Deck 7: Histology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/24
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Histology
1
A 68-year-old man with a history of Parkinson disease is hospitalized for pneumonia and sepsis. The patient is treated with intravenous (IV) fluids and antibiotics. He is also started on an infusion of IV dopamine for hemodynamic support. Although the manifestations of Parkinson disease are attributed to dopaminergic neuron degeneration in the substantia nigra, IV dopamine does not improve this patient's Parkinson symptoms. Which of the following cell structures accounts for this lack of responsiveness?
A)Desmosomes
B)Fenestrae
C)Gap junctions
D)Hemidesmosomes
E)Intermediate junctions
F)Tight junctions
A)Desmosomes
B)Fenestrae
C)Gap junctions
D)Hemidesmosomes
E)Intermediate junctions
F)Tight junctions
F
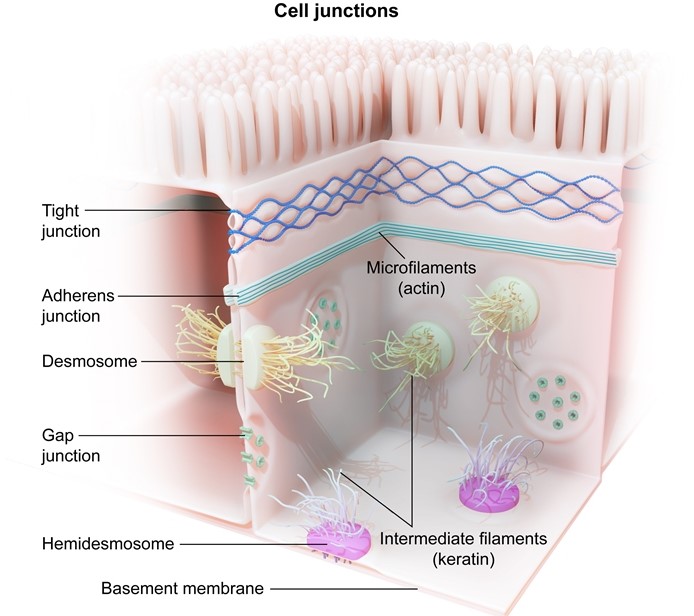
This patient's Parkinson symptoms do not improve with intravenous dopamine infusion because dopamine is unable to cross the blood-brain barrier. The blood-brain barrier is formed by tight junctions between nonfenestrated capillary endothelial cells that prevent the paracellular passage of fluid and solutes. Tight junctions, also known as zonulae occludentes, are composed of transmembrane proteins (eg, claudins and occludins) that associate with actin filaments, forming a beltlike seal around the apical intercellular space. This seal only permits the passage of substances from the blood to the brain via transcellular movement.
Transcellular movement of dopamine is limited by the molecule's low lipid solubility and the lack of dopamine-specific transport carriers in capillary endothelial cells of the blood-brain barrier. L-DOPA (dopamine precursor) also has low lipid solubility, but it is able to enter the brain due to its high affinity for the large neutral amino acid transporter.
(Choice A) Desmosomes (maculae adherentes) are spotlike junctions that anchor adjacent cells together via keratin intermediate filament interactions. Autoantibodies against desmosomes in the stratum spinosum of the skin cause pemphigus vulgaris.
(Choice B) Fenestrae are small pores within endothelial cells that allow free fluid exchange between the intravascular and extravascular spaces. They are found in capillaries perfusing the intestine, renal tubules, and endocrine glands.
(Choice C) Gap junctions are composed of connexin proteins that create channels between cells, permitting the free passage of small ions (eg, Ca2+) and molecules.
(Choice D) Hemidesmosomes are similar to desmosomes but bind the basal layer of epithelial cells to the basement membrane. Autoantibodies against hemidesmosomes in the skin cause bullous pemphigoid.
(Choice E) Intermediate junctions (zonula adherens or belt desmosomes) are located below tight junctions and form a beltlike anchor between adjacent cells in association with actin microfilaments.
Educational objective:
The blood-brain barrier is formed by tight junctions between nonfenestrated capillary endothelial cells that prevent the paracellular passage of fluid and solutes. This barrier only permits the passage of substances from the blood to the brain via transcellular movement across the endothelial plasma membrane, which is limited by diffusion or carrier-mediated transport.
__________
References:
Tight junction in blood-brain barrier: an overview of structure, regulation, and regulator substances.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22686334)

This patient's Parkinson symptoms do not improve with intravenous dopamine infusion because dopamine is unable to cross the blood-brain barrier. The blood-brain barrier is formed by tight junctions between nonfenestrated capillary endothelial cells that prevent the paracellular passage of fluid and solutes. Tight junctions, also known as zonulae occludentes, are composed of transmembrane proteins (eg, claudins and occludins) that associate with actin filaments, forming a beltlike seal around the apical intercellular space. This seal only permits the passage of substances from the blood to the brain via transcellular movement.
Transcellular movement of dopamine is limited by the molecule's low lipid solubility and the lack of dopamine-specific transport carriers in capillary endothelial cells of the blood-brain barrier. L-DOPA (dopamine precursor) also has low lipid solubility, but it is able to enter the brain due to its high affinity for the large neutral amino acid transporter.
(Choice A) Desmosomes (maculae adherentes) are spotlike junctions that anchor adjacent cells together via keratin intermediate filament interactions. Autoantibodies against desmosomes in the stratum spinosum of the skin cause pemphigus vulgaris.
(Choice B) Fenestrae are small pores within endothelial cells that allow free fluid exchange between the intravascular and extravascular spaces. They are found in capillaries perfusing the intestine, renal tubules, and endocrine glands.
(Choice C) Gap junctions are composed of connexin proteins that create channels between cells, permitting the free passage of small ions (eg, Ca2+) and molecules.
(Choice D) Hemidesmosomes are similar to desmosomes but bind the basal layer of epithelial cells to the basement membrane. Autoantibodies against hemidesmosomes in the skin cause bullous pemphigoid.
(Choice E) Intermediate junctions (zonula adherens or belt desmosomes) are located below tight junctions and form a beltlike anchor between adjacent cells in association with actin microfilaments.
Educational objective:
The blood-brain barrier is formed by tight junctions between nonfenestrated capillary endothelial cells that prevent the paracellular passage of fluid and solutes. This barrier only permits the passage of substances from the blood to the brain via transcellular movement across the endothelial plasma membrane, which is limited by diffusion or carrier-mediated transport.
__________
References:
Tight junction in blood-brain barrier: an overview of structure, regulation, and regulator substances.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22686334)
2
A 17-year-old boy comes to the office due to a facial lesion. The patient noticed a small area of rough skin on his lower lip several weeks ago, which has progressively enlarged. He reports no pain or itching. The patient had eczema during early childhood but has had no other chronic medical conditions. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination findings are shown in the exhibit. 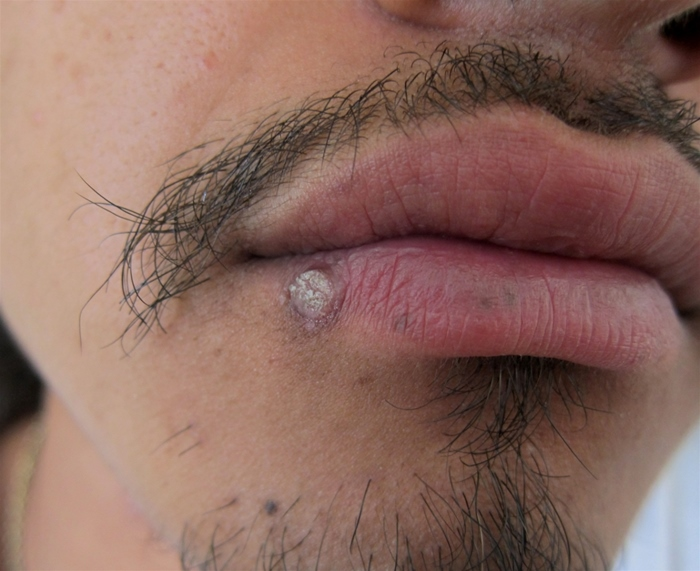
There are no other skin rashes, oral lesions, or enlarged lymph nodes. Which of the following histopathological findings are most likely present in this patient's skin lesion?
A)Acantholysis and multinucleated giant epithelial cells
B)Epidermal hyperplasia and cytoplasmic vacuolization
C)Subcorneal bacterial collection and neutrophilic infiltration
D)Subepidermal linear complement deposits and separation

There are no other skin rashes, oral lesions, or enlarged lymph nodes. Which of the following histopathological findings are most likely present in this patient's skin lesion?
A)Acantholysis and multinucleated giant epithelial cells
B)Epidermal hyperplasia and cytoplasmic vacuolization
C)Subcorneal bacterial collection and neutrophilic infiltration
D)Subepidermal linear complement deposits and separation
Epidermal hyperplasia and cytoplasmic vacuolization
3
A 35-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 0, at 12 weeks gestation comes to the office for evaluation of genital warts. She first noticed the warts last week and is concerned that it has persisted. The patient has occasional mild pruritus but no pain. She is currently sexually active with her boyfriend and engages in oral and vaginal intercourse. Examination shows several verrucous, skin-colored lesions over the labia majora. The patient asks whether the lesion could affect her future child. The virus involved in this patient's condition also has an affinity to infect which of the following structures?
A)Alveoli
B)False vocal cords
C)Paranasal sinuses
D)Trachea
E)True vocal cords
A)Alveoli
B)False vocal cords
C)Paranasal sinuses
D)Trachea
E)True vocal cords
E
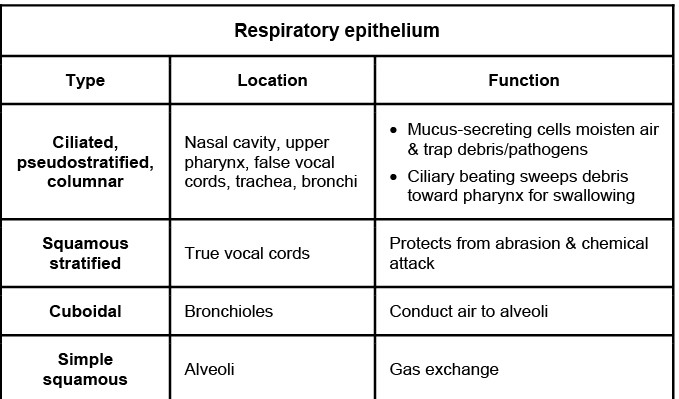
This patient's verrucous, skin-colored genital lesion is most consistent with condylomata acuminatum, also known as anogenital warts. Condylomata acuminatum is caused by human papillomavirus (HPV), a small double-stranded DNA virus with >100 subtypes. HPV is the most common sexually transmitted disease and can be transmitted by vaginal, anal, and oral intercourse. Most infections are cleared by host immunity, but types 6 and 11 can result in warts.
HPV infects basal epithelial cells through small breaks in the skin or mucosal surfaces. It has a predilection for stratified squamous epithelium, which is found in the anal canal, vagina, and cervix. In the respiratory tract, the true vocal cords are the only area covered with stratified squamous epithelium. The vocal cords undergo near-constant friction and abrasion to produce speech. Stratified squamous epithelium is protective, as deeper cells can replace surface cells that are damaged.
Infants can acquire respiratory papillomatosis via passage through the birth canal of mothers infected with the virus. Warty growths on the true vocal cords can lead to a weak cry, hoarseness, and stridor.
(Choice A) The alveoli are comprised of simple squamous epithelium. This thin and flat epithelium facilitates rapid transmembrane exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
(Choice B) The false vocal cords, also known as ventricular folds, are folds of mucous membrane lined in respiratory epithelium, which is ciliated, pseudostratified, columnar, and mucus-secreting. The false vocal cords are adjacent to the true vocal cords and help to lubricate the true vocal cords with mucus and protect the airway from foreign bodies.
(Choices C and D) The paranasal sinuses and trachea also are lined in respiratory epithelium. This ciliated, pseudostratified, columnar, and mucus-secreting epithelium protects the respiratory tract from debris and pathogens. Goblet cells secrete mucus to trap particulate matter, and the cilia beat in a rhythmic fashion to propel this mucus/debris toward the oral cavity, where it can be swallowed or coughed up.
Educational objective:
Human papilloma virus (HPV) is a small DNA virus with a tropism for stratified squamous epithelium, which protectively lines anatomical areas that undergo frequent friction and abrasion, including the true vocal cords, cervix, and anus. Infants can acquire respiratory papillomatosis via passage through an HPV-infected birth canal.
__________
References:
Epithelial Cell Responses to Infection with Human Papillomavirus
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22491770)
Prevalence of human papillomavirus (HPV) in upper respiratory tract mucosa in a group of pre-school children.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25528927)
Genital warts: a comprehensive review
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22768354)

This patient's verrucous, skin-colored genital lesion is most consistent with condylomata acuminatum, also known as anogenital warts. Condylomata acuminatum is caused by human papillomavirus (HPV), a small double-stranded DNA virus with >100 subtypes. HPV is the most common sexually transmitted disease and can be transmitted by vaginal, anal, and oral intercourse. Most infections are cleared by host immunity, but types 6 and 11 can result in warts.
HPV infects basal epithelial cells through small breaks in the skin or mucosal surfaces. It has a predilection for stratified squamous epithelium, which is found in the anal canal, vagina, and cervix. In the respiratory tract, the true vocal cords are the only area covered with stratified squamous epithelium. The vocal cords undergo near-constant friction and abrasion to produce speech. Stratified squamous epithelium is protective, as deeper cells can replace surface cells that are damaged.
Infants can acquire respiratory papillomatosis via passage through the birth canal of mothers infected with the virus. Warty growths on the true vocal cords can lead to a weak cry, hoarseness, and stridor.
(Choice A) The alveoli are comprised of simple squamous epithelium. This thin and flat epithelium facilitates rapid transmembrane exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
(Choice B) The false vocal cords, also known as ventricular folds, are folds of mucous membrane lined in respiratory epithelium, which is ciliated, pseudostratified, columnar, and mucus-secreting. The false vocal cords are adjacent to the true vocal cords and help to lubricate the true vocal cords with mucus and protect the airway from foreign bodies.
(Choices C and D) The paranasal sinuses and trachea also are lined in respiratory epithelium. This ciliated, pseudostratified, columnar, and mucus-secreting epithelium protects the respiratory tract from debris and pathogens. Goblet cells secrete mucus to trap particulate matter, and the cilia beat in a rhythmic fashion to propel this mucus/debris toward the oral cavity, where it can be swallowed or coughed up.
Educational objective:
Human papilloma virus (HPV) is a small DNA virus with a tropism for stratified squamous epithelium, which protectively lines anatomical areas that undergo frequent friction and abrasion, including the true vocal cords, cervix, and anus. Infants can acquire respiratory papillomatosis via passage through an HPV-infected birth canal.
__________
References:
Epithelial Cell Responses to Infection with Human Papillomavirus
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22491770)
Prevalence of human papillomavirus (HPV) in upper respiratory tract mucosa in a group of pre-school children.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25528927)
Genital warts: a comprehensive review
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22768354)
4
A 64-year-old man is brought to the emergency department due to worsening shortness of breath. The patient is able to speak in short sentences only and becomes hypoxemic with minimal exertion. His medical history includes hypertension and dyslipidemia. He smoked a pack of cigarettes a day for 40 years and worked for 25 years as a nickel miner. His father died of chronic respiratory failure. While in the emergency department, he rapidly develops respiratory failure and is intubated. Despite appropriate treatment, he dies several days later in the intensive care unit. Autopsy is performed, and examination of the bronchi reveals thickened bronchial walls, inflammatory infiltrates, mucous gland enlargement, and patchy squamous metaplasia of the bronchial mucosa. Which of the following factors was likely the greatest contributor to this patient's pathological findings?
A)Allergic
B)Behavioral
C)Genetic
D)Infectious
E)Neoplastic
F)Occupational
A)Allergic
B)Behavioral
C)Genetic
D)Infectious
E)Neoplastic
F)Occupational

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A 20-year-old woman comes to the office due to blisters around her mouth associated with a mild burning sensation. She reports that she has been having frequent recurrence of these lesions, which resolve spontaneously within a few days. She has no medical problems and does not take any medications. Physical examination findings are shown in the image below. 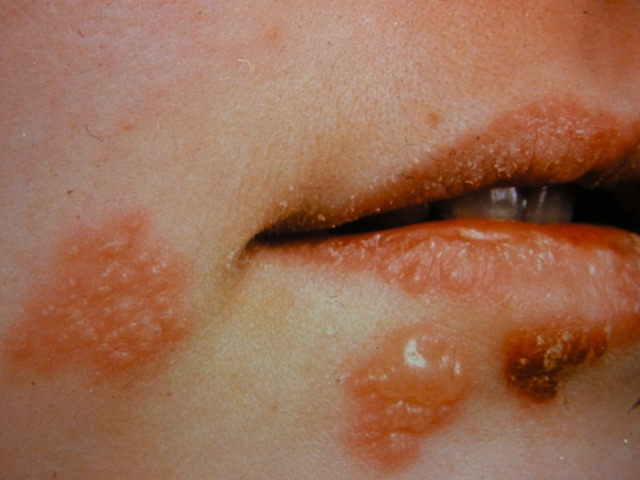 It is determined that the causative organism of this patient's condition remains in a latent state in the neuronal cell bodies of sensory ganglia. Upon reactivation, the virus is transported through the nerve axon to the skin. Which of the following proteins is most likely involved in the transport process leading to disease recurrence?
It is determined that the causative organism of this patient's condition remains in a latent state in the neuronal cell bodies of sensory ganglia. Upon reactivation, the virus is transported through the nerve axon to the skin. Which of the following proteins is most likely involved in the transport process leading to disease recurrence?
A)Dynein
B)Kinesin
C)Lamin
D)Selectin
E)Spectrin
F)Vimentin
 It is determined that the causative organism of this patient's condition remains in a latent state in the neuronal cell bodies of sensory ganglia. Upon reactivation, the virus is transported through the nerve axon to the skin. Which of the following proteins is most likely involved in the transport process leading to disease recurrence?
It is determined that the causative organism of this patient's condition remains in a latent state in the neuronal cell bodies of sensory ganglia. Upon reactivation, the virus is transported through the nerve axon to the skin. Which of the following proteins is most likely involved in the transport process leading to disease recurrence?A)Dynein
B)Kinesin
C)Lamin
D)Selectin
E)Spectrin
F)Vimentin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A researcher is investigating factors affecting adrenal hormone synthesis and release. An intact adrenal gland is obtained from a donor cadaver, and a histologic section through the entire gland is shown below. Cells from a specific part of the gland, indicated by the arrow, are extracted for further analysis. 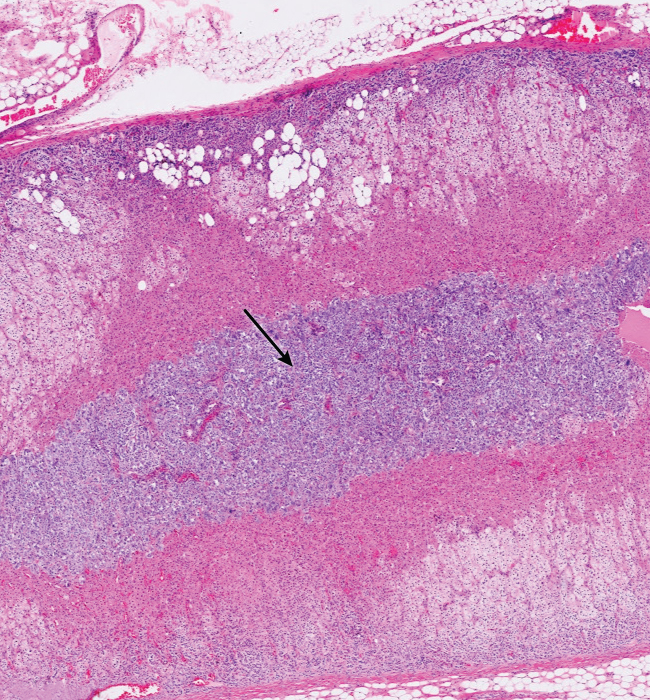 These cells are most likely to be directly activated by which of the following substances?
These cells are most likely to be directly activated by which of the following substances?
A)Acetylcholine
B)ACTH
C)Angiotensin II
D)Epinephrine
E)Norepinephrine
 These cells are most likely to be directly activated by which of the following substances?
These cells are most likely to be directly activated by which of the following substances?A)Acetylcholine
B)ACTH
C)Angiotensin II
D)Epinephrine
E)Norepinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A 23-year-old woman, gravida 2 para 1, at 39 weeks gestation comes to the labor and delivery unit with regular painful contractions. The patient's first pregnancy was uncomplicated and resulted in a full-term, spontaneous vaginal delivery 3 years ago, and her current pregnancy has been uncomplicated. She takes a prenatal vitamin daily and has no chronic medical conditions. In response to rising estrogen levels, the patient's myometrial cells increase the expression of genes that encode the oxytocin receptor and connexin 43. These molecular changes most likely result in increased formation of which of the following?
A)Adherens junctions
B)Desmosomes
C)Fenestrae
D)Gap junctions
E)Hemidesmosomes
F)Tight junctions
A)Adherens junctions
B)Desmosomes
C)Fenestrae
D)Gap junctions
E)Hemidesmosomes
F)Tight junctions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A 14-month-old girl is brought to the office due to a 2-month history of diarrhea. Her parents report that she has 3-5 loose, nonbloody bowel movements daily with occasional episodes of vomiting. She was breastfed exclusively until age 9 months and has since had a well-varied diet including whole milk, fruits, vegetables, bread, and meats. However, the girl has been less interested in food over the past several weeks. There is no history of travel or contacts with similar symptoms. On physical examination, the patient appears well but has lost 1.1 kg (2.5 lb) in the last 2 months. After laboratory evaluation, duodenal biopsy findings are shown in the exhibit. 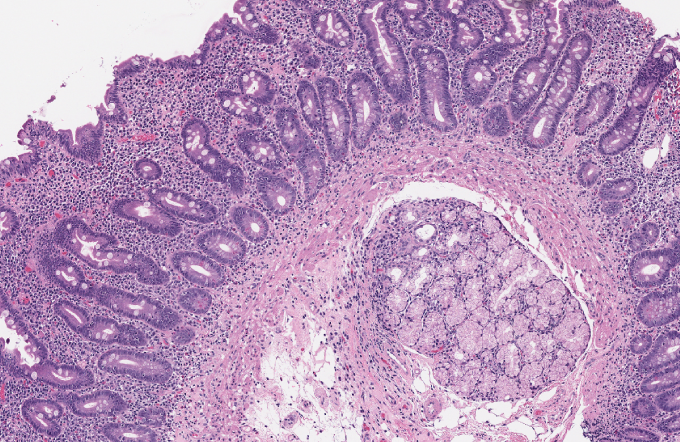
Which of the following would most likely improve this patient's symptoms?
A)Acid reduction therapy
B)Anti-inflammatory medications
C)Antibiotic therapy
D)Enzyme supplementation
E)Modified dairy diet
F)Modified grain diet

Which of the following would most likely improve this patient's symptoms?
A)Acid reduction therapy
B)Anti-inflammatory medications
C)Antibiotic therapy
D)Enzyme supplementation
E)Modified dairy diet
F)Modified grain diet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A 42-year-old woman, gravida 4 para 4, comes to the office due to heavy and painful menstrual bleeding over the past 3 months. The patient's last menstrual period was 3 weeks ago. Menarche was at age 10, and menstrual periods last for 3-5 days and occur every 30 days. She is sexually active with her husband and does not have pain with intercourse. The patient had a bilateral tubal ligation 3 years ago after the birth of her last child. She takes no medications and has no allergies. BMI is 24 kg/m2. Vital signs are normal. On bimanual examination, the uterus is uniformly enlarged and tender. Urine β-hCG is negative. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
A)Benign myometrial smooth muscle cell proliferation
B)Blastocyst implantation in the fallopian tube
C)Endometrial glands and stroma within the myometrium
D)Localized overgrowth of endometrium into the uterine cavity
E)Unregulated endometrial proliferation with increased gland-to-stroma ratio
A)Benign myometrial smooth muscle cell proliferation
B)Blastocyst implantation in the fallopian tube
C)Endometrial glands and stroma within the myometrium
D)Localized overgrowth of endometrium into the uterine cavity
E)Unregulated endometrial proliferation with increased gland-to-stroma ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In an experiment, laboratory animals are subjected to a toxic insult that specifically targets the protein kinesin. Which of the following is most likely to be absent from tissues on histological examination as a result?
A)Nissl substance in pyramidal neurons
B)Secretory vesicles in nerve terminals
C)T-tubules in skeletal muscle cells
D)Desmosomes in epithelial lining cells
E)Microvilli in intestinal epithelial cells
A)Nissl substance in pyramidal neurons
B)Secretory vesicles in nerve terminals
C)T-tubules in skeletal muscle cells
D)Desmosomes in epithelial lining cells
E)Microvilli in intestinal epithelial cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A 43-year-old man comes to the office due to shortness of breath and fatigue. Over the last 2 weeks, his fatigue has been so profound that he has "little energy, even to get out of bed." The patient has no chills but has experienced recent weight gain and ankle swelling. He has no prior medical conditions and takes no medications. Blood pressure is 168/94 mm Hg, and pulse is 95/min and regular. The patient has bilateral lower extremity pitting edema limited to the ankles. Urinalysis reveals 2+ protein, white blood cell count of 5-7/hpf, and red blood cell count of 75-100/hpf. He undergoes a kidney biopsy; immunofluorescent microscopy findings are shown in the image below. 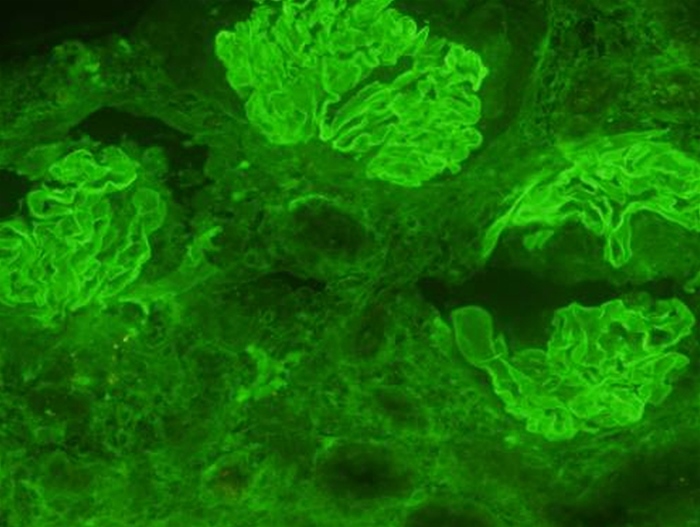 Which of the following would be the most likely finding on light microscopy in this patient?
Which of the following would be the most likely finding on light microscopy in this patient?
A)Amyloid deposition
B)Crescent formation
C)Diffuse capillary wall thickening
D)Nodular glomerulosclerosis
E)Normal glomeruli
 Which of the following would be the most likely finding on light microscopy in this patient?
Which of the following would be the most likely finding on light microscopy in this patient?A)Amyloid deposition
B)Crescent formation
C)Diffuse capillary wall thickening
D)Nodular glomerulosclerosis
E)Normal glomeruli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An autopsy is being performed on a 72-year-old man with a history of myocardial infarction. Light microscopy of a portion of the left ventricle reveals the findings shown in the image below: 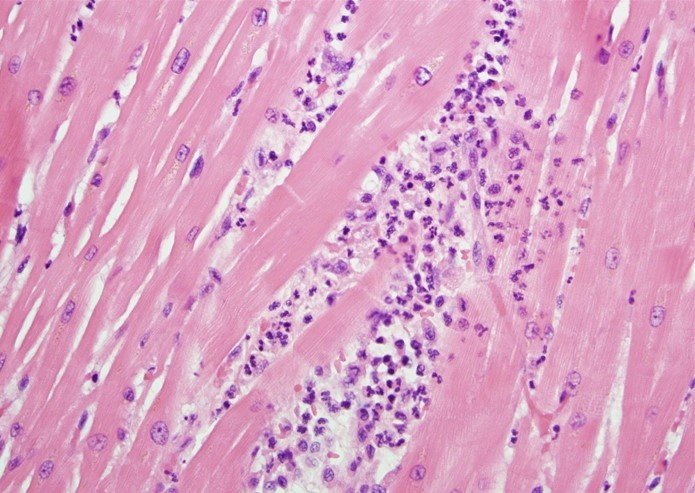 This patient most likely sustained the myocardial infarction during which of the following time frames prior to his death?
This patient most likely sustained the myocardial infarction during which of the following time frames prior to his death?
A)Less than 4 hours
B)1 to 3 days
C)7 to 10 days
D)2 weeks to 2 months
E)More than 2 months
 This patient most likely sustained the myocardial infarction during which of the following time frames prior to his death?
This patient most likely sustained the myocardial infarction during which of the following time frames prior to his death?A)Less than 4 hours
B)1 to 3 days
C)7 to 10 days
D)2 weeks to 2 months
E)More than 2 months

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A 28-year-old woman, gravida 3 para 3, comes to the emergency department with severe abdominal pain in the left lower quadrant and vaginal bleeding. She is saturating a pad every 3-4 hours. Her last menstrual period was 6 weeks ago. Past surgical history is significant for 3 cesarean deliveries and permanent sterilization via a bilateral tubal ligation. A urine pregnancy test is positive, and an ultrasound shows a 2-cm mass in the left adnexa adjacent to the ovary and a thickened endometrial stripe. If a uterine curettage is performed, which of the following findings would be expected in this patient?
A)Atypical endometrial cells, disorganized glands, and multiple mitoses
B)Dilated, coiled endometrial glands and edematous stroma
C)Enlarged chorionic villi and avascular edematous stroma
D)Inflammatory infiltration of endometrial glands
E)Straight, short endometrial glands and compact stroma
A)Atypical endometrial cells, disorganized glands, and multiple mitoses
B)Dilated, coiled endometrial glands and edematous stroma
C)Enlarged chorionic villi and avascular edematous stroma
D)Inflammatory infiltration of endometrial glands
E)Straight, short endometrial glands and compact stroma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Physicians involved in regenerative medicine research conduct a series of animal experiments to determine pulmonary tissue regeneration capacity. During one of the experiments, lung alveoli are exposed to NO2 and massive necrosis of the epithelial lining ensues. Histologic examination of the injured tissues a month later shows partial recovery of the alveolar epithelial lining. This regenerated tissue is most likely derived from which of the following cell types?
A)Alveolar macrophages
B)Ciliated epithelium
C)Club cells
D)Goblet cells
E)Type I pneumocytes
F)Type II pneumocytes
A)Alveolar macrophages
B)Ciliated epithelium
C)Club cells
D)Goblet cells
E)Type I pneumocytes
F)Type II pneumocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A 34-year-old woman comes to the office with bleeding from the right nipple. The patient has noticed blood staining her bra on several occasions over the past week but has no fever or breast pain. She has no chronic medical conditions and does not take any medications. Breast examination shows no palpable masses or skin changes. A thin, blood-tinged discharge can be expressed from the right nipple. There are no enlarged axillary lymph nodes. Which of the following is the most likely histopathologic finding in this patient's right breast?
A)Atypical cells infiltrating the nipple skin
B)Cysts lined by metaplastic apocrine cells
C)Epithelial cells lining fibrovascular cores
D)Necrotic adipocytes with inflammation
E)Stromal proliferation compressing the ducts to slits
A)Atypical cells infiltrating the nipple skin
B)Cysts lined by metaplastic apocrine cells
C)Epithelial cells lining fibrovascular cores
D)Necrotic adipocytes with inflammation
E)Stromal proliferation compressing the ducts to slits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Fourth-year medical students are recruited for a research study assessing their ability to interpret biopsy samples obtained during routine clinical practice. As part of the study, they are given samples of normal respiratory mucosa and asked to identify the cell types present after staining with hematoxylin and eosin. The students observe that the respiratory epithelium changes in composition as the airways continue distally from the trachea to the alveolar ducts. Which of the following features is last to disappear?
A)Cartilage
B)Cilia
C)Goblet cells
D)Mucous glands
E)Serous glands
A)Cartilage
B)Cilia
C)Goblet cells
D)Mucous glands
E)Serous glands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A 65-year-old woman comes to the emergency department with progressive fatigue and lower-extremity paresthesias. Medical history is otherwise insignificant and the patient takes no medications. Laboratory studies show a mean corpuscular volume of 112 fL. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy shows atrophic mucosa in the gastric body and fundus and a normal-appearing antrum. Destruction of which of the following gastric layers is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms? 
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A 67-year-old man is found dead in his home. The cause of death is not apparent; he had a long history of hypertension and he had a myocardial infarction a year ago. An autopsy is performed. Gross examination of the heart shows white scarring and enlargement of the left ventricle. Histologic findings from a section of the left ventricle are shown below. 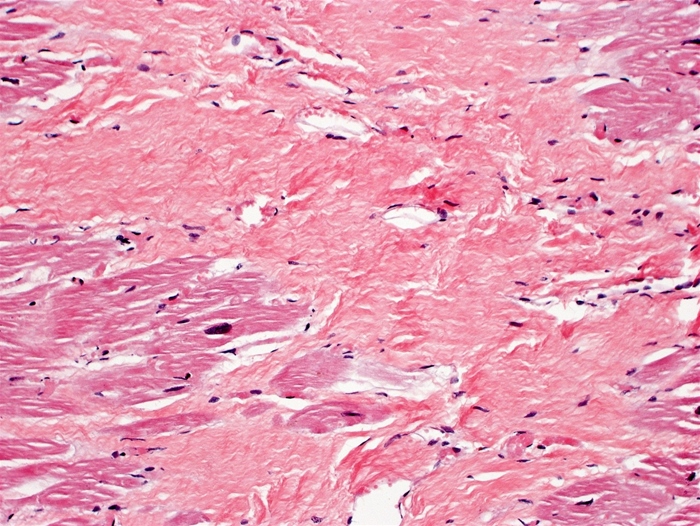 The type of collagen seen in the autopsy sample is most likely to be extensively found in which of the following normal body tissues?
The type of collagen seen in the autopsy sample is most likely to be extensively found in which of the following normal body tissues?
A)Basement membrane
B)Granulation tissue
C)Hyaline cartilage
D)Nucleus pulposus
E)Tendon
 The type of collagen seen in the autopsy sample is most likely to be extensively found in which of the following normal body tissues?
The type of collagen seen in the autopsy sample is most likely to be extensively found in which of the following normal body tissues?A)Basement membrane
B)Granulation tissue
C)Hyaline cartilage
D)Nucleus pulposus
E)Tendon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A 6mm punch biopsy of normal appearing epidermis reveals stellar cells that contain intracytoplasmic granules having the shape of a tennis racquet. These cells demonstrate some myeloid surface markers and can interact closely with T lymphocytes. The cells described above are best referred to as which of the following?
A)Kupffer cells
B)Langerhans cells
C)Merkel cells
D)Melanocytes
E)Macrophages
F)Epithelioid cells
A)Kupffer cells
B)Langerhans cells
C)Merkel cells
D)Melanocytes
E)Macrophages
F)Epithelioid cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A 62-year-old man comes to the office for the evaluation of jaundice. Medical history is significant for uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus and morbid obesity. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. There is no family history of liver disease. Vital signs are within normal limits. BMI is 47 kg/m2. Mild scleral icterus is present. Heart and lung sounds are normal. The abdomen is nontender and nondistended. Trace bilateral lower extremity edema is present. Laboratory studies reveal elevated transaminases. A liver biopsy is obtained, and trichrome staining shows the following: 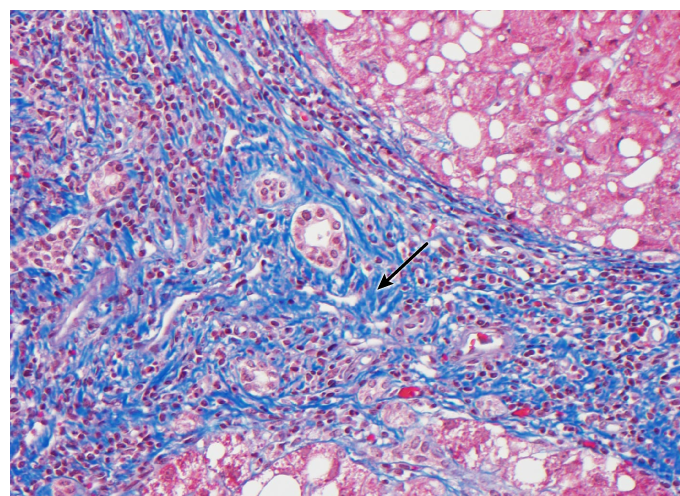 Which of the following cells is directly responsible for the histologic finding indicated by the arrow?
Which of the following cells is directly responsible for the histologic finding indicated by the arrow?
A)Cholangiocytes
B)Hepatocytes
C)Kupffer cells
D)Sinusoidal endothelial cells
E)Stellate (Ito) cells
 Which of the following cells is directly responsible for the histologic finding indicated by the arrow?
Which of the following cells is directly responsible for the histologic finding indicated by the arrow?A)Cholangiocytes
B)Hepatocytes
C)Kupffer cells
D)Sinusoidal endothelial cells
E)Stellate (Ito) cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An 8-year-old boy is brought to the office due to acute facial puffiness. His mother reports that for the preceding 24 hours he has been easily fatigued and has had dark urine. The patient was treated for a skin infection 3 weeks ago but has no chronic medical conditions. Temperature is 36.1 C (97 F) and blood pressure is 140/94 mm Hg. Physical examination shows periorbital edema and mild pitting edema along the ankles. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. A representative renal biopsy sample is shown in the below image. 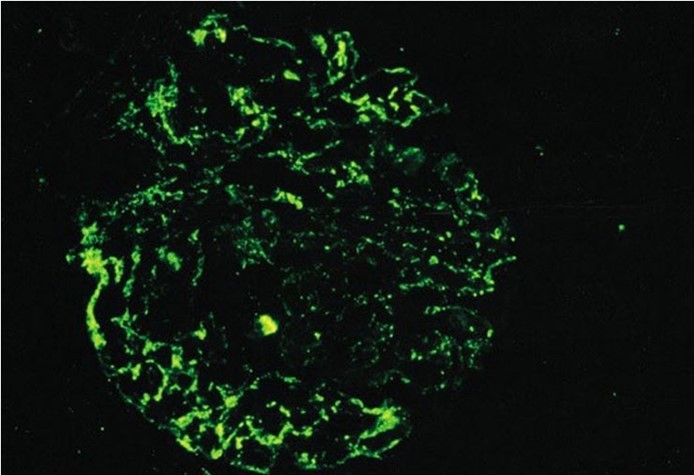 The fluorescent areas on the slide most likely indicate the presence of which of the following substances?
The fluorescent areas on the slide most likely indicate the presence of which of the following substances?
A)Albumin
B)C1q
C)C3
D)Fibrin
E)IgE
F)M protein
 The fluorescent areas on the slide most likely indicate the presence of which of the following substances?
The fluorescent areas on the slide most likely indicate the presence of which of the following substances?A)Albumin
B)C1q
C)C3
D)Fibrin
E)IgE
F)M protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A 3-year-old girl is brought to her pediatrician for a well child checkup. She has met all of the appropriate developmental milestones. Her height corresponds to the 60th percentile. Osteoblasts near the growth plates of her long bones secrete matrix material, and when they become trapped in the ossified matrix, they become known as osteocytes. These osteocytes remain connected to each other by:
A)Tight junctions
B)Hemidesmosomes
C)Intermediate junctions
D)Gap junctions
E)Desmosomes
A)Tight junctions
B)Hemidesmosomes
C)Intermediate junctions
D)Gap junctions
E)Desmosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A researcher is investigating the structure of the sarcomere using skeletal muscle obtained from an experimental animal. He develops monoclonal antibodies directed against a specific skeletal muscle protein and finds that these antibodies disrupt the binding of actin to structural support elements within the sarcomere. Electron microscopy of the sarcomere is shown in the image below. 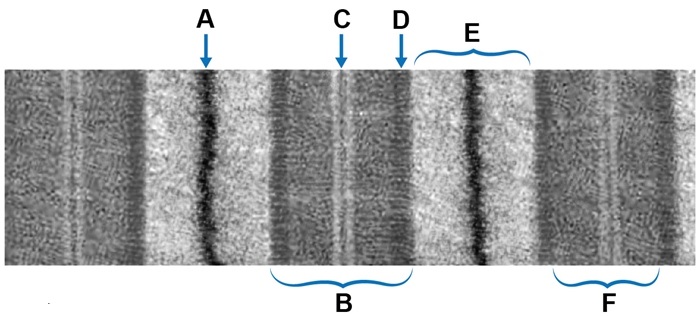 Which of the following labeled regions do these antibodies most likely bind?
Which of the following labeled regions do these antibodies most likely bind?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
F)F
 Which of the following labeled regions do these antibodies most likely bind?
Which of the following labeled regions do these antibodies most likely bind?A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
F)F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A 9-year-old girl is brought to the office due to 2 days of face and eye puffiness. The patient was treated for a rash on her leg with an antibiotic about 3 weeks ago. Temperature is 37.2 C (99 F) and blood pressure is 150/90 mm Hg. On physical examination, there is generalized edema but no rash. Urinalysis reveals proteinuria and hematuria. An electron microscopy image representative of this patient's disease process is shown below: 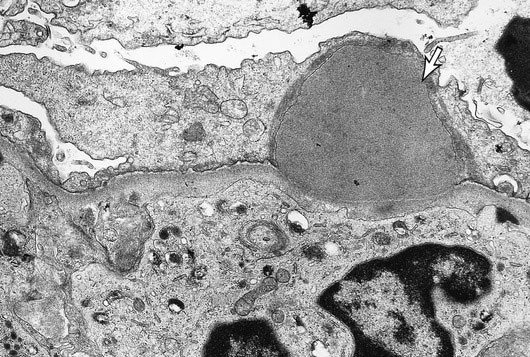 The area marked by the white arrow most likely represents which of the following?
The area marked by the white arrow most likely represents which of the following?
A)Albumin leakage
B)Eosinophil enzymes
C)Fibrin deposition
D)Hyaline accumulation
E)Immune complex deposits
F)Lipid droplet
G)Neutrophil enzymes
 The area marked by the white arrow most likely represents which of the following?
The area marked by the white arrow most likely represents which of the following?A)Albumin leakage
B)Eosinophil enzymes
C)Fibrin deposition
D)Hyaline accumulation
E)Immune complex deposits
F)Lipid droplet
G)Neutrophil enzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



