Deck 5: Obstetrics & Gynecology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/469
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Obstetrics & Gynecology
1
A 34-year-old woman, gravida 2 para 1, at 30 weeks gestation comes to the emergency department due to a severe, unilateral headache. The patient has a history of migraine headaches, and earlier today she developed a severe, throbbing headache on the right side of the head. She drank a can of caffeinated soda and tried to rest in a dark room, but the headache has not improved. The patient has had no nausea, vomiting, or changes in vision. She has no other chronic medical conditions, takes no daily medications, and has no known drug allergies. Temperature is 37.2 C (99 F), blood pressure is 126/82 mm Hg, and pulse is 92/min. Fetal heart rate is 150/min. Neurologic examination is normal. The remainder of the physical examination is unremarkable. Urine dipstick is negative for protein. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial pharmacotherapy for this patient?
A)Acetaminophen
B)Ergotamine
C)Ibuprofen
D)Magnesium sulfate
E)Oxycodone
A)Acetaminophen
B)Ergotamine
C)Ibuprofen
D)Magnesium sulfate
E)Oxycodone
A
Explanation:
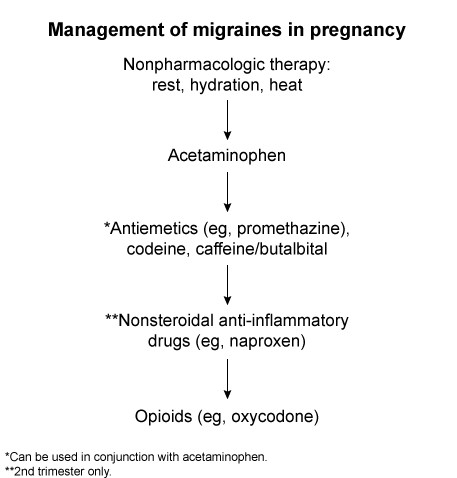 During pregnancy, headaches are common and typically benign. Headaches with atypical features (eg, altered mental status, neurologic deficits) or in patients ≥20 weeks gestation require evaluation to exclude other etiologies, such as preeclampsia or cerebral venous thrombosis, due to risk of adverse maternal (eg, stroke, disseminated intravascular coagulation) and fetal (eg, growth restriction, demise) outcomes. This patient has a throbbing, unilateral headache without changes in vision, consistent with a typical migraine without aura.
During pregnancy, headaches are common and typically benign. Headaches with atypical features (eg, altered mental status, neurologic deficits) or in patients ≥20 weeks gestation require evaluation to exclude other etiologies, such as preeclampsia or cerebral venous thrombosis, due to risk of adverse maternal (eg, stroke, disseminated intravascular coagulation) and fetal (eg, growth restriction, demise) outcomes. This patient has a throbbing, unilateral headache without changes in vision, consistent with a typical migraine without aura.
Management of migraines in pregnancy is complicated due to limited therapeutic options.
Acetaminophen is the preferred first-line option; patients also typically benefit from caffeine and limiting exposure to light and sound (eg, resting in a dark room).
In patients who do not improve with acetaminophen alone, a low-potency opioid (eg, acetaminophen-codeine), antiemetics (eg, promethazine), or caffeine/butalbital may be beneficial.
More potent opioids (eg, oxycodone) are typically not used due to their tendency to worsen gastrointestinal symptoms (eg, constipation, nausea) during pregnancy; however, they can be considered if all other options fail to improve symptoms (Choice E).
Parenteral antiemetics (eg, metoclopramide) are used acutely and are effective monotherapy.
(Choice B) Ergotamine is an effective migraine medication but is contraindicated in pregnancy due to risk of hypertonic uterine contractions and vasoconstriction, which can lead to adverse obstetric outcomes (eg, preterm labor, fetal growth restriction). Triptans (eg, sumatriptan) are also typically avoided in pregnancy due to risk of uteroplacental vasoconstriction, increased uterotonic activity, preterm delivery, and low birth weight.
(Choice C) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (eg, ibuprofen) can be used for headaches refractory to acetaminophen, but they are typically avoided in the first and third trimesters due to the risk of fetal complications (eg, spontaneous abortion, premature ductus arteriosus closure, oligohydramnios, renal dysfunction).
(Choice D) Magnesium sulfate is used for seizure prophylaxis in patients with preeclampsia with severe features (eg, new-onset hypertension at ≥20 weeks gestation with headache or vision changes). This patient is normotensive and has no proteinuria, making this diagnosis unlikely. Magnesium sulfate for migraine treatment has more limited efficacy.
Educational objective:
Acetaminophen is the first-line treatment option for migraines during pregnancy. Second- and third-line options include addition of opioids (eg, acetaminophen-codeine), antiemetics, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (in the second trimester only).
References:
Headache and pregnancy: a systematic review.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29052046)
Acute migraine headache: treatment strategies.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29671521)
Explanation:
 During pregnancy, headaches are common and typically benign. Headaches with atypical features (eg, altered mental status, neurologic deficits) or in patients ≥20 weeks gestation require evaluation to exclude other etiologies, such as preeclampsia or cerebral venous thrombosis, due to risk of adverse maternal (eg, stroke, disseminated intravascular coagulation) and fetal (eg, growth restriction, demise) outcomes. This patient has a throbbing, unilateral headache without changes in vision, consistent with a typical migraine without aura.
During pregnancy, headaches are common and typically benign. Headaches with atypical features (eg, altered mental status, neurologic deficits) or in patients ≥20 weeks gestation require evaluation to exclude other etiologies, such as preeclampsia or cerebral venous thrombosis, due to risk of adverse maternal (eg, stroke, disseminated intravascular coagulation) and fetal (eg, growth restriction, demise) outcomes. This patient has a throbbing, unilateral headache without changes in vision, consistent with a typical migraine without aura.Management of migraines in pregnancy is complicated due to limited therapeutic options.
Acetaminophen is the preferred first-line option; patients also typically benefit from caffeine and limiting exposure to light and sound (eg, resting in a dark room).
In patients who do not improve with acetaminophen alone, a low-potency opioid (eg, acetaminophen-codeine), antiemetics (eg, promethazine), or caffeine/butalbital may be beneficial.
More potent opioids (eg, oxycodone) are typically not used due to their tendency to worsen gastrointestinal symptoms (eg, constipation, nausea) during pregnancy; however, they can be considered if all other options fail to improve symptoms (Choice E).
Parenteral antiemetics (eg, metoclopramide) are used acutely and are effective monotherapy.
(Choice B) Ergotamine is an effective migraine medication but is contraindicated in pregnancy due to risk of hypertonic uterine contractions and vasoconstriction, which can lead to adverse obstetric outcomes (eg, preterm labor, fetal growth restriction). Triptans (eg, sumatriptan) are also typically avoided in pregnancy due to risk of uteroplacental vasoconstriction, increased uterotonic activity, preterm delivery, and low birth weight.
(Choice C) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (eg, ibuprofen) can be used for headaches refractory to acetaminophen, but they are typically avoided in the first and third trimesters due to the risk of fetal complications (eg, spontaneous abortion, premature ductus arteriosus closure, oligohydramnios, renal dysfunction).
(Choice D) Magnesium sulfate is used for seizure prophylaxis in patients with preeclampsia with severe features (eg, new-onset hypertension at ≥20 weeks gestation with headache or vision changes). This patient is normotensive and has no proteinuria, making this diagnosis unlikely. Magnesium sulfate for migraine treatment has more limited efficacy.
Educational objective:
Acetaminophen is the first-line treatment option for migraines during pregnancy. Second- and third-line options include addition of opioids (eg, acetaminophen-codeine), antiemetics, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (in the second trimester only).
References:
Headache and pregnancy: a systematic review.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29052046)
Acute migraine headache: treatment strategies.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29671521)
2
A 31-year-old woman at 12 weeks gestation comes to the office for recurrent headaches. The patient has a history of episodic migraines that typically resolve with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; but since becoming pregnant, the headaches have become more severe and frequent. Over the past month, the patient has had 5 migraine headaches with associated nausea and vomiting that required treatment in the emergency department. In addition, she has had to go to a dark room and rest for a few hours before recovering. The patient has no other chronic medical conditions and her only other medication is a daily prenatal vitamin. Temperature is 36.7 C (98 F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, and pulse is 76/min. Fetal heart rate is 160/min. Cranial nerves are intact. Deep tendon reflexes are 2+. Strength and sensation are normal in all extremities. Which of the following is the most appropriate preventive therapy for this patient?
A)Doxylamine
B)Ergotamine
C)Propranolol
D)Sertraline
E)Sumatriptan
F)Topiramate
A)Doxylamine
B)Ergotamine
C)Propranolol
D)Sertraline
E)Sumatriptan
F)Topiramate
C
Explanation:
 Migraine headaches are common in women of childbearing age (eg, 20-40) possibly due to cyclic increases and decreases in estrogen and progesterone. Migraines typically improve during pregnancy due to loss of these cyclic changes, but some women have worsening symptoms, likely due to an increase in other migraine risk factors (eg, sleep disturbance, physical exertion, emotional stress) that occur during pregnancy. This patient has frequent migraines (eg, ≥4 headaches per month) with significant impairment (eg, multiple emergency department visits) and would benefit from preventive therapy, which can decrease migraine frequency and severity.
Migraine headaches are common in women of childbearing age (eg, 20-40) possibly due to cyclic increases and decreases in estrogen and progesterone. Migraines typically improve during pregnancy due to loss of these cyclic changes, but some women have worsening symptoms, likely due to an increase in other migraine risk factors (eg, sleep disturbance, physical exertion, emotional stress) that occur during pregnancy. This patient has frequent migraines (eg, ≥4 headaches per month) with significant impairment (eg, multiple emergency department visits) and would benefit from preventive therapy, which can decrease migraine frequency and severity.
There are multiple preventive therapy options and the choice of medication should be based on patient comorbidities and medication risk profile, particularly during pregnancy due to potential fetal risks (eg, fetal anomalies, growth restriction). First-line prevention during pregnancy is with beta blockers such as propranolol or metoprolol, which have the best fetal safety profile. Calcium channel blockers (eg, verapamil) are also effective and safe in pregnancy. However, prolonged beta blocker use can potentially cause growth restriction (likely due to decreased placental perfusion from low blood pressure); therefore, patients should be initiated on the lowest effective dose and require frequent monitoring.
(Choice A) Doxylamine, a first generation antihistamine, often in combination with pyridoxine, is used as a preventive antiemetic (eg, hyperemesis) in pregnancy. It is not used for migraine prophylaxis.
(Choices B and E) Ergotamines and triptans (eg, sumatriptan) can be used to abort an acute migraine but are not typically used for migraine prevention. In addition, these medications are not used in pregnancy due to risks of fetal anomalies (ergotamine), growth restriction (triptans), and preterm labor (both).
(Choice D) Sertraline is safe for use in pregnancy to treat depression and anxiety. Unlike tricyclic antidepressants and venlafaxine, which are used for migraine prevention in nonpregnant patients, sertraline does not prevent migraines.
(Choice F) Topiramate is effective for migraine prevention but avoided in pregnancy due to risk of fetal abnormalities (eg, cleft palate, low birth weight).
Educational objective:
Preventive migraine therapy may benefit patients with severe migraine headaches (eg, ≥4 times per month, significant impairment). During pregnancy, first-line prevention is with beta blockers (eg, propranolol, metoprolol).
References:
Preventive treatment in migraine and the new US guidelines.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23717045)
Current prophylactic medications for migraine and their potential mechanisms of action.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29671241)
Explanation:
 Migraine headaches are common in women of childbearing age (eg, 20-40) possibly due to cyclic increases and decreases in estrogen and progesterone. Migraines typically improve during pregnancy due to loss of these cyclic changes, but some women have worsening symptoms, likely due to an increase in other migraine risk factors (eg, sleep disturbance, physical exertion, emotional stress) that occur during pregnancy. This patient has frequent migraines (eg, ≥4 headaches per month) with significant impairment (eg, multiple emergency department visits) and would benefit from preventive therapy, which can decrease migraine frequency and severity.
Migraine headaches are common in women of childbearing age (eg, 20-40) possibly due to cyclic increases and decreases in estrogen and progesterone. Migraines typically improve during pregnancy due to loss of these cyclic changes, but some women have worsening symptoms, likely due to an increase in other migraine risk factors (eg, sleep disturbance, physical exertion, emotional stress) that occur during pregnancy. This patient has frequent migraines (eg, ≥4 headaches per month) with significant impairment (eg, multiple emergency department visits) and would benefit from preventive therapy, which can decrease migraine frequency and severity.There are multiple preventive therapy options and the choice of medication should be based on patient comorbidities and medication risk profile, particularly during pregnancy due to potential fetal risks (eg, fetal anomalies, growth restriction). First-line prevention during pregnancy is with beta blockers such as propranolol or metoprolol, which have the best fetal safety profile. Calcium channel blockers (eg, verapamil) are also effective and safe in pregnancy. However, prolonged beta blocker use can potentially cause growth restriction (likely due to decreased placental perfusion from low blood pressure); therefore, patients should be initiated on the lowest effective dose and require frequent monitoring.
(Choice A) Doxylamine, a first generation antihistamine, often in combination with pyridoxine, is used as a preventive antiemetic (eg, hyperemesis) in pregnancy. It is not used for migraine prophylaxis.
(Choices B and E) Ergotamines and triptans (eg, sumatriptan) can be used to abort an acute migraine but are not typically used for migraine prevention. In addition, these medications are not used in pregnancy due to risks of fetal anomalies (ergotamine), growth restriction (triptans), and preterm labor (both).
(Choice D) Sertraline is safe for use in pregnancy to treat depression and anxiety. Unlike tricyclic antidepressants and venlafaxine, which are used for migraine prevention in nonpregnant patients, sertraline does not prevent migraines.
(Choice F) Topiramate is effective for migraine prevention but avoided in pregnancy due to risk of fetal abnormalities (eg, cleft palate, low birth weight).
Educational objective:
Preventive migraine therapy may benefit patients with severe migraine headaches (eg, ≥4 times per month, significant impairment). During pregnancy, first-line prevention is with beta blockers (eg, propranolol, metoprolol).
References:
Preventive treatment in migraine and the new US guidelines.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23717045)
Current prophylactic medications for migraine and their potential mechanisms of action.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29671241)
3
A 29-year-old woman, gravida 1 para 1, is evaluated in the emergency department for a headache. Three days ago, she had an uncomplicated vaginal delivery with neuraxial anesthesia. This morning, the patient developed an occipital headache that has not improved with acetaminophen. The headache has become progressively worse, and the patient cannot sit without becoming nauseated and vomiting. The patient has no chronic medical conditions and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Temperature is 36.7 C (98.1 F), blood pressure is 162/96 mm Hg, pulse is 98/min, and respirations are 18/min. On examination, heart sounds are normal with no rubs or murmurs, and the lungs are clear to auscultation. Cranial nerves are intact and deep tendon reflexes are 3+. There is 5/5 strength in the right lower extremity and 3/5 strength in the left. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)100% oxygen
B)CT scan of the head
C)Epidural blood patch
D)Lumbar puncture
E)Sumatriptan therapy
A)100% oxygen
B)CT scan of the head
C)Epidural blood patch
D)Lumbar puncture
E)Sumatriptan therapy
B
Explanation:
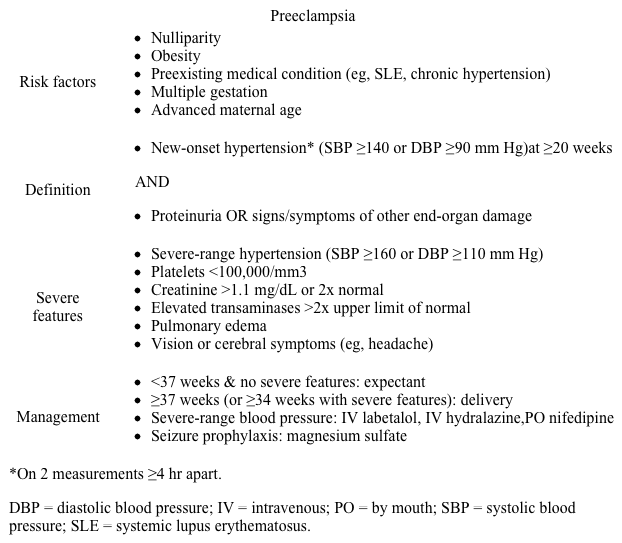 This postpartum patient with worsening headache and severe hypertension (eg, systolic ≥160 or diastolic ≥110 mm Hg) has preeclampsia with severe features, which can present up to 6 weeks after delivery. The most common presenting symptom is a severe headache in the bilateral occipital or frontal regions that does not improve with acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
This postpartum patient with worsening headache and severe hypertension (eg, systolic ≥160 or diastolic ≥110 mm Hg) has preeclampsia with severe features, which can present up to 6 weeks after delivery. The most common presenting symptom is a severe headache in the bilateral occipital or frontal regions that does not improve with acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Patients with preeclampsia are at increased risk of hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke due to acute elevations in cerebral perfusion pressure and vessel rupture (hemorrhagic), as well as preeclampsia-mediated vascular endothelial damage and microthrombi formation (ischemic). To decrease this risk, preeclamptic patients with severe-range blood pressures require aggressive antihypertensive therapy (eg, labetalol, nifedipine) and magnesium sulfate, which helps prevent eclamptic seizures that can worsen stroke symptoms.
Most preeclamptic patients do not require imaging; however, in those with focal neurologic deficits, such as this patient with asymmetric motor deficits (strength right > left), CT scan of the head should be performed to evaluate for possible stroke and help guide management.
(Choices A and E) Oxygen administration is used to alleviate cluster headaches, which typically present with a short-lived, unilateral, orbital headache with autonomic symptoms (eg, ptosis, lacrimation). Triptans (eg, sumatriptan) are used to treat migraines, which can present as occipital headaches with nausea, vomiting, and occasionally motor aura (eg, hemiplegic migraine). However, CT scan should be performed in this patient prior to attempting symptomatic therapy in order to exclude life-threatening causes of neurologic deficit.
(Choice C) An epidural blood patch is used to treat postdural puncture headaches, which can occur after neuraxial anesthesia and may present as an occipital headache that worsens with sitting or standing due to cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage. However, this type of headache is not associated with hypertension or focal neurologic deficits.
(Choice D) Lumbar puncture can evaluate for CSF infection (eg, meningitis, encephalitis), which may present with headache after neuraxial anesthesia. This patient is afebrile, making this diagnosis less likely. In addition, lumbar puncture is usually performed after CT scan to exclude a brain mass because there is a risk of herniation with mass effect.
Educational objective:
Preeclampsia can present up to 6 weeks postpartum with headache and hypertension. Patients with preeclampsia are at increased risk of stroke, and those with focal neurologic deficits should be evaluated with CT scan of the head.
References:
Preeclampsia: association with posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and stroke.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29438078)
Cerebrovascular complications in pregnancy and puerperium.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24431615)
Explanation:
 This postpartum patient with worsening headache and severe hypertension (eg, systolic ≥160 or diastolic ≥110 mm Hg) has preeclampsia with severe features, which can present up to 6 weeks after delivery. The most common presenting symptom is a severe headache in the bilateral occipital or frontal regions that does not improve with acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
This postpartum patient with worsening headache and severe hypertension (eg, systolic ≥160 or diastolic ≥110 mm Hg) has preeclampsia with severe features, which can present up to 6 weeks after delivery. The most common presenting symptom is a severe headache in the bilateral occipital or frontal regions that does not improve with acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.Patients with preeclampsia are at increased risk of hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke due to acute elevations in cerebral perfusion pressure and vessel rupture (hemorrhagic), as well as preeclampsia-mediated vascular endothelial damage and microthrombi formation (ischemic). To decrease this risk, preeclamptic patients with severe-range blood pressures require aggressive antihypertensive therapy (eg, labetalol, nifedipine) and magnesium sulfate, which helps prevent eclamptic seizures that can worsen stroke symptoms.
Most preeclamptic patients do not require imaging; however, in those with focal neurologic deficits, such as this patient with asymmetric motor deficits (strength right > left), CT scan of the head should be performed to evaluate for possible stroke and help guide management.
(Choices A and E) Oxygen administration is used to alleviate cluster headaches, which typically present with a short-lived, unilateral, orbital headache with autonomic symptoms (eg, ptosis, lacrimation). Triptans (eg, sumatriptan) are used to treat migraines, which can present as occipital headaches with nausea, vomiting, and occasionally motor aura (eg, hemiplegic migraine). However, CT scan should be performed in this patient prior to attempting symptomatic therapy in order to exclude life-threatening causes of neurologic deficit.
(Choice C) An epidural blood patch is used to treat postdural puncture headaches, which can occur after neuraxial anesthesia and may present as an occipital headache that worsens with sitting or standing due to cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage. However, this type of headache is not associated with hypertension or focal neurologic deficits.
(Choice D) Lumbar puncture can evaluate for CSF infection (eg, meningitis, encephalitis), which may present with headache after neuraxial anesthesia. This patient is afebrile, making this diagnosis less likely. In addition, lumbar puncture is usually performed after CT scan to exclude a brain mass because there is a risk of herniation with mass effect.
Educational objective:
Preeclampsia can present up to 6 weeks postpartum with headache and hypertension. Patients with preeclampsia are at increased risk of stroke, and those with focal neurologic deficits should be evaluated with CT scan of the head.
References:
Preeclampsia: association with posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and stroke.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29438078)
Cerebrovascular complications in pregnancy and puerperium.
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24431615)
4
A 39-year-old woman comes to the office due to worsening urinary symptoms for the past several weeks. The patient has increasingly had sudden, intermittent urges to urinate followed by small-volume urine. On several occasions, she has had difficulty reaching the bathroom in time and has involuntarily leaked a small amount of urine. The patient reports no fever, dysuria, hematuria, abdominal pain, or abnormal vaginal discharge. She was diagnosed with multiple sclerosis 3 years ago after an episode of gait unsteadiness. Since then, she has had several acute exacerbations, most recently 2 months ago, which were treated with glucocorticoids. Her other medical conditions include hypertension and glucocorticoid-induced hyperglycemia. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Vital signs are normal. Physical examination shows hyperreflexia of the lower extremities and mild intention tremor. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Urine dipstick is negative for leukocyte esterase and nitrite but positive for glucose. Postvoid bladder scan reveals a contracted, small bladder. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's urinary symptoms?
A)Demyelination of sacral spinal cord
B)Glucosuria-induced osmotic diuresis
C)Obstruction of bladder outlet
D)Overactivity of detrusor muscle
E)Weakness of pelvic floor muscles
A)Demyelination of sacral spinal cord
B)Glucosuria-induced osmotic diuresis
C)Obstruction of bladder outlet
D)Overactivity of detrusor muscle
E)Weakness of pelvic floor muscles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A 36-year-old primigravid woman at 34 weeks gestation arrives at the emergency department after being found unresponsive on the floor by her husband. She was found unconscious about 30 minutes ago and became gradually responsive over a few minutes. The husband reports the patient has had increasing nausea and vomiting over the past few hours and a severe frontal headache. Currently she has no symptoms other than the headache. Medical history is significant for migraines, and the patient takes no daily medications. Temperature is 36.7 C (98.1 F), blood pressure is 138/98 mm Hg, pulse is 78/min, and respirations are 20/min. Cranial nerves are intact, and the neck is supple. Funduscopic examination is normal. The lungs are clear to auscultation bilaterally. Cardiac examination demonstrates normal heart sounds. The abdomen is nontender, and the uterine fundus measures 34 weeks gestation. There is minimal pretibial edema, and deep tendon reflexes are 3+. Motor examination is normal. Laboratory results are as follows:  Urine drug screen is negative. CT scan of the head reveals bilateral frontal lobe edema but no mass lesions or bleeding. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
Urine drug screen is negative. CT scan of the head reveals bilateral frontal lobe edema but no mass lesions or bleeding. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)CT venography
B)Lumbar puncture
C)Magnesium sulfate infusion
D)Triptan abortive therapy
E)Video EEG
 Urine drug screen is negative. CT scan of the head reveals bilateral frontal lobe edema but no mass lesions or bleeding. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
Urine drug screen is negative. CT scan of the head reveals bilateral frontal lobe edema but no mass lesions or bleeding. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?A)CT venography
B)Lumbar puncture
C)Magnesium sulfate infusion
D)Triptan abortive therapy
E)Video EEG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A 58-year-old woman, gravida 2 para 2, comes to the office for evaluation of increased urinary frequency and painful urination. The patient developed these symptoms 2 days ago, and they did not improve despite increasing fluid intake and voiding regularly. She has had 2 other episodes of acute simple cystitis in the past 8 months, which resolved with antibiotics. The patient underwent menopause at age 53 and has had no episodes of postmenopausal bleeding. BMI is 28 kg/m2. Vital signs are normal. Physical examination shows mild suprapubic tenderness and no costovertebral tenderness. Pelvic examination shows thin vulvar tissue but no excoriations or lesions. Urinalysis is positive for leukocyte esterase and nitrites. The patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics and is asymptomatic a week later. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient's symptoms?
A)Cystoscopy
B)Daily probiotic consumption
C)Pelvic ultrasound
D)Topical corticosteroids
E)Urine cytology
F)Vaginal estrogen
A)Cystoscopy
B)Daily probiotic consumption
C)Pelvic ultrasound
D)Topical corticosteroids
E)Urine cytology
F)Vaginal estrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A 28-year-old woman, gravida 3 para 2, at 30 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department due to vaginal bleeding after a motor vehicle collision. The patient was restrained by a lap and shoulder belt, but the steering wheel struck her abdomen. Her underwear and pants are soaked with blood, and she states that she is "not sure if my water broke." Blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, pulse is 136/min, respirations are 22/min, and pulse oximetry is 98% on room air. Physical examination shows an alert but anxious-appearing woman with abdominal tenderness and cool extremities. On speculum examination, 100 mL of blood is evacuated from the vagina, and minimal active bleeding from the cervix is observed. Blood type is O, Rh positive. Fetal heart monitoring shows a baseline of 140/min with minimal to moderate variability; there are no late or variable decelerations. Tocometry reveals uterine contractions every 3 minutes. Intravenous fluids are started. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Emergency cesarean delivery
B)Fetal biophysical profile
C)Kleihauer-Betke test
D)Transfuse blood products
E)Vasopressor therapy
A)Emergency cesarean delivery
B)Fetal biophysical profile
C)Kleihauer-Betke test
D)Transfuse blood products
E)Vasopressor therapy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A 67-year-old woman, gravida 1 para 1, comes to the office for a routine health examination. The patient feels well. Her last menstrual period was at age 53 with no bleeding since. Pap test and human papillomavirus (HPV) cotesting were negative 2 years ago at age 65. All prior Pap tests were normal. The patient is sexually active in a monogamous relationship with her husband of 42 years. She has no medical conditions. The patient had an ovarian cystectomy via laparotomy at age 37 for a benign cystic teratoma. She takes no medications and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. There is no family history of cancer. BMI is 25 kg/m2. Pelvic examination shows a normal cervix without lesions; a smooth, anteverted, mobile uterus; and no adnexal masses. Screening mammography was normal 6 months ago, and screening colonoscopy was normal 2 years ago. Which of the following is the most appropriate recommendation for cervical cancer screening in this patient?
A)HPV testing only at this visit
B)No further screening
C)Pap and HPV testing at this visit
D)Pap test only at this visit
E)Repeat Pap test in 3 years
A)HPV testing only at this visit
B)No further screening
C)Pap and HPV testing at this visit
D)Pap test only at this visit
E)Repeat Pap test in 3 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A 17-year-old primigravida at 29 weeks gestation comes to the clinic due to headaches. For the last 2 weeks, she has had an intermittent throbbing pain in the left frontal region when she wakes up. The pain is sometimes accompanied by a rhythmic pulsating sound. Acetaminophen provides minimal improvement. The patient has had no fever, right upper quadrant pain, contractions, or vaginal bleeding. She recalls no trauma and has no chronic medical conditions. Prepregnancy BMI is 31 kg/m2, and the patient has gained 20 kg (44 lb) so far. Temperature is 37.1 C (98.8 F), blood pressure is 136/76 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 18/min. Fetal heart rate is 160/min. There is no neck stiffness. Visual field testing is normal. Funduscopic examination shows bilateral optic disc edema. Bilateral deep tendon reflexes are 2+. The remainder of the neurologic examination is unremarkable. Urinalysis has trace protein. Which of the following is the best next step in evaluation of this patient?
A)24-hour urine collection for total protein
B)Lumbar puncture
C)MRI of the brain
D)Polysomnography
E)Tonometry
A)24-hour urine collection for total protein
B)Lumbar puncture
C)MRI of the brain
D)Polysomnography
E)Tonometry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A 20-year-old woman, gravida 1 para 0, at 36 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department by her mother due to a seizure. The patient was sitting outside when she suddenly had a 2-minute seizure with loss of urinary continence. She is still confused when she arrives in the emergency department. Her mother reports that the patient has had increasing anxiety and has been acting out for the past several days. Her only surgery was a splenectomy after a motor vehicle collision last year. Temperature is 37.7 C (99.9 F), blood pressure is 158/98 mm Hg, and pulse is 120/min. The patient is agitated and diaphoretic. The pupils are dilated bilaterally. The cranial nerves are intact. The neck is supple and nontender. Cardiopulmonary examination is normal. The abdomen is gravid without rebound or guarding, and the uterus is nontender. There is 2+ pitting pedal edema bilaterally. Sensation and strength are normal in the bilateral upper and lower extremities. Laboratory results are as follows:  CT scan of the head is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
CT scan of the head is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A)Amphetamine intoxication
B)Eclampsia
C)Heat stroke
D)Hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelet count syndrome
E)Pneumococcal meningitis
 CT scan of the head is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
CT scan of the head is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?A)Amphetamine intoxication
B)Eclampsia
C)Heat stroke
D)Hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelet count syndrome
E)Pneumococcal meningitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A 70-year-old woman comes to the office for worsening constipation. The patient has chronic constipation for which she takes over-the-counter fiber supplements and stool softeners; however, for the past 3 months, the patient has had to push 2 fingers into her vagina to defecate. She has had increased bloating but no nausea, diarrhea, or abdominal pain. The patient has 1 son. Medical history includes hypothyroidism and type 2 diabetes mellitus for which she takes levothyroxine and metformin. A colonoscopy last year was normal. BMI is 32 kg/m2. Vital signs are normal. The abdomen is soft and nontender with normoactive bowel sounds. On rectal examination, the resting sphincter tone is normal and there are no palpable masses. With Valsalva maneuver, the posterior vaginal wall extends outside the hymenal ring. There is no fecal incontinence with Valsalva maneuver. Anocutaneous reflex is intact bilaterally. TSH is 3.9 mU/L and serum hemoglobin A1c is 7.5%. Fecal occult blood testing is negative. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's presentation?
A)Autonomic dysfunction due to neuropathy
B)External anal sphincter dysfunction
C)Levator ani muscle complex injury
D)Overuse of fiber supplementation
E)Subtherapeutic levothyroxine dosing
A)Autonomic dysfunction due to neuropathy
B)External anal sphincter dysfunction
C)Levator ani muscle complex injury
D)Overuse of fiber supplementation
E)Subtherapeutic levothyroxine dosing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A 31-year-old woman, gravida 1 para 0, at 32 weeks gestation comes to the office for a routine prenatal visit. The patient reports normal fetal movements and has had no abdominal pain or vaginal bleeding. Over the past 2 weeks, she has had intermittent uncomfortable sensations in her legs, especially at bedtime and when she sits for prolonged durations like watching a movie. The patient reports no leg pain or pins and needles sensation, and the symptoms improve once she gets up and moves around. Her husband states that she frequently gets in and out of bed. Medical history is significant for depression and anxiety during adolescence after her parents' divorce. Vital signs are within normal limits. Prepregnancy BMI was 30 kg/m2, and she has gained 6.8 kg (15 lb) during this pregnancy. Physical examination shows trace lower extremity edema, but no other abnormalities are present. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current symptoms?
A)Compressive neuropathy
B)Positional leg discomfort
C)Pregnancy-associated cramps
D)Prenatal anxiety disorder
E)Restless legs syndrome
A)Compressive neuropathy
B)Positional leg discomfort
C)Pregnancy-associated cramps
D)Prenatal anxiety disorder
E)Restless legs syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A 42-year-old woman comes to the emergency department for severe lower abdominal pain. The pain started several hours ago and has progressively worsened. She has associated nausea and vomiting but no fever, diarrhea, or abnormal vaginal discharge. The patient was diagnosed with adenomyosis last month due to increasingly heavy menses and dysmenorrhea and is currently taking tranexamic acid as needed. Her menses started yesterday, but she reports that the pain is more severe than usual and radiates to the left lower quadrant. Temperature is 37.8 C (100 F), blood pressure is 110/74 mm Hg, and pulse is 110/min. The abdomen is soft with normoactive bowel sounds, and there is voluntary guarding in the left lower quadrant. On pelvic examination, the uterus is globular and boggy, and there is dark red blood with small clots in the vagina. The left adnexa is tender on bimanual examination, and there are no palpable adnexal masses. Urine pregnancy testing is negative. Hemoglobin is 11 g/dL. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Discontinue tranexamic acid
B)Observation and serial abdominal examinations
C)Perform diagnostic laparoscopy
D)Perform endometrial ablation
E)Perform uterine artery embolization
F)Prescribe oral contraceptives
A)Discontinue tranexamic acid
B)Observation and serial abdominal examinations
C)Perform diagnostic laparoscopy
D)Perform endometrial ablation
E)Perform uterine artery embolization
F)Prescribe oral contraceptives

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A 29-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to vaginal spotting and discharge. She had a positive pregnancy test last week after missing her last menstrual period and estimates that she is at 5 weeks gestation. The patient has had increased vaginal discharge for the past 2 days but no pelvic pain or cramping. Today, she started having vaginal spotting, which prompted her to come to the emergency department. The patient had a spontaneous abortion 3 years ago that was treated with medication, but she has no chronic medical conditions. Temperature is 37.6 C (99.7 F), blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, and pulse is 90/min. The abdomen is soft, nontender, and without rebound or guarding. The cervix appears closed and without lesions, and there is bloody, yellow mucus at the external cervical os. The remainder of the physical examination is normal. Quantitative β-hCG level is 5,200 IU/L and blood type is O, Rh positive. Ultrasound shows an intrauterine fetal pole with a positive fetal heartbeat. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Anti-D immune globulin administration
B)Cervical biopsy
C)Empiric antibiotic therapy
D)Mifepristone
E)Misoprostol
F)Suction curettage
A)Anti-D immune globulin administration
B)Cervical biopsy
C)Empiric antibiotic therapy
D)Mifepristone
E)Misoprostol
F)Suction curettage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A 25-year-old woman, gravida 1 para 0, at 29 weeks gestation comes to the emergency department due to a headache. The patient has a history of migraines but has not had one during the pregnancy until today. She has no other chronic medical conditions. This morning, the patient woke with a left-sided frontal headache and blurry vision in the left eye. She took a dose of acetaminophen, but the headache did not improve and now is in the bilateral frontal region. The patient has no sick contacts but has had increased stress at work and is working longer hours. Her caffeine consumption has increased to 2-3 cups of coffee a day. Blood pressure is 156/92 mm Hg and pulse is 84/min. Fetal heart rate is 155/min. Repeat blood pressure a few hours later is 150/94 mm Hg. Cranial nerves are intact. There is no nuchal rigidity. The abdomen is soft, gravid, and nontender. Deep tendon reflexes are normal. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A)Caffeine side effect
B)Cluster headache
C)Migraine with aura
D)Preeclampsia
E)Tension-type headache
A)Caffeine side effect
B)Cluster headache
C)Migraine with aura
D)Preeclampsia
E)Tension-type headache

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A 45-year-old woman comes to the office for evaluation of irregular menstrual bleeding. For the past 8 months, the patient has had some intermenstrual spotting. The bleeding initially occurred for 1-2 days between menstrual cycles but now has become progressively prolonged and heavy, and she now bleeds almost daily. The patient previously used a progestin-releasing intrauterine device for contraception, but had it removed 2 years ago when her husband had a vasectomy. She takes no daily medications and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Vital signs are normal. BMI is 38 kg/m2. Bimanual examination shows no abnormalities. On speculum examination, dark-red blood is seen at the cervical os. There are no cervical or vaginal lesions. An endometrial biopsy reveals endometrial hyperplasia. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
A)Chronic polymicrobial infection within the endometrial cavity
B)Continuous exposure to exogenous progesterone
C)Distortion of the endometrial cavity by myocyte proliferation
D)Ectopic implantation of endometrial glands
E)Invasion of endometrial tissue into the myometrium
F)Peripheral aromatization of androgens to estrone
A)Chronic polymicrobial infection within the endometrial cavity
B)Continuous exposure to exogenous progesterone
C)Distortion of the endometrial cavity by myocyte proliferation
D)Ectopic implantation of endometrial glands
E)Invasion of endometrial tissue into the myometrium
F)Peripheral aromatization of androgens to estrone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An 18-year-old, nulliparous woman comes to the office with lower abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting for the past day. She has been unable to tolerate food or water for the past 8 hours. The patient is sexually active and uses oral contraceptive pills. She has had 3 lifetime sexual partners. Her last menstrual period was 15 days ago. The patient has no medication allergies. Temperature is 39 C (102.2 F), blood pressure is 100/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 110/min. Physical examination reveals dry mucous membranes and delayed capillary refill. The abdomen has diffuse tenderness over the lower quadrants. The external genitalia have no abnormalities; speculum examination shows purulent discharge from the cervical os. The uterus is small, anteverted, and tender to palpation and motion. The adnexa are markedly tender bilaterally, with no palpable masses. Cervical nucleic acid amplification testing is pending. Urine pregnancy test is negative. Laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Admit the patient and wait for nucleic acid amplification test results
B)Inpatient treatment with cephalosporin plus doxycycline
C)Outpatient treatment with cephalosporin plus doxycycline
D)Outpatient treatment with metronidazole plus clindamycin
E)Outpatient treatment with metronidazole plus doxycycline
 Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?A)Admit the patient and wait for nucleic acid amplification test results
B)Inpatient treatment with cephalosporin plus doxycycline
C)Outpatient treatment with cephalosporin plus doxycycline
D)Outpatient treatment with metronidazole plus clindamycin
E)Outpatient treatment with metronidazole plus doxycycline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A 36-year-old primigravida at 26 weeks gestation comes to the office for evaluation of painful urination. She has had urinary frequency since her first month of pregnancy, but a week ago she developed dysuria. The patient has also had chills and fatigue for the past 2 days. She has intermittent, nonpainful contractions but no vaginal bleeding or leakage of fluid. Fetal movement is normal. Three years ago, the patient was treated for pyelonephritis. She has no chronic medical conditions and has had no surgeries. Temperature is 100.4 F (38 C), blood pressure is 110/60 mm Hg, and pulse is 110/min. Fundal height is 26 cm and fetal heart tones are 170/min. There is tenderness over the right costovertebral angle. The uterus is nontender and the cervix is closed. Urinalysis is positive for leukocyte esterase and blood; a urine culture is collected. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis
B)Inpatient intravenous antibiotics
C)Oral antibiotics and follow-up in 2 days
D)Renal ultrasound
E)Voiding cystourethrogram
A)CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis
B)Inpatient intravenous antibiotics
C)Oral antibiotics and follow-up in 2 days
D)Renal ultrasound
E)Voiding cystourethrogram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A 20-year-old woman comes to the office for a refill of oral contraceptives. She is in a monogamous relationship that began 6 months ago and uses condoms as back-up contraception. The patient became sexually active at age 14 and has had 5 lifetime partners. Her last menstrual period was 2 weeks ago. She has regular menses lasting 4-5 days every 28 days. The patient has not received the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination series and has never had a Pap test. Three months ago, she had negative screening for sexually transmitted infection. The patient has no chronic medical conditions and has had no prior surgery. She smokes cigarettes socially but does not use alcohol or illicit drugs. Vital signs are normal. Physical examination shows normal external genitalia without any lesions. Which of the following is recommended for this patient?
A)HPV testing and, if negative, HPV vaccination
B)HPV vaccination alone
C)Pap testing alone
D)Pap with HPV testing
E)Reassurance and follow-up in 1 year
A)HPV testing and, if negative, HPV vaccination
B)HPV vaccination alone
C)Pap testing alone
D)Pap with HPV testing
E)Reassurance and follow-up in 1 year

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A 26-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to a bump on her vaginal introitus. The patient first noticed the mass 2 days ago, but it has increased in size and now causes discomfort when she walks or exercises. She had unprotected sex with a new partner 6 weeks ago and has had 10 lifetime partners. The patient had an abnormal Pap test last year but had a normal colposcopy. She smokes a half pack of cigarettes daily but does not use alcohol or illicit drugs. Temperature is 36.7 C (98.1 F), blood pressure is 110/60 mm Hg, and pulse is 80/min. On pelvic examination, the pubic hair is shaved. There is a 4-cm, mobile, soft, nontender cystic mass behind the right posterior labium majus that extends into the vagina. The remainder of the examination is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A)Bartholin duct cyst
B)Bartholin gland abscess
C)Condylomata acuminata
D)Condylomata lata
E)Epidermal inclusion cyst
F)Hidradenitis suppurativa
G)Lymphogranuloma venereum
A)Bartholin duct cyst
B)Bartholin gland abscess
C)Condylomata acuminata
D)Condylomata lata
E)Epidermal inclusion cyst
F)Hidradenitis suppurativa
G)Lymphogranuloma venereum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A 22-year-old nulligravid woman comes to the office for her first gynecologic examination and to discuss contraception options. Menarche was at age 13. Her last menses was 2 weeks ago; periods occur every 30 days and last for 4 days. The patient has no dysuria, urinary frequency, vaginal discharge, postcoital spotting, or abdominal pain. She became sexually active a few months ago with her boyfriend; she is monogamous and currently uses condoms for contraception. The patient takes no medications and has no allergies. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. The patient has received all recommended vaccinations except for the human papillomavirus series. Her mother was diagnosed with ovarian cancer at age 46 and is currently undergoing chemotherapy. Vital signs are normal. Complete physical examination, including pelvic examination, shows no abnormalities. A urine pregnancy test is negative. In addition to her first Pap test, which of the following is the best recommendation for this patient?
A)Cervical human papillomavirus testing
B)Cervical swab for chlamydia and gonorrhea
C)Clean-catch urinalysis
D)No additional testing needed
E)Nontreponemal serology for syphilis
F)Wet mount microscopy of cervical mucus
A)Cervical human papillomavirus testing
B)Cervical swab for chlamydia and gonorrhea
C)Clean-catch urinalysis
D)No additional testing needed
E)Nontreponemal serology for syphilis
F)Wet mount microscopy of cervical mucus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A 27-year-old nulliparous woman comes to the office due to left pelvic pain over the past 8 months. She has constant pelvic pressure exacerbated by exercise and sexual activity. The patient stopped taking combined oral contraceptives 2 years ago with the intention of having children but has not yet conceived. Her last menstrual period was 2 weeks ago. The patient's menstrual cycles are regular, occurring every 27 days with 4 days of bleeding. She was treated for trichomoniasis at age 20. Temperature is 37.2 C (99 F) and blood pressure is 120/72 mm Hg. Pelvic examination shows a normal-sized uterus with no abnormal cervical discharge. Bimanual examination reveals left adnexal tenderness. A unilocular mass with homogeneous, low-level echoes on the left ovary is seen on ultrasound. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A)Endometriosis
B)Epithelial ovarian cancer
C)Mature teratoma
D)Pedunculated leiomyoma
E)Pelvic congestion syndrome
F)Tuboovarian abscess
A)Endometriosis
B)Epithelial ovarian cancer
C)Mature teratoma
D)Pedunculated leiomyoma
E)Pelvic congestion syndrome
F)Tuboovarian abscess

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A 26-year-old primigravid woman at 14 weeks gestation comes to the office to establish prenatal care. The patient has had no vaginal bleeding or cramping. She has no chronic medical conditions, and her only medication is a daily prenatal vitamin. The patient follows a vegan diet and drinks 2 cups of coffee each morning. She is an avid runner and runs 5 miles most days. The patient does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Vital signs are normal. Prepregnancy BMI was 22 kg/m2. Physical examination is normal. Transvaginal ultrasound shows a single intrauterine gestation with a heart rate of 155/min. The patient asks about possible lifestyle modifications needed during pregnancy. Which of the following is the most appropriate recommendation for this patient?
A)Decrease current exercise regimen
B)Discontinue the vegan diet
C)Eliminate caffeine consumption from diet
D)Increase caloric intake by about 350 kcal/day
E)Limit total pregnancy weight gain to 10 kg (22 lb)
A)Decrease current exercise regimen
B)Discontinue the vegan diet
C)Eliminate caffeine consumption from diet
D)Increase caloric intake by about 350 kcal/day
E)Limit total pregnancy weight gain to 10 kg (22 lb)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A 63-year-old woman comes to the office for a routine annual examination. The patient feels well and has no concerns today. She underwent menopause at age 50 and has had no episodes of vaginal bleeding. The patient exercises multiple days a week and has no urinary or fecal leakage. BMI is 29 kg/m2. Blood pressure is 126/80 mm Hg and pulse is 80/min. Cardiopulmonary examination is normal. The abdomen is soft and nontender without palpable masses or hernias. On pelvic examination, vulvar atrophy is present, and the vagina appears pale and has minimal rugation but no lesions. The cervix appears normal and has no lesions or discharge. On Valsalva maneuver, there is a bulge of the anterior vaginal wall to the introitus. Postvoid bladder and renal ultrasound is normal. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient's pelvic organ prolapse?
A)Hormone replacement therapy
B)Pessary placement
C)Reassurance and observation
D)Surgical anterior vaginal wall repair
E)Urodynamic testing
A)Hormone replacement therapy
B)Pessary placement
C)Reassurance and observation
D)Surgical anterior vaginal wall repair
E)Urodynamic testing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A 30-year-old woman, gravida 1 para 0, at 26 weeks gestation comes to the office for a routine prenatal visit. She has had no contractions, vaginal bleeding, or leakage of fluid. Fetal movement is normal. The patient has no chronic medical conditions, and her only medications are a prenatal vitamin and iron supplement. Prepregnancy BMI was 18 kg/m2. She has gained less than the recommended 0.5 kg (1 lb) per week. Vital signs are normal. Fetal heart rate is 150/min. Fundal height is 24 cm. Ultrasound reveals a fetus measuring in the 25th percentile for gestational age. This patient is at increased risk for which of the following pregnancy-related complications?
A)Cesarean delivery
B)Fetal anemia
C)Placenta previa
D)Placental abruption
E)Preeclampsia
F)Preterm delivery
A)Cesarean delivery
B)Fetal anemia
C)Placenta previa
D)Placental abruption
E)Preeclampsia
F)Preterm delivery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A 19-year-old woman comes to the office for a routine physical examination. She feels well and has no concerns. The patient has had 2 sexual partners in the past 3 months and uses condoms for contraception. She has no significant medical history, takes no medications, and has no drug allergies. Temperature is 37.2 C (99 F), blood pressure is 120/72 mm Hg, and pulse is 72/min. Pelvic examination shows normal external genitalia. The cervix has no lesions, abnormal discharge, or friability. On bimanual examination, the uterus is small and mobile and has no cervical motion or fundal tenderness. A urine pregnancy test is negative. A cervical swab sent for nucleic acid amplification testing is positive for Chlamydia trachomatis but negative for Neisseria gonorrhoeae. The patient is still asymptomatic. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
A)Ceftriaxone and doxycycline
B)Ceftriaxone only
C)Doxycycline only
D)Reassurance and no treatment at this time
E)Repeat test for confirmation
A)Ceftriaxone and doxycycline
B)Ceftriaxone only
C)Doxycycline only
D)Reassurance and no treatment at this time
E)Repeat test for confirmation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A 27-year-old primigravid woman at 16 weeks gestation comes to the office for an initial prenatal visit. She has had no pelvic pain, vaginal bleeding, or abnormal discharge. The patient immigrated to the United States 6 years ago. She has no medical issues or previous surgeries. She had regular menses prior to pregnancy and has no history of sexually transmitted infections. Family history is noncontributory. The patient takes a daily prenatal vitamin and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg. BMI is 23 kg/m2. Fetal heart rate is 155/min. The patient's blood type is O, Rh negative. Rubella and varicella titers both show no immunity. Hemoglobin is 11.2 g/dL, and mean corpuscular volume is 84 fL. All other routine prenatal laboratory studies are normal. Which of the following is the best recommendation for this patient?
A)Hemoglobin electrophoresis
B)Mumps-measles-rubella vaccine postpartum
C)Repeat rubella and varicella titers in 4 weeks
D)Rho(D) immunoglobulin now
E)Tuberculin skin test
F)Varicella vaccine now
A)Hemoglobin electrophoresis
B)Mumps-measles-rubella vaccine postpartum
C)Repeat rubella and varicella titers in 4 weeks
D)Rho(D) immunoglobulin now
E)Tuberculin skin test
F)Varicella vaccine now

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A 22-year-old woman comes to the office for an initial prenatal visit. The patient is 19 weeks gestation by her last menstrual period. She emigrated from India 3 weeks ago and, as found on her medical screening, had a positive interferon gamma release assay. The patient otherwise has no medical conditions and no fever, cough, or weight loss. Temperature is 36.7 C (98.1 F), blood pressure is 100/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 70/min. BMI is 23 kg/m2. There is no lymphadenopathy. The lungs are clear to auscultation. The uterus is palpated just below the umbilicus. Transabdominal ultrasound shows a singleton intrauterine pregnancy at 19 weeks gestation and a normal fetal heart rate. Routine prenatal laboratory results, including HIV screening, are normal. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Begin isoniazid prophylaxis after 28 weeks gestation
B)Begin isoniazid prophylaxis now
C)Obtain chest x-ray
D)Perform tuberculin skin testing
E)Repeat interferon gamma release assay postpartum
F)Treat for active tuberculosis
A)Begin isoniazid prophylaxis after 28 weeks gestation
B)Begin isoniazid prophylaxis now
C)Obtain chest x-ray
D)Perform tuberculin skin testing
E)Repeat interferon gamma release assay postpartum
F)Treat for active tuberculosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A 29-year-old primigravida at 12 weeks gestation comes to the office for a prenatal visit. The patient feels some pelvic pressure but has no vaginal bleeding or discharge. She completed a course of antibiotics at 10 weeks gestation after a urine culture grew ≥100,000 colony-forming units of Escherichia coli. The patient has had some urinary frequency but no dysuria, urgency, or hematuria. She has no chronic medical conditions and has had no surgeries. Temperature is 98.6 F (37 C), blood pressure is 96/68 mm Hg, and pulse is 90/min. Fetal heart rate is 170/min on Doppler ultrasound. The uterus is nontender and palpable just above the pubic symphysis. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Daily antibiotic suppression
B)Postvoid residual volume test
C)Repeat urine culture
D)Routine prenatal care only
E)Voiding cystourethrogram
A)Daily antibiotic suppression
B)Postvoid residual volume test
C)Repeat urine culture
D)Routine prenatal care only
E)Voiding cystourethrogram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A 34-year-old woman, gravida 3 para 2, has a precipitous spontaneous vaginal delivery of a 4.2-kg (9 lb 5 oz) boy at 39 weeks gestation. After 15 minutes of gentle umbilical cord traction and fundal massage, the placenta is not delivered. Umbilical cord traction is continued; the umbilical cord abruptly avulses, and the patient suddenly develops severe abdominal pain. Blood pressure is 70/40 mm Hg and pulse is 62/min. On abdominal examination, the uterine fundus is not palpable at the umbilicus. There is copious vaginal bleeding with bright red blood and passage of large clots. On removal of the blood clots, a firm, rounded mass is visualized protruding from the vagina. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms? A)Placenta previa B)Prolapsed fibroid C)Uterine inversion D)Uterine rupture E)Vaginal hematoma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A 39-year-old woman, gravida 2 para 1, at 38 weeks gestation, comes to the office for a routine prenatal visit. The patient feels well and reports normal fetal activity. Last week, she had nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea for 24 hours, but she has been able to eat and drink normally for the past several days. For the past 2 days, the patient has had increased clear vaginal discharge with irregular, painful contractions but no vaginal bleeding. She has no chronic medical conditions, and her only medication is a prenatal vitamin. Temperature is 99.6 F (37.6 C), blood pressure is 132/86 mm Hg, and pulse is 96/min. The uterus is nontender and the fundal height is 34 cm. Fetal heart tones are 135/min. Fetal ultrasound shows a cephalic fetus, measuring at the 50th percentile for gestational age, and an amniotic fluid index of 2 cm (normal: >5 cm). Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's amniotic fluid level?
A)Fetal congenital infection
B)Maternal dehydration
C)Normal gestational age variant
D)Rupture of membranes
E)Uteroplacental insufficiency
A)Fetal congenital infection
B)Maternal dehydration
C)Normal gestational age variant
D)Rupture of membranes
E)Uteroplacental insufficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A 38-year-old woman at 6 weeks gestation comes to the office due to vaginal bleeding. The patient has had intermittent bleeding for the past week, which increases after intercourse. She has had no pelvic pain, nausea, or vomiting. Blood pressure is 124/68 mm Hg and pulse is 86/min. The abdomen is soft and nontender, without rebound or guarding. On pelvic examination, there is dark brown discharge pooling in the posterior vaginal vault. The cervix is closed, and there is a raised cervical mass that bleeds freely when manipulated with a swab. Ultrasound reveals a yolk sac and a 6-week intrauterine fetal pole with cardiac motion. Blood type is O, Rh positive. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Ceftriaxone and azithromycin
B)Cervical biopsy
C)Endometrial biopsy
D)Expectant management only
E)Kleihauer-Betke test
F)Quantitative β-hCG level
A)Ceftriaxone and azithromycin
B)Cervical biopsy
C)Endometrial biopsy
D)Expectant management only
E)Kleihauer-Betke test
F)Quantitative β-hCG level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A 20-year-old woman comes to the office due to dysuria for the past 2 days. She also has had urinary frequency but no fevers, chills, nausea, or hematuria. The patient became sexually active with her boyfriend 6 months ago. Since then, she has had 3 episodes of cystitis. The patient has no other medical conditions and no prior surgery. She takes no medications and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. The patient uses condoms for contraception, and her last menstrual period was 2 weeks ago. Temperature is 37.2 C (99 F). On abdominal examination, there is mild suprapubic tenderness. No costovertebral or flank tenderness is present. Antibiotic therapy is prescribed. A urine culture grows Escherichia coli. When the patient is called with the results, she reports complete resolution of her symptoms. Repeat urine culture 2 weeks later is negative. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient's recurrent cystitis?
A)Cystoscopy
B)Daily cranberry juice
C)Postcoital antibiotics
D)Renal ultrasound
E)Urodynamic testing
A)Cystoscopy
B)Daily cranberry juice
C)Postcoital antibiotics
D)Renal ultrasound
E)Urodynamic testing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A 33-year-old woman, gravida 2 para 1, comes to the clinic for a routine prenatal visit at 26 weeks gestation. Her pregnancy has been uncomplicated. The patient's BMI was 23 kg/m2 at her initial prenatal visit, and her laboratory results were as follows:  An ultrasound at 20 weeks gestation showed an anterior placenta and normal fetal anatomy. The patient's only concern today is lower leg swelling that occurs after prolonged standing but resolves with sitting or lying down. Her last pregnancy was complicated by Group B Streptococcus colonization requiring prophylaxis during delivery. The patient has no chronic medical problems and takes only prenatal vitamins. She is a radiologist and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Blood pressure is 135/80 mm Hg and pulse is 65/min. Physical examination shows minimal pedal edema and negative Homan sign bilaterally. Fundal height is 27 cm and fetal heart rate is 140/min. Which of the following tests should be obtained at this visit?
An ultrasound at 20 weeks gestation showed an anterior placenta and normal fetal anatomy. The patient's only concern today is lower leg swelling that occurs after prolonged standing but resolves with sitting or lying down. Her last pregnancy was complicated by Group B Streptococcus colonization requiring prophylaxis during delivery. The patient has no chronic medical problems and takes only prenatal vitamins. She is a radiologist and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Blood pressure is 135/80 mm Hg and pulse is 65/min. Physical examination shows minimal pedal edema and negative Homan sign bilaterally. Fundal height is 27 cm and fetal heart rate is 140/min. Which of the following tests should be obtained at this visit?
A)24-hour urine protein collection
B)Chlamydia trachomatis cervical polymerase chain reaction
C)Clean catch urine culture
D)Group B Streptococcus rectovaginal culture
E)Hepatitis B surface antigen blood test
F)Oral glucose challenge test
 An ultrasound at 20 weeks gestation showed an anterior placenta and normal fetal anatomy. The patient's only concern today is lower leg swelling that occurs after prolonged standing but resolves with sitting or lying down. Her last pregnancy was complicated by Group B Streptococcus colonization requiring prophylaxis during delivery. The patient has no chronic medical problems and takes only prenatal vitamins. She is a radiologist and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Blood pressure is 135/80 mm Hg and pulse is 65/min. Physical examination shows minimal pedal edema and negative Homan sign bilaterally. Fundal height is 27 cm and fetal heart rate is 140/min. Which of the following tests should be obtained at this visit?
An ultrasound at 20 weeks gestation showed an anterior placenta and normal fetal anatomy. The patient's only concern today is lower leg swelling that occurs after prolonged standing but resolves with sitting or lying down. Her last pregnancy was complicated by Group B Streptococcus colonization requiring prophylaxis during delivery. The patient has no chronic medical problems and takes only prenatal vitamins. She is a radiologist and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Blood pressure is 135/80 mm Hg and pulse is 65/min. Physical examination shows minimal pedal edema and negative Homan sign bilaterally. Fundal height is 27 cm and fetal heart rate is 140/min. Which of the following tests should be obtained at this visit?A)24-hour urine protein collection
B)Chlamydia trachomatis cervical polymerase chain reaction
C)Clean catch urine culture
D)Group B Streptococcus rectovaginal culture
E)Hepatitis B surface antigen blood test
F)Oral glucose challenge test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A 46-year-old woman comes to the office for evaluation of a vaginal mass. The patient has had intermittent vaginal pressure for the past 2 years that is now constant and worse with intercourse. She now notices a vaginal mass when voiding and sometimes sees light blood on the toilet paper after wiping. The patient has no chronic medical conditions. Her only surgery was a cervical conization 4 years ago; repeat Pap testing has since been normal. The patient had 3 uncomplicated vaginal deliveries in her 20s and a tubal ligation with her last delivery. She is recently divorced and has had 3 new sexual partners in the past year. The patient smokes a half pack of cigarettes daily and drinks 1-2 glasses of wine on the weekends. BMI is 23 kg/m². Vital signs are normal. On pelvic examination, there is a small erosion over the anterior vaginal wall but no lesions on the cervix. The cervix protrudes to the hymenal ring with Valsalva maneuver. The uterus is mobile and nontender, and there is a 2-cm pedunculated fundal uterine fibroid. Which of the following is the most likely contributing factor to this patient's clinical presentation?
A)Chronic tobacco use
B)Multiple pregnancies
C)Number of sexual partners
D)Prior cervical conization
E)Uterine leiomyomata
A)Chronic tobacco use
B)Multiple pregnancies
C)Number of sexual partners
D)Prior cervical conization
E)Uterine leiomyomata

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A 38-year-old woman, gravida 2 para 1, at 28 weeks gestation comes to the office for a routine prenatal visit. The patient has had no abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, or leakage of fluid. She reports active fetal movement. The patient has been on antiretroviral therapy since being diagnosed with HIV 3 years ago, and her last viral load was undetectable. She had negative syphilis and hepatitis C screening at her initial prenatal visit. Blood pressure is 122/74 mm Hg, and pulse is 86/min. The abdomen is nontender, and fundal height is 28 cm. Fetal heart tones are 140/min. The rest of the examination is normal. Laboratory results are as follows: 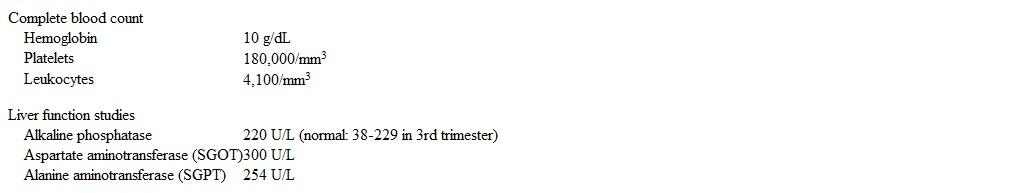 Ultrasound of the right upper quadrant shows no stones or dilation of the common bile duct. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
Ultrasound of the right upper quadrant shows no stones or dilation of the common bile duct. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)24-hour urine protein collection
B)Antinuclear antibody testing
C)Immediate delivery
D)Serum ceruloplasmin
E)Viral hepatitis serology
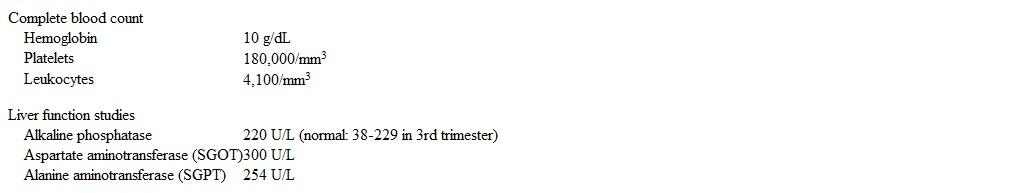 Ultrasound of the right upper quadrant shows no stones or dilation of the common bile duct. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
Ultrasound of the right upper quadrant shows no stones or dilation of the common bile duct. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?A)24-hour urine protein collection
B)Antinuclear antibody testing
C)Immediate delivery
D)Serum ceruloplasmin
E)Viral hepatitis serology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A 28-year-old woman comes to the office for evaluation of nipple discharge. The patient has had bilateral yellow nipple discharge for the past month. She has gained 5 lb (2.3 kg) in the past year. The patient has had no missed menses, and her last menstrual period was 2 weeks ago. She takes sertraline for anxiety and depression. The patient's mother had breast cancer at age 59. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. BMI is 29 kg/m2. Blood pressure is 122/74 mm Hg and pulse is 78 /min. On examination, there is dense breast tissue with no palpable dominant masses. The breasts are nontender and the nipples have bilateral white-yellow crusting. There is no axillary or clavicular lymphadenopathy. The remainder of the physical examination is unremarkable. Urine pregnancy test is negative. Laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Bilateral core needle biopsies
B)Cytology of the discharge
C)Discontinue sertraline
D)Mammography
E)MRI of the pituitary
F)No additional management indicated
 Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?A)Bilateral core needle biopsies
B)Cytology of the discharge
C)Discontinue sertraline
D)Mammography
E)MRI of the pituitary
F)No additional management indicated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A 32-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to left lower quadrant abdominal pain. The pain started suddenly this morning along with nausea, but she has had no vomiting or diarrhea. The patient has a history of heavy menstrual bleeding due to uterine fibroids, which was previously controlled with combined oral contraceptives. She recently stopped the pills to try for pregnancy, and her last menstrual period was 2 weeks ago. BMI is 30 kg/m2. Temperature is 37.2 C (99 F), blood pressure is 122/84 mm Hg, and pulse is 82/min. The abdomen is soft and diffusely tender to deep palpation in the left lower quadrant, but there is no rebound or guarding. The uterus is enlarged, irregular in contour, and nontender. Urine pregnancy testing is negative. Ultrasound reveals multiple subserosal and intramural uterine fibroids, a homogenous endometrial stripe, moderate free fluid in the pelvis, and a left ovary with a 4-cm cyst with thin walls. Which of the following is the best next step in the immediate management of this patient?
A)Broad-spectrum antibiotics
B)CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis
C)Diagnostic peritoneal lavage
D)Laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy
E)Laparotomy with myomectomy
F)Observation and reassurance only
A)Broad-spectrum antibiotics
B)CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis
C)Diagnostic peritoneal lavage
D)Laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy
E)Laparotomy with myomectomy
F)Observation and reassurance only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Two wide-bore intravenous lines are placed, and intravenous fluids are administered. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Administration of uterine relaxants
B)Administration of uterotonics
C)Emergent laparotomy
D)Manual replacement of the uterus
E)Removal of the placenta
A)Administration of uterine relaxants
B)Administration of uterotonics
C)Emergent laparotomy
D)Manual replacement of the uterus
E)Removal of the placenta

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A 25-year-old woman, gravida 2 para 2, comes to the office for a postpartum visit and to discuss contraception. Two weeks ago, the patient had a vaginal delivery at 36 weeks gestation. She is breastfeeding exclusively with no issues. Her lochia has decreased, and she has no pelvic pain. The patient would like to start reliable contraception as soon as possible because she conceived while breastfeeding after her first pregnancy. She takes a daily iron supplement for iron deficiency anemia due to heavy menstrual bleeding. The patient has no other chronic medical conditions and takes no medications. Vital signs are normal. Pelvic examination is deferred. Which of the following is the best contraceptive option for this patient?
A)Combined estrogen-progestin oral contraceptives
B)Copper-containing intrauterine device
C)Diaphragm and condoms
D)Endometrial ablation
E)Progestin-only oral contraceptives
F)Subdermal progestin-releasing implant
A)Combined estrogen-progestin oral contraceptives
B)Copper-containing intrauterine device
C)Diaphragm and condoms
D)Endometrial ablation
E)Progestin-only oral contraceptives
F)Subdermal progestin-releasing implant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A 29-year-old nulligravid woman comes to the office because she has not menstruated since stopping her birth control. Menarche was at age 14, and she had irregular, heavy menstrual periods from age 14-16. The patient then took combination oral contraceptives until 6 months ago. Since stopping her medication, she has had more frequent headaches and increasing acne but has had no weight changes, pelvic pain, or abnormal hair loss or growth. The patient is a high school teacher and coaches the cross-country and track teams. She runs recreationally and eats a well-balanced diet. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Vital signs are normal and BMI is 22 kg/m2. A few open comedones are seen on the forehead. The remainder of the physical examination, including pelvic examination, is normal. Urine pregnancy test is negative and pelvic ultrasound is normal. Which of the following is the best next step in evaluation of this patient?
A)Karyotype analysis
B)MRI of the pituitary
C)No further evaluation indicated
D)Serum 17-hydroxyprogesterone level
E)Serum prolactin level
A)Karyotype analysis
B)MRI of the pituitary
C)No further evaluation indicated
D)Serum 17-hydroxyprogesterone level
E)Serum prolactin level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A 23-year-old woman comes to the physician at 9 weeks gestation for prenatal counseling. This is her first pregnancy. She has no history of bleeding, and there is no history of hemophilia in her husband's family. However, the patient's father and other relatives have hemophilia A, and she is concerned about the possibility of her child having the disease. The following pedigree is created according to the patient's family history (arrow points to the patient).  Which of the following is the best response to this patient's concern?
Which of the following is the best response to this patient's concern?
A)The chance of having hemophilia does not depend on the child's sex
B)The probability of having a child who is a silent carrier is 50%
C)The probability of having a child with hemophilia is 25%
D)The probability of having a child with hemophilia is 50%
E)The probability of having a child with hemophilia is similar to that of the general population
 Which of the following is the best response to this patient's concern?
Which of the following is the best response to this patient's concern?A)The chance of having hemophilia does not depend on the child's sex
B)The probability of having a child who is a silent carrier is 50%
C)The probability of having a child with hemophilia is 25%
D)The probability of having a child with hemophilia is 50%
E)The probability of having a child with hemophilia is similar to that of the general population

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A 34-year-old woman, gravida 1 para 1, comes to the office for postpartum follow-up. She had a vaginal delivery 6 weeks ago that was complicated by severe postpartum bleeding requiring aggressive volume resuscitation and transfusion of 5 units of packed red blood cells. Since the delivery, the patient has been very fatigued with poor appetite. She is "very concerned" about having little energy to bond with her child; her family has been helping with the baby. The patient has been formula feeding her infant due to lack of milk production. Her prepregnancy weight was 63.5 kg (140 lb), weight at delivery was 82.5 kg (182 lb), and current weight is 56.2 kg (124 lb). Blood pressure is 90/69 mm Hg and pulse is 88/min. Examination shows a well-healed perineal laceration scar. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current symptoms?
A)Adjustment disorder with depressed mood
B)Pituitary ischemic necrosis
C)Postpartum depression
D)Postpartum thyroid inflammation
E)Primary adrenal insufficiency
F)Spontaneous pituitary hemorrhage
A)Adjustment disorder with depressed mood
B)Pituitary ischemic necrosis
C)Postpartum depression
D)Postpartum thyroid inflammation
E)Primary adrenal insufficiency
F)Spontaneous pituitary hemorrhage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A 28-year-old nulligravid woman comes to the office for a routine examination. She feels well but has tried to conceive for the past 12 months without success. The patient has had sexual intercourse with her husband 3 or 4 times a week without contraception. Her menses are irregular with frequent missed periods. Every time the patient misses a period, her home pregnancy tests are negative. She has no medical conditions and has had no surgeries. The patient takes a daily prenatal vitamin and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Vital signs are normal. There is no excess hair on physical examination. Breast examination shows no masses or nipple discharge. The abdomen is soft without masses. Pelvic examination shows normal external genitalia and a small, mobile uterus. Pelvic ultrasonography shows a normal uterus and bilateral ovaries. Laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A)Androgen-secreting tumor
B)Endometriosis
C)Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
D)Hypothyroidism
E)Pituitary adenoma
F)Polycystic ovary syndrome
G)Primary ovarian insufficiency
H)Tubal occlusion
 Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?A)Androgen-secreting tumor
B)Endometriosis
C)Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
D)Hypothyroidism
E)Pituitary adenoma
F)Polycystic ovary syndrome
G)Primary ovarian insufficiency
H)Tubal occlusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A 38-year-old nulligravid woman comes to the office due to persistent abnormal uterine bleeding. The patient's menstrual periods previously occurred monthly and consisted of 4 days of moderate bleeding and light cramping. However, for the past 8 months, she has had intermenstrual spotting and bleeding that have occurred at varying intervals and last 3-7 days. She was started on combination oral contraceptives 4 months ago, which has not improved the bleeding pattern. Temperature is 37.2 C (99 F), blood pressure is 126/76 mm Hg, and pulse is 86/min. BMI is 29 kg/m2. Speculum examination shows dark red blood in the posterior vaginal vault but no cervical or vaginal lesions. The remainder of the pelvic examination is normal. Laboratory results are as follows:  Urine pregnancy test is negative. Pelvic ultrasound shows an anteverted uterus and no adnexal masses. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient?
Urine pregnancy test is negative. Pelvic ultrasound shows an anteverted uterus and no adnexal masses. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient?
A)Coagulation studies
B)Endometrial ablation
C)Endometrial biopsy
D)Hysterosalpingogram
E)Progesterone withdrawal test
 Urine pregnancy test is negative. Pelvic ultrasound shows an anteverted uterus and no adnexal masses. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient?
Urine pregnancy test is negative. Pelvic ultrasound shows an anteverted uterus and no adnexal masses. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient?A)Coagulation studies
B)Endometrial ablation
C)Endometrial biopsy
D)Hysterosalpingogram
E)Progesterone withdrawal test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A 34-year-old woman comes to the office for evaluation of 3 months of amenorrhea. She first began experiencing irregular periods a year ago, and now they have stopped completely. The patient has no headaches, visual changes, galactorrhea, hair loss, or fatigue. She has a history of non-Hodgkin lymphoma for which she received chemotherapy 5 years ago; there are no signs of recurrence. The patient currently takes no medications. Family history is noncontributory. Her most recent Pap test was last year and all prior testing was normal. She has no history of sexually transmitted infections. The patient does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg and pulse is 78/min. BMI is 28 kg/m2. Physical examination reveals a nonenlarged thyroid without masses. Cardiopulmonary examination is normal. Pelvic examination reveals dry vaginal mucosa and a small, anteverted, mobile uterus with no adnexal masses. A pregnancy test is negative. Which of the following laboratory findings are most likely present in this patient?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A 16-year-old girl comes to the office for a routine health maintenance examination. The patient is in high school, is performing well academically, and plays on the tennis team. She has no concerns today. On review of systems, the patient has not reached menarche, but she says that her mother did not start menstruating until this age. She recently started wearing contact lenses for myopia and uses an over-the-counter cream for acne. Height is at the 70th percentile and weight is at the 25th percentile for age. Blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg and pulse is 60/min. Breast development is sexual maturity rating (Tanner stage) III. Pelvic examination shows sexual maturity rating (Tanner stage) III pubic hair development and normal external genitalia. Speculum examination reveals a well-rugated vagina but no cervix. FSH levels are within the normal pubertal range. Karyotype is 46, XX. Pelvic ultrasound reveals an absent uterus. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Dihydrotestosterone and testosterone level
B)Echocardiogram
C)Hymenal incision
D)MRI of the brain
E)Renal ultrasound
F)TSH and prolactin level
A)Dihydrotestosterone and testosterone level
B)Echocardiogram
C)Hymenal incision
D)MRI of the brain
E)Renal ultrasound
F)TSH and prolactin level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A 34-year-old woman comes to the office for evaluation of amenorrhea. Last year the patient had a missed abortion that was surgically managed with suction curettage. At her follow-up visit a few weeks later she had a copper-releasing intrauterine device placed. Her menstrual periods were initially irregular and heavy, but the bleeding became increasingly lighter. Now the patient has not had a menstrual period in 6 months. Prior to the intrauterine device placement she had regular menses. The patient has had no weight changes, changes in vision, or galactorrhea. She has generalized anxiety disorder. Her older brother has severe intellectual disability due to fragile X syndrome. Vital signs are normal. BMI is 22 kg/m2. Pelvic examination shows a small, mobile uterus with no adnexal masses. There is no tenderness over the perineum with speculum examination. Pregnancy test is negative. TSH is normal and FSH is elevated. A progesterone challenge is performed and the patient has no withdrawal bleeding. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A)Functional hypothalamic amenorrhea
B)Intrauterine adhesions
C)Intrauterine device-induced amenorrhea
D)Polycystic ovary syndrome
E)Primary ovarian insufficiency
A)Functional hypothalamic amenorrhea
B)Intrauterine adhesions
C)Intrauterine device-induced amenorrhea
D)Polycystic ovary syndrome
E)Primary ovarian insufficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A 32-year-old primigravida at 16 weeks gestation comes to the office due to urinary frequency and increased thirst. Although she limits fluids before bed, she still urinates 6-8 times a night. The patient previously had intermittent urinary frequency, but symptoms have worsened since she became pregnant. Family history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus in her mother and father. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory results are as follows:  A 24-hour urine collection shows a urine output of 5.5 L after an intake of 2 L. What is the most likely cause of this patient's urinary frequency?
A 24-hour urine collection shows a urine output of 5.5 L after an intake of 2 L. What is the most likely cause of this patient's urinary frequency?
A)Diabetes insipidus
B)Gestational diabetes mellitus
C)Normal pregnancy changes
D)Osmotic diuresis due to urea
E)Urinary tract infection
 A 24-hour urine collection shows a urine output of 5.5 L after an intake of 2 L. What is the most likely cause of this patient's urinary frequency?
A 24-hour urine collection shows a urine output of 5.5 L after an intake of 2 L. What is the most likely cause of this patient's urinary frequency?A)Diabetes insipidus
B)Gestational diabetes mellitus
C)Normal pregnancy changes
D)Osmotic diuresis due to urea
E)Urinary tract infection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A 34-year-old woman, gravida 1 para 1, comes to the office for infertility evaluation. She has been trying to conceive for the past year, but her cycles have become increasingly irregular, with the last menstrual period more than 3 months ago. Menses previously occurred every 27 days and lasted 4 days. The patient feels fatigued and has been waking up at night due to feeling too warm. She has been married for 6 years and has a 4-year-old daughter who was delivered vaginally without complications. The patient has hypothyroidism, for which she takes levothyroxine. She has no previous surgeries. The patient smokes a pack of cigarettes a day but does not use alcohol or illicit drugs. Both of her parents have type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMI is 24 kg/m2. Vital signs are normal. Pelvic examination shows normal external genitalia, a small mobile uterus, and normal bilateral ovaries. TSH is normal and a pregnancy test is negative. Which of the following would most likely be seen in this patient?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A 30-year-old woman, gravida 1 para 0, at 24 weeks gestation comes to the office for a prenatal visit. The patient feels well and has no vaginal bleeding, leakage of fluid, or contractions. She has had no headaches, changes in vision, or right upper quadrant pain. The patient has no chronic medical conditions and has had an uncomplicated pregnancy. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Temperature is 37.2 C (99 F), blood pressure is 152/88 mm Hg, pulse is 72/min, and respirations are 14/min. Oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. Physical examination is normal. Fetal heart rate is 150/min on Doppler ultrasound. Laboratory results are as follows:  A nonstress test is reactive. Repeat blood pressure is 154/86 mm Hg. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient's hypertension?
A nonstress test is reactive. Repeat blood pressure is 154/86 mm Hg. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient's hypertension?
A)24-hour urine collection for total protein
B)Immediate induction of labor
C)Magnesium sulfate infusion
D)No additional management indicated
E)Outpatient bed rest
 A nonstress test is reactive. Repeat blood pressure is 154/86 mm Hg. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient's hypertension?
A nonstress test is reactive. Repeat blood pressure is 154/86 mm Hg. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient's hypertension?A)24-hour urine collection for total protein
B)Immediate induction of labor
C)Magnesium sulfate infusion
D)No additional management indicated
E)Outpatient bed rest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A 14-year-old girl is brought to the office due to heavy vaginal bleeding. Since menarche at age 13, menses have been irregular but not painful. Her last menstrual period was 6 weeks ago, and her current menses started 7 days ago. She is soaking through a thick pad every 2 or 3 hours and bled through her clothing overnight. She has no history of recurrent epistaxis or bruising. The patient has no chronic medical conditions or previous surgeries. Her mother required a blood transfusion with delivery, but has had no other bleeding episodes. Blood pressure is 110/60 mm Hg and pulse is 65/min. The external genitalia are normal and consistent with sexual maturity rating (Tanner stage) 4 development. The abdomen is nontender, nondistended, and has no masses. On pelvic examination, there is dark red bleeding from the cervical os. Urine pregnancy test is negative. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
A)Cervical inflammation
B)Endometrial implantation within the myometrium
C)Hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis immaturity
D)Impaired platelet aggregation
E)Monoclonal myometrial proliferation
A)Cervical inflammation
B)Endometrial implantation within the myometrium
C)Hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis immaturity
D)Impaired platelet aggregation
E)Monoclonal myometrial proliferation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A 16-year-old girl is brought to the office because she has not started her menstrual period. The patient's 14-year-old sister underwent menarche a few months ago and her mother began menstruating at age 13. The girl has had no headaches, changes in vision, weight gain, nipple discharge, or abdominal pain. She has no chronic medical conditions and has had no surgeries. The patient is not sexually active and is not on contraception. She plays basketball for her high school team. Height is at the 85th percentile and weight is at the 25th percentile for age. Vital signs are normal. Breast, axillary, and pubic hair development are sexual maturity rating (Tanner stage) IV. The abdomen is soft, nontender, and has no palpable masses. On pelvic examination, the external genitalia appear normal and the vagina ends in a blind pouch. Pelvic ultrasound reveals bilateral ovaries, but no uterus or cervix. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A)Androgen insensitivity syndrome
B)Constitutional delay of puberty
C)Functional hypothalamic amenorrhea
D)Imperforate hymen
E)Müllerian agenesis
F)Transverse vaginal septum
G)Turner syndrome
A)Androgen insensitivity syndrome
B)Constitutional delay of puberty
C)Functional hypothalamic amenorrhea
D)Imperforate hymen
E)Müllerian agenesis
F)Transverse vaginal septum
G)Turner syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A 44-year-old woman comes to the office for evaluation of abnormal uterine bleeding. The patient has had intermenstrual bleeding over the past 3 months. Most of the time, she has had only spotting with wiping, but last week, she had slightly heavier bleeding that required her to use a menstrual pad. In addition to this intermenstrual bleeding, the patient also has monthly menses with 4-5 days of moderate bleeding and slight cramping on the first 2 days that typically resolves with ibuprofen. She has no chronic medical conditions and takes no daily medications. The patient had a bilateral tubal ligation after her last delivery at age 31. Vital signs are normal. BMI is 22 kg/m2. Speculum examination reveals a multiparous cervix with a small amount of bright red blood at the os and no visible cervical or vaginal lesions. On bimanual pelvic examination, the uterus is small, mobile, and nontender. No adnexal masses are palpated. FSH, TSH, and prolactin levels are normal. Urine pregnancy test is negative. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's abnormal uterine bleeding?
A)Adenomyosis
B)Endometrial hyperplasia
C)Endometrial polyp
D)Invasive cervical cancer
E)Perimenopause
F)Uterine leiomyomas
A)Adenomyosis
B)Endometrial hyperplasia
C)Endometrial polyp
D)Invasive cervical cancer
E)Perimenopause
F)Uterine leiomyomas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A 24-year-old primigravida comes to the office for her first prenatal visit. Her last menstrual period was 8 weeks ago and 2 home pregnancy tests have been positive. The patient feels generally well, although she has experienced mild intermittent nausea and anxiety during the pregnancy. Medical history is unremarkable, and her only medication is an over-the-counter prenatal vitamin. Thyroid function tests were normal on evaluation for fatigue and mild palpitations 6 months ago. The patient stopped drinking alcohol after finding out she was pregnant, and she does not use tobacco or illicit drugs. Blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg and pulse is 82/min. Physical examination findings are normal. Pelvic ultrasound shows a gestational sac containing a fetal pole and a yolk sac. Thyroid function study results are as follows:  Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current laboratory findings?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current laboratory findings?
A)Euthyroid sick syndrome
B)Graves disease
C)Hashimoto disease
D)Iodine deficiency
E)Normal physiologic changes
F)Subacute thyroiditis
 Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current laboratory findings?
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current laboratory findings?A)Euthyroid sick syndrome
B)Graves disease
C)Hashimoto disease
D)Iodine deficiency
E)Normal physiologic changes
F)Subacute thyroiditis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A 12-year-old girl is brought to the office for evaluation of increasing lower abdominal pain. The pain began last week, was initially colicky, and was relieved with ibuprofen. Now the pain is constant and the patient has pain with defecation and a sense of incomplete bowel evacuation. She has had decreased appetite for the last 3 days due to the pain but has had no fever, vomiting, diarrhea, or bloody stool. The patient has had intermittent lower abdominal pain for the last 6 months, but the pain usually resolves after a few days without intervention. She has no medical conditions or prior surgeries. She has not reached menarche. BMI is 19 kg/m2. There is a tender, symmetric suprapubic mass to the level of the umbilicus. External genitalia are normal and breast and pubic hair development is Tanner stage 2. There is a blue-tinged bulge between the labia. Rectal examination reveals an anterior tender, central mass. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)CA-125 and CEA levels
B)Diagnostic laparoscopy
C)Hymenal incision and drainage
D)Hysterosalpingogram
E)Karyotype analysis
F)Uterine myomectomy
A)CA-125 and CEA levels
B)Diagnostic laparoscopy
C)Hymenal incision and drainage
D)Hysterosalpingogram
E)Karyotype analysis
F)Uterine myomectomy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A 16-year-old girl comes to the emergency department with heavy vaginal bleeding for 3 days. The patient's menses have been irregular since menarche at age 14 and occur every 4-5 months; her previous menstrual period was almost 4 months ago. She has no medical problems and has had no surgeries. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. The patient is sexually active and uses condoms for contraception. Temperature is 37.2 C (99 F), blood pressure is 110/60 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 16/min. On pelvic examination, there is a moderate amount of blood in the vaginal vault and active bleeding from the cervical os. Bimanual examination shows a small uterus and no adnexal masses. Pelvic ultrasound reveals a small uterus with a thick endometrial stripe and normal ovaries. Urine pregnancy test is negative. Laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
A)Emergency dilation and curettage
B)High-dose gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists
C)High-dose oral contraceptive therapy
D)Packed red blood cell transfusion
E)Workup for coagulation factor deficiency
 Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?A)Emergency dilation and curettage
B)High-dose gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists
C)High-dose oral contraceptive therapy
D)Packed red blood cell transfusion
E)Workup for coagulation factor deficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A 13-year-old girl is brought to the office for evaluation of acne. She began to develop acne over her forehead and chin 4 months ago. She used over-the-counter topical salicylic acid, but the acne did not improve. Now, the patient has painful acne over her face and upper chest. She participates in a soccer league after school, and her mother feels that her exercise regimen is too strenuous and stressful and contributes to her acne. The patient has no medical conditions and has had no surgeries. She has not had a menstrual period. The girl has grown 10.1 cm (4 in) in the last year; her height and weight are at the 70th percentile for age. Vital signs are normal. Nodulocystic acne is present across the face and upper chest. There is no breast bud development. The abdomen is nontender and has no palpable masses. External pelvic examination shows the clitoris protruding from the clitoral hood and bilateral masses in the labia majora. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A)5-alpha-reductase deficiency
B)Androgen insensitivity syndrome
C)Nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia
D)Ovarian hyperthecosis
E)Polycystic ovary syndrome
F)Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor
A)5-alpha-reductase deficiency
B)Androgen insensitivity syndrome
C)Nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia
D)Ovarian hyperthecosis
E)Polycystic ovary syndrome
F)Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A 19-year-old woman comes to the office with a 6-month history of amenorrhea. Menarche occurred at age 11 and her menstrual cycles were regular until 9 months ago. The patient has no changes in vision or recent weight loss. She has no medical problems or previous surgeries. She eats a high-protein/low-fat diet and is a collegiate soccer player. The patient is sexually active and has no history of sexually transmitted infections. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg and pulse is 78/min. BMI is 20 kg/m2. On pelvic examination, the uterus is small, mobile, and nontender. The adnexae are not palpable. A pregnancy test is negative. Prolactin and TSH levels are normal. No menstrual bleeding occurred after a 10-day challenge with medroxyprogesterone acetate. Compared to the general population, this patient is at greatest risk for which of the following?
A)Decreased bone mineral density
B)Ectopic pregnancy
C)Endometrial hyperplasia
D)Epithelial ovarian cancer
E)Vasomotor symptoms (hot flushes)
A)Decreased bone mineral density
B)Ectopic pregnancy
C)Endometrial hyperplasia
D)Epithelial ovarian cancer
E)Vasomotor symptoms (hot flushes)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A 16-year-old girl comes to the office for evaluation of excessive facial hair. The patient has used multiple creams and makeup over the last year but is still embarrassed by the facial hair. She also has had irregular menstrual cycles since menarche at age 12; her last menstrual period was 6 weeks ago. She is an avid runner. Blood pressure is 122/70 mm Hg and pulse is 87/min. BMI is 20 kg/m2. Physical examination shows hirsutism. The patient has normal external female genitalia; the rest of the examination is unremarkable. Urine pregnancy test is negative. Laboratory results are as follows:  Serum glucose and electrolytes are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Serum glucose and electrolytes are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A)Adrenal carcinoma
B)Cushing syndrome
C)Germ cell tumor
D)Idiopathic hirsutism
E)Nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia
F)Polycystic ovary syndrome
G)Use of performance-enhancing agents
 Serum glucose and electrolytes are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Serum glucose and electrolytes are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?A)Adrenal carcinoma
B)Cushing syndrome
C)Germ cell tumor
D)Idiopathic hirsutism
E)Nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia
F)Polycystic ovary syndrome
G)Use of performance-enhancing agents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A 42-year-old woman comes to the office for a routine health examination. She is sexually active with a male partner and underwent a tubal ligation for contraception. The patient has had no abnormal bleeding or recent changes in weight. Menses are regular and last 3-5 days; her last menstrual period was 3 weeks ago. Ten years ago, the patient had genital warts successfully treated by laser ablation. Pap tests have been normal to date. She has had no other serious medical illness or surgeries and takes no medications. She has a family history of hypertension but no history of cancer. Pelvic examination shows a normal cervix without any visible lesions, a small anteverted uterus, and no adnexal masses. The Pap test shows atypical glandular cells. Which of the following is the next best step in management of this patient?
A)Endometrial biopsy
B)Hysterectomy
C)Hysteroscopy
D)Loop electrosurgical excision procedure
E)Return to routine Pap screening
F)Serum CA-125
A)Endometrial biopsy
B)Hysterectomy
C)Hysteroscopy
D)Loop electrosurgical excision procedure
E)Return to routine Pap screening
F)Serum CA-125

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A 26-year-old nulligravid woman comes to the office to discuss treatment of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 3, which was revealed on a Pap test 4 weeks ago and confirmed by colposcopic biopsies. The patient has one dose remaining of catch-up human papillomavirus vaccination. She has smoked a pack of cigarettes daily for 10 years and does not use alcohol or illicit drugs. The patient recently married and is planning to have children in the next few years. She currently receives progesterone injections for contraception and takes no other medications. Her father is currently undergoing chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer. Risks and benefits of treatment options are discussed. Which of the following is the most likely complication of treatment for this patient?
A)Asherman syndrome
B)Cervical stenosis
C)Sexual dysfunction
D)Thromboembolism
E)Urinary tract injury
F)Urogenital fistula
A)Asherman syndrome
B)Cervical stenosis
C)Sexual dysfunction
D)Thromboembolism
E)Urinary tract injury
F)Urogenital fistula

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A 29-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to fever, chills, and lower abdominal pain. Two days ago, the patient underwent dilation and curettage for a 9-week missed abortion. After the procedure, she initially had light spotting, but the bleeding has become increasingly heavy and malodorous within the last few hours. She has also developed increasing abdominal pain and a fever unrelieved by acetaminophen. The patient has no chronic medical conditions and has had no other surgeries. Temperature is 39.4 C (103 F), blood pressure is 88/50 mm Hg, and pulse is 118/min. On speculum examination, the cervix is visibly 1 cm dilated and has purulent discharge at the os. The uterus is enlarged and has cervical motion tenderness. Transvaginal ultrasound shows a thickened endometrial stripe. Urine pregnancy test is positive. The patient is started on broad-spectrum intravenous antibiotics and undergoes a suction dilation and sharp curettage. This patient is at increased risk for which of the following conditions?
A)Development of intrauterine synechiae
B)Dysplastic changes to the cervical epithelium
C)Implantation of ectopic endometrial tissue
D)Infarction of the pituitary gland
E)Malignant transformation of trophoblastic tissue
A)Development of intrauterine synechiae
B)Dysplastic changes to the cervical epithelium
C)Implantation of ectopic endometrial tissue
D)Infarction of the pituitary gland
E)Malignant transformation of trophoblastic tissue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A 33-year-old woman, gravida 2 para 2, comes to the office for evaluation of abnormal uterine bleeding. Ten months ago, the patient had a spontaneous vaginal delivery complicated by a postpartum hemorrhage that required a blood transfusion and emergent suction curettage. Since the delivery, the patient has had increasingly irregular menses and has been amenorrheic for the past 3 months. She is bottle-feeding her infant and is not taking contraceptives. The patient has lost 13.6 kg (30 lb) since the delivery and is now below her prepregnancy weight. BMI is 22 kg/m2. Blood pressure is 110/60 mm Hg and pulse is 62/min. Visual fields are intact. The thyroid has no palpable masses. Cardiopulmonary examination is unremarkable. Pelvic examination shows a minimally rugated vagina; the uterus and cervix are small and nontender to palpation. Urine pregnancy test is negative. Serum TSH and prolactin levels are normal; FSH is elevated. Pelvic ultrasound shows a uterus with a thin endometrium and no adnexal masses. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's presentation?
A)Accelerated ovarian follicle depletion
B)Chronic anovulation from polycystic ovaries
C)Decreased hypothalamic GnRH secretion
D)Endometrial cavity adhesions and fibrosis
E)Infarction of the pituitary gland
A)Accelerated ovarian follicle depletion
B)Chronic anovulation from polycystic ovaries
C)Decreased hypothalamic GnRH secretion
D)Endometrial cavity adhesions and fibrosis
E)Infarction of the pituitary gland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A 48-year-old woman, gravida 3 para 3, comes to the office for a follow-up visit due to a history of stage I hormone receptor-positive lobular breast carcinoma. She was diagnosed using needle-guided biopsy after a screening mammogram revealed irregular densities. The patient's condition was treated with mastectomy, radiation therapy, and adjuvant chemotherapy. She also has a history of hypertension and hyperlipidemia, which are controlled with daily medications. The patient quit smoking after the cancer diagnosis and tries to exercise 3 times a week. She is prescribed tamoxifen therapy for an anticipated duration of at least 5 years. As a result of tamoxifen initiation, this patient is at greatest risk for developing which of the following?
A)Cervical dysplasia
B)Coronary artery disease
C)Endometrial atrophy
D)Hot flashes
E)Increased bruising
F)Ovarian cancer
A)Cervical dysplasia
B)Coronary artery disease
C)Endometrial atrophy
D)Hot flashes
E)Increased bruising
F)Ovarian cancer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A 15-year-old girl is brought to the office due to irregular menstrual periods. Menarche was at age 13, and since then her periods have been irregular with cycles varying from 3 to 8 weeks. The patient has no chronic medical issues, has never had surgery, and takes no medications. Her mother and older sister have polycystic ovary syndrome, and both take oral contraceptives. The patient has never been sexually active. Vital signs are normal. Physical examination shows normal hair distribution with Tanner V secondary sexual characteristics. Abdominal examination is normal. There is dark red blood noted at the cervical os with no active bleeding. Serum prolactin and TSH levels are normal. Administration of micronized oral progesterone results in withdrawal bleeding in 3 days. Pelvic ultrasound reveals normal ovaries and uterus. Which of the following is the most likely explanation of this patient's irregular menstrual periods?
A)Androgen excess
B)Estrogen deficiency
C)Excess LH secretion
D)Insufficient gonadotropin secretion
E)Intrauterine adhesions
A)Androgen excess
B)Estrogen deficiency
C)Excess LH secretion
D)Insufficient gonadotropin secretion
E)Intrauterine adhesions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following is the most appropriate course of action for this patient?
A)Broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy
B)Cryotherapy of the lesion
C)Incision and drainage
D)Observation and expectant management
E)Topical podophyllotoxin
F)Vulvar biopsy
A)Broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy
B)Cryotherapy of the lesion
C)Incision and drainage
D)Observation and expectant management
E)Topical podophyllotoxin
F)Vulvar biopsy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A 15-year-old girl is brought to the office by her mother due to concerns that her daughter has not had a menstrual period. The patient was born at 36 weeks gestation but has had no developmental delay. She is doing well in school and plays on the tennis team. The patient is healthy and takes no medications. She is not sexually active and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Family history is significant for a maternal aunt with primary infertility and a maternal grandmother with ovarian cancer. Height is 174 cm (5 ft 7 in), and weight is 63 kg (138.9 lb). Vital signs are normal. There is no acne or excessive hair growth. Breast development is sexual maturity rating (Tanner) stage 5. There is scant axillary and pubic hair. On pelvic examination, the external genitalia appear normal and speculum examination shows a blind vaginal pouch. The uterus, cervix, and ovaries are absent on bimanual examination. Karyotype analysis of this patient is most likely to show which of the following?
A)45,X
B)46,XX
C)46,XY
D)47,XXY
E)47,XYY
A)45,X
B)46,XX
C)46,XY
D)47,XXY
E)47,XYY

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A 22-year-old woman comes to the clinic for a routine examination. The patient is well and has no concerns. She is a gymnast, and her main activity is the balance beam. Three months ago, she sustained a vulvar contusion during a competition but otherwise she has been healthy. The patient is sexually active with 2 male partners and uses an intrauterine device for contraception. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Examination shows a mobile, soft, nontender, flesh-colored, 2-cm cystic mass at the 4 o'clock position at the base of the left labium majus. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
A)Bartholin duct cyst
B)Condylomata acuminata
C)Gartner duct cyst
D)Hematoma
E)Molluscum contagiosum
F)Primary syphilis
G)Skene gland cyst
A)Bartholin duct cyst
B)Condylomata acuminata
C)Gartner duct cyst
D)Hematoma
E)Molluscum contagiosum
F)Primary syphilis
G)Skene gland cyst

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A 15-year-old girl comes to the office due to a self-palpated breast mass. The patient discovered the breast lump 2 days ago while taking a shower and noted that it is mildly tender. Breast development began at age 9 and menses at age 11. The patient's menstrual cycles were irregular for the first year after menarche, but now they occur monthly. Her last menstrual period was a week ago. She has no chronic medical conditions and takes no medications. The patient's mother has a history of breast cancer diagnosed at age 38. BMI is at the 75th percentile. Vital signs are normal. Physical examination reveals a firm, smooth, mobile mass in the superior outer quadrant of the right breast. There is no palpable lymphadenopathy. The remainder of the physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Excisional biopsy of the mass
B)Fine-needle aspiration
C)FSH, LH, and estradiol levels
D)MRI of the breasts
E)Observation and repeat examination in 6 weeks
F)Reassurance and no additional evaluation indicated
A)Excisional biopsy of the mass
B)Fine-needle aspiration
C)FSH, LH, and estradiol levels
D)MRI of the breasts
E)Observation and repeat examination in 6 weeks
F)Reassurance and no additional evaluation indicated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A 53-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to heavy vaginal bleeding. The bleeding started yesterday as dark brown vaginal spotting and has increased to now soaking a thick menstrual pad every 2 hours. Menarche was at age 14. Menopause was at age 45 and the patient has had no prior episodes of vaginal bleeding since then. She smoked half a pack of cigarettes daily for 20 years; she does not use alcohol or illicit drugs. The patient's mother died of breast cancer at age 77. Blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg and pulse is 94/min. BMI is 37 kg/m2. The abdomen is obese, soft, and nontender, with no rebound or guarding. Pelvic examination shows dark red blood in the posterior vaginal vault and a 3-cm friable mass on the ectocervix and extending laterally. The lesion is actively bleeding. Hemoglobin is 10.2 g/dL. Pelvic ultrasonography reveals a thin endometrial stripe and no adnexal masses. Which of the following is a risk factor for this patient's condition?
A)Chronic anovulation
B)Delayed menarche
C)Early menopause
D)Endometriosis
E)Family history
F)Obesity
G)Tobacco use
H)Use of progestin intrauterine device
A)Chronic anovulation
B)Delayed menarche
C)Early menopause
D)Endometriosis
E)Family history
F)Obesity
G)Tobacco use
H)Use of progestin intrauterine device

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A 27-year-old woman, gravida 2 para 1, at 28 weeks gestation comes to the office for follow-up of an abnormal Pap test. She feels fetal movement, has no vaginal bleeding or contractions, and has had an uneventful pregnancy to date. The patient's previous pregnancy 5 years ago was uncomplicated. She has not had a previous abnormal Pap test, but the last test was performed during her prior pregnancy. The patient has no medical issues or previous surgeries. She takes a multivitamin and an iron supplement. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Blood pressure is 120/74 mm Hg and pulse is 82/min. Fetal heart tones are normal. Physical examination reveals a gravid, nontender uterus. The cervix is long, closed, firm, and posterior, and the fetal presenting part is high. The Pap test showed a high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Human papillomavirus co-testing
B)Immediate colposcopy
C)Loop electrosurgical excision procedure
D)Repeat Pap test postpartum
E)Trichloroacetic acid therapy
A)Human papillomavirus co-testing
B)Immediate colposcopy
C)Loop electrosurgical excision procedure
D)Repeat Pap test postpartum
E)Trichloroacetic acid therapy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A 38-year-old woman comes to the office due to breast pain. For the past 2 months, the patient has had intermittent bilateral breast pain that usually begins the week prior to menses and subsides on the first day of her menstrual cycle. The pain is primarily in the bilateral upper outer quadrants and does not radiate to the back or neck. Six months ago, the patient started a new job that requires long hours of sedentary work; she has gained 4.5 kg (10 lb). She has no chronic medical conditions and takes no daily medications. The patient has regular monthly menses, and her last menstrual period was a week ago. BMI is 26 kg/m2. Vital signs are normal. Breast examination shows bilateral, symmetric, large breasts with slight tenderness over the upper outer quadrants. There are no skin changes, nipple discharge, masses, or axillary lymphadenopathy. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Breast-reduction surgery
B)Breast ultrasound and mammography
C)Combined estrogen/progestin oral contraceptives
D)Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
E)Supportive bra and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
A)Breast-reduction surgery
B)Breast ultrasound and mammography
C)Combined estrogen/progestin oral contraceptives
D)Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
E)Supportive bra and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A 37-year-old woman comes to the office for evaluation of abnormal vaginal discharge. She noticed increased clear, watery vaginal discharge 4 months ago and now has intermenstrual bleeding. She reports no pruritus or dysuria. The patient is sexually active with a male partner and uses condoms for contraception. She has had 5 lifetime sexual partners. She has no medical problems or previous surgeries. The patient has a 24-pack-year smoking history but does not use alcohol or illicit drugs. Blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg and pulse is 88/min. On pelvic examination, a raised, ulcerative lesion is noted on the cervix, and clear discharge is present. The vaginal mucosa is not erythematous and has no lesions. The uterus is small, mobile, and anteverted, with no adnexal masses or cervical motion tenderness. No inguinal lymphadenopathy is present. Which of the following is the best next step in the diagnosis of this patient's condition?
A)Cervical biopsy
B)Herpes simplex viral culture
C)Nucleic acid amplification testing for gonorrhea and chlamydia
D)Pelvic ultrasonography
E)Wet mount of cervical mucus
A)Cervical biopsy
B)Herpes simplex viral culture
C)Nucleic acid amplification testing for gonorrhea and chlamydia
D)Pelvic ultrasonography
E)Wet mount of cervical mucus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A 39-year-old woman, gravida 2 para 2, comes to the office for evaluation of increasing malaise. The patient has been exclusively breastfeeding her 3-month-old infant. For the past week, she has been taking dicloxacillin due to redness and pain in her right breast. Over the past few days, the patient has developed increasing malaise and a low appetite. She has had no nausea, diarrhea, or headache. The patient has no chronic medical conditions and takes no other daily medications. Her mother had breast cancer at age 54. Temperature is 37.7 C (99.9 F), blood pressure is 124/68 mm Hg, and pulse is 98/min. Both breasts have moderate engorgement. There is linear nipple cracking bilaterally. The right breast has tender nodularity, but the erythema has improved since last week's examination. The remainder of the physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Add fluconazole therapy
B)Add topical corticosteroids
C)Change antibiotics to cephalexin
D)Order breast ultrasound
E)Perform full-thickness skin biopsy
A)Add fluconazole therapy
B)Add topical corticosteroids
C)Change antibiotics to cephalexin
D)Order breast ultrasound
E)Perform full-thickness skin biopsy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A 60-year-old woman comes to the office for a breast cancer follow-up visit. The patient recently underwent a right mastectomy for a node-negative, estrogen- and progesterone-receptor-positive tumor. She was started on an aromatase inhibitor for adjuvant therapy; however, the medication was discontinued due to severe fatigue and poor sleep. As a result, she is scheduled to begin a 5-year course of adjuvant therapy with tamoxifen. The patient has no other chronic medical conditions and her only medication is a daily multivitamin. Her last menstrual period was 5 years ago. The patient's father had a myocardial infarction at age 65; family history is otherwise noncontributory. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Vital signs are stable. BMI is 21 kg/m2. The patient has many concerns about tamoxifen therapy and asks about potential side effects. Which of the following is the patient at greatest risk for developing due to tamoxifen therapy?
A)Decreased bone density
B)Dysplasia of the cervical transformation zone
C)Ectopic endometrial tissue in the myometrium
D)Hyperplasia of the endometrium
E)Intimal thickening of the coronary arteries
A)Decreased bone density
B)Dysplasia of the cervical transformation zone
C)Ectopic endometrial tissue in the myometrium
D)Hyperplasia of the endometrium
E)Intimal thickening of the coronary arteries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A 32-year-old woman comes to the office for evaluation of absent menses. The patient had a vaginal delivery 4 months ago, and she has not had a menstrual period since delivery. Her postpartum course was complicated by a postpartum hemorrhage, requiring blood transfusion and emergency suction and sharp curettage. At her postpartum visit 2 months ago, the patient was started on combination oral contraceptives and has had no vaginal bleeding or spotting during her week of placebo pills. Prior to this pregnancy, she had regular, monthly menstrual cycles with 3-4 days of moderate bleeding. The patient has had increased fatigue since returning to work and is bottle-feeding. She has no headaches, galactorrhea, or hot flushes. Vital signs are normal. BMI is 31 kg/m2. Pelvic examination shows clear vaginal discharge throughout the vault and a well-rugated vagina. The uterus is small and anteverted, and there are bilateral small, nontender ovaries. Urine pregnancy test is negative. FSH and TSH levels are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A)Asherman syndrome
B)Gestational trophoblastic disease
C)Polycystic ovary syndrome
D)Postpartum thyroiditis
E)Primary ovarian insufficiency
F)Sheehan syndrome
A)Asherman syndrome
B)Gestational trophoblastic disease
C)Polycystic ovary syndrome
D)Postpartum thyroiditis
E)Primary ovarian insufficiency
F)Sheehan syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A 16-year-old girl comes to the office due to not having started her menstrual period. The patient says that all her friends have started their periods and she is concerned that she is "behind." She has had no nipple discharge or change in vision or weight. The patient has no chronic medical conditions and takes no daily medications. She recently became sexually active and uses condoms for contraception. Height is at the 70th percentile and weight is at the 40th percentile for age. Vital signs are normal. On physical examination, there is sexual maturity rating (Tanner) stage 4 breast development with minimal axillary and pubic hair. The external genitalia are normal and the vagina is 3 cm in length; the cervix is not visible. No uterus, cervix, or ovaries are palpated on bimanual examination. Laboratory studies include a negative pregnancy test and a testosterone level of 400 ng/dL (normal: 15-75 [female]; 300-1,000 [male]). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A)5-alpha-reductase deficiency
B)Androgen insensitivity syndrome
C)Müllerian agenesis
D)Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor
E)Transverse vaginal septum
F)Turner syndrome
A)5-alpha-reductase deficiency
B)Androgen insensitivity syndrome
C)Müllerian agenesis
D)Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor
E)Transverse vaginal septum
F)Turner syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Six weeks after a spontaneous, uncomplicated term vaginal delivery, a 32-year-old woman, gravida 1 para 1, comes to the emergency department due to left breast pain. The patient first noticed pain and redness on her left breast a week ago. She has continued to breast feed her infant from the unaffected breast. The patient has no chronic medical conditions and her only medication is a daily multivitamin. Temperature is 38.3 C (101 F). Physical examination shows an area of erythema extending from the areola to the lateral edge of the left breast and surrounding a well-circumscribed, 4-cm area of fluctuance. Axillary lymphadenopathy is present. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Breast binding and acetaminophen
B)Core needle and skin punch biopsies
C)Ice packs and use of a supportive bra
D)Needle aspiration and antibiotics
E)Warm compresses and massage
A)Breast binding and acetaminophen
B)Core needle and skin punch biopsies
C)Ice packs and use of a supportive bra
D)Needle aspiration and antibiotics
E)Warm compresses and massage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A 41-year-old woman comes to the office for evaluation of nipple discharge. The patient has had 2 episodes of blood-tinged discharge from the right breast over the last 2 weeks. She has no associated breast pain, palpable masses, or trauma. On review of systems, the patient has had a slightly increased number of headaches; she takes ibuprofen at least twice a week for them. She has no chronic medical conditions. The patient takes combined estrogen/progestin oral contraceptives, and her last menstrual period was 2 weeks ago. There is no family history of breast, endometrial, or colorectal cancer. Vital signs are normal. Examination of the right breast shows no palpable masses, skin changes, or lymph node enlargement. There is scant discharge, which is guaiac positive, from the right nipple. Examination of the left breast is normal. Mammography is normal. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A)Breast ultrasound
B)Discontinuation of combined oral contraceptives
C)Empiric antibiotic therapy
D)MRI of the pituitary
E)Reassurance and routine mammography only
A)Breast ultrasound
B)Discontinuation of combined oral contraceptives
C)Empiric antibiotic therapy
D)MRI of the pituitary
E)Reassurance and routine mammography only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 469 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



