Deck 14: Chemical Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/34
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Chemical Equilibrium
1
Which of the following is true about a system that has reached chemical equilibrium:
A) the net concentrations of products and reactants are not changing
B) there is a dynamic balance between forward and reverse processes
C) the concentration of the products equals that of the reactants
D) a and b
E) a and c
A) the net concentrations of products and reactants are not changing
B) there is a dynamic balance between forward and reverse processes
C) the concentration of the products equals that of the reactants
D) a and b
E) a and c
D
2
Which of the following is a true statement:
A) K, Kp, and Kc can all be dimensionless quantities
B) K will always have the same dimension as Kp
C) KP can never equal Kc
D) It is not possible to calculate K with only thermodynamic tables
A) K, Kp, and Kc can all be dimensionless quantities
B) K will always have the same dimension as Kp
C) KP can never equal Kc
D) It is not possible to calculate K with only thermodynamic tables
A
3
Under what circumstances will Kp = K
A) Kp can never numerically equal K
B) Kp is always numerically equal to K
C) Kp will equal K when pressures are recorded in Torr and Pref = 760
D) Kp will equal K when pressures are recorded in the Pascals (SI Units)
A) Kp can never numerically equal K
B) Kp is always numerically equal to K
C) Kp will equal K when pressures are recorded in Torr and Pref = 760
D) Kp will equal K when pressures are recorded in the Pascals (SI Units)
C
4
Under what circumstances will Kc = K
A) Kc equals K when molar concentration units are used and Cref = 1M
B) Kc equals K when molal concentrations are used and Cref = 1m
C) Kc will equal K only in very dilute solution
D) a and c
A) Kc equals K when molar concentration units are used and Cref = 1M
B) Kc equals K when molal concentrations are used and Cref = 1m
C) Kc will equal K only in very dilute solution
D) a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is a true statement
A) Qc can approach KC, but never equal Kc
B) If Qc > Kc, reactants will be favored
C) if Qc < Kc, reactants will be favored
D) a and b
E) a and c
A) Qc can approach KC, but never equal Kc
B) If Qc > Kc, reactants will be favored
C) if Qc < Kc, reactants will be favored
D) a and b
E) a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
It is determined that a certain reaction between two aqueous species is exothermic and produces at least one product that is a gas. Which set of reaction conditions would most decrease the yield of product?
A) High temperature, low pressure
B) Low temperature, high pressure
C) High temperature, high pressure
D) Low temperature, low pressure
A) High temperature, low pressure
B) Low temperature, high pressure
C) High temperature, high pressure
D) Low temperature, low pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is temperature dependant
A) KP
B) KC
C) partition coefficients
D) activity coefficients
E) all of the above
A) KP
B) KC
C) partition coefficients
D) activity coefficients
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Consider the following reaction in aqueous solution:
2A + 3B + C![<strong>Consider the following reaction in aqueous solution: 2A + 3B + C D + E Which of the following is the correct law of mass action for this reaction?</strong> A) K<sub>c</sub>=[2A][3B][C][D]<sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup>[E]<sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup> B) K<sub>c</sub>=[A]<sup>2</sup>[B]<sup>3</sup>[C] \ [D][E] C) K<sub>c</sub>=[A]<sup>-</sup><sup>2</sup>[B]<sup>-</sup><sup>3</sup>[C]<sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup>[D][E] D) K<sub>c</sub>=[D][E] / [A]<sup>-</sup><sup>2</sup>[B]<sup>-</sup><sup>3</sup>[C]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB10703/11ed398b_8351_d9b5_a786_f917bb285181_TB10703_11.jpg) D + E
D + E
Which of the following is the correct law of mass action for this reaction?
A) Kc=[2A][3B][C][D]-1[E]-1
B) Kc=[A]2[B]3[C] \ [D][E]
C) Kc=[A]-2[B]-3[C]-1[D][E]
D) Kc=[D][E] / [A]-2[B]-3[C]
2A + 3B + C
![<strong>Consider the following reaction in aqueous solution: 2A + 3B + C D + E Which of the following is the correct law of mass action for this reaction?</strong> A) K<sub>c</sub>=[2A][3B][C][D]<sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup>[E]<sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup> B) K<sub>c</sub>=[A]<sup>2</sup>[B]<sup>3</sup>[C] \ [D][E] C) K<sub>c</sub>=[A]<sup>-</sup><sup>2</sup>[B]<sup>-</sup><sup>3</sup>[C]<sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup>[D][E] D) K<sub>c</sub>=[D][E] / [A]<sup>-</sup><sup>2</sup>[B]<sup>-</sup><sup>3</sup>[C]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB10703/11ed398b_8351_d9b5_a786_f917bb285181_TB10703_11.jpg) D + E
D + EWhich of the following is the correct law of mass action for this reaction?
A) Kc=[2A][3B][C][D]-1[E]-1
B) Kc=[A]2[B]3[C] \ [D][E]
C) Kc=[A]-2[B]-3[C]-1[D][E]
D) Kc=[D][E] / [A]-2[B]-3[C]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Equal volumes of two immiscible liquids, A and B, are placed in a separatory funnel. A small amount of solute (S) is dissolved in the liquids and is partitioned between the A and B layers with a partition coefficient of [S]A / [S]B=0.6. If liquid B is removed from the flask, will the concentration of S remaining in the flask be
A) greater than the initial concentration
B) less than the initial concentration
C) equal to the initial concentration
D) impossible to determine
A) greater than the initial concentration
B) less than the initial concentration
C) equal to the initial concentration
D) impossible to determine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The greater the value of the partition ratio K of the solute between the stationary phase and the mobile phase of a chromatographic column:
A) The slower the solute travels through the stationary phase of the column
B) The faster the solute travels through the stationary phase of the column
C) There is no difference in the rate or travel of the solute, the rate of travel is based solely on the mobile phase
D) a and c
E) b and c
A) The slower the solute travels through the stationary phase of the column
B) The faster the solute travels through the stationary phase of the column
C) There is no difference in the rate or travel of the solute, the rate of travel is based solely on the mobile phase
D) a and c
E) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A certain chemical reaction sets up an equilibrium as follows:
A2(g) + 3B2(g)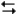 2AB3(g)
2AB3(g)
At a certain temperature equilibrium is established with equilibrium partial pressures for A2, B2, and AB3 of 0.11, 0.34, and 1.33 atm respectively. What is the value of the equilibrium constant at this temperature?
A) 410
B) 355
C) 0.0281
D) There is not enough information to answer the question
E) None of the above
A2(g) + 3B2(g)
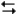 2AB3(g)
2AB3(g)At a certain temperature equilibrium is established with equilibrium partial pressures for A2, B2, and AB3 of 0.11, 0.34, and 1.33 atm respectively. What is the value of the equilibrium constant at this temperature?
A) 410
B) 355
C) 0.0281
D) There is not enough information to answer the question
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
At 25°C, Kp=2.86×1024 for the reaction:
2SO2(g) + O2(g)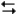 2SO3(g)
2SO3(g)
At this temperature, what is the value of Kp for the reaction
SO3(g)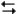 SO2(g) +
SO2(g) + 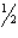 O2(g)
O2(g)
A) 1.69×1012
B) 5.91×10-13
C) 2.86×1024
D) 3.50×10-25
E) There is not enough information to answer the question
2SO2(g) + O2(g)
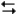 2SO3(g)
2SO3(g)At this temperature, what is the value of Kp for the reaction
SO3(g)
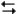 SO2(g) +
SO2(g) + 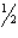 O2(g)
O2(g)A) 1.69×1012
B) 5.91×10-13
C) 2.86×1024
D) 3.50×10-25
E) There is not enough information to answer the question

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Exhibit 14-1
The following question(s) pertain to the equilibrium 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) → N2(g) + 2H2O(g) with initial partial pressures of PNO=0.3 atm,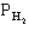 =0.4 atm,
=0.4 atm, 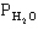 =0.4 atm.
=0.4 atm.
Refer to Exhibit 14-1. At a certain temperature equilibrium is established and it is determined that the partial pressure of water is 0.228 atm. What are the equilibrium partial pressures of NO, H2, and N2 respectively?
A) 0.172 atm, 0.172 atm, 0.472 atm
B) 0.192 atm, 0.192 atm, 0.466 atm,
C) 0.578 atm, 0.172 atm, 0.578 atm
D) 0.114 atm, 0.114 atm, 0.472 atm
The following question(s) pertain to the equilibrium 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) → N2(g) + 2H2O(g) with initial partial pressures of PNO=0.3 atm,
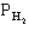 =0.4 atm,
=0.4 atm, 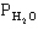 =0.4 atm.
=0.4 atm.Refer to Exhibit 14-1. At a certain temperature equilibrium is established and it is determined that the partial pressure of water is 0.228 atm. What are the equilibrium partial pressures of NO, H2, and N2 respectively?
A) 0.172 atm, 0.172 atm, 0.472 atm
B) 0.192 atm, 0.192 atm, 0.466 atm,
C) 0.578 atm, 0.172 atm, 0.578 atm
D) 0.114 atm, 0.114 atm, 0.472 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Exhibit 14-1
The following question(s) pertain to the equilibrium 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) → N2(g) + 2H2O(g) with initial partial pressures of PNO=0.3 atm,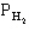 =0.4 atm,
=0.4 atm, 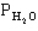 =0.4 atm.
=0.4 atm.
Refer to Exhibit 14-1. What is the numerical value of the equilibrium constant Kp at this temperature
A) 3.63
B) .275
C) 28.0
D) .483
E) None of the above
The following question(s) pertain to the equilibrium 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) → N2(g) + 2H2O(g) with initial partial pressures of PNO=0.3 atm,
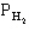 =0.4 atm,
=0.4 atm, 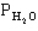 =0.4 atm.
=0.4 atm.Refer to Exhibit 14-1. What is the numerical value of the equilibrium constant Kp at this temperature
A) 3.63
B) .275
C) 28.0
D) .483
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Exhibit 14-1
The following question(s) pertain to the equilibrium 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) → N2(g) + 2H2O(g) with initial partial pressures of PNO=0.3 atm,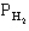 =0.4 atm,
=0.4 atm, 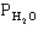 =0.4 atm.
=0.4 atm.
Refer to Exhibit 14-1. What is the numerical value of the thermodynamic equilibrium constant K at this temperature
A) 28.0
B) 3.63
C) 1.13
D) .483
E) Not enough information is given to answer the question
The following question(s) pertain to the equilibrium 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) → N2(g) + 2H2O(g) with initial partial pressures of PNO=0.3 atm,
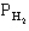 =0.4 atm,
=0.4 atm, 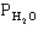 =0.4 atm.
=0.4 atm.Refer to Exhibit 14-1. What is the numerical value of the thermodynamic equilibrium constant K at this temperature
A) 28.0
B) 3.63
C) 1.13
D) .483
E) Not enough information is given to answer the question

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
At 100 C, the following two reactions have the denoted equilibrium constants.
2NO(g) + Br ₂(g) 2NOBr(g) K=2.4
Br²(g) + Cl2(g) 2BrCl(g) K=7.5
What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction?
2NOBr(g) + Cl2(g) 2NO(g) + 2BrCl(g)
2NO(g) + 2BrCl(g)
A) 180
B) 0.055
C) 3.125
D) .320
E) None of the above
2NO(g) + Br ₂(g) 2NOBr(g) K=2.4
Br²(g) + Cl2(g) 2BrCl(g) K=7.5
What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction?
2NOBr(g) + Cl2(g)
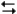 2NO(g) + 2BrCl(g)
2NO(g) + 2BrCl(g)A) 180
B) 0.055
C) 3.125
D) .320
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
At 600 K, the enthalpy of a certain reaction is -22 kJ with an equilibrium constant of 4500. What will be the value of the equilibrium constant at 300 K?
A) 0.0121
B) 54.7
C) .3203.7×105
D) Not enough information is given to answer the question
E) None of the above
A) 0.0121
B) 54.7
C) .3203.7×105
D) Not enough information is given to answer the question
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A certain endothermic reaction is known to have an equilibrium constant of 50 at 100 K. What can you say about the value of the equilibrium constant at 298 K?
A) It will be less that 50
B) It will be greater than 50
C) It will equal 50
D) Not enough information is given to answer the question
E) None of the above
A) It will be less that 50
B) It will be greater than 50
C) It will equal 50
D) Not enough information is given to answer the question
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A researcher constructed a reaction vessel and connected it to a spectrophotometer so that the concentrations of all species in the vessel could be measured simultaneously. At 25°C all of the concentrations were measured and the equilibrium constant (Kc) was calculated to be 3445. The temperature was increased to 75°C, the concentrations measured, and the equilibrium constant calculated to be 9015. What is the DHrxn?
A) -45.1 kJ
B) 45.1 kJ
C) -16.6 kJ
D) -7.2 kJ
E) None of the above
A) -45.1 kJ
B) 45.1 kJ
C) -16.6 kJ
D) -7.2 kJ
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
At 50°C the thermodynamic equilibrium constant for the reaction
2NO2(g)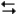 N2O4(g)
N2O4(g)
Is 1.18. If a reaction vessel is initially charged with 0.5 atm of NO2 at this temperature. What will be the partial pressure of N2O4 be when the reaction reaches equilibrium?
A) 0.102 atm
B) 0.147 atm
C) 0.175 atm
D) 0.270 atm
E) None of the above
2NO2(g)
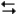 N2O4(g)
N2O4(g)Is 1.18. If a reaction vessel is initially charged with 0.5 atm of NO2 at this temperature. What will be the partial pressure of N2O4 be when the reaction reaches equilibrium?
A) 0.102 atm
B) 0.147 atm
C) 0.175 atm
D) 0.270 atm
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Fifty grams of solid I2 is placed in a 1 liter evacuated cell and allowed to come to equilibrium with its vapor at 120°C. What is the partial pressure of I2 vapor in the cell when it reaches equilibrium?
A) 18 Torr
B) 134 Torr
C) 299 Torr
D) 790 Torr
E) None of the above
A) 18 Torr
B) 134 Torr
C) 299 Torr
D) 790 Torr
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Exhibit 14-2
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction H2(g) + I2(g)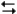 2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.
2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.
Refer to Exhibit 14-2. What is the value of the equilibrium constant at this temperature?
A) 8.65×10-15
B) 204
C) 10.2
D) 1.00
E) None of the above
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction H2(g) + I2(g)
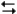 2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.
2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.Refer to Exhibit 14-2. What is the value of the equilibrium constant at this temperature?
A) 8.65×10-15
B) 204
C) 10.2
D) 1.00
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Exhibit 14-2
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction H2(g) + I2(g)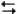 2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.
2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.
Refer to Exhibit 14-2. What is the value of Q?
A) 1.00
B) 5.00
C) 0.200
D) 0.100
E) None of the above
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction H2(g) + I2(g)
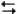 2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.
2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.Refer to Exhibit 14-2. What is the value of Q?
A) 1.00
B) 5.00
C) 0.200
D) 0.100
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Exhibit 14-2
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction H2(g) + I2(g)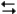 2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.
2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.
Refer to Exhibit 14-2. Based on the equilibrium constant and the value of Q, will more reactants or products be formed as the system approaches equilibrium at this temperature?
A) More products will be formed
B) More reactants will be formed
C) Not enough data to answer the question
D) None of the above
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction H2(g) + I2(g)
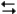 2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.
2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.Refer to Exhibit 14-2. Based on the equilibrium constant and the value of Q, will more reactants or products be formed as the system approaches equilibrium at this temperature?
A) More products will be formed
B) More reactants will be formed
C) Not enough data to answer the question
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Exhibit 14-2
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction H2(g) + I2(g)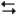 2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.
2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.
Refer to Exhibit 14-2. What will be the partial pressure of HI when the system reaches equilibrium?
A) 0.200 atm
B) 0.037 atm
C) 0.526 atm
D) 0.373 atm
E) Not enough data to answer the question
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction H2(g) + I2(g)
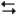 2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.
2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.Refer to Exhibit 14-2. What will be the partial pressure of HI when the system reaches equilibrium?
A) 0.200 atm
B) 0.037 atm
C) 0.526 atm
D) 0.373 atm
E) Not enough data to answer the question

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Exhibit 14-2
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction H2(g) + I2(g)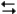 2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.
2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.
Refer to Exhibit 14-2. What will be the total pressure in the reaction cell when the system reaches equilibrium?
A) 0.200 atm
B) 0.374 atm
C) 0.427 atm
D) 0.600 atm
E) Not enough data to answer the question
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction H2(g) + I2(g)
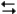 2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.
2HI(g) at 150°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressure of all the species in the reaction (both reactants and products) is 0.200 atm.Refer to Exhibit 14-2. What will be the total pressure in the reaction cell when the system reaches equilibrium?
A) 0.200 atm
B) 0.374 atm
C) 0.427 atm
D) 0.600 atm
E) Not enough data to answer the question

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Exhibit 14-3
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g)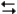 2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.
2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.
Refer to Exhibit 14-3. What is the value of the equilibrium constant Kp at this temperature?
A) 0.652
B) 2.78×10-21
C) 3.59×1020
D) 1.92×10-14
E) None of the above
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g)
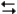 2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.
2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.Refer to Exhibit 14-3. What is the value of the equilibrium constant Kp at this temperature?
A) 0.652
B) 2.78×10-21
C) 3.59×1020
D) 1.92×10-14
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Exhibit 14-3
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g)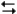 2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.
2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.
Refer to Exhibit 14-3. What is the value of Q?
A) 10
B) 1
C) 1670
D) 67
E) None of the above
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g)
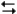 2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.
2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.Refer to Exhibit 14-3. What is the value of Q?
A) 10
B) 1
C) 1670
D) 67
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Exhibit 14-3
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g)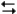 2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.
2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.
Refer to Exhibit 14-3. Based on the equilibrium constant and the value of Q, will more reactants or products be formed as the system approaches equilibrium at this temperature?
A) More products will be formed
B) More reactants will be formed
C) Not enough data to answer the question
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g)
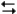 2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.
2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.Refer to Exhibit 14-3. Based on the equilibrium constant and the value of Q, will more reactants or products be formed as the system approaches equilibrium at this temperature?
A) More products will be formed
B) More reactants will be formed
C) Not enough data to answer the question

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Exhibit 14-3
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g)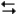 2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.
2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.
Refer to Exhibit 14-3. What will be the partial pressure of NH3 when the system reaches equilibrium at this temperature?
A) 0.896 atm
B) 0.305 atm
C) 0.037 atm
D) 0.600 atm
E) None of the above
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g)
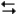 2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.
2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.Refer to Exhibit 14-3. What will be the partial pressure of NH3 when the system reaches equilibrium at this temperature?
A) 0.896 atm
B) 0.305 atm
C) 0.037 atm
D) 0.600 atm
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Exhibit 14-3
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g)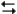 2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.
2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.
Refer to Exhibit 14-3. What will be the total pressure in the reaction vessel when the system reaches equilibrium at this temperature?
A) 1.24 atm
B) 0.900 atm
C) 0.744 atm
D) 0.305 atm
E) None of the above
The following question(s) pertain to the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g)
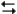 2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.
2NH3(g) at 200°C with the reaction vessel being charged in such a way that the initial partial pressures of N2, H2, and NH3 are 0.200, 0.300, and 0.600 atm respectively.Refer to Exhibit 14-3. What will be the total pressure in the reaction vessel when the system reaches equilibrium at this temperature?
A) 1.24 atm
B) 0.900 atm
C) 0.744 atm
D) 0.305 atm
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A certain chemical reaction sets up an equilibrium as follows
3A2(aq) + 2B3(aq)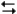 6AB(aq)
6AB(aq)
After being started with unknown amounts of A2 and B3. Once the system reaches equilibrium the concentrations of A2, B3, and AB are precisely determined. What other quantities can be determined?
A) Q, Kc, K, DG°
B) Q, Kc, DG, DG°
C) Q, K, DG, DG°
D) K, Kc, DG, DG°
E) Q, Kc, K, DG
3A2(aq) + 2B3(aq)
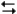 6AB(aq)
6AB(aq)After being started with unknown amounts of A2 and B3. Once the system reaches equilibrium the concentrations of A2, B3, and AB are precisely determined. What other quantities can be determined?
A) Q, Kc, K, DG°
B) Q, Kc, DG, DG°
C) Q, K, DG, DG°
D) K, Kc, DG, DG°
E) Q, Kc, K, DG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
At room temperature cyclohexane exists almost exclusively in the chair conformation (99.99%). But at 800°C, 30% of the cyclohexane molecules exist in the twist-boat conformation.
What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at 800°C?
C6H12(chair)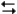 C6H12(twist-boat)
C6H12(twist-boat)
A) 0.30
B) 0.23
C) 2.3
D) 0.43
E) 0.77
What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at 800°C?
C6H12(chair)
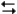 C6H12(twist-boat)
C6H12(twist-boat)A) 0.30
B) 0.23
C) 2.3
D) 0.43
E) 0.77

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
At room temperature cyclohexane exists almost exclusively in the chair conformation (99.99%). But at 800°C, 30% of the cyclohexane molecules exist in the twist-boat conformation.
Compared to its value at 25°C, the value of DG° at 800°C for the reaction
C6H12(chair)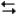 C6H12(twist-boat)
C6H12(twist-boat)
Should
A) be larger in magnitude and have the same sign
B) be larger in magnitude and have the opposite sign
C) be smaller in magnitude and have the same sign
D) be smaller in magnitude and have the opposite sign
E) not enough information to answer the question
Compared to its value at 25°C, the value of DG° at 800°C for the reaction
C6H12(chair)
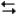 C6H12(twist-boat)
C6H12(twist-boat)Should
A) be larger in magnitude and have the same sign
B) be larger in magnitude and have the opposite sign
C) be smaller in magnitude and have the same sign
D) be smaller in magnitude and have the opposite sign
E) not enough information to answer the question

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



