Deck 24: The Surge of Nationalism From Liberal to Extreme Nationalism
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/77
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 24: The Surge of Nationalism From Liberal to Extreme Nationalism
1
After the failure of the revolutions of 1848, most German nationalists
A) emigrated to the Americas.
B) renewed their efforts at organizing a popular uprising.
C) had a new respect for the realities of power and came to back Prussia's efforts at unification.
D) gravitated toward Marxism as a new powerful revolutionary ideology.
E) none of the above
A) emigrated to the Americas.
B) renewed their efforts at organizing a popular uprising.
C) had a new respect for the realities of power and came to back Prussia's efforts at unification.
D) gravitated toward Marxism as a new powerful revolutionary ideology.
E) none of the above
had a new respect for the realities of power and came to back Prussia's efforts at unification.
2
The Risorgimento may be best related to
A) the Italian Renaissance.
B) economic liberalism and economic revival of northern Italy.
C) the Italian Zollverein.
D) revival of papal authority.
E) Italian nationalism.
A) the Italian Renaissance.
B) economic liberalism and economic revival of northern Italy.
C) the Italian Zollverein.
D) revival of papal authority.
E) Italian nationalism.
Italian nationalism.
3
In the years immediately after the collapse of the Napoleonic system, Italian nationalism was cultivated by all the following EXCEPT
A) the peasant majority.
B) intellectuals.
C) the middle class.
D) students.
E) secret societies.
A) the peasant majority.
B) intellectuals.
C) the middle class.
D) students.
E) secret societies.
the peasant majority.
4
Giuseppe Mazzini founded Young Italy after his release from imprisonment for his participation in
A) the revolution in the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies in the early 1820s.
B) an attempt to invade Savoy in 1834.
C) a constitutional government established in Naples in 1820.
D) an unsuccessful insurrection by the Carbonari in the Papal states during 1831-1832.
E) the revolutions of 1848.
A) the revolution in the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies in the early 1820s.
B) an attempt to invade Savoy in 1834.
C) a constitutional government established in Naples in 1820.
D) an unsuccessful insurrection by the Carbonari in the Papal states during 1831-1832.
E) the revolutions of 1848.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Mazzini believed that God's plan for humanity involved
A) a single world-state governed according to democratic principles.
B) a world of independent republics founded on nationality and democracy.
C) eventual disappearance of the state.
D) papal rule over the entire planet.
E) a strong dictatorial leader.
A) a single world-state governed according to democratic principles.
B) a world of independent republics founded on nationality and democracy.
C) eventual disappearance of the state.
D) papal rule over the entire planet.
E) a strong dictatorial leader.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
By 1900, which of the following major changes occurred?
A) The Hapsburg Empire collapsed and broke up into several states, two of which were nation-states.
B) Italy and Germany each were unified, and Hungary received autonomy.
C) France began to experience separatist movements in Corsica and the Basque territories.
D) The gap between the north and the south in Italy led to the creation of two separate states.
E) Polish efforts to receive autonomy from Russia succeeded, but similar efforts by the Irish failed.
A) The Hapsburg Empire collapsed and broke up into several states, two of which were nation-states.
B) Italy and Germany each were unified, and Hungary received autonomy.
C) France began to experience separatist movements in Corsica and the Basque territories.
D) The gap between the north and the south in Italy led to the creation of two separate states.
E) Polish efforts to receive autonomy from Russia succeeded, but similar efforts by the Irish failed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The text characterizes Giuseppe Mazzini as a
A) liberal and a romantic.
B) conservative and a realist.
C) socialist and a romantic.
D) conservative and a romantic.
E) practitioner of realpolitik.
A) liberal and a romantic.
B) conservative and a realist.
C) socialist and a romantic.
D) conservative and a romantic.
E) practitioner of realpolitik.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Giuseppe Garibaldi's convictions and accomplishments include all the following EXCEPT
A) women's equality, workers' rights, end to the death penalty, and liberation of all subjugated nations.
B) effective leadership of a popular uprising.
C) armed liberation of Sicily and a bloodless takeover of Naples.
D) a surprisingly easy conquest of Rome.
E) the subordination of his own personal ambitions to the needs of Italy.
A) women's equality, workers' rights, end to the death penalty, and liberation of all subjugated nations.
B) effective leadership of a popular uprising.
C) armed liberation of Sicily and a bloodless takeover of Naples.
D) a surprisingly easy conquest of Rome.
E) the subordination of his own personal ambitions to the needs of Italy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
All of the following can be said of Mazzini EXCEPT he
A) believed that national unity would enhance individual liberty.
B) believed that Rome had led the ancient world, the Italian papacy led Latin Christendom in the Middle Ages, and a new Rome in the form of a united Italy would usher in a new era of freedom for other nations.
C) was convinced that Italian unification could only come from top leaders.
D) dedicated his life to the creation of a republican Italy.
E) possessed great charisma, vision, and determination.
A) believed that national unity would enhance individual liberty.
B) believed that Rome had led the ancient world, the Italian papacy led Latin Christendom in the Middle Ages, and a new Rome in the form of a united Italy would usher in a new era of freedom for other nations.
C) was convinced that Italian unification could only come from top leaders.
D) dedicated his life to the creation of a republican Italy.
E) possessed great charisma, vision, and determination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Early successes of revolutionaries in 1848 included each of the following EXCEPT
A) ouster of the king of Piedmont-Sardinia.
B) liberation of the city of Milan from Austrian rule.
C) a liberal constitution in Sicily.
D) establishment of a new Roman Republic.
E) departure of the pope from Rome.
A) ouster of the king of Piedmont-Sardinia.
B) liberation of the city of Milan from Austrian rule.
C) a liberal constitution in Sicily.
D) establishment of a new Roman Republic.
E) departure of the pope from Rome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements concerning Italy after the withdrawal of Napoleonic rulers is accurate?
A) Intellectuals and rural masses alike expressed great concern for national revival.
B) The middle class appealed to the greatness of the Roman Empire and the Renaissance as inspiration for expelling the Austrians.
C) Italians who had served under Napoleon willingly agreed to the restoration of clerical and feudal privileges.
D) Italian merchants showed little interest in breaking down trade barriers between the states, preferring to concentrate their energies in their own territories.
E) All Italians showed disinterest in continuing the process of enlightened reform initiated by the French.
A) Intellectuals and rural masses alike expressed great concern for national revival.
B) The middle class appealed to the greatness of the Roman Empire and the Renaissance as inspiration for expelling the Austrians.
C) Italians who had served under Napoleon willingly agreed to the restoration of clerical and feudal privileges.
D) Italian merchants showed little interest in breaking down trade barriers between the states, preferring to concentrate their energies in their own territories.
E) All Italians showed disinterest in continuing the process of enlightened reform initiated by the French.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following was NOT a result of the victory of Piedmont-Sardinia in 1859 against the Austrians?
A) Piedmont-Sardinia gained Lombardy.
B) New revolutionary governments in central Italy decided to accept the leadership of Piedmont-Sardinia.
C) Piedmont-Sardinia annexed Venetia.
D) Nice and Savoy were awarded to France.
E) Austria abandoned much of its Italian territory.
A) Piedmont-Sardinia gained Lombardy.
B) New revolutionary governments in central Italy decided to accept the leadership of Piedmont-Sardinia.
C) Piedmont-Sardinia annexed Venetia.
D) Nice and Savoy were awarded to France.
E) Austria abandoned much of its Italian territory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
After the failure of the revolutions of 1848, the main Italian effort at unification shifted
A) toward a greater emphasis on organizing a mass uprising of the people.
B) away from a popular uprising and toward support for the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia.
C) away from a popular uprising and toward support for the pope.
D) toward "organic work," that is, the buildup of the country's economy and culture.
E) toward fomenting a war among Italy's neighbors, France and Austria.
A) toward a greater emphasis on organizing a mass uprising of the people.
B) away from a popular uprising and toward support for the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia.
C) away from a popular uprising and toward support for the pope.
D) toward "organic work," that is, the buildup of the country's economy and culture.
E) toward fomenting a war among Italy's neighbors, France and Austria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
All of the following worked against the unification of Italy in 1815 EXCEPT
A) Bourbon control of the south, Papal control of central Italy, Hapsburg dominance in the north.
B) a very weak desire among the Italians to unite.
C) major economic differences between the industrializing north and the rural south.
D) the goal of all Italians to reject the Old Regime.
E) poor transportation and communications among the different regions of Italy.
A) Bourbon control of the south, Papal control of central Italy, Hapsburg dominance in the north.
B) a very weak desire among the Italians to unite.
C) major economic differences between the industrializing north and the rural south.
D) the goal of all Italians to reject the Old Regime.
E) poor transportation and communications among the different regions of Italy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Count Camillo di Cavour sought to improve Piedmont's image in foreign affairs by strengthening the economy in which of the following ways?
A) reorganizing the currency, taxes, and the national debt
B) building railways and steamships
C) fostering improved agricultural methods
D) encouraging new businesses
E) all of the above
A) reorganizing the currency, taxes, and the national debt
B) building railways and steamships
C) fostering improved agricultural methods
D) encouraging new businesses
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the hope of securing foreign support against Austria, in 1858, Cavour signed a secret agreement with
A) Britain.
B) Prussia.
C) France.
D) Russia.
E) Spain.
A) Britain.
B) Prussia.
C) France.
D) Russia.
E) Spain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The Carbonari may be best described as
A) the most important of the secret nationalist societies in Italy.
B) a group of middle-class businessmen who sought to encourage literacy.
C) underpaid and oppressed charcoal gatherers in Sicily.
D) the secret police of Hapsburg territories in Italy.
E) workers in the new industries of northern Italy.
A) the most important of the secret nationalist societies in Italy.
B) a group of middle-class businessmen who sought to encourage literacy.
C) underpaid and oppressed charcoal gatherers in Sicily.
D) the secret police of Hapsburg territories in Italy.
E) workers in the new industries of northern Italy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Nationalism became "the dominant spiritual force in European life" in the late nineteenth century. This nationalism
A) continued to champion the same liberal and romantic nationalism that had inspired the revolutions of 1848.
B) embraced realpolitik , the political counterpart to realism and positivism.
C) drew increasingly on the tradition of the Enlightenment for inspiration.
D) believed ideals were noble sentiments that could create effective action.
E) all of the above
A) continued to champion the same liberal and romantic nationalism that had inspired the revolutions of 1848.
B) embraced realpolitik , the political counterpart to realism and positivism.
C) drew increasingly on the tradition of the Enlightenment for inspiration.
D) believed ideals were noble sentiments that could create effective action.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The French occupation of Italy during the Napoleonic Wars brought the
A) elimination of trade barriers.
B) introduction of a standard system of law throughout much of Italy.
C) concept of the state as a community of citizens.
D) introduction of constitutions and representative assemblies.
E) all of the above
A) elimination of trade barriers.
B) introduction of a standard system of law throughout much of Italy.
C) concept of the state as a community of citizens.
D) introduction of constitutions and representative assemblies.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
After Garibaldi fled Italy to avoid arrest, he spent thirteen years learning revolutionary tactics in
A) India.
B) Hungary.
C) Prussia.
D) the Caribbean.
E) South America.
A) India.
B) Hungary.
C) Prussia.
D) the Caribbean.
E) South America.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When the German Empire was created in 1871, it included all the following EXCEPT
A) Alsace-Lorriane.
B) the Polish territories of Posen and West Prussia.
C) the territories of the Austrian Empire and Luxembourg.
D) Schleswig-Holstein.
E) Bavaria, Württemberg, and Baden.
A) Alsace-Lorriane.
B) the Polish territories of Posen and West Prussia.
C) the territories of the Austrian Empire and Luxembourg.
D) Schleswig-Holstein.
E) Bavaria, Württemberg, and Baden.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The reform movement initiated after the Prussians' defeat at Jena in 1806
A) resulted in full citizenship for Jews.
B) greatly reduced monarchical power.
C) offered a promising beginning of liberalism in Prussia .
D) wrested economic, political, and military power away from the Junkers.
E) gave the middle class the leading voice in central government.
A) resulted in full citizenship for Jews.
B) greatly reduced monarchical power.
C) offered a promising beginning of liberalism in Prussia .
D) wrested economic, political, and military power away from the Junkers.
E) gave the middle class the leading voice in central government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Houston Stewart Chamberlain's Foundations of the Nineteenth Century argued that the decline of Rome could be attributed to
A) its loss of cultural leadership in the West.
B) its intermixing of races.
C) its failure to incorporate stronger races.
D) its use of the Latin language.
E) its inferior technology compared to the Germanic tribes.
A) its loss of cultural leadership in the West.
B) its intermixing of races.
C) its failure to incorporate stronger races.
D) its use of the Latin language.
E) its inferior technology compared to the Germanic tribes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the first half of the nineteenth century, the power and effectiveness of the Prussia government were aided by
A) a close alliance of the monarchy and the Junkers, the landed aristocracy.
B) the absence of powerful bourgeois opposition.
C) a well-trained, effective military.
D) reforms from above that strengthened civic pride.
E) all of the above
A) a close alliance of the monarchy and the Junkers, the landed aristocracy.
B) the absence of powerful bourgeois opposition.
C) a well-trained, effective military.
D) reforms from above that strengthened civic pride.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
As a result of the Franco-Prussian War
A) the South German states joined a Prussian-dominated Germany.
B) Napoleon III was captured.
C) Paris suffered a lengthy siege.
D) the German Empire was declared at Versailles.
E) all of the above
A) the South German states joined a Prussian-dominated Germany.
B) Napoleon III was captured.
C) Paris suffered a lengthy siege.
D) the German Empire was declared at Versailles.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The Settlement of 1867 succeeded in
A) pacifying the Czechs.
B) granting Poles autonomy in Galicia.
C) removing the Hapsburgs from control of Hungary.
D) giving Hungary complete control over its internal affairs.
E) reestablishing Austrian influence among German states after its defeat in the Seven Weeks' War.
A) pacifying the Czechs.
B) granting Poles autonomy in Galicia.
C) removing the Hapsburgs from control of Hungary.
D) giving Hungary complete control over its internal affairs.
E) reestablishing Austrian influence among German states after its defeat in the Seven Weeks' War.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Houston Stewart Chamberlain's Foundations of the Nineteenth Century
A) had an impact primarily in the nineteenth century.
B) was greeted by William II with disdain.
C) may be viewed as a spiritual forerunner of Nazism.
D) was banned from publication in the German Empire.
E) grudgingly acknowledged that Jesus was a Jew.
A) had an impact primarily in the nineteenth century.
B) was greeted by William II with disdain.
C) may be viewed as a spiritual forerunner of Nazism.
D) was banned from publication in the German Empire.
E) grudgingly acknowledged that Jesus was a Jew.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Immediately after successfully weathering the revolutions of 1848-1849, the Hapsburg monarchy
A) pursued a policy of accommodation with its restive non-German populations.
B) increasingly leaned on Prussia for support.
C) converted itself into the Dual Monarchy of Austria and Hungary.
D) pursued a policy of intense centralization.
E) fell into a state of lethargy consistent with the popular saying "the situation is hopeless but not serious."
A) pursued a policy of accommodation with its restive non-German populations.
B) increasingly leaned on Prussia for support.
C) converted itself into the Dual Monarchy of Austria and Hungary.
D) pursued a policy of intense centralization.
E) fell into a state of lethargy consistent with the popular saying "the situation is hopeless but not serious."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The Zollverein was
A) an association of German university professors who advocated free trade.
B) a customs union embracing all German states except Austria.
C) an umbrella organization of nationalist student groups.
D) an association of German university professors who advocated economic nationalism.
E) the abolition of all internal customs duties in Prussia.
A) an association of German university professors who advocated free trade.
B) a customs union embracing all German states except Austria.
C) an umbrella organization of nationalist student groups.
D) an association of German university professors who advocated economic nationalism.
E) the abolition of all internal customs duties in Prussia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The Volkish movement had the least appeal for
A) the working class.
B) peasants.
C) artisans and small shopkeepers.
D) scholars and students.
E) the bourgeoisie.
A) the working class.
B) peasants.
C) artisans and small shopkeepers.
D) scholars and students.
E) the bourgeoisie.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How did William I overcome the opposition of liberals to his plans for expanding the military?
A) He took funds granted by Parliament for government expenses and used them to institute army reforms instead.
B) He appointed Otto von Bismarck as his chief aide to deal with Parliament.
C) Taxes were collected without Parliament's approval, liberals were fired or imprisoned, and the press was censored.
D) He enjoyed support from the army and the people.
E) all of the above
A) He took funds granted by Parliament for government expenses and used them to institute army reforms instead.
B) He appointed Otto von Bismarck as his chief aide to deal with Parliament.
C) Taxes were collected without Parliament's approval, liberals were fired or imprisoned, and the press was censored.
D) He enjoyed support from the army and the people.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The Italian Mazzini and the Czech Palacky were each powerful examples of
A) national leaders in the Hapsburg Empire who opposed the policy of centralization and Germanization.
B) liberal nationalists who believed that love of and devotion to one's country would lead to love of and devotion to humanity.
C) working class leaders whose primary goal was social harmony and economic justice.
D) extreme nationalists who believed in a Darwinian struggle among nations.
E) Volkish thinkers.
A) national leaders in the Hapsburg Empire who opposed the policy of centralization and Germanization.
B) liberal nationalists who believed that love of and devotion to one's country would lead to love of and devotion to humanity.
C) working class leaders whose primary goal was social harmony and economic justice.
D) extreme nationalists who believed in a Darwinian struggle among nations.
E) Volkish thinkers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Extreme nationalists at the turn of the twentieth century had come to believe
A) that war was inevitable and desirable.
B) all members of a nation must be united under the same national government.
C) their nation had the right to recover lost territories, even by force, and to dominate inferior nations.
D) the spiritual energies traditionally found in religious fervor needed to be channeled into a passionate loyalty to the nation.
E) all of the above
A) that war was inevitable and desirable.
B) all members of a nation must be united under the same national government.
C) their nation had the right to recover lost territories, even by force, and to dominate inferior nations.
D) the spiritual energies traditionally found in religious fervor needed to be channeled into a passionate loyalty to the nation.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Before 1870, the strongest resistance to Bismarck and his policies came from
A) the Catholic and Protestant Churches.
B) the Rhineland, which had the strongest ties to France and the Enlightenment.
C) the Catholic South German states.
D) liberals and the bourgeoisie as a whole.
E) the younger generation of military officers.
A) the Catholic and Protestant Churches.
B) the Rhineland, which had the strongest ties to France and the Enlightenment.
C) the Catholic South German states.
D) liberals and the bourgeoisie as a whole.
E) the younger generation of military officers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In the half century following the Settlement of 1867, the two dominant nationalities in the empire of Francis Joseph were
A) Germans and Magyars.
B) Magyars and Slovaks.
C) Germans and Romanians.
D) Romanians and Slovaks.
E) Slovaks and Croats.
A) Germans and Magyars.
B) Magyars and Slovaks.
C) Germans and Romanians.
D) Romanians and Slovaks.
E) Slovaks and Croats.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Nationalism came to appeal to the majority of Europeans by the twentieth century in all the following ways EXCEPT
A) nationalism championed popular myths.
B) conservatives embraced nationalism when it ceased to be overwhelmingly liberal.
C) most Europeans had stopped identifying themselves as Christians by 1900.
D) both the bourgeoisie and the peasantry were attracted by the nationalists' condemnation of Marxism.
E) those that supported a strong state saw nationalism as a means of unifying the people behind the government.
A) nationalism championed popular myths.
B) conservatives embraced nationalism when it ceased to be overwhelmingly liberal.
C) most Europeans had stopped identifying themselves as Christians by 1900.
D) both the bourgeoisie and the peasantry were attracted by the nationalists' condemnation of Marxism.
E) those that supported a strong state saw nationalism as a means of unifying the people behind the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
By 1871
A) German unification finally permitted European fears and tensions to subside.
B) Metternich's concerns for the stability of the European state system had proven unfounded.
C) a new, united Germany had emerged, with an educated, disciplined, and confident population.
D) German power was only matched by that of Austria.
E) Germany 's industries and commerce were yet to experience the Industrial Revolution.
A) German unification finally permitted European fears and tensions to subside.
B) Metternich's concerns for the stability of the European state system had proven unfounded.
C) a new, united Germany had emerged, with an educated, disciplined, and confident population.
D) German power was only matched by that of Austria.
E) Germany 's industries and commerce were yet to experience the Industrial Revolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In Germany, Volkish thinkers
A) considered the ancient German tribes as an inferior stage of German development when compared to Rome.
B) celebrated the achievements of German industrialization.
C) identified parliamentary democracy as a foreign idea that corrupted the pure German spirit.
D) believed that the humanist outlook of the German Enlightenment and liberalism manifested the true German spirit.
E) were criticized by university professor Wilhelm von Riehl and Julius Langbehn.
A) considered the ancient German tribes as an inferior stage of German development when compared to Rome.
B) celebrated the achievements of German industrialization.
C) identified parliamentary democracy as a foreign idea that corrupted the pure German spirit.
D) believed that the humanist outlook of the German Enlightenment and liberalism manifested the true German spirit.
E) were criticized by university professor Wilhelm von Riehl and Julius Langbehn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
How did Bismarck unify Germany?
A) Bismarck provoked and won a war with Denmark over Schleswig-Holstein.
B) Bismarck provoked and won a war with Austria.
C) Bismarck created a federation of North German states.
D) Bismarck provoked and won a war with France.
E) all of the above
A) Bismarck provoked and won a war with Denmark over Schleswig-Holstein.
B) Bismarck provoked and won a war with Austria.
C) Bismarck created a federation of North German states.
D) Bismarck provoked and won a war with France.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Bismarck's success in unifying Germany had all the following effects EXCEPT
A) many liberals abandoned their commitment to parliamentary government.
B) German society seemed to have a growing fascination with state power and militarism.
C) France was seriously antagonized.
D) the balance of power in Europe that had existed since 1815 was overturned.
E) Germany became intensely isolationist, turning its nationalism inward instead of taking up an interest in world affairs.
A) many liberals abandoned their commitment to parliamentary government.
B) German society seemed to have a growing fascination with state power and militarism.
C) France was seriously antagonized.
D) the balance of power in Europe that had existed since 1815 was overturned.
E) Germany became intensely isolationist, turning its nationalism inward instead of taking up an interest in world affairs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following contributed to anti-Semitic sentiments at the end of the nineteenth century?
A) the old belief that Jews were cursed because they had murdered Christ
B) the use of anti-Semitism by the radical right to mobilize and unite all social classes
C) the belief that Jews were materialistic and cowardly
D) the association of Jews with the corrupting influences of capitalism and liberalism
E) all of the above
A) the old belief that Jews were cursed because they had murdered Christ
B) the use of anti-Semitism by the radical right to mobilize and unite all social classes
C) the belief that Jews were materialistic and cowardly
D) the association of Jews with the corrupting influences of capitalism and liberalism
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
According to the text, Richard Wagner contributed to dangerous elements in German nationalism by his
A) glorification of pre-Christian German myths.
B) intense anti-Semitism.
C) message that the Enlightenment was a foreign corrupting influence on Germany.
D) belief that the true German spirit was now corrupted by materialism and greed.
E) all of the above
A) glorification of pre-Christian German myths.
B) intense anti-Semitism.
C) message that the Enlightenment was a foreign corrupting influence on Germany.
D) belief that the true German spirit was now corrupted by materialism and greed.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When Theodor Mommsen wrote, " They listen only to their own envy and hatred, to the meanest instincts , " he was referring to
A) socialists.
B) the working class.
C) nationalists.
D) anti-Semites.
E) the clergy.
A) socialists.
B) the working class.
C) nationalists.
D) anti-Semites.
E) the clergy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Key Terms
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Risorgimento
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Risorgimento

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Key Terms
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Settlement of 1867
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Settlement of 1867

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Theodor Herzl may be remembered for
A) leading laissez-faire economics in Prussia.
B) spreading ideas of racial struggle throughout Europe.
C) helping to develop Zionism.
D) using anti-Semitism as leader of the Christian Social Party in Austria.
E) being Dreyfus's lawyer in his famous trial.
A) leading laissez-faire economics in Prussia.
B) spreading ideas of racial struggle throughout Europe.
C) helping to develop Zionism.
D) using anti-Semitism as leader of the Christian Social Party in Austria.
E) being Dreyfus's lawyer in his famous trial.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Key Terms
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Frankfurt Assembly
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Frankfurt Assembly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Key Terms
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Zollverein
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Zollverein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Key Terms
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Reich
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Reich

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Zionism defined the Jews as a nation and
A) stated that anywhere the Torah resides, there the Jewish homeland lies.
B) advocated their assimilation into European societies.
C) called Jews to return to Palestine.
D) sought a complete break with the religious basis of their identity.
E) stated that their future depended on the revival of the Hebrew language.
A) stated that anywhere the Torah resides, there the Jewish homeland lies.
B) advocated their assimilation into European societies.
C) called Jews to return to Palestine.
D) sought a complete break with the religious basis of their identity.
E) stated that their future depended on the revival of the Hebrew language.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Key Terms
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Seven Weeks' War
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Seven Weeks' War

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Anti-Semitism can be connected to
A) pogroms instigated by the Russian government.
B) conservative causes in Germany and Austria.
C) the creation of Zionism.
D) dramatic divisions in French society.
E) all of the above
A) pogroms instigated by the Russian government.
B) conservative causes in Germany and Austria.
C) the creation of Zionism.
D) dramatic divisions in French society.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The Pan-German League argued in an article from 1913 that members of "subordinate races" were eligible only for which "positions of a non-political nature"?
A) postal and secretary positions
B) teaching positions
C) commercial commissions and chambers of commerce
D) road and bridge commissions
E) entry-level military positions
A) postal and secretary positions
B) teaching positions
C) commercial commissions and chambers of commerce
D) road and bridge commissions
E) entry-level military positions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Key Terms
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
extreme nationalism
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
extreme nationalism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Key Terms
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Young Italy
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Young Italy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following statements concerning racial nationalism is NOT true?
A) It denied equality and scorned toleration.
B) It played only a minor role in nineteenth-century intellectual life.
C) It attacked and undermined the Enlightenment tradition.
D) It presented racial hatred as something virtuous and idealistic.
E) It demonstrated how receptive the mind is to dangerous myths.
A) It denied equality and scorned toleration.
B) It played only a minor role in nineteenth-century intellectual life.
C) It attacked and undermined the Enlightenment tradition.
D) It presented racial hatred as something virtuous and idealistic.
E) It demonstrated how receptive the mind is to dangerous myths.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Key Terms
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
realpolitik
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
realpolitik

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The work Jewish France was responsible for
A) directing the anger of Frenchmen against Dreyfus.
B) describing life in Jewish ghettos in France.
C) reminding Frenchmen of the contributions that Jews had made to the development of the French nation.
D) spreading anti-Semitism by accusing Jews of introducing capitalism to France and gaining control of the country.
E) defending the principles of equality embodied in the French Revolution.
A) directing the anger of Frenchmen against Dreyfus.
B) describing life in Jewish ghettos in France.
C) reminding Frenchmen of the contributions that Jews had made to the development of the French nation.
D) spreading anti-Semitism by accusing Jews of introducing capitalism to France and gaining control of the country.
E) defending the principles of equality embodied in the French Revolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
To which country was Hans Kohn referring when he wrote that it "became the father of modern anti-Semitism; there the systems were thought out and the slogans coined"?
A) Russia
B) the Muslim Ottoman Empire
C) Germany
D) Romania
E) France
A) Russia
B) the Muslim Ottoman Empire
C) Germany
D) Romania
E) France

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Key Terms
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Carbonari
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Carbonari

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Instructions: Please use this outline map of Europe to answer the question(s).
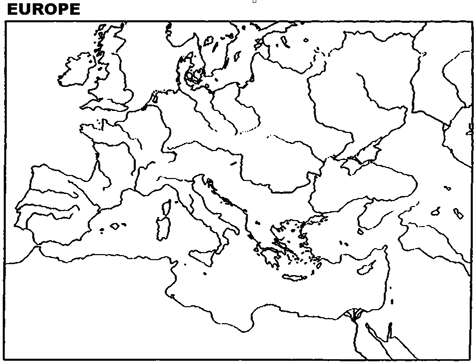
Locate and label those territories given to Napoleon III: Savoy and Nice.

Locate and label those territories given to Napoleon III: Savoy and Nice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Instructions: Please write a thorough, well-organized essay to answer each question.
What factors led to the increase in anti-Semitism in Europe in the nineteenth century, and how was anti-Semitism made manifest in word and deed?
What factors led to the increase in anti-Semitism in Europe in the nineteenth century, and how was anti-Semitism made manifest in word and deed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Instructions: Please write a thorough, well-organized essay to answer each question.
In which lands did nineteenth-century nationalism promote unity, and in which did it lead to conflict and division? How did nationalism change the map of nineteenth-century Europe?
In which lands did nineteenth-century nationalism promote unity, and in which did it lead to conflict and division? How did nationalism change the map of nineteenth-century Europe?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Instructions: Please write a thorough, well-organized essay to answer each question.
Discuss the impact of nationalism on the Hapsburg Empire in the second half of the nineteenth century. How did it change the structure and geography of the lands ruled by the Hapsburgs?
Discuss the impact of nationalism on the Hapsburg Empire in the second half of the nineteenth century. How did it change the structure and geography of the lands ruled by the Hapsburgs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Key Terms
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Volkish thought
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Volkish thought

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Key Terms
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Zionism
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
Zionism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Key Terms
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
anti-Semitism
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
anti-Semitism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Key Terms
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
pogroms
Instructions: Please define the following key terms. Show Who? What? Where? When? Why Important?
pogroms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Instructions: Please use this outline map of Europe to answer the question(s).
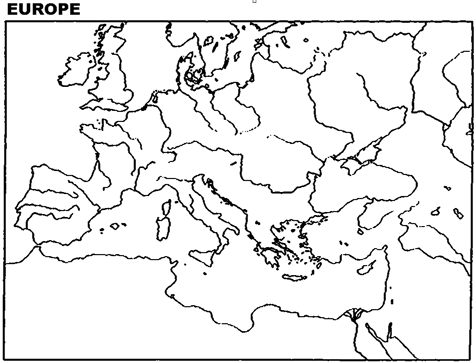
Mark the boundaries of the German Confederation in 1815. Mark the boundary of the North German Confederation and the boundary of the German Empire.

Mark the boundaries of the German Confederation in 1815. Mark the boundary of the North German Confederation and the boundary of the German Empire.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Instructions: Please write a thorough, well-organized essay to answer each question.
Why did liberalism decline and militarism rise in Germany between 1848 and 1870?
Why did liberalism decline and militarism rise in Germany between 1848 and 1870?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Instructions: Please write a thorough, well-organized essay to answer each question.
Reflect on the place of nationalism in the broader societal and intellectual changes of the late nineteenth century.
Reflect on the place of nationalism in the broader societal and intellectual changes of the late nineteenth century.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Instructions: Please write a thorough, well-organized essay to answer each question.
Discuss the evolution of nationalism in the nineteenth century.
Discuss the evolution of nationalism in the nineteenth century.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Instructions: Please use this outline map of Europe to answer the question(s).
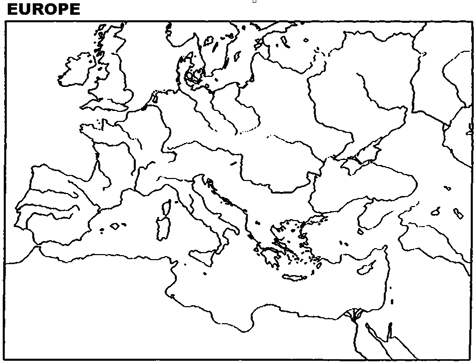
Locate and label the following: the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies; the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia; the Papal States; Parma; Modena; Tuscany; Venetia; and Lombardy. Next to each, place the date when the areas were incorporated into Italy.

Locate and label the following: the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies; the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia; the Papal States; Parma; Modena; Tuscany; Venetia; and Lombardy. Next to each, place the date when the areas were incorporated into Italy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Instructions: Please write a thorough, well-organized essay to answer each question.
Explain the meaning of Volkish thought. Refer to some of the major theorists of Volkish thought and comment on their ideas.
Explain the meaning of Volkish thought. Refer to some of the major theorists of Volkish thought and comment on their ideas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Instructions: Please write a thorough, well-organized essay to answer each question.
What were the goals of Zionism, and who were its major proponents? To what threats was Zionism responding?
What were the goals of Zionism, and who were its major proponents? To what threats was Zionism responding?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Instructions: Please write a thorough, well-organized essay to answer each question.
How and why did extreme nationalism offer ordinary Europeans a sense of certainty in a time of social turmoil and economic dislocation?
How and why did extreme nationalism offer ordinary Europeans a sense of certainty in a time of social turmoil and economic dislocation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Instructions: Please write a thorough, well-organized essay to answer each question.
Trace the main events of the unification of either Italy or Germany. Discuss the role of individual leaders in unifying their people.
Trace the main events of the unification of either Italy or Germany. Discuss the role of individual leaders in unifying their people.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



