Deck 28: Clinical Microbiology and Epidemiology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 28: Clinical Microbiology and Epidemiology
1
A person exhibiting glomerular nephritis and rheumatic fever must have had what type of previous infection?
A) Shigella sonnei
B) Escherichia coli
C) Streptococcus pyogenes
D) Treponema pallidum
E) Mycobacterium tuberculosis
A) Shigella sonnei
B) Escherichia coli
C) Streptococcus pyogenes
D) Treponema pallidum
E) Mycobacterium tuberculosis
C
2
Shigella sonnei is the cause of an infection commonly seen in infant day-care facilities due to
A) a high prevalence of the microbe in young children.
B) its ability to contaminate and grow on plastic toys.
C) its inherent antimicrobial nature (it is bleach and cleaning-product resistant).
D) diaper changes and hands not being properly washed.
E) Gram-positive cell wall structure making the bacteria environmentally resistant.
A) a high prevalence of the microbe in young children.
B) its ability to contaminate and grow on plastic toys.
C) its inherent antimicrobial nature (it is bleach and cleaning-product resistant).
D) diaper changes and hands not being properly washed.
E) Gram-positive cell wall structure making the bacteria environmentally resistant.
D
3
Hektoen agar will grow all of the following microorganisms EXCEPT
A) Klebsiella pneumoniae.
B) Escherichia coli.
C) Salmonella enteritidis.
D) Shigella sonnei.
E) Streptococcus pneumoniae.
A) Klebsiella pneumoniae.
B) Escherichia coli.
C) Salmonella enteritidis.
D) Shigella sonnei.
E) Streptococcus pneumoniae.
E
4
Laboratory analysis of a patient suspected to have bacterial meningitis would be performed with which type of sample?
A) urine sample
B) blood draw
C) throat swab
D) sputum sampling
E) lumbar puncture
A) urine sample
B) blood draw
C) throat swab
D) sputum sampling
E) lumbar puncture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The cause of the infection from which a patient suffers is best known as the
A) clinical agent.
B) etiological agent.
C) pathogenic culprit.
D) epidemiological agent.
E) antibiotic menace.
A) clinical agent.
B) etiological agent.
C) pathogenic culprit.
D) epidemiological agent.
E) antibiotic menace.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A person who begins to exhibit symptoms of bronchitis and bacterial pneumonia after recovering from the flu would be exhibiting
A) drug resistance.
B) antiviral susceptibility.
C) underlying immunodeficiency.
D) biological meltdown.
E) disease sequelae.
A) drug resistance.
B) antiviral susceptibility.
C) underlying immunodeficiency.
D) biological meltdown.
E) disease sequelae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A Gram-negative diplococcus result on a laboratory test would rule out all of the following bacteria EXCEPT
A) Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
B) Listeria monocytogenes.
C) Staphylococcus epidermidis.
D) Haemophilus influenzae.
E) Escherichia coli.
A) Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
B) Listeria monocytogenes.
C) Staphylococcus epidermidis.
D) Haemophilus influenzae.
E) Escherichia coli.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following clinical specimens would be expected to be sterile in a healthy individual?
A) blood
B) urine
C) sputum
D) stool
E) skin and wound swabs
A) blood
B) urine
C) sputum
D) stool
E) skin and wound swabs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The Lancefield groupings are for ________ bacteria and are based on ________.
A) Streptococcus; carbohydrate peptidoglycans
B) Escherichia; lipopolysaccharides
C) Staphylococcus; peptidoglycan amino acids
D) Neisseria; hopanoids
E) Pseudomonas; optochin sensitivity
A) Streptococcus; carbohydrate peptidoglycans
B) Escherichia; lipopolysaccharides
C) Staphylococcus; peptidoglycan amino acids
D) Neisseria; hopanoids
E) Pseudomonas; optochin sensitivity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An abscess caused by the anaerobic species Clostridium perfringens would best be collected and transported by
A) aspiration into an oxygen-filled tube.
B) swabbing onto blood agar media.
C) aspiration into a nitrogen-filled tube.
D) draining with a catheter.
E) draining into a syringe.
A) aspiration into an oxygen-filled tube.
B) swabbing onto blood agar media.
C) aspiration into a nitrogen-filled tube.
D) draining with a catheter.
E) draining into a syringe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When sampling clinical specimens to determine the cause of a disease, samples are often plated on selective media. The reason for this is to
A) initiate an epidemiological investigation.
B) prevent the growth of normal flora.
C) determine the antibiotic resistance prior to isolation of the pathogen.
D) prevent aerobes from growing.
E) ensure proper biosafety procedures.
A) initiate an epidemiological investigation.
B) prevent the growth of normal flora.
C) determine the antibiotic resistance prior to isolation of the pathogen.
D) prevent aerobes from growing.
E) ensure proper biosafety procedures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Collection of specimen samples from places on or in the body that contain normal flora usually requires
A) initial plating on nonselective media.
B) direct Gram staining.
C) initial plating on selective media.
D) direct PCR identification.
E) immunofluorescent staining.
A) initial plating on nonselective media.
B) direct Gram staining.
C) initial plating on selective media.
D) direct PCR identification.
E) immunofluorescent staining.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Chocolate agar is considered ________ in comparison to blood agar.
A) more nutrient rich (capable of growing a greater variety of bacteria)
B) less nutrient rich (capable of growing fewer variety of bacteria)
C) equally nutrient rich (since they both contain red blood cells)
D) a chemically defined media (whereas blood agar is not)
E) better for determining hemolytic bacterial reactions
A) more nutrient rich (capable of growing a greater variety of bacteria)
B) less nutrient rich (capable of growing fewer variety of bacteria)
C) equally nutrient rich (since they both contain red blood cells)
D) a chemically defined media (whereas blood agar is not)
E) better for determining hemolytic bacterial reactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Catheterization would be an appropriate method of microbial collection for
A) Streptococcus pneumoniae (lung infection).
B) Escherichia coli (UTI infection).
C) Shigella dysenteriae (GI infection).
D) Propionibacterium acnes (skin infection).
E) Helicobacter pylori (stomach infection).
A) Streptococcus pneumoniae (lung infection).
B) Escherichia coli (UTI infection).
C) Shigella dysenteriae (GI infection).
D) Propionibacterium acnes (skin infection).
E) Helicobacter pylori (stomach infection).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The figure below shows cells stained bright fuchsia. This stain is called a(an) ________ and is used to stain ________. 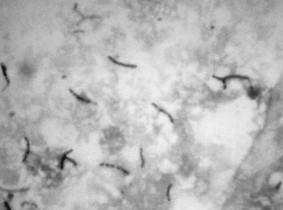
A) Gram stain; Bacillus anthracis
B) Gram stain; Mycobacterium sp.
C) acid-fast stain; Mycobacterium sp.
D) acid-fast stain; Bacillus anthracis
E) Ziehl-Neelsen; Bacillus anthracis

A) Gram stain; Bacillus anthracis
B) Gram stain; Mycobacterium sp.
C) acid-fast stain; Mycobacterium sp.
D) acid-fast stain; Bacillus anthracis
E) Ziehl-Neelsen; Bacillus anthracis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the figure shown below, we see someone wearing a specific biosafety suit. This suit would NOT be required for studying a(n) 
A) outbreak of a lethal disease with no known etiological agent.
B) Ebola outbreak.
C) anthrax outbreak.
D) biosafety level 4 agent.
E) lethal disease with no known treatment or vaccine.

A) outbreak of a lethal disease with no known etiological agent.
B) Ebola outbreak.
C) anthrax outbreak.
D) biosafety level 4 agent.
E) lethal disease with no known treatment or vaccine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The diagram shown below shows information relative to Gram-negative rods. We CANNOT consider this diagram to be a(n)

A) example of tests available on an API 20E strip.
B) algorithm.
C) dichotomous key.
D) example of tests used to determine which type of Enterobacteriaceae an unknown might be.
E) random collection of tests for Gram-negative bacteria.

A) example of tests available on an API 20E strip.
B) algorithm.
C) dichotomous key.
D) example of tests used to determine which type of Enterobacteriaceae an unknown might be.
E) random collection of tests for Gram-negative bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Catalase-positive organisms such as ________ produce ________ as end products when exposed to hydrogen peroxide.
A) Streptomyces; KCl and CO2
B) Streptococcus; H2O2 and H2O
C) Lactobacillales; CO2 and O2
D) Stachybotrys; HOCl and H2O
E) Staphylococcus; H2O and O2
A) Streptomyces; KCl and CO2
B) Streptococcus; H2O2 and H2O
C) Lactobacillales; CO2 and O2
D) Stachybotrys; HOCl and H2O
E) Staphylococcus; H2O and O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Haemophilius influenzae requires ________ and ________ for confirmatory growth of an organism in vitro.
A) catalase; oxidase (N disk)
B) Eosin-Methylene Blue (EMB) agar; MacConkey agar
C) citrate; bile salts
D) hemin (X factor); NAD (V factor)
E) phenylalanine; ortho-Nitrophenyl-b-galactoside (ONPG)
A) catalase; oxidase (N disk)
B) Eosin-Methylene Blue (EMB) agar; MacConkey agar
C) citrate; bile salts
D) hemin (X factor); NAD (V factor)
E) phenylalanine; ortho-Nitrophenyl-b-galactoside (ONPG)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A bacterial diagnosis of Mycobacterium avium in a sputum sample from an AIDS patient would be best determined by which method?
A) blood agar culture
B) acid-fast (Ziehl-Neelsen) staining
C) MacConkey agar culture
D) Gram staining
E) bacitracin susceptibility
A) blood agar culture
B) acid-fast (Ziehl-Neelsen) staining
C) MacConkey agar culture
D) Gram staining
E) bacitracin susceptibility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
RNA sensors can be used to detect pathogens such as ZIKA virus. The steps below are steps used in testing for ZIKA virus. Which has the required steps in the correct order? 1- LacZ gene product is detected via a color change.
2- DNA is added to an RNA switch that has a hairpin to block transcription of lacZ.
3- Multiple copies of DNA matching ZIKA are produced.
4- In the presence of the ZIKA-trigger RNA, the "toehold" switch is bound and releases the lacZ rbs and start codon so transcription can occur.
5- Reverse transcriptase is used to produce cDNA from the ZIKA RNA.
A) 5-2-4-1-3
B) 3-2-4-1-5
C) 5-4-3-2-1
D) 1-2-3-4-5
E) 5-3-2-4-1
2- DNA is added to an RNA switch that has a hairpin to block transcription of lacZ.
3- Multiple copies of DNA matching ZIKA are produced.
4- In the presence of the ZIKA-trigger RNA, the "toehold" switch is bound and releases the lacZ rbs and start codon so transcription can occur.
5- Reverse transcriptase is used to produce cDNA from the ZIKA RNA.
A) 5-2-4-1-3
B) 3-2-4-1-5
C) 5-4-3-2-1
D) 1-2-3-4-5
E) 5-3-2-4-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The figure shown below is a picture of a gel with multiplex PCR products from Clostridium botulinum isolates. Lane 1 contains DNA molecular weight markers and lanes 2-5 are positive strains as controls for toxins type A, type B, type E, and type F, respectively. Based on the bands shown, what can we say about the isolate results in lane 6? 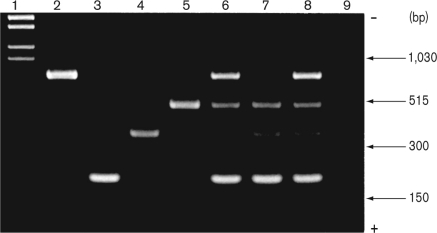
A) The isolate in lane 6 produces all four toxins but not endotoxin.
B) The PCR products from isolate in lane 6 are consistent with that isolate having toxins A, F, and B but not E.
C) The isolate in lane 6 produces all four toxins.
D) There is no band for endotoxin in lane 6 but the isolate makes three other toxins.
E) The gel shows definitive proof that this strain produces three toxins.

A) The isolate in lane 6 produces all four toxins but not endotoxin.
B) The PCR products from isolate in lane 6 are consistent with that isolate having toxins A, F, and B but not E.
C) The isolate in lane 6 produces all four toxins.
D) There is no band for endotoxin in lane 6 but the isolate makes three other toxins.
E) The gel shows definitive proof that this strain produces three toxins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following organisms falls within biosafety group category II?
A) Ebola virus
B) SARS
C) Mycobacterium tuberculosis
D) Escherichia coli strain K-12
E) Campylobacter jejuni
A) Ebola virus
B) SARS
C) Mycobacterium tuberculosis
D) Escherichia coli strain K-12
E) Campylobacter jejuni

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Most point-of-care diagnostics rely on
A) immunochromatographic assays.
B) Qt-polymerase chain reaction.
C) ELISA kits.
D) immunofluorescence.
E) API platforms.
A) immunochromatographic assays.
B) Qt-polymerase chain reaction.
C) ELISA kits.
D) immunofluorescence.
E) API platforms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A hemolysis reaction (on a blood agar plate) with an unidentified colony that results in a green zone due to oxidized iron in nonlysed red blood cells would be called
A) beta-hemolytic.
B) nonhemolytic.
C) gamma-hemolytic.
D) alpha-hemolytic.
E) epsilon-hemolytic.
A) beta-hemolytic.
B) nonhemolytic.
C) gamma-hemolytic.
D) alpha-hemolytic.
E) epsilon-hemolytic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Humans are an incidental (dead-end) host in which clinical disease?
A) West Nile virus
B) Mycobacterium tuberculosis
C) Streptococcus pyogenes
D) Staphylococcus aureas
E) picornavirus
A) West Nile virus
B) Mycobacterium tuberculosis
C) Streptococcus pyogenes
D) Staphylococcus aureas
E) picornavirus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following genera of bacteria would NOT change the color of N,N,N',N'7' -tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine to purple/black upon exposure?
A) Salmonella
B) Brucella
C) Pseudomonas
D) Bordetella
E) Campylobacter
A) Salmonella
B) Brucella
C) Pseudomonas
D) Bordetella
E) Campylobacter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A proper course of action for a patient presenting with Ebola would be
A) quarantine and laboratory determination of Ebola IgG antibodies.
B) vaccination and laboratory growth of Ebola in culture.
C) course of antibiotics and laboratory determination of Ebola antigen.
D) antiviral therapy followed by a course of antibiotics.
E) in-home supportive therapy and laboratory PCR detection.
A) quarantine and laboratory determination of Ebola IgG antibodies.
B) vaccination and laboratory growth of Ebola in culture.
C) course of antibiotics and laboratory determination of Ebola antigen.
D) antiviral therapy followed by a course of antibiotics.
E) in-home supportive therapy and laboratory PCR detection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Symptoms of headache, fever, stiff neck, and confusion in combination with mosquito bites can indicate which viral infection?
A) Ebola
B) West Nile
C) influenza
D) rabies
E) HIV
A) Ebola
B) West Nile
C) influenza
D) rabies
E) HIV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The figure below shows the mass to charge ratios of two pathogenic Neisseria sp. The molecule being measured is ________ and the technique being used is ________. 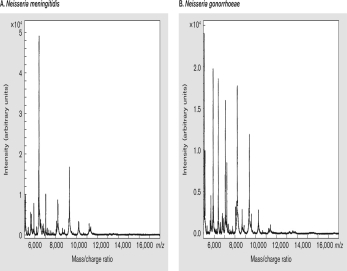
A) protein; riboswitch sensor
B) protein; MALDI-TOF-MS
C) DNA; riboswitch sensor
D) DNA; MALDI-TOF-MS
E) RNA; riboswitch sensor

A) protein; riboswitch sensor
B) protein; MALDI-TOF-MS
C) DNA; riboswitch sensor
D) DNA; MALDI-TOF-MS
E) RNA; riboswitch sensor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
As point of care (POC) tests are developed, two concerns are sensitivity and specificity. Which of the following statements are true with respect to these terms?
A) Sensitivity deals with how much you can dilute the sample to get a result, whereas specificity deals with how much you dilute a control serum to get a result.
B) Sensitivity deals with how many false positives you get, whereas specificity deals with false negatives.
C) Sensitivity deals with distinguishing between closely related samples such as group A Streptococcus versus group B Streptococcus. Specificity quantitates those differences.
D) Sensitivity deals with how often a test is positive when the patient has the disease, whereas specificity deals with how often the test is negative when the patient does not have the disease.
E) The sensitivity and specificity of a test must be confirmatory or the test is useless.
A) Sensitivity deals with how much you can dilute the sample to get a result, whereas specificity deals with how much you dilute a control serum to get a result.
B) Sensitivity deals with how many false positives you get, whereas specificity deals with false negatives.
C) Sensitivity deals with distinguishing between closely related samples such as group A Streptococcus versus group B Streptococcus. Specificity quantitates those differences.
D) Sensitivity deals with how often a test is positive when the patient has the disease, whereas specificity deals with how often the test is negative when the patient does not have the disease.
E) The sensitivity and specificity of a test must be confirmatory or the test is useless.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is NOT true of newer clinical techniques compared to conventional techniques that require culturing?
A) The new techniques require no special equipment or training.
B) They require less time since bacteria do not have to grow.
C) Some of the newer techniques can be quantitated.
D) Some newer molecular techniques can be applied to viruses and unculturable bacteria.
E) They may rely on the presence of DNA, RNA, antigens or other proteins, and antibodies for detection of the pathogen.
A) The new techniques require no special equipment or training.
B) They require less time since bacteria do not have to grow.
C) Some of the newer techniques can be quantitated.
D) Some newer molecular techniques can be applied to viruses and unculturable bacteria.
E) They may rely on the presence of DNA, RNA, antigens or other proteins, and antibodies for detection of the pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An antigen-capture ELISA could be looking for all of the following in a person who is presumed to have a severe acute lung infection EXCEPT
A) mycobacterium antigens.
B) SARS antigens.
C) Haemophilus sp. antigens.
D) pneumococcal antigens.
E) anti-influenza antibodies.
A) mycobacterium antigens.
B) SARS antigens.
C) Haemophilus sp. antigens.
D) pneumococcal antigens.
E) anti-influenza antibodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
PCR-based detection of a person thought to have HIV would require all of the following EXCEPT
A) primers specific for HIV genes.
B) a thermocycler.
C) HIV agar media.
D) gel electrophoresis.
E) HIV genome isolation/extraction.
A) primers specific for HIV genes.
B) a thermocycler.
C) HIV agar media.
D) gel electrophoresis.
E) HIV genome isolation/extraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Fluorescent antibody staining works well for clinical diagnosis on what types of antigens?
A) ribosomal
B) cytoplasmic
C) nuclear
D) capsular
E) plasmid
A) ribosomal
B) cytoplasmic
C) nuclear
D) capsular
E) plasmid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Lowenstein-Jensen agar is used to culture ________ bacteria.
A) all Gram-negative
B) beta lactase-producing
C) mycolic acid-containing
D) all Gram-positive
E) toxin-producing enteric
A) all Gram-negative
B) beta lactase-producing
C) mycolic acid-containing
D) all Gram-positive
E) toxin-producing enteric

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Direct fluorescent staining of infected tissue samples taken from a patient allows for rapid identification under what circumstances?
A) hard-to-culture organisms
B) protist infections
C) Gram-negative organisms
D) intracellular infections
E) metabolically active organisms
A) hard-to-culture organisms
B) protist infections
C) Gram-negative organisms
D) intracellular infections
E) metabolically active organisms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Point-of-care diagnostics are advantageous for all of the following reasons EXCEPT
A) culturing is not required.
B) therapy can begin sooner.
C) patient compliance is improved.
D) antibiotics can be prescribed more effectively.
E) lower risk of spreading infection.
A) culturing is not required.
B) therapy can begin sooner.
C) patient compliance is improved.
D) antibiotics can be prescribed more effectively.
E) lower risk of spreading infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Eukaryotic parasites, such as Giardia lamblia, are usually diagnosed by
A) immunofluorescence.
B) PCR.
C) RFLP.
D) biochemical testing.
E) direct microscopy.
A) immunofluorescence.
B) PCR.
C) RFLP.
D) biochemical testing.
E) direct microscopy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A serum antibody ELISA would be looking for which of the following in a person who is presumed to have a necrotizing fasciitis infection?
A) anti-group A streptococcal antibodies
B) antimeningococcal antibodies
C) group A streptococcal-specific antigens
D) enzyme-linked antibody
E) anti-group B streptococcal antibodies
A) anti-group A streptococcal antibodies
B) antimeningococcal antibodies
C) group A streptococcal-specific antigens
D) enzyme-linked antibody
E) anti-group B streptococcal antibodies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Looking at the laboratory results presented here, what three interpretations can be made?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following would NOT be a task for an epidemiologist?
A) keeping track of the incidence and prevalence of disease and reportable diseases
B) helping to assess the effectiveness of treatments of preventions
C) performing basic research to understand how the etiological agents causes symptoms
D) coordinating global measures to minimize an outbreak or epidemic
E) finding patient zero
A) keeping track of the incidence and prevalence of disease and reportable diseases
B) helping to assess the effectiveness of treatments of preventions
C) performing basic research to understand how the etiological agents causes symptoms
D) coordinating global measures to minimize an outbreak or epidemic
E) finding patient zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which infectious disease is on the CDC bioterrorism list due to the general population NOT being vaccinated for this disease since the 1970s?
A) bubonic plague
B) rabies
C) smallpox
D) tuberculosis
E) Machupo virus
A) bubonic plague
B) rabies
C) smallpox
D) tuberculosis
E) Machupo virus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
John Snow, the "father of epidemiology," is known for deducing the source of which etiologic agent in the 1854 London outbreak?
A) Shigella dysenterie
B) Vibrio cholerae
C) Haemophilius influenzae
D) Giardia lamblia
E) Yersinia pestis
A) Shigella dysenterie
B) Vibrio cholerae
C) Haemophilius influenzae
D) Giardia lamblia
E) Yersinia pestis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The use of a laminar flow hood when studying the organism Francisella tularensis is an example of level ________ biological safety.
A) 0
B) I
C) II
D) III
E) IV
A) 0
B) I
C) II
D) III
E) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Describe the general protocol used to diagnose a patient with a Salmonella typhimurium infection (from collection to testing).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The following are all concerns of the influence of global climate change on infectious diseases EXCEPT that
A) global climate change will increase the incidence of antibiotic resistance.
B) the habitat of insect vectors increases in size as temperatures rise.
C) extending ranges of vectors may bring them in contact with new hosts.
D) climate change may bring more flooding, thus increasing the spread of gastrointestinal illness.
E) infectious disease cycles may speed up or extend through longer portions of the year.
A) global climate change will increase the incidence of antibiotic resistance.
B) the habitat of insect vectors increases in size as temperatures rise.
C) extending ranges of vectors may bring them in contact with new hosts.
D) climate change may bring more flooding, thus increasing the spread of gastrointestinal illness.
E) infectious disease cycles may speed up or extend through longer portions of the year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Tuberculosis has become a reemerging pathogen today in large part due to
A) increased incidence of HIV infection.
B) airline travel reducing geographical distances.
C) surge in reservoir animal populations carrying the disease to humans.
D) strict compliance with drug regimens.
E) concurrent increases in hepatitis C infection.
A) increased incidence of HIV infection.
B) airline travel reducing geographical distances.
C) surge in reservoir animal populations carrying the disease to humans.
D) strict compliance with drug regimens.
E) concurrent increases in hepatitis C infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Compare and contrast the dichotomous key approach to bacterial determination with the seven-digit-number approach when using the API strip system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A defining commonality between biosafety risk group II handling techniques and a biosafety IV facility would be the need for
A) a personal positive-pressure suit.
B) an isolation facility.
C) a negative-pressurized lab space.
D) directional air flow in the room.
E) the use of aseptic techniques.
A) a personal positive-pressure suit.
B) an isolation facility.
C) a negative-pressurized lab space.
D) directional air flow in the room.
E) the use of aseptic techniques.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Looking at the laboratory results presented here, what three interpretations can be made?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Gaëtan Dugas is frequently referred to as the individual who began the spread of HIV within the gay male community in North America in the 1970s. In epidemiology, he is known as
A) the first patient.
B) the superspreader.
C) patient 1.
D) the index case.
E) patient zero.
A) the first patient.
B) the superspreader.
C) patient 1.
D) the index case.
E) patient zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Collaborators necessary to solve and control a human epidemic include
A) epidemiologists.
B) ecologists.
C) veterinarians.
D) scientists.
E) epidemiologists, ecologists, veterinarians, and scientists.
A) epidemiologists.
B) ecologists.
C) veterinarians.
D) scientists.
E) epidemiologists, ecologists, veterinarians, and scientists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The correct definition of "bioweapon" is any
A) agent categorized as a biosafety level IV organism.
B) infectious disease spread person to person with a low mortality rate.
C) agent causing widespread psychological trauma, with few casualties.
D) microbial agent or pieces of microbes that can be loaded into bombs.
E) infectious agent or toxin that has a high virulence and/or mortality rate.
A) agent categorized as a biosafety level IV organism.
B) infectious disease spread person to person with a low mortality rate.
C) agent causing widespread psychological trauma, with few casualties.
D) microbial agent or pieces of microbes that can be loaded into bombs.
E) infectious agent or toxin that has a high virulence and/or mortality rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Molecular screening is now being used to detect individuals with early stages of TB because
A) skin testing is unreliable and needs refrigeration that many countries may not have.
B) vaccination with Bacille Calmette-Guérin does not protect against multidrug resistance.
C) many countries do not have disposable needles for skin testing.
D) it can detect infection earlier than chest X-rays and sputum sampling.
E) it can be used more safely on children with the disease.
A) skin testing is unreliable and needs refrigeration that many countries may not have.
B) vaccination with Bacille Calmette-Guérin does not protect against multidrug resistance.
C) many countries do not have disposable needles for skin testing.
D) it can detect infection earlier than chest X-rays and sputum sampling.
E) it can be used more safely on children with the disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is a reportable, biosafety level III organism that causes low-grade fever, chills, headache, and malaise followed by a dry cough, shortness of breath, and chest heaviness?
A) methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureas
B) Plasmodium falciparum
C) West Nile virus
D) Bacillus anthracis
E) Yersinia pestis
A) methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureas
B) Plasmodium falciparum
C) West Nile virus
D) Bacillus anthracis
E) Yersinia pestis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Bubonic plague is endemic in many countries in Africa and in the former Soviet Union. This indicates that
A) plague was once a huge problem and has now evolved to not cause infection.
B) plague has been eradicated from these areas.
C) large numbers of people are infected in these areas and it is spreading.
D) the disease is always present in the population at a low frequency.
E) human-to-human contact transfers plague.
A) plague was once a huge problem and has now evolved to not cause infection.
B) plague has been eradicated from these areas.
C) large numbers of people are infected in these areas and it is spreading.
D) the disease is always present in the population at a low frequency.
E) human-to-human contact transfers plague.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The graph shown below diagrams the number of cases of a disease versus time. The high peak near the right-hand side would be considered a(n) 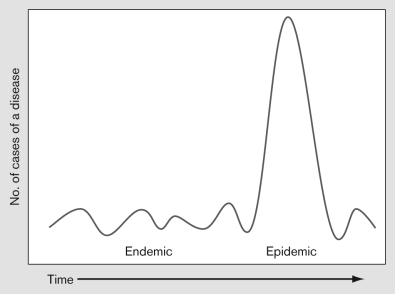
A) prevalence.
B) incidence.
C) endemic.
D) epidemic.
E) pandemic.

A) prevalence.
B) incidence.
C) endemic.
D) epidemic.
E) pandemic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In determining the bacterial etiology of a patient with an infection, the first laboratory test should be what, and why? What type of testing would then follow?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following criteria is NOT required in order for a mosquito-borne virus to become endemic in a new location?
A) A person infected elsewhere must travel to the new area.
B) A local mosquito must bite a person who has the disease in order to spread it to someone else.
C) The virus must move from an Aedes mosquito to another insect vector.
D) The virus must move from the local mosquito to a local animal that can then serve as a reservoir.
E) The local mosquito must bite another human in that area and give him or her the disease.
A) A person infected elsewhere must travel to the new area.
B) A local mosquito must bite a person who has the disease in order to spread it to someone else.
C) The virus must move from an Aedes mosquito to another insect vector.
D) The virus must move from the local mosquito to a local animal that can then serve as a reservoir.
E) The local mosquito must bite another human in that area and give him or her the disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The clinical microbiology laboratory just received a sputum (deep-lung) sample that so far has been very slow-growing in nonselective agar, as well as not Gram stainable. What tests should be performed next, and why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Compare and contrast the use of the serum antibody ELISA with the antigen-capture ELISA in the detection of Ebola.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Compare and contrast the handling of rabies (a category III organism) with Lassa fever (a category IV organism).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
As a disease detective investigating an outbreak in the cafeteria of your college, what would be some of the first steps you would need to take to begin your investigation, other than laboratory testing?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Compare and contrast the use of point-of-care rapid tests as diagnostic methods in doctors' offices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
How were Koch's postulates modified in the discovery of Tropheryma whipplei, the causative agent of Whipple's disease?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Compare and contrast the epidemiological terms "endemic," "epidemic," and "pandemic." Give an example of each to support your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
How does a multiplex PCR reaction differ from a traditional PCR detection method? In addition, describe an example of how multiplex can be used in diagnostics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
How would a serum antibody ELISA work in the detection of Lyme disease?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
How have changes within our human culture caused new diseases to emerge? Explain your answer using a specific example that supports your statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Why are clinical viral diseases more challenging to diagnose than are clinical bacterial diseases?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Describe what the One Health Initiative is and the role it played in the 2006 outbreak of food-borne O157:H7 in spinach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
How can reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) be used to determine the presence and viral load of HIV infection?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Describe the chain of command that is followed when a patient sees his or her doctor and is diagnosed with a reportable disease such as listeriosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Once cultured, bacteria from septic infections or urine can be quickly identified by MALDI-TOF-MS. What is this technique and how does it work?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



