Deck 1: OMG Certified UML Professional (OCUP 2) - Intermediate Level
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/71
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: OMG Certified UML Professional (OCUP 2) - Intermediate Level
1
What is permitted for the profile mechanism?
A) creates new metamodels
B) removes existing metamodels
C) extends existing metamodels
D) changes existing metamodels
A) creates new metamodels
B) removes existing metamodels
C) extends existing metamodels
D) changes existing metamodels
C
2
What does the composite structure notation in the exhibit mean? 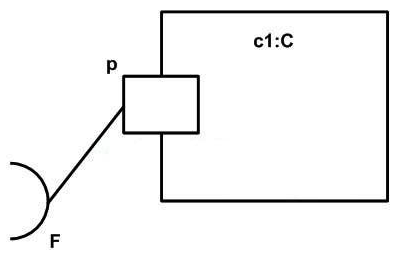
A) port p is connected to an object called F.
B) Port p realizes the features defined by interface F.
C) Port p requires the features defined by interface F.
D) Class C has internal structure.
E) Object c1 is a kind of component.

A) port p is connected to an object called F.
B) Port p realizes the features defined by interface F.
C) Port p requires the features defined by interface F.
D) Class C has internal structure.
E) Object c1 is a kind of component.
C
3
Refer to the exhibit. 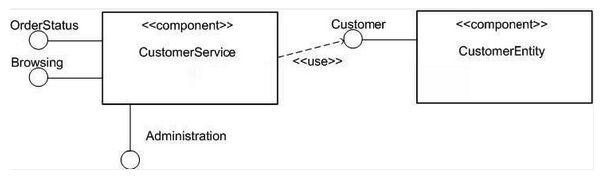 How many interfaces does the Customer Service component make visible to its clients?
How many interfaces does the Customer Service component make visible to its clients?
A) 3
B) 1
C) 0
D) 4
E) 2
 How many interfaces does the Customer Service component make visible to its clients?
How many interfaces does the Customer Service component make visible to its clients?A) 3
B) 1
C) 0
D) 4
E) 2
A
4
What characteristic does a Connectable Element possess?
A) represents the end of a communication channel
B) can be connected to other elements by connectors
C) can have associations
D) can own connectors
A) represents the end of a communication channel
B) can be connected to other elements by connectors
C) can have associations
D) can own connectors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is NOT a purpose of a port owned by a classifier?
A) server as an end point for connectors
B) hides the internals of that classifier from other classifiers
C) provides a distinct point of interaction between the classifier and its environment
D) specifies an association to the classifier
A) server as an end point for connectors
B) hides the internals of that classifier from other classifiers
C) provides a distinct point of interaction between the classifier and its environment
D) specifies an association to the classifier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is NOT true of a profile?
A) Applying a profile means that it is allowed, but not required to apply the stereotypes that are part of the profile.
B) A profile can be removed at any time from a model.
C) A profile can be combined with others applied on the same model.
D) Applying a profile means that it is required to apply the stereotypes that are part of the profile.
A) Applying a profile means that it is allowed, but not required to apply the stereotypes that are part of the profile.
B) A profile can be removed at any time from a model.
C) A profile can be combined with others applied on the same model.
D) Applying a profile means that it is required to apply the stereotypes that are part of the profile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What kinds of arrows connect to central buffers?
A) object flows
B) state transitions
C) unidirectional associations
D) control flows
E) message passing
F) dependencies
A) object flows
B) state transitions
C) unidirectional associations
D) control flows
E) message passing
F) dependencies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the difference between a stereotype and a metaclass?
A) Metaclasses can be specialized, but stereotypes cannot be specialized.
B) Stereotypes can be specialized, but metaclasses cannot be specialized.
C) A metaclass is a limited kind of a stereotype that can only be used in conjunction with one of the stereotypes it limits.
D) A stereotype is a limited kind of a metaclass that can be only be used in conjunction with one of the metaclasses it extends.
E) A stereotype is a specialization of a metaclass that can be used by itself, whereas a metaclass must be used with a stereotype.
A) Metaclasses can be specialized, but stereotypes cannot be specialized.
B) Stereotypes can be specialized, but metaclasses cannot be specialized.
C) A metaclass is a limited kind of a stereotype that can only be used in conjunction with one of the stereotypes it limits.
D) A stereotype is a limited kind of a metaclass that can be only be used in conjunction with one of the metaclasses it extends.
E) A stereotype is a specialization of a metaclass that can be used by itself, whereas a metaclass must be used with a stereotype.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What statements are true about a composite structure? (Choose two.)
A) Destroying an instance of a structured classifier normally destroys instances of its parts.
B) Structured classifiers cannot contain instances of structured classifiers.
C) The behavior of a structured classifier must be completely defined through the collaboration of owned or referenced instances.
D) Collaborations are structured classifier.
E) A structured classifier is also an encapsulated classifier.
A) Destroying an instance of a structured classifier normally destroys instances of its parts.
B) Structured classifiers cannot contain instances of structured classifiers.
C) The behavior of a structured classifier must be completely defined through the collaboration of owned or referenced instances.
D) Collaborations are structured classifier.
E) A structured classifier is also an encapsulated classifier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If the node in the exhibit receives a value, what happens to other values flowing in the diagram containing the node? 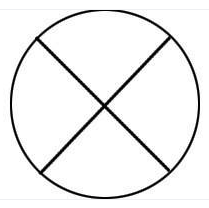
A) nothing
B) They stop for a time specified by the small circle.
C) They are aborted.
D) They stop until the small circle emits a value.

A) nothing
B) They stop for a time specified by the small circle.
C) They are aborted.
D) They stop until the small circle emits a value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the difference between a tag definition and a tagged value?
A) The properties of metaclasses are sometimes referred to as tag definitions. When a metaclass is applied to a model element, the values of the properties may be referred to as tagged values.
B) The properties of stereotypes are sometimes referred to as tagged values. When a stereotype is applied to a model element, the values of the properties may be referred to as tag definitions.
C) The properties of stereotypes are sometimes referred to as tag definitions. When a stereotype is applied to a model element, the values of the properties may be referred to as tagged values.
D) They are synonyms.
A) The properties of metaclasses are sometimes referred to as tag definitions. When a metaclass is applied to a model element, the values of the properties may be referred to as tagged values.
B) The properties of stereotypes are sometimes referred to as tagged values. When a stereotype is applied to a model element, the values of the properties may be referred to as tag definitions.
C) The properties of stereotypes are sometimes referred to as tag definitions. When a stereotype is applied to a model element, the values of the properties may be referred to as tagged values.
D) They are synonyms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is true of a composite state with two regions?
A) is a kind of submachine state
B) is equivalent to two states with one region each
C) is executed concurrently
D) is an orthogonal state
E) can have separate entry and exit actions for each region
A) is a kind of submachine state
B) is equivalent to two states with one region each
C) is executed concurrently
D) is an orthogonal state
E) can have separate entry and exit actions for each region

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the exhibit, what is true about Mbreak? 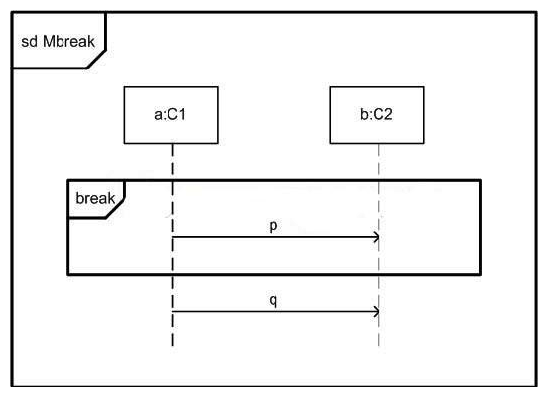
A) Either p or q appears in a trace, but not both.
B) p appers in all traces.
C) q appers in all traces.
D) Both p and q appear in all traces.

A) Either p or q appears in a trace, but not both.
B) p appers in all traces.
C) q appers in all traces.
D) Both p and q appear in all traces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In the exhibit, if all incoming arrows provide the same value, how many values does the pin have? 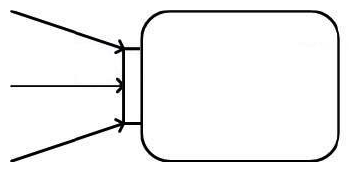
A) three.
B) two
C) one
D) none

A) three.
B) two
C) one
D) none

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What does a state list represent?
A) set of states that share a single outgoing transition
B) notational shorthand for a set of states
C) set of states that share the same entry and exit actions
D) list of the substates of a composite state
A) set of states that share a single outgoing transition
B) notational shorthand for a set of states
C) set of states that share the same entry and exit actions
D) list of the substates of a composite state

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is true about the composite structure exhibit? 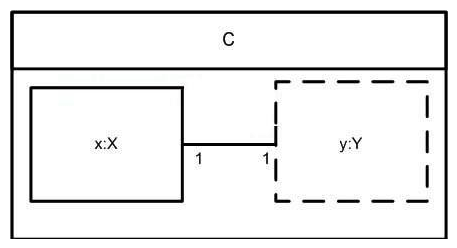
A) Every instance of X must be connected to an instance of Y.
B) All instances corresponding to x and y will be destroyed when an instance of C is destroyed.
C) Every instance of Y must be connected to an instance of X.
D) C has at least two properties.

A) Every instance of X must be connected to an instance of Y.
B) All instances corresponding to x and y will be destroyed when an instance of C is destroyed.
C) Every instance of Y must be connected to an instance of X.
D) C has at least two properties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What determines whether a clause executes?
A) behaviors
B) classes
C) parameters
D) guards
E) test nodes
A) behaviors
B) classes
C) parameters
D) guards
E) test nodes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the exhibit, if the incoming arrows provide one control value and two data values, what values are provided to the outgoing arrows? 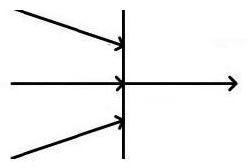
A) the two data values
B) a single control value
C) a single data value combining the original two data values
D) both the control and two data values

A) the two data values
B) a single control value
C) a single data value combining the original two data values
D) both the control and two data values

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is true about guards on interaction operands?
A) should not refer to any dynamic variables, i.e., to attributes of the lifelines
B) must only cover one lifeline, namely the one lifeline having the first event occurrence of the interaction operand
C) must always cover all lifelines covered by the operand
D) must cover the same lifelines on all interaction operands within one combined fragment
A) should not refer to any dynamic variables, i.e., to attributes of the lifelines
B) must only cover one lifeline, namely the one lifeline having the first event occurrence of the interaction operand
C) must always cover all lifelines covered by the operand
D) must cover the same lifelines on all interaction operands within one combined fragment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What kind of relationship is an extension in UML 2.0?
A) generalization
B) dependency
C) association
D) reification
A) generalization
B) dependency
C) association
D) reification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is NOT a correct assertion?
A) A model element can be extended by several stereotypes at the same time.
B) Un-applying a profile from a model deleted stereotypes extending the model.
C) Stereotypes extending a model element can be retracted at any time.
D) Stereotypes extending a model element are immutable.
A) A model element can be extended by several stereotypes at the same time.
B) Un-applying a profile from a model deleted stereotypes extending the model.
C) Stereotypes extending a model element can be retracted at any time.
D) Stereotypes extending a model element are immutable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What can return a result on an output pin?
A) Destroy Object Action
B) Call behavior Action
C) Add Variable Value Action
D) Send Object Action
E) Broadcast Signal Operation
A) Destroy Object Action
B) Call behavior Action
C) Add Variable Value Action
D) Send Object Action
E) Broadcast Signal Operation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What does the composite structure exhibit show? 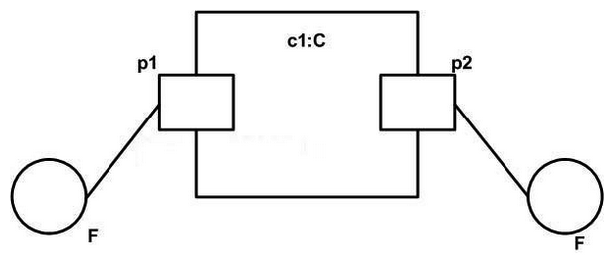
A) The diagram is not valid.
B) Requests for behavioral features of interface F through ports p1a nd p2 will always result in the same behavior.
C) The two F interfaces must come from different packages.
D) Requests for behavioral features of interface F through

A) The diagram is not valid.
B) Requests for behavioral features of interface F through ports p1a nd p2 will always result in the same behavior.
C) The two F interfaces must come from different packages.
D) Requests for behavioral features of interface F through

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is an invocation action on a port used for?
A) invoking the behavior of the classifier that owns the port
B) creating a link and attach it to that port
C) relaying the invocation via links connected to that port
D) sending a message to that port
E) receiving a message on that port
A) invoking the behavior of the classifier that owns the port
B) creating a link and attach it to that port
C) relaying the invocation via links connected to that port
D) sending a message to that port
E) receiving a message on that port

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is NOT true of a CreateObjectAction? (Choose two.)
A) output pin has multiplicity [1..*]
B) classifier cannot be an association class
C) output pin has multiplicity [1..1]
D) classifier must be abstract
E) classifier cannot be abstract
F) type of the output pin is the classifier
A) output pin has multiplicity [1..*]
B) classifier cannot be an association class
C) output pin has multiplicity [1..1]
D) classifier must be abstract
E) classifier cannot be abstract
F) type of the output pin is the classifier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What does the history of a state represent?
A) most recent transition that was taken out of the state
B) most recent active configuration of its substates
C) number of times that the state has been active before
D) most recent transition that was taken into the state.
A) most recent transition that was taken out of the state
B) most recent active configuration of its substates
C) number of times that the state has been active before
D) most recent transition that was taken into the state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is a Connection Point Reference used to declare?
A) a pointer to a connection point
B) a submachine state
C) an entry or exit point of a submachine state
D) an entry or exit point of a state
E) a pseudostate
A) a pointer to a connection point
B) a submachine state
C) an entry or exit point of a submachine state
D) an entry or exit point of a state
E) a pseudostate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the exhibit, what is true about the diagram MOpt? 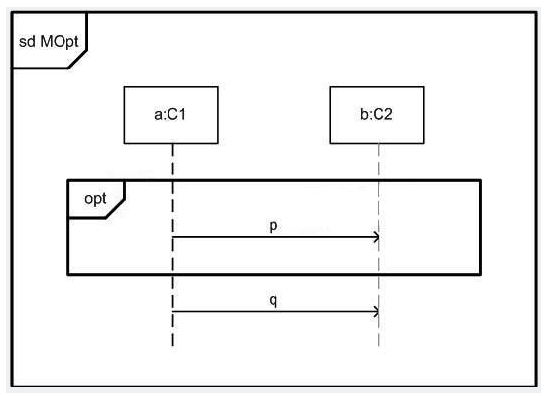
A) Receiving p will come before sending q.
B) All traces of MOpt include message q.
C) All traces of MOpt include message p.
D) No traces of MOpt include both messages p and q.

A) Receiving p will come before sending q.
B) All traces of MOpt include message q.
C) All traces of MOpt include message p.
D) No traces of MOpt include both messages p and q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
How many arrows can connect to a partition?
A) any number
B) none
C) two
D) one
A) any number
B) none
C) two
D) one

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In the exhibit, what is true about Mpar? 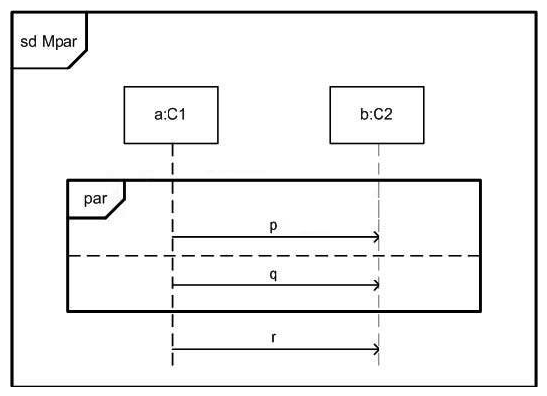
A) There are legal traces that do not contain message q.
B) Every trace contains all three messages.
C) Receiving p must always precede receiving q.
D) Sending p must always precede sending q.

A) There are legal traces that do not contain message q.
B) Every trace contains all three messages.
C) Receiving p must always precede receiving q.
D) Sending p must always precede sending q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In the exhibit, what is true about the deployment location? 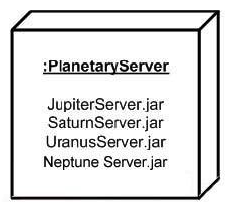
A) is at the "instance" level
B) is parameterized by four Deployment Specifications
C) is over-crowded
D) is at the "type" level

A) is at the "instance" level
B) is parameterized by four Deployment Specifications
C) is over-crowded
D) is at the "type" level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What are valid ways to present a component's artifacts file, such as a jar file? (Choose two.)
A) stereotype of class with keyword <> with a solid arrow pointing to the related component
B) stereotype of class with keyword <> with a dashed arrow pointing to the related component
C) stereotype of a component with keyword <> with a dashed arrow pointing to the related component
D) as a compartment of a related component
E) stereotype of a component with keyword <> with a solid arrow pointing to the related component
A) stereotype of class with keyword <
B) stereotype of class with keyword <
C) stereotype of a component with keyword <
D) as a compartment of a related component
E) stereotype of a component with keyword <

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is a combined fragment?
A) more than one interaction combined in an interaction overview diagram
B) an interaction occurrence covering more than one lifeline
C) the combination of decomposed lifelines
D) a construct with interaction operands and in interaction operator.
A) more than one interaction combined in an interaction overview diagram
B) an interaction occurrence covering more than one lifeline
C) the combination of decomposed lifelines
D) a construct with interaction operands and in interaction operator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the exhibit, what applies if the interaction constraint is false when the loop is entered? 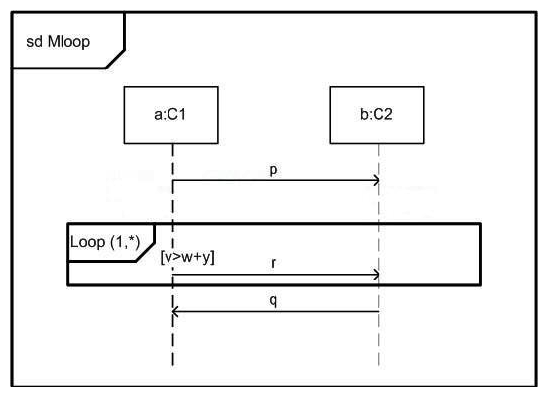
A) All valid traces will include message r.
B) Valid traces include both the case where the loop iterates once, and when it iterates zero times.
C) The specification if illegal.
D) The loop body is not included in a valid trace.

A) All valid traces will include message r.
B) Valid traces include both the case where the loop iterates once, and when it iterates zero times.
C) The specification if illegal.
D) The loop body is not included in a valid trace.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is true for part decomposition in interaction diagrams?
A) cannot be reused as decomposition from another lifeline
B) must match the constructs of the decomposed lifeline
C) must always be owned by the same interaction as the decomposed lifeline
D) always refers to methods of the decomposed lifeline
A) cannot be reused as decomposition from another lifeline
B) must match the constructs of the decomposed lifeline
C) must always be owned by the same interaction as the decomposed lifeline
D) always refers to methods of the decomposed lifeline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What might a connector specify?
A) dependencies
B) classes
C) associations
D) messages
E) links
A) dependencies
B) classes
C) associations
D) messages
E) links

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A protocol state machine can be used to describe which aspect of a component?
A) configuration of an assembly
B) external contract of a component
C) signal flow among connectors
D) internals of a component
A) configuration of an assembly
B) external contract of a component
C) signal flow among connectors
D) internals of a component

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Refer to the exhibit. How many interfaces does the TradeBroker component make visible to its clients? 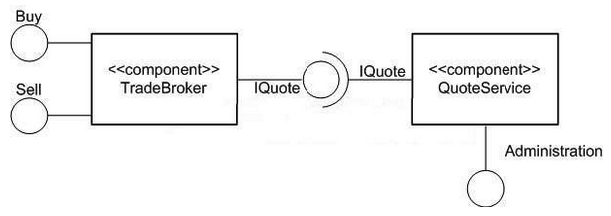
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 4
E) 3

A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 4
E) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which relationships would make the model in the exhibit ill-formed? 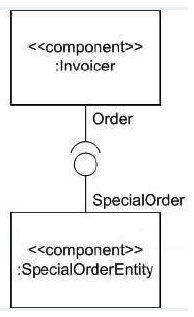
A) Special Order and Order are related to each other via a dependency.
B) Special Order and order are related to each other via an association.
C) Order is a subtype of Special Order.
D) Special Order is a subtype of Order.

A) Special Order and Order are related to each other via a dependency.
B) Special Order and order are related to each other via an association.
C) Order is a subtype of Special Order.
D) Special Order is a subtype of Order.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Instances of the Communication Path class connect instances of which classes in a deployment diagram?
A) Instance Specification and Deployment Specification
B) Deployment Target and Deployed Artifact
C) Node and Property
D) Node and Signal
E) two Nodes
A) Instance Specification and Deployment Specification
B) Deployment Target and Deployed Artifact
C) Node and Property
D) Node and Signal
E) two Nodes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is NOT true about a roles and role bindings?
A) A role binding is an association.
B) A role binding maps a connectable element to a role in a collaboration occurrence.
C) The same object may play roles in multiple collaborations.
D) A role types by an interface specifies a set of features required by a participant in a collaboration.
E) The same connectable element may be bound to multiple roles in a single collaboration occurrence.
A) A role binding is an association.
B) A role binding maps a connectable element to a role in a collaboration occurrence.
C) The same object may play roles in multiple collaborations.
D) A role types by an interface specifies a set of features required by a participant in a collaboration.
E) The same connectable element may be bound to multiple roles in a single collaboration occurrence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What value should insertAt be set to when adding a new value to the end of a 5-element ordered structural feature using an AddStructuralFeatureValueAction?
A) any integer greater than 5
B) -1
C) infinity
D) 0
A) any integer greater than 5
B) -1
C) infinity
D) 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is the notation for gates?
A) circular disc at the interaction frame
B) small arrow either into or out from the fragment frame
C) point on the fragment frame with an optional name
D) small rectangle on the fragment with associated name
A) circular disc at the interaction frame
B) small arrow either into or out from the fragment frame
C) point on the fragment frame with an optional name
D) small rectangle on the fragment with associated name

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What situation results from performing a Create Object Action on an abstract class?
A) arbitrary object of one of its subclasses being created
B) object of the specified class being created
C) undefined behavior
D) error log entry being created
E) exception being raised
A) arbitrary object of one of its subclasses being created
B) object of the specified class being created
C) undefined behavior
D) error log entry being created
E) exception being raised

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which is true of a provided interface associated with a port?
A) identifiers the services that the object owning the port expects of objects connected via that port.
B) represents an interface that must be defined within the classifier that owns the port
C) represents an interface that must be defined in the same package in which the classifier owning the port is defined
D) identifies the services that the object owning the port can offer to other objects connected via that port
A) identifiers the services that the object owning the port expects of objects connected via that port.
B) represents an interface that must be defined within the classifier that owns the port
C) represents an interface that must be defined in the same package in which the classifier owning the port is defined
D) identifies the services that the object owning the port can offer to other objects connected via that port

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What does a choice pseudostate designate?
A) point at which outgoing guards are evaluated
B) point whose outgoing transitions are optional
C) point with an associated Boolean condition
D) a conditional fork pseudostate
E) point that is chosen dynamically during execution
A) point at which outgoing guards are evaluated
B) point whose outgoing transitions are optional
C) point with an associated Boolean condition
D) a conditional fork pseudostate
E) point that is chosen dynamically during execution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which is a correct representation of multiple extension and generalization/specialization? (Choose two.) 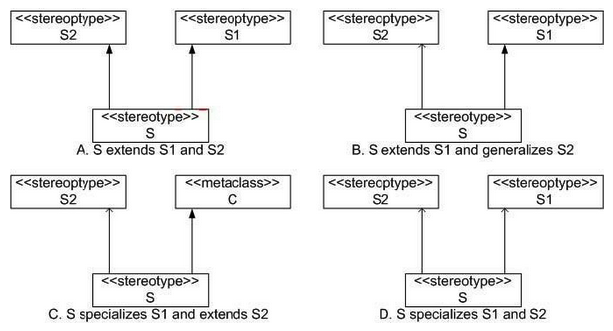
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Where is an interaction constraint placed?
A) either on the top of an operand or at the bottom of an operand
B) always at the top of an interaction
C) above the first event within an interaction operand
D) directly outside the combined fragment
A) either on the top of an operand or at the bottom of an operand
B) always at the top of an interaction
C) above the first event within an interaction operand
D) directly outside the combined fragment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is true about a pseudostate?
A) a state that can be specialized for different purposes
B) a state entry or exit point
C) a specification of a potential state
D) not a state but a vertex
A) a state that can be specialized for different purposes
B) a state entry or exit point
C) a specification of a potential state
D) not a state but a vertex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is true of a completion transition?
A) is executed when the state machine is terminated
B) is only triggered by a completion event
C) has no trigger defined
D) is executed when the final state is reached
A) is executed when the state machine is terminated
B) is only triggered by a completion event
C) has no trigger defined
D) is executed when the final state is reached

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What most accurately describes the semantics modeled by the exhibit? 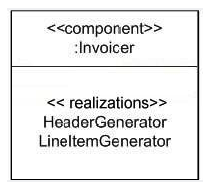
A) HeaderGenerator and LineItemGenerator are Invoicer ports.
B) An Invoicer component is composed of HeaderGenerator component and a LineItemGenerator component.
C) HeaderGenerator and LineItemGenerator realize Invoicer.
D) Invoicer realizes Header Generator and Line Item Generator

A) HeaderGenerator and LineItemGenerator are Invoicer ports.
B) An Invoicer component is composed of HeaderGenerator component and a LineItemGenerator component.
C) HeaderGenerator and LineItemGenerator realize Invoicer.
D) Invoicer realizes Header Generator and Line Item Generator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What situation results from an Apply Function Action?
A) reads objects and produces output values
B) produces output values
C) writes objects and produces output values
D) reads objects, write objects, and produces output values
E) performs any set of UML actions
A) reads objects and produces output values
B) produces output values
C) writes objects and produces output values
D) reads objects, write objects, and produces output values
E) performs any set of UML actions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is true of a local transition of a state?
A) any transition that occurs only in that state
B) a transition that cannot be triggered if no substate is active
C) a transition that will not execute the exit and entry actions of the state but only those of its substates
D) equivalent to an internal transition
A) any transition that occurs only in that state
B) a transition that cannot be triggered if no substate is active
C) a transition that will not execute the exit and entry actions of the state but only those of its substates
D) equivalent to an internal transition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Assume component A provides an interface P and requires an interface R. In order for a component B to be substituted for component A, what must be true?
A) The interface that B requires must be type conformant with respect to the interface that A provides.
B) The interface that B requires must be type conformant with respect to the interface that A requires, and the interface that B provides must be type conformant with respect to the interface that A provides.
C) The interface that A requires must be type conformant with respect to the interface that B provides.
D) Components must be related to each other via a dependency.
A) The interface that B requires must be type conformant with respect to the interface that A provides.
B) The interface that B requires must be type conformant with respect to the interface that A requires, and the interface that B provides must be type conformant with respect to the interface that A provides.
C) The interface that A requires must be type conformant with respect to the interface that B provides.
D) Components must be related to each other via a dependency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In a state machine, what is true for a "do activity of a state"?
A) starts executing when the state is entered
B) specifies a condition that must always be true when the state is active
C) can only appear in a composite state
D) executes repeatedly as long as the state is active E. is equivalent to an entry action of a state
A) starts executing when the state is entered
B) specifies a condition that must always be true when the state is active
C) can only appear in a composite state
D) executes repeatedly as long as the state is active E. is equivalent to an entry action of a state

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What situation results from performing a Create Object Action on an abstract class?
A) undefined behavior
B) arbitrary object of one of its subclasses being created
C) exception being raised
D) error log entry created
E) object of the specified class being created
A) undefined behavior
B) arbitrary object of one of its subclasses being created
C) exception being raised
D) error log entry created
E) object of the specified class being created

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What is implied when a transition terminates on the outer border of a composite state that has an initial and a history pseudostate?
A) The outgoing transition from the final pseudostate is taken.
B) The state is not entered.
C) The outgoing transition from the initial pseudostate is taken.
D) The outgoing transition from the history pseudostate is taken.
A) The outgoing transition from the final pseudostate is taken.
B) The state is not entered.
C) The outgoing transition from the initial pseudostate is taken.
D) The outgoing transition from the history pseudostate is taken.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What is wrong with the Sale instance diagram shown in the exhibit? 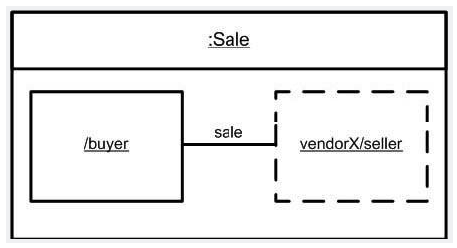
A) Buyer instance name is missing.
B) Link name should be underlined.
C) Sale instance name is missing.
D) Link should be shown with a dashed line.
E) Types of the buyer and seller parts are missing.

A) Buyer instance name is missing.
B) Link name should be underlined.
C) Sale instance name is missing.
D) Link should be shown with a dashed line.
E) Types of the buyer and seller parts are missing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is true about a collaboration?
A) identifies a protocol state machine
B) describes the internal structure of a structured classifier
C) describes one or more interactions working together
D) describes how multiple classifiers achieve a task together
A) identifies a protocol state machine
B) describes the internal structure of a structured classifier
C) describes one or more interactions working together
D) describes how multiple classifiers achieve a task together

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In the exhibit, what is true for Mcritical? 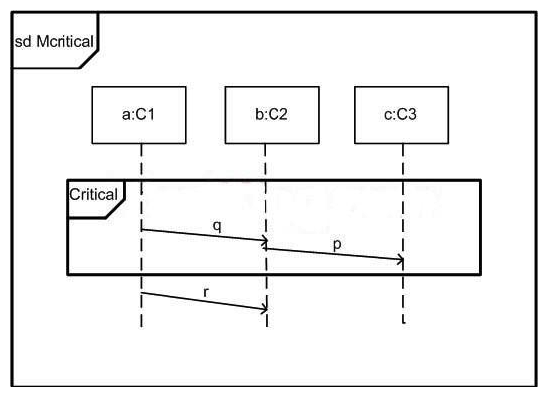
A) r can be sent whenever p has been sent.
B) Whenever q and p have been sent, r can be sent.
C) There are legal traces according to Mcritical where r is absent.
D) The reception of p must precede sending of r.

A) r can be sent whenever p has been sent.
B) Whenever q and p have been sent, r can be sent.
C) There are legal traces according to Mcritical where r is absent.
D) The reception of p must precede sending of r.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How can the internals of a component be presented?
A) using a complex component connector
B) in a compartment of the component box or via boxes nested within the component box
C) in a compartment of the component box or component requires port
D) component provides port or a component requires port
A) using a complex component connector
B) in a compartment of the component box or via boxes nested within the component box
C) in a compartment of the component box or component requires port
D) component provides port or a component requires port

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is NOT a valid Variable Action?
A) Remove Variable Value Action
B) Add Variable Value Action
C) Clear Variable Action
D) Read Variable Action
E) Set Variable Action
A) Remove Variable Value Action
B) Add Variable Value Action
C) Clear Variable Action
D) Read Variable Action
E) Set Variable Action

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What will be deleted when performing a Destroy Object Action on an object that participates in a composition association with many components?
A) component objects
B) objects, all its links and all linked objects
C) objects and all its links
D) objects and all its component objects
E) object
A) component objects
B) objects, all its links and all linked objects
C) objects and all its links
D) objects and all its component objects
E) object

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What must be true for a connector to be well formed if a delegation connector delegates to more than one target port?
A) The interfaces of the target ports must have no features in common.
B) The interface of at least one of the target ports must be signature compatible with the interface that is the type of the source port.
C) The interface of each of the target ports must be signature compatible with the interface that is the type of the source port.
D) The union of the interfaces of the target ports must be signature compatible with the interface that is the type of the source port.
A) The interfaces of the target ports must have no features in common.
B) The interface of at least one of the target ports must be signature compatible with the interface that is the type of the source port.
C) The interface of each of the target ports must be signature compatible with the interface that is the type of the source port.
D) The union of the interfaces of the target ports must be signature compatible with the interface that is the type of the source port.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is the semantic difference between the two figures in the exhibit? 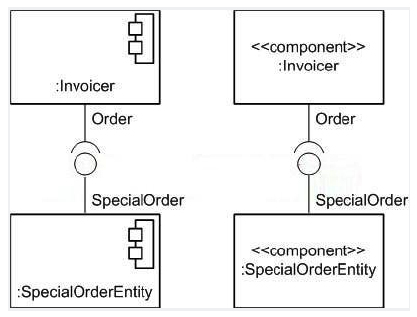
A) One is white-box view, while the other is a black-box view.
B) One is a deployment diagram, while the other is a class diagram.
C) There is no semantic difference.
D) One is a UML 2.0 diagram, while other is a UML 1.5 diagram.

A) One is white-box view, while the other is a black-box view.
B) One is a deployment diagram, while the other is a class diagram.
C) There is no semantic difference.
D) One is a UML 2.0 diagram, while other is a UML 1.5 diagram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A component may legally participate in which relationship(s)?
A) associations and generalizations
B) dependencies, associations, and generalizations
C) dependencies and generalizations
D) dependencies
A) associations and generalizations
B) dependencies, associations, and generalizations
C) dependencies and generalizations
D) dependencies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Why are profiles NOT a first class extension mechanism?
A) They do not allow for modifying existing metamodels.
B) They do not permit customizing for domains, platforms, and methods.
C) They permit removing constraints that apply to existing metamodels.
D) They do not allow for modifying existing stereotypes.
A) They do not allow for modifying existing metamodels.
B) They do not permit customizing for domains, platforms, and methods.
C) They permit removing constraints that apply to existing metamodels.
D) They do not allow for modifying existing stereotypes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What objects receive a signal sent by a Broadcast Signal Action?
A) objects that are instantiated from classes in the package of the action
B) all objects
C) objects are determined by semantic variation
D) objects that are on the same node as the actions
E) all objects that have a reception for the signal
A) objects that are instantiated from classes in the package of the action
B) all objects
C) objects are determined by semantic variation
D) objects that are on the same node as the actions
E) all objects that have a reception for the signal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Refer to the exhibit. What is the significance of the fact that the Administration interface symbol extends downward rather than leftward? 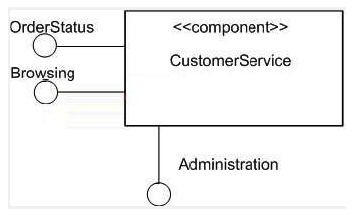
A) The interface is the primary provided interface for the component.
B) The interface is not publicly visible on the component.
C) There is no significance.
D) The interface is the primary interface for the component.
E) The interface cannot be provided via a port.
F) The interface does not require a delegation connector.

A) The interface is the primary provided interface for the component.
B) The interface is not publicly visible on the component.
C) There is no significance.
D) The interface is the primary interface for the component.
E) The interface cannot be provided via a port.
F) The interface does not require a delegation connector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What may a profile NOT own?
A) metaclasses
B) stereotypes
C) new associations
D) associations that redefine existing associations
A) metaclasses
B) stereotypes
C) new associations
D) associations that redefine existing associations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In the exhibit, what represents an interaction occurrence? 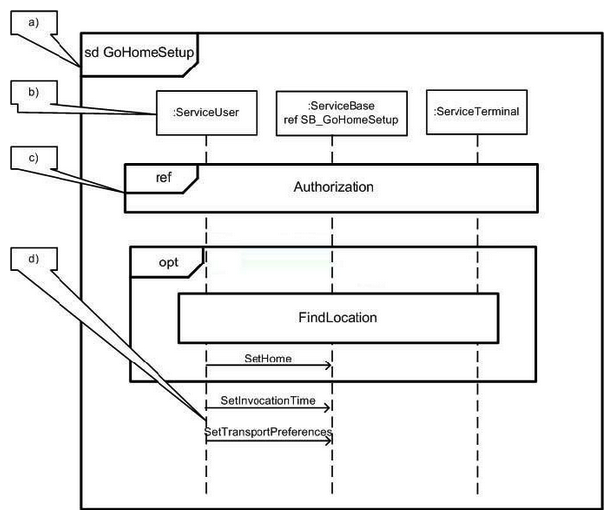
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



