Deck 17: Glacial and Periglacial Processes and Landforms
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/159
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Glacial and Periglacial Processes and Landforms
1
Continuous ice sheets,ice caps,and ice fields are drained on their periphery by
A)piedmont glaciers.
B)mountain glaciers.
C)outlet glaciers.
D)valley glaciers.
E)cirque glaciers.
A)piedmont glaciers.
B)mountain glaciers.
C)outlet glaciers.
D)valley glaciers.
E)cirque glaciers.
C
2
Which of the following is true of the snowline?
A)it increases in elevation with increasing latitude.
B)it decreases in elevation with increasing latitude.
C)it occurs at approximately the same elevation at all latitudes because the environmental lapse rate is approximately the same at all latitudes.
D)it is moving lower with climate change.
E)it is not affected by climate change.
A)it increases in elevation with increasing latitude.
B)it decreases in elevation with increasing latitude.
C)it occurs at approximately the same elevation at all latitudes because the environmental lapse rate is approximately the same at all latitudes.
D)it is moving lower with climate change.
E)it is not affected by climate change.
B
3
A valley glacier that extends beyond the confines of its valley and coalesces with other valley glaciers along the base of a mountain range is termed
A)an ice field.
B)a piedmont glacier.
C)a cirque glacier.
D)a valley glacier.
E)an ice sheet
A)an ice field.
B)a piedmont glacier.
C)a cirque glacier.
D)a valley glacier.
E)an ice sheet
B
4
Melting and refreezing of snow acts to ________ ice density and ________ the sphericity (roundness)of the original snowflakes.
A)increase increase
B)increase decrease
C)decrease increase
D)decrease decrease
A)increase increase
B)increase decrease
C)decrease increase
D)decrease decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A glacier that is confined in a bowl-shaped recess is called a
A)piedmont glacier.
B)mountain glacier.
C)cirque glacier.
D)valley glacier.
E)paternoster glacier.
A)piedmont glacier.
B)mountain glacier.
C)cirque glacier.
D)valley glacier.
E)paternoster glacier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Glacial ice is
A)essentially the same as snow.
B)formed after a slow transformation process that may take a thousand years in Antarctica.
C)made of metamorphic rock.
D)generally less dense than snow and firn.
E)filled with air bubbles.
A)essentially the same as snow.
B)formed after a slow transformation process that may take a thousand years in Antarctica.
C)made of metamorphic rock.
D)generally less dense than snow and firn.
E)filled with air bubbles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A general term for a mass of perennial ice,resting on land or floating shelf-like in the sea adjacent to land is
A)the snowline.
B)an iceberg.
C)a glacier.
D)moraine.
E)nunatk.
A)the snowline.
B)an iceberg.
C)a glacier.
D)moraine.
E)nunatk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is true?
A)25% of glaciers in the European Alps have receded in the past 50 years.
B)Peyto Glacier has experienced significant loss of net mass balance in recent years.
C)39% of global sea level rise is coming from melting Alaskan glaciers.
D)Mt.St.Helens and Mt.Shasta have seen 37% increases in glacial mass from 1983-2007.
E)the Columbia Ice Sheet is growing in size as its snowlines move lower in elevation.
A)25% of glaciers in the European Alps have receded in the past 50 years.
B)Peyto Glacier has experienced significant loss of net mass balance in recent years.
C)39% of global sea level rise is coming from melting Alaskan glaciers.
D)Mt.St.Helens and Mt.Shasta have seen 37% increases in glacial mass from 1983-2007.
E)the Columbia Ice Sheet is growing in size as its snowlines move lower in elevation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The process of calving in the glacial environment produces
A)baby steers.
B)nunataks.
C)roche moutonn .
.
D)icebergs.
E)moraines.
A)baby steers.
B)nunataks.
C)roche moutonn
 .
.D)icebergs.
E)moraines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is correctly matched?
A)ice sheet - controlled by the topography
B)ice cap - completely buries the underlying landscape,but covers less than 50 000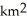 .
.
C)ice field - more than 10 000 feet thick
D)ice cap - nunataks visible
E)ice field - dome shape
A)ice sheet - controlled by the topography
B)ice cap - completely buries the underlying landscape,but covers less than 50 000
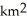 .
.C)ice field - more than 10 000 feet thick
D)ice cap - nunataks visible
E)ice field - dome shape

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The bulk of ice on Earth is in
A)North America,specifically Alaska.
B)European and Asian mountain ranges.
C)Greenland and Antarctica.
D)floating ice shelves and packs.
E)the islands of the Arctic archipelago.
A)North America,specifically Alaska.
B)European and Asian mountain ranges.
C)Greenland and Antarctica.
D)floating ice shelves and packs.
E)the islands of the Arctic archipelago.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A continuous mass of ice covering a large landmass is known as a
A)tidal glacier.
B)mountain glacier.
C)continental glacier.
D)valley glacier.
E)piedmont glacier.
A)tidal glacier.
B)mountain glacier.
C)continental glacier.
D)valley glacier.
E)piedmont glacier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Alpine glaciers include
A)ice caps,ice sheets and cirque glaciers.
B)valley glaciers and cirque glaciers
C)cirque glaciers and ice fields.
D)valley glaciers and ice sheets.
E)cirque glaciers and ice caps.
A)ice caps,ice sheets and cirque glaciers.
B)valley glaciers and cirque glaciers
C)cirque glaciers and ice fields.
D)valley glaciers and ice sheets.
E)cirque glaciers and ice caps.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Approximately what percentage of the world's freshwater is frozen?
A)10 percent
B)30 percent
C)50 percent
D)77 percent
E)93 percent
A)10 percent
B)30 percent
C)50 percent
D)77 percent
E)93 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is true of valley glaciers?
A)the snowfield sources for these glaciers are usually found right at the snowline.
B)they occur in an unconfined environment-like an open plain.
C)they may range in length from 100 m to 100 km.
D)they remain stationary and do not move.
E)they are known for eroding the least amount of all glaciers.
A)the snowfield sources for these glaciers are usually found right at the snowline.
B)they occur in an unconfined environment-like an open plain.
C)they may range in length from 100 m to 100 km.
D)they remain stationary and do not move.
E)they are known for eroding the least amount of all glaciers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The type of glacier that dominates Greenland and Antarctica is
A)valley glacier.
B)piedmont glacier.
C)ice sheet.
D)ice field.
E)ice cap
A)valley glacier.
B)piedmont glacier.
C)ice sheet.
D)ice field.
E)ice cap

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In terms of areal extent,which of the following sequences is in order from most to least area covered?
A)ice sheet,ice field,ice cap
B)ice field,ice sheet,ice cap
C)ice sheet,valley glacier,piedmont glacier
D)ice sheet,ice cap,icefield
E)piedmont glacier,ice cap,icefield
A)ice sheet,ice field,ice cap
B)ice field,ice sheet,ice cap
C)ice sheet,valley glacier,piedmont glacier
D)ice sheet,ice cap,icefield
E)piedmont glacier,ice cap,icefield

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is true?
A)Antarctica contains more than 29 million cubic kilometers of ice.
B)71% of Earth's fresh water is frozen.
C)1)1% of Earth's land is covered by glaciers.
D)75% of European Alpine glaciers have receded in the last 50 years.
E)globally,snowlines are lower in elevation than at any other time in recorded history
A)Antarctica contains more than 29 million cubic kilometers of ice.
B)71% of Earth's fresh water is frozen.
C)1)1% of Earth's land is covered by glaciers.
D)75% of European Alpine glaciers have receded in the last 50 years.
E)globally,snowlines are lower in elevation than at any other time in recorded history

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Meltponds on ice-shelf and tidewater glacier surfaces
A)represent a positive feedback mechanism caused by increasing temperatures from both the air above and the sea below.
B)have always existed and do not indicate any kind of change in Earth's temperatures.
C)cause catastrophic flooding when the ice that holds them bursts.
D)cannot be linked in any way with global climate change.
E)represent a negative feedback mechanism that might be useful for slowing global temperature increases.
A)represent a positive feedback mechanism caused by increasing temperatures from both the air above and the sea below.
B)have always existed and do not indicate any kind of change in Earth's temperatures.
C)cause catastrophic flooding when the ice that holds them bursts.
D)cannot be linked in any way with global climate change.
E)represent a negative feedback mechanism that might be useful for slowing global temperature increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which is true of the Peyto and an other alpine glaciers?
A)glaciers in the mountains of North America have gained on average more than 50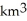 per year from the 1950s to today.
per year from the 1950s to today.
B)39% of global sea level rise is coming from the melting of Alaskan glaciers.
C)Peyto Glacier has retreated most years since 1965.
D)forecasts are for increased ice accumulation with global warming as more moisture becomes available to the atmosphere.
E)all Alaska glaciers gained mass since 1985.
A)glaciers in the mountains of North America have gained on average more than 50
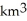 per year from the 1950s to today.
per year from the 1950s to today.B)39% of global sea level rise is coming from the melting of Alaskan glaciers.
C)Peyto Glacier has retreated most years since 1965.
D)forecasts are for increased ice accumulation with global warming as more moisture becomes available to the atmosphere.
E)all Alaska glaciers gained mass since 1985.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Small bedrock protrusions at the base of a glacier are often overrun by a process known as ________,which occurs because ________.
A)ablation ice melts when it is sufficiently compressed
B)ablation ice deforms when it is subjected to pressure
C)regelation ice melts when it is sufficiently compressed
D)regelation ice deforms when it is subjected to pressure
E)ice plucking ice deforms when it is sufficiently compressed
A)ablation ice melts when it is sufficiently compressed
B)ablation ice deforms when it is subjected to pressure
C)regelation ice melts when it is sufficiently compressed
D)regelation ice deforms when it is subjected to pressure
E)ice plucking ice deforms when it is sufficiently compressed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Because the upper regions of a glacier flow ________ than the base of the glacier,the upper part of the glacier tends to be ________.
A)faster compressed
B)faster stretched
C)slower compressed
D)slower stretched
A)faster compressed
B)faster stretched
C)slower compressed
D)slower stretched

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Basal slip is facilitated by
A)regelation. ,the presence of water and saturated sediments.
B)presence of melt water,debris incorporated in the ice,and frozen sediments beneath.
C)saturated sediments,debris incorporated in the ice,and rebound pressure from the bed.
D)rebound pressure from the bed,regelation,and water.
E)water,rebound pressure from the bed,and geothermal heat.
A)regelation. ,the presence of water and saturated sediments.
B)presence of melt water,debris incorporated in the ice,and frozen sediments beneath.
C)saturated sediments,debris incorporated in the ice,and rebound pressure from the bed.
D)rebound pressure from the bed,regelation,and water.
E)water,rebound pressure from the bed,and geothermal heat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The zone where positive gains end and losses begin in the glacial mass balance is called
A)an equilibrium line.
B)medial moraine.
C)firn line.
D)the ice field line.
E)the surge line.
A)an equilibrium line.
B)medial moraine.
C)firn line.
D)the ice field line.
E)the surge line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A visible snowline across the surface of a glacier is called
A)an equilibrium line.
B)a medial moraine.
C)a firn line.
D)the ice line.
E)a recessional moraine.
A)an equilibrium line.
B)a medial moraine.
C)a firn line.
D)the ice line.
E)a recessional moraine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The opposite of the accumulation zone in a glacier is the
A)abrasion zone.
B)equilibrium line.
C)ablation zone.
D)snow and firn area.
E)surge line.
A)abrasion zone.
B)equilibrium line.
C)ablation zone.
D)snow and firn area.
E)surge line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is considered to be a possible mechanism for glacier surges?
A)basal slip and fracturing.
B)slight floating of the glacier and basal slip
C)fracturing and basal debris load
D)slight floating of the glacier and basal debris loading.
E)regelation and basal slip.
A)basal slip and fracturing.
B)slight floating of the glacier and basal slip
C)fracturing and basal debris load
D)slight floating of the glacier and basal debris loading.
E)regelation and basal slip.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is generally true of the basal layer of a glacier?
A)it can extend about one meter above the ground surface.
B)it tends to flow more quickly than the overlying parts of the glacier.
C)it contains more debris than other parts of the glacier.
D)crevasses form in this region of the glacier.
E)it behaves as a brittle solid.
A)it can extend about one meter above the ground surface.
B)it tends to flow more quickly than the overlying parts of the glacier.
C)it contains more debris than other parts of the glacier.
D)crevasses form in this region of the glacier.
E)it behaves as a brittle solid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Why,specifically,is glacial ice analogous to a metamorphic rock?
A)it has a definite chemical composition.
B)it has a crystalline structure.
C)it forms as a result of recrystallization caused by pressure.
D)it is solid.
E)it is changed by deep freezing.
A)it has a definite chemical composition.
B)it has a crystalline structure.
C)it forms as a result of recrystallization caused by pressure.
D)it is solid.
E)it is changed by deep freezing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is correctly matched?
A)firn - zone of mass ablation
B)melting - zone of accumulation
C)net mass loss - equilibrium line
D)sublimation - zone of ablation
E)positive balance - loss greater than gain.
A)firn - zone of mass ablation
B)melting - zone of accumulation
C)net mass loss - equilibrium line
D)sublimation - zone of ablation
E)positive balance - loss greater than gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Crevasses usually form as a result of
A)regelation.
B)ablation.
C)deposition.
D)tensional forces.
E)compressional forces.
A)regelation.
B)ablation.
C)deposition.
D)tensional forces.
E)compressional forces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is true of compound valley glaciers?
A)they are formed by the merging of ice caps.
B)they contain medial moraines.
C)they can flow over topographic divides,such as mountains.
D)they are one type of continental glacier.
E)they develop only in the southern hemisphere.
A)they are formed by the merging of ice caps.
B)they contain medial moraines.
C)they can flow over topographic divides,such as mountains.
D)they are one type of continental glacier.
E)they develop only in the southern hemisphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is correctly matched?
A)crevasses - horizontal cracks from friction or tension
B)ice regelation - the melting and refreezing of surface ice
C)glacial ice - a metamorphic version of snow and firn
D)firn - freshly fallen snow on the ice surface
E)englacial - on the ice surface
A)crevasses - horizontal cracks from friction or tension
B)ice regelation - the melting and refreezing of surface ice
C)glacial ice - a metamorphic version of snow and firn
D)firn - freshly fallen snow on the ice surface
E)englacial - on the ice surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Glacier surges may be associated with
A)ice quakes,mass imbalance,and water pressure.
B)mass imbalance,basal debris load,and rebound pressure from the bed.
C)water pressure,rebound pressure from the bed,and basal debris load.
D)basal debris load,ice quakes,and water pressure.
E)water pressure,basal debris load,and rebound pressure from the bed.
A)ice quakes,mass imbalance,and water pressure.
B)mass imbalance,basal debris load,and rebound pressure from the bed.
C)water pressure,rebound pressure from the bed,and basal debris load.
D)basal debris load,ice quakes,and water pressure.
E)water pressure,basal debris load,and rebound pressure from the bed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is true of glacial movement?
A)the rate of surface motion is usually identical to the basal slip rate.
B)the internal flow just below the surface is greater than the basal flow.
C)all glaciers move just a few centimeters per year.
D)the basal ice layer does not move downslope.
E)greatest erosion occurs at the ice surface.
A)the rate of surface motion is usually identical to the basal slip rate.
B)the internal flow just below the surface is greater than the basal flow.
C)all glaciers move just a few centimeters per year.
D)the basal ice layer does not move downslope.
E)greatest erosion occurs at the ice surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following represents a form of glacial erosion?
A)ablation.
B)abrasion.
C)pressure release jointing.
D)hydrolysis.
E)crystallization.
A)ablation.
B)abrasion.
C)pressure release jointing.
D)hydrolysis.
E)crystallization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Relative to glacial mass balance,which of the following is correct?
A)a positive net balance occurs during a cold period,and a negative net balance occurs during a warm period.
B)glacial mass is increased by evaporation,sublimation,and deflation.
C)glacial mass is increased by a combination of processes called ablation.
D)worldwide,most glaciers are showing marked net increase in mass at present.
E)where the balance is zero,the ice advances.
A)a positive net balance occurs during a cold period,and a negative net balance occurs during a warm period.
B)glacial mass is increased by evaporation,sublimation,and deflation.
C)glacial mass is increased by a combination of processes called ablation.
D)worldwide,most glaciers are showing marked net increase in mass at present.
E)where the balance is zero,the ice advances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
During a glacier surge,a glacier may move forward at a speed of up to
A)1 cm per day.
B)1 metre per day.
C)tens of meters per day.
D)a few kilometers per hour.
E)a thousand metres in a day.
A)1 cm per day.
B)1 metre per day.
C)tens of meters per day.
D)a few kilometers per hour.
E)a thousand metres in a day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The transformation of snow into glacial ice in Antarctica takes ________ than in midlatitude alpine glaciers because ________.
A)less time less snow falls per year in polar regions
B)longer less melting and refreezing occurs in Antarctica
C)less time more snow falls each year in polar regions
D)less time less melting and refreezing occurs in the midlatitudes
E)longer it has to pile much deeper.
A)less time less snow falls per year in polar regions
B)longer less melting and refreezing occurs in Antarctica
C)less time more snow falls each year in polar regions
D)less time less melting and refreezing occurs in the midlatitudes
E)longer it has to pile much deeper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Snow that has a compact,granular structure is known as
A)snowflakes.
B)firn.
C)glacial ice.
D)meta-ice.
E)sastrugi
A)snowflakes.
B)firn.
C)glacial ice.
D)meta-ice.
E)sastrugi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Unsorted and unstratified glacial deposits (not landforms)are called
A)till.
B)outwash.
C)moraine.
D)alluvium.
E)colluvium.
A)till.
B)outwash.
C)moraine.
D)alluvium.
E)colluvium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The material in a glacial moraine is
A)sorted by weight.
B)sorted by size.
C)unsorted.
D)stratified.
E)cross-bedded
A)sorted by weight.
B)sorted by size.
C)unsorted.
D)stratified.
E)cross-bedded

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following are erosional features formed by an alpine glaciers?
A)cirque,drumlin,esker
B)horn,cirque,col
C)drumlin,esker,horn
D)col,esker,moraine
E)esker,drumlin,horn
A)cirque,drumlin,esker
B)horn,cirque,col
C)drumlin,esker,horn
D)col,esker,moraine
E)esker,drumlin,horn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Erosion by alpine glaciers ________ the ruggedness of the landscape.
A)increases
B)decreases
C)has no net effect on
A)increases
B)decreases
C)has no net effect on

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The material deposited behind a end moraine (i.e. ,the side on which the ice was located)forms a(n)________,whereas that deposited in front of the end moraine forms a(n)________.
A)outwash plain till plain
B)till plain outwash plain
C)esker drumlin field
D)drumlin field esker
E)marsh outwash plain
A)outwash plain till plain
B)till plain outwash plain
C)esker drumlin field
D)drumlin field esker
E)marsh outwash plain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A specific landform produced by the deposition of glacial till is known as
A)glacial drift.
B)outwash.
C)a moraine.
D)alluvium.
E)esker.
A)glacial drift.
B)outwash.
C)a moraine.
D)alluvium.
E)esker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When two valley glaciers join together,they form a ________ at the point at which they merge.
A)terminal moraine
B)till plain
C)recessional moraine
D)medial moraine
E)lateral
A)terminal moraine
B)till plain
C)recessional moraine
D)medial moraine
E)lateral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following types of moraines is oriented parallel to the direction of ice flow?
A)terminal
B)recessional
C)medial
A)terminal
B)recessional
C)medial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The general term for all glacial deposits is
A)till.
B)outwash.
C)glacial drift.
D)alluvium.
E)colluvium.
A)till.
B)outwash.
C)glacial drift.
D)alluvium.
E)colluvium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Unlike a stream-cut valley that assumes a characteristic ________-shape,a glacially-carved valley evidences a characteristic ________-shape.
A)U V
B)V U
C)flat rounded
D)steep shallow
E)wide deep
A)U V
B)V U
C)flat rounded
D)steep shallow
E)wide deep

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Drowned glacial valleys are known as
A)kettle holes.
B)tarns.
C)fjords.
D)paternoster lakes.
E)bergschrund.
A)kettle holes.
B)tarns.
C)fjords.
D)paternoster lakes.
E)bergschrund.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A pyramidal peak formed in glaciated mountains is
A)a col.
B)an arëte.
C)a horn.
D)a cirque.
A)a col.
B)an arëte.
C)a horn.
D)a cirque.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The rock material that is trapped within a glacier that is not moving
A)does not move because the glacier does not move.
B)moves by the process of regelation.
C)moves as a result of the deformation of ice.
D)moves by the process of basal sliding.
E)moves by alternating compression and tension.
A)does not move because the glacier does not move.
B)moves by the process of regelation.
C)moves as a result of the deformation of ice.
D)moves by the process of basal sliding.
E)moves by alternating compression and tension.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Horns and cirques are typical features in
A)a till plain deposited by continental glaciers.
B)a mountain range that was sculpted by alpine glaciers.
C)unsorted glacial deposits left by continental glaciers.
D)loess deposits that have been heavily sculpted by wind action.
E)subtropical desert landscapes.
A)a till plain deposited by continental glaciers.
B)a mountain range that was sculpted by alpine glaciers.
C)unsorted glacial deposits left by continental glaciers.
D)loess deposits that have been heavily sculpted by wind action.
E)subtropical desert landscapes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A tarn is a lake in a
A)till plain.
B)horn.
C)cirque.
D)glacial valley.
E)glacial trough.
A)till plain.
B)horn.
C)cirque.
D)glacial valley.
E)glacial trough.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following would be found in an alpine glacial valley?
A)paternoster lakes
B)kames
C)kettle lakes
D)esker
E)drumlins
A)paternoster lakes
B)kames
C)kettle lakes
D)esker
E)drumlins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following are erosional landforms created by alpine glaciation?
A)drumlins
B)eskers
C)till plains
D)cols and horns
E)deranged drainage
A)drumlins
B)eskers
C)till plains
D)cols and horns
E)deranged drainage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is a depositional landform created by glaciation?
A)cols
B)horns
C)U-shaped valleys
D)outwash plain of stratified drift
E)arete
A)cols
B)horns
C)U-shaped valleys
D)outwash plain of stratified drift
E)arete

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Glacial polish results from
A)abrasion.
B)ice plucking.
C)regelation.
D)rotation of ice about a vertical axis.
E)headwall erosion.
A)abrasion.
B)ice plucking.
C)regelation.
D)rotation of ice about a vertical axis.
E)headwall erosion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Roches moutonn  es form as a result of.
es form as a result of.
A)abrasion on both the stoss (upstream)and lee (downstream)side of a rocky outcrop.
B)ice plucking on both the stoss and lee side of a rocky outcrop.
C)abrasion on the stoss side and ice plucking on the lee side of a rocky outcrop.
D)ice plucking on the stoss side and abrasion on the lee side of a rocky outcrop.
E)glacial deformation of the bed.
 es form as a result of.
es form as a result of.A)abrasion on both the stoss (upstream)and lee (downstream)side of a rocky outcrop.
B)ice plucking on both the stoss and lee side of a rocky outcrop.
C)abrasion on the stoss side and ice plucking on the lee side of a rocky outcrop.
D)ice plucking on the stoss side and abrasion on the lee side of a rocky outcrop.
E)glacial deformation of the bed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Drumlins are formed in ________,and their tapered ends point ________.
A)outwash plains upstream
B)outwash plains downstream
C)till plains upstream
D)till plains downstream
A)outwash plains upstream
B)outwash plains downstream
C)till plains upstream
D)till plains downstream

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The presence of till indicates
A)direct deposition by a glacier.
B)deposition by wind.
C)deposition by water.
A)direct deposition by a glacier.
B)deposition by wind.
C)deposition by water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The term periglacial refers to
A)areas that are on top of a glacier.
B)regions that are too warm for ground ice.
C)cold-climate processes along the margins of glaciers.
D)processes and effects that existed during the last ice age but not today.
E)the area directly beneath a glacier.
A)areas that are on top of a glacier.
B)regions that are too warm for ground ice.
C)cold-climate processes along the margins of glaciers.
D)processes and effects that existed during the last ice age but not today.
E)the area directly beneath a glacier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following is correctly matched?
A)an erosional form - recessional moraine
B)a depositional form - nunatak
C)a depositional form - drumlin
D)a depositional form - roche moutonn .
.
E)an erosional form - esker
A)an erosional form - recessional moraine
B)a depositional form - nunatak
C)a depositional form - drumlin
D)a depositional form - roche moutonn
 .
.E)an erosional form - esker

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following is associated with a glacial outwash plain?
A)drumlin
B)kettle
C)kame
D)esker
E)till
A)drumlin
B)kettle
C)kame
D)esker
E)till

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Till plains refer to
A)the flat bottomland located in U-shaped glaciated valleys.
B)sorted and stratified fluvial deposits.
C)unsorted coarse deposits characterized by low,rolling relief.
D)glacial deposits that have been actively farmed by humans.
E)plains of sorted material laid down by braided streams.
A)the flat bottomland located in U-shaped glaciated valleys.
B)sorted and stratified fluvial deposits.
C)unsorted coarse deposits characterized by low,rolling relief.
D)glacial deposits that have been actively farmed by humans.
E)plains of sorted material laid down by braided streams.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The presence of stratified,or sorted,glacial sediment indicates that
A)it was deposited in terminal moraines by continental glaciers.
B)it was deposited by glacial meltwater.
C)it was deposited as till by a continental glacier.
D)it was deposited as a medial moraine.
E)it was carried on top of the glacier.
A)it was deposited in terminal moraines by continental glaciers.
B)it was deposited by glacial meltwater.
C)it was deposited as till by a continental glacier.
D)it was deposited as a medial moraine.
E)it was carried on top of the glacier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Flowing soil in an area of frozen ground is known as
A)patterned ground.
B)permafrost.
C)gelifluction,or the more general term solifluction.
D)periglacial flow.
E)outwash plain.
A)patterned ground.
B)permafrost.
C)gelifluction,or the more general term solifluction.
D)periglacial flow.
E)outwash plain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of these statements is correct?
A)periglacial regions occupy about 40 percent of Earth's land area.
B)subarctic and tundra climates ,with seasonally snow-free ground,are periglacial regions.
C)permanently frozen subsurface ground is called frostiground.
D)periglacial regions feature hot springs.
E)periglacial regions are always at latitudes higher than 66 degrees.
A)periglacial regions occupy about 40 percent of Earth's land area.
B)subarctic and tundra climates ,with seasonally snow-free ground,are periglacial regions.
C)permanently frozen subsurface ground is called frostiground.
D)periglacial regions feature hot springs.
E)periglacial regions are always at latitudes higher than 66 degrees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Louis Agassiz developed a theory to explain the presence of boulders that differ in composition and origin from the ground on which they rest.He regarded these glacially deposited forms as
A)erratics.
B)horns.
C)tarns.
D)nunataks.
E)eskers
A)erratics.
B)horns.
C)tarns.
D)nunataks.
E)eskers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Sorted glacial drift characteristic of stream-deposited material is called
A)till.
B)erratic.
C)moraine.
D)stratified drift.
E)till plain.
A)till.
B)erratic.
C)moraine.
D)stratified drift.
E)till plain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Areas of permafrost,ground ice,and frost action are in which climate types?
A)subarctic and tundra
B)mesothermal
C)desert
D)humid continental
E)arid
A)subarctic and tundra
B)mesothermal
C)desert
D)humid continental
E)arid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Drumlins look like ________ and they occur ________.
A)mesas in isolation
B)mesas in swarms
C)inverted spoons in isolation
D)inverted spoons in swarms
E)roches moutonnes in isolation
A)mesas in isolation
B)mesas in swarms
C)inverted spoons in isolation
D)inverted spoons in swarms
E)roches moutonnes in isolation


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following is true regarding permafrost?
A)it develops where soil or rock temperatures are below freezing for at least two years.
B)it is an area that is covered by glaciers.
C)the surface layer in a permafrost region never thaws-even during the warm season.
D)it occurs at a lower elevation in the midlatitudes than in the high latitudes.
E)it is always associated with water - liquid or solid.
A)it develops where soil or rock temperatures are below freezing for at least two years.
B)it is an area that is covered by glaciers.
C)the surface layer in a permafrost region never thaws-even during the warm season.
D)it occurs at a lower elevation in the midlatitudes than in the high latitudes.
E)it is always associated with water - liquid or solid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A characteristic area of low,rolling relief,deranged drainage patterns,and unsorted materials is a(n)
A)valley train.
B)lateral moraine.
C)medial moraine.
D)till plain.
E)outwash plain.
A)valley train.
B)lateral moraine.
C)medial moraine.
D)till plain.
E)outwash plain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Kettle holes are formed by
A)scouring.
B)abrasion.
C)ice that melts after having been buried by glacial sediments.
D)solution of limestone by glacial meltwater.
E)plucking
A)scouring.
B)abrasion.
C)ice that melts after having been buried by glacial sediments.
D)solution of limestone by glacial meltwater.
E)plucking

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Erratics are
A)strangely shaped,erratically spaced drumlins.
B)erratically spaced moraine deposits.
C)rocks that are not native to an area.
D)unusually shaped rocks.
E)winding glacial rivers.
A)strangely shaped,erratically spaced drumlins.
B)erratically spaced moraine deposits.
C)rocks that are not native to an area.
D)unusually shaped rocks.
E)winding glacial rivers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following is a depositional feature formed by,or in association with,a continental glacier?
A)valley train deposit
B)terminal moraine
C)lateral moraine
D)esker
E)recessional moraine
A)valley train deposit
B)terminal moraine
C)lateral moraine
D)esker
E)recessional moraine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Thoreau's Walden Pond is an example of which of the following?
A)kame
B)kettle
C)esker
D)drumlin
E)tarn
A)kame
B)kettle
C)esker
D)drumlin
E)tarn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A winding hill of sorted sand and gravel deposits is known as a(n)________ and is deposited by a(n)________ glacier.
A)drumlin continental
B)drumlin alpine
C)esker alpine
D)esker continental
E)medial moraine alpine
A)drumlin continental
B)drumlin alpine
C)esker alpine
D)esker continental
E)medial moraine alpine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 159 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



