Deck 6: Tcp/Ip Past, Present, and Future
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/86
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Tcp/Ip Past, Present, and Future
1
A master DNS server is the DNS server that is the main administrative server for a zone and thus is also called the authoritative server for that zone.
False
2
IP can convert packets from one size to another for dissimilar networks.
True
3
A(n)namespace is a partition in a DNS server that contains specific kinds of records in a lookup table.
False
4
Telnet is an application protocol within TCP/IP that provides support for terminal emulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A Windows 2000 Server can be configured to operate as a Telnet server, so that information on it can be accessed from any computer using Telnet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A(n)universal packet is one that is sent to all nodes on a network.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
IP was originally designed for point-to-point communications between computers on the same network.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The DNS dynamic update protocol enables information in a DNS server to be automatically updated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A(n)pointer resource record is the first record in a DNS zone and indicates if a server is authoritative for the current zone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An important advantage of SNMP is that it operates independently on the network, which means that it does not depend on a two-way connection at the protocol level with other network entities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The information in the window portion of a TCP frame works in conjunction with flow control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
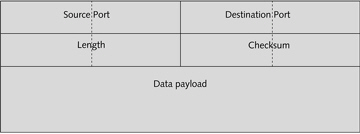 The figure above is an example of a(n)TCP frame .
The figure above is an example of a(n)TCP frame .
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The purpose of IPv6 is to provide a logical growth path from IPv4 so that applications and network devices can handle new demands as they arise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
With TCP, the sequence number shows the frame sequence in a stream of frames, but does not indicate the amount of data in the frame.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The extension header(s)must appear in the packet before the IPv6 main header.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
RMON is a monitoring standard that uses remote network nodes, such as workstations or network devices, to perform network monitoring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Delay is the time it takes for networked information to travel from the transmitting device to the receiving device.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
IP is a connectionless protocol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
FTP enables a packet to reach different subnetworks on a LAN and different networks on a WAN.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
IPv6 addressing enables one IP identifier to be associated with several different interfaces, so it can better handle multimedia traffic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An IP header is a minimum of ____ in length.
A)32 bits
B)20 bytes
C)8 bytes
D)40 bytes
A)32 bits
B)20 bytes
C)8 bytes
D)40 bytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
____ is not a file transfer protocol supported by TCP/IP.
A)FTP
B)TFTP
C)IP
D)NFS
A)FTP
B)TFTP
C)IP
D)NFS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
____ networks can implement TCP/IP.
A)Novell NetWare
B)UNIX
C)Windows-based
D)All of the above.
A)Novell NetWare
B)UNIX
C)Windows-based
D)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A TCP header is a minimum of ____ in length.
A)32 bits
B)20 bytes
C)8 bytes
D)16 bytes
A)32 bits
B)20 bytes
C)8 bytes
D)16 bytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The T in TCP stands for ____.
A)Transmission
B)Telnet
C)Transfer
D)Terminal
A)Transmission
B)Telnet
C)Transfer
D)Terminal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The ____ header has a TOS (type of service)field which indicates the precedence or priority given to the packet contents.
A)UDP
B)IP
C)TCP
D)Both B and C.
A)UDP
B)IP
C)TCP
D)Both B and C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which is not true about the sequence number in a TCP header?
A)It enables TCP to ensure that all frames are received.
B)It is used to identify duplicate frames.
C)It is used to place frames back in the correct order when they arrive through different network routes or channels.
D)None of the above.
A)It enables TCP to ensure that all frames are received.
B)It is used to identify duplicate frames.
C)It is used to place frames back in the correct order when they arrive through different network routes or channels.
D)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
TCP port ____ is used for Telnet applications.
A)21
B)23
C)53
D)25
A)21
B)23
C)53
D)25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
TCP port ____ is used for FTP commands.
A)21
B)23
C)20
D)25
A)21
B)23
C)20
D)25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Each frame in a transmission is assigned a ____-bit sequential number.
A)8
B)16
C)32
D)64
A)8
B)16
C)32
D)64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
IP version ____ is used on most networks.
A)3
B)4
C)5
D)6
A)3
B)4
C)5
D)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
____ is the file transfer option preferred by Internet users.
A)FTP
B)TFTP
C)IP
D)NFS
A)FTP
B)TFTP
C)IP
D)NFS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which type of network uses transport options that are not compatible with TCP/IP?
A)FDDI
B)X.25
C)Token Ring
D)None of the above.
A)FDDI
B)X.25
C)Token Ring
D)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Although not OSI compliant, IP works at the equivalent of the ____ layer of the OSI reference model.
A)Transport
B)Data Link
C)Application
D)Network
A)Transport
B)Data Link
C)Application
D)Network

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
After checking the sequence number, TCP sends back the ____ number, showing that the frame was received.
A)checksum
B)FIN
C)acknowledgment
D)verification
A)checksum
B)FIN
C)acknowledgment
D)verification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A packet is the same as a ____.
A)datagram
B)TCP segment
C)data payload
D)IP segment
A)datagram
B)TCP segment
C)data payload
D)IP segment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
IP does not perform ____.
A)data transfer
B)flow control
C)packet addressing
D)None of the above.
A)data transfer
B)flow control
C)packet addressing
D)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
____enabled different types of DEC and IBM computers to connect for network communications and to run applications over a network in which the hosts were separated geographically.
A)TCP
B)IP
C)NCP
D)FTP
A)TCP
B)IP
C)NCP
D)FTP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The essential TCP functions are similar to those of the OSI ____ layer.
A)Transport
B)Data Link
C)Application
D)Network
A)Transport
B)Data Link
C)Application
D)Network

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
TCP/IP was introduced in the ____.
A)1950s
B)1960s
C)1970s
D)1980s
A)1950s
B)1960s
C)1970s
D)1980s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which is not true about FTP?
A)It can transfer a portion of a file or records within a file.
B)FTP data transmissions are reliable.
C)It is well suited for exchanging even large files over a WAN.
D)None of the above.
A)It can transfer a portion of a file or records within a file.
B)FTP data transmissions are reliable.
C)It is well suited for exchanging even large files over a WAN.
D)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An IPv6 ____ packet contains a destination address that is associated with multiple interfaces, usually on different nodes. It goes only to the closest interface and does not attempt to reach the other interfaces with the same address.
A)unicast
B)anycast
C)multicast
D)Both B and C.
A)unicast
B)anycast
C)multicast
D)Both B and C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which is not true about SMTP?
A)It can send only text files.
B)It requires the use of a logon ID and password for the remote system.
C)It provides an alternative to FTP for sending a file from one computer system to another.
D)None of the above.
A)It can send only text files.
B)It requires the use of a logon ID and password for the remote system.
C)It provides an alternative to FTP for sending a file from one computer system to another.
D)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The ____ zone holds the pointer resource record, which contains the IP-address-to-host name records.
A)reverse lookup
B)pointer lookup
C)forward lookup
D)master lookup
A)reverse lookup
B)pointer lookup
C)forward lookup
D)master lookup

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An Ethernet packet that is under 64 bytes but that contains all of the normal fields is called a ____ packet.
A)midget
B)runt
C)short
D)small
A)midget
B)runt
C)short
D)small

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The IPv6 ____ field is a modification of the IPv4 TTL field.
A)Flow Label
B)Extension headers
C)Hop Limit
D)Traffic Class
A)Flow Label
B)Extension headers
C)Hop Limit
D)Traffic Class

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
____ is a connection-oriented protocol.
A)FTP
B)NFS
C)TFTP
D)Both A and B.
A)FTP
B)NFS
C)TFTP
D)Both A and B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Telnet runs in the TCP/IP layer that is equivalent to the OSI ____ layer.
A)Transport
B)Data Link
C)Session
D)Network
A)Transport
B)Data Link
C)Session
D)Network

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
TCP/IP is a layered set of protocols identical to the OSI protocol layers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
IPv6 networks ____ when transmitting multimedia traffic.
A)use broadcasting
B)designate all the recipients' interfaces as the same address
C)use multicast grouping
D)Both A and B.
A)use broadcasting
B)designate all the recipients' interfaces as the same address
C)use multicast grouping
D)Both A and B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which is not true about Telnet?
A)It comes with nearly all vendor implementations of TCP/IP.
B)It is an open standard.
C)Telnet communications consist of a header and application data that are encapsulated within the TCP data portion of the TCP segment.
D)None of the above.
A)It comes with nearly all vendor implementations of TCP/IP.
B)It is an open standard.
C)Telnet communications consist of a header and application data that are encapsulated within the TCP data portion of the TCP segment.
D)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A ____ resource record is a type of DNS record that enables DNS to recognize multiple servers and to locate commonly used TCP/IP services that are associated with specific servers.
A)pointer
B)start of authority
C)service
D)locator
A)pointer
B)start of authority
C)service
D)locator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which is not true about TFTP?
A)It is designed for tasks such as the transfer of data to enable a diskless workstation to boot using files transmitted from a server.
B)It is connectionless.
C)It is intended for the transfer of small files in situations in which there is no need for security.
D)None of the above.
A)It is designed for tasks such as the transfer of data to enable a diskless workstation to boot using files transmitted from a server.
B)It is connectionless.
C)It is intended for the transfer of small files in situations in which there is no need for security.
D)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Class ____ addresses are not intended for unicast addressing methods.
A)B
B)D
C)C
D)None of the above.
A)B
B)D
C)C
D)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The ____ zone links computer names to IP addresses.
A)reverse lookup
B)pointer lookup
C)forward lookup
D)master lookup
A)reverse lookup
B)pointer lookup
C)forward lookup
D)master lookup

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
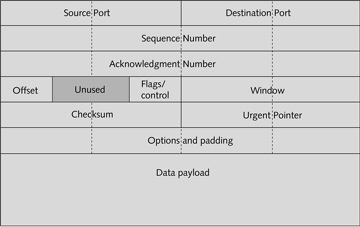 The figure above shows a TCP frame.
The figure above shows a TCP frame.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The D in DHCP stands for ____.
A)Data
B)Domain
C)Decimal
D)Dynamic
A)Data
B)Domain
C)Decimal
D)Dynamic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
An IPv6 ____ packet contains a destination address that is associated with multiple interfaces, usually on different nodes. It is directed to each of the interfaces with that address.
A)unicast
B)anycast
C)multicast
D)Both B and C.
A)unicast
B)anycast
C)multicast
D)Both B and C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The ____ registers root domain names.
A)IEEE
B)ICANN
C)NIST
D)Federal Government
A)IEEE
B)ICANN
C)NIST
D)Federal Government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The M in MIB stands for ____.
A)Multiple
B)Management
C)Mail
D)Message
A)Multiple
B)Management
C)Mail
D)Message

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is the difference between unicast and multicast packets? Which is used more often by an application?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When computers talk over the Internet, the language they speak is the ________________________________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
When transmitting to a node on a network that uses a packet size of less than 1280 octets, IPv6 ____________________ the packet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Secondary DNS servers are used for administration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
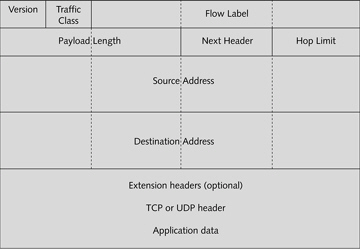 The figure above is an example of a TCP packet.
The figure above is an example of a TCP packet.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The actual data carried within the TCP segment is called the ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The IP address format is called the _________________________ address.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A(n)____________________ is used to show the class of addressing used and to divide a network into subnetworks to control network traffic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What does UDP stand for? Briefly state the advantages and disadvantages of using it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The process of converting an IP address to a computer name or vice versa is called resolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
CIDR addressing puts a colon (:)after the dotted decimal notation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
To what does a sliding window refer? What is a sliding window? How is it adjusted?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The checksum in UDP is used differently than it is in TCP to compare the received frame with the one that was sent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A network management station is a computer with software that monitors networked devices that are equipped to communicate via SNMP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A(n)____________________ is a logical grouping of network resources such as computers, printers, and network devices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A(n)____________________ is a password used by network agents and the network management station so their communications cannot be easily intercepted by an unauthorized workstation or device.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Where would you find the TTL field? What is it, and what function does it perform?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In an IP packet, ____________________ fills the options area when there is not enough data to complete the allocated area, because the total size of the IP header must be divisible by 32.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Functioning like a virtual circuit, a(n)____________________ enables communication between individual processes at two communicating nodes or devices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
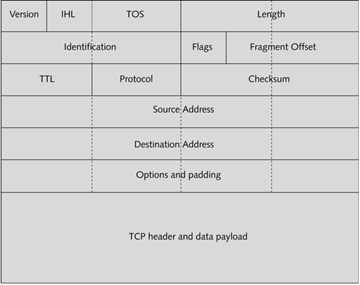 The figure above is an example of an IP packet.
The figure above is an example of an IP packet.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



