Deck 11: Pharmacology and Toxicology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/509
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Pharmacology and Toxicology
1
A newborn is being evaluated due to low growth perecentile. the patient is delivered via elective cesarean section at 38 weeks gestation. APGAR scores are 8 and 9 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. Head circumference measures <10th percentile, and the placenta has numerous calcifications. Serology is consistent with congenital toxoplasmosis. As part of treatment, he is prescribed a combination of pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine. A medical student in the round has asked about the reason to use two different medications to treat this patient?
A)Broader spectrum of coverage
B)Enhanced intracellular drug penetration
C)Enzymatic inhibition of an inactivating enzyme
D)Reduced urinary excretion of active metabolites
E)Synergistic reduction of DNA synthesis
A)Broader spectrum of coverage
B)Enhanced intracellular drug penetration
C)Enzymatic inhibition of an inactivating enzyme
D)Reduced urinary excretion of active metabolites
E)Synergistic reduction of DNA synthesis
Synergistic reduction of DNA synthesis
2
A 17-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her mother for the evaluation of irregular menstrual bleeding. Menses have occurred at 60- to 90-day intervals since menarche at the age of 12 years. Her last menstrual period was 4 weeks ago. She is sexually active with one male partner, and they use condoms consistently. She reports that she currently has no desire to have children. She is 165 cm (5 ft 5 in) tall and weighs 85 kg (187 lb); BMI is 31 kg/m2. Examination shows scattered pustules on the forehead and oily skin. There is coarse hair on the chin and upper lip. Fingerstick blood glucose concentration is 190 mg/dL. A urine pregnancy test is negative. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
A)Letrozole
B)Danazol
C)Leuprolide
D)Clomiphene citrate
E)Metformin
F)Combination oral contraceptives
G)Insulin
A)Letrozole
B)Danazol
C)Leuprolide
D)Clomiphene citrate
E)Metformin
F)Combination oral contraceptives
G)Insulin
Combination oral contraceptives
3
A 60-year-old male is admitted to the hospital after an infectice endocardaitis diagnosis. As part of the patient's treatment, 240 mg of intravenous gentamicin is started. The pharmacy calculates that, in this patient, gentamicin has a volume of distribution of 30 L, a half-life of 4 hours, and demonstrates first-order and one-compartment kinetics. Which of the following is the most likely serum drug concentration just before the next dose 8 hours later?
A)0)5 mg/L
B)1 mg/L
C)1)5 mg/L
D)2 mg/L
E)3 mg/L
A)0)5 mg/L
B)1 mg/L
C)1)5 mg/L
D)2 mg/L
E)3 mg/L
2 mg/L
4
A 57-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department because of crampy abdominal pain and foul-smelling, watery diarrhea. One week ago, she underwent treatment of cellulitis with clindamycin. Her temperature is 38.4°C (101.1°F). Abdominal examination shows mild tenderness in the left lower quadrant. Her leukocyte count is 12,800/mm3. An enzyme immunoassay is positive for glutamate dehydrogenase antigen and toxins A and B. Treatment is begun with a drug that inhibits the sigma subunit of the RNA polymerase. The patient was most likely treated with which of the following drugs?
A)Vancomycin
B)Clindamycin
C)Moxifloxacin
D)Metronidazole
E)Fidaxomicin
A)Vancomycin
B)Clindamycin
C)Moxifloxacin
D)Metronidazole
E)Fidaxomicin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A 35-year-old women is brought to the hospital due to fever, chills and malaise. She has a history of reccurent urinary tract infection. The patient is febrile, tachycardic, and hypotensive. on exam, she has a costovertebral angle tenderness. urinalysis shows many white blood cell. An imaging reveales a nephrogenic abscess. The patient is prescribed an intravenous antibiotic administered every 12 hours. Calculation of the maintenance dose will most likely require which of the following parameters?
A)Drug clearance rate
B)Number of doses needed to reach steady state
C)Size of the loading dose
D)Total body weight of the patient
E)Volume of distribution of the drug
A)Drug clearance rate
B)Number of doses needed to reach steady state
C)Size of the loading dose
D)Total body weight of the patient
E)Volume of distribution of the drug

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A 47-year-old man with gastroesophageal reflux disease comes to the physician because of severe burning chest pain and belching after meals. He has limited his caffeine intake and has been avoiding food close to bedtime. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy shows erythema and erosions in the distal esophagus. Which of the following is the mechanism of action of the most appropriate drug for this patient?
A)Enhancement of the mucosal barrier
B)Inhibition of D2 receptors
C)Neutralization of gastric acid
D)Inhibition of H2 receptors
E)Inhibition of ATPase
A)Enhancement of the mucosal barrier
B)Inhibition of D2 receptors
C)Neutralization of gastric acid
D)Inhibition of H2 receptors
E)Inhibition of ATPase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A pharmacist is developing a new medication to treat a resistant psudomonaus infection. It has a volume of distribution of 11L. It is eliminated by first-order kinetics and has a half-life of 10 hours. If given by a continuous infusion, approximately how much time would it require for the drug to achieve a 95% plasma steady state concentration?
A)10 hours
B)20 hours
C)30 hours
D)40 hours
A)10 hours
B)20 hours
C)30 hours
D)40 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A 47-year-old man with gastroesophageal reflux disease comes to the physician because of severe burning chest pain and belching after meals. He has limited his caffeine intake and has been avoiding food close to bedtime. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy shows erythema and erosions in the distal esophagus. Which of the following is the mechanism of action of the most appropriate drug for this patient?
A)Enhancement of the mucosal barrier
B)Inhibition of D2 receptors
C)Neutralization of gastric acid
D)Inhibition of H2 receptors
E)Inhibition of ATPase
A)Enhancement of the mucosal barrier
B)Inhibition of D2 receptors
C)Neutralization of gastric acid
D)Inhibition of H2 receptors
E)Inhibition of ATPase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A group of scientists is working on new osteoporosis drugs. They are testing Substance X, a new drug that exhibits the following metabolic effects when administered via infusion in varying doses (as shown in the graphs below). 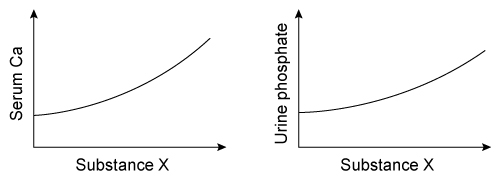 Which of the following most closely resembles the metabolic effects of Substance X?
Which of the following most closely resembles the metabolic effects of Substance X?
A)1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D analog
B)Fibroblast growth factor 23 inhibitor
C)Pyrophosphate analog
D)Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANK-L) inhibitor
E)Recombinant parathyroid hormone
 Which of the following most closely resembles the metabolic effects of Substance X?
Which of the following most closely resembles the metabolic effects of Substance X?A)1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D analog
B)Fibroblast growth factor 23 inhibitor
C)Pyrophosphate analog
D)Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANK-L) inhibitor
E)Recombinant parathyroid hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Healthy adult volunteers are enrolled in a phase I clinical trial investigating the properties of a newly developed oral antimicrobial agent. The drug is administered in different amounts to the volunteers over the course of several weeks to determine the best dosage that minimizes toxicity while maintaining trough levels above the minimum inhibitory concentration. While reviewing the data, the researchers note that the drug's half-life seems to vary amongst the study participants. An increase in which of the following pharmacologic parameters is most likely responsible for the longer half-life seen in certain individuals?
A)Drug glucuronidation
B)Glomerular filtration rate
C)Oral bioavailability
D)Peak serum drug levels
E)Volume of distribution
A)Drug glucuronidation
B)Glomerular filtration rate
C)Oral bioavailability
D)Peak serum drug levels
E)Volume of distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A 64-year-old woman with osteoarthritis is brought to the emergency room because of a 2-day history of nausea and vomiting. Over the past few weeks, she has been taking acetaminophen frequently for worsening knee pain. Examination shows scleral icterus and tender hepatomegaly. She appears confused. Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level is 845 U/L, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) is 798 U/L, and alkaline phosphatase is 152 U/L. Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of this patient's liver failure?
A)Glucuronide-conjugate formation
B)Salicylic acid formation
C)N-acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimine formation
D)N-acetylcysteine formation
E)Sulfate-conjugate formation
A)Glucuronide-conjugate formation
B)Salicylic acid formation
C)N-acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimine formation
D)N-acetylcysteine formation
E)Sulfate-conjugate formation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A 50-year-old man comes to the hospital due to recurrent left lower leg pain, and erythema. The patient's medical history includes type 2 diabetes mellitus and depression. His medications include metformin, paroxetine, and a multivitamin. The patient is diagnosed with cellulitis, admitted to the hospital, and started on antibiotics. He is continued on her home medications. Three days later, the patient becomes agitated and delirious with severe abdominal cramps and diarrhea. Her temperature is 39.2 C (102.6 F), blood pressure is 180/100 mm Hg, and heart rate is 120/min and regular. On examination, the patient is diaphoretic and tremulous, and his pupils are dilated. Bilateral hyperreflexia and ankle clonus are present. He begins to have seizures. Which of the following antibiotics was the patient most likely given to treat the cellulitis?
A)Clindamycin
B)Doxycycline
C)Linezolid
D)Penicillin
E)Vancomycin
A)Clindamycin
B)Doxycycline
C)Linezolid
D)Penicillin
E)Vancomycin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A 34-year-old man comes to the physician because of palpitations, shortness of breath, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps for 2 months. Physical examination shows cutaneous flushing of the face. Auscultation of the chest shows bilateral wheezing. A 24-hour urine collection shows increased 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIA A) concentration. A contrast-enhanced CT scan of the abdomen shows an intestinal tumor with extensive metastasis to the liver. A diagnosis of an inoperable disease is made and the patient is started on treatment with octreotide. Six weeks later, the patient's symptoms have improved except for his abdominal pain and frequent loose stools. The physician suggests enrolling the patient in a trial to test additional treatment with a new drug that has been shown to improve symptoms in other patients with the same condition. The expected beneficial effect of this new drug is most likely caused by inhibition of which of the following?
A)Dopamine Beta-hydroxylase
B)Vasoactive intestinal peptide
C)Plasma kallikrein
D)Histidine decarboxylase
E)Tryptophan hydroxylase
A)Dopamine Beta-hydroxylase
B)Vasoactive intestinal peptide
C)Plasma kallikrein
D)Histidine decarboxylase
E)Tryptophan hydroxylase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A researcher is working to develop a newly developed synthetic opioid that has twice the analgesic capability of morphine. After oral ingestion of a fixed dose by several volunteers, the plasma concentration of the drug is measured and determined to be subtherapeutic. Rectal administration of the same dose of the drug shows a plasma concentration well within the therapeutic range, almost double the level measured after oral intake. Which of the following best accounts for the observed difference in drug concentration following rectal administration when compared to oral administration?
A)Decreased drug delivery to the liver
B)Greater blood flow to this region of the intestine
C)Increased absorption rate of the drug
D)Larger mucosal surface area
E)Reduced renal blood flow
A)Decreased drug delivery to the liver
B)Greater blood flow to this region of the intestine
C)Increased absorption rate of the drug
D)Larger mucosal surface area
E)Reduced renal blood flow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A 35-year-old woman with irritable bowel syndrome comes to the physician because of increased diarrhea. She has not had any fever, bloody stools, nausea, or vomiting. The increase in stool frequency began when she started a new job. She is started on loperamide, and her symptoms improve. Which of the following is the primary mechanism of action of this drug?
A)M-opioid receptor agonism
B)5-HT3 receptor antagonism
C)Acetylcholine receptor antagonism
D)Physical protection of stomach mucosa
E)D2 receptor antagonism
F)H2 receptor antagonism
A)M-opioid receptor agonism
B)5-HT3 receptor antagonism
C)Acetylcholine receptor antagonism
D)Physical protection of stomach mucosa
E)D2 receptor antagonism
F)H2 receptor antagonism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A 79-year-old woman is brought to the hospital after falling down one hour ago. The patient reports frequent dizziness and a dizzy epiosde that leads to fall down. She has a medical history includes moderate dementia, hypertension, transient ischemic attack, depression, and chronic insomnia. In the ER she looks disoriented to time and place but otherwise is normal. Imaging shows no abnormalities. Blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 76/min and regular. The patient's medication schedule includes 10 different drugs that are used to manage her chronic conditions. Which of the following medications should be discontinued at this time?
A)Amlodipine
B)Aspirin
C)Diphenhydramine
D)Donepezil
E)Hydrochlorothiazide
F)Sertraline
A)Amlodipine
B)Aspirin
C)Diphenhydramine
D)Donepezil
E)Hydrochlorothiazide
F)Sertraline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A 48-year-old woman comes to the physician because of recurrent right upper abdominal pain for 3 weeks. The pain usually occurs after meals and tends to radiate to the right shoulder. She reports that she otherwise feels well. She has more energy since she started an intermittent fasting diet and has rapidly lost 9.0 kg (20 lbs). She is 160 cm (5 ft 3 in) tall and weighs 100 kg (220 lb); BMI is 39 kg/m2. Physical examination shows a nontender abdomen. Abdominal ultrasonography shows several small stones in the gallbladder without calcification. When discussing treatment options, she states that she does not wish to undergo surgery and asks about other possibilities. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy to address the underlying cause of this patient's condition?
A)Gemfibrozil
B)Ursodeoxycholic acid
C)Ezetimibe
D)Dicyclomine
E)Colestipol
F)Hydromorphone
A)Gemfibrozil
B)Ursodeoxycholic acid
C)Ezetimibe
D)Dicyclomine
E)Colestipol
F)Hydromorphone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A pharmacist is trying to study the effect of tamoxifen on treatment of patient with recurrent breast cancer. He also detects that the serum level of the active tamoxifen metabolites are low between the relapsed patients. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the drug's ineffectiveness in this subset of patients?
A)Activating mutation affecting a downstream signal transducer
B)Decreased hepatic N-acetyltransferase activity
C)Deficiency of thiopurine methyltransferase enzyme
D)Overexpression of P-glycoprotein in the tumor cells
E)Polymorphism of a cytochrome P450 enzyme
A)Activating mutation affecting a downstream signal transducer
B)Decreased hepatic N-acetyltransferase activity
C)Deficiency of thiopurine methyltransferase enzyme
D)Overexpression of P-glycoprotein in the tumor cells
E)Polymorphism of a cytochrome P450 enzyme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A 36-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his girlfriend because of increasing confusion for the past 6 hours. He drinks large amounts of alcohol daily and occasionally uses illicit drugs. He is lethargic and oriented only to person. Physical examination shows jaundice, hepatomegaly, and scattered petechiae over the trunk and back. Neurologic examination shows normal, reactive pupils and a flapping tremor when the wrists are extended. A drug with which of the following mechanism of action would be most appropriate for this patient's condition?
A)Inhibition of M-opioid receptors
B)Inhibition of D2 receptors
C)Excretion of NH4
D)Excretion of free iron
E)Activation of GABA receptors
F)Production of NH3
G)Production of glutathione
A)Inhibition of M-opioid receptors
B)Inhibition of D2 receptors
C)Excretion of NH4
D)Excretion of free iron
E)Activation of GABA receptors
F)Production of NH3
G)Production of glutathione

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A 72-year-old woman comes to the physician for difficulty swallowing and a burning sensation in her throat for the past 4 weeks. She has increased her fluid consumption to help with swallowing when eating. She reports having used new medication for osteoprosis. She uses a daily low-dose inhaled corticosteroid and an albuterol inhaler as needed for allergic asthma. She is 170 cm (5 ft 6 in) tall and weighs 75 kg (165 lbs); her BMI is 26 kg/m2. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows no abnormalitie. It is determined that the patient's current symptoms are caused by one of her medications, which is discontinued. Her symptoms subsequently resolve. The medication responsible for this patient's presentation is also associated with which of the following side effects?
A)Chronic kidney disease
B)Hypercalcemia
C)Osteonecrosis of the jaw
D)Venous thromboembolism
E)Vitamin B12 deficiency
A)Chronic kidney disease
B)Hypercalcemia
C)Osteonecrosis of the jaw
D)Venous thromboembolism
E)Vitamin B12 deficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Eight weeks after starting a new weight-loss medication, a 43-year-old woman with obesity comes to the physician because of greasy diarrhea, excessive belching, and flatulence. She also complains of progressively worsening night-time vision. She has had no fever, chills, or vomiting. Physical examination shows dry, scaly skin on her extremities and face. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism of action of the drug she is taking?
A)Stimulation of monoamine neurotransmitter release
B)Inhibition of serotonin reuptake
C)Stimulation of norepinephrine release
D)Inhibition of lipase
E)Secretion of glucose-dependent insulin
A)Stimulation of monoamine neurotransmitter release
B)Inhibition of serotonin reuptake
C)Stimulation of norepinephrine release
D)Inhibition of lipase
E)Secretion of glucose-dependent insulin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A 70-year-old man with metastatic prostatic cancer is brought to the hospital due to worsining fatigue for the past several days. A year ago, the patient was diagnosed with prostatic cancer, which has progressed despite chemotherapy treatment and metastasized to the bone. The patient is receiving palliative care, and her pain has been adequately controlled with a stable dose of oral morphine. Temperature is 36.7 C (98 F), blood pressure is 110/62 mm Hg, pulse is 92/min, and respirations are 8/min. On physical examination, the patient is somnolent and responds to painful stimuli only. The pupils are small and sluggish to react. The lungs are clear to auscultation, and heart sounds are normal. The abdomen is soft and nondistended. Arterial blood gas analysis shows respiratory acidosis. Which of the following medication-related events most likely precipitated her current condition?
A)Decreased first-pass metabolism
B)Decreased hepatic metabolism
C)Increased enterohepatic circulation
D)Increased metabolite accumulation
E)Increased volume of distribution
A)Decreased first-pass metabolism
B)Decreased hepatic metabolism
C)Increased enterohepatic circulation
D)Increased metabolite accumulation
E)Increased volume of distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A 24-year-old nulligravid woman comes to the physician for the evaluation of an abnormal hair growth on her face. She is 161 cm (5 ft 3 in) tall and weighs 80 kg (176 lb); BMI is 31 kg/m2. Examination shows moderate obesity with mild hirsutism on the face and chest. The patient is initiated on a combination oral contraceptive. Which of the following describes the primary mechanism by which this agent reduces hirsutism?
A)Blockade of ornithine decarboxylase
B)Decreased androgen production
C)Increased insulin sensitivity
D)Inhibition of 5-alpha-reductase
E)Inhibition of androgen receptors
A)Blockade of ornithine decarboxylase
B)Decreased androgen production
C)Increased insulin sensitivity
D)Inhibition of 5-alpha-reductase
E)Inhibition of androgen receptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An investigator is studying the effect of a new drug on gastric mucosa cells. She finds that under physiologic conditions, the new drug acts as a competitive antagonist of a G-protein coupled receptor that is located on the cell membrane of parietal cells. Activation of this type of receptor increases the intracellular concentration of cyclic adenosine monophosphate. The mechanism of action of the new drug is most similar to that of which of the following?
A)Atropine
B)Octreotide
C)Misoprostol
D)Cimetidine
E)Dexlansoprazole
A)Atropine
B)Octreotide
C)Misoprostol
D)Cimetidine
E)Dexlansoprazole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A 50-year-old woman is diagnosed with metastatic cervical cancer. The patient is treated with an opioid analgesic for bone pain that is well controlled . and recently she feel that the dose is ineffective and reports nausea, itching, and constipation. Her physician suggests to increase the opioid dose. The patient is concerned about side effects with higher dosages, noting that her son has a history of opioid dependence, and "I watched him suffer a lot of bad reactions." The physician explains the concept of tolerance to opioids and that high doses are commonly required to control pain. Over the next few weeks, the patient would likely experience which of the following?
A)Euphoria
B)Increased itching
C)Persistent nausea and vomiting
D)Respiratory depression
E)Sedation
F)Urinary retention.
G)Worsening constipation
A)Euphoria
B)Increased itching
C)Persistent nausea and vomiting
D)Respiratory depression
E)Sedation
F)Urinary retention.
G)Worsening constipation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A 58-year-old man is brought to the physician by his wife because of a 10-day history of progressively worsening diarrhea and bloating. He has been having 8-10 episodes of loose, watery stools each day, including during the night. He does not have nausea, vomiting, or blood in his stool. He has a history of metastatic colon cancer and started chemotherapy 2 weeks ago. He also has Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, for which he takes procainamide. He smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 25 years and drank 2-3 beers daily but quit both last year when his grandson was born. His temperature is 37.3°C (99.1°F), pulse is 114/min, respirations are 22/min, and blood pressure is 105/68 mm Hg. Physical examination shows pale skin with a decreased turgor; capillary refill time is 2 seconds. His abdomen is distended and tender on palpation; bowel sounds are hyperactive. Laboratory studies show:
Hematocrit 55%
Leukocyte count 18,000/mm3
Serum
Na+ 149 mEq/L
K+ 3.3 mEq/L
Cl- 117 mEq/L
Magnesium 1.8 mg/dL
HCO3- 20 mEq/L
Glucose 78 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.0 mg/dL
Blood and stool cultures are negative. A test for Clostridioides difficile toxins is negative. In addition to oral rehydration, which of the following is the most appropriate initial step in management?
A)Rectal budesonide
B)Oral rifaximin
C)Oral vancomycin
D)Intravenous octreotide
E)Oral loperamide
Hematocrit 55%
Leukocyte count 18,000/mm3
Serum
Na+ 149 mEq/L
K+ 3.3 mEq/L
Cl- 117 mEq/L
Magnesium 1.8 mg/dL
HCO3- 20 mEq/L
Glucose 78 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.0 mg/dL
Blood and stool cultures are negative. A test for Clostridioides difficile toxins is negative. In addition to oral rehydration, which of the following is the most appropriate initial step in management?
A)Rectal budesonide
B)Oral rifaximin
C)Oral vancomycin
D)Intravenous octreotide
E)Oral loperamide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A 60-year-old amn is being evaluated for occasional pain the chest which resolves with sublingual nirtoglycerin. He has a chronic stable angina and hypertesnion for which he takes multiple medications for his conditions.Blood pressure is 140/80 mm Hg and pulse is 68/min and regular. Examination reveals normal heart sounds. While discussing a plan to start isosorbide dinitrate therapy, the patient becomes concerned about the high dose of oral isosorbide dinitrate compared to sublingual nitroglycerin. Which of the following is the most likely reason for using a high dose of oral nitrate?
A)Drug tolerance prevention
B)High first-pass metabolism
C)High serum protein binding
D)High volume of distribution
E)Low intestinal absorption
A)Drug tolerance prevention
B)High first-pass metabolism
C)High serum protein binding
D)High volume of distribution
E)Low intestinal absorption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A 54-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife because of burning oral mucosal pain, chest pain, and shortness of breath that began after ingestion of an unknown substance one hour ago. The patient reports that the pain is worse when swallowing. Two years ago, he was diagnosed with major depressive disorder but does not adhere to his medication regimen. The patient does not answer questions about suicidal ideation and the substance he ingested. He works as a farmer. His wife reports that he smokes one pack of cigarettes and drinks 6 oz of homemade vodka daily. The patient is oriented to person, place, and time. His pulse is 95/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 130/85 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 95%. Examination of the oropharynx shows profuse salivation with mild erythema of the buccal mucosa, tongue, and epiglottis area. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's clinical findings?
A)Potassium hydroxide
B)Parathion
C)Ethylene glycol
D)Methanol
E)Amitriptyline
A)Potassium hydroxide
B)Parathion
C)Ethylene glycol
D)Methanol
E)Amitriptyline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A 60-year-old amn is being evaluated for occasional pain the chest which resolves with sublingual nirtoglycerin. He has a chronic stable angina and hypertesnion for which he takes multiple medications for his conditions.Blood pressure is 140/80 mm Hg and pulse is 68/min and regular. Examination reveals normal heart sounds. While discussing a plan to start isosorbide dinitrate therapy, the patient becomes concerned about the high dose of oral isosorbide dinitrate compared to sublingual nitroglycerin. Which of the following is the most likely reason for using a high dose of oral nitrate?
A)Drug tolerance prevention
B)High first-pass metabolism
C)High serum protein binding
D)High volume of distribution
E)Low intestinal absorption
A)Drug tolerance prevention
B)High first-pass metabolism
C)High serum protein binding
D)High volume of distribution
E)Low intestinal absorption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Four days after undergoing a total abdominal hysterectomy for atypical endometrial hyperplasia, a 59-year-old woman reports abdominal bloating and discomfort. She has also had nausea without vomiting. She has no appetite despite not having eaten since the surgery and drinking only sips of water. Her postoperative pain has been well controlled on a hydromorphone patient-controlled analgesia (PC A) pump. Her indwelling urinary catheter was removed on the second postoperative day and she is now voiding freely. Although she lays supine in bed for most of the day, she is able to walk around the hospital room with the help of a physical therapist. Her temperature is 36.5°C (97.7°F), pulse is 84/min, respirations are 10/min, and blood pressure is 132/92 mm Hg. She is 175 cm (5 ft 9 in) tall and weighs 115 kg (253 lb); BMI is 38 kg/m2. Examination shows a mildly distended, tympanic abdomen; bowel sounds are absent. Laboratory studies are within normal limits. An x-ray of the abdomen shows uniform distribution of gas in the small bowel, colon, and rectum without air-fluid levels. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
A)Gastrografin enema
B)Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
C)Reduce use of opioid therapy
D)Colonoscopy
E)Return to operating room for bowel resection
F)Begin total parenteral nutrition
G)Slowly advance diet
A)Gastrografin enema
B)Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
C)Reduce use of opioid therapy
D)Colonoscopy
E)Return to operating room for bowel resection
F)Begin total parenteral nutrition
G)Slowly advance diet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A new aminoglycoside antibiotic is developed to treat resistent pseudomonas . The volume of distribution of the drug is measured in a group of volunteers and is determined to be 4.5 L. This new drug is most likely to have which of the following properties?
A)It has low molecular weight
B)It is lipophilic
C)It does not bind to albumin
D)It is highly charged
E)It has high oral bioavailability
A)It has low molecular weight
B)It is lipophilic
C)It does not bind to albumin
D)It is highly charged
E)It has high oral bioavailability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A 54-year-old woman comes to the physician because of abdominal distention and mild diffuse abdominal discomfort for the past week. She has not had nausea, vomiting, fever, or chills. She was diagnosed with alcoholic liver cirrhosis 2 years ago. Examination shows a protruding, distended abdomen that is dull to percussion with a positive fluid wave. Ultrasonography shows mild to moderate ascites. Appropriate treatment of the patient's condition is started. Four days later, the patient experiences palpitations and chest pain at home. She is brought to the emergency department, where her temperature is 37.3°C (99.1°F), pulse is 182/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 82/50 mm Hg. An ECG shows ventricular tachycardia. Initial laboratory studies show:
Serum
Na+ 131 mEq/L
K+ 2.9 mEq/L
Cl- 92 mEq/L
Bicarbonate 34 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen 42 mg/dL
Creatinine 4.8 mg/dL
Glucose 90 mg/dL
Ca2+ 8.1 mg/dL
Mg2+ 1.3 mEq/L
Phosphate 4.7 mg/dL
Arterial Blood Gas
PH 7.52
PCO2 45 mm Hg
PO2 90.2 mm Hg
She is successfully cardioverted to normal sinus rhythm. Which of the following treatments is most likely responsible for this patient's presentation?
A)Hydrochlorothiazide
B)Furosemide
C)Acetazolamide
D)Lisinopril
E)Spironolactone
F)Mannitol
Serum
Na+ 131 mEq/L
K+ 2.9 mEq/L
Cl- 92 mEq/L
Bicarbonate 34 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen 42 mg/dL
Creatinine 4.8 mg/dL
Glucose 90 mg/dL
Ca2+ 8.1 mg/dL
Mg2+ 1.3 mEq/L
Phosphate 4.7 mg/dL
Arterial Blood Gas
PH 7.52
PCO2 45 mm Hg
PO2 90.2 mm Hg
She is successfully cardioverted to normal sinus rhythm. Which of the following treatments is most likely responsible for this patient's presentation?
A)Hydrochlorothiazide
B)Furosemide
C)Acetazolamide
D)Lisinopril
E)Spironolactone
F)Mannitol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A researcher is deveolping a new medication to treat a severe kidney infection, which is desired to be non-renal clearance to decrease the side effect on the kidenys at the same time to be metabolised and cleared in the liver hepatic metabolism. Which of the following characteristics should the antibiotic also have if hepatic metabolism and clearance is desired?
A)Low volume of distribution
B)Poor oral absorption
C)High lipophilicity
D)Low rate of redistribution
E)Poor penetration into the CNS
A)Low volume of distribution
B)Poor oral absorption
C)High lipophilicity
D)Low rate of redistribution
E)Poor penetration into the CNS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A 23-year-old woman comes to the physician due to acute nausea and vomiting. She recently returned from a vacation to Mexico and started to feel "queasy" on the last day of her trip. The patient then developed nausea with frequent vomiting and intermittent bouts of watery diarrhea. She has no visible blood in her stools. Her temperature is 36.8 C (98 F), blood pressure is 118/70 mm Hg, pulse is 86/min, and respirations are 12/min. Abdominal examination shows mild tenderness and increased bowel sounds. Improvement of this patient's vomiting would best be achieved by a medication targeting which of the following receptors?
A)5-HT3 receptor
B)M-opioid receptor
C)Dopamine receptor
D)Histamine H1 receptor
E)Histamine H2 receptor
F)Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor
G)Somatostatin receptor
A)5-HT3 receptor
B)M-opioid receptor
C)Dopamine receptor
D)Histamine H1 receptor
E)Histamine H2 receptor
F)Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor
G)Somatostatin receptor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A 50-year-old man is brought to the hospital due to refuse to eat over the past 2 days. He states that he has mouth ulcers which are very painful. He has a history of chronic kideny disease and a recent psoriasis diagnosis for which he takes a methotrexate therapy. His therapy regimen is supposed to be every 3 days but he reports taking his medication every day. Temperature is 38.1 C (100.6 F). Examination reveals multiple aphthous ulcers in the oral pharynx. A complete blood cell count is as follows:  Which of the following is the best next step in management?
Which of the following is the best next step in management?
A)Allopurinol
B)Amifostine
C)Dexrazoxane
D)Filgrastim
E)Folinic acid
F)Mesna
G)Ondansetron
 Which of the following is the best next step in management?
Which of the following is the best next step in management?A)Allopurinol
B)Amifostine
C)Dexrazoxane
D)Filgrastim
E)Folinic acid
F)Mesna
G)Ondansetron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A 78-year-old male nursing home resident is brought to the physician because of abdominal pain and discomfort. He has a history of advanced dementia and is only partially able to verbalize his symptoms. He has had intermittent abdominal discomfort for years, with no other related symptoms. He denies diarrhea and rectal bleeding but has not had a bowel movement in approximately 5 days. The patient is largely bed-bound, and only has minimal activity with the help of nurses and physical therapists. Past regular colonoscopies have shown only benign lesions. His other medical problems include dementia, coronary artery disease, hypertension, spinal stenosis, and osteoarthritis of his hips and knees. Abdominal examination does not show tenderness, masses, or hepatosplenomegaly, although fullness is appreciated. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Polyethylene glycol is administered and produces a bowel movement within 24 hours. The mechanism of action of polyethylene glycol in this patient is most similar to the pathophysiology of which of the following disorders?
A)Irritable bowel syndrome
B)Crohn's disease
C)Lactase deficiency
D)Carcinoid syndrome
E)Rectal prolapse
A)Irritable bowel syndrome
B)Crohn's disease
C)Lactase deficiency
D)Carcinoid syndrome
E)Rectal prolapse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A 72-year-old man comes to the office for evaluation of constipation. His stools have been hard and pelletlike for as long as he can remember. The patient has a bowel movement every 3-4 days and frequently strains when using the bathroom. He has had associated abdominal discomfort but no hematochezia, melena, vomiting, or unexpected weight changes. The symptoms have not improved despite fiber supplementation. Vital signs are within normal limits. The abdomen is mildly distended with decreased bowel sounds. In addition to increasing water consumption, the patient is advised to try bisacodyl for constipation. What is the primary mechanism of action of this medication?
A)Decreases surface tension of stool
B)Draws water into the stool by creating an osmotic gradient
C)Draws water into the stool by directly activating chloride channels
D)Improves peristalsis by blocking mu-receptors
E)Improves peristalsis by stimulating enteric nerves
A)Decreases surface tension of stool
B)Draws water into the stool by creating an osmotic gradient
C)Draws water into the stool by directly activating chloride channels
D)Improves peristalsis by blocking mu-receptors
E)Improves peristalsis by stimulating enteric nerves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A 22-year-old woman is evaluated in the office due to progressive acne on her face, chest and back. Although, she takes oral doxycyclin regularly, her acne has worsened over last month. The patient was recently diagnosed with iron deficiency anemia due to abnormal uterine bleeding and began taking a combined oral contraceptive and an iron supplement. Physical examination shows comedones and pustules on her face and upper back. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's worsening symptoms?
A)Adverse effect of the hormonal therapy
B)Bacterial resistance to the antibiotic
C)Decreased absorption of the antibiotic
D)Increased clearance of the antibiotic
E)Increased protein binding of the antibiotic
A)Adverse effect of the hormonal therapy
B)Bacterial resistance to the antibiotic
C)Decreased absorption of the antibiotic
D)Increased clearance of the antibiotic
E)Increased protein binding of the antibiotic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A 33-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 4-month history of intermittent lower abdominal cramps associated with diarrhea, bloating, and mild nausea. During this period, she has had a 5-kg (11-lb) weight loss. She feels like she cannot fully empty her bowels. She has no history of serious illness. She has a high-fiber diet. Her father is of Ashkenazi Jewish descent. She has smoked 2 packs of cigarettes daily for 15 years. She appears well. Her temperature is 36.9°C (98.5°F), pulse is 90/min, and blood pressure is 130/90 mm Hg. The lungs are clear to auscultation. Cardiac examination shows no murmurs, rubs, or gallops. The abdomen is tender to palpation without rebound or guarding. Abdominal CT scan reveals inflammatory changes affecting the ascending colon, sigmoid colon, and terminal ileum. Intestinal biopsy reveals the following: 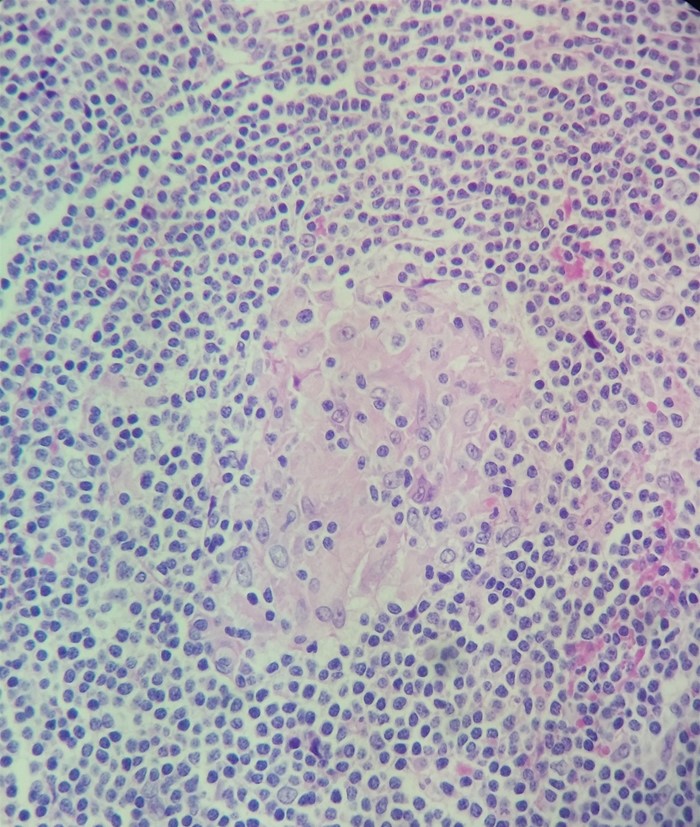 Effective treatment of this patient's condition could be achieved by targeting which of the following molecules?
Effective treatment of this patient's condition could be achieved by targeting which of the following molecules?
A)BCR-ABL protein tyrosine kinase
B)CD20 lymphocyte antigen
C)mTOR protein kinase
D)Programmed cell death-1 protein
E)Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
 Effective treatment of this patient's condition could be achieved by targeting which of the following molecules?
Effective treatment of this patient's condition could be achieved by targeting which of the following molecules?A)BCR-ABL protein tyrosine kinase
B)CD20 lymphocyte antigen
C)mTOR protein kinase
D)Programmed cell death-1 protein
E)Tumor necrosis factor-alpha

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A 68-year-old woman comes to the physician due to nausea and anorexia. Three months ago, she underwent heart transplantation for restrictive cardiomyopathy and she is treated with cyclosporine Her pulse is 76/min and blood pressure is 158/82 mm Hg. There is a well-healed scar on her chest. Serum creatinine is 3.4 mg/dL, and the serum cyclosporine level is markedly increased. A month ago, he had normal blood pressure and normal levels of cyclosporine and serum creatinine
Further questioning reveals that the patient has been drinking increased amounts of grapefruit juice lately as part of an attempt to improve his overall health. Which of the following mechanisms is most likely responsible for this patient's current condition?
A)Alteration of gastric acidity
B)Inhibition of cytochrome P450 enzymes in the gut wall
C)Modification of transmembrane drug transport
D)Pharmacodynamic potentiation
E)Reduction of plasma protein binding
Further questioning reveals that the patient has been drinking increased amounts of grapefruit juice lately as part of an attempt to improve his overall health. Which of the following mechanisms is most likely responsible for this patient's current condition?
A)Alteration of gastric acidity
B)Inhibition of cytochrome P450 enzymes in the gut wall
C)Modification of transmembrane drug transport
D)Pharmacodynamic potentiation
E)Reduction of plasma protein binding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A 64-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to intractable nausea and vomiting. She has not been able to keep anything down and feels weak and tired. The patient has had no diarrhea, constipation, or abdominal pain. She was diagnosed with breast cancer 4 weeks ago and received her first cycle of chemotherapy 1 week ago. Vital signs are within normal limits. Mucous membranes are dry. Cardiopulmonary examination is normal. Bowel sounds are normal. Which of the following agents would be most helpful in treating this patient's symptoms?
A)Histamine H1 blocker
B)Motilin receptor agonist
C)Mu opioid receptor agonist
D)Muscarinic M1 receptor antagonist
E)Serotonin 5-HT3 receptor antagonist
A)Histamine H1 blocker
B)Motilin receptor agonist
C)Mu opioid receptor agonist
D)Muscarinic M1 receptor antagonist
E)Serotonin 5-HT3 receptor antagonist

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A 68-year-old man comes to the physician because of severe muscle aches and fatigue for 2 days. Last week he was diagnosed with atypical pneumonia and treated with clarithromycin. He has hyperlipidemia and coronary artery disease with an acute myocardial infarction 2 years ago. Physical examination shows diffuse tenderness in the proximal muscles of the upper and lower extremities. Serum creatine kinase activity is elevated. Which of the following drug combinations is most likely responsible for this patient's condition?
A)Atorvastatin and cholestyramine
B)Atorvastatin and ezetimibe
C)Atorvastatin and gemfibrozil
D)Gemfibrozil and ezetimibe
E)Niacin and ezetimibe
F)Niacin and gemfibrozil
A)Atorvastatin and cholestyramine
B)Atorvastatin and ezetimibe
C)Atorvastatin and gemfibrozil
D)Gemfibrozil and ezetimibe
E)Niacin and ezetimibe
F)Niacin and gemfibrozil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A group of researchers is looking into why people who have had a gastrectomy lose more weight than can be explained by dietary changes alone. They recruit several subjects for a clinical study who have had distal gastrectomy for benign gastric-outlet obstruction. Control subjects with similar baseline weights are also enrolled and instructed to follow a diet similar to the postgastrectomy subjects during the study period. In both groups, plasma levels of several hormones are measured serially over a 24-hour period. Levels of one of the hormones are shown in the graph below:  This profile most likely represents which of the following hormones?
This profile most likely represents which of the following hormones?
A)Cholecystokinin
B)Gastrin
C)Ghrelin
D)Insulin
E)Leptin
F)Motilin
 This profile most likely represents which of the following hormones?
This profile most likely represents which of the following hormones?A)Cholecystokinin
B)Gastrin
C)Ghrelin
D)Insulin
E)Leptin
F)Motilin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A 68-year-old man comes to the physician because of severe muscle aches and fatigue for 2 days. Last week he was diagnosed with atypical pneumonia and treated with clarithromycin. He has hyperlipidemia and coronary artery disease with an acute myocardial infarction 2 years ago. Physical examination shows diffuse tenderness in the proximal muscles of the upper and lower extremities. Serum creatine kinase activity is elevated. Which of the following drug combinations is most likely responsible for this patient's condition?
A)Atorvastatin and cholestyramine
B)Atorvastatin and ezetimibe
C)Atorvastatin and gemfibrozil
D)Gemfibrozil and ezetimibe
E)Niacin and ezetimibe
F)Niacin and gemfibrozil
A)Atorvastatin and cholestyramine
B)Atorvastatin and ezetimibe
C)Atorvastatin and gemfibrozil
D)Gemfibrozil and ezetimibe
E)Niacin and ezetimibe
F)Niacin and gemfibrozil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Dyslipidemia is diagnosed in a 34-year-old man. He also has other medical conditions, like a myocardial infarction about a week ago. At the age of 48, his father suffered a myocardial infarction and passed away. Other family members have experienced hypertension and myocardial infarctions. After suffering a myocardial infarction, the patient gave up smoking and drinking. Simvastatin and cholestyramine have been started for him. Which of the following best describes the independent effects of simvastatin and cholestyramine, respectively, on hepatic cholesterol synthesis?
A)Increase and increase
B)Increase and decrease
C)Decrease and increase
D)Decrease and decrease
E)Increase and no change
A)Increase and increase
B)Increase and decrease
C)Decrease and increase
D)Decrease and decrease
E)Increase and no change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A 46-year-old woman is admitted to the hospital because of tarry-black stools and epigastric pain for 2 weeks. The epigastric pain is relieved after meals, but worsens after 1-2 hours. She has a history of hypertension and hyperlipidemia, for which he takes amlodipine and simvastatin. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Helicobacter pylori infection is diagnosed and she is started on treatment and has had partial symptom improvement. After two weeks she presents with progressive myopathy and fatigue. Physical examination shows diffuse muscle tenderness. Laboratory evaluation reveals elevated blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine levels. Urine microscopy shows no red or white blood cells. Which of the following medications most likely precipitated this patient's current condition?
A)Amoxicillin
B)Bismuth subsalicylate
C)Calcium carbonate
D)Clarithromycin
E)Metronidazole
A)Amoxicillin
B)Bismuth subsalicylate
C)Calcium carbonate
D)Clarithromycin
E)Metronidazole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An episode of nausea and episodic abdominal pain that has been present for several months, especially after a fatty meal, brings a 52-year-old postmenopausal woman to the physician's office for evaluation. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illegal substances, and she has no history of diseases. 33 kg/m2 is her BMI. Upon physical examination, the abdomen is soft and non-tender, and the bowel sounds normally. It has an 8 centimeter liver span. Murphy's sign is negative. While an abdominal ultrasound reveals a small, non-obstructing gallstone, an abdominal x-ray shows no calcifications. The patient prefers nonoperative management. Which of the following would best treat this patient's condition?
A)Bile acid supplement
B)Cholestyramine therapy
C)Estrogen replacement therapy
D)Fenofibrate therapy
E)Iron chelation therapy
F)Phosphate-binding agent
G)Rapid weight loss
A)Bile acid supplement
B)Cholestyramine therapy
C)Estrogen replacement therapy
D)Fenofibrate therapy
E)Iron chelation therapy
F)Phosphate-binding agent
G)Rapid weight loss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A 60-year-old woman is diagnosed with breast cancer following a routine mammogram. She also has a positive lymph node metastasis for which a treatment with systemic chemotherapy is started. After, Two weeks she comes with 4 days of frequent urination, suprapubic pain, dysuria, and progressive hematuria. She has had no fevers or chills. Temperature is 37.1 C (98.8 F). Suprapubic tenderness is present on abdominal examination. Hemoglobin is 9.8 g/dL. Urinalysis shows numerous red blood cells but no leukocyte esterase or bacteria. Which of the following could have prevented this patient's current condition?
A)Dexrazoxane
B)Filgrastim
C)Folinic acid
D)Mesna
E)Ondansetron
A)Dexrazoxane
B)Filgrastim
C)Folinic acid
D)Mesna
E)Ondansetron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A 42-year-old woman visits the office complaining of nightly regurgitation and frequent episodes of burning in her chest. Hypertension is a medical history. Vital signs are in the normal range. 30 kg/m2 is the BMI. The rest of the physical examination is normal, and there is no abdominal pain. The woman displays an over-the-counter antacid that she has been using to treat her symptoms to the doctor which contains magnesium and aluminum hydroxide. Which of the following is the most likely rationale for combining both mineral salts in this antacid preparation?
A)Improve systemic absorption
B)Minimize drug interactions
C)Prevent rebound acid secretion
D)Reduce adverse effects
E)Reduce the risk of alkalosis and renal failure
A)Improve systemic absorption
B)Minimize drug interactions
C)Prevent rebound acid secretion
D)Reduce adverse effects
E)Reduce the risk of alkalosis and renal failure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A clinical trial is being conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a novel therapy to treat refractory Crohn disease. The medication is a monoclonal antibody against the a4B7 integrin, which inhibits migration of T-lymphocytes into the intestinal parenchyma and produces a gut-selective anti-inflammatory effect. Patients who have active, moderate to severe Crohn disease and have failed conventional therapy are enrolled in the study. Many of these patients have renal or hepatic dysfunction, and some take other medications that affect cytochrome P450 enzymes. Which of the following is the most appropriate dose adjustment in this patient population to decrease drug toxicity?
A)Higher dose in patients taking cytochrome P450 inducers
B)Lower dose in patients with decreased glomerular filtration
C)Lower dose in patients with hepatocellular dysfunction
D)Lower dose in patients with renal tubular dysfunction
E)No dose adjustment necessary
A)Higher dose in patients taking cytochrome P450 inducers
B)Lower dose in patients with decreased glomerular filtration
C)Lower dose in patients with hepatocellular dysfunction
D)Lower dose in patients with renal tubular dysfunction
E)No dose adjustment necessary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A 56-year-old man visits the emergency room after experiencing significant sudden widespread stomach discomfort. Epigastric pain that the patient has been dealing with for three months has responded to treatment with proton-pump inhibitors. A stiff abdomen with rebound tenderness is apparent on physical examination. Abdominal radiographs reveal free air under the diaphragm. Therapy for support is started. A massive, perforated stomach ulcer with characteristics indicative of malignancy is discovered during an exploratory laparotomy. He undergoes partial gastrectomy with gastrojejunostomy. Long-term supplementation with which of the following is most important in this patient?
A)Ascorbic acid
B)Biotin
C)Iron
D)Pantothenic acid
E)Pyridoxine
A)Ascorbic acid
B)Biotin
C)Iron
D)Pantothenic acid
E)Pyridoxine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A-60-year-old man is brought to the hospital after a sudden hand drop during breakfas meal and slurred speach which resolved after 20 minutes. The patient has had no shaking movements, headache, nausea, photophobia, or anxiety. He has a history of hypertension and hypercholesterolemia and takes amlodipine and rosuvastatin, respectively. His blood pressure is 120/75 mm Hg and pulse is 72/min and regular. Neurologic examination is unremarkable. Fingerstick glucose is within normal limits. ECG shows normal sinus rhythm. Carotid Doppler reveals mild left common carotid artery stenosis. MRI of the brain and echocardiogram are unremarkable. If the patient is started on an additional medication that is indicated for her condition, which of the following adverse effects is most likely to occur?
A)Central nervous system depression
B)Gastrointestinal bleeding
C)Hyperpnea and vertigo
D)Orthostatic hypotension
E)Sexual dysfunction
F)Urinary bladder cancer
A)Central nervous system depression
B)Gastrointestinal bleeding
C)Hyperpnea and vertigo
D)Orthostatic hypotension
E)Sexual dysfunction
F)Urinary bladder cancer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A 40-year-old woman arrives to the clinic with intermittent abdominal bloating and diarrhea that has lasted for four weeks. Although she has observed mucus in her stools, she has not seen any blood. Occasionally, the patient also has slight heartburn. She doesn't have chills, a fever, or weight loss. Additionally, the patient has detected a bad taste in dairy products, thus they are no longer consumed. Past medical history is significant for chronic allergic rhinitis. Current medications include only a multivitamin supplemen. Physical examination and vital signs are normal. After a basic evaluation, the patient is started on a trial of diphenoxylate therapy. Which of the following is the primary target of this drug?
A)Absorption
B)Digestion
C)Inflammation
D)Motility
E)Secretion
A)Absorption
B)Digestion
C)Inflammation
D)Motility
E)Secretion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A 65-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of intermittent palpitations and shortness of breath. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no other abnormalities. An ECG shows an absence of P waves, an oscillating baseline, and irregular RR intervals at a rate of approximately 95 beats per minute. she is diagnosed with atrial fibrillation and started the appropirate drugs includes warfarin. In the follow up she did well with no complians till yesterday when she presented with sudden-onset right-side weakness and difficulty speaking. Her son adds that she started taking a new drug 2 weeks ago, but he does not remember its name. Physical examination shows right hemiplegia, right hemisensory loss, expressive aphasia, and right homonymous hemianopia. MRI of the head shows a left middle cerebral artery territory infarct. Transesophageal echocardiogram reveals a small thrombus in the left atrium. This patient most likely started taking which of the following drugs recently?
A)Amiodarone
B)Cimetidine
C)Ciprofloxacin
D)Clarithromycin
E)Fluconazole
F)Penicillin V
G)St John's wort
A)Amiodarone
B)Cimetidine
C)Ciprofloxacin
D)Clarithromycin
E)Fluconazole
F)Penicillin V
G)St John's wort

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A 72-year-old man arrives at the office due to constipation. His stools have been harder, smaller, and more challenging to pass. Bloating has been linked to this, but not vomiting. Despite fiber supplements, polyethylene glycol, and bisacodyl, symptoms have not subsided. The patient received palliative chemotherapy two months ago after being recently diagnosed with metastatic pancreatic cancer. His malignancy produces excruciating stomach discomfort that requires to be treated with high-dose oxycodone. Vital indicators are in the expected range. The abdomen is mildly distended with decreased bowel sounds. Which of the following medications acts as a mu-opioid receptor antagonist that could alleviate this patient's constipation without inducing withdrawal symptoms?
A)Diphenoxylate
B)Loperamide
C)Lubiprostone
D)Methylnaltrexone
E)Naloxone
A)Diphenoxylate
B)Loperamide
C)Lubiprostone
D)Methylnaltrexone
E)Naloxone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A 45-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a 1-day history of black, tarry stools. He has also had upper abdominal pain that occurs immediately after eating. Three weeks ago, he developed lower back pain with stiffness and was started on naproxen and cyclobenzaprine. He has no prior medical conditions. He has an allergy to penicillin that causes a rash and pruritus. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy reveals gastric mucosal erythema and erosions. Which of the following best explains this patient's current symptoms?
A)Exaggerated drug sensitivity
B)Idiosyncratic drug reaction
C)Immunologic drug reaction
D)Predictable drug reaction
E)Pseudoallergic drug reaction
A)Exaggerated drug sensitivity
B)Idiosyncratic drug reaction
C)Immunologic drug reaction
D)Predictable drug reaction
E)Pseudoallergic drug reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A 78-year-old man is discovered lifeless and sent to the medical room by ambulance. He has a complicated medical history and takes a number of drugs, but there are no known drug allergies, according to the family, who arrived first. Intracranial bleeding is discovered by non-contrast CT scanning of the head. The patient is given a recombinant biologic agent that has antigen homology with factor Xa but no catalytic effect. The agent is most likely to antagonize the effects of which of the following drugs?
A)Apixaban
B)Aspirin
C)Dabigatran
D)Ticagrelor
E)Warfarin
A)Apixaban
B)Aspirin
C)Dabigatran
D)Ticagrelor
E)Warfarin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
64-year-old woman with osteoarthritis is brought to the hospital because of a 2-day history of nausea and vomiting. Over the past few weeks, she has been taking acetaminophen frequently for worsening knee pain. Examination shows scleral icterus and tender hepatomegaly. She appears confused. Pupils are normal in size and reactive to light. Neurologic examination shows no abnormalities Laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of drug toxicity in this patient?
Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of drug toxicity in this patient?
A)Cytotoxic T-cell response to hepatocyte proteins
B)Drug-mediated inhibition of bile flow
C)Drug metabolite-induced mitochondrial dysfunction
D)Drug-induced disruption of fatty acid metabolism
E)Reactive oxygen species-induced stellate cell activation
 Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of drug toxicity in this patient?
Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of drug toxicity in this patient?A)Cytotoxic T-cell response to hepatocyte proteins
B)Drug-mediated inhibition of bile flow
C)Drug metabolite-induced mitochondrial dysfunction
D)Drug-induced disruption of fatty acid metabolism
E)Reactive oxygen species-induced stellate cell activation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A 52-year-old man visits the emergency room (ED) after experiencing substernal burning pain for two hours. He took several antacid tablets at home before visiting the ED, but they did not provide any relief. Other medical issues for the patient include hypertension and hyperlipidemia. His blood pressure is 160/90 mm Hg, his temperature is 36.7 C (98 F), and his pulse is 92 beats per minute. A cardiovascular examination reveals murmur-free S1 and S2, which are also normal. No abdominal soreness is present. ST-segment depression is visible on the ECG in leads II, III, and aVF. Troponin is 0.06 ng/mL (normal <0.01 ng/mL). As part of this patient's treatment, enoxaparin therapy is initiated. This drug is expected to bind to which of the following substances in this patient's blood?
A)Antithrombin III
B)Fibrin
C)Plasminogen
D)Protein C
E)Prothrombin
A)Antithrombin III
B)Fibrin
C)Plasminogen
D)Protein C
E)Prothrombin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Parents of a 16-year-old child who has tremors and trouble walking bring him to the office. His academic performance has dropped over the past year, and he has become moodier and more aggressive. His parents also observe that he has been sleeping more than normal, and that for the past two months, he hasn't been eating well. The patient's tremor in both hands started around three weeks ago, and it is most noticeable when he reaches for something or tries to write. Over the past week, the tremor has dramatically deteriorated, and he has started to walk with an uneven, wide-based gait. Elevated serum transaminases and 24-hour urine copper excretion are seen in laboratory tests. Therapy with penicillamine is indicated for the patient. This medication primarily works through which of the following mechanisms?
A)Decreasing intestinal absorption of copper
B)Increasing urinary excretion of copper
C)Repletion of intracellular glutathione
D)Stimulation of defective gene expression
E)Stimulation of canalicular transport proteins
A)Decreasing intestinal absorption of copper
B)Increasing urinary excretion of copper
C)Repletion of intracellular glutathione
D)Stimulation of defective gene expression
E)Stimulation of canalicular transport proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A 25-year-old male visits the office complaining of recent bilateral hip pain. He had trouble walking as a result of the discomfort, which crept up on him slowly at first. The patient has never experienced trauma. His medical history is important because he has taken phenytoin for the past five years to treat a seizure disorder. The patient stays away from alcohol and tobacco use. An X-ray of the hip joint reveals diffuse cortical thinning and bilateral, symmetric, narrow radiolucent lines that are 2-3 mm wide with sclerotic borders as well as diffuse cortical thinning. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current condition?
A)Decreased aromatization of testosterone to estrogen
B)Drug-induced decoupling of bone resorption and bone formation
C)Increased drug binding to intestinal phosphorus with fecal excretion
D)Increased metabolism of 25-hydroxyvitamin D to inactive metabolites
A)Decreased aromatization of testosterone to estrogen
B)Drug-induced decoupling of bone resorption and bone formation
C)Increased drug binding to intestinal phosphorus with fecal excretion
D)Increased metabolism of 25-hydroxyvitamin D to inactive metabolites

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A 60-year-old man visits the office with low back discomfort that has persisted for two months and is unresponsive to over-the-counter medications. Sleeping is disrupted by the discomfort because it is worse at night. On examination, the prostate is indurated and hard, and the lumbar vertebrae are painful to the touch. Leuprolide therapy is initiated following a thorough assessment. Which of the following changes in testosterone (solid line) and dihydrotestosterone (dashed line) levels are most likely to occur in this patient after initiation of therapy?
A)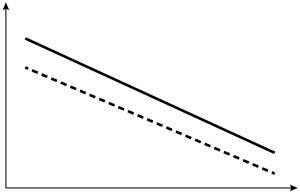
B)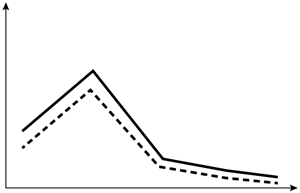
C)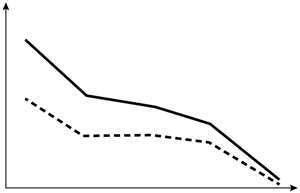
D)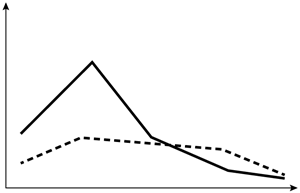
E)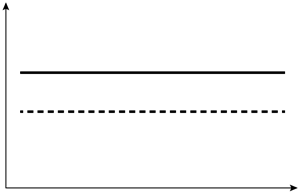
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A 29-year-old nulligravid woman comes to the office complaining of increasing bilateral nipple discharge that has been staining her bra for the past two months. The patient has not experienced any breast pain, headaches, or changes in eyesight, nor has she felt any breast mass. Three months have passed since her last period, and home pregnancy tests have come back negative. She used to have normal 28-day menstrual periods in the past. The patient is healthy and does not take any drugs. Vital signs are in the expected range. Visual fields are intact by confrontation upon evaluation. On nipple compression, a yellowish fluid can be expressed bilaterally. Neither lymphadenopathy nor breast lumps exist. An examination of the pelvis reveals no abnormality. Testing of serum beta-hCG is negative. Brain imaging shows a 0.6-cm pituitary mass. Pharmacotherapeutic treatment is begun, and on a follow-up visit the patient reports that her symptoms are improving. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism of action of this medication?
A)Increased estrogen effect on the pituitary
B)Inhibition of gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion
C)Inhibition of hypothalamic dopaminergic neurons
D)Stimulation of pituitary dopamine receptors
E)Stimulation of thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptors
A)Increased estrogen effect on the pituitary
B)Inhibition of gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion
C)Inhibition of hypothalamic dopaminergic neurons
D)Stimulation of pituitary dopamine receptors
E)Stimulation of thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A 48-year-old woman who has type 2 diabetes mellitus visits the office for follow-up care. She has had diabetes for ten years, and despite using numerous oral antidiabetic medications, her glycemic control has gradually gotten worse. The patient stopped taking her oral medications three months ago (with the exception of metformin) and began receiving daily injections of insulin glargine; she has since visited with the diabetes educator several times to go through proper injection technique and titrate up the dosage. However, since initiating insulin, the patient reports gaining 4.5 kg (10 lb) of weight. She claims, "I think I should eat more. I don't want to continue it if that's how insulin will be." Which of the following is the most appropriate response to this patient's statement?
A)"Regular exercise can reduce insulin-induced weight gain. What are your current exercise habits?"
B)"Some patients eat more after starting insulin because they fear their sugar may drop. Have you noticed that happening to you?"
C)"Sometimes stress can increase your appetite. How are things in your life right now?"
D)"Unfortunately, although insulin controls diabetes, it can cause weight gain. But the benefits outweigh the side effects."
A)"Regular exercise can reduce insulin-induced weight gain. What are your current exercise habits?"
B)"Some patients eat more after starting insulin because they fear their sugar may drop. Have you noticed that happening to you?"
C)"Sometimes stress can increase your appetite. How are things in your life right now?"
D)"Unfortunately, although insulin controls diabetes, it can cause weight gain. But the benefits outweigh the side effects."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A 67-year-old woman comes to the office suffering from polymyalgia rheumatica. She was diagnosed a year ago and has had to take prednisone at supraphysiologic doses to control her symptoms. The patient has no other medical conditions. She gets enough calcium and vitamin D through her diet and supplements. The patient does not use tobacco or alcohol. The physical examination is unremarkable. Serum creatinine, 25-hydroxyvitamin D, and calcium levels are normal, according to laboratory results. When compared to her bone density at age 65, her bone density as measured by dual x-ray absorptiometry (DX A) shows a significant decline. Which of the following is most likely contributing to this patient's bone loss?
A)Increased activity of osteoprotegerin
B)Increased levels of insulin-like growth factor-1
C)Inhibition of osteoblast precursor cell replication and differentiation
D)Inhibition of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B
E)Suppression of parathyroid hormone release
A)Increased activity of osteoprotegerin
B)Increased levels of insulin-like growth factor-1
C)Inhibition of osteoblast precursor cell replication and differentiation
D)Inhibition of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B
E)Suppression of parathyroid hormone release

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A 60-year-old man is brought to the emergency department due to persistent dyspnea. He has a history of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. He has had no lightheadedness or chest pain. Blood pressure is 128/72 mm Hg and pulse is 81/min. After stabilization of the patient condition and medications are modified, he is discharged with the addition of a combination pill that inhibits neprilysin and blocks angiotensin II receptors. Which of the following is the most likely effect of this medication?
A)Decreased renal free-water reabsorption
B)Decreased venous compliance
C)Increased myocardial contractility
D)Increased peripheral arterial resistance
E)Increased urinary sodium excretion
A)Decreased renal free-water reabsorption
B)Decreased venous compliance
C)Increased myocardial contractility
D)Increased peripheral arterial resistance
E)Increased urinary sodium excretion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A study is being carried out to determine the effect of parathyroid hormone (PTH) on bone remodeling. Half of the study participants receive intermittent PTH injections, while the other half receive a continuous PTH infusion. The findings show that intermittent PTH injections have different effects on bone metabolism than continuous infusion. . Which of the following is most likely to be the predominant bone effect with intermittent injections?
A)Increased activity of matrix metalloproteinases
B)Increased levels of osteoprotegerin
C)Osteoclast apoptosis
D)Stimulation of osteoblast activity
E)Suppression of RANK and RANK-ligand activity
A)Increased activity of matrix metalloproteinases
B)Increased levels of osteoprotegerin
C)Osteoclast apoptosis
D)Stimulation of osteoblast activity
E)Suppression of RANK and RANK-ligand activity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A 60-year-old man comes to the office for follow up appointment, he feels shortenss of breath while walking his dog around the block. He states that he is experiencing a dyspnea while sleeping therefor he uses 3 pillows or sleep on the recliner. The patient had an acute myocardial infarction 2 years ago and has been nonadherent with his medications. Temperature is 36.9 C (98 F), blood pressure is 125/74 mm Hg, pulse is 92/min, and respirations are 21/min. Physical examination shows bibasilar lung crackles, jugular venous distension, and bilateral pitting edema in the lower extremities. Chest x-ray reveals cardiomegaly and pulmonary venous congestion. Which of the following factors is most likely contributing to this patient's symptoms?
A)Decreased arteriolar resistance
B)Decreased plasma renin activity
C)Decreased ventricular end-diastolic pressure
D)Increased plasma brain natriuretic peptide concentration
E)Increased sympathetic nervous system activity
A)Decreased arteriolar resistance
B)Decreased plasma renin activity
C)Decreased ventricular end-diastolic pressure
D)Increased plasma brain natriuretic peptide concentration
E)Increased sympathetic nervous system activity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A 60-year-old man comes in for a check-up after visiting the emergency room for a cough. The patient was diagnosed with acute bronchitis, and the symptoms were alleviated by symptomatic treatment. During that visit, a chest x-ray revealed no lung abnormalities, but the bones appeared osteopenic. There is no bone pain and no fractures, according to the patient. He has had radiation therapy for prostate cancer and is currently taking leuprolide. The patient has no other health issues and no known drug allergies. He enjoys a glass of wine every day and does not use tobacco or illegal drugs. He follows a healthy diet and exercises on a regular basis Blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg and pulse is 80/min. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. A dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DX A) scan shows low bone mineral density. Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of the observed finding in this patient?
A)Decreased estrogen and testosterone levels
B)Decreased intestinal calcium absorption
C)Impaired 25-hydroxycholecalciferol activation
D)Increased parathyroid hormone levels
E)Paraneoplastic effects of the cancer cells
A)Decreased estrogen and testosterone levels
B)Decreased intestinal calcium absorption
C)Impaired 25-hydroxycholecalciferol activation
D)Increased parathyroid hormone levels
E)Paraneoplastic effects of the cancer cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A 60-year-old man comes to the office for follow up appointment, he feels shortenss of breath while walking his dog around the block. He states that he is experiencing a dyspnea while sleeping therefor he uses 3 pillows or sleep on the recliner. The patient had an acute myocardial infarction 2 years ago and has been nonadherent with his medications. Temperature is 36.9 C (98 F), blood pressure is 125/74 mm Hg, pulse is 92/min, and respirations are 21/min. Physical examination shows bibasilar lung crackles, jugular venous distension, and bilateral pitting edema in the lower extremities. Chest x-ray reveals cardiomegaly and pulmonary venous congestion. Which of the following factors is most likely contributing to this patient's symptoms?
A)Decreased arteriolar resistance
B)Decreased plasma renin activity
C)Decreased ventricular end-diastolic pressure
D)Increased plasma brain natriuretic peptide concentration
E)Increased sympathetic nervous system activity
A)Decreased arteriolar resistance
B)Decreased plasma renin activity
C)Decreased ventricular end-diastolic pressure
D)Increased plasma brain natriuretic peptide concentration
E)Increased sympathetic nervous system activity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A 44-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of anxiety, difficulty falling asleep, heat intolerance, and a 6-kg (13.2-lb) weight loss. she also reports a double vision and worsening eye irritation. . The patient has no prior medical problems and takes no medications. Her pulse is 115/min and blood pressure is 140/60 mm Hg . Ophthalmologic examination shows swelling of the eyelids and proptosis bilaterally. Appropriate therapy is begun. On a follow-up visit 4 weeks later, her eye symptoms have improved, and examination reveals a small decrease in proptosis with no redness. The drug that improved her ocular symptoms most likely did so by affecting which of the following?
A)Inflammatory infiltration
B)Iodine organification
C)Iodine uptake by the thyroid
D)Sympathetic hyperactivity
E)T3/T4 release by the thyroid
A)Inflammatory infiltration
B)Iodine organification
C)Iodine uptake by the thyroid
D)Sympathetic hyperactivity
E)T3/T4 release by the thyroid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A 65-year-old woman arrives at the emergency department complaining of left leg pain and swelling that has been bothering her for the past day. She has not experienced any trauma or fever. The patient has a history of high blood pressure, congestive heart failure, type 2 diabetes, and osteoporosis. Her mother and sister both had breast cancer in their families. She is on several medications. The temperature is 37.8 ° C. (100 degrees F), the blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg, and the pulse rate is 99 beats per minute. On ambient air, pulse oximetry shows 98 percent. Auscultation reveals clear lungs and normal heart sounds without murmur. Tenderness and edema are present in the left lower extremity up to the mid thigh. An occluding thrombus in the left femoral and popliteal veins is revealed by venous Doppler ultrasonography. Which of the following pharmacotherapies most likely contributed to this patient's current condition?
A)Alendronate
B)Chlorthalidone
C)Empagliflozin
D)Liraglutide
E)Raloxifene
F)Sacubitril-valsartan
G)Spironolactone
A)Alendronate
B)Chlorthalidone
C)Empagliflozin
D)Liraglutide
E)Raloxifene
F)Sacubitril-valsartan
G)Spironolactone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A 27-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 2-month history of palpitations, diaphoresis, and a 5-kg (11-lb) weight loss. The patient has no other medical problems and takes no medication. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Her pulse is 101/min and blood pressure is 141/84 mm Hg. Physical examination shows a diffusely enlarged of thyroid gland and nontender on palpation and a fine tremor when the fingers are outstretched. Laboratory studies show markedly decreased serum TSH and elevated thyroxine levels. Methimazole monotherapy is initiated. Two months later, her symptoms had resolved. The treatment most likely improved this patient's condition by directly inhibiting which of the following processes?
A)Colloid production
B)Coupling of iodotyrosines
C)Iodide uptake by the thyroid gland
D)Peripheral thyroxine to triiodothyronine conversion
E)Triiodothyronine/thyroxine effect on target tissues
A)Colloid production
B)Coupling of iodotyrosines
C)Iodide uptake by the thyroid gland
D)Peripheral thyroxine to triiodothyronine conversion
E)Triiodothyronine/thyroxine effect on target tissues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A 34-year-old woman visits the office because she is unable to lose weight despite diet and exercise. She claims she gained a significant amount of weight after quitting smoking four years ago. In the previous year, the patient tried several commercial weight-loss diet programs without success. She hopes to lose at least 4.5 kg (10 lb) in the next few months before her wedding. The patient has no other medical conditions and is not on any medications. The blood pressure is 122/80 mm Hg, and the pulse rate is 78 beats per minute. The BMI is 33 kg/m22. Physical examination reveals an obese habitus but nothing else notable. Laboratory testing for secondary causes of weight gain is unrevealing. In addition to encouraging continued efforts at lifestyle change, the physician prescribes a short course of oral phentermine for weight loss. The weight loss induced by this medication is caused by which of the following mechanisms?
A)Delayed gastric emptying
B)Lipase inhibition
C)Opioid antagonist
D)Reduced presynaptic reuptake of serotonin
E)Release of norepinephrine
A)Delayed gastric emptying
B)Lipase inhibition
C)Opioid antagonist
D)Reduced presynaptic reuptake of serotonin
E)Release of norepinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A 69-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 30 minutes after sudden onset of painless loss of vision in his right eye. Over the last several years, he has noticed increased blurring of vision; he says the blurring has made it difficult to read, but he can read better if he holds the book below or above eye level. He has smoked 1 pack of cigarettes daily for 40 years. He has no history of diabetes mellitus or hypertension Ophthalmologic examination of the right eye shows a grayish discoloration of the macula with areas of adjacent hemorrhage. Which of the following should be specifically targeted in treatment of this patient's condition?
A)CD20 lymphocyte glycoprotein
B)Epidermal growth factor receptor
C)Interleukin-2
D)Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
E)Vascular endothelial growth factor
A)CD20 lymphocyte glycoprotein
B)Epidermal growth factor receptor
C)Interleukin-2
D)Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
E)Vascular endothelial growth factor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A 30-year-old woman comes to the physician with fever and malaise. For the past two days, she has felt fatigued and weak and has had chills. Last night, had a temperature of 40.8°C (104.2°F). She has had a sore throat since this morning. The patient was recently diagnosed with Graves disease and started on an antithyroid medication. Physical examination shows an erythematous pharynx and a normal-sized thyroid. There is no tremor of the outstretched hands. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current condition?
A)Acute adrenal insufficiency
B)Drug-induced granulocyte destruction
C)Excessive thyroid suppression
D)Thyroid hormone-induced severe hypermetabolism
E)Viral destruction of neutrophils
A)Acute adrenal insufficiency
B)Drug-induced granulocyte destruction
C)Excessive thyroid suppression
D)Thyroid hormone-induced severe hypermetabolism
E)Viral destruction of neutrophils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A 48-year-old woman with a complicated medical history visits the clinic because her body habitus has changed. Her legs are "like sticks," she says, and her "belly is getting bigger." The patient is also becoming increasingly tired, but does not experience excessive daytime somnolence. She has been homeless for the majority of the last five years, but has been in a residential care facility for the past year. She is distractible and has an inappropriate affect on physical examination, but she is cooperative. Otherwise, the neurologic and mental status examination is normal. There is adipose tissue loss from the extremities and face, as well as an increase in abdominal girth. Which of the following types of medications is most likely to be responsible for this patient's symptoms?
A)Antiretroviral medication
B)HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor
C)Loop diuretic
D)Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug
E)Proton pump inhibitor
F)Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
G)Thyroperoxidase inhibitor
A)Antiretroviral medication
B)HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor
C)Loop diuretic
D)Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug
E)Proton pump inhibitor
F)Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
G)Thyroperoxidase inhibitor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A 65-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of the sudden onset of severe right eye pain, blurred vision, nausea, and vomiting. He has had an upper respiratory tract infection for the past 2 days which developd an allergic eye symptoms for which he used over-the-counter eye drop to treat his symptoms,. Examination shows a rock-hard, injected right globe and a fixed, mid-dilated pupil on the right. Gonioscopy shows that the iris meets the cornea at an angle of 10° (N = 20-45°). Which of the following medications was most likely used by this patient?
A)Alpha-adrenergic agonist
B)Beta blocker
C)Mast cell stabilizer
D)Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
E)Prostaglandin analogue
A)Alpha-adrenergic agonist
B)Beta blocker
C)Mast cell stabilizer
D)Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
E)Prostaglandin analogue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A 31-year-old woman comes to the physician for palpitations, and anxiety. During this time, she has had a 2-kg (4.4-lb) weight loss. The patient has no prior medical problems and takes no medications. Blood pressure is 140/70 mm Hg and pulse is 120/min. Physical examination shows a diffusely enlarged, warm thyroid gland. There is a fine tremor in her outstretched hands. ECG shows sinus tachycardia. Serum TSH is decreased and free thyroxine (T4) is increased. The patient is treated with multiple drugs, including propranolol. In addition to its beta-adrenergic receptor-blocking activity, this drug is likely to decrease which of the following?
A)Binding of triiodothyronine (T3) to its receptors
B)New thyroid hormone synthesis
C)Peripheral conversion of T4 to T3
D)Release of T4 by the thyroid gland
E)Serum levels of TSH receptor antibodies
A)Binding of triiodothyronine (T3) to its receptors
B)New thyroid hormone synthesis
C)Peripheral conversion of T4 to T3
D)Release of T4 by the thyroid gland
E)Serum levels of TSH receptor antibodies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A 34-year-old man comes to the office with his girlfriend for a type 1 diabetes mellitus check-up. He was diagnosed with diabetes 15 years ago and is currently on a combination of basal and rapid-acting insulin injections. The patient has had intermittent episodes of hypoglycemia, with blood glucose levels ranging from 35 to 54 mg/dL. He was taken to the emergency room two weeks ago after passing out due to low glucose levels. When hypoglycemia is associated with impaired consciousness, the patient is prescribed an injectable medication to be administered at home by a caregiver. This medication rapidly improves hypoglycemia by which of the following mechanisms?
A)Decreasing uptake of glucose by fat and muscles
B)Decreasing uptake of glucose by the liver
C)Increasing gastrointestinal absorption of glucose
D)Increasing gluconeogenesis
E)Increasing glycogenolysis
A)Decreasing uptake of glucose by fat and muscles
B)Decreasing uptake of glucose by the liver
C)Increasing gastrointestinal absorption of glucose
D)Increasing gluconeogenesis
E)Increasing glycogenolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 509 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



