Deck 2: Certified Quality Auditor
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/95
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Certified Quality Auditor
1
Auditor independence includes freedom from which of the following?
A) Bias II. Conflict of interest III. External influences IV. Previous exposure to the area
B) I and II only
C) II and IV only
D) I, II, and III only
E) II, III and IV only
A) Bias II. Conflict of interest III. External influences IV. Previous exposure to the area
B) I and II only
C) II and IV only
D) I, II, and III only
E) II, III and IV only
C
2
An auditor finds deficiencies in the order entry, purchasing, product test, and shipping functions of a potential supplier. Which of them should have the highest priority in the audit report?
A) Order entry
B) Product test
C) Purchasing
D) Shipping
A) Order entry
B) Product test
C) Purchasing
D) Shipping
B
3
After an external audit, the auditee may be asked to evaluate which of the following auditor skills or elements of the audit?
A) Interviewing, interaction, accuracy of the audit report
B) Audit scheduling, auditor training records, observing an audit
C) Communication, listening, checklist preparation
D) Clarity of past audit reports, number of findings, lack of bias
A) Interviewing, interaction, accuracy of the audit report
B) Audit scheduling, auditor training records, observing an audit
C) Communication, listening, checklist preparation
D) Clarity of past audit reports, number of findings, lack of bias
A
4
Audits are conducted against a performance standard to ensure which of the following?
A) Meaningful measurements II. Objectively evaluated performance III. Perceptive observations
B) I only
C) I and II only
D) II and III only
E) I, II, and III
A) Meaningful measurements II. Objectively evaluated performance III. Perceptive observations
B) I only
C) I and II only
D) II and III only
E) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following requests by an auditor is likely to obtain the most objective evidence for verification?
A) "What kind of information do you receive?"
B) "Who provides the information to you?"
C) "Describe how you receive information."
D) "Show me the information you have received."
A) "What kind of information do you receive?"
B) "Who provides the information to you?"
C) "Describe how you receive information."
D) "Show me the information you have received."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following qualifications would contribute most to an auditor being able to function effectively in various industrial or service disciplines?
A) Familiarity with technical standards and regulations
B) A college degree in a specific technical area
C) A working knowledge of typical corporate organizational structures
D) Extensive background in calibration and metrology techniques
A) Familiarity with technical standards and regulations
B) A college degree in a specific technical area
C) A working knowledge of typical corporate organizational structures
D) Extensive background in calibration and metrology techniques

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
An auditor is performing an audit of a drilling machine that produces 100 pieces a day and that is showing improved quality. Which of the following rules should be used for determining the proper sample size for a fixed level of confidence?
A) The moving average should be calculated.
B) The sample size should be decreased as the quality improves.
C) The AQL of the raw material should be used.
D) A 10% sample size should be used, regardless of the change in quality.
A) The moving average should be calculated.
B) The sample size should be decreased as the quality improves.
C) The AQL of the raw material should be used.
D) A 10% sample size should be used, regardless of the change in quality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Generally, which of the following is the most meaningful way to trace a finished product?
A) Forward from starting with the acquisition of raw materials
B) Forward from the first production activity
C) Backward from the start of the assembly process
D) Backward from the end point
A) Forward from starting with the acquisition of raw materials
B) Forward from the first production activity
C) Backward from the start of the assembly process
D) Backward from the end point

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
While performing an internal audit, an auditor notices that an operator on one shift skips part of the documented procedure. In this situation, the auditor should do which of the following?
A) Make a note on the checklist and initial it.
B) Report it to the operator's supervisor or manager.
C) Question the operator about the observation.
D) Ask another operator to evaluate the situation.
A) Make a note on the checklist and initial it.
B) Report it to the operator's supervisor or manager.
C) Question the operator about the observation.
D) Ask another operator to evaluate the situation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The objective evidence supporting an audit observation must be
A) recorded on the working papers
B) verified by the escort
C) mentioned to the auditee
D) written as a nonconformance
A) recorded on the working papers
B) verified by the escort
C) mentioned to the auditee
D) written as a nonconformance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A quality audit contributes to improvement of the quality of a company's products and services by
A) identifying under-performers
B) identifying the need for corrective action
C) suggesting ways to improve performance
D) improving customer satisfaction
A) identifying under-performers
B) identifying the need for corrective action
C) suggesting ways to improve performance
D) improving customer satisfaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following types of tools or techniques is considered qualitative?
A) Histograms
B) Frequency distributions
C) Pareto charts
D) Process observations
A) Histograms
B) Frequency distributions
C) Pareto charts
D) Process observations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A root cause analysis can best be described as a process that is used to
A) evaluate corrective action plans
B) determine the basic reason for an undesirable condition
C) identify the symptoms of an undesirable condition
D) differentiate between major and minor problems
A) evaluate corrective action plans
B) determine the basic reason for an undesirable condition
C) identify the symptoms of an undesirable condition
D) differentiate between major and minor problems

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An audit report should contain which of the following?
A) Audit findings
B) Root cause analysis
C) Corrective action
D) Re-audit schedule
A) Audit findings
B) Root cause analysis
C) Corrective action
D) Re-audit schedule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
To determine whether a finding is a minor, isolated incident or a serious, chronic problem, an auditor should consult with the
A) auditee's quality assurance inspector
B) auditee's department manager
C) audit team
D) client
A) auditee's quality assurance inspector
B) auditee's department manager
C) audit team
D) client

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When a proposed corrective action plan is judged unacceptable, an auditor should do which of the following?
A) Revise the submitted plan on the basis of the auditor's knowledge and technical expertise.
B) Notify the auditee and request that a new plan be submitted by the next level of management.
C) Discuss the plan's deficiencies with the auditee and request a revised plan.
D) Suggest that the auditee benchmark the deficient area and then rewrite the plan.
A) Revise the submitted plan on the basis of the auditor's knowledge and technical expertise.
B) Notify the auditee and request that a new plan be submitted by the next level of management.
C) Discuss the plan's deficiencies with the auditee and request a revised plan.
D) Suggest that the auditee benchmark the deficient area and then rewrite the plan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which two of the following conditions must be met in order to infer statistical significance about the results of an audit sample?
A) The population must be homogeneous. II. The sample size must be greater than 10. III. The sample must be random. IV. The sample must be taken from multiple locations.
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) III and IV
A) The population must be homogeneous. II. The sample size must be greater than 10. III. The sample must be random. IV. The sample must be taken from multiple locations.
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) III and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Who makes the final determination regarding the distribution of the audit report?
A) The lead auditor
B) The audit group manager
C) The auditee
D) The client
A) The lead auditor
B) The audit group manager
C) The auditee
D) The client

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The confidence level in a sampling plan is defined as the
A) degree of uncertainty that the selected sample contains at least one example of any errors that are present
B) degree of certainty that the selected sample contains at least one example of any errors that are present
C) lowest performance level that can be considered acceptable for the function being audited
D) maximum error rate that can be considered acceptable for the function being audited
A) degree of uncertainty that the selected sample contains at least one example of any errors that are present
B) degree of certainty that the selected sample contains at least one example of any errors that are present
C) lowest performance level that can be considered acceptable for the function being audited
D) maximum error rate that can be considered acceptable for the function being audited

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following would NOT normally be used as a major category in a cause and effect diagram?
A) Modifications
B) Methods
C) Materials
D) Machines
A) Modifications
B) Methods
C) Materials
D) Machines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Audit team members are responsible for which two of the following?
A) Initiating the audit II. Remaining within the scope of the audit III. Compiling and analyzing evidence IV. Recommending specific corrective actions
B) I and III
C) I and IV
D) II and III
E) II and IV
A) Initiating the audit II. Remaining within the scope of the audit III. Compiling and analyzing evidence IV. Recommending specific corrective actions
B) I and III
C) I and IV
D) II and III
E) II and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
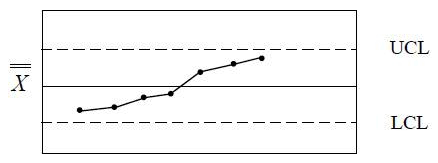 The process information shown in the graph above is indicative of a
The process information shown in the graph above is indicative of aA) cycle
B) run
C) trend
D) shift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
"What are your defined responsibilities in the calibration laboratory?" The question above is an example of what type of questioning technique?
A) Open-ended
B) Close-ended
C) Leading
D) Discovery
A) Open-ended
B) Close-ended
C) Leading
D) Discovery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following indicates that a quality system is effective?
A) The required system is in place and continuous improvement is evident.
B) An audit was conducted and no non-conformances were found.
C) An audit report states that the intent of the standard is being met.
D) No corrective action requests have been issued for a specified period of time.
A) The required system is in place and continuous improvement is evident.
B) An audit was conducted and no non-conformances were found.
C) An audit report states that the intent of the standard is being met.
D) No corrective action requests have been issued for a specified period of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following behaviors is LEAST important for an auditor to exhibit?
A) Remaining calm throughout the audit
B) Displaying honesty and forthrightness
C) Adhering to the original audit plan
D) Working in a planned and systematic manner
A) Remaining calm throughout the audit
B) Displaying honesty and forthrightness
C) Adhering to the original audit plan
D) Working in a planned and systematic manner

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is the most fundamental role of the audit function?
A) Reporting identified problems to the supervisor of the audited area
B) Monitoring performance of the organization and determining corrective action for substandard performance
C) Reporting findings to upper management to ensure that proper corrective action is taken
D) Verifying the effectiveness of the organization's quality system in preventing substandard performance
A) Reporting identified problems to the supervisor of the audited area
B) Monitoring performance of the organization and determining corrective action for substandard performance
C) Reporting findings to upper management to ensure that proper corrective action is taken
D) Verifying the effectiveness of the organization's quality system in preventing substandard performance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
During a supplier audit, all of the following documentation can be reviewed EXCEPT
A) reports of internal audits performed by the supplier
B) information concerning the company's parts inventory
C) quality records for a product made for another customer
D) operating or working instructions
A) reports of internal audits performed by the supplier
B) information concerning the company's parts inventory
C) quality records for a product made for another customer
D) operating or working instructions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
For third-party audits, which two of the following factors should be considered by the auditor when agreeing to the amount of time needed to complete corrective action?
A) The resources available to the auditor for determining when follow-up can occur II. The resources available to the auditee to enact the corrective action III. The auditee's experience in project evaluation techniques IV. The number of findings recorded during the audit
B) I and III
C) I and IV
D) II and III
E) II and IV
A) The resources available to the auditor for determining when follow-up can occur II. The resources available to the auditee to enact the corrective action III. The auditee's experience in project evaluation techniques IV. The number of findings recorded during the audit
B) I and III
C) I and IV
D) II and III
E) II and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An audit schedule is an integral part of which of the following phases of the auditing process?
A) Initiation
B) Preparation
C) Closing
D) Reporting
A) Initiation
B) Preparation
C) Closing
D) Reporting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following best describes a frequency distribution?
A) A graph for presenting data along a scale of reference and the number of times each item occurs
B) A time-ordered chart of subgroup averages and control limits
C) A plot of the probability of accepting a hypothesis when it is actually false
D) A graph indicating the difference between an actual value and its predicted value
A) A graph for presenting data along a scale of reference and the number of times each item occurs
B) A time-ordered chart of subgroup averages and control limits
C) A plot of the probability of accepting a hypothesis when it is actually false
D) A graph indicating the difference between an actual value and its predicted value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
An auditee is likely to be most threatened by an auditor's use of which of the following interviewing techniques?
A) Paraphrasing an auditee's response while writing it down
B) Being silent while waiting for an auditee to respond to a question
C) Underlining key facts when recording an auditee's response
D) Using a tape recorder to record an auditee's response
A) Paraphrasing an auditee's response while writing it down
B) Being silent while waiting for an auditee to respond to a question
C) Underlining key facts when recording an auditee's response
D) Using a tape recorder to record an auditee's response

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The most important item to check when auditing against a specification is the
A) list of documents within the specification
B) copy of the previous revision of the specification
C) document control procedure
D) revision level of the specification
A) list of documents within the specification
B) copy of the previous revision of the specification
C) document control procedure
D) revision level of the specification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An auditee who objects to any part of an audit plan should first make those objections known to the
A) lead auditor
B) audit team members
C) audit program manager
D) client
A) lead auditor
B) audit team members
C) audit program manager
D) client

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Who is responsible for preparing the corrective action plan?
A) The auditor
B) The auditee
C) The registrar
D) The audit manager
A) The auditor
B) The auditee
C) The registrar
D) The audit manager

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The best way to communicate audit results to upper management would be to
A) provide a list of findings of noncompliance and supporting objective evidence
B) present a list of all items of nonconformance that require corrective action
C) present a report of the performance against the audit standard of all areas included in the audit scope
D) present an evaluation of overall quality performance and provide an executive summary in the formal report
A) provide a list of findings of noncompliance and supporting objective evidence
B) present a list of all items of nonconformance that require corrective action
C) present a report of the performance against the audit standard of all areas included in the audit scope
D) present an evaluation of overall quality performance and provide an executive summary in the formal report

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An auditee has responded to all requests for corrective action in a timely manner. Which of the following is the next step for the auditor?
A) Close all those findings in which the response is accompanied by adequate objective evidence.
B) Evaluate the adequacy of the responses.
C) Schedule a follow-up audit to verify corrective action.
D) Schedule a follow-up audit for critical items and schedule verification for other routine items at the next scheduled audit.
A) Close all those findings in which the response is accompanied by adequate objective evidence.
B) Evaluate the adequacy of the responses.
C) Schedule a follow-up audit to verify corrective action.
D) Schedule a follow-up audit for critical items and schedule verification for other routine items at the next scheduled audit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following authorities initially determines whether a third-party audit should be conducted?
A) Client
B) Lead auditor
C) Auditee
D) Audit team
A) Client
B) Lead auditor
C) Auditee
D) Audit team

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An auditee's procedures require that all design drawings be dated and signed. During a design review, an auditor notices that several drawings are signed, but not dated. The missing dates are examples of what kind of data?
A) Quantitative
B) Measured
C) Variable
D) Qualitative
A) Quantitative
B) Measured
C) Variable
D) Qualitative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In quality auditing, a finding is defined as
A) an observation of common behaviors
B) an item of objective evidence found during an audit
C) a fundamental deficiency that can lead to nonconformance
D) a conclusion of importance based on evidence
A) an observation of common behaviors
B) an item of objective evidence found during an audit
C) a fundamental deficiency that can lead to nonconformance
D) a conclusion of importance based on evidence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
An internal audit schedule should be prioritized on the basis of all of the following criteria EXCEPT the
A) cost of the activities
B) risk of the activities
C) size of the auditee's department
D) management's requests
A) cost of the activities
B) risk of the activities
C) size of the auditee's department
D) management's requests

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
During an audit, the client learns that the auditor has recently completed a quality system audit of a major competitor. The client then questions the auditor about the competitor's audit results. The best action for the auditor to take is to
A) discuss the results of the audit with the client, only if the competitor agrees
B) go offline with the client, explain that the question is unethical, and that if the client persists, additional action by the auditor will be taken
C) explain to the client that it would be inappropriate to discuss the results of that audit
D) obtain permission from the competitor to use the results of the audit as examples for future clients, provided that the examples are not specific to business affairs or technical processes
A) discuss the results of the audit with the client, only if the competitor agrees
B) go offline with the client, explain that the question is unethical, and that if the client persists, additional action by the auditor will be taken
C) explain to the client that it would be inappropriate to discuss the results of that audit
D) obtain permission from the competitor to use the results of the audit as examples for future clients, provided that the examples are not specific to business affairs or technical processes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The following portion of the test includes several Case Studies. Each Case Study includes introductory information about a specific company or audit situation, followed immediately by a set of questions related to the situation described and various audit-related documents, identified by company name. All of the audit-related documents for these Case Studies are presented in a separate booklet labeled: CONFIDENTIAL Audit Documents These documents were drawn from actual companies and are designed to be examples of genuine audit materials. Their format and contents have not been altered, and they are intended to represent working documents from everyday situations. Although the documents for the Case Studies are presented separately, the test will be scored as a whole, on a total of 150 questions. You may go back and check your work on any part of the examination until time is called at the end of the testing period. Two auditors are conducting an internal audit of the Quality Electronics and Elements Co. (QEE) system procedures. During the first day of the audit, the following observations were made. An outbound carton with obvious damage was examined by the auditor on the shipping dock. A shipment of six (6) boxes to Allied Supply was returned because the customer-required certifications did not accompany the product. Unsigned product verification documents were found on stored products. Of three (3) cartons found in the accepted materials station, only two of the cartons had labels indicating their contents. When the auditor pointed this out, a customer service representative immediately affixed the proper label to the one unlabeled carton. The auditor also found that "Accepted Material Traveler Cards" were not attached to any of the cartons in the accepted materials station. Who is responsible for evaluating the adequacy of QEE's handling and storage practices?
A) The shipping manager
B) Individual shipping and receiving clerks
C) The quality assurance manager
D) The customer service department
A) The shipping manager
B) Individual shipping and receiving clerks
C) The quality assurance manager
D) The customer service department

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The main function of an audit checklist is to
A) identify the specific products to be examined
B) serve as a guide for members of the audit team
C) save time by auditing only the items listed
D) expedite the preparation of the final audit report
A) identify the specific products to be examined
B) serve as a guide for members of the audit team
C) save time by auditing only the items listed
D) expedite the preparation of the final audit report

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following best describes quality control?
A) The overall intentions and directions of an organization with regard to quality, as formally expressed by top management
B) The activities that establish the objectives and requirements for quality and for the application of quality system elements
C) The organizational structure and the procedures, processes, and resources needed to implement quality management
D) The operational techniques and activities that are used to fulfill requirements for quality
A) The overall intentions and directions of an organization with regard to quality, as formally expressed by top management
B) The activities that establish the objectives and requirements for quality and for the application of quality system elements
C) The organizational structure and the procedures, processes, and resources needed to implement quality management
D) The operational techniques and activities that are used to fulfill requirements for quality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is a benefit of performing a systems audit of a current supplier?
A) Identifying the supplier's potential capability
B) Assuring the supplier's capability
C) Determining whether the company should do business with the supplier
D) Evaluating continuing conformance to quality standards
A) Identifying the supplier's potential capability
B) Assuring the supplier's capability
C) Determining whether the company should do business with the supplier
D) Evaluating continuing conformance to quality standards

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The following portion of the test includes several Case Studies. Each Case Study includes introductory information about a specific company or audit situation, followed immediately by a set of questions related to the situation described and various audit-related documents, identified by company name. All of the audit-related documents for these Case Studies are presented in a separate booklet labeled: CONFIDENTIAL Audit Documents These documents were drawn from actual companies and are designed to be examples of genuine audit materials. Their format and contents have not been altered, and they are intended to represent working documents from everyday situations. Although the documents for the Case Studies are presented separately, the test will be scored as a whole, on a total of 150 questions. You may go back and check your work on any part of the examination until time is called at the end of the testing period. Two auditors are conducting an internal audit of the Quality Electronics and Elements Co. (QEE) system procedures. During the first day of the audit, the following observations were made. An outbound carton with obvious damage was examined by the auditor on the shipping dock. A shipment of six (6) boxes to Allied Supply was returned because the customer-required certifications did not accompany the product. Unsigned product verification documents were found on stored products. Of three (3) cartons found in the accepted materials station, only two of the cartons had labels indicating their contents. When the auditor pointed this out, a customer service representative immediately affixed the proper label to the one unlabeled carton. The auditor also found that "Accepted Material Traveler Cards" were not attached to any of the cartons in the accepted materials station. If the audit also revealed that customer-required certifications were not included with a shipment, a finding should be written against which department?
A) Quality Assurance
B) Purchasing
C) Production Control
D) Shipping
A) Quality Assurance
B) Purchasing
C) Production Control
D) Shipping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Within most organizations, the responsibility for planning and carrying out a programmed series of quality system audits rests with the
A) quality systems engineering function
B) audit program management function
C) financial audits department
D) planning and scheduling department
A) quality systems engineering function
B) audit program management function
C) financial audits department
D) planning and scheduling department

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Managing the quality audit process includes ensuring that which of the following audit functions occur?
A) Preparing and issuing the annual audit schedule II. Issuing audit reports in a timely manner III. Identifying appropriate corrective actions IV. Assessing the effectiveness of the quality audit process
B) I and II only
C) I and III only
D) II and IV only
E) I, II, and IV only
A) Preparing and issuing the annual audit schedule II. Issuing audit reports in a timely manner III. Identifying appropriate corrective actions IV. Assessing the effectiveness of the quality audit process
B) I and II only
C) I and III only
D) II and IV only
E) I, II, and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Auditors who audit outside their own country should be familiar with
A) their own biases
B) the auditee's attitude
C) industry practices at the audit site
D) the local customs at the audit site
A) their own biases
B) the auditee's attitude
C) industry practices at the audit site
D) the local customs at the audit site

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
During an audit interview, the auditee is not providing needed information about the process for which the auditee has sole responsibility. In an effort to minimize any miscommunication, the auditor should
A) continue to repeat the questions until the auditee answers
B) explain to the interviewee the consequences of being uncooperative
C) terminate the interview and skip that section of the plan
D) request that the escort clarify the questions to the auditee
A) continue to repeat the questions until the auditee answers
B) explain to the interviewee the consequences of being uncooperative
C) terminate the interview and skip that section of the plan
D) request that the escort clarify the questions to the auditee

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is an example of a short-term corrective action?
A) Improving process capability
B) Analyzing a field failure
C) Obtaining missing signatures on a purchase order
D) Correcting the problem of obsolete drawings
A) Improving process capability
B) Analyzing a field failure
C) Obtaining missing signatures on a purchase order
D) Correcting the problem of obsolete drawings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following represents a sound time-management technique?
A) Scheduling interviews simultaneously at two different facilities
B) Constantly revising the audit schedule to accommodate follow-up questions
C) Anticipating needs and making them known to the auditee in advance
D) Determining the detailed audit schedule at the audit opening meeting
A) Scheduling interviews simultaneously at two different facilities
B) Constantly revising the audit schedule to accommodate follow-up questions
C) Anticipating needs and making them known to the auditee in advance
D) Determining the detailed audit schedule at the audit opening meeting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The authority for auditors to perform external second-party audits is provided by
A) a company's quality assurance manual
B) the quality standard being audited against
C) the established audit procedures
D) the purchase contract
A) a company's quality assurance manual
B) the quality standard being audited against
C) the established audit procedures
D) the purchase contract

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The following portion of the test includes several Case Studies. Each Case Study includes introductory information about a specific company or audit situation, followed immediately by a set of questions related to the situation described and various audit-related documents, identified by company name. All of the audit-related documents for these Case Studies are presented in a separate booklet labeled: CONFIDENTIAL Audit Documents These documents were drawn from actual companies and are designed to be examples of genuine audit materials. Their format and contents have not been altered, and they are intended to represent working documents from everyday situations. Although the documents for the Case Studies are presented separately, the test will be scored as a whole, on a total of 150 questions. You may go back and check your work on any part of the examination until time is called at the end of the testing period. Two auditors are conducting an internal audit of the Quality Electronics and Elements Co. (QEE) system procedures. During the first day of the audit, the following observations were made. An outbound carton with obvious damage was examined by the auditor on the shipping dock. A shipment of six (6) boxes to Allied Supply was returned because the customer-required certifications did not accompany the product. Unsigned product verification documents were found on stored products. Of three (3) cartons found in the accepted materials station, only two of the cartons had labels indicating their contents. When the auditor pointed this out, a customer service representative immediately affixed the proper label to the one unlabeled carton. The auditor also found that "Accepted Material Traveler Cards" were not attached to any of the cartons in the accepted materials station. Which department is responsible for determining whether an outbound product has been damaged in handling or storage?
A) Inventory Control
B) Quality Assurance
C) Shipping
D) Engineering
A) Inventory Control
B) Quality Assurance
C) Shipping
D) Engineering

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The most important objective in the development of a supplier evaluation system is to reduce
A) the number of suppliers
B) the number of audit hours
C) inspection at the customer site
D) inspection at the supplier site
A) the number of suppliers
B) the number of audit hours
C) inspection at the customer site
D) inspection at the supplier site

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
During the course of a 10-day system audit, when should the auditee be briefed?
A) Every day
B) Every other day
C) As requested by the auditee
D) At the beginning and the end of the audit
A) Every day
B) Every other day
C) As requested by the auditee
D) At the beginning and the end of the audit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The following portion of the test includes several Case Studies. Each Case Study includes introductory information about a specific company or audit situation, followed immediately by a set of questions related to the situation described and various audit-related documents, identified by company name. All of the audit-related documents for these Case Studies are presented in a separate booklet labeled: CONFIDENTIAL Audit Documents These documents were drawn from actual companies and are designed to be examples of genuine audit materials. Their format and contents have not been altered, and they are intended to represent working documents from everyday situations. Although the documents for the Case Studies are presented separately, the test will be scored as a whole, on a total of 150 questions. You may go back and check your work on any part of the examination until time is called at the end of the testing period. Two auditors are conducting an internal audit of the Quality Electronics and Elements Co. (QEE) system procedures. During the first day of the audit, the following observations were made. An outbound carton with obvious damage was examined by the auditor on the shipping dock. A shipment of six (6) boxes to Allied Supply was returned because the customer-required certifications did not accompany the product. Unsigned product verification documents were found on stored products. Of three (3) cartons found in the accepted materials station, only two of the cartons had labels indicating their contents. When the auditor pointed this out, a customer service representative immediately affixed the proper label to the one unlabeled carton. The auditor also found that "Accepted Material Traveler Cards" were not attached to any of the cartons in the accepted materials station. The auditor's finding on products without "Accepted Material Traveler Cards" should be written against which of the following departments?
A) Production Control
B) Quality Assurance
C) Shipping
D) Engineering
A) Production Control
B) Quality Assurance
C) Shipping
D) Engineering

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
During the closing meeting, the lead auditor should do which of the following?
A) Accept the presentation of objective evidence.
B) Review the auditor's qualifications.
C) Perform a causal analysis with the auditee.
D) Present a summary of audit results.
A) Accept the presentation of objective evidence.
B) Review the auditor's qualifications.
C) Perform a causal analysis with the auditee.
D) Present a summary of audit results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Management can best ensure support for the audit function from other departments by
A) continually evaluating the audit results
B) reviewing audit follow-up activities and ensuring that corrective action requests are closed in a timely manner
C) hiring personnel who have knowledge of quality procedures and by providing continuing education
D) emphasizing the importance and usefulness of audits to the organization
A) continually evaluating the audit results
B) reviewing audit follow-up activities and ensuring that corrective action requests are closed in a timely manner
C) hiring personnel who have knowledge of quality procedures and by providing continuing education
D) emphasizing the importance and usefulness of audits to the organization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
During an audit, the best way to determine whether an audited process is consistent with the requirements of the relevant written procedure is by
A) doing a statistical analysis of historical data
B) physically observing the actual practice
C) questioning the personnel who perform the procedure
D) evaluating anecdotal evidence
A) doing a statistical analysis of historical data
B) physically observing the actual practice
C) questioning the personnel who perform the procedure
D) evaluating anecdotal evidence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The fraction of nonconforming products is plotted on which of the following types of control charts?
A) p chart
B) u chart
C) np chart
D) c chart
A) p chart
B) u chart
C) np chart
D) c chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
During the opening meeting, it is the auditee's responsibility to
A) prepare the meeting agenda
B) set the audit schedule
C) state the audit purpose and scope
D) identify safety requirements
A) prepare the meeting agenda
B) set the audit schedule
C) state the audit purpose and scope
D) identify safety requirements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If the audit escort for one area is repeatedly late or unavailable, what is the best option open to the auditor?
A) Notify the auditee management of the consequences created by the delays.
B) Narrow the scope of the audit to accommodate the delays.
C) Proceed without the escort.
D) Assess system effectiveness using objective evidence from other areas.
A) Notify the auditee management of the consequences created by the delays.
B) Narrow the scope of the audit to accommodate the delays.
C) Proceed without the escort.
D) Assess system effectiveness using objective evidence from other areas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Auditors can use flowcharts in their work in order to
A) analyze the causal factors of process dispersion
B) understand the overall process or system being audited
C) distinguish variations in a process over time
D) determine process capability and uniformity
A) analyze the causal factors of process dispersion
B) understand the overall process or system being audited
C) distinguish variations in a process over time
D) determine process capability and uniformity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
When is it acceptable to grant an extension of the time frame for a corrective action?
A) When the auditor cannot perform the follow-up audit as scheduled
B) When the auditee determines that the proposed corrective action is not cost-effective
C) When the corrective action plan requires more time than originally anticipated
D) When there has been a change in operators who perform the task
A) When the auditor cannot perform the follow-up audit as scheduled
B) When the auditee determines that the proposed corrective action is not cost-effective
C) When the corrective action plan requires more time than originally anticipated
D) When there has been a change in operators who perform the task

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
An auditee responds to a corrective action request by stating that the problem has never occurred before and is "not the norm for our operation." Which of the following is the most appropriate action for the lead auditor?
A) Note that the deficiency is the result of a random occurrence.
B) Draft a response explicitly requesting a more concise root-cause analysis.
C) Confer with the audit client to assess the appropriateness of the response.
D) Schedule a follow-up audit immediately.
A) Note that the deficiency is the result of a random occurrence.
B) Draft a response explicitly requesting a more concise root-cause analysis.
C) Confer with the audit client to assess the appropriateness of the response.
D) Schedule a follow-up audit immediately.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A root cause of a nonconformance is defined as a problem that
A) is discovered by conducting designed experiments
B) is established through the use of fishbone diagrams
C) must be reviewed by the material review board
D) must be corrected in order to prevent a recurrence
A) is discovered by conducting designed experiments
B) is established through the use of fishbone diagrams
C) must be reviewed by the material review board
D) must be corrected in order to prevent a recurrence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following is an audit reporting technique for prioritizing audit findings?
A) Weibull distribution
B) Risk-benefit ratio
C) Cognitive dissonance
D) Ishikawa diagram
A) Weibull distribution
B) Risk-benefit ratio
C) Cognitive dissonance
D) Ishikawa diagram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is most important for an auditor to convey at an initial audit interview?
A) A give-and-take atmosphere that focuses on compromise
B) A formal approach that is guided by specific roles for each participant
C) An interest in cooperation and open dialogue
D) A personal approach to information gathering
A) A give-and-take atmosphere that focuses on compromise
B) A formal approach that is guided by specific roles for each participant
C) An interest in cooperation and open dialogue
D) A personal approach to information gathering

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The accuracy of quality audit documentation is especially important in which of the following situations?
A) One of the audit team members is aware of a possible personal bias related to the audit.
B) The documentation is likely to be used as evidence in litigation.
C) An audit has yielded more documentation than expected.
D) The documentation supports an auditor's viewpoint.
A) One of the audit team members is aware of a possible personal bias related to the audit.
B) The documentation is likely to be used as evidence in litigation.
C) An audit has yielded more documentation than expected.
D) The documentation supports an auditor's viewpoint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following conclusions can be made by an auditor who observes that statistical process control (SPC) charts posted near operator workstations are done correctly and are regularly completed throughout the plant?
A) Commitment of management to quality is strong
B) Processes are being improved continually
C) Shop floor staff have been fully trained
D) SPC charts are available
A) Commitment of management to quality is strong
B) Processes are being improved continually
C) Shop floor staff have been fully trained
D) SPC charts are available

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Partitioning or segmenting an audit is a useful way to
A) understand resource flows
B) simulate operating conditions
C) determine the relationship among parts
D) manage a large audit
A) understand resource flows
B) simulate operating conditions
C) determine the relationship among parts
D) manage a large audit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What action should an auditor take if an auditee responds to a procedural noncompliance by stating that the procedure conflicts with a written company policy?
A) Close out the corrective action request.
B) Notify the auditee to comply with the procedure.
C) Void the noncompliance.
D) Request that the auditee resolve the conflict.
A) Close out the corrective action request.
B) Notify the auditee to comply with the procedure.
C) Void the noncompliance.
D) Request that the auditee resolve the conflict.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following audit strategies is a common technique to assess compliance to a specific requirement at all locations where that requirement is applicable?
A) Discovery method
B) Element method
C) Department method
D) Process method
A) Discovery method
B) Element method
C) Department method
D) Process method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
When lower-tier documents are compared to higher-tier documents before the fieldwork starts, the comparison is called a
A) desk audit
B) process audit
C) conformance audit
D) management audit
A) desk audit
B) process audit
C) conformance audit
D) management audit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following is the greatest benefit of an internal audit program to an organization?
A) It fulfills most contractual quality requirements.
B) It provides feedback for continuous improvement.
C) It prepares an organization for third-party audits.
D) It frequently eliminates the need for external audits.
A) It fulfills most contractual quality requirements.
B) It provides feedback for continuous improvement.
C) It prepares an organization for third-party audits.
D) It frequently eliminates the need for external audits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
An audit trail is necessary in order to
A) schedule and budget for audit assignments
B) show how and when items were reviewed
C) provide management with justification for an audit
D) provide the audit manager with audit results
A) schedule and budget for audit assignments
B) show how and when items were reviewed
C) provide management with justification for an audit
D) provide the audit manager with audit results

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
As the last step before distributing an audit plan, an auditor should have the plan
A) approved by the client
B) approved by the auditee
C) reviewed by the organization to be audited
D) reviewed by auditee management
A) approved by the client
B) approved by the auditee
C) reviewed by the organization to be audited
D) reviewed by auditee management

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following statistics would best describe the central tendency of a sample of data?
A) Mode
B) Mean
C) Standard deviation
D) Range
A) Mode
B) Mean
C) Standard deviation
D) Range

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following methods can an audit program manager use to establish consistency among auditors?
A) Develop performance appraisals for all auditors
B) Assign auditors to permanent audit teams
C) Require auditors to read audit journals and references
D) Require auditors to develop their own procedures manual
A) Develop performance appraisals for all auditors
B) Assign auditors to permanent audit teams
C) Require auditors to read audit journals and references
D) Require auditors to develop their own procedures manual

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



