Deck 13: Physiology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/272
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Physiology
1
A 32-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to sudden-onset left-sided facial droop and arm weakness. The patient also has had right leg swelling after a recent road trip. She has no chronic medical conditions, and her only medication is an oral contraceptive. CT scan of the head shows a right middle cerebral artery territory acute infarction. Lower extremity ultrasound examination reveals a right femoral vein thrombus. No obvious cardiac structural abnormalities are detected on an echocardiogram. Agitated normal saline is injected into a peripheral vein to evaluate for abnormal right-to-left shunting. No bubbles are seen in the left side of the heart after several minutes. Which of the following is most appropriate to increase right-sided heart pressure to reveal an obscure intracardiac shunt?
A)Abrupt standing from supine position
B)Amyl nitrate injection
C)Breath-holding after exhalation
D)Sustained hand grip
E)Valsalva maneuver release phase
A)Abrupt standing from supine position
B)Amyl nitrate injection
C)Breath-holding after exhalation
D)Sustained hand grip
E)Valsalva maneuver release phase
E
This patient has a deep venous thrombosis and has experienced a large stroke, suggesting paradoxical embolization of thrombus (ie, passage from the venous circulation to the arterial circulation). Because thrombi are too large to pass through the pulmonary capillaries, paradoxical embolization typically occurs via an intracardiac right-to-left shunt. In this case, echocardiography did not reveal overt septal abnormalities (ie, atrial septal defect or ventricular septal defect), raising strong suspicion for a patent foramen ovale (PFO).
PFO is common, affecting up to 30% of adults. It results from failure of the septum primum and septum secundum to fuse during early childhood, creating a one-way tissue valve. This valve is forced closed when left atrial pressure exceeds right atrial pressure (which is most of the time), but it opens when right atrial pressure exceeds left atrial pressure, allowing for transient right-to-left shunting.
To test for the presence of a PFO, normal saline bubbles are injected intravenously, and echocardiography is performed to observe whether the bubbles pass from the right atrium into the left atrium. The release phase of a Valsalva maneuver increases venous return to the right atrium and consequently increases right atrial pressure to facilitate right-to-left shunting of saline bubbles and confirm the diagnosis (the strain phase of Valsalva maneuver decreases venous return to the RA and discourages shunting through a PFO).
(Choices A, B, and C) Medications and physiologic maneuvers that reduce venous return to the right atrium discourage right-to-left shunting through a PFO. Abrupt standing from a supine position causes blood to pool in the lower extremities, amyl nitrate (an inhaled nitrate) causes venous vasodilation, and exhalation causes increased intrathoracic pressure (resulting in partial collapse of the inferior vena cava at end-expiration), all of which reduce venous return to the right atrium.
(Choice D) Sustained hand grip increases systemic vascular resistance, increasing pressure in the left ventricle and left atrium and discouraging shunting through a PFO.
Educational objective:
Paradoxical embolization, or passage of a thromboembolism from the venous circulation to the arterial circulation, most commonly occurs through a patent foramen ovale (PFO). A PFO is a one-way tissue valve in the atrial septum that opens only when right atrial pressure exceeds left atrial pressure; venous return to the right atrium increases during the release (ie, relaxation) phase of a Valsalva maneuver and encourages opening of a PFO.
This patient has a deep venous thrombosis and has experienced a large stroke, suggesting paradoxical embolization of thrombus (ie, passage from the venous circulation to the arterial circulation). Because thrombi are too large to pass through the pulmonary capillaries, paradoxical embolization typically occurs via an intracardiac right-to-left shunt. In this case, echocardiography did not reveal overt septal abnormalities (ie, atrial septal defect or ventricular septal defect), raising strong suspicion for a patent foramen ovale (PFO).
PFO is common, affecting up to 30% of adults. It results from failure of the septum primum and septum secundum to fuse during early childhood, creating a one-way tissue valve. This valve is forced closed when left atrial pressure exceeds right atrial pressure (which is most of the time), but it opens when right atrial pressure exceeds left atrial pressure, allowing for transient right-to-left shunting.
To test for the presence of a PFO, normal saline bubbles are injected intravenously, and echocardiography is performed to observe whether the bubbles pass from the right atrium into the left atrium. The release phase of a Valsalva maneuver increases venous return to the right atrium and consequently increases right atrial pressure to facilitate right-to-left shunting of saline bubbles and confirm the diagnosis (the strain phase of Valsalva maneuver decreases venous return to the RA and discourages shunting through a PFO).
(Choices A, B, and C) Medications and physiologic maneuvers that reduce venous return to the right atrium discourage right-to-left shunting through a PFO. Abrupt standing from a supine position causes blood to pool in the lower extremities, amyl nitrate (an inhaled nitrate) causes venous vasodilation, and exhalation causes increased intrathoracic pressure (resulting in partial collapse of the inferior vena cava at end-expiration), all of which reduce venous return to the right atrium.
(Choice D) Sustained hand grip increases systemic vascular resistance, increasing pressure in the left ventricle and left atrium and discouraging shunting through a PFO.
Educational objective:
Paradoxical embolization, or passage of a thromboembolism from the venous circulation to the arterial circulation, most commonly occurs through a patent foramen ovale (PFO). A PFO is a one-way tissue valve in the atrial septum that opens only when right atrial pressure exceeds left atrial pressure; venous return to the right atrium increases during the release (ie, relaxation) phase of a Valsalva maneuver and encourages opening of a PFO.
2
A 46-year-old man comes to the office for an annual examination. He has an uncomfortable heartbeat sensation at night that he tries to decrease by sleeping on his right side. The patient has had mild shortness of breath with exertion over the last 6 months, but he has no chest pain. He was told during a wellness check approximately 2 years ago that he had a heart murmur. The patient has no other medical problems. Physical examination reveals bounding femoral pulses and carotid pulsations that are accompanied by head bobbing. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A)Aortic regurgitation
B)Aortic stenosis
C)Atrial septal defect
D)Coarctation of the aorta
E)Mitral regurgitation
F)Mitral stenosis
G)Pulmonary stenosis
H)Tricuspid regurgitation
A)Aortic regurgitation
B)Aortic stenosis
C)Atrial septal defect
D)Coarctation of the aorta
E)Mitral regurgitation
F)Mitral stenosis
G)Pulmonary stenosis
H)Tricuspid regurgitation
A
This presentation is most suggestive of aortic regurgitation. The inability of aortic valve leaflets to effectively close during diastole leads to regurgitation of blood back into the left ventricular (LV) cavity with an increase in LV end-diastolic volume and wall stress. The resultant chamber enlargement and eccentric hypertrophy increase total stroke volume, which is often felt as a sense of pounding or an uncomfortable feeling of heartbeat (especially when lying on the left side).
Physical examination reveals an early "blowing" diastolic decrescendo murmur best heard at the left sternal border in the third or fourth intercostal space. The precordial impulse is hyperdynamic and displaced laterally and downward. Bounding femoral and carotid pulses, marked by abrupt distension and quick collapse ("water-hammer" pulses), are the result of the wide pulse pressure. Some patients exhibit head bobbing with carotid pulsations (de Musset sign) due to transfer of momentum from the large LV stroke volume to the head and neck. Significant systolic pulsations may also be noticed in other organs (eg, liver, spleen, retina) and the fingertips.
(Choice B) Patients with severe aortic stenosis have a characteristic arterial pulse - small pulse amplitude (pulsus parvus) with a delayed peak and slower upstroke of the arterial pulse (pulsus tardus) due to diminished stroke volume and prolonged ejection time.
(Choice C) The presence of atrial septal defect leads to left-to-right intracardiac shunting, which can cause a hyperdynamic right ventricular impulse. It does not cause any significant change in arterial pulse character.
(Choice D) Coarctation of the aorta causes systolic hypertension in the upper extremities along with characteristic diminished and/or delayed femoral pulses (brachial-femoral delay).
(Choice E) Arterial pulse, pulse pressure, and forward stroke volume remain normal in patients with chronic (compensated) mitral regurgitation.
(Choice F) Arterial pulses are reduced in volume and amplitude in patients with mitral stenosis due to decreased LV end-diastolic volume and stroke volume.
(Choices G and H) Tricuspid regurgitation and/or pulmonary stenosis are right-sided valvular lesions and do not cause any specific arterial pulse pattern on physical examination.
Educational objective:
Aortic regurgitation causes an increase in total stroke volume with abrupt distension and rapid falloff of peripheral arterial pulses, resulting in a wide pulse pressure. This leads to bounding peripheral pulses and head bobbing with each heartbeat.
__________
References:
Valvular heart disease: aortic regurgitation.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15998697)
This presentation is most suggestive of aortic regurgitation. The inability of aortic valve leaflets to effectively close during diastole leads to regurgitation of blood back into the left ventricular (LV) cavity with an increase in LV end-diastolic volume and wall stress. The resultant chamber enlargement and eccentric hypertrophy increase total stroke volume, which is often felt as a sense of pounding or an uncomfortable feeling of heartbeat (especially when lying on the left side).
Physical examination reveals an early "blowing" diastolic decrescendo murmur best heard at the left sternal border in the third or fourth intercostal space. The precordial impulse is hyperdynamic and displaced laterally and downward. Bounding femoral and carotid pulses, marked by abrupt distension and quick collapse ("water-hammer" pulses), are the result of the wide pulse pressure. Some patients exhibit head bobbing with carotid pulsations (de Musset sign) due to transfer of momentum from the large LV stroke volume to the head and neck. Significant systolic pulsations may also be noticed in other organs (eg, liver, spleen, retina) and the fingertips.
(Choice B) Patients with severe aortic stenosis have a characteristic arterial pulse - small pulse amplitude (pulsus parvus) with a delayed peak and slower upstroke of the arterial pulse (pulsus tardus) due to diminished stroke volume and prolonged ejection time.
(Choice C) The presence of atrial septal defect leads to left-to-right intracardiac shunting, which can cause a hyperdynamic right ventricular impulse. It does not cause any significant change in arterial pulse character.
(Choice D) Coarctation of the aorta causes systolic hypertension in the upper extremities along with characteristic diminished and/or delayed femoral pulses (brachial-femoral delay).
(Choice E) Arterial pulse, pulse pressure, and forward stroke volume remain normal in patients with chronic (compensated) mitral regurgitation.
(Choice F) Arterial pulses are reduced in volume and amplitude in patients with mitral stenosis due to decreased LV end-diastolic volume and stroke volume.
(Choices G and H) Tricuspid regurgitation and/or pulmonary stenosis are right-sided valvular lesions and do not cause any specific arterial pulse pattern on physical examination.
Educational objective:
Aortic regurgitation causes an increase in total stroke volume with abrupt distension and rapid falloff of peripheral arterial pulses, resulting in a wide pulse pressure. This leads to bounding peripheral pulses and head bobbing with each heartbeat.
__________
References:
Valvular heart disease: aortic regurgitation.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15998697)
3
A 50-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to intermittent palpitations over the last 6 months. The patient describes them as "very uncomfortable" and says the episodes occur randomly, last for several hours, and resolve spontaneously or with sleep. The current episode started an hour ago and has been accompanied by lightheadedness. He has no medical history and says that he does not like seeing doctors. He is a lifetime nonsmoker. The patient drinks beer on weekends. He has no family history of cardiovascular disease. Temperature is normal and blood pressure is 122/75 mm Hg. BMI is 30 kg/m2. Chest examination reveals no murmurs and the lungs are clear on auscultation. There is trace peripheral edema. Cardiac rhythm strip obtained in the emergency department is shown in the exhibit.
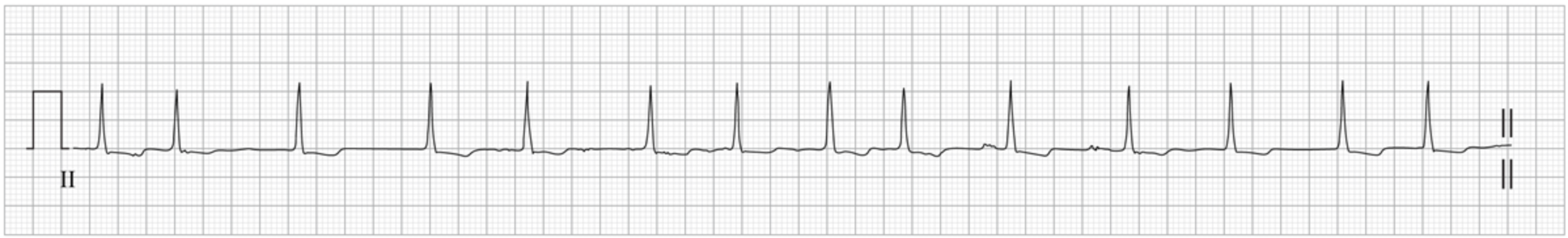
Aberrant electrical activity in which of the following anatomic structures is the most likely trigger for this patient's current condition?
A)Crista terminalis
B)Papillary muscles
C)Pulmonary veins
D)Right ventricular outflow tract
E)Sinoatrial node
F)Tricuspid valve annulus

Aberrant electrical activity in which of the following anatomic structures is the most likely trigger for this patient's current condition?
A)Crista terminalis
B)Papillary muscles
C)Pulmonary veins
D)Right ventricular outflow tract
E)Sinoatrial node
F)Tricuspid valve annulus
Pulmonary veins
4
A 34-year-old woman comes to the office due to exertional dyspnea. The patient has a history of IgA nephropathy; she received hemodialysis for 2 years before undergoing kidney transplantation last month. Chest x-ray reveals cardiomegaly and pulmonary congestion. Further evaluation determines that her symptoms are likely due to persistence of the arteriovenous fistula that was used for hemodialysis. Which of the following physiologic changes are most likely present in this patient due to the fistula?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A healthy 80-year-old man has participated in a longitudinal study over the past 30 years to study the effects of aging on overall cardiovascular status. He has undergone annual testing with echocardiography and his left ventricular ejection fraction has remained stable throughout the 30 years. Which of the following changes is most likely responsible for the preserved left ventricular ejection fraction in this patient?
A)Cardiomyocyte hypertrophy
B)Increased arterial reserve capacity
C)Increased left ventricular compliance
D)Increased left ventricular diastolic volume
E)Stable ventricular myocyte number
A)Cardiomyocyte hypertrophy
B)Increased arterial reserve capacity
C)Increased left ventricular compliance
D)Increased left ventricular diastolic volume
E)Stable ventricular myocyte number

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A 44-year-old man is hospitalized with multiple injuries following a motor vehicle collision. An arteriovenous fistula created by an injury would most likely result in which of the following changes to the left ventricular pressure-volume loop?Solid line = preinjury
Dashed line = postinjury
A)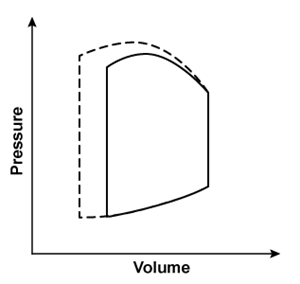
B)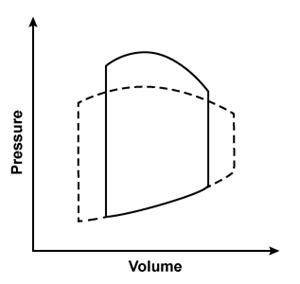
C)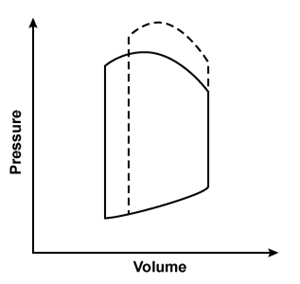
D)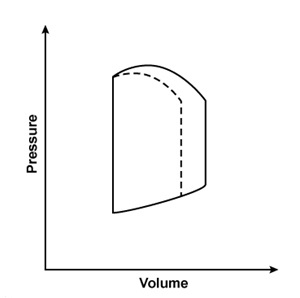
Dashed line = postinjury
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A 56-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to chest palpitations. He feels that his heartbeat is fast and very irregular. The patient has no chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness. Physical examination confirms the presence of an irregularly irregular rhythm with a heart rate of 120/min. He hosted a party last night for his wife's birthday and consumed a large amount of alcohol. The patient normally drinks only 2-3 times a year. He is otherwise healthy and takes no medications. Which of the following ECG findings is most likely in this patient?
A)Absent P waves
B)High voltage in precordial leads
C)Prolonged QRS complex
D)Prolonged QT interval
E)ST elevation
A)Absent P waves
B)High voltage in precordial leads
C)Prolonged QRS complex
D)Prolonged QT interval
E)ST elevation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A 14-year-old girl is brought to the office to establish medical care. The patient recently immigrated to the United States with her parents from Vietnam. Vital signs are within normal limits. Phonocardiogram obtained at the left upper sternal border is shown below. 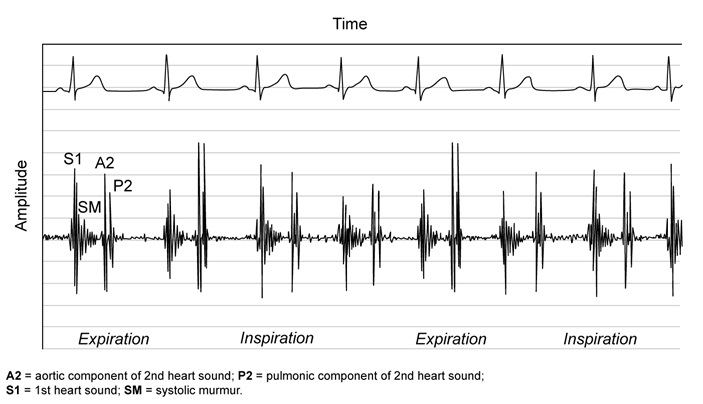 Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's heart murmur?
Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's heart murmur?
A)Abnormal narrowing of the aortic valve
B)Incomplete ventricular septum development
C)Increased pulmonary blood flow
D)Regurgitation of blood from the aorta
 Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's heart murmur?
Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's heart murmur?A)Abnormal narrowing of the aortic valve
B)Incomplete ventricular septum development
C)Increased pulmonary blood flow
D)Regurgitation of blood from the aorta

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Physiologists conducting research on the electrical properties of the heart measure action potential conduction velocity at 4 different points within normal cardiac tissue. The results, expressed in terms of speed of conduction (meters per second), are as follows:Point 1 - 0.05 m/sec
Point 2 - 0.3 m/sec
Point 3 - 1.1 m/sec
Point 4 - 2.2 m/secFrom the following list of locations, which most likely corresponds to the order of points 1-2-3-4 (AV = atrioventricular)?
A)Atrial muscle, ventricular muscle, Purkinje system, AV node
B)AV node, Purkinje system, ventricular muscle, atrial muscle
C)AV node, ventricular muscle, atrial muscle, Purkinje system
D)Purkinje system, AV node, ventricular muscle, atrial muscle
E)Ventricular muscle, AV node, Purkinje system, atrial muscle
Point 2 - 0.3 m/sec
Point 3 - 1.1 m/sec
Point 4 - 2.2 m/secFrom the following list of locations, which most likely corresponds to the order of points 1-2-3-4 (AV = atrioventricular)?
A)Atrial muscle, ventricular muscle, Purkinje system, AV node
B)AV node, Purkinje system, ventricular muscle, atrial muscle
C)AV node, ventricular muscle, atrial muscle, Purkinje system
D)Purkinje system, AV node, ventricular muscle, atrial muscle
E)Ventricular muscle, AV node, Purkinje system, atrial muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A 54-year-old man is admitted to the hospital due to cough, shortness of breath, and chest discomfort. He has a known history of coronary artery disease and underwent coronary artery bypass graft surgery 3 years ago. As a result of drug therapy, the left ventricular pressure-volume loop changes from a solid to a dashed line, as shown in the graph below (the loop is unchanged in areas where no dashed line is seen): 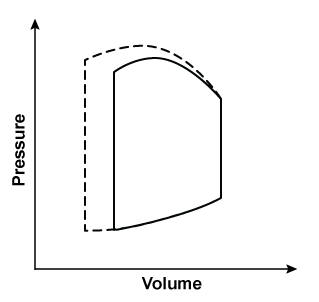 Which of the following parameters is most likely increased as a result of this change?
Which of the following parameters is most likely increased as a result of this change?
A)End-diastolic pressure
B)End-systolic volume
C)Stroke volume
D)Ventricular compliance
E)Ventricular preload
 Which of the following parameters is most likely increased as a result of this change?
Which of the following parameters is most likely increased as a result of this change?A)End-diastolic pressure
B)End-systolic volume
C)Stroke volume
D)Ventricular compliance
E)Ventricular preload

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Autopsy of a 78-year-old man demonstrates decreased left ventricular cavity size and a sigmoid-shaped ventricular septum. Light microscopy shows increased collagen content within the ventricular wall. Some myocardial cells also have brownish perinuclear cytoplasmic inclusions. The changes described are most consistent with which of the following conditions?
A)Dilated cardiomyopathy
B)Hemolytic anemia
C)Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
D)Ischemic heart disease
E)Long-standing hypertension
F)Normal aging
A)Dilated cardiomyopathy
B)Hemolytic anemia
C)Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
D)Ischemic heart disease
E)Long-standing hypertension
F)Normal aging

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A 56-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to palpitations that started several hours ago. He has not had similar symptoms before. The patient has had no chest pain, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, or syncope. He drinks alcohol on weekends and does not use illicit drugs. He has no family history of heart disease. Blood pressure is 145/78 mm Hg. BMI is 40 kg/m2. ECG is shown in the exhibit.
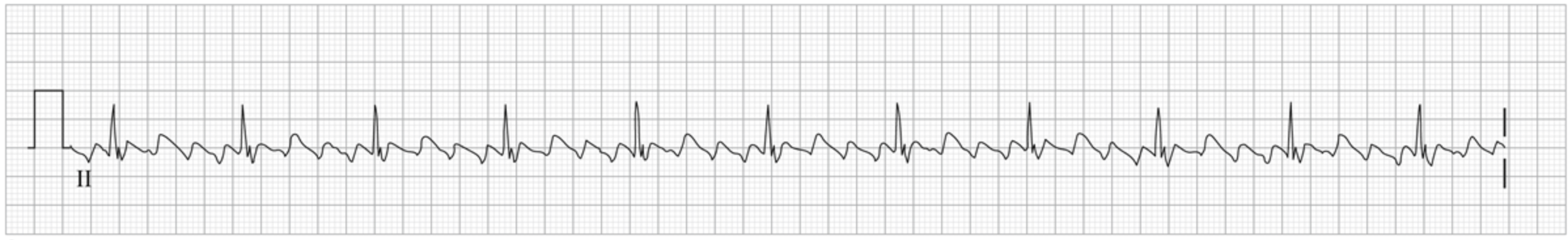
The patient is treated medically in the emergency department. He is then taken to the electrophysiology laboratory for radiofrequency catheter ablation to terminate his arrhythmia. The ablation procedure should create a conduction block through which of the following areas?
A)Accessory pathway bypassing the atrioventricular node
B)Area between the tricuspid valve and inferior vena cava in the right atrium
C)Area in the right ventricular outflow tract
D)Ostia of the pulmonary veins in the left atrium
E)Slow pathway of the atrioventricular node

The patient is treated medically in the emergency department. He is then taken to the electrophysiology laboratory for radiofrequency catheter ablation to terminate his arrhythmia. The ablation procedure should create a conduction block through which of the following areas?
A)Accessory pathway bypassing the atrioventricular node
B)Area between the tricuspid valve and inferior vena cava in the right atrium
C)Area in the right ventricular outflow tract
D)Ostia of the pulmonary veins in the left atrium
E)Slow pathway of the atrioventricular node

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A 55-year-old man undergoes an elective surgery under general anesthesia. Two hours into the surgery, his left ventricular pressure-volume loop has changed from the solid line to the dashed line, as shown in the image below (the loop is unchanged in areas where there is no dashed line): 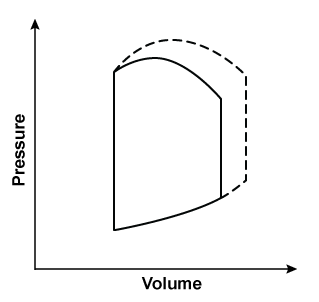 Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's hemodynamic change?
Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's hemodynamic change?
A)Abdominal aorta clamping
B)Blood volume loss
C)Dobutamine administration
D)Myocardial infarction
E)Normal saline infusion
 Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's hemodynamic change?
Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's hemodynamic change?A)Abdominal aorta clamping
B)Blood volume loss
C)Dobutamine administration
D)Myocardial infarction
E)Normal saline infusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A 34-year-old man comes to the clinic for evaluation of a heart murmur. The patient has no chest pain, palpitations, dizziness, or shortness of breath at rest. He also exercises regularly without any abnormal symptoms. Cardiac auscultation in the second right intercostal space reveals an ejection click along with a soft systolic murmur radiating to the neck. A normal volume and pressure tracing of the left ventricle is shown in the image below. Which of the following letters corresponds to the opening of the valve most likely affected in this patient? 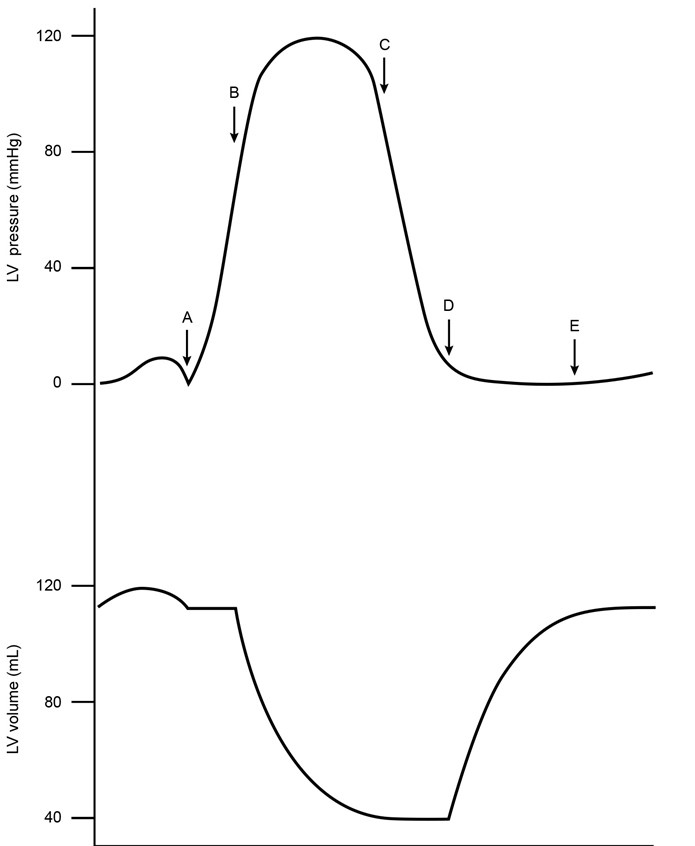
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A 46-year-old man comes to the office with chest pain and dyspnea on exertion. He has no known medical problems and leads a sedentary lifestyle. He is a lifetime nonsmoker. Noninvasive cardiac testing is nondiagnostic. Left and right heart catheterization is planned. During the procedure, the catheter records periodic pressure changes with a maximum of 25 mm Hg and minimum of 2 mm Hg. The catheter is advanced further, and then shows periodic pressure changes with a maximum of 25 mm Hg and a minimum of 10 mm Hg. Assuming the results of the procedure are normal, the first set of readings was most likely obtained from which of the following locations?
A)Left atrium
B)Left ventricle
C)Pulmonary artery
D)Right atrium
E)Right ventricle
A)Left atrium
B)Left ventricle
C)Pulmonary artery
D)Right atrium
E)Right ventricle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A 33-year-old man comes to the office due to fatigue and decreased exercise tolerance over the past 6 months. The patient was diagnosed with infective endocarditis in the setting of intravenous drug use a year ago and completed a course of antibiotic therapy. He has not used drugs since then. The patient has no other medical problems and takes no medications. A cardiac murmur is heard on auscultation. Both carotid arteries demonstrate a rapid rise and fall of the arterial pulse. Partial compression of the femoral arteries by the stethoscope elicits a systolic-diastolic bruit. Which of the following sets of pressure findings is most likely to be observed during cardiac catheterization of this patient?
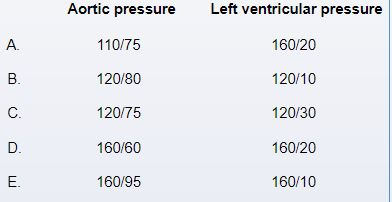


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A 54-year-old man is being evaluated for exertional dyspnea that started 6 months ago. The patient has no associated cough or wheezing. There is no known history of heart disease in his family. ECG, chest x-ray, exercise stress test, and echocardiogram are obtained to evaluate his symptoms. He subsequently undergoes right and left cardiac catheterization, and the results are as follows:  What additional information is necessary to calculate cardiac output in this patient?
What additional information is necessary to calculate cardiac output in this patient?
A)Arteriovenous difference in oxygen content
B)Oxygen-binding capacity of hemoglobin
C)Percentage of hemoglobin saturation
D)Rate of oxygen consumption
E)Respiratory quotient
 What additional information is necessary to calculate cardiac output in this patient?
What additional information is necessary to calculate cardiac output in this patient?A)Arteriovenous difference in oxygen content
B)Oxygen-binding capacity of hemoglobin
C)Percentage of hemoglobin saturation
D)Rate of oxygen consumption
E)Respiratory quotient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A 39-year-old man comes to the office due to increasing fatigue for the past 2 weeks. The patient reports no prior medical conditions, although he recently had a self-limiting upper respiratory illness. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs and has not traveled recently. Temperature is 37.2 C (99 F), blood pressure is 116/66 mm Hg, pulse is 100/min, and respirations are 20/min. Physical examination reveals lung crackles. Echocardiography shows no valvular abnormalities and the following parameters: 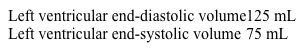 Based on the observed findings, which of the following is most accurate about this patient?
Based on the observed findings, which of the following is most accurate about this patient?
A)Cardiac output is 4 L/min
B)Cardiac output is 6 L/min
C)Left ventricular ejection fraction is 40%
D)Left ventricular ejection fraction is 60%
E)Stroke volume is 40 mL
F)Stroke volume is 60 mL
 Based on the observed findings, which of the following is most accurate about this patient?
Based on the observed findings, which of the following is most accurate about this patient?A)Cardiac output is 4 L/min
B)Cardiac output is 6 L/min
C)Left ventricular ejection fraction is 40%
D)Left ventricular ejection fraction is 60%
E)Stroke volume is 40 mL
F)Stroke volume is 60 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A 69-year-old man is brought to the emergency department with sudden onset palpitations and dyspnea. His medical history is significant for hypertension and gastroesophageal reflux disease. ECG reveals a heart rate of 120/min with an irregularly irregular rhythm, narrow QRS complexes, and no organized P waves. Which of the following physiologic factors most likely determines the ventricular contraction rate in this patient?
A)Atrial muscle depolarization rate
B)Atrioventricular node refractory period
C)Bundle branch conductivity
D)Purkinje system pacemaker activity
E)Sinoatrial node discharge rate
F)Ventricular muscle refractory period
A)Atrial muscle depolarization rate
B)Atrioventricular node refractory period
C)Bundle branch conductivity
D)Purkinje system pacemaker activity
E)Sinoatrial node discharge rate
F)Ventricular muscle refractory period

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A 43-year-old man is evaluated for occasional palpitations provoked by anxiety. The patient describes a sudden-onset pounding sensation in the chest followed by lightheadedness and shortness of breath. He has never had syncope. The patient has no history of heart disease, and family history is unremarkable. After initial evaluation, he is treated with verapamil and reports marked improvement in the frequency of palpitation episodes. The tracing below shows the electrical activity of a specific type of cardiac cell in the patient's heart. 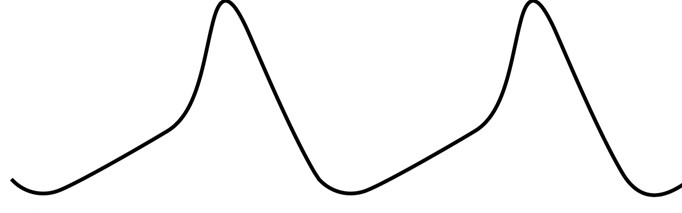 Which of the following effects would verapamil administration most likely have on these cells?
Which of the following effects would verapamil administration most likely have on these cells?
A)Decreased excitation and contraction coupling
B)Increased action potential amplitude
C)Lowered threshold potential
D)Reduced refractory period
E)Slowed spontaneous depolarization
 Which of the following effects would verapamil administration most likely have on these cells?
Which of the following effects would verapamil administration most likely have on these cells?A)Decreased excitation and contraction coupling
B)Increased action potential amplitude
C)Lowered threshold potential
D)Reduced refractory period
E)Slowed spontaneous depolarization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Researchers are studying the coronary circulation in various healthy and diseased states. They measure blood flow and pressure (blue circle) in one of the epicardial coronary arteries of an experimental animal with cardiovascular physiology similar to that of humans. Then they clamp the artery to simulate 60% atherosclerotic stenosis and remeasure the flow and pressure distal to the lesion. Which of the following changes are most likely to be observed once steady state is achieved? 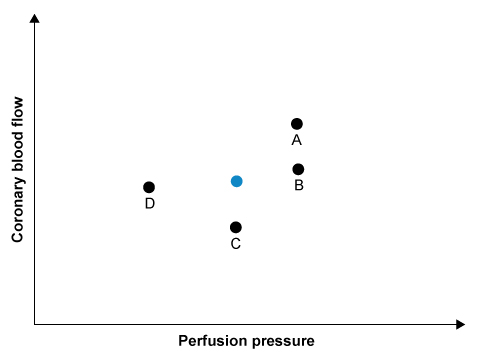
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A 22-year-old man comes to the clinic for a routine physical. The patient has no medical problems and takes no medication. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. He plays on his college football team and participates in intense training sessions and weekly games. Review of systems is unremarkable. Blood pressure is 120/76 mm Hg, pulse is 68/min, and respirations are 15/min. BMI is 28 kg/m2. Blood pressures in the upper and lower extremities are equal. There is no jugular venous distension. Carotid upstrokes are brisk. There is a grade 2/6 early systolic murmur along the left sternal border. The murmur decreases in intensity with hand grip and passive leg elevation. Lung sounds are normal without crackles or wheezes. Echocardiogram is most likely to demonstrate which of the following findings?
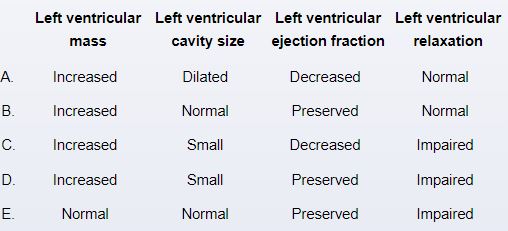


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A 66-year-old man comes to the office for a follow-up appointment. The patient has a history of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and has had persistent dyspnea despite taking the maximal dosage of his heart failure medications. He has had no lightheadedness or chest pain. Blood pressure is 133/72 mm Hg and pulse is 76/min. Physical examination shows normal lung sounds and no lower extremity edema. His medical treatment is modified with the addition of a combination pill that inhibits neprilysin and blocks angiotensin II receptors. Which of the following is the most likely effect of this medication?
A)Decreased renal free-water reabsorption
B)Decreased venous compliance
C)Increased myocardial contractility
D)Increased peripheral arterial resistance
E)Increased urinary sodium excretion
A)Decreased renal free-water reabsorption
B)Decreased venous compliance
C)Increased myocardial contractility
D)Increased peripheral arterial resistance
E)Increased urinary sodium excretion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A 44-year-old man comes to the office due to increasing shortness of breath. While climbing the stairs to his second-floor apartment, the patient must now stop halfway to catch his breath. He has a history of nonischemic cardiomyopathy and chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. After evaluation, treatment with a new medication is begun that improves his symptoms by increasing urine output and decreasing peripheral vascular resistance. The medication works by inhibiting a metalloprotease to prolong the action of endogenous polypeptides. These polypeptides are most likely secreted by which of the following cell types?
A)Adrenal zona glomerulosa cells
B)Cardiomyocytes
C)Hepatic stellate cells
D)Myocardial Purkinje fibers
E)Renal juxtaglomerular cells
F)Vascular endothelial cells
A)Adrenal zona glomerulosa cells
B)Cardiomyocytes
C)Hepatic stellate cells
D)Myocardial Purkinje fibers
E)Renal juxtaglomerular cells
F)Vascular endothelial cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A 64-year-old man presents to the office with chest discomfort and mild shortness of breath that started one hour ago after an argument with his wife. He has a long history of hypertension and diabetes mellitus. His blood pressure is 180/100 mmHg and his heart rate is 100/min. An EKG taken in the emergency department shows no signs of acute ischemia. Cardiac auscultation in the left decubitus position on full expiration reveals a presystolic sound. Which of the following best explains this physical examination finding?
A)Papillary muscle dysfunction
B)Left ventricular hypertrophy
C)Increased left ventricular preload
D)Aortic regurgitation
E)Mitral leaflet fusion and fibrosis
A)Papillary muscle dysfunction
B)Left ventricular hypertrophy
C)Increased left ventricular preload
D)Aortic regurgitation
E)Mitral leaflet fusion and fibrosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A 67-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his son after a syncopal episode. The son was helping his father clean out the garage when the father said he felt dizzy. As the son was helping him into a chair, the patient lost consciousness. He woke up spontaneously about a minute later without any disorientation or confusion. ECG demonstrates bradycardia with a regular rhythm and narrow QRS complexes. There is complete desynchronization between the P waves and QRS complexes. Which of the following locations is most likely pacing this patient's ventricles?
A)His bundle
B)Left bundle branch
C)Left ventricular muscle
D)Purkinje system
E)Sinoatrial node
A)His bundle
B)Left bundle branch
C)Left ventricular muscle
D)Purkinje system
E)Sinoatrial node

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A 32-year-old man is evaluated in the emergency department due to fever, night sweats, and chills over the last several days. The patient has been using intravenous drugs recently as he is "stressed out." He has otherwise been in good health with no medical problems. Temperature is 38.3 C (101 F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, and pulse is 105/min and regular. Further evaluation reveals aortic valve endocarditis with an intracardiac abscess and small fistula formation between the aortic root and right ventricle. Doppler ultrasound interrogation of the fistula will most likely reveal which of the following blood flow patterns?
A)Flow from the aortic root to the right ventricle continuously
B)Flow from the aortic root to the right ventricle only in diastole
C)Flow from the aortic root to the right ventricle only in systole
D)Flow from the right ventricle to the aortic root continuously
E)Flow from the right ventricle to the aortic root only in diastole
F)Flow from the right ventricle to the aortic root only in systole
A)Flow from the aortic root to the right ventricle continuously
B)Flow from the aortic root to the right ventricle only in diastole
C)Flow from the aortic root to the right ventricle only in systole
D)Flow from the right ventricle to the aortic root continuously
E)Flow from the right ventricle to the aortic root only in diastole
F)Flow from the right ventricle to the aortic root only in systole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A 55-year-old man is immediately brought to the hospital after experiencing a sudden collapse at home 20 minutes ago. The patient reported chest pain and then collapsed to the floor while trying to sit down. Medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Temperature is 36.7 C (98.1 F), blood pressure is 80/50 mm Hg, pulse is 120/min, and respirations are 22/min. On examination, the patient is in marked respiratory distress. Bilateral crackles are present. An S3 is audible. ECG reveals ST-segment elevation in leads V2 through V6. Which of the following hemodynamic changes are most likely present in this patient?
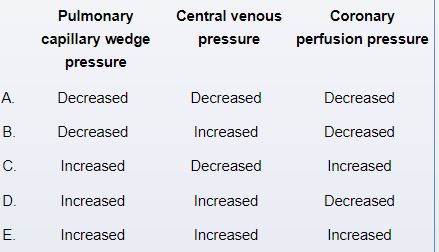


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Researchers are observing how coronary blood flow changes in response to progressive increases in the mean arterial blood pressure (see graph below). 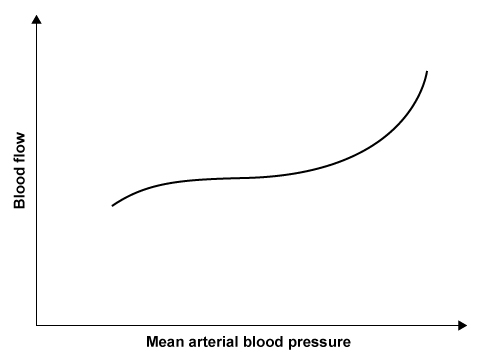 The mostly horizontal portion of the slope indicates a region where coronary blood flow is relatively insensitive to blood pressure changes. Within this zone of autoregulation, the metabolic demands of the myocardium are the main determinant of coronary blood flow. Which of the following endogenous factors is most responsible for controlling coronary blood flow within this range?
The mostly horizontal portion of the slope indicates a region where coronary blood flow is relatively insensitive to blood pressure changes. Within this zone of autoregulation, the metabolic demands of the myocardium are the main determinant of coronary blood flow. Which of the following endogenous factors is most responsible for controlling coronary blood flow within this range?
A)Acetylcholine
B)Angiotensin II
C)Histamine
D)Nitric oxide
E)Norepinephrine
F)Serotonin
 The mostly horizontal portion of the slope indicates a region where coronary blood flow is relatively insensitive to blood pressure changes. Within this zone of autoregulation, the metabolic demands of the myocardium are the main determinant of coronary blood flow. Which of the following endogenous factors is most responsible for controlling coronary blood flow within this range?
The mostly horizontal portion of the slope indicates a region where coronary blood flow is relatively insensitive to blood pressure changes. Within this zone of autoregulation, the metabolic demands of the myocardium are the main determinant of coronary blood flow. Which of the following endogenous factors is most responsible for controlling coronary blood flow within this range?A)Acetylcholine
B)Angiotensin II
C)Histamine
D)Nitric oxide
E)Norepinephrine
F)Serotonin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A 65-year-old man reports multiple episodes of lightheadedness while buttoning a tight shirt collar. During 2 episodes, he passed out briefly but sustained no injuries. His blood pressure was 70/40 mm Hg and pulse was 45/min during one of the episodes. Past medical history is significant for hypertension and diet-controlled diabetes mellitus. The patient is a lifetime nonsmoker and drinks alcohol on social occasions. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 125/72 mm Hg and pulse is 76/min without orthostatic changes. Stimulation of afferent sensory fibers in which of the following nerves is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
A)Accessory
B)Glossopharyngeal
C)Hypoglossal
D)Trigeminal
E)Vagus
A)Accessory
B)Glossopharyngeal
C)Hypoglossal
D)Trigeminal
E)Vagus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A 70-year-old woman comes to the office due to progressive exertional dyspnea over the last year. She has no chest pain or lower-extremity swelling. The patient has long-standing hypertension but has not always been adherent to her medical regimen. She is a lifetime nonsmoker. Blood pressure is 164/73 mm Hg and pulse is 88/min and regular. An S4 is heard on cardiac auscultation. The lungs are clear. Echocardiogram reveals left atrial enlargement, moderate concentric left ventricular hypertrophy, and a left ventricular ejection fraction of 67%. Which of the following changes are most likely to be seen in this patient?
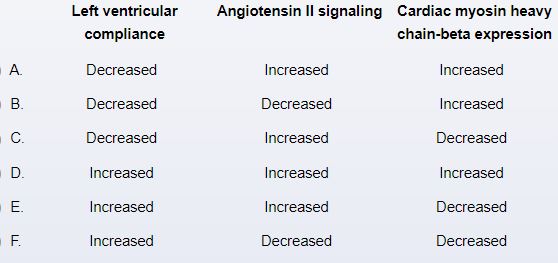


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A multinational research institute conducting experiments on human circulatory physiology enrolls a healthy 30-year-old male volunteer to assess the oxygen consumption rate of various organs. During the study, the blood oxygen content of the aorta and several other vessels is measured at rest. The greatest difference in these measurements will most likely be between the aorta and which of the following blood vessels?
A)Brachial vein
B)Coronary sinus
C)Internal jugular vein
D)Portal vein
E)Pulmonary artery
F)Renal vein
A)Brachial vein
B)Coronary sinus
C)Internal jugular vein
D)Portal vein
E)Pulmonary artery
F)Renal vein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A 43-year-old man comes to the office due to occasional chest discomfort over the last 6 weeks. He thinks he is most likely experiencing musculoskeletal pain but is concerned due to family history of heart disease. The patient has no medical conditions and does not use tobacco. He leads an active lifestyle and exercises every day. He undergoes treadmill exercise stress testing. Baseline blood pressure is 122/75 mm Hg and pulse is 54/min. After 10 minutes of exercise, his blood pressure is 155/80 mm Hg and pulse is 150/min. He has no chest pain and ECG shows no abnormalities. Compared to pretest conditions, which of the following is the single most important limiting factor for left ventricular myocardial blood supply during the test?
A)Contraction force
B)Coronary vasoconstriction
C)Diastolic aortic pressure
D)Duration of diastole
E)Intraventricular pressure
F)Systolic ventricular wall stress
A)Contraction force
B)Coronary vasoconstriction
C)Diastolic aortic pressure
D)Duration of diastole
E)Intraventricular pressure
F)Systolic ventricular wall stress

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Special electrodes are used to detect the change in membrane potential of a specific type of cardiac cell. These changes are recorded on the graph below.  The deflection indicated by the arrow is most likely caused by movement of which of the following ions?
The deflection indicated by the arrow is most likely caused by movement of which of the following ions?
A)Sodium
B)Potassium
C)Calcium
D)Chloride
E)Sodium and potassium
F)Calcium and potassium
 The deflection indicated by the arrow is most likely caused by movement of which of the following ions?
The deflection indicated by the arrow is most likely caused by movement of which of the following ions?A)Sodium
B)Potassium
C)Calcium
D)Chloride
E)Sodium and potassium
F)Calcium and potassium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Electrophysiologists conduct a study in which they record the membrane potential changes of cardiac cells while exposing them to various agents. A tracing from one of the experiments is shown below. 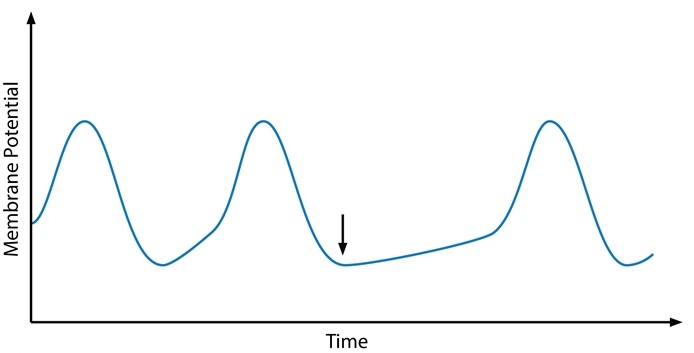 Which of the following substances was most likely applied to the cells at the point indicated by the arrow?
Which of the following substances was most likely applied to the cells at the point indicated by the arrow?
A)Adenosine
B)Aldosterone
C)Angiotensin II
D)Glucagon
E)Glycine
F)Norepinephrine
 Which of the following substances was most likely applied to the cells at the point indicated by the arrow?
Which of the following substances was most likely applied to the cells at the point indicated by the arrow?A)Adenosine
B)Aldosterone
C)Angiotensin II
D)Glucagon
E)Glycine
F)Norepinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A 63-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to dyspnea. Over the past several days, the patient has experienced progressively worsening shortness of breath while walking his dog around the block. In addition, he could not breathe while lying in bed last night and fell asleep only after moving to a recliner. The patient had an acute myocardial infarction 2 years ago and has been nonadherent with his medications and follow-up appointments. Temperature is 36.7 C (98 F), blood pressure is 122/74 mm Hg, pulse is 94/min, and respirations are 22/min. Physical examination shows bibasilar lung crackles, jugular venous distension, and bilateral pitting edema in the lower extremities. Chest x-ray reveals cardiomegaly and pulmonary venous congestion. Which of the following factors is most likely contributing to this patient's symptoms?
A)Decreased arteriolar resistance
B)Decreased plasma renin activity
C)Decreased ventricular end-diastolic pressure
D)Increased plasma brain natriuretic peptide concentration
E)Increased sympathetic nervous system activity
A)Decreased arteriolar resistance
B)Decreased plasma renin activity
C)Decreased ventricular end-diastolic pressure
D)Increased plasma brain natriuretic peptide concentration
E)Increased sympathetic nervous system activity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A 65-year-old woman is brought to the hospital due to sudden-onset chest heaviness and shortness of breath that began an hour ago. Her medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus, obesity, and hypertension. Temperature is 36.7 C (98.1 F), blood pressure is 80/50 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 20/min. Extremities are cold and clammy. Diaphoresis is present. ECG shows ST-segment elevation in the lateral leads. Which of the following hemodynamic changes are most likely present in this patient?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A 45-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to a 2-day history of dyspnea, orthopnea, and ankle swelling. This morning, he also had nausea, vomiting, and a headache. Blood pressure is elevated, and physical examination shows pulmonary crackles and bilateral pitting edema up to the knees. A sodium nitroprusside infusion is begun. Which of the following left ventricular pressure/volume relationships best represents the effects of this therapy?*Solid line = before nitroprusside; dashed line = during nitroprusside infusion.
A)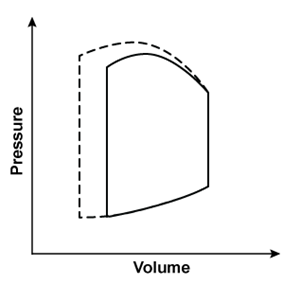
B)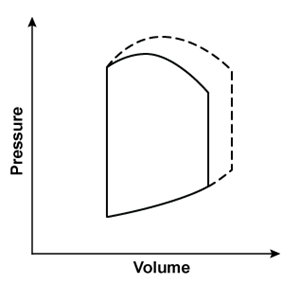
C)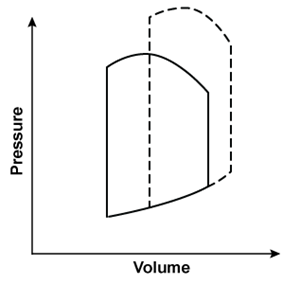
D)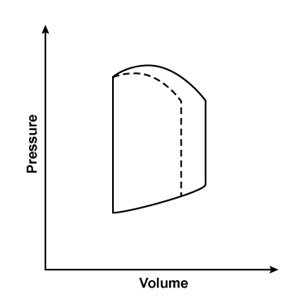
E)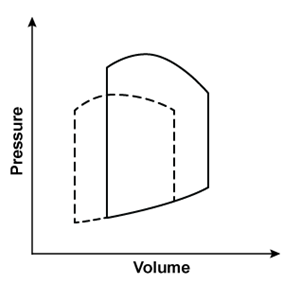
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A 53-year-old man comes to the office due to difficulty breathing and increasing fatigue. He has shortness of breath at night and has been sleeping in a recliner to help relieve his dyspnea. Medical history is significant for hypertension and hyperlipidemia. Two months ago, the patient suffered a myocardial infarction that was not revascularized due to a delay in seeking treatment. He quit smoking afterward, but had previously smoked a pack of cigarettes daily for 25 years. On cardiac auscultation, a low-frequency diastolic heart sound is heard shortly after the second heart sound when the patient lies in the left lateral decubitus position. Cardiac imaging shows hypokinesis of the left ventricular free wall. Which of the following is most likely to accentuate this patient's abnormal auscultation finding?
A)Amyl nitrite inhalation
B)Furosemide injection
C)Having the patient stand up
D)Listening at end expiration
E)Valsalva strain phase
A)Amyl nitrite inhalation
B)Furosemide injection
C)Having the patient stand up
D)Listening at end expiration
E)Valsalva strain phase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A large pharmaceutical company is conducting research on an experimental drug that affects blood flow in diseased tissue. A healthy 30-year-old man is enrolled in the trial, and patterns of normal blood flow through various tissues are studied. One of the patterns is shown in the image below:  The blood flow curve was most likely obtained from tissue of which of the following?
The blood flow curve was most likely obtained from tissue of which of the following?
A)Adrenal medulla
B)Brain cortex
C)Left ventricular myocardium
D)Renal cortex
E)Renal medulla
F)Right ventricular myocardium
G)Subcortical nuclei
 The blood flow curve was most likely obtained from tissue of which of the following?
The blood flow curve was most likely obtained from tissue of which of the following?A)Adrenal medulla
B)Brain cortex
C)Left ventricular myocardium
D)Renal cortex
E)Renal medulla
F)Right ventricular myocardium
G)Subcortical nuclei

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A 20-year-old, previously healthy woman is brought to the emergency department after a motor vehicle collision. The patient was a restrained, rear-seat passenger when another car struck the side door. There was extensive damage to the vehicle, resulting in a prolonged extrication time. On arrival at the emergency department, blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg and pulse is 120/min. On physical examination, the patient is alert but appears anxious, pale, and diaphoretic. There is no obvious head or neck injury. The lungs are clear bilaterally and cardiac auscultation reveals tachycardia. The abdomen is soft. Several actively bleeding lacerations are present on the lower extremities. X-rays show pelvic and left femoral shaft fractures. Which of the following findings are most likely present in this patient?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Researchers conduct an experiment to determine hemodynamic changes during exercise. Invasive monitoring of various parameters is performed to obtain a left ventricular pressure-volume loop. Compared to at rest, which of the following changes is most likely to be observed during moderate to heavy exercise?(solid line: at rest; dashed line: during exercise)
A)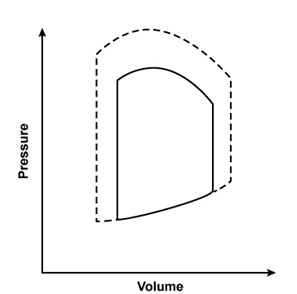
B)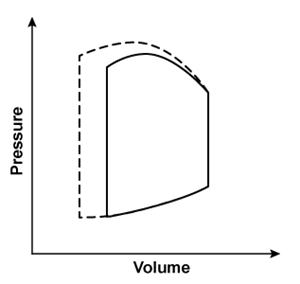
C)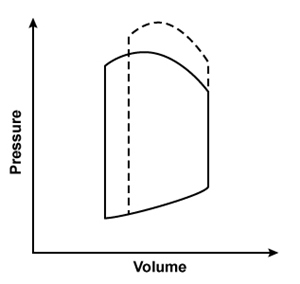
D)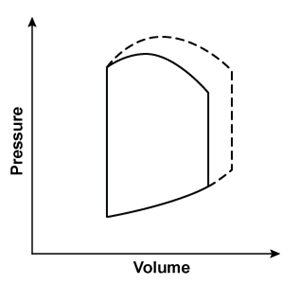
E)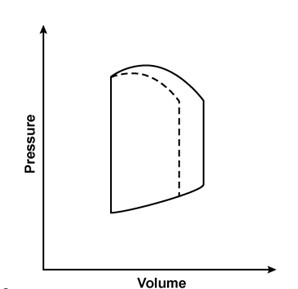
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In an experiment, 3 L of isotonic saline are infused intravenously into a healthy volunteer after multiple baseline physiologic parameters are recorded. Serial blood pressure measurements show an increase in the systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Ultrasonography reveals an increase in the left ventricular volume and engorgement of the inferior vena cava. Blood levels of a peptide hormone have also increased compared to baseline. This hormone is most likely to increase which of the following in this test subject?
A)Acid content of the urine
B)Glomerular filtration rate
C)Renal sodium reabsorption
D)Renal water reabsorption
E)Vascular resistance
A)Acid content of the urine
B)Glomerular filtration rate
C)Renal sodium reabsorption
D)Renal water reabsorption
E)Vascular resistance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A 48-year-old man with diet-controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus is being evaluated for occasional retrosternal chest pain. He has no history of hypertension, and his blood pressure measurements during office visits were always within normal limits. There is no family history of cardiovascular disease. The patient undergoes exercise treadmill stress testing. He walks for 7 minutes on the treadmill and stops due to fatigue but does not experience chest pain. His ECG does not show any abnormal changes. Heart rate ranges from 70/min at rest to 132/min at peak and mean blood pressure ranges from 95 mm Hg at rest to 112 mm Hg at peak. Which of the following parameters was most likely decreased during peak stress compared to the resting state in this patient?
A)Cardiac output
B)Left ventricular end-diastolic pressure
C)Pulmonary artery systolic pressure
D)Systemic systolic blood pressure
E)Total systemic vascular resistance
A)Cardiac output
B)Left ventricular end-diastolic pressure
C)Pulmonary artery systolic pressure
D)Systemic systolic blood pressure
E)Total systemic vascular resistance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
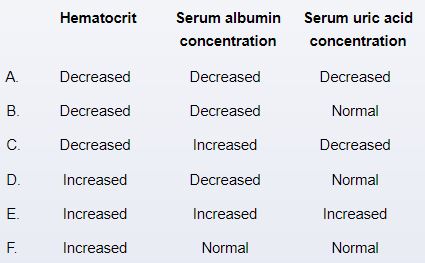
An 8-month-old previously healthy infant is brought to the urgent care clinic due to vomiting and watery diarrhea for the past 3 days. He attends a day care where recently several other children had similar symptoms. His mother states that the infant is less active and has no interest in feeding. Physical examination shows a listless infant with tachycardia, dry mucous membranes, and decreased skin turgor. The abdomen is nontender with hyperactive bowel sounds. Compared to pre-illness levels, which of the following sets of laboratory findings are most likely present in this patient?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A 34-year-old woman who recently emigrated from Russia comes to the physician due to weakness, exertional dyspnea, and orthopnea. On cardiac auscultation, a snap followed by a rumbling diastolic murmur is heard over the cardiac apex. The snap most likely occurs nearest to which of the following points on the cardiac pressure-volume loop? 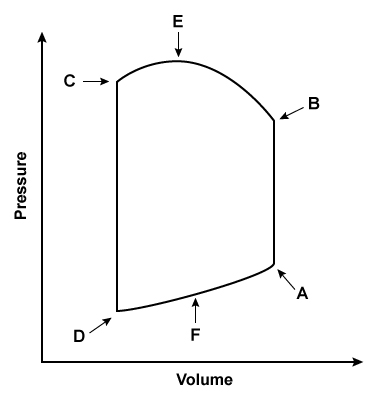
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
F)F

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
F)F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A 28-year-old professional endurance athlete comes to the office after his team physician detected a heart murmur. The patient has no symptoms and has no exercise limitations. Medical history is nonsignificant. Blood pressure is 110/66 mm Hg and pulse is 54/min. Physical examination shows a soft systolic murmur best heard at the left second intercostal space in the supine position. The murmur disappears when the patient is upright but reappears after brief exercise. Which of the following cardiovascular adaptations best explains this patient's finding?
A)Decreased pulmonary vascular capacitance
B)Decreased vagal tone
C)Increased stroke volume
D)Increased systemic vascular resistance
E)Increased ventricular wall thickness
A)Decreased pulmonary vascular capacitance
B)Decreased vagal tone
C)Increased stroke volume
D)Increased systemic vascular resistance
E)Increased ventricular wall thickness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A 32-year-old woman comes to the outpatient clinic due to shortness of breath for the past 6 months. The patient says she can walk only 3-4 blocks on level ground before feeling out of breath. She also has an occasional dry cough at night. The patient denies any chest pain, palpitations, syncope, weight loss, or lower extremity swelling. She immigrated from Guatemala 8 years ago. Medical history is unremarkable. On physical examination, the patient appears comfortable. Blood pressure is 128/75 mm Hg and pulse is 78/min and regular. Peripheral pulses are full and symmetric. The lungs are clear on auscultation. S1 is loud. With the patient positioned on her left side and breath held at the end of expiration, a diastolic murmur is heard at mid- and end diastole. Otherwise, examination is unremarkable. Which of the following are the most likely left ventricular hemodynamic findings at rest in this patient?
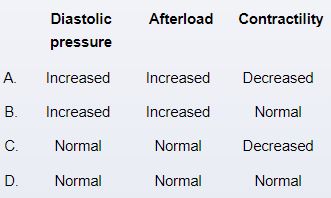


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A 44-year-old man with progressive dyspnea is diagnosed with dilated cardiomyopathy. Despite optimal medical therapy, he continues to have symptoms and disease progression is noted. He undergoes cardiac transplantation after a suitable donor becomes available. Permission is obtained from the patient to study his diseased heart for intracellular calcium regulation. Microelectrodes placed into cardiac muscle cells detect a rapid decrease in cytoplasmic calcium level immediately preceding relaxation. Which of the following proteins is most likely responsible for the observed change in electrolyte levels?
A)Calmodulin
B)Na+/Ca2+ exchanger
C)Ryanodine receptors
D)Troponin C
E)Voltage-dependent calcium channels
A)Calmodulin
B)Na+/Ca2+ exchanger
C)Ryanodine receptors
D)Troponin C
E)Voltage-dependent calcium channels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A 4-week-old boy undergoes cardiac catheterization for closure of a patent ductus arteriosus. The patient was born at 26 weeks gestation due to placental abruption. He has been cared for in the neonatal intensive care unit since delivery. Pulse oximetry shows 99% in the right hand and left foot. Echocardiography shows a moderately sized patent ductus arteriosus. After catheterization but before closure, blood gases are obtained from several locations. Compared with the partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) of a normal infant, this patient would be expected to have a higher PaO2 in which of the following locations?
A)Ascending aorta
B)Descending aorta
C)Left atrium
D)Pulmonary artery
E)Right atrium
A)Ascending aorta
B)Descending aorta
C)Left atrium
D)Pulmonary artery
E)Right atrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A 32-year-old man comes to the office due to progressive dyspnea, dizziness, and chest discomfort. He has no prior medical problems but had a mild respiratory illness 2 weeks earlier that resolved spontaneously. His father has a history of myocardial infarction. Echocardiography shows pericardial fluid accumulation with late diastolic collapse of the right atrium. Which of the following physical examination findings is most likely to be seen in this patient?
A)Beat-to-beat variation in pulse amplitude
B)Drop in pulse amplitude during inspiration
C)Pulse with 2 distinct peaks
D)Rapidly rising pulse with high amplitude
E)Slow-rising low-amplitude pulse
A)Beat-to-beat variation in pulse amplitude
B)Drop in pulse amplitude during inspiration
C)Pulse with 2 distinct peaks
D)Rapidly rising pulse with high amplitude
E)Slow-rising low-amplitude pulse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A 2-year-old, previously healthy boy is brought to the emergency department due to a 4-day history of poor feeding, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. The patient has had 5-7 bowel movements every day for the past 4 days. Temperature is 36.8 C (98.2 F) and blood pressure is 65/42 mm Hg. On physical examination, the patient is lethargic. Mucous membranes are dry, and the eyes are sunken. The lungs are clear to auscultation. No murmurs are heard. Abdominal examination shows distension and tenderness; bowel sounds are hyperactive throughout. Which of the following changes is most likely present in this patient?
A)Extravasation of fluid from systemic capillaries
B)Increased arteriolar capacitance
C)Increased central venous pressure
D)Increased ventilatory rate
E)Relaxation of venous smooth muscle
A)Extravasation of fluid from systemic capillaries
B)Increased arteriolar capacitance
C)Increased central venous pressure
D)Increased ventilatory rate
E)Relaxation of venous smooth muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A 38-year-old woman is being evaluated for shortness of breath. The patient has had poor exercise tolerance for the last several months that she initially attributed to deconditioning. Over the last several weeks, her symptoms have gotten progressively worse and she currently feels short of breath even during mild exertion. The patient has no family history of heart disease. As part of her evaluation, she undergoes right and left heart catheterization. The following data are obtained:  Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
A)Aortic stenosis
B)Cardiac tamponade
C)Dilated cardiomyopathy
D)Mitral stenosis
E)Restrictive cardiomyopathy
 Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?A)Aortic stenosis
B)Cardiac tamponade
C)Dilated cardiomyopathy
D)Mitral stenosis
E)Restrictive cardiomyopathy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A 43-year-old man comes to the emergency department after experiencing 4 episodes of coffee ground emesis that started earlier this morning. He also describes epigastric pain over the last 3-4 months that was relieved by over-the-counter antacids. He has no other past medical history. The patient has smoked a pack of cigarettes daily for the last 20 years but does not use alcohol or illicit drugs. Blood pressure is 70/40 mm Hg and pulse is 130/min and regular. Extremities are cool to the touch with loss of skin turgor. Intravenous access is obtained via 2 large-bore peripheral catheters, and rapid infusion of 2 liters of normal saline is initiated. This intervention is most likely to increase which of the following hemodynamic parameters?
A)Aortic wall elasticity
B)Diastolic ventricular compliance
C)End-diastolic sarcomere length
D)Heart rate
E)Plasma renin activity
F)Total peripheral resistance
G)Ventricular muscle contraction velocity
A)Aortic wall elasticity
B)Diastolic ventricular compliance
C)End-diastolic sarcomere length
D)Heart rate
E)Plasma renin activity
F)Total peripheral resistance
G)Ventricular muscle contraction velocity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A 43-year-old man is being evaluated for occasional retrosternal chest pressure that develops with moderate exertion and sometimes occurs when resting. He does not use alcohol, tobacco, or illicit drugs. The patient has an extensive family history of coronary artery disease. His temperature is 36.7 C (98 F), blood pressure is 124/72 mm Hg, pulse is 81/min, and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Coronary angiography shows mild luminal irregularities but no significant obstructive lesions. Acetylcholine infusion during the procedure results in dilation of epicardial coronary vessels. A reaction involving which of the following amino acids is most likely responsible for the observed dilation?
A)Arginine
B)Aspartate
C)Glutamate
D)Tryptophan
E)Tyrosine
A)Arginine
B)Aspartate
C)Glutamate
D)Tryptophan
E)Tyrosine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A 26-year-old man collapsed while playing basketball and could not be resuscitated. Prior to the episode, he had exertional dyspnea and lightheadedness. Autopsy is performed. The lungs are completely normal. The heart is shown in the exhibit.
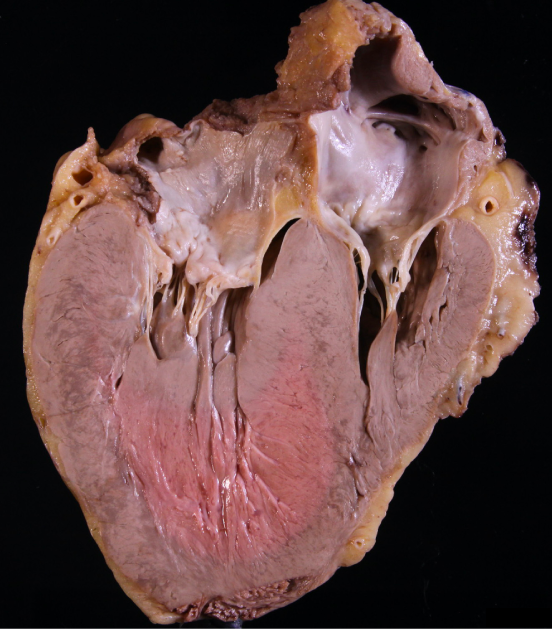
If the patient had been examined prior to death, which of the following would most likely have been present?
A)Delayed carotid upstroke
B)Early systolic murmur at the apex
C)Mid-diastolic murmur at the apex
D)S4
E)Single S2

If the patient had been examined prior to death, which of the following would most likely have been present?
A)Delayed carotid upstroke
B)Early systolic murmur at the apex
C)Mid-diastolic murmur at the apex
D)S4
E)Single S2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The cardiac output and venous return curves of a healthy person are shown below with solid lines. 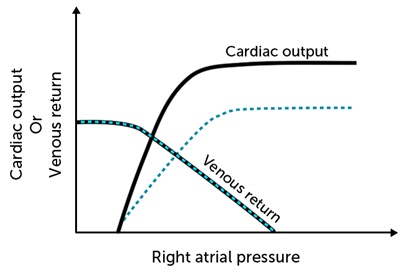 Which of the following is the most likely cause of the change depicted by the dashed lines?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of the change depicted by the dashed lines?
A)Excessive hydration
B)Acute hemorrhage
C)Chronic anemia
D)Myocardial infarction
E)Anaphylaxis
 Which of the following is the most likely cause of the change depicted by the dashed lines?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of the change depicted by the dashed lines?A)Excessive hydration
B)Acute hemorrhage
C)Chronic anemia
D)Myocardial infarction
E)Anaphylaxis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A 12-day-old girl is evaluated in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) due to a murmur. The patient was born at 25 weeks gestation and was admitted to the NICU for respiratory support. She was born to a 21-year-old primigravida whose pregnancy was complicated by preeclampsia. Cardiac auscultation reveals a continuous murmur at the left sternal border, and bounding femoral and palmar pulses are palpable. Echocardiography confirms the diagnosis. Compared with a normal infant, this patient most likely has which of the following changes in cardiac parameters?
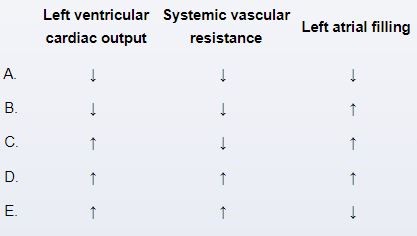


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A 52-year-old man comes to the office with a 2-week history of shortness of breath and dry cough. The patient has noticed decreased exercise tolerance that limits his daily activities. A Doppler probe placed at the cardiac apex reveals the following blood flow pattern across the patient's mitral valve. 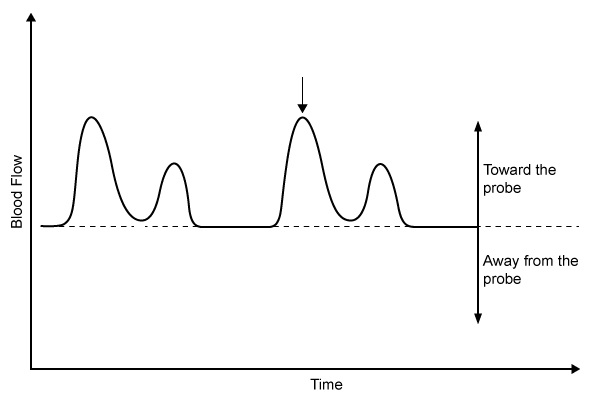 The point marked by the arrow would best correspond to which of the following auscultation findings?
The point marked by the arrow would best correspond to which of the following auscultation findings?
A)Fourth heart sound
B)Midsystolic click
C)Second heart sound
D)Third heart sound
 The point marked by the arrow would best correspond to which of the following auscultation findings?
The point marked by the arrow would best correspond to which of the following auscultation findings?A)Fourth heart sound
B)Midsystolic click
C)Second heart sound
D)Third heart sound

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A 32-year-old woman comes to the office for preconception medical evaluation. She feels well, reports no health issues, and has had regular menstruations. The patient is an elite long-distance swimmer and recently retired from professional career of 10 years. She still continues to practice swimming regularly. The patient does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Blood pressure is 114/66 mm Hg and pulse is 60/min. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Compared to a person of similar age and sex with sedentary lifestyle, which of the following cardiac changes are most likely present in this patient?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A 17-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department after passing out. The patient was standing behind the dugout watching his friends play baseball when he suddenly felt warm and light-headed. Then he remembers awakening on the ground. Bystanders reported that the patient was unresponsive for approximately 2 minutes. He feels fatigued but does not have chest pain or shortness of breath. The patient has no significant medical history and does not use alcohol or drugs. Temperature is 36.7 C (98.1 F), supine blood pressure is 105/60 mm Hg and standing blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg, pulse is 84/min, and respirations are 16/min. Pulse oximetry is 100% on room air. The patient is awake and alert. Pupils are equal and reactive. Heart and lung examinations are normal. The abdomen is soft and nontender. Neurologic examination is normal. ECG is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's syncope?
A)Increased automaticity of the Purkinje fibers
B)Increased parasympathetic output to the heart
C)Increased sympathetic output to the small vessels
D)Reentry arrhythmia using the atrioventricular node
E)Systolic anterior motion of the mitral valve
A)Increased automaticity of the Purkinje fibers
B)Increased parasympathetic output to the heart
C)Increased sympathetic output to the small vessels
D)Reentry arrhythmia using the atrioventricular node
E)Systolic anterior motion of the mitral valve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A 54-year-old woman comes to the clinic due to difficulty hearing for the past few weeks. During the neurologic examination, the physician assesses her hearing using a vibrating tuning fork. The handle of the tuning fork is placed on her left mastoid process until the sound is no longer audible. The tines are then quickly placed near the patient's left auditory meatus, and she reports hearing no sound. When the handle of the vibrating fork is placed on the middle of her forehead, she hears the vibration more strongly in her left ear than her right. This patient is most likely experiencing which of the following types of hearing loss?
A)Conductive loss in both ears
B)Conductive loss in left ear
C)Conductive loss in right ear
D)Sensorineural loss in both ears
E)Sensorineural loss in left ear
F)Sensorineural loss in right ear
A)Conductive loss in both ears
B)Conductive loss in left ear
C)Conductive loss in right ear
D)Sensorineural loss in both ears
E)Sensorineural loss in left ear
F)Sensorineural loss in right ear

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A 66-year-old man comes to the office to discuss his sexual health. He thinks that he has symptoms of low testosterone, similar to those described in an article he recently read in a health magazine. The patient has normal sexual desire but reduced spontaneous erections and reduced semen volume with ejaculation. He requires more stimulation to achieve a satisfactory erection and has a longer sexual refractory period than before. The patient has no known medical conditions and takes no medications. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Vital signs are normal. BMI is 24.5 kg/m2. Physical examination, including examination of the testes, is normal. After laboratory testing is completed, the physician finds no evidence of organic disease and concludes that the results are consistent with normal aging. Compared to a healthy young man, which of the following sets of test results would be most consistent with the physician's conclusion?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Membrane potential changes in an isolated cardiac muscle cell are recorded along with ion movements across the cell membrane (see graph below). 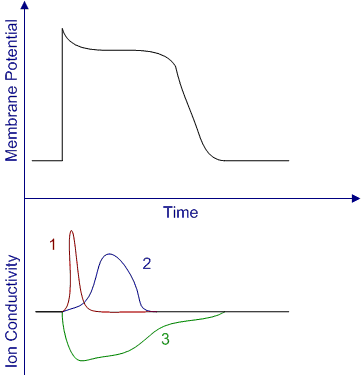 Which of the following ion sequences corresponds to regions 1-2-3 on the graph, respectively?
Which of the following ion sequences corresponds to regions 1-2-3 on the graph, respectively?
A)Potassium, sodium, calcium
B)Sodium, calcium, potassium
C)Calcium, sodium, chloride
D)Calcium, sodium, potassium
E)Sodium, potassium, calcium
 Which of the following ion sequences corresponds to regions 1-2-3 on the graph, respectively?
Which of the following ion sequences corresponds to regions 1-2-3 on the graph, respectively?A)Potassium, sodium, calcium
B)Sodium, calcium, potassium
C)Calcium, sodium, chloride
D)Calcium, sodium, potassium
E)Sodium, potassium, calcium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A 45-year-old woman participates in a cardiovascular health study. She undergoes continuous 24-hour ECG monitoring with a wearable device. A few instances of the following pattern were found on her ECG: 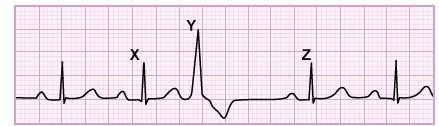 Which of the following best represents the relative left ventricular end-diastolic volumes just prior to the heart beats represented by the letters?
Which of the following best represents the relative left ventricular end-diastolic volumes just prior to the heart beats represented by the letters?
A)X=Y=Z
B)X>Y>Z
C)Y>X>Z
D)Y=Z>X
E)Z>X>Y
 Which of the following best represents the relative left ventricular end-diastolic volumes just prior to the heart beats represented by the letters?
Which of the following best represents the relative left ventricular end-diastolic volumes just prior to the heart beats represented by the letters?A)X=Y=Z
B)X>Y>Z
C)Y>X>Z
D)Y=Z>X
E)Z>X>Y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A 6-week-old infant is brought to the office due to difficulty feeding. The patient was born at 39 weeks gestation via spontaneous vaginal delivery. He is breastfeeding for 5 minutes per side every 3 hours. The patient has profuse sweating and difficulty breathing with feeds. Weight is at the 5th percentile. On examination, the patient is tachypneic. Cardiac examination shows a holosystolic murmur at the left lower sternal border; a palpable thrill is present at the left sternal border. Compared to a healthy infant, this patient likely has which of the following intracardiac pressure changes?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A 23-year-old man comes to the emergency department with sudden onset of heart palpitations that started while he was at his desk at work. The patient has no known medical problems and does not use tobacco or illicit drugs. He drinks alcohol occasionally on the weekends. Initial blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg and pulse is 160/min and regular. Gentle neck massage just below the angle of the right mandible provides immediate improvement of his condition. His blood pressure is now 120/80 mm Hg and pulse is 75/min. Which of the following mechanisms is responsible for improvement of this patient's condition?
A)Decreased baroreceptor firing rate
B)Increased sympathetic output to the sinoatrial node
C)Increased systemic vascular resistance
D)Prolonged atrioventricular node refractory period
E)Prolonged ventricular myocardium refractory period
A)Decreased baroreceptor firing rate
B)Increased sympathetic output to the sinoatrial node
C)Increased systemic vascular resistance
D)Prolonged atrioventricular node refractory period
E)Prolonged ventricular myocardium refractory period

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A 78-year-old man is being evaluated for headaches that are relieved by over-the-counter acetaminophen. He takes no other medications and is a lifelong nonsmoker. The patient's blood pressure is 180/70 mm Hg and pulse is 75/min and regular. During a prior office visit, blood pressure was 175/68 mm Hg. Physical examination shows an S4 but is otherwise unremarkable. CT scan of the head reveals no significant abnormalities. Which of the following age-related changes best explains this patient's blood pressure readings?
A)Decreased diameter of the aortic lumen
B)Decreased stroke volume
C)Increased arterial collagen deposition
D)Increased renal arterial resistance
E)Increased sympathetic tone
A)Decreased diameter of the aortic lumen
B)Decreased stroke volume
C)Increased arterial collagen deposition
D)Increased renal arterial resistance
E)Increased sympathetic tone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A 24-year-old woman participates in a study of changes in blood pressure during aerobic exercise. She is healthy and takes no medications. During the study she is asked to run on a treadmill at incrementally increasing speed until her heart rate reaches 90% of her expected maximum heart rate. Compared to at rest, which of the following changes in blood pressure are expected during this time?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A 35-year-old woman comes to the office for a follow-up appointment after recent hospitalization. The patient presented to the emergency department with fever and malaise and was diagnosed with infective endocarditis. She underwent a prolonged course of antibiotic therapy and her last dose was 5 days ago. She has no fever or shortness of breath and has resumed her daily activities. The patient has no other medical problems. Blood pressure is 128/72 mm Hg and pulse is 78/min. Auscultatory findings recorded at the left sternal border are shown in the phonocardiogram below. 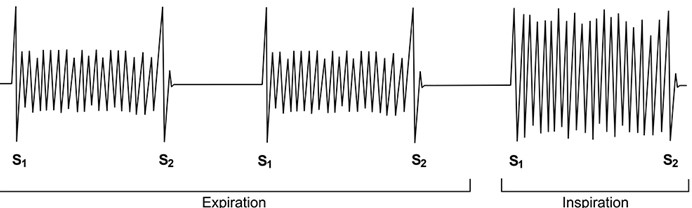 Which of the following is the most likely cause of the murmur depicted above?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of the murmur depicted above?
A)Aortic stenosis
B)Mitral regurgitation
C)Mitral stenosis
D)Pulmonary regurgitation
E)Tricuspid regurgitation
 Which of the following is the most likely cause of the murmur depicted above?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of the murmur depicted above?A)Aortic stenosis
B)Mitral regurgitation
C)Mitral stenosis
D)Pulmonary regurgitation
E)Tricuspid regurgitation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
An individual with a point mutation affecting the gene responsible for neurophysin synthesis is most likely to suffer from:
A)Short stature
B)Hyperpigmentation
C)Diabetes insipidus
D)Hypothyroidism
E)Infertility
A)Short stature
B)Hyperpigmentation
C)Diabetes insipidus
D)Hypothyroidism
E)Infertility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The circuit shown below has an inflow pressure of 120 mmHg and an outflow pressure of 40 mmHg. 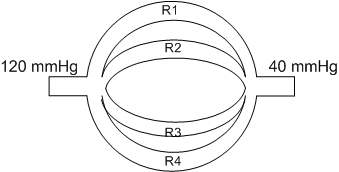 Resistance in each of the four vessels shown is 2 mmHg/mL/min (R1 = R2 = R3 = R4 = 2 mmHg/mL/min). What is the total peripheral resistance of the circuit shown on the slide?
Resistance in each of the four vessels shown is 2 mmHg/mL/min (R1 = R2 = R3 = R4 = 2 mmHg/mL/min). What is the total peripheral resistance of the circuit shown on the slide?
A)8 mmHg/ml/min
B)4 mmHg/ml/min
C)2 mmHg/ml/min
D)1 mmHg/ml/min
E)0)5 mmHg/ml/min
 Resistance in each of the four vessels shown is 2 mmHg/mL/min (R1 = R2 = R3 = R4 = 2 mmHg/mL/min). What is the total peripheral resistance of the circuit shown on the slide?
Resistance in each of the four vessels shown is 2 mmHg/mL/min (R1 = R2 = R3 = R4 = 2 mmHg/mL/min). What is the total peripheral resistance of the circuit shown on the slide?A)8 mmHg/ml/min
B)4 mmHg/ml/min
C)2 mmHg/ml/min
D)1 mmHg/ml/min
E)0)5 mmHg/ml/min

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A 30-year longitudinal study that follows untreated individuals with no known cardiovascular disease from age 50 to 80 is performed to investigate normal age-related cardiovascular changes. Several parameters are measured annually. Patients age 80 are most likely to show which of the following changes compared to when they were age 50?
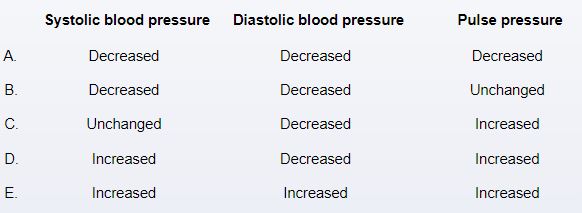


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
On physical examination, jugular venous pressure is elevated, breath sounds are decreased at the right lung base with dullness to percussion, and 2+ bilateral lower extremity pitting edema is present. Chest x-ray shows cephalization of the blood vessels, Kerley B lines, and a right pleural effusion. Thoracentesis is performed for pleural fluid analysis. In comparison to plasma fluid, which of the following pleural fluid findings is most likely to be observed?
A)High amylase content
B)High protein content
C)High white blood cell count
D)Low glucose content
E)Low lactate dehydrogenase content
A)High amylase content
B)High protein content
C)High white blood cell count
D)Low glucose content
E)Low lactate dehydrogenase content

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A 26-year-old woman comes to the clinic due to worsening generalized weakness, myalgias, and unintentional weight loss. She has primary hypothyroidism for which she takes levothyroxine. Blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg supine and 90/60 mm Hg standing. She appears mildly emaciated. Cardiopulmonary examination reveals no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show mild normochromic, normocytic anemia; eosinophil count of 15%; and serum glucose of 65 mg/dL. Which of the following additional changes is most likely in this patient?
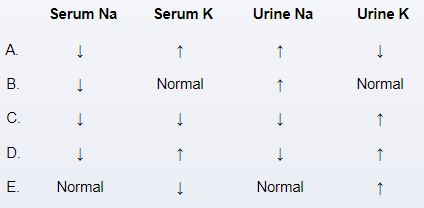


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A 43-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to nausea and vomiting with left-sided chest pain. She states that the pain began 30 minutes ago while playing with her children. She has a history of dyslipidemia and hypertension. The patient's mother died from a myocardial infarction at age 51. Physical examination reveals mild tenderness to palpation over the left chest. An ECG and cardiac biomarkers are normal. She is scheduled for an exercise stress test. During the test, which of the following parameters is likely to be the most similar between the systemic and pulmonary circulation?
A)Arterial oxygen content
B)Arterial resistance
C)Blood flow per minute
D)Diastolic arterial pressure
E)Driving pressure for blood flow
F)Mean arterial pressure
A)Arterial oxygen content
B)Arterial resistance
C)Blood flow per minute
D)Diastolic arterial pressure
E)Driving pressure for blood flow
F)Mean arterial pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A 21-year-old man undergoes a routine pre-employment physical examination. During testicular examination, he is found to have only 1 testis in his scrotum. Further evaluation reveals an elevated serum FSH level and a normal serum LH level. Production of which of the following substances is likely to be impaired in this patient?
A)Testosterone
B)Dihydrotestosterone
C)DHEA
D)Inhibin B
E)Cortisol
A)Testosterone
B)Dihydrotestosterone
C)DHEA
D)Inhibin B
E)Cortisol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A 63-year-old man with long-standing hypertension has undergone multiple changes in his antihypertensive regimen over the years with only minimal improvement in his blood pressure. A CT study of his thoracolumbar spine is performed for evaluation of chronic back pain, and the study incidentally reveals a small right kidney. Angiography demonstrates atherosclerotic narrowing of the right renal artery. The left renal artery is intact. You conclude that the flow in the right-sided artery is decreased by a factor of 16 compared to the left. By what percentage has the radius of the lumen been reduced?
A)25%
B)33%
C)50%
D)75%
E)90%
A)25%
B)33%
C)50%
D)75%
E)90%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A 10-year-old boy is brought to the clinic by his parents due to chronic fatigue, shortness of breath, and failure to gain weight. The child was recently adopted from an orphanage in Asia. He weighs 20 kg (44.2 lb). Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination reveals a loud systolic murmur. Echocardiogram shows pulmonary stenosis and subaortic ventricular septal defect with deviation of the origin of the aorta to the right. The mother describes occasional episodes of severe dyspnea and cyanosis, during which the child quickly assumes a squatting position. Which of the following mechanisms during squatting relieves this child's symptoms?
A)Decreasing left ventricular workload
B)Decreasing pulmonary blood flow
C)Decreasing pulmonary vascular resistance
D)Improving lung compliance
E)Increasing systemic vascular resistance
A)Decreasing left ventricular workload
B)Decreasing pulmonary blood flow
C)Decreasing pulmonary vascular resistance
D)Improving lung compliance
E)Increasing systemic vascular resistance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A 44-year-old previously healthy woman comes to the emergency department due to a 2-day history of left flank pain, dysuria, fever, and chills. Temperature is 38.9 C (102 F), blood pressure is 80/40 mm Hg, and pulse is 140/min and regular. Physical examination shows left costovertebral angle tenderness. Laboratory studies reveal leukocytosis, pyuria, and bacteriuria. Empiric broad-spectrum antibiotics and intravenous fluids are administered. The patient remains persistently hypotensive, and an intravenous phenylephrine infusion is begun. Several minutes later, her heart rate decreases to 100/min. Compared to just prior to the infusion, which of the following intracellular changes are expected in this patient?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 272 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



