Deck : 5 the Fulfi Llment Process
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/22
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck : 5 the Fulfi Llment Process
1
What is the credit management master record? How is it related to the customer master record?
Credit management master:
Credit management master is an addition to customer master data, in this master data, credit for customers are managed. It should be maintained for all customers and it should contain the following three elements.
General data:
It contains data that is applicable at client level, which is relevant to multiple credit control areas.
Examples are customer address, credit limit granted for a customer throughout the enterprise and other communication data.
Credit control area segment:
It contains data, which is relevant to single credit control area. Examples are risk category of the customer and credit limit granted for a customer in specified credit control area.
Overview:
It contains key data from all sections of the credit master record.
Relationship of credit management master with customer master record:
Customer master record of a company uses risk category from credit control area segment to determine riskiness in extending credit for a customer and it is used to assess customer's probability of paying the invoices.
Customer master record of a company uses the overview segment for decision making regarding the extension of credit to customer.
Credit management master is an addition to customer master data, in this master data, credit for customers are managed. It should be maintained for all customers and it should contain the following three elements.
General data:
It contains data that is applicable at client level, which is relevant to multiple credit control areas.
Examples are customer address, credit limit granted for a customer throughout the enterprise and other communication data.
Credit control area segment:
It contains data, which is relevant to single credit control area. Examples are risk category of the customer and credit limit granted for a customer in specified credit control area.
Overview:
It contains key data from all sections of the credit master record.
Relationship of credit management master with customer master record:
Customer master record of a company uses risk category from credit control area segment to determine riskiness in extending credit for a customer and it is used to assess customer's probability of paying the invoices.
Customer master record of a company uses the overview segment for decision making regarding the extension of credit to customer.
2
Describe the steps in the fulfi llment process in terms of triggers, data, steps, and outcomes.
Steps in fulfillment process:
The steps in fulfillment process begins with presales activities, further moves to sales order processing, billing, shipping and the process concludes with receiving payment.
The process fulfillment consists of four key elements, which highlights the process steps in detail, they are:
• Trigger
• Data
• Steps
• Outcomes
Elements of the presales activity in steps:
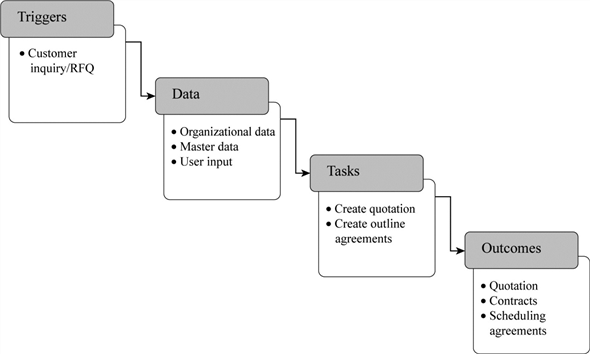 Trigger:
Trigger:
Communication initiated by the customer such as an inquiry about a product or a request for quotation (RFQ) will trigger the presales activity.
In sales order processing, the fulfillment process is triggered by the receipt of purchase order from a customer.
Data:
Inquiry from a customer or to create a quotation several types of master and organizational data are required. The data related with customers, materials, and their pricing are specified here.
Data consists of user input such as customer and material numbers, dates, and quantities. These user input data are helpful in obtaining organizational data from master data in the system.
Tasks:
The tasks involved after a quotation is triggered are creating a sales order. With the help of sales order, the order can be tracked and managed easily.
After the sales order is created for a product, it is packed and shipped. The above all activities belong to sales order processing step.
Outcomes:
The outcome of fulfillment process is communications with the customer regarding the quotation, the output conditions of the quotations are determined.
In case of sales order processing, the order is shipped to the customer and billing for the customer is prepared and sent to the customer and final step is customer sends payment for the materials received is the outcome.
Elements of the sales order in steps:
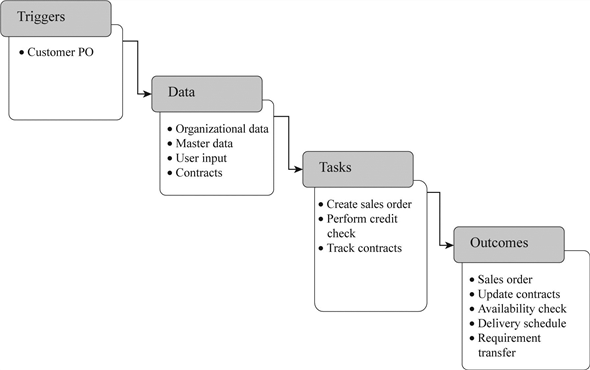 Trigger:
Trigger:
The process is triggered by the purchase order (PO) sent from a customer to the company. This PO initiates the process of creating sales order in the SAP ERP system.
Data:
Inquiry from a customer or to create a quotation several types of master and organizational data are required. The data related with customers, materials, and their pricing are specified here.
Data includes customer master data such as shipping and billing data.
Tasks:
The task involved after a quotation is triggered is creating a sales order. One or more quotations can be referenced during the creation of a sales order. With the help of sales order, the order can be tracked and managed easily.
Most of the data specified sales order can also be found in quotation. Examples are delivery data, item number, material name and quantity. A quotation can used to create multiple sales orders.
Outcomes:
The outcome of fulfillment process is sales order creation along with this contracts should be updated. Then, some additional consequences should be considered, they are, availability check, transfer of requirements and delivery schedule.
Elements of shipping in steps:
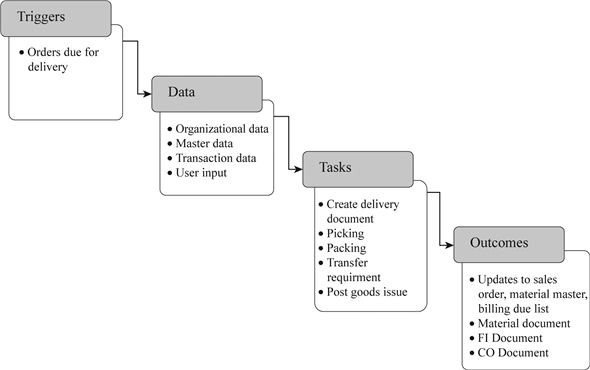 Trigger:
Trigger:
The process is triggered when the orders become due to delivery. Several tasks are necessary to complete the shipping process.
Data:
Delivery document is the central document of the shipping process. It contains the details from which plant the materials should be shipped to which partner. Further, delivery document identifies the material's storage locations.
Tasks:
Several tasks should be completed during shipping, they are,
• Creating delivery document
• Packing
• Picking
• Transfer requirement
• Post goods issue.
The authorization for delivery is provided by the creation of delivery document.
Outcomes:
The outcome of shipping process depends on updating the material master, sales documents and billing due list. Transaction data should be recorded in the financial document, controlling document and material document.
The shipping process ends with goods issue and it is the starting process of financial impacts.
Elements of shipping in steps:
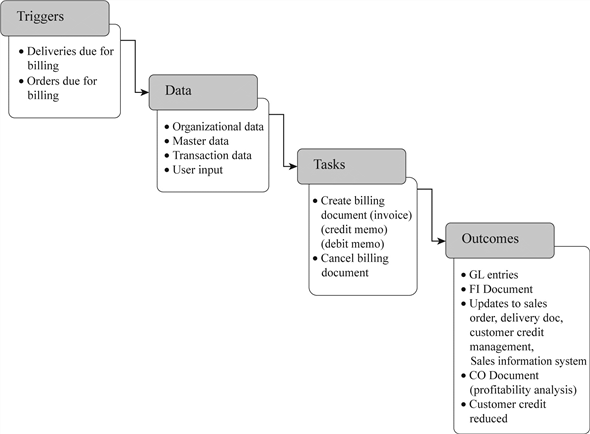 Trigger:
Trigger:
The process is triggered either by materials (deliveries) that have been shipped or by orders that are yet to be delivered. This step is used to create several documents such as product's invoices and credit and debit memos.
Data:
Data from delivery document and sales order such as material number and quantities are used as a reference for billing. Customer master and pricing conditions from master data are used as a source for partner function and pricing data.
Organizational data such as client, company code and sales area which are relevant to fulfillment process is utilized by billing.
Tasks:
The important task of billing process is to create a billing document (invoice), which is created on the basis of delivery or sales order. Cancelling the invoice is another task of billing process.
Outcomes:
The outcome of billing process is updating the material master, sales documents, customer credit and sales information system. Transaction data should be recorded in the financial document, controlling document and invoice document.
The billing process impacts financially, so accounting data such as customer account, account receivable reconciliation and sales revenue should be updated.
The steps in fulfillment process begins with presales activities, further moves to sales order processing, billing, shipping and the process concludes with receiving payment.
The process fulfillment consists of four key elements, which highlights the process steps in detail, they are:
• Trigger
• Data
• Steps
• Outcomes
Elements of the presales activity in steps:
 Trigger:
Trigger: Communication initiated by the customer such as an inquiry about a product or a request for quotation (RFQ) will trigger the presales activity.
In sales order processing, the fulfillment process is triggered by the receipt of purchase order from a customer.
Data:
Inquiry from a customer or to create a quotation several types of master and organizational data are required. The data related with customers, materials, and their pricing are specified here.
Data consists of user input such as customer and material numbers, dates, and quantities. These user input data are helpful in obtaining organizational data from master data in the system.
Tasks:
The tasks involved after a quotation is triggered are creating a sales order. With the help of sales order, the order can be tracked and managed easily.
After the sales order is created for a product, it is packed and shipped. The above all activities belong to sales order processing step.
Outcomes:
The outcome of fulfillment process is communications with the customer regarding the quotation, the output conditions of the quotations are determined.
In case of sales order processing, the order is shipped to the customer and billing for the customer is prepared and sent to the customer and final step is customer sends payment for the materials received is the outcome.
Elements of the sales order in steps:
 Trigger:
Trigger: The process is triggered by the purchase order (PO) sent from a customer to the company. This PO initiates the process of creating sales order in the SAP ERP system.
Data:
Inquiry from a customer or to create a quotation several types of master and organizational data are required. The data related with customers, materials, and their pricing are specified here.
Data includes customer master data such as shipping and billing data.
Tasks:
The task involved after a quotation is triggered is creating a sales order. One or more quotations can be referenced during the creation of a sales order. With the help of sales order, the order can be tracked and managed easily.
Most of the data specified sales order can also be found in quotation. Examples are delivery data, item number, material name and quantity. A quotation can used to create multiple sales orders.
Outcomes:
The outcome of fulfillment process is sales order creation along with this contracts should be updated. Then, some additional consequences should be considered, they are, availability check, transfer of requirements and delivery schedule.
Elements of shipping in steps:
 Trigger:
Trigger: The process is triggered when the orders become due to delivery. Several tasks are necessary to complete the shipping process.
Data:
Delivery document is the central document of the shipping process. It contains the details from which plant the materials should be shipped to which partner. Further, delivery document identifies the material's storage locations.
Tasks:
Several tasks should be completed during shipping, they are,
• Creating delivery document
• Packing
• Picking
• Transfer requirement
• Post goods issue.
The authorization for delivery is provided by the creation of delivery document.
Outcomes:
The outcome of shipping process depends on updating the material master, sales documents and billing due list. Transaction data should be recorded in the financial document, controlling document and material document.
The shipping process ends with goods issue and it is the starting process of financial impacts.
Elements of shipping in steps:
 Trigger:
Trigger: The process is triggered either by materials (deliveries) that have been shipped or by orders that are yet to be delivered. This step is used to create several documents such as product's invoices and credit and debit memos.
Data:
Data from delivery document and sales order such as material number and quantities are used as a reference for billing. Customer master and pricing conditions from master data are used as a source for partner function and pricing data.
Organizational data such as client, company code and sales area which are relevant to fulfillment process is utilized by billing.
Tasks:
The important task of billing process is to create a billing document (invoice), which is created on the basis of delivery or sales order. Cancelling the invoice is another task of billing process.
Outcomes:
The outcome of billing process is updating the material master, sales documents, customer credit and sales information system. Transaction data should be recorded in the financial document, controlling document and invoice document.
The billing process impacts financially, so accounting data such as customer account, account receivable reconciliation and sales revenue should be updated.
3
Describe the structure of the following documents
a. Sales order
b. Delivery document
c. Billing document
a. Sales order
b. Delivery document
c. Billing document
Structure of the following documents:
a. Sales order:
An internal document in an organization, which contains required information to fill the customer order in a consistent and standardized form called as sales order.
Structure of the sales order document:
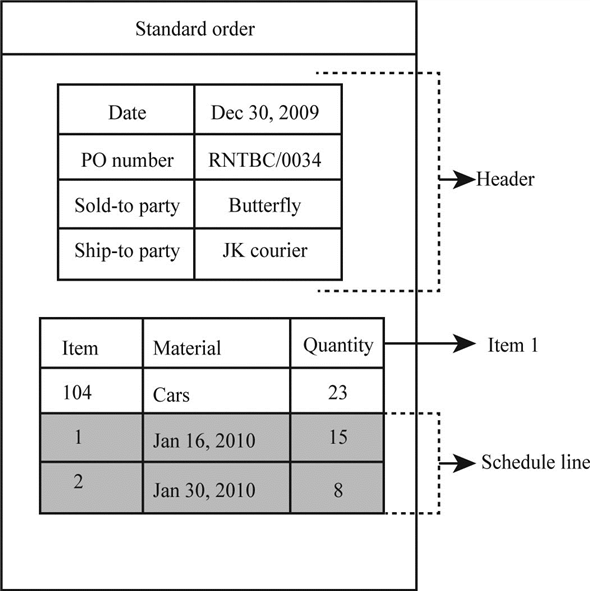 The above diagram represents a standard sales order with some data filled in it by company for its customer "Butterfly".
The above diagram represents a standard sales order with some data filled in it by company for its customer "Butterfly".
Standard sales order document is split into three sections:
• Header
• Item
• Schedule lines
Header:
The header section in the sales order document contains valid data for the entire sales order. Examples are dates, PO number of a customer, total order and partner functions.
Item:
A sales order document can contain one or more sales items; it contains data about the item included in the sales order. Examples of sales items are item number, material name and quantity.
Schedule lines:
The last section in the sales order document is schedule lines, which specifies delivery dates and quantity of the delivery on the specified date. One or more schedule lines can be included in a document item.
b. Delivery document:
Delivery document is the central document for shipping a material. It contains data about the materials, which are to be shipped, name of the partner function and location of the plant from which the material is shipped.
Structure of the delivery document:
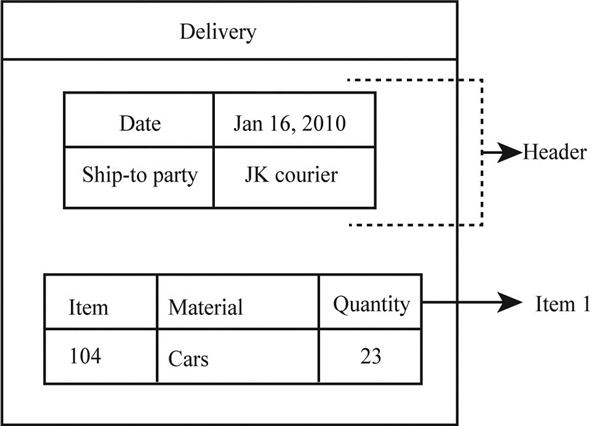 The above diagram represents a standard delivery document with some data filled in it by company for its customer "Butterfly".
The above diagram represents a standard delivery document with some data filled in it by company for its customer "Butterfly".
Standard delivery document is split into two sections:
• Header
• Item
Header:
The header section in the delivery document contains valid data for the entire document. Data such as delivery date, partner functions (ship-to party), shipping address, and total quantity.
Item:
Delivery document can contain one or more sales items; it contains data about the shipment. The data such as item number, material name, weight, and quantity.
c. Billing document:
Documents related with payment for a material such as invoices, debit and credit memos are created with the help of billing. Billing document can be made for the materials that has been shipped or for the materials that is yet to be delivered.
Structure of the billing document:
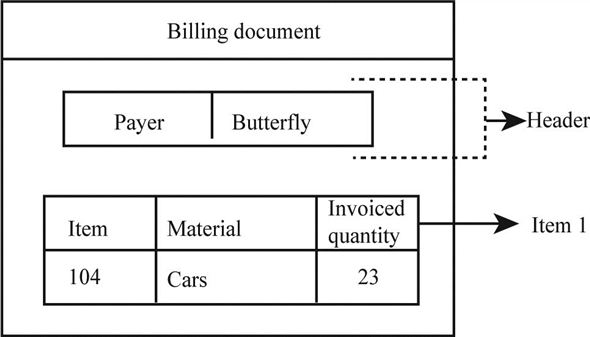 The above diagram represents a standard billing document with some data filled in it by company for its customer "Butterfly".
The above diagram represents a standard billing document with some data filled in it by company for its customer "Butterfly".
Standard billing document is split into two sections:
• Header
• Item
Header:
The header section in the billing document contains data used for partner identification. Data such as partner functions (ship-to party), payer name, payment currency, payment terms, and conditions, billing date.
Item:
Billing document can contain one or more sales items; it contains data about the item number, material name, weight and invoiced quantity.
a. Sales order:
An internal document in an organization, which contains required information to fill the customer order in a consistent and standardized form called as sales order.
Structure of the sales order document:
 The above diagram represents a standard sales order with some data filled in it by company for its customer "Butterfly".
The above diagram represents a standard sales order with some data filled in it by company for its customer "Butterfly".Standard sales order document is split into three sections:
• Header
• Item
• Schedule lines
Header:
The header section in the sales order document contains valid data for the entire sales order. Examples are dates, PO number of a customer, total order and partner functions.
Item:
A sales order document can contain one or more sales items; it contains data about the item included in the sales order. Examples of sales items are item number, material name and quantity.
Schedule lines:
The last section in the sales order document is schedule lines, which specifies delivery dates and quantity of the delivery on the specified date. One or more schedule lines can be included in a document item.
b. Delivery document:
Delivery document is the central document for shipping a material. It contains data about the materials, which are to be shipped, name of the partner function and location of the plant from which the material is shipped.
Structure of the delivery document:
 The above diagram represents a standard delivery document with some data filled in it by company for its customer "Butterfly".
The above diagram represents a standard delivery document with some data filled in it by company for its customer "Butterfly".Standard delivery document is split into two sections:
• Header
• Item
Header:
The header section in the delivery document contains valid data for the entire document. Data such as delivery date, partner functions (ship-to party), shipping address, and total quantity.
Item:
Delivery document can contain one or more sales items; it contains data about the shipment. The data such as item number, material name, weight, and quantity.
c. Billing document:
Documents related with payment for a material such as invoices, debit and credit memos are created with the help of billing. Billing document can be made for the materials that has been shipped or for the materials that is yet to be delivered.
Structure of the billing document:
 The above diagram represents a standard billing document with some data filled in it by company for its customer "Butterfly".
The above diagram represents a standard billing document with some data filled in it by company for its customer "Butterfly".Standard billing document is split into two sections:
• Header
• Item
Header:
The header section in the billing document contains data used for partner identification. Data such as partner functions (ship-to party), payer name, payment currency, payment terms, and conditions, billing date.
Item:
Billing document can contain one or more sales items; it contains data about the item number, material name, weight and invoiced quantity.
4
Explain the relationship between each of the following pairs of key elements of the fulfi llment process:
a. Quotations and sales orders
b. Sales orders and deliveries
c. Deliveries and transfer orders
d. Deliveries and billing documents
a. Quotations and sales orders
b. Sales orders and deliveries
c. Deliveries and transfer orders
d. Deliveries and billing documents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Explain how the steps in the fulfi llment process impact the general ledger accounts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Briefl y discuss the organizational levels relevant to the fulfi llment pro-cess. Be sure to explain the relationships among the various levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
How do companies manage payments that are less than the amount of the invoice?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is a distribution chain? How is it relevant to the fulfi llment process?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Briefl y describe the credit management process. Which steps of the fulfi ll-ment process are relevant to credit management?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Explain the relationships among the following organizational levels: sales organization, distribution channel, division, and sales area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Briefl y explain how the fulfi llment process is integrated with other processes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is a credit control area? Explain the difference between a centralized and a decentralized model of credit control areas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is a document fl ow?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Briefl y discuss the master data relevant to the fulfi llment process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Provide examples of works lists and online lists associated with the fulfi ll-ment process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Explain the relationship between the master data and organizational data in the fulfi llment process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Provide an example of reporting using standard analysis in fulfi llment. Make certain to include the concept of drill down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Describe, with examples, the data in the three segments of a customer master.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
At what organizational levels are the material master defi ned as it relates to the fulfi llment process? Provide examples of data in the material master.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Explain the role of each partner function in the fulfi llment process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the purpose of a customer-material info record? Provide exam-ples of the types of data it contains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
How is pricing determined in the fulfi llment process? Provide examples of data relevant to pricing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



