describe Peter Mitchell's chemiosmotic model for coupling the electron transfer system with ATP synthesis.
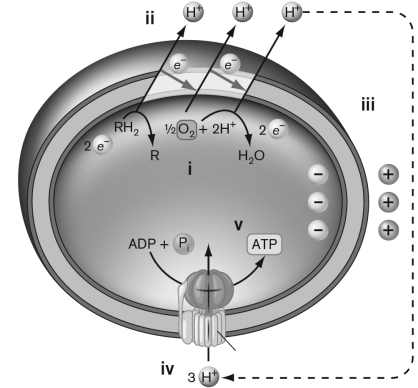


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In oxygenic photosynthesis, __________ is the electron donor, whereas in anaerobic photosynthesis it can be succinate or __________.
A) H2S; S0
B) O2; H2
C) O2; H2O
D) H2O; H2S
E) H2S; SO
A) H2S; S0
B) O2; H2
C) O2; H2O
D) H2O; H2S
E) H2S; SO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The figure below represents absorbance spectra of a cytochrome from the membrane of the archaeon Haloferax volcanii. The spectrum from the reduced form is represented by a continuous line and the oxidized form by a dashed line. Describe the differences between the spectra and which wavelength you would use to study the redox reactions of this cytochrome.
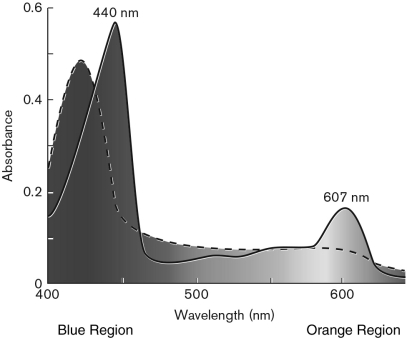


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following definitions is FALSE?
A) Photosynthesis is hotolysis followed by CO2 fixation and biosynthesis.
B) Photolysis is light absorption coupled to splitting of a molecule.
C) Photophosphorylation is the reaction ADP + Pi ATP catalyzed by photons.
D) Photoexcitation is light absorption causing an electron to transfer to a higher energy state.
E) Photoionization is light absorption that causes electron separation.
A) Photosynthesis is hotolysis followed by CO2 fixation and biosynthesis.
B) Photolysis is light absorption coupled to splitting of a molecule.
C) Photophosphorylation is the reaction ADP + Pi ATP catalyzed by photons.
D) Photoexcitation is light absorption causing an electron to transfer to a higher energy state.
E) Photoionization is light absorption that causes electron separation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which organism can respire with uranium and remediate uranium-contaminated water?
A) R. palustris
B) Shewanella sp
C) G. metallireducens
D) Salmonella sp
E) Brucella sp
A) R. palustris
B) Shewanella sp
C) G. metallireducens
D) Salmonella sp
E) Brucella sp

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The organism __________ is also known as "the bacterium that eats everything." It conducts photoheterotrophy and fixes nitrogen as ammonium while generating H₂. It also produces ATP via cyclic photophosphorylation in photosystem II.
A) Pseudochrobactrum saccharolyticum
B) Nitrobacter winogradskyi
C) Bradyrhizobium japonicum
D) Rhodopseudomonas palustris
E) Brucella pinnipedialis
A) Pseudochrobactrum saccharolyticum
B) Nitrobacter winogradskyi
C) Bradyrhizobium japonicum
D) Rhodopseudomonas palustris
E) Brucella pinnipedialis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In the Rhodospirillum rubrum photosystem II, bacteriochloropyll P870 can absorb weak infrared wavelengths in the __________ range.
A) 600-650
B) 650-700
C) 700-750
D) 750-800
E) 800-1,100
A) 600-650
B) 650-700
C) 700-750
D) 750-800
E) 800-1,100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Explain what kind of reaction bacteriorhodopsin performs and what it accomplishes for the cell. What is the name of the bacteriorhodopsin homologs, in what type of organisms were they identified, and what led to their discovery?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is dissimilatory metal reduction? How is it different from assimilatory metal reduction? Is there application of the dissimilatory metal reduction phenomenon?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
How does bacteriorhodopsin couple photoexcitation with proton pumping? How is ATP synthesized in bacteriorhodopsin-containing organisms?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Why and how is it that mitochondria have only a single electron transport system (ETS), unlike many bacteria?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the figure below to describe Salmonella enterica respiration on tetrathionate. What is the advantage of using this anaerobic respiratory mechanism?
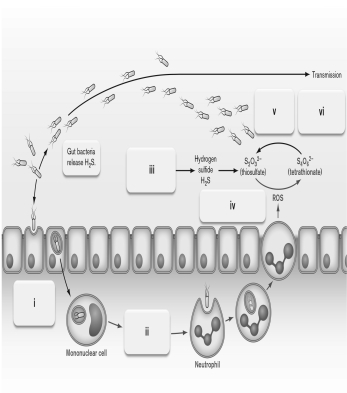


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Describe the role of the thylakoids in purple bacteria and cyanobacteria. Why is it that pumping protons into the lumen is essentially equivalent to pumping protons out of the cell?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What are methanotrophs? What is their role in the global carbon cycle?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the figure below to describe how Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans can utilize iron as an electron donor for ATP production. Discuss how other microbes benefit from or contribute to the process.
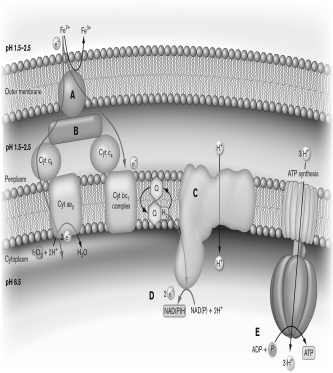


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is photoheterotrophy? Give examples of photoheterotrophic organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
How does photosystem I allow Chlorobium and other green sulfur bacteria to live near deep-sea vents?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The F₁Fₒ ATP synthase is a remarkably complex enzyme, its subunit structure highly conserved across life domains. Is it possible to use this enzyme as an antibiotic target?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Is the synthesis of ATP by the F₁Fₒ ATPase reversible? If so, are there any examples?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
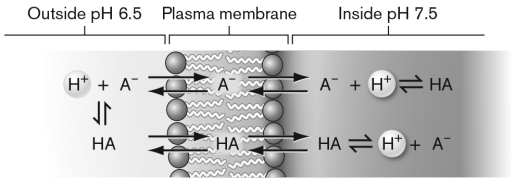
Use the figure below to describe how an uncoupler functions. Can an uncoupler be used as an antibiotic to treat bacterial infections?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



