Deck 13: Introduction to Conventional Tolerancing
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/15
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Introduction to Conventional Tolerancing
1
A tolerance that is expressed as plus and minus values is a ____________________ tolerance.
bilateral
2
MAX. is the abbreviation for maximum.
False
3
The symbol/abbreviation for "number of places" is ____________________.
X
4
When the upper and lower limits of a dimension have different values, the tolerances are called ___________________________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When dimensions require greater accuracy than a general note on the drawing provides, individual tolerances or limits must be shown for that dimension.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In metric dimensioning, the dimension and its tolerance need not be expressed to the same number of decimal places.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the limit dimensioning method, only the maximum and minimum dimensions are specified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When limit dimensions are applied to a diameter, the diameter symbol (Ø) is placed to the left of both the upper and lower limit dimension.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The maximum and minimum sizes permitted for a specific dimension is the ____.
A) tolerance
B) limits of size
C) basic size
D) deviation
A) tolerance
B) limits of size
C) basic size
D) deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When unilateral tolerancing is used in metric dimensioning and either the plus or minus value is nil, a single ____________________ is shown without a plus or minus sign.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The intentional difference in size of mating parts is ____.
A) allowance
B) tolerance
C) limits of size
D) deviation
A) allowance
B) tolerance
C) limits of size
D) deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the dimension 2.500 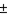 .005, the
.005, the 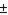 .005 would be referred to as a(n) ____.
.005 would be referred to as a(n) ____.
A) unequal bilateral tolerance
B) equal limits of size
C) equal unilateral tolerance
D) equal bilateral tolerance
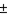 .005, the
.005, the 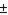 .005 would be referred to as a(n) ____.
.005 would be referred to as a(n) ____.A) unequal bilateral tolerance
B) equal limits of size
C) equal unilateral tolerance
D) equal bilateral tolerance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The total permissible variation in the size of a dimension is the ____.
A) tolerance
B) allowance
C) limits of size
D) deviattion
A) tolerance
B) allowance
C) limits of size
D) deviattion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The symbol for "plus or minus" is ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The theoretical size from which the limits for that dimension are derived, by application of the allowance and tolerance, is the ____.
A) limits of size
B) allowance
C) basic size
D) tolerance
A) limits of size
B) allowance
C) basic size
D) tolerance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



