Deck 6: Atoms and Spectra
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/125
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Atoms and Spectra
1
Diagram 6-2 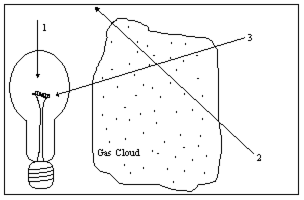
Diagram 6-2 illustrates a light source, a gas cloud, and three different lines of sight. Along which line of sight would an observer see a continuous spectrum?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 2 and 3
E) none of them

Diagram 6-2 illustrates a light source, a gas cloud, and three different lines of sight. Along which line of sight would an observer see a continuous spectrum?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 2 and 3
E) none of them
A
2
Which of the following can be determined by using the Doppler effect?
I) the speed at which a star is moving away from an observer
II) the transverse velocity of a star
III) the radial velocity of a star
IV) the speed at which a car is traveling toward an observer
A) I & IV
B) II & III
C) II & IV
D) I & III
E) I, III, & IV
I) the speed at which a star is moving away from an observer
II) the transverse velocity of a star
III) the radial velocity of a star
IV) the speed at which a car is traveling toward an observer
A) I & IV
B) II & III
C) II & IV
D) I & III
E) I, III, & IV
E
3
You are standing near a railroad track and a train is moving toward you at 60 mph and blowing its horn. What will you notice as the train moves past you?
A) As the train approaches, the horn will sound lower in pitch than when the train is moving away.
B) As the train approaches, the horn will sound higher in pitch than when the train is moving away.
C) There will be no change in the pitch of the horn as it moves by.
D) The horn will get louder as the train moves away from you.
E) The horn will get quieter as the train moves toward you.
A) As the train approaches, the horn will sound lower in pitch than when the train is moving away.
B) As the train approaches, the horn will sound higher in pitch than when the train is moving away.
C) There will be no change in the pitch of the horn as it moves by.
D) The horn will get louder as the train moves away from you.
E) The horn will get quieter as the train moves toward you.
B
4
The neutral hydrogen atom consists of
A) one proton and one neutron.
B) one proton.
C) one proton, one neutron, and one electron.
D) one proton and one electron.
E) an isotope and an ion.
A) one proton and one neutron.
B) one proton.
C) one proton, one neutron, and one electron.
D) one proton and one electron.
E) an isotope and an ion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
____ has a negative charge and a mass about 2000 times smaller than a proton.
A) A neutron
B) An electron
C) A molecule
D) A nucleus
E) An isotope
A) A neutron
B) An electron
C) A molecule
D) A nucleus
E) An isotope

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Figure 6-1 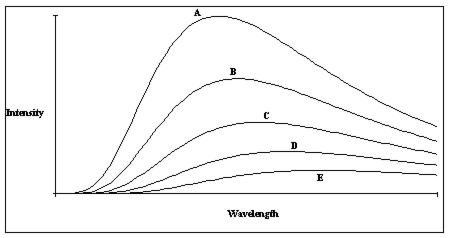
A plot of the continuous spectra of five different stars is shown in Figure 6-1. Based on these spectra, which of the stars has the lowest temperature?
A) Star A
B) Star B
C) Star C
D) Star D
E) Star E

A plot of the continuous spectra of five different stars is shown in Figure 6-1. Based on these spectra, which of the stars has the lowest temperature?
A) Star A
B) Star B
C) Star C
D) Star D
E) Star E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A neutral atom always contains
A) the same number of protons as it does neutrons.
B) the same number of electrons as it does neutrons.
C) the same number of protons as it does electrons.
D) twice as many protons as it does neutrons.
E) twice as many neutrons as it does protons.
A) the same number of protons as it does neutrons.
B) the same number of electrons as it does neutrons.
C) the same number of protons as it does electrons.
D) twice as many protons as it does neutrons.
E) twice as many neutrons as it does protons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The process of removing an electron from a stable nucleus is known as
A) ionization.
B) Doppler broadening.
C) collisional broadening.
D) a red shift.
E) quantum mechanics.
A) ionization.
B) Doppler broadening.
C) collisional broadening.
D) a red shift.
E) quantum mechanics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Diagram 6-2 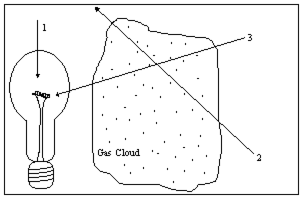
Diagram 6-2 illustrates a light source, a gas cloud, and three different lines of sight. Along which line of sight would an observer see an emission spectrum?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 2 and 3
E) none of them

Diagram 6-2 illustrates a light source, a gas cloud, and three different lines of sight. Along which line of sight would an observer see an emission spectrum?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 2 and 3
E) none of them

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Figure 6-1 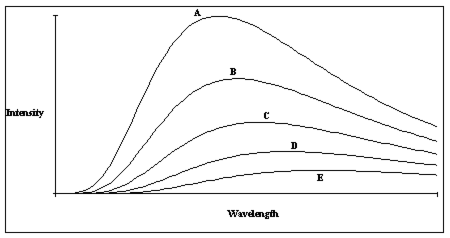
A plot of the continuous spectra of five different stars is shown in Figure 6-1. Based on these spectra, which of the stars is the hottest?
A) Star A
B) Star B
C) Star C
D) Star D
E) Star E

A plot of the continuous spectra of five different stars is shown in Figure 6-1. Based on these spectra, which of the stars is the hottest?
A) Star A
B) Star B
C) Star C
D) Star D
E) Star E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Diagram 6-2 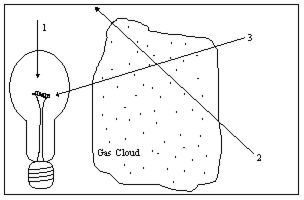
Diagram 6-2 illustrates a light source, a gas cloud, and three different lines of sight. Along which line of sight would an observer see an absorption spectrum?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 2 and 3
E) none of them

Diagram 6-2 illustrates a light source, a gas cloud, and three different lines of sight. Along which line of sight would an observer see an absorption spectrum?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 2 and 3
E) none of them

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The ____ is responsible for binding the electrons to the nucleus.
A) Kirchhoff's law
B) ground state
C) temperature
D) Coulomb force
E) Balmer series
A) Kirchhoff's law
B) ground state
C) temperature
D) Coulomb force
E) Balmer series

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A(n) ____ contains two or more atoms that are bound together by exchanging or sharing electrons with each other.
A) nucleus
B) ion
C) proton
D) electron cloud
E) molecule
A) nucleus
B) ion
C) proton
D) electron cloud
E) molecule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Diagram 6-1 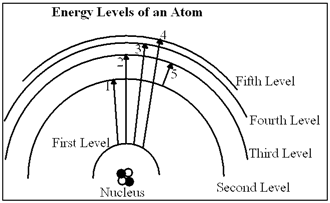
In Diagram 6-1, which of the transitions would absorb a photon with the greatest energy?
A) Transition 1
B) Transition 2
C) Transition 3
D) Transition 4
E) Transition 5

In Diagram 6-1, which of the transitions would absorb a photon with the greatest energy?
A) Transition 1
B) Transition 2
C) Transition 3
D) Transition 4
E) Transition 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Diagram 6-1 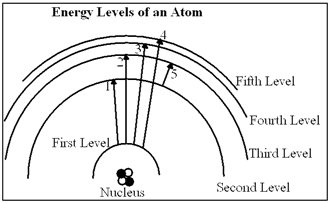
In Diagram 6-1, which of the transitions would absorb a photon with the smallest energy?
A) Transition 1
B) Transition 2
C) Transition 3
D) Transition 4
E) Transition 5

In Diagram 6-1, which of the transitions would absorb a photon with the smallest energy?
A) Transition 1
B) Transition 2
C) Transition 3
D) Transition 4
E) Transition 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The ____ of a gas is a measure of the average speed of the particles (atoms or molecules) in the gas.
A) heat
B) composition
C) temperature
D) blue shift
E) binding energy
A) heat
B) composition
C) temperature
D) blue shift
E) binding energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An atom can be excited
A) if it emits a photon.
B) if it collides with another atom or electron.
C) if it absorbs a photon.
D) if it emits a photon or if it collides with another atom or electron.
E) if it collides with another atom or electron or if it absorbs a photon.
A) if it emits a photon.
B) if it collides with another atom or electron.
C) if it absorbs a photon.
D) if it emits a photon or if it collides with another atom or electron.
E) if it collides with another atom or electron or if it absorbs a photon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The lowest energy level in an atom is
A) the absolute zero temperature.
B) the ground state.
C) the ionization level.
D) responsible for Doppler shifts.
E) the energy level from which the Paschen series of hydrogen originates.
A) the absolute zero temperature.
B) the ground state.
C) the ionization level.
D) responsible for Doppler shifts.
E) the energy level from which the Paschen series of hydrogen originates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Absolute zero is
A) zero degrees Celsius.
B) the temperature at which atoms have no remaining energy from which we can extract heat.
C) the temperature at which water freezes.
D) zero degrees Celsius and the temperature at which water freezes.
E) none of the others.
A) zero degrees Celsius.
B) the temperature at which atoms have no remaining energy from which we can extract heat.
C) the temperature at which water freezes.
D) zero degrees Celsius and the temperature at which water freezes.
E) none of the others.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An atom that is excited
A) is also ionized.
B) is an isotope.
C) has had its electron moved to the lowest energy level.
D) can emit a photon when the electron moves to a lower energy level.
E) can emit a photon when the electron moves to a higher energy level.
A) is also ionized.
B) is an isotope.
C) has had its electron moved to the lowest energy level.
D) can emit a photon when the electron moves to a lower energy level.
E) can emit a photon when the electron moves to a higher energy level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The H δ line has a wavelength of 410.2 nm when observed in the laboratory. If the H δ line appears in a stars spectrum at 410.0 nm, what is the radial velocity of the star?
A) 146 km/s away from the observer
B) 146 km/s toward the observer
C) 6.0 × 107 m/s away from the observer
D) 6.0 × 107 m/s toward the observer
E) The radial velocity of the star cannot be determined from this information.
A) 146 km/s away from the observer
B) 146 km/s toward the observer
C) 6.0 × 107 m/s away from the observer
D) 6.0 × 107 m/s toward the observer
E) The radial velocity of the star cannot be determined from this information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following cannot be determined from the spectrum of a star?
A) chemical composition
B) surface temperature
C) radial (along line of sight) velocity
D) tangential (perpendicular to line of sight) velocity
E) radial (along line of sight) velocity
A) chemical composition
B) surface temperature
C) radial (along line of sight) velocity
D) tangential (perpendicular to line of sight) velocity
E) radial (along line of sight) velocity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
At what wavelength would a star radiate the greatest amount of energy if the star has a surface temperature of 60,000 K?
A) 50 nm
B) 500 nm
C) 300 nm
D) 1.8 × 1011 nm
E) 180 nm
A) 50 nm
B) 500 nm
C) 300 nm
D) 1.8 × 1011 nm
E) 180 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
One star has a temperature of 30,000 K and another star has a temperature of 6,000 K. Compared to the cooler star, how much more energy per second will the hotter star radiate from each square meter of its surface?
A) 5 times
B) 25 times
C) 8.1 × 1017 times
D) 625 times
E) 1.3 × 1015 times
A) 5 times
B) 25 times
C) 8.1 × 1017 times
D) 625 times
E) 1.3 × 1015 times

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The Sun has a surface temperature of approximately 5800 K. At what wavelength does the maximum energy radiated by the Sun occur?
A) 5800 nm
B) 300 nm
C) 174 nm
D) 500 nm
E) 3000 nm
A) 5800 nm
B) 300 nm
C) 174 nm
D) 500 nm
E) 3000 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
At what wavelength would a star radiate the greatest amount of energy if the star has a surface temperature of 10,000 K?
A) 10 nm
B) 100 nm
C) 300 nm
D) 1.0 × 104 nm
E) 3.0 × 1010 nm
A) 10 nm
B) 100 nm
C) 300 nm
D) 1.0 × 104 nm
E) 3.0 × 1010 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The H γ line has a wavelength of 434.0 nm when observed in the laboratory. If the H γ line appears in a stars spectrum at 434.5 nm, what is the radial velocity of the star?
A) 346 km/s away from the observer
B) 346 km/s toward the observer
C) 1.3 × 108 m/s away from the observer
D) 1.3 × 108 m/s toward the observer
E) The radial velocity of the star cannot be determined from this information.
A) 346 km/s away from the observer
B) 346 km/s toward the observer
C) 1.3 × 108 m/s away from the observer
D) 1.3 × 108 m/s toward the observer
E) The radial velocity of the star cannot be determined from this information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The temperature of an object from which no heat energy can be extracted is
A) 0 ° F.
B) 0 ° C.
C) 0 K.
D) 100 K.
E) 100 ° C.
A) 0 ° F.
B) 0 ° C.
C) 0 K.
D) 100 K.
E) 100 ° C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The radiation emitted from a star has a maximum intensity at a wavelength of 500 nm. What is the temperature of this star?
A) 6,000 K
B) 5,000 K
C) 1.5 × 109 K
D) 500 K
E) 10,000 K
A) 6,000 K
B) 5,000 K
C) 1.5 × 109 K
D) 500 K
E) 10,000 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the order of star colors with increasing temperature?
A) red, yellow, blue
B) blue, red, yellow
C) red, blue, yellow
D) yellow, red, blue
E) blue, yellow, red
A) red, yellow, blue
B) blue, red, yellow
C) red, blue, yellow
D) yellow, red, blue
E) blue, yellow, red

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Each element has its own set of characteristic absorption lines because
A) the temperature of each element can varies.
B) elements can exist in different forms of matter.
C) electron energy levels differ for each element.
D) each element has a different mass.
E) absorption lines depend upon the speed of the object.
A) the temperature of each element can varies.
B) elements can exist in different forms of matter.
C) electron energy levels differ for each element.
D) each element has a different mass.
E) absorption lines depend upon the speed of the object.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The Doppler effect states that the motion of any object can
A) shift the wavelength of spectral lines.
B) change the speed of light emitted from the object.
C) enhance the chemical composition of the object.
D) make the object appear hotter.
E) make the object appear cooler.
A) shift the wavelength of spectral lines.
B) change the speed of light emitted from the object.
C) enhance the chemical composition of the object.
D) make the object appear hotter.
E) make the object appear cooler.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
____ is a set of rules that describes how atoms and subatomic particles behave.
A) Kirchhoff's law
B) Blackbody radiation law
C) The Coulomb force
D) Quantum mechanics
E) The binding energy
A) Kirchhoff's law
B) Blackbody radiation law
C) The Coulomb force
D) Quantum mechanics
E) The binding energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If you move an electron in an atom from a low energy level to a higher energy level within the atom, we say that the atom is
A) in the ground state.
B) ionized.
C) dissociated.
D) in an excited state.
E) neutralized.
A) in the ground state.
B) ionized.
C) dissociated.
D) in an excited state.
E) neutralized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The neutral carbon atom consists of
A) one proton and one neutron.
B) six protons.
C) one proton, one neutron, and one electron.
D) six protons and six electrons.
E) an isotope and an ion.
A) one proton and one neutron.
B) six protons.
C) one proton, one neutron, and one electron.
D) six protons and six electrons.
E) an isotope and an ion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The radiation emitted from a star has a maximum intensity at a wavelength of 300 nm. What is the temperature of this star?
A) 300 K
B) 100 K
C) 900,000,000 K
D) 90,000 K
E) 10,000 K
A) 300 K
B) 100 K
C) 900,000,000 K
D) 90,000 K
E) 10,000 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The bluer the light, the ____ each photon contains.
A) more energy
B) less energy
C) less speed
D) more speed
E) none of the above
A) more energy
B) less energy
C) less speed
D) more speed
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
How much energy is radiated each second by one square meter of a star whose temperature is 10,000 K? Note: σ in the Stefan-Boltzmann law is equal to 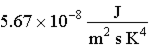 .
.
A) 5.67 × 1012 J
B) 5.67 × 108 J
C) 5.67 × 104 J
D) 300 nm
E) 300,000,000 nm
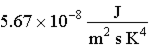 .
.A) 5.67 × 1012 J
B) 5.67 × 108 J
C) 5.67 × 104 J
D) 300 nm
E) 300,000,000 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Atoms that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons are called
A) ions.
B) molecules
C) atomic pairs.
D) nuclear pairs.
E) isotopes.
A) ions.
B) molecules
C) atomic pairs.
D) nuclear pairs.
E) isotopes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
One star has a temperature of 10,000 K and another star has a temperature of 5,000 K. Compared to the cooler star, how much more energy per second will the hotter star radiate from each square meter of its surface?
A) 16 times
B) 2 times
C) 1 × 1016 times
D) 625 times
E) 25 times
A) 16 times
B) 2 times
C) 1 × 1016 times
D) 625 times
E) 25 times

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41

Which spectrum is shown above?
A) emission
B) absorption
C) blackbody
D) None of the other choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The number of ____ in the nucleus determines what element the nucleus is.
A) protons
B) electrons
C) neutrons
D) None of these determines the element.
E) All of these determine the element.
A) protons
B) electrons
C) neutrons
D) None of these determines the element.
E) All of these determine the element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which one of the hydrogen atoms below is EMITTING light at a wavelength in the Balmer series?
A) second energy level to first (most bound)
B) third energy level to second
C) fourth energy level to third
D) second energy level to third
E) first energy level to second
A) second energy level to first (most bound)
B) third energy level to second
C) fourth energy level to third
D) second energy level to third
E) first energy level to second

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The figure shows a color image of Betelgeuse, a red giant star. Which of the surface temperatures below best matches Betelgeuse's surface temperature? Hint: Our Sun at 6000 K is yellow. 
A) 64,000 K
B) 32,000 K
C) 16,000 K
D) 8000 K
E) 2000 K

A) 64,000 K
B) 32,000 K
C) 16,000 K
D) 8000 K
E) 2000 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The nucleus is made of ____
A) electrons only.
B) protons only.
C) neutrons only.
D) electrons and protons, usually.
E) protons and neutrons, usually.
A) electrons only.
B) protons only.
C) neutrons only.
D) electrons and protons, usually.
E) protons and neutrons, usually.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which spectrum is shown above?
A) continuous
B) emission
C) absorption
D) blackbody

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The process of making an electron less tightly bound to an atom's nucleus is known as
A) excitation.
B) Doppler broadening.
C) collisional broadening.
D) a red shift.
E) quantum mechanics.
A) excitation.
B) Doppler broadening.
C) collisional broadening.
D) a red shift.
E) quantum mechanics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48

Which spectrum is shown above?
A) continuous
B) emission
C) absorption
D) All of the other choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Two white dwarf stars are the same size, but one has a surface temperature twice as hot as the other. The hotter star will radiate
A) half as much energy per second as the cooler star.
B) the same amount of energy per second as the cooler star.
C) four times as much energy per second as the cooler star.
D) sixteen times as much energy per second as the cooler star.
A) half as much energy per second as the cooler star.
B) the same amount of energy per second as the cooler star.
C) four times as much energy per second as the cooler star.
D) sixteen times as much energy per second as the cooler star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which property does color best represent?
A) velocity
B) thermal energy
C) temperature
D) heat
A) velocity
B) thermal energy
C) temperature
D) heat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which one of the hydrogen atoms below is EMITTING light? The electron jumps from the
A) second energy level to first (most bound).
B) third energy level to fourth.
C) fourth energy level to fifth.
D) second energy level to third.
E) first energy level to second.
A) second energy level to first (most bound).
B) third energy level to fourth.
C) fourth energy level to fifth.
D) second energy level to third.
E) first energy level to second.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52

Which spectrum is shown above?
A) emission
B) absorption
C) continuous
D) blackbody

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When an electron transitions from a higher orbital level to a lower orbital level, a photon is ______.
A) absorbed
B) transitioned to somewhere else in that same orbit
C) emitted
D) None of the other choices are correct as a photon is not a product of or source to the transition.
A) absorbed
B) transitioned to somewhere else in that same orbit
C) emitted
D) None of the other choices are correct as a photon is not a product of or source to the transition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is not a fundamental component of the atom?
A) proton
B) neutron
C) ion
D) electron
A) proton
B) neutron
C) ion
D) electron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If a light-emitting object is moving away from you, you observe its wavelengths to be ________ its wavelengths if it were at rest.
A) longer than
B) shorter than
C) the same as
A) longer than
B) shorter than
C) the same as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The most massive part of the atom is(are) the ____ which has(have) a ____ charge.
A) electrons; negative
B) nucleus; negative
C) electrons; positive
D) nucleus; positive
A) electrons; negative
B) nucleus; negative
C) electrons; positive
D) nucleus; positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An atom can be ionized by ____ it.
A) removing electrons from
B) adding an electron to
C) removing a proton from
D) Either removing electron from or and adding an electron to
A) removing electrons from
B) adding an electron to
C) removing a proton from
D) Either removing electron from or and adding an electron to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Suppose the laboratory wavelength of a spectral line is 600 nm. In a star it is measured to be 599.4 nm. Is the star moving toward or away from us, relative to the line of sight? How fast is it moving? (Hint: c = 300,000 km/s)
A) toward; 300 km/s
B) away; 300 km/s
C) at rest; 0 km/s
D) sideways; 300 km/s
E) toward; 150 km/s
A) toward; 300 km/s
B) away; 300 km/s
C) at rest; 0 km/s
D) sideways; 300 km/s
E) toward; 150 km/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The wavelength of the hydrogen line from level 1 to level 2 in a hot star is ____________ the wavelength of the same line in a cool star. The stars have the same radial velocities away from Earth.
A) larger than
B) the same as
C) smaller than
D) not enough information to answer
A) larger than
B) the same as
C) smaller than
D) not enough information to answer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If continuous spectrum light from a star passes through a cool, low-density gas on its way to your telescope and spectroscope, ____ spectrum on the continuous spectrum results.
A) a dark (absorption) line
B) a bright (emission) line
C) continuous
A) a dark (absorption) line
B) a bright (emission) line
C) continuous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
____________________ is a measure of the amount of energy due to the motion of the particles in a gas, liquid, or solid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The ____________________ of a star can be determined from its color.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What holds the electron to the nucleus of an atom?
A) Coulomb force
B) binding energy
C) thermal energy
D) heat
A) Coulomb force
B) binding energy
C) thermal energy
D) heat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Since an electron is so less massive than a proton, what is the approximate mass and charge of a neutral hydrogen atom?
A) the mass of an electron, negative
B) the mass of a proton, neutral
C) the mass of a neutron, positive
D) the mass of a proton and neutron, positive
A) the mass of an electron, negative
B) the mass of a proton, neutral
C) the mass of a neutron, positive
D) the mass of a proton and neutron, positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
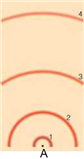
In the above model of an atom, where is the neutron located, assuming a neutron is present?
A) A
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In the diagram below, draw the transition that would emit a photon with the shortest wavelength. 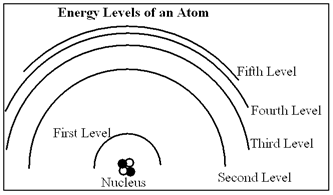


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Where are neutrons found in the hydrogen atom?
A) nucleus
B) cloud surrounding the nucleus
C) outside the atom
D) None of the other choices are correct.
A) nucleus
B) cloud surrounding the nucleus
C) outside the atom
D) None of the other choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What is a blackbody?
A) a perfect emitter and a perfect absorber of light
B) a perfectly opaque object
C) a dense object having a temperature above absolute zero
D) All of the other choices are correct.
A) a perfect emitter and a perfect absorber of light
B) a perfectly opaque object
C) a dense object having a temperature above absolute zero
D) All of the other choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The process of removing an electron from a stable nucleus is known as ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If the radial velocity of a star is positive, the star is moving _________________ you.
A) parallel to
B) away from
C) towards
D) in circles around
A) parallel to
B) away from
C) towards
D) in circles around

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71

In the above image of a glowing gas cloud, you mainly see the color pink. Which spectra would you mostly expect from this gas cloud?
A) absorption
B) continuous
C) emission
D) blackbody

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
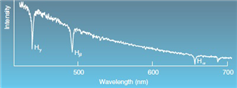
Which series is shown above?
A) Lyman
B) Paschen
C) Balmer
D) None of the other choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
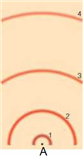
In the above model of an atom, where would the proton be located?
A) A
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If the change in wavelength is less than zero, then the radial velocity tells you that the star is moving _______________ you.
A) parallel to
B) away from
C) towards
D) in circles around
A) parallel to
B) away from
C) towards
D) in circles around

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
To create the above spectra, which of the following is NOT true?
A) A dense gas is excited and the light produced is over all wavelengths.
B) A low-density gas is excited and the light produced is over discrete wavelengths.
C) Light from a low-density gas passes through a warm, dense gas and the light that is produced is at all wavelengths except for a few discrete wavelengths.
D) All of the other choices are not true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76

To create the above spectra, which of the following is NOT true?
A) Light from a blackbody passed though a cool, low-density gas.
B) Light from a continuous spectrum passed through a cool, low-density gas.
C) Light from a hot, dense gas produced light at all wavelengths.
D) All of the other choices are not true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The higher the surface temperature of the star, the _______________ the wavelength of maximum intensity and the ____________ total radiation emitted from surface per second.
A) lower, less
B) higher, more
C) lower, more
D) higher, less
A) lower, less
B) higher, more
C) lower, more
D) higher, less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
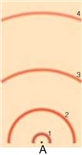
In the above model of an atom, if you were to draw an electron's transition from the second excited state to the third excited state, what numbers would this correspond from/to? What kind of spectrum would be produced?
A) 3 to 4, absorption
B) 2 to 3, absorption
C) 3 to 4, emission
D) 2 to 3, emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
I. 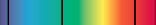
II)
III)

Which spectra, and in which order, would you expect to generate the pink color in the above cloud of gas?
A) II then III
B) I then II then III
C) III then II
D) III
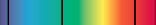
II)

III)


Which spectra, and in which order, would you expect to generate the pink color in the above cloud of gas?
A) II then III
B) I then II then III
C) III then II
D) III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
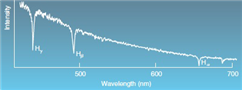
What kind of spectra is shown above?
A) continuous
B) blackbody
C) emission
D) absorption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



