Deck 25: Microbial Pathogenesis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Microbial Pathogenesis
1
Yellow fever and West Nile virus are both
A) cancer causing.
B) hemorrhagic viruses.
C) close relatives of herpes virus.
D) diarrheagenic viruses.
E) flaviviruses.
A) cancer causing.
B) hemorrhagic viruses.
C) close relatives of herpes virus.
D) diarrheagenic viruses.
E) flaviviruses.
E
2
Pathogenicity islands include all of the following EXCEPT that
A) genes are not expressed as operons.
B) GC/AT ratio differs from the rest of the genome.
C) residual phage genomes flank the island.
D) they are often linked to tRNA.
E) they encode the type III protein secretion (T3SS) export systems.
A) genes are not expressed as operons.
B) GC/AT ratio differs from the rest of the genome.
C) residual phage genomes flank the island.
D) they are often linked to tRNA.
E) they encode the type III protein secretion (T3SS) export systems.
A
3
Superantigens
A) bore holes on eukaryotic cell membranes.
B) inhibit phagocytosis.
C) prevent degranulation of macrophages.
D) are antipyrogenic.
E) activate immune cells without being processed.
A) bore holes on eukaryotic cell membranes.
B) inhibit phagocytosis.
C) prevent degranulation of macrophages.
D) are antipyrogenic.
E) activate immune cells without being processed.
E
4
Synthesis of flagella and pili filaments in Gram-negatives share which of the following attributes?
A) Protein export systems are used to deliver subunits to the outside.
B) Chaperones are not needed for protein transport.
C) There is no periplasmic stopover.
D) Flagellar and pili proteins are added in sequence intracellularly.
E) Flagellar and pili proteins do not extend beyond the periplasm.
A) Protein export systems are used to deliver subunits to the outside.
B) Chaperones are not needed for protein transport.
C) There is no periplasmic stopover.
D) Flagellar and pili proteins are added in sequence intracellularly.
E) Flagellar and pili proteins do not extend beyond the periplasm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Exotoxins
A) are secreted by Gram-positive bacteria only.
B) primarily contain glycolipids.
C) are protein toxins made by Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
D) serve as adhesins for mucosal pathogens.
E) contain lipid A.
A) are secreted by Gram-positive bacteria only.
B) primarily contain glycolipids.
C) are protein toxins made by Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
D) serve as adhesins for mucosal pathogens.
E) contain lipid A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Multivalent adhesion molecule 7, or MAM7, is a unique adhesion because it
A) is expressed late in an infection.
B) is found only in Gram-positive organisms.
C) is important in initiating infection.
D) decreases the LD50 of an organism.
E) acts as a toxin.
A) is expressed late in an infection.
B) is found only in Gram-positive organisms.
C) is important in initiating infection.
D) decreases the LD50 of an organism.
E) acts as a toxin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Biofilms play a major role in enhancing bacterial virulence because
A) biofilm strains are mutants.
B) the exopolymer matrix is highly toxic and mutagenic.
C) biofilm bacteria are intracellular pathogens.
D) bacteria in biofilms are more resistant to antimicrobials and phagocytosis.
E) low bacteria density does not alert the human immune system.
A) biofilm strains are mutants.
B) the exopolymer matrix is highly toxic and mutagenic.
C) biofilm bacteria are intracellular pathogens.
D) bacteria in biofilms are more resistant to antimicrobials and phagocytosis.
E) low bacteria density does not alert the human immune system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Consider two isolates, A and B. Microbe A had an LD₅₀ of 5 ´ 10⁴, while microbe B recorded an LD₅₀ of 5 ´ 10⁷. Which isolate is more virulent?
A) unable to know based on information provided
B) microbe A
C) microbe B
D) They are equally virulent.
E) The values indicate that neither one is virulent.
A) unable to know based on information provided
B) microbe A
C) microbe B
D) They are equally virulent.
E) The values indicate that neither one is virulent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The disease filariasis, commonly known as elephantiasis, is caused by a(n)
A) ectoparasite.
B) endoparasite.
C) insect.
D) bacterium.
E) fungus.
A) ectoparasite.
B) endoparasite.
C) insect.
D) bacterium.
E) fungus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following are also categorized as frank, or strict, pathogens?
A) parasites
B) endoparasites
C) ectoparasites
D) primary pathogens
E) opportunistic pathogens
A) parasites
B) endoparasites
C) ectoparasites
D) primary pathogens
E) opportunistic pathogens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A life-threatening lung infection caused by biofilm formation in cystic fibrosis patients is
A) Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
B) Staphylococcus epidermidis.
C) Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
D) Vibrio cholerae.
E) Bordetella pertussis.
A) Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
B) Staphylococcus epidermidis.
C) Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
D) Vibrio cholerae.
E) Bordetella pertussis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The term used to designate how many bacteria or viruses are required to kill 50% of an experimental group of hosts is
A) ID50.
B) LD50.
C) pathogenicity.
D) infectivity.
E) virulence.
A) ID50.
B) LD50.
C) pathogenicity.
D) infectivity.
E) virulence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements is NOT correct about disease reservoirs?
A) Reservoirs are mammals or birds, but not insects.
B) A vector can be the reservoir of a disease.
C) A reservoir is an integral part of the disease cycle.
D) Disease-control measures must consider the biological reservoir.
E) A reservoir is ultimately the source of infection in a population.
A) Reservoirs are mammals or birds, but not insects.
B) A vector can be the reservoir of a disease.
C) A reservoir is an integral part of the disease cycle.
D) Disease-control measures must consider the biological reservoir.
E) A reservoir is ultimately the source of infection in a population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Type I and Type IV pili both
A) are similar in mode of secretion.
B) are mannose resistant.
C) have an assembly that does not involve the secA general secretory pathway.
D) are encoded by a pathogenicity island.
E) are exclusively used for pathogenesis.
A) are similar in mode of secretion.
B) are mannose resistant.
C) have an assembly that does not involve the secA general secretory pathway.
D) are encoded by a pathogenicity island.
E) are exclusively used for pathogenesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A chef cut her finger accidentally. The next morning, she felt pain and warmth and had a little swelling and redness on that finger (which are signs of inflammation). By that night, she was just fine. Which of the following pertains to the chef?
A) She had an overt microbial disease.
B) She had an infection.
C) The inflammation was a response to the cut, not a microbe.
D) Microbial toxins, not the vegetative cells, induced inflammation.
E) The cut introduced ectoparasites that could not survive.
A) She had an overt microbial disease.
B) She had an infection.
C) The inflammation was a response to the cut, not a microbe.
D) Microbial toxins, not the vegetative cells, induced inflammation.
E) The cut introduced ectoparasites that could not survive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The likely mode of transmission of a bacterial disease in which incidence increases with a prolonged warm summer is
A) direct transmission.
B) airborne transmission.
C) insect vector transmission.
D) common source fomite.
E) sexual transmission.
A) direct transmission.
B) airborne transmission.
C) insect vector transmission.
D) common source fomite.
E) sexual transmission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following diseases is transmitted by the mosquito Aedes aegypti?
A) yellow fever
B) Ebola
C) epidemic typhus
D) listeriosis
E) SARS
A) yellow fever
B) Ebola
C) epidemic typhus
D) listeriosis
E) SARS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The toxin gene in Corynebacterium diphtheriae is located on
A) the plasmid.
B) mobile genes called transposons.
C) bacterial chromosomes.
D) lysogenic phage genomes.
E) the plasma membrane.
A) the plasmid.
B) mobile genes called transposons.
C) bacterial chromosomes.
D) lysogenic phage genomes.
E) the plasma membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The current classification of bacteria pili is based on ________ rather than ________.
A) phenotype; function
B) function; amino acid sequence
C) protein sequence; phenotype
D) origin; protein sequence
E) size; phenotype
A) phenotype; function
B) function; amino acid sequence
C) protein sequence; phenotype
D) origin; protein sequence
E) size; phenotype

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An example of vertical transmission of infectious agents is
A) Staphylococcus spp. gaining antibiotic resistance genes through conjugation.
B) HIV passing from mother to child in utero.
C) an infectious ameba obtained from a water sample.
D) influenza being passed by a sneeze.
E) hepatitis being transmitted by an infected needle stick.
A) Staphylococcus spp. gaining antibiotic resistance genes through conjugation.
B) HIV passing from mother to child in utero.
C) an infectious ameba obtained from a water sample.
D) influenza being passed by a sneeze.
E) hepatitis being transmitted by an infected needle stick.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following does NOT result from the release of endotoxin from Gram-negative bacteria?
A) fever
B) activation of the alternate complement pathway
C) vasodilation
D) hypertension
E) shock
A) fever
B) activation of the alternate complement pathway
C) vasodilation
D) hypertension
E) shock

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following statements is NOT correct about a patient who died from endotoxin pathologies?
A) Disseminated intravascular coagulation may have contributed to death.
B) The methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, or MRSA, superbug is a likely suspect.
C) The patient may have died from hypotension.
D) The patient may not have run a fever if AIDS was present.
E) The lipid A in the endotoxin is responsible for the virulence.
A) Disseminated intravascular coagulation may have contributed to death.
B) The methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, or MRSA, superbug is a likely suspect.
C) The patient may have died from hypotension.
D) The patient may not have run a fever if AIDS was present.
E) The lipid A in the endotoxin is responsible for the virulence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Protein A helps Staphylococcus aureus avoid
A) antibiotics.
B) apoptosis.
C) phagocytosis.
D) cytotoxic T cells.
E) phagosome-lysosome fusion.
A) antibiotics.
B) apoptosis.
C) phagocytosis.
D) cytotoxic T cells.
E) phagosome-lysosome fusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A possible role for quorum sensing in pathogenicity is that it
A) detects and responds to the pH as an indicator of the environment.
B) delays production of toxins that may alert the host to the presence of the bacteria.
C) monitors and responds to concentrations of ions such as magnesium.
D) senses and responds to the population of phagocytes at the infection site.
E) helps the pathogen escape the adaptive immune response.
A) detects and responds to the pH as an indicator of the environment.
B) delays production of toxins that may alert the host to the presence of the bacteria.
C) monitors and responds to concentrations of ions such as magnesium.
D) senses and responds to the population of phagocytes at the infection site.
E) helps the pathogen escape the adaptive immune response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Bacteria that exhibit antigenic shifts and phase variations will most likely cause
A) host immunity.
B) recurrent infections in the exposed host.
C) death each time a host is infected.
D) subclinical infections.
E) mild, acute infections.
A) host immunity.
B) recurrent infections in the exposed host.
C) death each time a host is infected.
D) subclinical infections.
E) mild, acute infections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following produces a toxin that disrupts protein synthesis?
A) Clostridium perfringens
B) Shigella dysenteriae
C) Listeria monocytogenes
D) Staphylococcus aureus
E) Bacillus anthracis
A) Clostridium perfringens
B) Shigella dysenteriae
C) Listeria monocytogenes
D) Staphylococcus aureus
E) Bacillus anthracis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following protein secretory systems injects effector molecules directly from the bacterial cytoplasm into the host cytoplasm?
A) type I
B) type II
C) type III
D) type IV
E) types I, II, III, and IV
A) type I
B) type II
C) type III
D) type IV
E) types I, II, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Petechiae, which result from large amounts of endotoxin, are distinguished by which symptom?
A) diarrhea
B) a pseudomembrane
C) elephantiasis
D) fever
E) a rash
A) diarrhea
B) a pseudomembrane
C) elephantiasis
D) fever
E) a rash

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin
A) damages membranes.
B) increases protein synthesis.
C) activates second messenger pathways.
D) activates immune response.
E) acts as a capsule.
A) damages membranes.
B) increases protein synthesis.
C) activates second messenger pathways.
D) activates immune response.
E) acts as a capsule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The cholera and Escherichia coli (traveler's diarrhea) toxins ________, leading to high levels of cAMP in cells.
A) ADP ribosylate the Gs factor
B) ADP ribosylate adenyl cyclase
C) inactivate ATP
D) are bacterial adenylate cyclase
E) phosphorylate the G factor
A) ADP ribosylate the Gs factor
B) ADP ribosylate adenyl cyclase
C) inactivate ATP
D) are bacterial adenylate cyclase
E) phosphorylate the G factor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What type of toxin is the alpha hemolysin of Staphylococcus aureus?
A) protein synthesis inhibitor
B) protease
C) superantigen
D) cell membrane disruptor
E) second messenger pathway disruptor
A) protein synthesis inhibitor
B) protease
C) superantigen
D) cell membrane disruptor
E) second messenger pathway disruptor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Toxins with ADP ribosyltransferase activity cause
A) membrane pore formation.
B) immune system activation.
C) proteolytic degradation of host proteins.
D) adenylate cyclase inhibition.
E) inhibition of elongation factor 2.
A) membrane pore formation.
B) immune system activation.
C) proteolytic degradation of host proteins.
D) adenylate cyclase inhibition.
E) inhibition of elongation factor 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
E. coli O157:H7 has a very low infectious dose because
A) it is encapsulated.
B) disease results from a synergistic action with Shigella.
C) it is resistant to usually lethal gastric acid.
D) the intestine has many receptors for the toxin.
E) it secretes a superantigen.
A) it is encapsulated.
B) disease results from a synergistic action with Shigella.
C) it is resistant to usually lethal gastric acid.
D) the intestine has many receptors for the toxin.
E) it secretes a superantigen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The anthrax, Escherichia coli, cholera, and Bordetella toxins all
A) inhibit protein synthesis.
B) possess ADP ribosyltransferase activity.
C) cause diarrhea.
D) disrupt the cell membrane.
E) trigger apoptosis.
A) inhibit protein synthesis.
B) possess ADP ribosyltransferase activity.
C) cause diarrhea.
D) disrupt the cell membrane.
E) trigger apoptosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Binding of the protein ________ of the EPEC pathogenicity system directly triggers a remarkable reorganization of host cellular cytoskeletal components.
A) actin
B) SPI-1
C) intimin
D) Nef
E) Ivet
A) actin
B) SPI-1
C) intimin
D) Nef
E) Ivet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is classified as an intracellular bacterial pathogen?
A) HIV
B) Streptococcus mutans
C) Listeria monocytogenes
D) Neisseria gonorrhoeae
E) Bacillus anthracis
A) HIV
B) Streptococcus mutans
C) Listeria monocytogenes
D) Neisseria gonorrhoeae
E) Bacillus anthracis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following species causes whooping cough?
A) Streptococcus mutans
B) Staphylococcus aureus
C) Bordetella pertussis
D) Neisseria gonorrhoeae
E) Mycoplasma
A) Streptococcus mutans
B) Staphylococcus aureus
C) Bordetella pertussis
D) Neisseria gonorrhoeae
E) Mycoplasma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Thick polysaccharide capsules are important virulence assets for
A) Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholera.
B) Clostridium tetani and Bacillus anthracis.
C) Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Streptococcus pneumonia.
D) Salmonella spp. and Staphylococcus aureus.
E) Helicobacter pylori and Enterobacter cloacae.
A) Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholera.
B) Clostridium tetani and Bacillus anthracis.
C) Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Streptococcus pneumonia.
D) Salmonella spp. and Staphylococcus aureus.
E) Helicobacter pylori and Enterobacter cloacae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The ability to survive in the harsh environment of the phagolysosome is a virulence factor produced by
A) uropathogenic Escherichia coli.
B) Vibrio cholera.
C) Bordetella pertussis.
D) Helicobacter pylori.
E) Coxilla burnetti.
A) uropathogenic Escherichia coli.
B) Vibrio cholera.
C) Bordetella pertussis.
D) Helicobacter pylori.
E) Coxilla burnetti.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is a nonproteinaceous, yet toxic, compound found in all Gram-negative bacteria?
A) endotoxin
B) exotoxin
C) type I pili
D) type III pili
E) type IV pili
A) endotoxin
B) exotoxin
C) type I pili
D) type III pili
E) type IV pili

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Briefly describe three classic modes of action of bacterial toxins. How are they similar? How are they different?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Agent A has an LD₅₀ of 400. Agent B has an LD₅₀ of 600. Which is the more pathogenic agent, A or B? What is the relationship between this measure and microbial virulence?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following techniques would be used to identify unknown virulence genes that are only expressed in the host?
A) in situ hybridization of cultured bacteria
B) creating a genomic library of open reading frames of pathogen
C) mutational studies in vitro
D) culture techniques
E) in vivo expression technology
A) in situ hybridization of cultured bacteria
B) creating a genomic library of open reading frames of pathogen
C) mutational studies in vitro
D) culture techniques
E) in vivo expression technology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Koch's molecular postulates were originally formulated by
A) Robert Koch.
B) Louis Pasteur.
C) Thomas Rivers.
D) Matthew Lawrenz.
E) Stanley Falkow.
A) Robert Koch.
B) Louis Pasteur.
C) Thomas Rivers.
D) Matthew Lawrenz.
E) Stanley Falkow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Type IV pili are essential for the interaction of Neisseria meningitidis with brain endothelial cells. Describe the difference between the type IV and type I pili binding, and explain why knowing the type of binding is important in pathogenesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Tropheryma whipplei is the causative agent for Whipple's disease. It could not be cultured until recently, when the genomic data showed that it
A) was auxotrophic for some amino acids.
B) was an obligate intracellular pathogen.
C) needed a helper virus to grow.
D) needed high levels of iron.
E) is a virus that needs cell culture.
A) was auxotrophic for some amino acids.
B) was an obligate intracellular pathogen.
C) needed a helper virus to grow.
D) needed high levels of iron.
E) is a virus that needs cell culture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Describe what is happening at step 1 in the figure below.
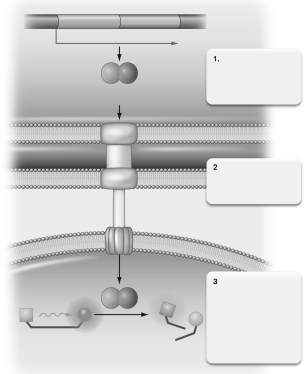


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the rationale for designating disease-causing protozoa and worms as parasites, not as pathogens?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Salmonella and Shigella both
A) produce shiga toxin.
B) are Gram-positive rods.
C) are resistant to gastric acid.
D) cause typhoid fever.
E) are facultative intracellular pathogens.
A) produce shiga toxin.
B) are Gram-positive rods.
C) are resistant to gastric acid.
D) cause typhoid fever.
E) are facultative intracellular pathogens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Autophagy is used by a host cell to
A) activate G-proteins.
B) regulate phagocytosis.
C) scavenge nutrients from damaged organelles.
D) fight extracellular pathogens.
E) induce apoptosis.
A) activate G-proteins.
B) regulate phagocytosis.
C) scavenge nutrients from damaged organelles.
D) fight extracellular pathogens.
E) induce apoptosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
How does a pathogenicity island increase the "fitness" of a microorganism (pathogen) to interact with a host and cause disease?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Identify the parts labeled C, D, E, G, L, M, N in the figure below, and state what their purpose is.
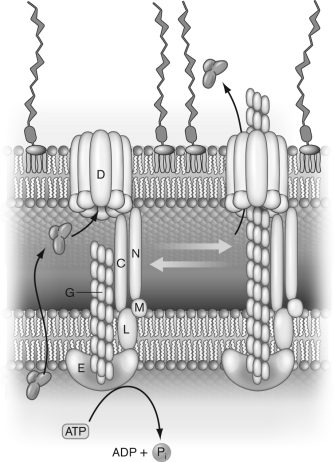


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following types of information CANNOT be derived from the full genome of a noncultured bacterial pathogen?
A) nutritional requirements
B) toxin production
C) infectious and lethal doses
D) pathogenic islands
E) cell receptor binding and tissue tropism
A) nutritional requirements
B) toxin production
C) infectious and lethal doses
D) pathogenic islands
E) cell receptor binding and tissue tropism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Mycobacterium, Trypanosomia, and Leishmania spp. are all unique in that once they are intracellular, they down-regulate the IFN-gamma receptor, causing
A) immune-response suppression.
B) opsonization.
C) complement activation.
D) superantigen reactions.
E) high fever responses.
A) immune-response suppression.
B) opsonization.
C) complement activation.
D) superantigen reactions.
E) high fever responses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following bacteria would you expect to cause the most severe blood disease in a susceptible host?
A) a rapidly growing encapsulated bacteria
B) a flagellated acidophile
C) a barophilic strain
D) a piliated slow-growing bacteria
E) a halophilic psychrophile
A) a rapidly growing encapsulated bacteria
B) a flagellated acidophile
C) a barophilic strain
D) a piliated slow-growing bacteria
E) a halophilic psychrophile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is considered a virulence factor?
A) TNF-Alpha
B) RNA
C) IFN-gamma
D) Strep. pyogenes
E) capsules
A) TNF-Alpha
B) RNA
C) IFN-gamma
D) Strep. pyogenes
E) capsules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Microbes can be transmitted indirectly from one person to another by inanimate objects, collectively called fomites. Describe the role of fomites in the spread of influenza.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Define a fomite and give at least two specific examples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which organism did Koch use to synthesize his two postulates?
A) Bacillus anthracis
B) Staph. aureus
C) Ebola
D) SARS
E) MERs
A) Bacillus anthracis
B) Staph. aureus
C) Ebola
D) SARS
E) MERs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What characteristics of a pathogen distinguish it from a commensal, in terms of its ability to infect and replicate within a eukaryotic host?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What are ubiquitination signals? Describe how a microbe can redirect these signals for its own purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Two Streptococcus pneumoniae strains, agent 1 and agent 2, are administered to groups of animals at different doses. Mortality rates are then measured for the animals that received each dose level of each agent. Agent 1 is found to have an LD₅₀ of 400. Agent 2 is found to have an LD₅₀ of 600. Which one is producing a capsule and which one is not? How do you know?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What process is occurring in the figure below? Describe that process.
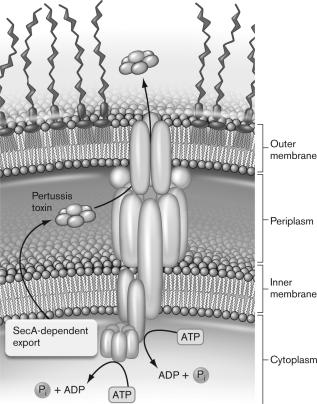


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
There is no host cell receptor for the enteropathogenic Escherichia coli intimin adhesion. How does this pathogen successfully colonize human intestines?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Why is a microbial agent that prevents phagosome-lysosome fusion more virulent as an intracellular pathogen than one that is not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Describe what is occurring in the figure below.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
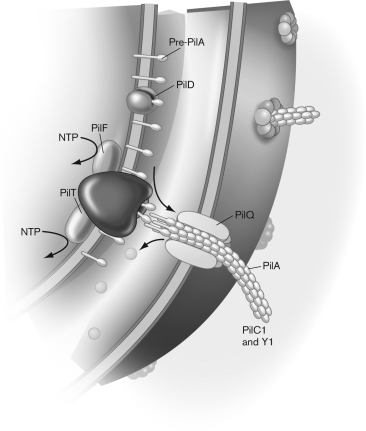
Describe what kind of assembly is occurring in the figure below, and identify the molecules that are present.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Describe the use of digital gene expression (DGE) in host-pathogen relations. How does it work and what information can it tell us?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What would be expected to happen to the Helicobacter pylori bacteria in a patient who has taken a large amount of antacids in the last month?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Diphtheria toxin is a classic AB exotoxin. How does it cause host cell damage?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



