Deck 9: Microbiology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/336
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Microbiology
1
An 8-year-old girl is brought to the office for evaluation of a skin rash on her upper back. The rash is not painful but is mildly pruritic. She has no prior medical conditions, takes no medications, and is up to date with vaccinations. Vital signs are within normal limits. Right scapular area skin examination is shown in the exhibit.
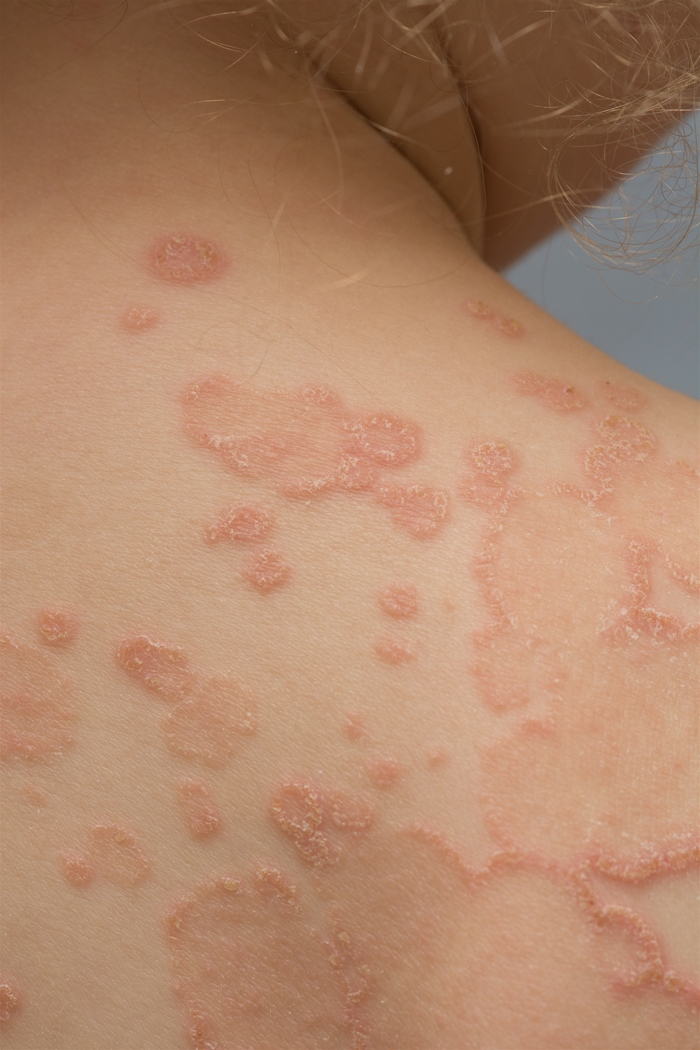
The remainder of the examination is normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current condition?
A)Deep tissue invasion by normal skin flora
B)Epidermal damage from excessive sun exposure
C)Immunologic response to bacterial pharyngitis
D)Microbial infection of keratinized structures
E)Proliferation of pathogen transmitted by tick bite

The remainder of the examination is normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current condition?
A)Deep tissue invasion by normal skin flora
B)Epidermal damage from excessive sun exposure
C)Immunologic response to bacterial pharyngitis
D)Microbial infection of keratinized structures
E)Proliferation of pathogen transmitted by tick bite
Microbial infection of keratinized structures
2
A 29-year-old man is evaluated for a skin rash involving his hands, feet, and scalp for the last 2 weeks. The rash is mildly pruritic and has progressively worsened. The patient has a history of HIV and is not adherent with antiretroviral therapy. Skin examination shows erythematous patches with scales and crusting. Biopsy of the rash shows organisms burrowed in the epidermis, as shown below: 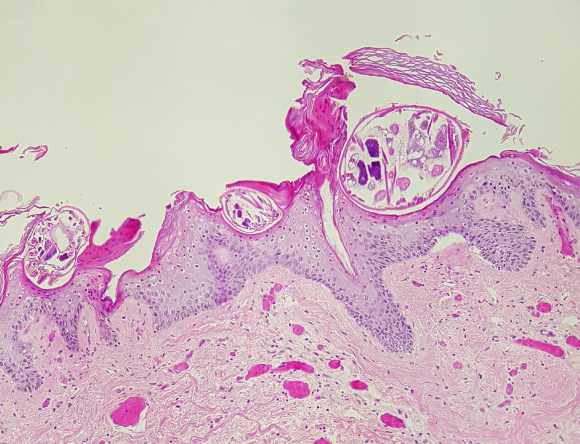 Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?
Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?
A)Systemic acyclovir
B)Systemic terbinafine
C)Topical glucocorticoid
D)Topical mupirocin
E)Topical permethrin
 Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?
Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?A)Systemic acyclovir
B)Systemic terbinafine
C)Topical glucocorticoid
D)Topical mupirocin
E)Topical permethrin
E
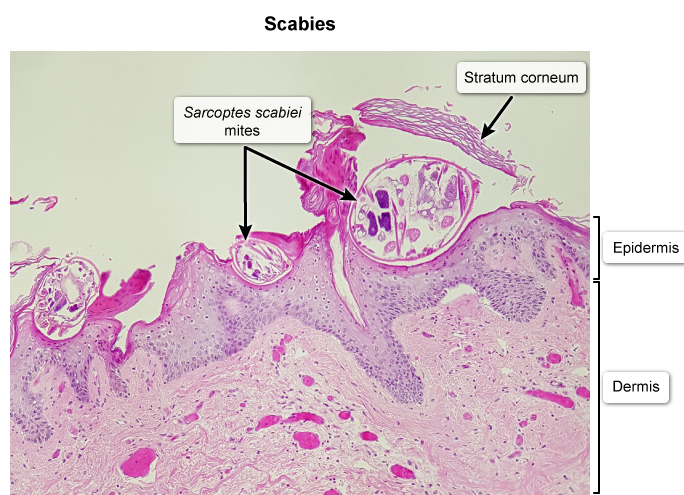
Scabies is a skin infection caused by the human itch mite, Sarcoptes scabiei. Transmission occurs from prolonged skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual but may occasionally occur due to contact with contaminated fomites (eg, bedsheets, clothing). Mites burrow under the epidermis and evoke a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction to mite feces and eggs, which leads to an intensely pruritic rash. The mites can often be seen on microscopy.
Classic scabies is associated with a mild mite burden (10-15 mites). Patients usually have several small erythematous papules on the sides/webs of the fingers, wrists, elbows, axillae, waist, and genitalia. Excoriations and burrows (thin, serpiginous red tracks) may be seen. In contrast, patients with impaired cell-mediated immunity (eg, HIV) are unable to contain the infection and usually develop crusted scabies, which is associated with thousands or millions of mites. These patients often have mild pruritis (because the inflammatory response is muted) and several erythematous patches with scaling and crusting.
Treatment is required to prevent discomfort, transmission, and potential complications (eg, secondary bacterial infection). First-line therapy includes topical permethrin, which blocks mite neurotransmission by impairing voltage-gated sodium channels. Oral ivermectin, an antiparasitic agent that binds chloride ion channels in invertebrate nerve and muscle cells, is an alternate medication for classic scabies that is used in combination with permethrin for crusted scabies.
(Choice A) Oral acyclovir is used for human herpes simplex virus outbreaks, which are usually characterized by vesicular lesions on an erythematous base. The orolabial mucosa and genital area are affected most commonly. Histopathology would show epidermal blisters with acantholysis and multinucleated cells.
(Choice B) Oral terbinafine can be used for patients with dermatophytic infections of the skin. Dermatophytes often cause an erythematous scaly rash and erosions. Microscopy typically reveals fungal spores and/or hyphae.
(Choice C) Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that can be treated with topical glucocorticoids. It is usually associated with symmetric, sharply defined skin plaques with overlying scales on the extensor elbows, knees, and scalp. Microscopy generally shows uniform epidermal hyperplasia, parakeratosis, dilated capillaries in the papillary dermis, and perivascular lymphocytes.
(Choice D) Topical mupirocin is used for the treatment of impetigo, a superficial bacterial infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. The condition typically presents as a localized papulovesicular rash with surrounding erythema and adherent golden crusts involving the face or extremities.
Educational objective:
Scabies is a human mite infection associated with a pruritic papular rash with excoriations and burrows. Patients with impaired cell-mediated immunity (eg, HIV) often develop a very high mite burden. Treatment with topical permethrin and/or ivermectin is generally curative.

Scabies is a skin infection caused by the human itch mite, Sarcoptes scabiei. Transmission occurs from prolonged skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual but may occasionally occur due to contact with contaminated fomites (eg, bedsheets, clothing). Mites burrow under the epidermis and evoke a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction to mite feces and eggs, which leads to an intensely pruritic rash. The mites can often be seen on microscopy.
Classic scabies is associated with a mild mite burden (10-15 mites). Patients usually have several small erythematous papules on the sides/webs of the fingers, wrists, elbows, axillae, waist, and genitalia. Excoriations and burrows (thin, serpiginous red tracks) may be seen. In contrast, patients with impaired cell-mediated immunity (eg, HIV) are unable to contain the infection and usually develop crusted scabies, which is associated with thousands or millions of mites. These patients often have mild pruritis (because the inflammatory response is muted) and several erythematous patches with scaling and crusting.
Treatment is required to prevent discomfort, transmission, and potential complications (eg, secondary bacterial infection). First-line therapy includes topical permethrin, which blocks mite neurotransmission by impairing voltage-gated sodium channels. Oral ivermectin, an antiparasitic agent that binds chloride ion channels in invertebrate nerve and muscle cells, is an alternate medication for classic scabies that is used in combination with permethrin for crusted scabies.
(Choice A) Oral acyclovir is used for human herpes simplex virus outbreaks, which are usually characterized by vesicular lesions on an erythematous base. The orolabial mucosa and genital area are affected most commonly. Histopathology would show epidermal blisters with acantholysis and multinucleated cells.
(Choice B) Oral terbinafine can be used for patients with dermatophytic infections of the skin. Dermatophytes often cause an erythematous scaly rash and erosions. Microscopy typically reveals fungal spores and/or hyphae.
(Choice C) Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that can be treated with topical glucocorticoids. It is usually associated with symmetric, sharply defined skin plaques with overlying scales on the extensor elbows, knees, and scalp. Microscopy generally shows uniform epidermal hyperplasia, parakeratosis, dilated capillaries in the papillary dermis, and perivascular lymphocytes.
(Choice D) Topical mupirocin is used for the treatment of impetigo, a superficial bacterial infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. The condition typically presents as a localized papulovesicular rash with surrounding erythema and adherent golden crusts involving the face or extremities.
Educational objective:
Scabies is a human mite infection associated with a pruritic papular rash with excoriations and burrows. Patients with impaired cell-mediated immunity (eg, HIV) often develop a very high mite burden. Treatment with topical permethrin and/or ivermectin is generally curative.
3
A 28-year-old man comes to the office due to a rash on the lower extremity. The patient noticed a pruritic papule on the dorsum of his right foot just prior to returning from a south Florida beach 2 days ago. He walked barefoot on the beach but does not recall any trauma. Since his return home, the rash and itching have progressively worsened. The patient has no other medical problems and takes no medications. Physical examination findings are shown below. 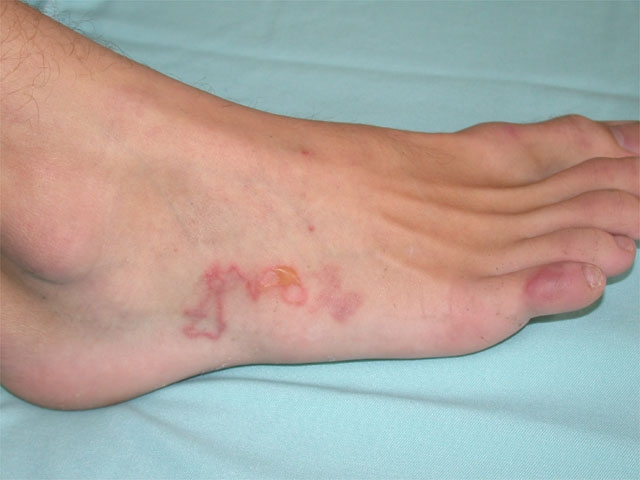 Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current condition?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current condition?
A)Brown recluse spider bite
B)Hookworm infection
C)Mycobacterium marinum infection
D)Sporothrix schenckii infection
E)Staphylococcus aureus infection
F)Vibrio vulnificus infection
 Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current condition?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current condition?A)Brown recluse spider bite
B)Hookworm infection
C)Mycobacterium marinum infection
D)Sporothrix schenckii infection
E)Staphylococcus aureus infection
F)Vibrio vulnificus infection
B
This patient, who developed a serpiginous, pruritic rash shortly after walking barefoot on a beach, likely has hookworm infection. Hookworms spread when egg-containing feces are deposited into shady, warm, moist sand or soil. Eggs hatch into larvae and are transmitted when they come into direct contact with human skin (eg, when walking barefoot).
Dermal penetration is usually marked by a pruritic maculopapular lesion ("ground itch") at the site of larval entry (eg, foot, toe webs). Spread of larvae through the adjacent dermal tissue can lead to the formation of migrating, reddish-brown, serpiginous tracks. Deeper spread may occur, depending on the species of infecting hookworm, as follows:
Human hookworms (eg, Necator americanus, A duodenale) penetrate the basement membrane and spread from the dermis to the bloodstream. They rupture into the alveoli and are coughed up and swallowed into the small intestine. There, larvae mature into adult hookworms that feed on blood from the duodenal mucosa (often causing iron deficiency anemia) and shed up to 10,000 eggs/day, thereby spreading the infection to others.
Cat and dog hookworms (eg, Ancylostoma braziliense, A caninum) cause a dermal eruption in humans but are unable to penetrate the cutaneous basement membrane and spread to deeper tissues. Therefore, larvae do not mature into adult hookworms or spread from human-to-human (humans are incidental hosts).
(Choice A) A brown recluse spider bite usually appears as a red plaque or papule with central pallor; it may develop a dark central eschar that ulcerates due to necrosis. Pain is often severe.
(Choice C) Mycobacterium marinum lesions usually form a few weeks after exposure to contaminated fresh/salt water (eg, swimming pool, fish tank). Lesions begin as solitary papules or nodules that eventually ulcerate and scar. Serpiginous tracts would be uncommon.
(Choice D) Sporothrix schenckii, a dimorphic fungus, is usually transmitted when contaminated organic material (eg, moss, soil) is inoculated into the skin or subcutaneous tissue. A papule forms at the inoculation site and usually ulcerates; additional lesions form along the proximal route of lymphatic drainage.
(Choice E) Staphylococcus aureus is the most common cause of purulent cellulitis. Lesions tend to develop over days and are characterized by painful areas of fluctuance with surrounding erythema.
(Choice F) Vibrio vulnificus is a free-living bacterium that grows in brackish water and marine environments. It can contaminate wounds and cause mild cellulitis. More severe manifestations (eg, myositis, necrotizing fasciitis, sepsis) can develop in patients with certain underlying comorbidities (eg, liver disease, hemochromatosis).
Educational objective:
Hookworm infections are transmitted via direct contact between human skin and contaminated soil/sand (eg, walking barefoot). Dermal penetration is often characterized by an intensely pruritic papule that may form serpiginous tracks due to the subcutaneous migration of hookworm larvae.
This patient, who developed a serpiginous, pruritic rash shortly after walking barefoot on a beach, likely has hookworm infection. Hookworms spread when egg-containing feces are deposited into shady, warm, moist sand or soil. Eggs hatch into larvae and are transmitted when they come into direct contact with human skin (eg, when walking barefoot).
Dermal penetration is usually marked by a pruritic maculopapular lesion ("ground itch") at the site of larval entry (eg, foot, toe webs). Spread of larvae through the adjacent dermal tissue can lead to the formation of migrating, reddish-brown, serpiginous tracks. Deeper spread may occur, depending on the species of infecting hookworm, as follows:
Human hookworms (eg, Necator americanus, A duodenale) penetrate the basement membrane and spread from the dermis to the bloodstream. They rupture into the alveoli and are coughed up and swallowed into the small intestine. There, larvae mature into adult hookworms that feed on blood from the duodenal mucosa (often causing iron deficiency anemia) and shed up to 10,000 eggs/day, thereby spreading the infection to others.
Cat and dog hookworms (eg, Ancylostoma braziliense, A caninum) cause a dermal eruption in humans but are unable to penetrate the cutaneous basement membrane and spread to deeper tissues. Therefore, larvae do not mature into adult hookworms or spread from human-to-human (humans are incidental hosts).
(Choice A) A brown recluse spider bite usually appears as a red plaque or papule with central pallor; it may develop a dark central eschar that ulcerates due to necrosis. Pain is often severe.
(Choice C) Mycobacterium marinum lesions usually form a few weeks after exposure to contaminated fresh/salt water (eg, swimming pool, fish tank). Lesions begin as solitary papules or nodules that eventually ulcerate and scar. Serpiginous tracts would be uncommon.
(Choice D) Sporothrix schenckii, a dimorphic fungus, is usually transmitted when contaminated organic material (eg, moss, soil) is inoculated into the skin or subcutaneous tissue. A papule forms at the inoculation site and usually ulcerates; additional lesions form along the proximal route of lymphatic drainage.
(Choice E) Staphylococcus aureus is the most common cause of purulent cellulitis. Lesions tend to develop over days and are characterized by painful areas of fluctuance with surrounding erythema.
(Choice F) Vibrio vulnificus is a free-living bacterium that grows in brackish water and marine environments. It can contaminate wounds and cause mild cellulitis. More severe manifestations (eg, myositis, necrotizing fasciitis, sepsis) can develop in patients with certain underlying comorbidities (eg, liver disease, hemochromatosis).
Educational objective:
Hookworm infections are transmitted via direct contact between human skin and contaminated soil/sand (eg, walking barefoot). Dermal penetration is often characterized by an intensely pruritic papule that may form serpiginous tracks due to the subcutaneous migration of hookworm larvae.
4
A 6-month-old boy is brought to the emergency department due to poor feeding, irritability, and rash. He was well-appearing until 2 days ago, when he developed little interest in drinking and a progressive rash. Physical examination reveals diffuse erythema and desquamation that is most prominent at the neck, axillae, inguinal folds, and perioral region. The perioral area also has crusting and the lips are dry and cracked, but the mucosal membranes are normal. The epidermis easily comes off with gentle pressure at the erythematous areas. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
A)Autoantibody binding to epithelial cell surface
B)Cell-mediated hypersensitivity
C)Endotoxin-mediated inflammatory response
D)Exotoxin-mediated skin damage
E)Mast cell degranulation
A)Autoantibody binding to epithelial cell surface
B)Cell-mediated hypersensitivity
C)Endotoxin-mediated inflammatory response
D)Exotoxin-mediated skin damage
E)Mast cell degranulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A 34-year-old man is admitted to the intensive care unit due to fever, chills, shortness of breath, and altered mental status. His symptoms began 3 days ago and have progressively worsened over the last 24 hours. His past medical history is significant for a motor vehicle accident 2 years ago in which he sustained blunt abdominal trauma and required emergency laparotomy due to internal bleeding. His blood pressure is 81/44 mm Hg and pulse is 122/min. He is started on broad-spectrum antibiotics, intravenous fluids, and vasopressors. His condition continues to deteriorate and he dies in the hospital several hours later despite extensive resuscitation efforts. Blood cultures obtained on admission grow Streptococcus pneumoniae. Impairment of which of the following mechanisms most likely contributed to the severity of this patient's infection?
A)Complement production
B)Immediate hypersensitivity
C)Intracellular killing
D)Systemic bacterial clearance
E)Type I interferon release
A)Complement production
B)Immediate hypersensitivity
C)Intracellular killing
D)Systemic bacterial clearance
E)Type I interferon release

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A 46-year-old man comes to the office due to skin lesions that developed on his left arm over the past few days. The lesions are not particularly painful. The patient has never had similar symptoms. He has had no fevers and otherwise feels fine. Past medical history is insignificant. The patient takes no medications and has no allergies. Temperature is 37.1 C (98.8 F). The lesions are shown in the image below. 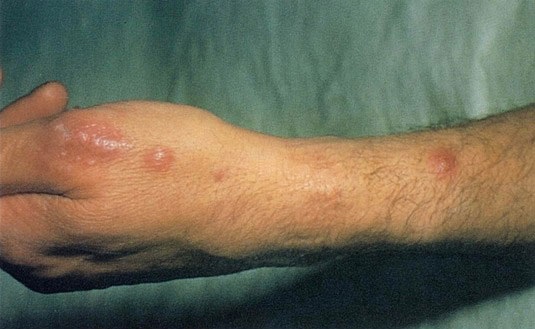 Following pathologic sampling, the lesions are determined to be fungal in etiology. Which of the following scenarios is most likely a component of this patient's history?
Following pathologic sampling, the lesions are determined to be fungal in etiology. Which of the following scenarios is most likely a component of this patient's history?
A)Animal contact
B)Bat guano exposure
C)Exposure to seawater
D)Immune system disease
E)Recent antibiotic use
F)Thorn prick
 Following pathologic sampling, the lesions are determined to be fungal in etiology. Which of the following scenarios is most likely a component of this patient's history?
Following pathologic sampling, the lesions are determined to be fungal in etiology. Which of the following scenarios is most likely a component of this patient's history?A)Animal contact
B)Bat guano exposure
C)Exposure to seawater
D)Immune system disease
E)Recent antibiotic use
F)Thorn prick

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A 68-year-old woman comes to the office for evaluation of a skin rash. The patient says that red, painful papules erupted on her right chest 5 days ago and quickly turned into vesicles containing clear fluid. The lesions are now beginning to crust and are less painful. She has never had similar lesions and does not recall coming into contact with a person having a similar illness. Medical history is significant only for well-controlled hypertension. Physical examination shows a grouped vesicular rash involving the right T4 dermatome that is beginning to heal with crusting. The rash does not cross the midline. Lightly touching the skin elicits sharp pain. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. This patient is at greatest risk of developing which of the following complications as a result of her current condition?
A)Dissemination of rash to other body areas
B)Painful swelling of the large joints
C)Persistent pain in the affected region
D)Recurrent episodes of gross hematuria
E)Sensory loss in "glove and stocking" pattern
A)Dissemination of rash to other body areas
B)Painful swelling of the large joints
C)Persistent pain in the affected region
D)Recurrent episodes of gross hematuria
E)Sensory loss in "glove and stocking" pattern

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A 3-year-old boy is brought to the office due to a 1-day history of fever and irritability. The mother states that the boy has been tugging at his right ear. The patient has had 2 previous episodes of acute otitis media. Temperature is 38.1 C (100.6 F). Otoscopic examination shows a perforated right tympanic membrane with erythema and purulent exudate. Cultures from the exudate yield small, oxidase-positive, gram-negative coccobacilli that grow on factor X- and factor V-supplemented media, consistent with Haemophilus influenzae. The patient's immunizations are up to date. Which of the following best explains this patient's susceptibility to the pathogen causing his current infection?
A)No vaccine is effective against H influenzae
B)The patient has defective cell-mediated immunity
C)The patient has defective neutrophil function
D)The strain responsible for this patient's disease does not produce a capsule
E)The strain responsible for this patient's disease produces exotoxin
A)No vaccine is effective against H influenzae
B)The patient has defective cell-mediated immunity
C)The patient has defective neutrophil function
D)The strain responsible for this patient's disease does not produce a capsule
E)The strain responsible for this patient's disease produces exotoxin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A 55-year-old man comes to the emergency department with fever and chills. He has a history of acute myeloid leukemia for which he is receiving chemotherapy. His temperature is 38.3 C (101 F), blood pressure is 90/50 mm Hg, pulse is 124/min, and respirations are 22/min. Physical examination is notable for multiple skin patches with necrotic centers and occasional ulcerations, as shown in the image below. 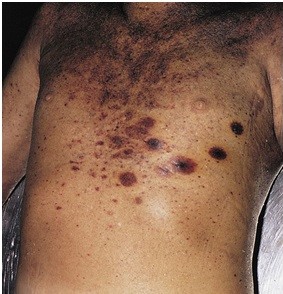 Laboratory results are as follows:
Laboratory results are as follows:  Blood cultures are drawn. Which of the following organisms is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
Blood cultures are drawn. Which of the following organisms is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
A)Escherichia coli
B)Haemophilus influenzae
C)Klebsiella pneumoniae
D)Pseudomonas aeruginosa
E)Streptococcus pneumoniae
F)Streptococcus pyogenes
 Laboratory results are as follows:
Laboratory results are as follows:  Blood cultures are drawn. Which of the following organisms is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
Blood cultures are drawn. Which of the following organisms is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?A)Escherichia coli
B)Haemophilus influenzae
C)Klebsiella pneumoniae
D)Pseudomonas aeruginosa
E)Streptococcus pneumoniae
F)Streptococcus pyogenes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A 62-year-old man is brought to the emergency department from a homeless shelter due to alcohol intoxication. The patient has no other symptoms or history of significant medical conditions. Examination of the scalp reveals the findings shown in the exhibit. 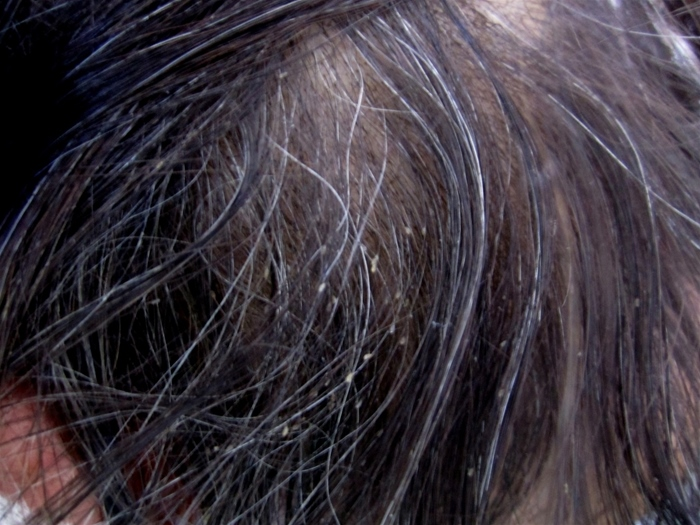
Which of the following organisms is most likely responsible for this patient's condition?
A)Cimex lectularius
B)Malassezia species
C)Pediculus humanus capitis
D)Pthirus pubis
E)Sarcoptes scabiei
F)Trichophyton tonsurans

Which of the following organisms is most likely responsible for this patient's condition?
A)Cimex lectularius
B)Malassezia species
C)Pediculus humanus capitis
D)Pthirus pubis
E)Sarcoptes scabiei
F)Trichophyton tonsurans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A 60-year-old woman comes to the physician with 10 days of diffuse itching. A rash began on her hands and quickly spread to involve her wrists, arms, and axillae. She has difficulty sleeping and complains of intense itching in these areas. She works in a day care center and primarily takes care of children age 2-5. The patient has no other medical conditions and takes no chronic medications. Vital signs are normal. Her BMI is 24 kg/m2. Skin examination shows small erythematous papules on the palms with excoriations, scattered vesicles, and pustules on the finger webs, palms, and wrist creases, as seen in the image below. She has similar lesions in her axillary skin folds bilaterally. The remainder of the examination is within normal limits. 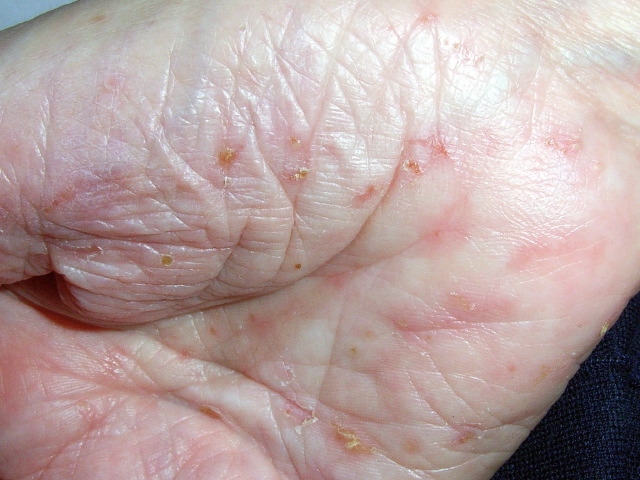 Which of the following is the most likely finding on skin sampling of this patient's lesions?
Which of the following is the most likely finding on skin sampling of this patient's lesions?
A)Budding yeast
B)Molluscum bodies
C)Multinucleated giant cells
D)Necrotic keratinocytes in the epidermis
E)Sarcoptes scabiei mite and eggs
 Which of the following is the most likely finding on skin sampling of this patient's lesions?
Which of the following is the most likely finding on skin sampling of this patient's lesions?A)Budding yeast
B)Molluscum bodies
C)Multinucleated giant cells
D)Necrotic keratinocytes in the epidermis
E)Sarcoptes scabiei mite and eggs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A 22-year-old man comes to the office due to skin lesions. The patient noticed a nonpainful, nonpruritic skin bump on his right knee 3 months ago, which progressively increased in size and number. He has no prior health issues and takes no medications. The patient is outdoors frequently for work and recreational activities. He is sexually active. Physical examination findings are shown in the exhibit. 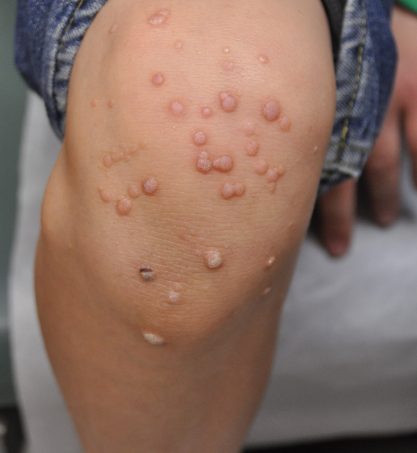
Which of the following microbial organisms is most likely responsible for this patient's current condition?
A)Coxsackievirus
B)Herpes simplex virus
C)Human papillomavirus
D)Neisseria gonorrhoeae
E)Pox virus
F)Treponema pallidum

Which of the following microbial organisms is most likely responsible for this patient's current condition?
A)Coxsackievirus
B)Herpes simplex virus
C)Human papillomavirus
D)Neisseria gonorrhoeae
E)Pox virus
F)Treponema pallidum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A 38-year-old woman comes to the office for evaluation of a skin lesion. It began as a pink papule on her right arm and has progressively enlarged over several weeks. The lesion is not pruritic or painful and has not been associated with fever or other systemic symptoms. The patient returned from a trip to Costa Rica 5 weeks ago. During her travel, she stayed at a beachside resort and hiked in the rainforest. Skin examination findings are shown below. Biopsy of the lesion reveals intracellular, round-oval protozoa with rod-shaped kinetoplasts. Which of the following most likely led to this patient's current condition? 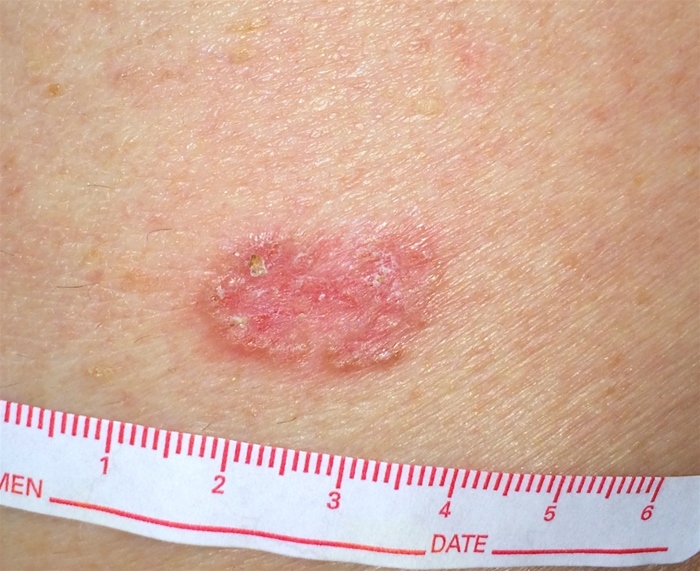
A)Bite from infected sand fly
B)Contact with infected person
C)Exposure to decaying vegetation
D)Handling of infected animal
E)Swimming in contaminated water

A)Bite from infected sand fly
B)Contact with infected person
C)Exposure to decaying vegetation
D)Handling of infected animal
E)Swimming in contaminated water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A 73-year-old woman comes to the physician complaining of progressive, severe pain and discharge from her left ear for the past 2 days. She has had type 2 diabetes for many years and has been noncompliant with her medications and follow-up appointments. On examination, moving or touching the pinna produces extreme pain. Otoscopic examination shows granulation tissue in the left ear canal with a scant amount of discharge. The tympanic membrane is clear, and there is no middle ear effusion. Initial cultures from the ear show a Gram-negative rod. Which of the following microbiological characteristics best describes the infecting organism?
A)Comma-shaped and grows well in high pH
B)Fast lactose fermenter
C)Motile and oxidase positive
D)Nonmotile and a lactose nonfermenter
E)Requires factors V and X for growth
A)Comma-shaped and grows well in high pH
B)Fast lactose fermenter
C)Motile and oxidase positive
D)Nonmotile and a lactose nonfermenter
E)Requires factors V and X for growth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A 36-year-old man comes to the office to discuss a skin rash on his shoulders and upper chest. The patient first noticed the rash 2 months ago while vacationing at a beach resort. The rash has worsened progressively and is associated with mild pruritus, but he has no other associated symptoms. The patient is a road construction worker, and often works in hot, humid areas. Past medical history is notable for seasonal allergies and childhood asthma. He does not use tobacco or alcohol. Skin examination findings are shown in the image below. 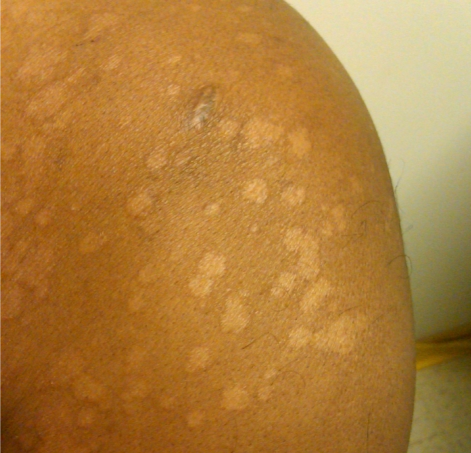 Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
A)Blastomyces dermatitidis
B)Candida albicans
C)Histoplasma capsulatum
D)Malassezia globosa
E)Microsporum canis
F)Rhizopus species
G)Sporothrix schenckii
 Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?A)Blastomyces dermatitidis
B)Candida albicans
C)Histoplasma capsulatum
D)Malassezia globosa
E)Microsporum canis
F)Rhizopus species
G)Sporothrix schenckii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A 3-year-old boy is brought to the clinic due to left ear pain over the past 3 days. Last week, the patient developed a runny nose and cough, which resolved 2 days prior to the development of ear pain. He has no chronic medical conditions. Temperature is 38.4 C (101.1 F). There is purulent drainage from the left ear. Otoscopic examination of the left ear reveals a normal-appearing external canal and an erythematous tympanic membrane with purulent fluid pooling within the distal external canal. Which of the following organisms is the most likely cause of this patient's diagnosis?
A)Klebsiella pneumoniae
B)Moraxella catarrhalis
C)Proteus mirabilis
D)Pseudomonas aeruginosa
E)Staphylococcus aureus
F)Streptococcus pneumoniae
A)Klebsiella pneumoniae
B)Moraxella catarrhalis
C)Proteus mirabilis
D)Pseudomonas aeruginosa
E)Staphylococcus aureus
F)Streptococcus pneumoniae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A 58-year-old asymptomatic woman comes to the office for a health checkup prior to starting volunteer work at a hospital. She has a history of hypothyroidism and takes levothyroxine. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Her examination findings are unremarkable. During a laboratory test, her white blood cells are incubated with mycobacterial antigens. Compared to the control, a large amount of interferon-gamma is detected in her blood sample. Which of the following cell types is most directly responsible for this finding?
A)B lymphocytes
B)Basophils
C)Eosinophils
D)Monocytes
E)Neutrophils
F)T lymphocytes
A)B lymphocytes
B)Basophils
C)Eosinophils
D)Monocytes
E)Neutrophils
F)T lymphocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A 34-year-old woman comes to the office due to skin changes. Blotches of skin on her arms appear to be of a different color, and she also has a tingling sensation in her hands. These symptoms have developed over the past several months. The patient has no other past medical history. She is a political refugee from East Africa. On examination, there are patchy areas of skin anesthesia and hypopigmentation on her upper extremities. Nerve biopsy evaluated under light microscopy shows many organisms invading Schwann cells. HIV testing is negative. Which of the following organisms is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
A)Borrelia burgdorferi
B)Campylobacter fetus
C)Corynebacterium diphtheriae
D)Mycobacterium leprae
E)Treponema pallidum
A)Borrelia burgdorferi
B)Campylobacter fetus
C)Corynebacterium diphtheriae
D)Mycobacterium leprae
E)Treponema pallidum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A 64-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to worsening left lower extremity pain, swelling, and redness over the past 3 days. The patient has had no trauma but reports feeling feverish. Medical history is significant for hypertension and obesity. Temperature is 38 C (100.4 F), blood pressure is 130/86 mm Hg, pulse is 92/min, and respirations are 18/min. BMI is 35 kg/m2. Physical examination shows diffuse erythema extending up to the left midcalf with indistinct border. There is increased warmth, tenderness, and edema of the left leg. No areas of fluctuation or purulent exudate are present, but the interdigital skin of the feet is macerated and fissured. Laboratory testing shows neutrophilic leukocytosis, and Doppler ultrasonography is negative for deep venous thrombosis. Infection with which of the following organisms is most likely responsible for this patient's current symptoms?
A)Beta-hemolytic streptococci
B)Candida albicans
C)Clostridium perfringens
D)Mycobacterium marinum
E)Pseudomonas aeruginosa
F)Staphylococcus epidermidis
A)Beta-hemolytic streptococci
B)Candida albicans
C)Clostridium perfringens
D)Mycobacterium marinum
E)Pseudomonas aeruginosa
F)Staphylococcus epidermidis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A 34-year-old woman comes to the office due to 3 days of discomfort and swelling in the right axilla. The patient has no known medical problems. She is the local community veterinarian and volunteers as a swim coach at her children's school. She owns a parrot and a hamster. Temperature is 36.9 C (98.4 F). On physical examination, there is an enlarged, tender axillary lymph node on the right, measuring about 3 cm and with slight surrounding erythema but no skin breakdown. There is no other area of lymphadenopathy present. Several scratch marks are seen on the right arm. The organism responsible for the lymphadenopathy is also associated with which of the following conditions?
A)Bacillary angiomatosis
B)Bladder cancer
C)Condylomata acuminata
D)Hemolytic uremic syndrome
E)Malignant external otitis
F)Toxic shock syndrome
A)Bacillary angiomatosis
B)Bladder cancer
C)Condylomata acuminata
D)Hemolytic uremic syndrome
E)Malignant external otitis
F)Toxic shock syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A 34-year-old nulligravid woman comes to the office due to vulvar itching and vaginal discharge. She has no other concerns. The patient is sexually active with her fiancé and takes oral contraceptives daily. She does not use barrier contraception. She took antibiotics 2 weeks ago for sinusitis but has no other medical problems. Pelvic examination shows an erythematous vulva and a thick white discharge that adheres to the vaginal wall. The rest of the physical examination is normal. Microscopic examination reveals budding cells. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of her current condition?
A)Decreased glycogen concentration in the vaginal epithelium
B)Decreased number of gram-positive bacteria in the vagina
C)Decreased thickness of the vaginal epithelium
D)Increased alkaline secretions by the cervical mucosa
E)Viral DNA incorporation into lower genital epithelia
A)Decreased glycogen concentration in the vaginal epithelium
B)Decreased number of gram-positive bacteria in the vagina
C)Decreased thickness of the vaginal epithelium
D)Increased alkaline secretions by the cervical mucosa
E)Viral DNA incorporation into lower genital epithelia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A 36-year-old immigrant from Peru comes to the office due to difficulty swallowing liquids. He also has difficulty belching. Eating slowly and extending the neck partially relieves his symptoms. The patient has had no fever, weight loss, chest pain, cough, dyspnea, or neurologic symptoms. He has no chronic medical problems and takes no medications. He has been an active smoker for the last 18 years but does not use alcohol or illicit drugs. The patient is afebrile with normal vital signs. BMI is 24 kg/m2. On examination, the abdomen is soft, nondistended, and nontender, with no masses or organomegaly. Bowel sounds are normal. Other examination findings are unremarkable. Barium swallow shows a dilated esophagus, and manometry confirms absent peristalsis in the smooth muscle portion of the esophagus. If this patient's symptoms are caused by an infection, which of the following organisms is the most likely cause?
A)Candida albicans
B)Clostridium botulinum
C)Cytomegalovirus
D)Helicobacter pylori
E)Schistosoma mansoni
F)Trypanosoma cruzi
A)Candida albicans
B)Clostridium botulinum
C)Cytomegalovirus
D)Helicobacter pylori
E)Schistosoma mansoni
F)Trypanosoma cruzi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A 32-year-old man is being evaluated due to several weeks of watery diarrhea. He has also had intermittent, crampy abdominal pain and has lost 7 kg (15.4 lb) during this period. The patient has a history of HIV and was hospitalized 6 months ago for Pneumocystis pneumonia. On physical examination, the patient is afebrile, and the abdomen is soft and nontender with no organomegaly. Stool tests for leukocytes and occult blood are negative. Endoscopy is performed, and mucosal biopsy shows an inflammatory infiltrate in the lamina propria and pathogens lining the epithelium, as shown in the exhibit.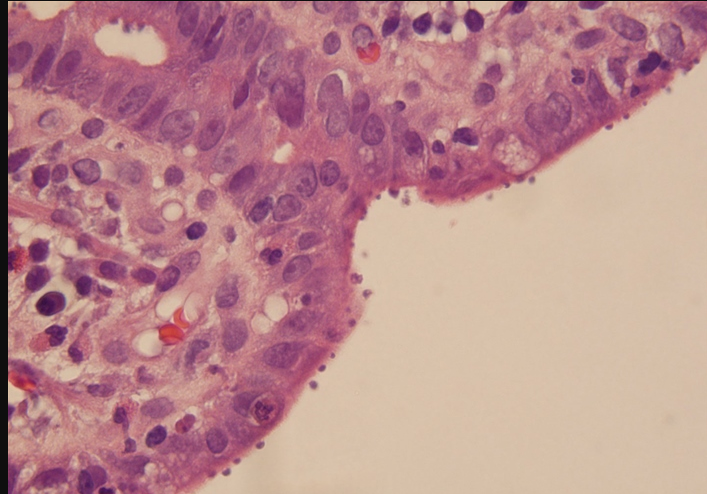
The organisms have a cystic appearance on modified acid-fast staining. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
A)Clostridium difficile
B)Cryptosporidium parvum
C)Entamoeba histolytica
D)Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli
E)Giardia lamblia
F)Mycobacterium avium complex
G)Salmonella enteritidis

The organisms have a cystic appearance on modified acid-fast staining. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
A)Clostridium difficile
B)Cryptosporidium parvum
C)Entamoeba histolytica
D)Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli
E)Giardia lamblia
F)Mycobacterium avium complex
G)Salmonella enteritidis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A 46-year-old homeless man comes to the emergency department with fever and chest pain that worsens with swallowing. The patient has been hospitalized several times recently with Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia. He has a history of intravenous drug use. His temperature is 37.8 C (100 F). Oropharyngeal examination is remarkable only for poor dentition. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is performed and reveals esophageal hyperemia and linear ulcerations. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
A)Babesia microti
B)Cryptococcus neoformans
C)Cytomegalovirus
D)Isospora belli
E)Toxoplasma gondii
F)Trypanosoma cruzi
G)Varicella zoster virus
A)Babesia microti
B)Cryptococcus neoformans
C)Cytomegalovirus
D)Isospora belli
E)Toxoplasma gondii
F)Trypanosoma cruzi
G)Varicella zoster virus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A 23-year-old woman comes to the emergency department for evaluation of right lower abdominal pain and bloody vaginal discharge. Her symptoms began this morning and are progressively worsening. She is sexually active with 1 male partner. The patient takes no daily medications and has no known drug allergies. Her last menstrual period was 5 weeks ago, and she has never been pregnant. Blood pressure is 112/70 mm Hg while supine and 96/60 mm Hg while standing. The patient is tachycardic and ill appearing. On pelvic examination, the uterus is small and mobile, and there is right adnexal tenderness. Laboratory results are as follows:  This patient's clinical presentation is most likely due to a prior infection with which of the following pathogens?
This patient's clinical presentation is most likely due to a prior infection with which of the following pathogens?
A)Escherichia coli
B)Gardnerella vaginalis
C)Herpes simplex virus
D)Human papillomavirus
E)Neisseria gonorrhoeae
F)Treponema pallidum
G)Trichomonas vaginalis
 This patient's clinical presentation is most likely due to a prior infection with which of the following pathogens?
This patient's clinical presentation is most likely due to a prior infection with which of the following pathogens?A)Escherichia coli
B)Gardnerella vaginalis
C)Herpes simplex virus
D)Human papillomavirus
E)Neisseria gonorrhoeae
F)Treponema pallidum
G)Trichomonas vaginalis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A 34-year-old woman comes to the office with recent onset of malaise. The patient reports feeling "run down and under the weather" but otherwise has no symptoms. She is an avid cyclist and is concerned about her ability to participate in a charity race in 3 days. The patient works as a nurse at a local hospital and lives at home with her husband and 2-year-old son. She occasionally smokes when she goes out, but since she began feeling ill, she no longer has the desire to smoke. Physical examination is notable for hepatomegaly. Laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following is most likely to be elicited on further history taking?
Which of the following is most likely to be elicited on further history taking?
A)Had a tattoo recently at a local tattoo parlor
B)Had an accidental needlestick exposure at work
C)Had boiled eggs from the hospital cafeteria
D)Had steamed oysters at a neighborhood restaurant
E)Had unprotected sexual intercourse with a new partner
 Which of the following is most likely to be elicited on further history taking?
Which of the following is most likely to be elicited on further history taking?A)Had a tattoo recently at a local tattoo parlor
B)Had an accidental needlestick exposure at work
C)Had boiled eggs from the hospital cafeteria
D)Had steamed oysters at a neighborhood restaurant
E)Had unprotected sexual intercourse with a new partner

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A 32-year-old woman, gravida 1 para 1, comes to the office for vaginal discharge. The patient has no chronic medical conditions and takes no daily medications. Her last menstrual period was 3 weeks ago. The patient has recently become sexually active with a new partner and uses an intrauterine device for contraception. Cytology of the discharge is shown in the image below: 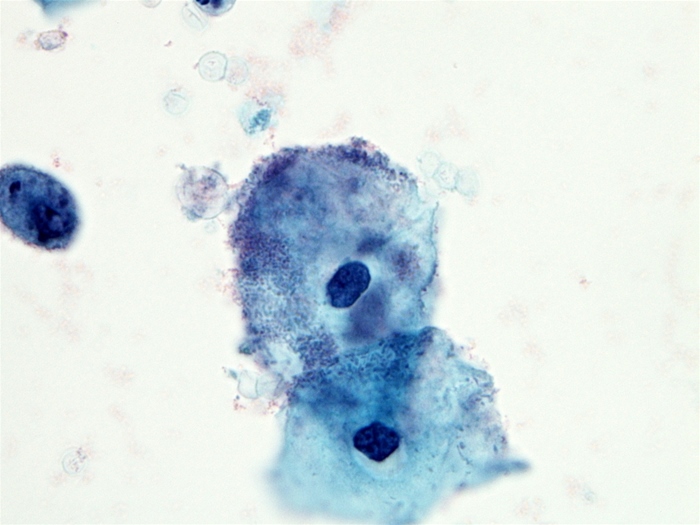 Which of the following best describes the predominant organism causing this patient's condition?
Which of the following best describes the predominant organism causing this patient's condition?
A)Anaerobic gram-variable rod
B)Diploid fungus
C)Gram-negative diplococcus
D)Intracellular gram-negative bacterium
E)Motile protozoan
F)Naked DNA virus
 Which of the following best describes the predominant organism causing this patient's condition?
Which of the following best describes the predominant organism causing this patient's condition?A)Anaerobic gram-variable rod
B)Diploid fungus
C)Gram-negative diplococcus
D)Intracellular gram-negative bacterium
E)Motile protozoan
F)Naked DNA virus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A 16-year-old, previously healthy girl comes to the office due to vaginal discharge that began 5 days ago. The discharge is grayish-white and fishy smelling. The patient is sexually active with a male partner and occasionally uses condoms. Temperature is 36.7 C (98.1 F), blood pressure is 106/52 mm Hg, and pulse is 78/min. Examination shows a small amount of grayish discharge in the vaginal vault. The cervix appears normal. Which of the following would most likely be seen on wet mount microscopy?
A)Epithelial cells covered with bacteria
B)Epithelial cells with rare leukocytes
C)Gram-negative intracellular diplococci
D)Leukocytes and pear-shaped organisms
E)Pseudohyphae with leukocytes
A)Epithelial cells covered with bacteria
B)Epithelial cells with rare leukocytes
C)Gram-negative intracellular diplococci
D)Leukocytes and pear-shaped organisms
E)Pseudohyphae with leukocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A 79-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department from the nursing home due to explosive diarrhea. Laboratory studies show leukocytosis, and results from a stool specimen return positive for Clostridium difficile toxin genes by polymerase chain reaction. Three days later, one of the nurses who cared for the patient at the nursing home is admitted with diarrhea and is found to have C difficile infection. However, the other nurses who also took care of the patient are asymptomatic and do not develop the infection. If all the nurses were similarly exposed to C difficile, which of the following is the most likely reason that the asymptomatic nurses did not develop the infection?
A)Adequate pancreatic enzyme secretion
B)Intact cell-mediated immunity
C)Preformed antispore immunoglobulins
D)Preserved intestinal microbiome
E)Rapid gastrointestinal transit and expulsion of spores
A)Adequate pancreatic enzyme secretion
B)Intact cell-mediated immunity
C)Preformed antispore immunoglobulins
D)Preserved intestinal microbiome
E)Rapid gastrointestinal transit and expulsion of spores

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A 23-year-old man has 2 days of fever, cough, sore throat, and runny nose. His temperature is 38 C (100.4 F). Lung sounds are clear to auscultation. A nasopharyngeal swab is obtained. Naked viral particles are seen, and purified RNA molecules are extracted from these particles. Once introduced into human cells, the purified RNA molecules induce viral protein synthesis and viral genome replication. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
A)HIV
B)Influenza virus type A
C)Respiratory syncytial virus
D)Rhinovirus
E)Rotavirus
A)HIV
B)Influenza virus type A
C)Respiratory syncytial virus
D)Rhinovirus
E)Rotavirus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A 22-year-old woman comes to the emergency department with dysuria, vulvar pain, and pruritus. The patient has also felt feverish and fatigued for the last few days. She has a new sexual partner and has been using a hormonal vaginal ring for contraception. Physical examination reveals bilateral inguinal lymphadenopathy and tender vesicular lesions covering the labia majora and perineum. Which of the following conditions will most likely result as a sequela of this patient's infection?
A)Fluctuant lymphadenitis
B)Locomotor ataxia
C)Postherpetic neuralgia
D)Recurrent genital ulcers
E)Squamous cell vulvar carcinoma
A)Fluctuant lymphadenitis
B)Locomotor ataxia
C)Postherpetic neuralgia
D)Recurrent genital ulcers
E)Squamous cell vulvar carcinoma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A 5-month-old boy is brought to the emergency department due to poor feeding, weakness, and complete loss of extremity muscle tone. Vaccinations are up to date, and there is no significant medical history. The patient receives formula as his sole source of nutrition except for occasional fruit juice and honey. Which of the following is most likely to confirm the diagnosis in this patient?
A)Blood test for liver enzymes
B)Blood test for viral titers
C)Stool test for bacterial toxins
D)Stool test for occult blood
E)Urine test for amino acids
F)Urine test for glucose and ketones
A)Blood test for liver enzymes
B)Blood test for viral titers
C)Stool test for bacterial toxins
D)Stool test for occult blood
E)Urine test for amino acids
F)Urine test for glucose and ketones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A 46-year-old HIV-positive man is hospitalized with fever, cramping abdominal pain, and watery diarrhea. Evaluation shows high fever, hypotension, tachycardia, and lower abdominal distension and tenderness. Abdominal x-ray reveals free intraperitoneal air, and the patient is taken for urgent exploratory laparotomy. Operative findings include an erythematous and dilated colon. A focus of bowel wall necrosis with perforation is resected. Histopathologic analysis reveals acute inflammatory changes, epithelial necrosis, and a layer of denuded epithelium, fibrin, and inflammatory cells overlaying the mucosa. Which of the following pathogens is most likely responsible for this patient's current condition?
A)Campylobacter jejuni
B)Clostridioides difficile
C)Salmonella typhi
D)Shigella flexneri
E)Vibrio cholerae
A)Campylobacter jejuni
B)Clostridioides difficile
C)Salmonella typhi
D)Shigella flexneri
E)Vibrio cholerae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A 22-year-old male presents to the emergency department complaining of fever, abdominal pain, and vomiting. He has had these symptoms for the past four days, but has not sought medical attention because of concerns over the cost of treatment. On examination, the patient appears acutely ill. There is right lower quadrant tenderness with rebound as well as a palpable mass. CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis demonstrates a periappendiceal fluid collection. Culture of this fluid would most likely isolate which of the following organisms?
A)Staphylococcus aureus
B)Actinomyces
C)Candida albicans
D)Bacteroides fragilis
E)Entamoeba histolytica
A)Staphylococcus aureus
B)Actinomyces
C)Candida albicans
D)Bacteroides fragilis
E)Entamoeba histolytica

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A 65-year-old man comes to the office due to pain, redness, and swelling in his right calf. The patient is diagnosed with cellulitis and is started on clindamycin. A few days after starting treatment, he develops watery diarrhea and abdominal cramps. The patient is hospitalized, and complete blood count reveals leukocytosis. The toxin responsible for his current condition most directly impairs which of the following components of intestinal mucosal cells?
A)Apical ion transport
B)Cell membrane integrity
C)Cytoskeleton integrity
D)Mitochondrial energy production
E)Ribosomal protein synthesis
A)Apical ion transport
B)Cell membrane integrity
C)Cytoskeleton integrity
D)Mitochondrial energy production
E)Ribosomal protein synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A 20-year-old woman comes to the office due to increasing vaginal discharge and vulvar pruritus. The patient has had vaginal discharge for the past 4 days. She is sexually active with multiple partners and uses oral contraceptive pills. Vital signs are normal. Pelvic examination is performed, and wet mount microscopy of a vaginal swab is shown in the exhibit. 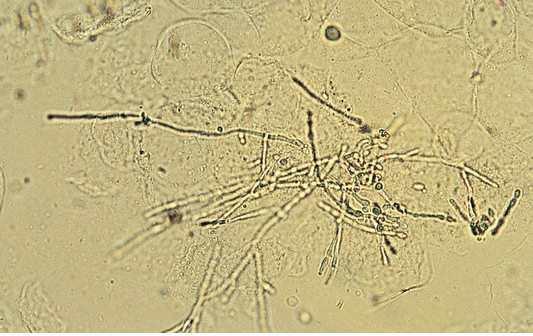
Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy for this patient?
A)Acyclovir
B)Ceftriaxone
C)Clindamycin
D)Doxycycline
E)Fluconazole
F)Metronidazole

Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy for this patient?
A)Acyclovir
B)Ceftriaxone
C)Clindamycin
D)Doxycycline
E)Fluconazole
F)Metronidazole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A 24-year-old woman comes to the office due to copious green vaginal discharge and burning with urination for 3 days. The patient had a yeast infection a year ago, which was treated with over-the-counter medication. She has recently become sexually active with a new partner and occasionally uses condoms. Physical examination shows a yellow-green, frothy vaginal discharge and diffuse vaginal erythema but no lesions. The uterus is anteverted with no cervical motion tenderness. Which of the following is the best test to confirm the diagnosis in this patient?
A)Cervical cytology
B)Gram stain
C)Potassium hydroxide testing
D)Urine culture
E)Vaginal pH
F)Wet mount saline microscopy
A)Cervical cytology
B)Gram stain
C)Potassium hydroxide testing
D)Urine culture
E)Vaginal pH
F)Wet mount saline microscopy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A 24-year-old woman comes to the office due to spotting after vaginal intercourse. She also has some yellow vaginal discharge and dysuria but no pelvic pain or cramping. The patient has taken combination oral contraceptives for the past 3 years and has had no menses for the past year. Her mother was diagnosed with cervical cancer at age 47. BMI is 35 kg/m2. Vital signs are normal. On examination, the abdomen is soft and nontender. Speculum examination reveals purulent discharge from the cervical os, and the cervix is friable. On bimanual examination, there is no cervical motion tenderness, and the adnexa are nontender bilaterally. Urine pregnancy testing is negative. Microscopy of the discharge shows abundant neutrophils. If left untreated, this patient's condition could lead to which of the following complications?
A)Accelerated ovarian follicle depletion
B)Cervical cancer
C)Cervical insufficiency
D)Endometrial hyperplasia
E)Recurrent urinary tract infection
F)Tubal factor infertility
A)Accelerated ovarian follicle depletion
B)Cervical cancer
C)Cervical insufficiency
D)Endometrial hyperplasia
E)Recurrent urinary tract infection
F)Tubal factor infertility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An 8-year-old boy with acute lymphoblastic leukemia receiving maintenance chemotherapy is hospitalized due to fever and neutropenia. Treatment with broad spectrum intravenous antibiotics is begun and the patient's fever resolves. His neutrophil count increases with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor therapy and blood cultures remain negative. On day 5 of hospitalization, the patient experiences nausea, abdominal cramping, and 6-8 episodes of watery diarrhea. Temperature is 37.7 C (100 F). Physical examination shows mild lower abdominal tenderness without guarding or rebound tenderness. Stool testing for occult blood is negative. Which of the following is the single best stool test to establish the cause of this patient's diarrhea?
A)Culture on sorbitol-MacConkey agar
B)Enzyme immunoassay for bacterial antigen
C)Latex agglutination for viral antigens
D)Microscopy after modified acid-fast staining
E)Microscopy for ova and parasites
F)PCR for bacterial gene encoding a toxin
A)Culture on sorbitol-MacConkey agar
B)Enzyme immunoassay for bacterial antigen
C)Latex agglutination for viral antigens
D)Microscopy after modified acid-fast staining
E)Microscopy for ova and parasites
F)PCR for bacterial gene encoding a toxin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A 24-year-old woman comes to the office due to 2 days of burning during urination and increased urinary frequency and urgency. The patient has had no fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, flank pain, or vaginal discharge, but reports darkening of the urine. She has no other medical conditions and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. The patient is sexually active with her boyfriend and takes an oral contraceptive for birth control. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows mild suprapubic tenderness. There is no costovertebral angle tenderness. Which of the following pathogens is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
A)Candida albicans
B)Chlamydia trachomatis
C)Escherichia coli
D)Gardnerella vaginalis
E)Group B streptococcus
F)Klebsiella pneumoniae
G)Neisseria gonorrhoeae
H)Proteus mirabilis
I)Pseudomonas aeruginosa
J)Staphylococcus aureus
A)Candida albicans
B)Chlamydia trachomatis
C)Escherichia coli
D)Gardnerella vaginalis
E)Group B streptococcus
F)Klebsiella pneumoniae
G)Neisseria gonorrhoeae
H)Proteus mirabilis
I)Pseudomonas aeruginosa
J)Staphylococcus aureus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A 23-year-old man comes to the physician due to a 2-month history of fatigue, malaise, and abdominal discomfort. He is found to have tender hepatomegaly with elevated liver function tests. The patient has never been vaccinated against hepatitis. He has had no raw or uncooked foods recently and recalls no ill contacts. There is no history of blood transfusion. The patient is a graduate student who immigrated to the United States 2 years ago and has not traveled outside the country since. He smokes 2 packs of cigarettes a day and consumes 1 or 2 bottles of beer on weekends. The patient does not use illicit drugs. He has had several episodes of unprotected sex with different female partners within the past year. Which of the following is most likely to be present in this patient?
A)HAV in the stool
B)Serum anti-HAV IgM
C)Serum anti-HBsAg IgG
D)Serum HBsAg
E)Hepatitis C virus RNA viral load in blood
F)Serum anti-hepatitis D virus IgG
A)HAV in the stool
B)Serum anti-HAV IgM
C)Serum anti-HBsAg IgG
D)Serum HBsAg
E)Hepatitis C virus RNA viral load in blood
F)Serum anti-hepatitis D virus IgG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A 54-year-old man comes to the emergency department after vomiting blood. He has also had melena, fatigue, and lethargy over the last 24 hours. The patient emigrated from sub-Saharan Africa 20 years ago and occasionally returns to visit friends and family. Temperature is 37.5 C (99.5 F), blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, and pulse is 115/min. Abdominal palpation reveals an enlarged liver and a spleen tip below the level of the umbilicus. Laboratory results are as follows: 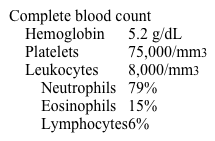 Upper endoscopy reveals bleeding esophageal varices. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's symptoms?
Upper endoscopy reveals bleeding esophageal varices. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's symptoms?
A)Cysticercosis
B)Hookworm infection
C)Malaria
D)Schistosomiasis
E)Toxoplasmosis
 Upper endoscopy reveals bleeding esophageal varices. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's symptoms?
Upper endoscopy reveals bleeding esophageal varices. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's symptoms?A)Cysticercosis
B)Hookworm infection
C)Malaria
D)Schistosomiasis
E)Toxoplasmosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A 65-year-old man comes to the office after his wife insisted he get a checkup. The patient feels well and has no chronic medical conditions but has not seen a physician in many years. He received blood transfusions after a motor vehicle trauma in his 20s. The patient does not use tobacco or illicit drugs but drinks 2 or 3 alcoholic beverages daily. Physical examination reveals no hepatomegaly, ascites, or dilation of the superficial abdominal veins. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Serology is positive for hepatitis C antibodies. Chronic hepatitis C infection is confirmed with positive HCV RNA testing. After appropriate counseling is provided, combination therapy with sofosbuvir and ledipasvir is planned. This treatment is most likely to help clear the infection through which of the following mechanisms?
A)Blocking reverse transcription of viral RNA
B)Enhancing antiviral host immune response
C)Impairing viral entry into host cells
D)Inhibiting viral genome replication and assembly
E)Preventing new virion release from infected host cells
A)Blocking reverse transcription of viral RNA
B)Enhancing antiviral host immune response
C)Impairing viral entry into host cells
D)Inhibiting viral genome replication and assembly
E)Preventing new virion release from infected host cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A 4-year-old, previously healthy boy is brought to the emergency department due to fever, abdominal pain, and frequent bloody diarrhea for 2 days. A few children at day care have developed diarrhea over the past week as well. He takes no medications and has not traveled outside the United States. Temperature is 39 C (102.2 F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 90/min. Physical examination shows increased bowel sounds and left sided abdominal tenderness. Which of the following is the most likely causal organism?
A)Clostridioides difficile
B)Clostridium perfringens
C)Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
D)Salmonella typhi
E)Shigella sonnei
A)Clostridioides difficile
B)Clostridium perfringens
C)Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
D)Salmonella typhi
E)Shigella sonnei

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A 64-year-old man comes to the office due to 3 days of diarrhea. He began to have nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea 24 hours after eating chicken salad at a fast-food restaurant. The patient continues to have 4-6 episodes of diarrhea per day with no blood in the stool. His wife, who ate the same food, had a few loose stools but felt well afterward. The patient takes a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor for psoriatic arthritis and a proton pump inhibitor for gastritis. Temperature is 38 C (100.4 F), blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 88/min. Abdominal examination reveals mild diffuse tenderness to palpation and increased bowel sounds. Cultures of the stool yield gram-negative bacilli that are non-lactose fermenting and oxidase negative. Which of the following is the most likely complication associated with this patient's current infection?
A)Chronic malabsorption
B)Generalized seizure
C)Guillain-Barré syndrome
D)Hemolytic uremic syndrome
E)Long-bone osteomyelitis
A)Chronic malabsorption
B)Generalized seizure
C)Guillain-Barré syndrome
D)Hemolytic uremic syndrome
E)Long-bone osteomyelitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A 57-year-old woman is hospitalized with high-grade fevers, chills, and right upper abdominal pain. The patient lives in Wisconsin and has no history of international travel. Her temperature is 40 C (104 F). Physical examination of the abdomen shows rebound tenderness. Laboratory studies show elevated aspartate and alanine aminotransferases. Imaging studies reveal a fluid-filled cavity within the right lobe of the liver as shown below. 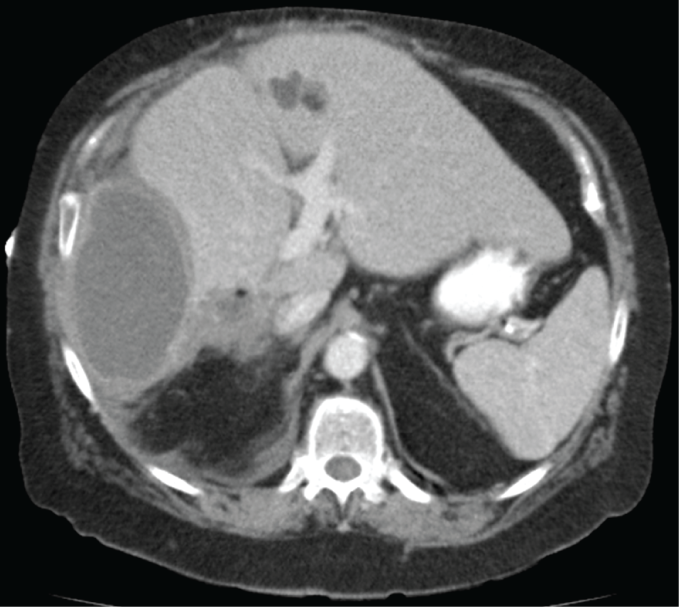 Which of the following microorganism/route combinations is most likely to be the cause of this patient's infection?
Which of the following microorganism/route combinations is most likely to be the cause of this patient's infection?
A)Chlamydia trachomatis due to ascending cholangitis
B)Cytomegalovirus by direct invasion from a nearby source
C)Entamoeba histolytica due to a penetrating stab wound
D)Staphylococcus aureus by hematogenous route
E)Streptococcus pneumoniae by portal vein
 Which of the following microorganism/route combinations is most likely to be the cause of this patient's infection?
Which of the following microorganism/route combinations is most likely to be the cause of this patient's infection?A)Chlamydia trachomatis due to ascending cholangitis
B)Cytomegalovirus by direct invasion from a nearby source
C)Entamoeba histolytica due to a penetrating stab wound
D)Staphylococcus aureus by hematogenous route
E)Streptococcus pneumoniae by portal vein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A 5-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department with worsening somnolence, lethargy, and decreased urine output. The patient has no prior medical conditions but had abdominal cramps and diarrhea several days ago that later became frankly bloody. Physical examination shows mild pallor and moist mucous membranes. Laboratory studies reveal elevated blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine levels. Peripheral blood smear shows fragmented erythrocytes. This patient's condition is most likely related to consumption of which of the following foods?
A)Canned beans
B)Custard
C)Fried rice
D)Mayonnaise
E)Oysters
F)Raw eggs
G)Undercooked beef
A)Canned beans
B)Custard
C)Fried rice
D)Mayonnaise
E)Oysters
F)Raw eggs
G)Undercooked beef

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Volunteer studies are used to determine the infectious dose of Salmonella required to cause gastroenteritis. The curve obtained during the studies is shown in the diagram as line 2. Which of the following organisms could be represented by line 1 on this diagram? 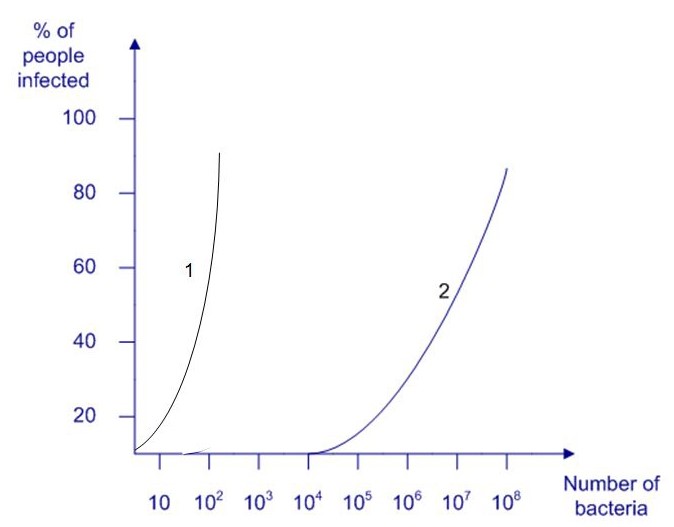
A)Clostridium perfringens
B)Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
C)Shigella flexneri
D)Vibrio cholerae
E)Vibrio parahaemolyticus

A)Clostridium perfringens
B)Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
C)Shigella flexneri
D)Vibrio cholerae
E)Vibrio parahaemolyticus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A 3-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department with abrupt-onset vomiting followed by frequent, large-volume, watery diarrhea for the last day. She has no prior medical conditions but has not received recommended vaccinations. Temperature is 37.8 C (100 F). Physical examination shows mild dehydration. The abdomen is soft and mildly tender to palpation throughout. Bowel sounds are increased. Polymerase chain reaction testing of the stool sample yields a virus with a segmented, double-stranded RNA genome. Which of the following pathologic findings is most likely to be present in this patient?
A)Blunting of the villi in the duodenum and proximal jejunum
B)Extensive colonic mucosal injury with yellow-white adherent layer
C)Flask-shaped ulcerations in the cecum and ascending colon
D)Foamy macrophages in the small intestinal lamina propria
E)Inflammatory infiltration and necrosis of the Peyer patches
A)Blunting of the villi in the duodenum and proximal jejunum
B)Extensive colonic mucosal injury with yellow-white adherent layer
C)Flask-shaped ulcerations in the cecum and ascending colon
D)Foamy macrophages in the small intestinal lamina propria
E)Inflammatory infiltration and necrosis of the Peyer patches

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An 8-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department due to 24 hours of fever and chills. Temperature is 38.3 C (101 F). On examination, the patient is lethargic with dry mucous membranes. There are no oropharyngeal lesions, and tympanic membranes are normal. The lungs are clear on auscultation, and heart sounds are normal. The abdomen is soft and nontender. There is no skin rash. Laboratory testing shows a leukocyte count of 24,000/mm3 with 15% bands, 80% neutrophils, and 5% lymphocytes. Peripheral blood smear is shown in the exhibit. 
Blood cultures are obtained and intravenous fluids and empiric antibiotics are initiated. The patient's blood cultures are most likely to grow which of the following organisms?
A)Escherichia coli
B)Pseudomonas aeruginosa
C)Staphylococcus aureus
D)Streptococcus pneumoniae
E)Streptococcus pyogenes
F)Viridans streptococci

Blood cultures are obtained and intravenous fluids and empiric antibiotics are initiated. The patient's blood cultures are most likely to grow which of the following organisms?
A)Escherichia coli
B)Pseudomonas aeruginosa
C)Staphylococcus aureus
D)Streptococcus pneumoniae
E)Streptococcus pyogenes
F)Viridans streptococci

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A 14-year-old girl comes to the emergency department due to rapidly progressive exertional dyspnea and generalized weakness, which were preceded by a mild febrile illness several days ago. She has a history of sickle cell disease and takes a daily folic acid supplement. Her temperature is 37.2 C (99.1 F), blood pressure is 115/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 112/min and regular. On examination, the patient has conjunctival pallor but no icterus. A cardiac flow murmur is present. The abdomen is soft and nontender with no organomegaly. Laboratory studies show a hematocrit of 16% with reticulocyte count of 0.1% (normal range, 0.5%-1.5%). Leukocyte and platelet counts are normal. Which of the following best describes the virus most likely responsible for this patient's current condition?
A)Enveloped double-stranded DNA virus
B)Enveloped negative-sense RNA virus
C)Enveloped positive-sense RNA virus
D)Nonenveloped double-stranded DNA virus
E)Nonenveloped positive-sense RNA virus
F)Nonenveloped single-stranded DNA virus
A)Enveloped double-stranded DNA virus
B)Enveloped negative-sense RNA virus
C)Enveloped positive-sense RNA virus
D)Nonenveloped double-stranded DNA virus
E)Nonenveloped positive-sense RNA virus
F)Nonenveloped single-stranded DNA virus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A 35-year-old man comes to the office due to 3 months of progressive swelling under his left jaw. The swelling spontaneously opened and drained pus a month ago but has not improved or resolved. The patient has no medical conditions other than dental caries; he had a tooth extracted prior to symptom onset. Physical examination shows an indurated, nontender mass in the left submandibular area with a small opening on the overlying skin. Gentle pressure on the mass yields thick pus containing sand/grain-like particles. The microbial pathogen with which of the following characteristics is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
A)Bipolar-staining, gram-negative bacilli
B)Coagulase-producing, gram-positive cocci
C)Conidia-forming, dimorphic fungus
D)Filamentous, branching, gram-positive bacilli
E)Oxidase-positive, gram-negative bacilli
A)Bipolar-staining, gram-negative bacilli
B)Coagulase-producing, gram-positive cocci
C)Conidia-forming, dimorphic fungus
D)Filamentous, branching, gram-positive bacilli
E)Oxidase-positive, gram-negative bacilli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An 8-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department due to 2 days of fever, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. The patient has no significant medical history and has received all recommended vaccinations. He attends a primary school and has not traveled recently. The family recently brought home a new puppy from a kennel. The patient's stool is positive for occult blood but negative for ova and parasites. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
A)Bacillus cereus
B)Campylobacter
C)Giardia lamblia
D)Norovirus
E)Staphylococcus aureus
F)Vibrio parahaemolyticus
A)Bacillus cereus
B)Campylobacter
C)Giardia lamblia
D)Norovirus
E)Staphylococcus aureus
F)Vibrio parahaemolyticus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A 34-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to 5 days of progressive anorexia, nausea, and abdominal pain. The patient is a known hepatitis B carrier. He admits to using IV drugs and has shared needles with other drug users on several occasions. His temperature is 37.7 C (99.9 F). Examination shows scleral icterus and mild, tender hepatomegaly. Laboratory studies are notable for highly elevated levels of liver aminotransferases and serum bilirubin and also show the following results:  This patient's chronic infection assists which of the following life cycle aspects of the current infectious agent?
This patient's chronic infection assists which of the following life cycle aspects of the current infectious agent?
A)Coating of viral particles
B)Integration into host genome
C)Intracellular survival
D)Replication of viral RNA
E)Translation of viral transcripts
 This patient's chronic infection assists which of the following life cycle aspects of the current infectious agent?
This patient's chronic infection assists which of the following life cycle aspects of the current infectious agent?A)Coating of viral particles
B)Integration into host genome
C)Intracellular survival
D)Replication of viral RNA
E)Translation of viral transcripts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A diarrheal outbreak is reported at a private school in Columbus, Ohio. Six healthy children age 10-11 and two teachers developed acute vomiting and diarrhea within a 2-day period. They describe the diarrhea as watery and without blood or mucus. Three of those affected are febrile during their illness. None of the patients have traveled abroad recently, and all are up to date with their vaccinations. Stool test results are pending. Which of the following pathogens is the most likely cause of the illness?
A)Adenovirus
B)Campylobacter jejuni
C)Clostridioides (formerly Clostridium) difficile
D)Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
E)Norovirus
F)Rotavirus
G)Salmonella typhi
A)Adenovirus
B)Campylobacter jejuni
C)Clostridioides (formerly Clostridium) difficile
D)Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
E)Norovirus
F)Rotavirus
G)Salmonella typhi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A 23-year-old woman is evaluated due to 10 days of nonproductive cough, low-grade fever, headache, and malaise. The patient has no other medical problems and takes no medications. Lung examination reveals scattered rales. Chest x-ray reveals bilateral patchy areas of consolidation. She has mild anemia and an elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase level. The patient is treated for presumed Mycoplasma pneumonia with azithromycin. Two months later, her symptoms and the anemia have resolved. Which of the following best explains the resolution of this patient's anemia?
A)Elimination of bacterial cell wall antigens
B)Elimination of intraerythrocytic microorganisms
C)Fading of immune response against the bacteria
D)Replenishment of body iron stores
E)Replenishment of intracellular enzyme stores
A)Elimination of bacterial cell wall antigens
B)Elimination of intraerythrocytic microorganisms
C)Fading of immune response against the bacteria
D)Replenishment of body iron stores
E)Replenishment of intracellular enzyme stores

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A 6-year-old previously healthy girl is brought to the emergency department due to a day of fever, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. The symptoms began abruptly with high fever and cramping, periumbilical abdominal pain and were quickly followed by low-volume diarrhea mixed with blood and mucus. The patient has had no sick contacts and has not traveled recently; the family had dinner at a buffet restaurant 3 days ago. Temperature is 38.9 C (102 F). Physical examination reveals mild diffuse abdominal tenderness with no guarding or rebound tenderness. Bowel sounds are hyperactive. Stool occult blood testing is positive, and there are numerous leukocytes in the stool. Culture of the stool yields gram-negative, oxidase-positive, curved rods. Which of the following is the most likely pathogen responsible for this patient's symptoms?
A)Campylobacter jejuni
B)Escherichia coli
C)Salmonella enterica
D)Shigella flexneri
E)Vibrio cholerae
A)Campylobacter jejuni
B)Escherichia coli
C)Salmonella enterica
D)Shigella flexneri
E)Vibrio cholerae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A pharmaceutical researcher is trying to develop a vaccine against the hepatitis C virus. She infects a chimpanzee with hepatitis C virus of known genotype and subtype. Several weeks later, a liver sample is obtained, and viral RNAs are extracted from the hepatocytes. A genetic study of the viral genomes reveals that the extracted RNA sequences vary significantly from that of the original infecting virus. This genetic instability is most likely due to the lack of which of the following features during the viral replication process?
A)3' → 5' exonuclease activity
B)5' → 3' exonuclease activity
C)Glycosylase activity
D)Ligase activity
E)Nucleotide specificity
F)Primase activity
A)3' → 5' exonuclease activity
B)5' → 3' exonuclease activity
C)Glycosylase activity
D)Ligase activity
E)Nucleotide specificity
F)Primase activity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A 24-year-old woman comes to the office due to lower abdominal pain and malodorous vaginal discharge. The patient has had increasing vaginal discharge for the past 3 weeks and increasing lower abdominal pain for the last few days. She has no chronic medical conditions or medication allergies. The patient is sexually active and uses a copper-containing intrauterine device for contraception. Temperature is 38.3 C (100.9 F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 78/min. The lower abdomen is tender to palpation with no rebound or guarding. On pelvic examination, the strings of the intrauterine device are seen, and cervical motion tenderness and mucopurulent cervical discharge are present. Culture of the discharge shows thin, elongated, gram-positive bacilli in an acute-angle branching pattern. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy for this patient?
A)Fluconazole
B)Metronidazole
C)Nitrofurantoin
D)Penicillin
E)Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
A)Fluconazole
B)Metronidazole
C)Nitrofurantoin
D)Penicillin
E)Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A 34-year-old man comes to the office to establish medical care. The patient recently emigrated from Eastern Asia. He has no chronic medical conditions but reports intermittent abdominal discomfort and episodic diarrhea over the past several months. He has also had occasional dry cough and throat irritation. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Serologic testing for Strongyloides stercoralis IgG is positive. Detection of which of the following is most suggestive of active infection by the pathogen in this patient?
A)Multiloculated liver cyst
B)Perianal egg deposition
C)Proglottids in the stool
D)Rhabditiform larvae in the stool
E)Trophozoites and cysts in the stool
A)Multiloculated liver cyst
B)Perianal egg deposition
C)Proglottids in the stool
D)Rhabditiform larvae in the stool
E)Trophozoites and cysts in the stool

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A 45-year-old woman with HIV comes to the office due to the appearance of multiple tender nodules on her lower extremities over the past several weeks. The patient tried to squeeze open the lesions, but this led to profuse bleeding with no expression of pus. She works at a pet store in Mississippi and has regular contact with a variety of animals. Skin examination findings are shown below. 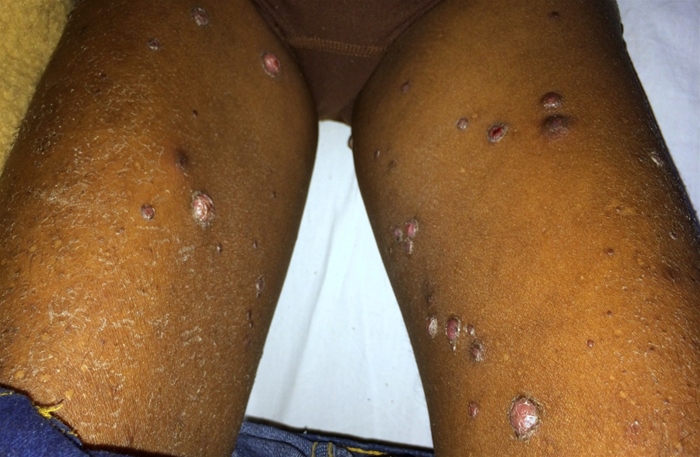 Biopsy of the lesions reveals large endothelial cells forming vascular channels with a mixed neutrophilic and lymphocytic infiltrate. Immunohistochemical staining for human herpesvirus 8 is negative. Infection with which of the following pathogens is most likely responsible for this patient's skin condition?
Biopsy of the lesions reveals large endothelial cells forming vascular channels with a mixed neutrophilic and lymphocytic infiltrate. Immunohistochemical staining for human herpesvirus 8 is negative. Infection with which of the following pathogens is most likely responsible for this patient's skin condition?
A)Actinomyces israelii
B)Bartonella henselae
C)Blastomyces dermatitidis
D)Mycobacterium marinum
E)Staphylococcus aureus
 Biopsy of the lesions reveals large endothelial cells forming vascular channels with a mixed neutrophilic and lymphocytic infiltrate. Immunohistochemical staining for human herpesvirus 8 is negative. Infection with which of the following pathogens is most likely responsible for this patient's skin condition?
Biopsy of the lesions reveals large endothelial cells forming vascular channels with a mixed neutrophilic and lymphocytic infiltrate. Immunohistochemical staining for human herpesvirus 8 is negative. Infection with which of the following pathogens is most likely responsible for this patient's skin condition?A)Actinomyces israelii
B)Bartonella henselae
C)Blastomyces dermatitidis
D)Mycobacterium marinum
E)Staphylococcus aureus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A 56-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to 1 day of fever. She has a history of a hematologic malignancy and recently completed a cycle of chemotherapy through an indwelling central venous catheter. Temperature is 38.3 C (100.9 F). Laboratory studies are notable for neutropenia, with an absolute neutrophil count of 380/mm3. The patient is started on broad-spectrum antibiotics. Three days later, she continues to be febrile. Fungal cultures grow a species of Candida with a mutation in a gene coding an enzyme responsible for synthesizing a fungal cell wall polysaccharide. The organism is most likely to be resistant to which of the following antifungal agents as a result of this mutation?
A)Amphotericin B
B)Caspofungin
C)Flucytosine
D)Griseofulvin
E)Itraconazole
F)Terbinafine
A)Amphotericin B
B)Caspofungin
C)Flucytosine
D)Griseofulvin
E)Itraconazole
F)Terbinafine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Several individuals in a Florida neighborhood develop a febrile illness during the summer. Most of them experience abrupt-onset fever, headache, confusion, and lethargy. Some patients also develop tremors, seizures, and focal motor or sensory deficits. Physical examination shows signs of meningeal irritation and altered mental status. Cerebrospinal fluid evaluation reveals lymphocytic pleocytosis with no organisms seen on Gram stain. Brain imaging shows no abnormalities. Which of the following would be most helpful in controlling this disease outbreak?
A)Control of vector arthropods
B)Decontamination of bat droppings
C)Isolation of infected individuals
D)Purification of drinking water
E)Vaccination of all individuals
A)Control of vector arthropods
B)Decontamination of bat droppings
C)Isolation of infected individuals
D)Purification of drinking water
E)Vaccination of all individuals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A 35-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to a 4-day history of fever, abdominal pain, and profuse, watery diarrhea. The patient also has nausea and vomiting. She prepares her own food and frequently tastes it while cooking. The patient has no chronic medical conditions and takes no medication. Temperature is 38.8 C (101.8 F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 100/min. Abdominal examination shows mild, diffuse tenderness. Bowel sounds are increased. Examination of the stool shows numerous leukocytes. Which of the following is the most likely pathogen?
A)Campylobacter jejuni
B)Clostridioides difficile
C)Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
D)Listeria monocytogenes
E)Norovirus
A)Campylobacter jejuni
B)Clostridioides difficile
C)Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
D)Listeria monocytogenes
E)Norovirus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Researchers studying fungal pathogens isolated an ergosterol biosynthetic gene by polymerase chain reaction. Using homologous recombination, they then developed a new strain of Candida with a mutated allele for that gene. The mutant strain was cultured in the presence of several different antifungal agents. Compared to isolates from the wild-type strain, isolates from the mutant Candida strain exhibited enhanced growth in the presence of drug X. Further investigation revealed that the mechanism of resistance to drug X was a decrease in ergosterol incorporation into the cell membrane. Based on this data, drug X is likely to be most closely related to which of the following antifungal agents?
A)Caspofungin
B)Cyclosporine
C)Flucytosine
D)Griseofulvin
E)Nystatin
A)Caspofungin
B)Cyclosporine
C)Flucytosine
D)Griseofulvin
E)Nystatin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A 1-month-old boy is brought to the emergency department during winter with cough and difficulty breathing. He has had rhinorrhea, cough, and congestion for the past 3 days. Today, the patient began breathing harder and faster with increased cough. Temperature is 37.8 C (100 F) and respirations are 68/min. Oxygen saturation is 91%. The patient is alert and awake and has subcostal and suprasternal retractions. Mucous membranes are moist, and the anterior fontanelle is open and flat. Physical examination reveals diffuse expiratory wheezes and scattered rales. Which of the following pathogens is most likely causing this patient's condition?
A)Adenovirus
B)Bordetella pertussis
C)Mycoplasma pneumoniae
D)Parainfluenza virus
E)Respiratory syncytial virus
F)Streptococcus pneumoniae
A)Adenovirus
B)Bordetella pertussis
C)Mycoplasma pneumoniae
D)Parainfluenza virus
E)Respiratory syncytial virus
F)Streptococcus pneumoniae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A 24-year-old man comes to the emergency department with leg swelling. His dog, which is fully vaccinated and has lived with him for the past year, bit him on the left leg last night, leading to a break in the skin and bleeding. The patient irrigated the wound with bottled water and soap and managed his pain with acetaminophen. This morning, the wound area became warm, red, and swollen. On examination, temperature is 36.4 C (97.5 F). There is an open wound on the left leg, with surrounding erythema, warmth, and tenderness. No wound drainage or crepitus is present. The distal pulses are palpable. Wound cultures grow gram-negative coccobacilli; the culture has a mouse-like odor. Which of the following organisms is most likely responsible for this patient's current presentation?
A)Bartonella henselae
B)Campylobacter jejuni
C)Clostridium perfringens
D)Coxiella burnetii
E)Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
F)Francisella tularensis
G)Fusobacterium
H)Pasteurella multocida
I)Proteus mirabilis
A)Bartonella henselae
B)Campylobacter jejuni
C)Clostridium perfringens
D)Coxiella burnetii
E)Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
F)Francisella tularensis
G)Fusobacterium
H)Pasteurella multocida
I)Proteus mirabilis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A 24-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to bloody diarrhea. His symptoms began 10 days ago with episodic abdominal discomfort and loose stools. The symptoms have progressively worsened, and he has had 6-8 stools mixed with blood and mucus over the past 2 days. The patient recently returned from a 2-week trip to Egypt and felt well while traveling. Temperature is 38 C (100.4 F), blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 86/min. The abdomen is soft with mild tenderness on palpation of lower quadrants. There is no guarding or rebound tenderness, and bowel sounds are hyperactive. Stool testing is negative for C difficile toxin, and stool culture yields no bacteria. Sigmoidoscopy reveals colonic ulcers with undermining edges that contain trophozoites. The causative organism for this patient's current condition can also produce which of the following manifestations?
A)Bile duct obstruction
B)Cystic brain lesions
C)Granulomatous cystitis
D)Itchy cutaneous eruptions
E)Liver abscess
A)Bile duct obstruction
B)Cystic brain lesions
C)Granulomatous cystitis
D)Itchy cutaneous eruptions
E)Liver abscess

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A 48-year-old man comes to the hospital due to 10 days of persistent fever, chills, fatigue, and dyspnea. He had a splenectomy at age 28 after a motor vehicle accident and received the appropriate vaccines. The patient does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. He recently traveled from New York City to Connecticut for a family wedding. His temperature is 38.6 C (101.5 F), blood pressure is 118/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 108/min. Lung examination reveals coarse crackles. Laboratory studies are as follows:  Chest x-ray reveals bilateral infiltrates. A peripheral blood smear shows normocytic, normochromic anemia with ring- and cross-shaped intraerythrocytic inclusions. The vector responsible for this patient's current condition can also transmit which of the following organisms?
Chest x-ray reveals bilateral infiltrates. A peripheral blood smear shows normocytic, normochromic anemia with ring- and cross-shaped intraerythrocytic inclusions. The vector responsible for this patient's current condition can also transmit which of the following organisms?
A)Borrelia burgdorferi
B)Dengue virus
C)Haemophilus influenzae
D)Histoplasma capsulatum
E)Neisseria meningitidis
F)Plasmodium falciparum
 Chest x-ray reveals bilateral infiltrates. A peripheral blood smear shows normocytic, normochromic anemia with ring- and cross-shaped intraerythrocytic inclusions. The vector responsible for this patient's current condition can also transmit which of the following organisms?
Chest x-ray reveals bilateral infiltrates. A peripheral blood smear shows normocytic, normochromic anemia with ring- and cross-shaped intraerythrocytic inclusions. The vector responsible for this patient's current condition can also transmit which of the following organisms?A)Borrelia burgdorferi
B)Dengue virus
C)Haemophilus influenzae
D)Histoplasma capsulatum
E)Neisseria meningitidis
F)Plasmodium falciparum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A 43-year-old man undergoes induction chemotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia. Three weeks later, he is hospitalized with fever, cough, and generalized weakness. On physical examination, his temperature is 38.1 C (100.7 F), blood pressure is 102/68 mm Hg, and pulse is 125/min. The patient's pulse oximetry shows 95% on room air. Crackles are heard over the right upper lung. His hemoglobin level is 9.5 g/dL, and leukocyte count is 900/mm3 with an absolute neutrophil count of 100/mm3. Chest x-ray reveals a dense infiltrate involving the right upper lung lobe. Broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy is instituted. Five days later, the patient is still febrile. Bronchoscopy with biopsy is performed and the tissue samples from the bronchoscopy grow mold. Which of the following organisms is most likely responsible for this patient's current condition?
A)Aspergillus fumigatus
B)Candida albicans
C)Cryptococcus neoformans
D)Pneumocystis jirovecii
E)Rhizopus oryzae
A)Aspergillus fumigatus
B)Candida albicans
C)Cryptococcus neoformans
D)Pneumocystis jirovecii
E)Rhizopus oryzae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A group of researchers collected demographic and clinical data from multiple hospitals across the nation to determine epidemiological features of nosocomial bloodstream infections. In this study, a nosocomial bloodstream infection was diagnosed if blood cultures drawn 48 hours after admission yielded a pathogenic organism. Analysis of the data collected over several decades shows that staphylococci are increasingly responsible for the identified cases. An increased use of which of the following is most likely the underlying cause of the observed trend?
A)Bioprosthetic heart valves
B)Broad-spectrum antibiotics
C)Illicit injection drugs
D)Immunomodulating therapies
E)Indwelling urinary catheters
F)Intravascular catheters
A)Bioprosthetic heart valves
B)Broad-spectrum antibiotics
C)Illicit injection drugs
D)Immunomodulating therapies
E)Indwelling urinary catheters
F)Intravascular catheters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A 65-year-old man is brought to the emergency department due to high fevers and confusion. His family says that for the past couple of days, he has been acting strangely and has been disoriented. He has also had severe headaches. This morning he was difficult to arouse and reportedly had a seizure on the way to the hospital. His temperature is 39.4 C (103 F), blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, and pulse is 112/min. The patient is obtunded with preserved brainstem reflexes and reduced motor responses to pain. CT scan of the head without contrast is negative. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis reveals an elevated opening pressure with a hemorrhagic lymphocytic pleocytosis, increased protein, and normal glucose. An MRI of the brain reveals an abnormal signal in the bilateral temporal lobes. A drug that inhibits which of the following would be most effective in treating this patient's condition?
A)Bacterial cell wall synthesis
B)Bacterial folic acid metabolism
C)Bacterial nucleic acid synthesis
D)Bacterial ribosomes
E)Viral DNA polymerase
F)Viral protease
G)Viral reverse transcriptase
H)Viral RNase H
A)Bacterial cell wall synthesis
B)Bacterial folic acid metabolism
C)Bacterial nucleic acid synthesis
D)Bacterial ribosomes
E)Viral DNA polymerase
F)Viral protease
G)Viral reverse transcriptase
H)Viral RNase H

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A 47-year-old man comes to the office due to persistent fever, night sweats, and fatigue. Thorough evaluation yields a diagnosis of chronic myeloid leukemia. While undergoing treatment for his malignancy, the patient experiences headaches, scant nasal discharge, and left eye symptoms. Physical examination reveals tenderness over the paranasal sinuses and left-sided orbital swelling and cellulitis. Mild proptosis and ptosis of the left eye are also present. Biopsy of the sinus mucosa is shown in the image below: 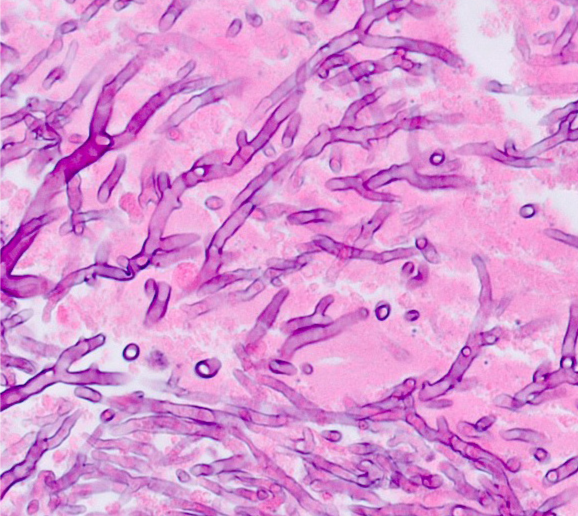 Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
A)Aspergillus fumigatus
B)Blastomyces dermatitidis
C)Candida albicans
D)Coccidioides immitis
E)Cryptococcus neoformans
F)Histoplasma capsulatum
G)Malassezia furfur
H)Microsporum canis
I)Rhizopus species
J)Sporothrix schenckii
 Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?A)Aspergillus fumigatus
B)Blastomyces dermatitidis
C)Candida albicans
D)Coccidioides immitis
E)Cryptococcus neoformans
F)Histoplasma capsulatum
G)Malassezia furfur
H)Microsporum canis
I)Rhizopus species
J)Sporothrix schenckii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A 65-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to fevers and malaise for the last 48 hours. The patient initially experienced fevers and chills, which subsequently progressed to fatigue to the point that he had difficulty performing routine tasks this morning. He has also had a mild headache. The patient lives in eastern Massachusetts with his wife. He is retired and spends time gardening and swimming at a local public pool. The patient traveled to Thailand 2 years ago with his family and to Florida 2 months ago. Temperature is 38.9 C (102 F), blood pressure is 122/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 114/min and regular. The oropharynx is dry and has no lesions. Lung examination demonstrates coarse crackles bilaterally. The abdomen is soft and mildly tender throughout with palpable splenomegaly. He has no rash or open wounds. Peripheral blood smear is shown in the exhibit.
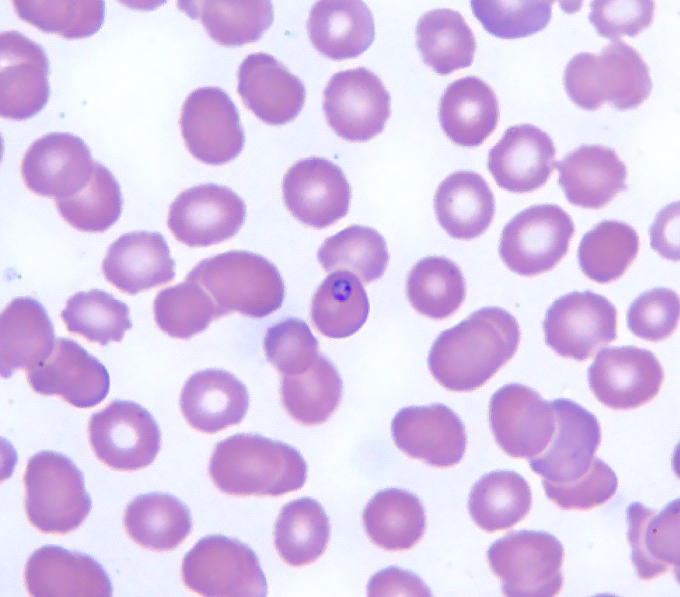
Which of the following is the most likely source of this patient's infection?
A)Aedes mosquito
B)Brown recluse spider
C)Dog bite
D)Freshwater consumption
E)Ixodes tick
F)Scratch from a garden bush
G)Spore inhalation

Which of the following is the most likely source of this patient's infection?
A)Aedes mosquito
B)Brown recluse spider
C)Dog bite
D)Freshwater consumption
E)Ixodes tick
F)Scratch from a garden bush
G)Spore inhalation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A 76-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to fever and burning with urination for 2 days and right-sided back pain for 1 day. Her temperature is 38.3 C (101 F), blood pressure is 110/80 mm Hg, pulse is 94/min, and respirations are 18/min. Examination is notable for right-sided flank tenderness to palpation. Urinalysis is positive for nitrites, leukocyte esterase, and bacteria. Urine and blood cultures are obtained, and the patient is started on antibiotic therapy. The next day, urine culture grows >100,000 colony-forming units/mL of Escherichia coli. The organism is found to have a methyltransferase that methylates ribosomal RNA. This enzyme most likely confers resistance to which of the following classes of antibiotics?
A)Aminoglycosides
B)Carbapenems
C)Glycopeptides
D)Penicillins
E)Quinolones
A)Aminoglycosides
B)Carbapenems
C)Glycopeptides
D)Penicillins
E)Quinolones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A 34-year-old man came to the office due to white plaques on his buccal mucosa that he incidentally discovered while brushing his teeth. After appropriate workup, he was found to be HIV positive, with a CD4+ T lymphocyte count of 280/mm3. He was referred to an infectious diseases specialist for follow-up but was noncompliant with appointments. The patient returns 3 years later due to several months of pain and itching in the perirectal area. He also has intermittent rectal bleeding and often sees bright red blood on the tissue after wiping. The patient did not seek medical care because he thought he had hemorrhoids. On examination, a single, hard mass with superficial ulceration measuring approximately 2x2 cm is noted in the anal canal. No hemorrhoids are present. There is no palpable regional lymphadenopathy. Which of the following pathogens is most likely responsible for this patient's current anal pathology?
A)Adenovirus
B)Candida albicans
C)Chlamydia trachomatis
D)Cytomegalovirus
E)Epstein-Barr virus
F)Herpes simplex virus type 2
G)Human papillomavirus
A)Adenovirus
B)Candida albicans
C)Chlamydia trachomatis
D)Cytomegalovirus
E)Epstein-Barr virus
F)Herpes simplex virus type 2
G)Human papillomavirus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The patient is hospitalized, and appropriate treatment is begun. After discussing the underlying cause of his condition-immunosuppression due to HIV infection-the patient agrees to take antiretroviral therapy consistently. One of the medications in his treatment regimen leads to the production of immature, noninfectious virions containing large polyproteins. Which of the following viral processes is most likely directly inhibited by this agent? A)Expression of glycoproteins on the virus cell surface B)Integration of the viral DNA molecule into the host genome C)Production of functional viral-encoded enzymes D)Removal of viral template RNA from the RNA-DNA hybrid E)Translation of virus-encoded regulatory proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A 43-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to 2 weeks of intermittent fevers, malaise, and headaches. He has a history of HIV and has not been taking his antiretroviral drugs recently. Five years ago, the patient spent a year in jail. Temperature is 38.2 C (100.8 F). Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis shows markedly elevated protein and low glucose, and CSF cultures grow Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Resistance testing shows the following:  Which of the following best explains the resistance pattern seen in these bacteria?
Which of the following best explains the resistance pattern seen in these bacteria?
A)Altered structure of bacterial ribosomal proteins
B)Altered structure of enzymes involved in DNA winding-unwinding
C)Altered structure of enzymes involved in RNA synthesis
D)Decreased activity of bacterial catalase-peroxidase
E)Increased activity of enzymes involved in cell wall polysaccharide synthesis
 Which of the following best explains the resistance pattern seen in these bacteria?
Which of the following best explains the resistance pattern seen in these bacteria?A)Altered structure of bacterial ribosomal proteins
B)Altered structure of enzymes involved in DNA winding-unwinding
C)Altered structure of enzymes involved in RNA synthesis
D)Decreased activity of bacterial catalase-peroxidase
E)Increased activity of enzymes involved in cell wall polysaccharide synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Another isolate of Streptococcus pneumoniae from a patient with meningitis is also incubated with low-dose radioactive ceftriaxone and subjected to protein electrophoresis. Only two bands are detected using radioautography. Which of the following best explains the observed finding? A)Action of beta-lactamases B)Change in protein structure C)Salvage metabolic pathway D)Transmembranous efflux pumps E)Upregulation of protein synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A 34-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to 2 days of fever, malaise, and myalgia. He has also had worsening shortness of breath and cough. The patient works in the mail room at a large company, does not smoke cigarettes, and drinks alcohol occasionally. Chest imaging shows lung infiltrates and prominent widening of the mediastinum. Sputum and blood cultures yield large, gram-positive rods that form colonies resembling a "Medusa head." Which of the following is the most likely bacterial virulence factor contributing to this patient's condition?
A)Antiphagocytic D-glutamate capsule
B)Antiphagocytic polysaccharide capsule
C)IgG-binding, outer membrane protein
D)Intracellular polyphosphate granules
E)Peritrichous flagella
A)Antiphagocytic D-glutamate capsule
B)Antiphagocytic polysaccharide capsule
C)IgG-binding, outer membrane protein
D)Intracellular polyphosphate granules
E)Peritrichous flagella

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 336 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



