Deck 21: Microbial Ecology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Microbial Ecology
1
The algal and fungal interaction within a lichen would best be described as
A) mutualism.
B) synergism.
C) commensalism.
D) amensalism.
E) parasitism.
A) mutualism.
B) synergism.
C) commensalism.
D) amensalism.
E) parasitism.
A
2
Lichens consist of an intimate mutualistic symbiosis between a fungus, an alga, and/or cyanobacteria. What is one primary role of the cyanobacteria in this association?
A) protection of the symbionts
B) nitrogen fixation
C) decomposition of toxic compounds
D) recycling of waste products
E) degradation of lignin
A) protection of the symbionts
B) nitrogen fixation
C) decomposition of toxic compounds
D) recycling of waste products
E) degradation of lignin
B
3
The following image illustrates a syntrophic relationship between an archaeon and a bacterium. The technique used to generate this image was 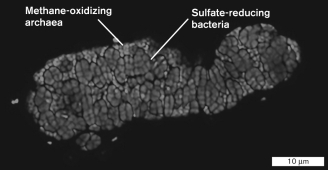
A) light microscopy.
B) transmission electron microscopy.
C) metagenomics.
D) fluorescence in situ hybridization.
E) atomic force microscopy.

A) light microscopy.
B) transmission electron microscopy.
C) metagenomics.
D) fluorescence in situ hybridization.
E) atomic force microscopy.
D
4
Culturing methods often detect organisms that may be rare in the environment but prevail when nutrients appear. What are these typically called?
A) weed organisms
B) protists
C) rhizobia
D) OTUs
E) microbial dark matter
A) weed organisms
B) protists
C) rhizobia
D) OTUs
E) microbial dark matter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which step is NOT common for metagenomic processing and analysis?
A) FISH
B) binning
C) functional annotation
D) contig assembly
E) scaffold assembly
A) FISH
B) binning
C) functional annotation
D) contig assembly
E) scaffold assembly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Synechococcus, a cyanobacterium, is a free-living marine organism that fixes CO₂ into biomass while producing molecular oxygen utilized by swarms of heterotrophic bacteria. Which of the following is the most likely habitat of this bacterium?
A) euphotic zone of the pelagic environment
B) the benthos
C) the littoral zone
D) lake sediments
E) aphotic zone
A) euphotic zone of the pelagic environment
B) the benthos
C) the littoral zone
D) lake sediments
E) aphotic zone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The relationship among endosymbiotic microbes in the termite gut that results in complex metabolic fluxes with a negative DG, which would NOT happen for individual members, is called
A) mutualism.
B) parasitism.
C) exothermic association.
D) predation.
E) syntrophy.
A) mutualism.
B) parasitism.
C) exothermic association.
D) predation.
E) syntrophy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The reactions on the right side of the following table occur only 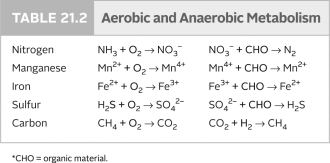
A) under thermophilic conditions.
B) under anaerobic conditions.
C) deep within Earth's crust.
D) under aerobic conditions.
E) in the euphotic zone.

A) under thermophilic conditions.
B) under anaerobic conditions.
C) deep within Earth's crust.
D) under aerobic conditions.
E) in the euphotic zone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is NOT true regarding food webs in ecosystems?
A) Primary producers assimilate minerals into biomass.
B) Primary producers absorb energy from outside the ecosystem.
C) Grazers convert 10% of carbon back to carbon dioxide.
D) Consumers convert 90% of biomass carbon to atmospheric CO2.
E) All energy gained by an ecosystem is eventually lost as heat.
A) Primary producers assimilate minerals into biomass.
B) Primary producers absorb energy from outside the ecosystem.
C) Grazers convert 10% of carbon back to carbon dioxide.
D) Consumers convert 90% of biomass carbon to atmospheric CO2.
E) All energy gained by an ecosystem is eventually lost as heat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What does functional annotation in metagenomic analysis involve?
A) determining the number of species in the sample
B) calculating the %G+C in the metagenome
C) finding homologs or recurring peptide motifs that infer the function of the sequence
D) making contigs and scaffolds and assembling the sequence
E) analyzing the RNA sequences to see what was transcribed
A) determining the number of species in the sample
B) calculating the %G+C in the metagenome
C) finding homologs or recurring peptide motifs that infer the function of the sequence
D) making contigs and scaffolds and assembling the sequence
E) analyzing the RNA sequences to see what was transcribed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A rarefaction curve is the
A) number of sequences generated from a metagenome.
B) number of SSU rRNA sequences found in a metagenome.
C) number of OTUs found as a function of increasing sample size.
D) total number of OTUs from all combined genes in a metagenome.
E) number of organisms in an environment.
A) number of sequences generated from a metagenome.
B) number of SSU rRNA sequences found in a metagenome.
C) number of OTUs found as a function of increasing sample size.
D) total number of OTUs from all combined genes in a metagenome.
E) number of organisms in an environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following are the main consumers of biomass in the ocean?
A) multicellular organisms
B) fish and tube worms
C) protists and viruses
D) heterotrophic bacteria
E) fungi
A) multicellular organisms
B) fish and tube worms
C) protists and viruses
D) heterotrophic bacteria
E) fungi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The Dutch microbiologist van Niel first demonstrated anoxygenic photosynthesis in soil and water bacteria. He generalized his work by hypothesizing that
A) every molecule in nature can be used as a source of nitrogen by some microorganism.
B) photosynthesis results in oxygen production.
C) microbes are found in every environment on Earth.
D) microbes cannot live deep within Earth.
E) photosynthesis occurs deep within Earth.
A) every molecule in nature can be used as a source of nitrogen by some microorganism.
B) photosynthesis results in oxygen production.
C) microbes are found in every environment on Earth.
D) microbes cannot live deep within Earth.
E) photosynthesis occurs deep within Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The term "metagenome" was coined by Jo Handelsman and colleagues in 1998 to refer to
A) shotgun cloning.
B) screening of libraries for expression of genes.
C) the DNA sequence obtained directly from a mixture of genomes.
D) the DNA sequence taken directly from a colony.
E) all uncultured organisms from a community.
A) shotgun cloning.
B) screening of libraries for expression of genes.
C) the DNA sequence obtained directly from a mixture of genomes.
D) the DNA sequence taken directly from a colony.
E) all uncultured organisms from a community.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The instrument shown in step 5 of the figure below is used for what metagenomics step? 
A) DNA isolation
B) DNA sequencing
C) sample filtering
D) cell lysis
E) sequence assembly

A) DNA isolation
B) DNA sequencing
C) sample filtering
D) cell lysis
E) sequence assembly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What does the following rarefaction curve NOT suggest about the samples? 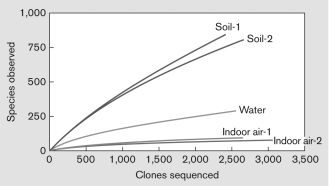
A) More soil sequences were collected.
B) Indoor air samples appear to be sequenced at enough depth.
C) Water samples were not sequenced at enough depth.
D) More sequencing should be done for these samples.
E) Soil samples were not sequenced at enough depth.

A) More soil sequences were collected.
B) Indoor air samples appear to be sequenced at enough depth.
C) Water samples were not sequenced at enough depth.
D) More sequencing should be done for these samples.
E) Soil samples were not sequenced at enough depth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In wetlands, Beggiatoa oxidize H₂S for energy. Removal of H₂S enables growth of other microbes for which H₂S is toxic. However, Beggiatoa derives no benefit from these microbes. This interaction is an example of
A) syntrophy.
B) mutualism.
C) commensalism.
D) amensalism.
E) synergism.
A) syntrophy.
B) mutualism.
C) commensalism.
D) amensalism.
E) synergism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The availability of oxygen and other electron acceptors is the most important determinant of the types of metabolism in a habitat. Which of the following is NOT true about anaerobic environments?
A) They have slower rates of assimilation compared to aerobic habitats.
B) Their rates of dissimilation are slower compared to aerobic environments.
C) Microbes sometimes use minerals such as NO2- to oxidize organic compounds.
D) Anaerobic microbial biomass far exceeds that of the oxygenated biosphere.
E) Respiration of organic compounds is highly dissimilatory, reducing them to CO2.
A) They have slower rates of assimilation compared to aerobic habitats.
B) Their rates of dissimilation are slower compared to aerobic environments.
C) Microbes sometimes use minerals such as NO2- to oxidize organic compounds.
D) Anaerobic microbial biomass far exceeds that of the oxygenated biosphere.
E) Respiration of organic compounds is highly dissimilatory, reducing them to CO2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Metatranscriptomics is the study of ________ obtained from an environmental community.
A) lipids
B) proteins
C) organisms
D) DNA
E) RNA
A) lipids
B) proteins
C) organisms
D) DNA
E) RNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The ________ is a set of conditions, including its habitat, resources, and relations with other species of the ecosystem, that enable an organism to grow and reproduce.
A) benthos
B) environment
C) niche
D) metagenome
E) resource requirement
A) benthos
B) environment
C) niche
D) metagenome
E) resource requirement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A holobiont is defined as an
A) organism that benefits while providing no benefit or a hidden benefit to its host.
B) interaction that harms one partner nonspecifically without an intimate symbiosis.
C) organism that forms an intimate relationship with another, where both benefit.
D) entity composed of multiple types of organisms, including microbes.
E) intimate relationship in which one member benefits while harming a host.
A) organism that benefits while providing no benefit or a hidden benefit to its host.
B) interaction that harms one partner nonspecifically without an intimate symbiosis.
C) organism that forms an intimate relationship with another, where both benefit.
D) entity composed of multiple types of organisms, including microbes.
E) intimate relationship in which one member benefits while harming a host.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The depth of the photic zone at the coastal shelf of marine habitats is
A) 100-200 m.
B) 10-20 m.
C) about 1 m.
D) about 0.1 m.
E) about 2 m.
A) 100-200 m.
B) 10-20 m.
C) about 1 m.
D) about 0.1 m.
E) about 2 m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Animal intestinal microbiota typically yields ________, which the host animal can absorb and digest to completion through aerobic respiration.
A) celluloses
B) CO2
C) oligosaccharides
D) polysaccharides
E) short-chain fatty acids
A) celluloses
B) CO2
C) oligosaccharides
D) polysaccharides
E) short-chain fatty acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which region of marine habitat refers to the microscopic interface between water and air?
A) pelagic zone
B) neuston
C) euphotic zone
D) aphotic zone
E) benthic zone
A) pelagic zone
B) neuston
C) euphotic zone
D) aphotic zone
E) benthic zone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Lakes that have dilute concentrations of nutrients are termed
A) eutrophic.
B) syntrophic.
C) aphotic.
D) oligotrophic.
E) atrophic.
A) eutrophic.
B) syntrophic.
C) aphotic.
D) oligotrophic.
E) atrophic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A graduate student filtered a liter of seawater using a Millipore filter membrane of 2 mm pore size. Her filtrate
A) is sterile.
B) contains microplankton.
C) contains picoplankton.
D) contains nanoplankton.
E) contains all plankton.
A) is sterile.
B) contains microplankton.
C) contains picoplankton.
D) contains nanoplankton.
E) contains all plankton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The high biological oxygen demand that accompanies algal bloom in eutrophic lakes increases the span of the ________ zone.
A) oxygenic epilimnion
B) anoxic hypolimnion
C) coastal shelf
D) anoxic benthic
E) oxygenic neuston
A) oxygenic epilimnion
B) anoxic hypolimnion
C) coastal shelf
D) anoxic benthic
E) oxygenic neuston

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is responsible for the characteristic odor of soil?
A) Vibrio sp.
B) Bacillus sp.
C) Streptomyces sp.
D) Staphylococcus sp.
E) Pseudomonas sp.
A) Vibrio sp.
B) Bacillus sp.
C) Streptomyces sp.
D) Staphylococcus sp.
E) Pseudomonas sp.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which term represents the region of soil influenced by plant roots? 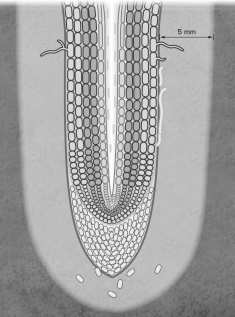
A) stele
B) cortex
C) root cap
D) rhizoplane
E) rhizosphere

A) stele
B) cortex
C) root cap
D) rhizoplane
E) rhizosphere

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The ________ region of an oligotrophic lake extends to about 10 meters below the surface.
A) neuston
B) benthic
C) epilimnion
D) hypolimnion
E) euphotic
A) neuston
B) benthic
C) epilimnion
D) hypolimnion
E) euphotic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
All of the following are likely to be found among the benthic microbes EXCEPT
A) barophiles.
B) psychrophiles.
C) thermophiles.
D) phototrophs.
E) methanogens.
A) barophiles.
B) psychrophiles.
C) thermophiles.
D) phototrophs.
E) methanogens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Eutrophic lakes typically support ten times the microbial concentrations of an oligotrophic lake. Which of the following statements is NOT true of eutrophic lakes?
A) Biochemical oxygen demand is high.
B) Population of aquatic animals is high.
C) Nitrogen and phosphorous levels are usually high.
D) Photosynthetic activities are altered.
E) Algal blooms are common.
A) Biochemical oxygen demand is high.
B) Population of aquatic animals is high.
C) Nitrogen and phosphorous levels are usually high.
D) Photosynthetic activities are altered.
E) Algal blooms are common.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Much of the microbial fermentation in humans occurs in the
A) stomach.
B) colon.
C) rumen.
D) small intestine.
E) esophagus.
A) stomach.
B) colon.
C) rumen.
D) small intestine.
E) esophagus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Thousands of species of microbes in the cow ________ ferment and break down plant material to small particles.
A) rumen
B) stomach
C) omasum
D) reticulum
E) intestine
A) rumen
B) stomach
C) omasum
D) reticulum
E) intestine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Nonphotosynthetic ________ provide minerals and protection for lichen symbiotic partners.
A) plankton
B) proteobacteria
C) algae
D) fungi
E) cyanobacteria
A) plankton
B) proteobacteria
C) algae
D) fungi
E) cyanobacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Compared to eutrophic lakes, the biochemical oxygen demand, or BOD, of oligotrophic lakes is
A) low.
B) similar.
C) high.
D) unpredictable.
E) extremely high.
A) low.
B) similar.
C) high.
D) unpredictable.
E) extremely high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following plays an important role in keeping the water column clear enough for the penetration of light?
A) algae
B) bacteria
C) fish
D) invertebrates
E) viruses
A) algae
B) bacteria
C) fish
D) invertebrates
E) viruses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The flame-like vertical forms and breakaway pieces of mat in ice-covered Antarctic lakes are caused by 
A) limited light penetration in the lake.
B) denitrification.
C) sulfur-reducing bacteria.
D) oxygen production.
E) freeze-thaw cycles.

A) limited light penetration in the lake.
B) denitrification.
C) sulfur-reducing bacteria.
D) oxygen production.
E) freeze-thaw cycles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Bacteria found growing in between crystals of solid bedrock as deep as 3 km below Earth's surface are called
A) endophytes.
B) symbionts.
C) endoliths.
D) decomposers.
E) saprophytes.
A) endophytes.
B) symbionts.
C) endoliths.
D) decomposers.
E) saprophytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following refers to the zone of a lake with higher relative oxygen concentrations?
A) neuston
B) epilimnion
C) thermocline
D) hypolimnion
E) benthos
A) neuston
B) epilimnion
C) thermocline
D) hypolimnion
E) benthos

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Explain the difference between assimilation and dissimilation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
One of the most important ecological roles of the Florida Everglades is that
A) it is home to beautiful birds.
B) it filters much of the water supply for Florida communities.
C) many bacteria reside in it.
D) nutrients can easily be leached to the lakes.
E) tourists come to see it in large numbers.
A) it is home to beautiful birds.
B) it filters much of the water supply for Florida communities.
C) many bacteria reside in it.
D) nutrients can easily be leached to the lakes.
E) tourists come to see it in large numbers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Compare and contrast the photic zones of freshwater lake and pelagic ecosystems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Describe the interaction of Vibrio cholerae with copepods. How did sari cloth help decrease the incidence of cholera in Bangladesh?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following organisms forms a specific mutualistic association with legumes?
A) rhizobia
B) agrobacteria
C) E. coli
D) morels
E) Vibrio sp.
A) rhizobia
B) agrobacteria
C) E. coli
D) morels
E) Vibrio sp.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Name two factors that differentiate aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems and explain how they affect food cycles in these systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the legume-rhizobium symbiosis, nitrogen fixation is carried out in nodules by
A) bacteroids that lack a cell wall.
B) intact rhizobia in the plant cortex.
C) plant cells in the presence of symbiotic bacteria.
D) bacteroids in oxygen-rich nodules.
E) photosynthetic bacteroids in plants.
A) bacteroids that lack a cell wall.
B) intact rhizobia in the plant cortex.
C) plant cells in the presence of symbiotic bacteria.
D) bacteroids in oxygen-rich nodules.
E) photosynthetic bacteroids in plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Lignin decomposition forms
A) arbuscules.
B) detritus.
C) fruiting bodies.
D) humus.
E) rhizopus.
A) arbuscules.
B) detritus.
C) fruiting bodies.
D) humus.
E) rhizopus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Describe the steps in sequencing a metagenome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
How do metatranscriptomics and metaproteomics address functional limitations of metagenomics?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Bacteroids remain sequestered within a sac of plant-derived membrane known as the
A) flavonoid.
B) infection thread.
C) Nod factor.
D) nucleosome.
E) symbiosome.
A) flavonoid.
B) infection thread.
C) Nod factor.
D) nucleosome.
E) symbiosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Rhizosphere bacteria benefit their host plant by
A) degrading plant lignin.
B) attracting symbiotic nematodes.
C) improving water uptake.
D) producing large amounts of photosynthate.
E) discouraging growth of plant pathogens.
A) degrading plant lignin.
B) attracting symbiotic nematodes.
C) improving water uptake.
D) producing large amounts of photosynthate.
E) discouraging growth of plant pathogens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Fungi play a much larger and more significant role in the decomposition of terrestrial biomass than they do in marine ecosystems. This is because fungi
A) do not thrive in a marine environment.
B) outcompete bacteria in terrestrial habitats.
C) can degrade the abundant lignin in terrestrial habitats.
D) decompose leghemoglobin rapidly.
E) degrade human waste faster than bacteria.
A) do not thrive in a marine environment.
B) outcompete bacteria in terrestrial habitats.
C) can degrade the abundant lignin in terrestrial habitats.
D) decompose leghemoglobin rapidly.
E) degrade human waste faster than bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Vascular abuscular mycorrhizae (VAM) are an example of which of the following?
A) ectomycorrhizae
B) endomycorrhizae
C) free-living fungus
D) lignin decomposer
E) nitrogen fixer
A) ectomycorrhizae
B) endomycorrhizae
C) free-living fungus
D) lignin decomposer
E) nitrogen fixer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Most forest trees require mycorrhizae for growth because
A) forest soils are rich in phosphorous.
B) mycorrhizae limit toxic metal uptake.
C) the mycorrhizal form an ammensalic association.
D) mycorrhizae significantly increase the uptake of nutrients.
E) forest trees do not have deep roots.
A) forest soils are rich in phosphorous.
B) mycorrhizae limit toxic metal uptake.
C) the mycorrhizal form an ammensalic association.
D) mycorrhizae significantly increase the uptake of nutrients.
E) forest trees do not have deep roots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following require endosymbiotic protists and bacteria to digest plant material such as lignin and cellulose?
A) termites
B) cattle
C) gorillas
D) humans
E) microplankton
A) termites
B) cattle
C) gorillas
D) humans
E) microplankton

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What are the benefits and limitations of different environmental sequencing methods? Explain why ribosomal gene sequencing can be used as an initial screen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Propose a method to measure biomass production in terms of DNA synthesis. What are the limitations?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
How do microbes live if their metabolic process to generate energy has a positive DG?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Explain at least three ways in which metagenomes may overlook organisms in the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is coral bleaching? What is its possible cause?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Explain how metagenomics and metatranscriptomics have been used to assess ocean diversity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The net biomass of a population does not indicate productivity within an ecosystem. Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Describe the technique pioneered by Robert Hungate of the University of California at Davis to study anaerobic microbiology of the rumen. What types of questions can be answered with this technique?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Define BOD, and explain why it can be used to measure the pollution level of lakes. Describe how effluents carrying high levels of nutrients can cause eutrophication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In any environment, pathogens are always outnumbered by a vast community of neutral or helpful microbes. Describe some beneficial as well as devastating incidences of plant pathogens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Describe the process of haustorial parasitism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Explain how viruses select for increased diversity of microbial plankton in the oceans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Explain how endoliths derive energy inside bedrock, where there is no sunlight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Describe the initiation process for legume-rhizobium symbiosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



