Deck 6: Cellular Respiration: Obtaining Energy from Food
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/51
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Cellular Respiration: Obtaining Energy from Food
1
A horse eating some hay is an example of ________.
A) an autotroph eating a producer
B) an autotroph eating a consumer
C) a consumer eating a producer
D) a consumer eating a heterotroph
A) an autotroph eating a producer
B) an autotroph eating a consumer
C) a consumer eating a producer
D) a consumer eating a heterotroph
C
2
The ultimate source of the energy in food is ________.
A) the sun
B) producers
C) ATP
D) consumers
A) the sun
B) producers
C) ATP
D) consumers
A
3
Photosynthetic organisms like grass are able to ________.
A) make all of their organic matter from organic molecules in the soil.
B) use water they take in through their leaves as a final electron acceptor.
C) change the light energy from sunlight into sugars
D) use substances in the air as a major source of carbon.
A) make all of their organic matter from organic molecules in the soil.
B) use water they take in through their leaves as a final electron acceptor.
C) change the light energy from sunlight into sugars
D) use substances in the air as a major source of carbon.
D
4
A process is referred to as aerobic if it requires ________.
A) oxygen
B) carbon dioxide
C) ATP
D) carbohydrates
A) oxygen
B) carbon dioxide
C) ATP
D) carbohydrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following are produced as a result of cellular respiration?
A) ATP and water
B) carbon dioxide and ATP
C) carbon dioxide, water, and ATP
D) oxygen and glucose
A) ATP and water
B) carbon dioxide and ATP
C) carbon dioxide, water, and ATP
D) oxygen and glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is the CORRECT sequence of stages in cellular respiration?
A) glycolysis, citric acid cycle, electron transport
B) citric acid cycle, glycolysis, electron transport
C) citric acid cycle, electron transport, glycolysis
D) electron transport, glycolysis, citric acid cycle
A) glycolysis, citric acid cycle, electron transport
B) citric acid cycle, glycolysis, electron transport
C) citric acid cycle, electron transport, glycolysis
D) electron transport, glycolysis, citric acid cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The waste products of cellular respiration include ________.
A) water only
B) carbon dioxide only
C) water and carbon dioxide
D) water and glucose
A) water only
B) carbon dioxide only
C) water and carbon dioxide
D) water and glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
During cellular respiration,electrons move through a series of electron acceptor molecules.Which of the following is a TRUE statement about this process?
A) The electrons gain energy as they move from one electron acceptor to another.
B) Oxygen is eventually reduced by the electrons to form water.
C) The electrons release large amounts of energy each time they are transferred from one electron acceptor to another.
D) Glucose is eventually reduced by the electrons to form water.
A) The electrons gain energy as they move from one electron acceptor to another.
B) Oxygen is eventually reduced by the electrons to form water.
C) The electrons release large amounts of energy each time they are transferred from one electron acceptor to another.
D) Glucose is eventually reduced by the electrons to form water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The first electron acceptor of cellular respiration is ________.
A) CO₂
B) O₂
C) NAD⁺
D) H₂O
A) CO₂
B) O₂
C) NAD⁺
D) H₂O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Oxygen is a product of cellular respiration; carbon dioxide is a product of photosynthesis.
B) Lactic acid is a product of aerobic respiration; ethyl alcohol is a product of fermentation.
C) Oxidation is the loss of electrons; reduction is the gain of electrons.
D) Glucose is a product of aerobic respiration; lactic acid is a product of anaerobic respiration.
A) Oxygen is a product of cellular respiration; carbon dioxide is a product of photosynthesis.
B) Lactic acid is a product of aerobic respiration; ethyl alcohol is a product of fermentation.
C) Oxidation is the loss of electrons; reduction is the gain of electrons.
D) Glucose is a product of aerobic respiration; lactic acid is a product of anaerobic respiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Plant cells ________.
A) do not need chloroplasts because their mitochondria meet their energy needs
B) have chloroplasts and mitochondria
C) use carbon dioxide but do not use oxygen
D) do not need mitochondria because their chloroplasts meet their energy needs
A) do not need chloroplasts because their mitochondria meet their energy needs
B) have chloroplasts and mitochondria
C) use carbon dioxide but do not use oxygen
D) do not need mitochondria because their chloroplasts meet their energy needs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Plants use photosynthesis to
A) store chemical energy, and they use cellular respiration to harvest energy.
B) change light energy into chemical energy as well as to harvest chemical energy.
C) harvest energy, and they use cellular respiration to store chemical energy.
D) change light energy into sugars.
A) store chemical energy, and they use cellular respiration to harvest energy.
B) change light energy into chemical energy as well as to harvest chemical energy.
C) harvest energy, and they use cellular respiration to store chemical energy.
D) change light energy into sugars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Respiration describes the exchange of gases between your blood and the air.Cellular respiration ________.
A) produces ATP
B) produces oxygen
C) produces glucose
D) uses carbon dioxide
A) produces ATP
B) produces oxygen
C) produces glucose
D) uses carbon dioxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Photosynthetic organisms are ________.
A) producers that make all of their organic matter from organic molecules that they take in
B) consumers that obtain organic molecules from other living organisms
C) producers that make all their own organic matter from inorganic molecules
D) decomposers that obtain nutrients from the soil
A) producers that make all of their organic matter from organic molecules that they take in
B) consumers that obtain organic molecules from other living organisms
C) producers that make all their own organic matter from inorganic molecules
D) decomposers that obtain nutrients from the soil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Lactic acid build up in muscles is a sign that ________.
A) aerobic respiration capacity has not been reached
B) respiration is operating effectively
C) insufficient oxygen is reaching the muscles
D) the muscles will be able to operate continuously for a long time
A) aerobic respiration capacity has not been reached
B) respiration is operating effectively
C) insufficient oxygen is reaching the muscles
D) the muscles will be able to operate continuously for a long time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What compound directly provides energy for cellular work?
A) C₆H₁₂O₆
B) glucose
C) ATP
D) fat
A) C₆H₁₂O₆
B) glucose
C) ATP
D) fat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Where in the cell does glycolysis occur?
A) cytoplasm
B) endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
C) within the fluid just inside the inner mitochondrial membrane
D) between the inner and outer mitochondrial membrane
A) cytoplasm
B) endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
C) within the fluid just inside the inner mitochondrial membrane
D) between the inner and outer mitochondrial membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of these equations describes aerobic cellular respiration?
A) glucose → lactic acid + energy
B) energy + carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen + water
C) glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy
D) none of the above
A) glucose → lactic acid + energy
B) energy + carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen + water
C) glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Humans are both ________.
A) heterotrophs and consumers
B) heterotrophs and producers
C) producers and decomposers
D) autotrophs and producers
A) heterotrophs and consumers
B) heterotrophs and producers
C) producers and decomposers
D) autotrophs and producers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The final electron acceptor of aerobic respiration is ________.
A) ATP
B) oxygen
C) lactic acid
D) NAD⁺
A) ATP
B) oxygen
C) lactic acid
D) NAD⁺

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Aerobic cellular respiration generates about ________ ATP from one glucose.
A) 2
B) 6
C) 38
D) The number generated depends on whether the end product of aerobic respiration is lactic acid or ethyl alcohol.
A) 2
B) 6
C) 38
D) The number generated depends on whether the end product of aerobic respiration is lactic acid or ethyl alcohol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A product of glycolysis is ________.
A) lactic acid
B) ethyl alcohol
C) O₂
D) pyruvic acid
A) lactic acid
B) ethyl alcohol
C) O₂
D) pyruvic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What waste product do yeast produce under anaerobic conditions?
A) ethyl alcohol
B) pyruvic acid
C) lactic acid
D) creatine
A) ethyl alcohol
B) pyruvic acid
C) lactic acid
D) creatine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Several students were talking about which came first in the history of the Earth.Which student has the best understanding of what happened?
A) Photosynthetic producers must have come first to provide food for other organisms.
B) Anaerobic bacteria must have come first because there was no carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
C) Photosynthetic producers must have come first to provide oxygen for other organisms.
D) Anaerobic organisms must have come first because there was no oxygen in the atmosphere.
A) Photosynthetic producers must have come first to provide food for other organisms.
B) Anaerobic bacteria must have come first because there was no carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
C) Photosynthetic producers must have come first to provide oxygen for other organisms.
D) Anaerobic organisms must have come first because there was no oxygen in the atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Anaerobic respiration produces a maximum of ________ ATP per glucose.
A) 0
B) 2
C) 10
D) 38
A) 0
B) 2
C) 10
D) 38

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What must pyruvic acid be converted to before it can enter the citric acid cycle?
A) acetyl CoA
B) lactic acid
C) ethyl alcohol
D) citric acid
A) acetyl CoA
B) lactic acid
C) ethyl alcohol
D) citric acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In Texas,a man showed up at a medical facility claiming that he felt drunk when he had not ingested any alcohol.Indeed his blood alcohol measured 0.37,many times the legal limit.Although he was a home brewer,he claimed that this intoxication had been happening often without his drinking any alcohol.Which of these hypotheses and actions might be most useful in diagnosing this problem?
A) His home brew concoctions have created a type of alcohol that lasts a long time. Have him refrain from home brewing for a week and recheck his blood alcohol.
B) He might have recently had a round of antibiotics that killed the bacteria that usually live in his gut and allowed a yeast species to overgrow. Put him on probiotics and a low carb diet for a week and recheck his blood alcohol.
C) The fumes from the alcohol that he is using as a cleaning solution might be getting into his bloodstream. Ask him if he is using alcohol externally.
D) Maybe he feels drunk because he has been eating mushrooms that have sprouted during this very wet weather. Check him for fungal toxins.
A) His home brew concoctions have created a type of alcohol that lasts a long time. Have him refrain from home brewing for a week and recheck his blood alcohol.
B) He might have recently had a round of antibiotics that killed the bacteria that usually live in his gut and allowed a yeast species to overgrow. Put him on probiotics and a low carb diet for a week and recheck his blood alcohol.
C) The fumes from the alcohol that he is using as a cleaning solution might be getting into his bloodstream. Ask him if he is using alcohol externally.
D) Maybe he feels drunk because he has been eating mushrooms that have sprouted during this very wet weather. Check him for fungal toxins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The second stage of aerobic respiration is ________.
A) ATP production
B) the citric acid cycle
C) lactic acid fermentation
D) glycolysis
A) ATP production
B) the citric acid cycle
C) lactic acid fermentation
D) glycolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which part of cellular respiration produces the most NADH?
A) electron transport chain
B) citric acid cycle
C) glycolysis
D) fermentation
A) electron transport chain
B) citric acid cycle
C) glycolysis
D) fermentation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Electron transport takes place in the ________.
A) mitochondria
B) chloroplasts
C) cytoplasm
D) ribosomes
A) mitochondria
B) chloroplasts
C) cytoplasm
D) ribosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to ________.
A) produce more ATP than is possible through complete aerobic respiration
B) produce ATP using the electron transport chain
C) regenerate NADH
D) produce ATP without O₂
A) produce more ATP than is possible through complete aerobic respiration
B) produce ATP using the electron transport chain
C) regenerate NADH
D) produce ATP without O₂

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Some friends are trying to make wine in their basement.They've added yeast to a sweet grape juice mixture and have allowed the yeast to grow.After several days,they find that sugar levels in the grape juice have dropped,but there's no alcohol in the mixture.The most likely explanation is that ________.
A) the mixture needs more sugar; yeast need a lot of energy before they can begin to produce alcohol
B) the mixture needs less oxygen; yeast only produce alcohol in the absence of oxygen
C) the mixture needs more oxygen; yeast need oxygen to break down sugar to produce alcohol
D) the mixture needs less sugar; high sugar concentrations stimulate cellular respiration, and alcohol is not a by-product of cellular respiration
A) the mixture needs more sugar; yeast need a lot of energy before they can begin to produce alcohol
B) the mixture needs less oxygen; yeast only produce alcohol in the absence of oxygen
C) the mixture needs more oxygen; yeast need oxygen to break down sugar to produce alcohol
D) the mixture needs less sugar; high sugar concentrations stimulate cellular respiration, and alcohol is not a by-product of cellular respiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
ATP synthase plays a role in ________.
A) pulling electrons down the electron transport chain
B) glycolysis
C) pumping hydrogen ions across the inner mitochondrial membrane
D) generating ATP
A) pulling electrons down the electron transport chain
B) glycolysis
C) pumping hydrogen ions across the inner mitochondrial membrane
D) generating ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A child is born with a rare disease in which mitochondria are missing from certain skeletal muscle cells.Physicians find that the muscle cells function.Not surprisingly,they also find that ________.
A) the muscles contain large amounts of lactic acid following even mild physical exercise
B) the muscles contain large amounts of carbon dioxide following even mild physical exercise
C) the muscles require extremely high levels of oxygen to function
D) the muscle cells cannot split glucose to pyruvic acid
A) the muscles contain large amounts of lactic acid following even mild physical exercise
B) the muscles contain large amounts of carbon dioxide following even mild physical exercise
C) the muscles require extremely high levels of oxygen to function
D) the muscle cells cannot split glucose to pyruvic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In aerobic respiration,how many molecules of acetic acid are produced from six molecules of glucose?
A) 1
B) 38
C) 6
D) 12
A) 1
B) 38
C) 6
D) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is a result of glycolysis?
A) production of CO₂
B) conversion of glucose to pyruvic acid
C) a net loss of two ATPs per glucose molecule
D) conversion of NADH to NAD⁺
A) production of CO₂
B) conversion of glucose to pyruvic acid
C) a net loss of two ATPs per glucose molecule
D) conversion of NADH to NAD⁺

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Large amounts of oxygen gas first appeared in Earth's atmosphere about ________ years ago.
A) 500,000
B) 10 million
C) 2.7 billion
D) 3.5 billion
A) 500,000
B) 10 million
C) 2.7 billion
D) 3.5 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In cellular respiration,most ATP is produced DIRECTLY as a result of ________.
A) the movement of hydrogen ions across the inner mitochondrial membrane
B) the citric acid cycle
C) fermentation
D) the electron transport chain
A) the movement of hydrogen ions across the inner mitochondrial membrane
B) the citric acid cycle
C) fermentation
D) the electron transport chain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of these stages of cell respiration can occur without the others?
A) the electron transport chain
B) the citric acid cycle
C) lactic acid fermentation
D) glycolysis
A) the electron transport chain
B) the citric acid cycle
C) lactic acid fermentation
D) glycolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following metabolic pathways is common to both aerobic and anaerobic processes of sugar breakdown?
A) the citric acid cycle
B) the electron transport chain
C) conversion of pyruvic acid to lactic acid
D) glycolysis
A) the citric acid cycle
B) the electron transport chain
C) conversion of pyruvic acid to lactic acid
D) glycolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Art Questions
What does the figure below show?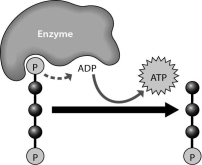
A) the synthesis of ADP
B) the breakdown of ATP to perform cellular work
C) the removal of a phosphate group from ADP
D) the synthesis of ATP through the addition of a phosphate group

What does the figure below show?

A) the synthesis of ADP
B) the breakdown of ATP to perform cellular work
C) the removal of a phosphate group from ADP
D) the synthesis of ATP through the addition of a phosphate group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The table below shows experimental data from poultry scientists. Examine the table to answer the following questions.
Oviposition time, egg weight, chicken hatch weight and hatch weight/egg weight from young and mid-age broiler breeder flocks.
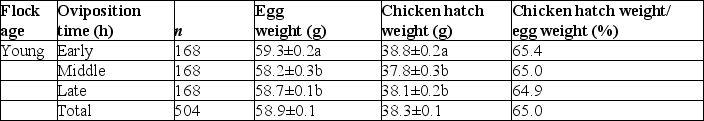
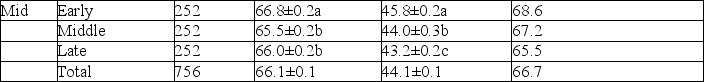
If the egg was weighed halfway between being laid and hatching,how would you expect that weight to compare to the weight of the newly hatched chick?
A) The egg would weigh more at this midpoint than when newly hatched because, during development, the chick gains new parts.
B) The egg would weigh more at this midpoint than when newly hatched because it is taking in oxygen.
C) The egg would weigh less at this midpoint than when newly hatched because the shell wears away over time.
D) The egg would weigh less at this midpoint than when newly hatched because some of the mass of the egg would be released through cell respiration.
Oviposition time, egg weight, chicken hatch weight and hatch weight/egg weight from young and mid-age broiler breeder flocks.


If the egg was weighed halfway between being laid and hatching,how would you expect that weight to compare to the weight of the newly hatched chick?
A) The egg would weigh more at this midpoint than when newly hatched because, during development, the chick gains new parts.
B) The egg would weigh more at this midpoint than when newly hatched because it is taking in oxygen.
C) The egg would weigh less at this midpoint than when newly hatched because the shell wears away over time.
D) The egg would weigh less at this midpoint than when newly hatched because some of the mass of the egg would be released through cell respiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
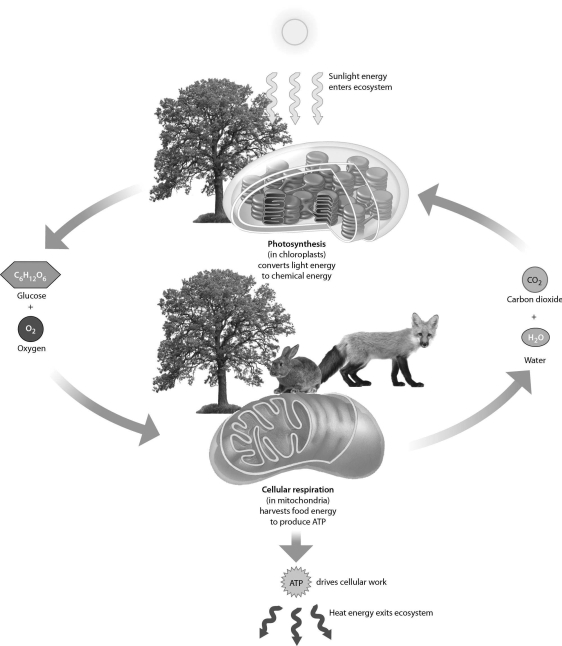
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Art Questions

Examine the figure above.Most of the mass of the tree shown in the figure comes from ________.
A) water
B) glucose
C) the air
D) the soil

Examine the figure above.Most of the mass of the tree shown in the figure comes from ________.
A) water
B) glucose
C) the air
D) the soil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The table below shows experimental data from poultry scientists. Examine the table to answer the following questions.
Oviposition time, egg weight, chicken hatch weight and hatch weight/egg weight from young and mid-age broiler breeder flocks.


What are (is)the main factor(s)causing differences between the chick hatch weight and the weight of the egg when it is laid?
A) The only factor that causes the chick to weigh less than the egg when it is laid is the removal of the shell.
B) Not only does the hatchling have no shell, but it has lost some of its mass (weight) to the air during development.
C) During development, the chick gains new parts so the weight increases.
D) Egg weight at oviposition includes a lot of water that evaporates during development.
Oviposition time, egg weight, chicken hatch weight and hatch weight/egg weight from young and mid-age broiler breeder flocks.


What are (is)the main factor(s)causing differences between the chick hatch weight and the weight of the egg when it is laid?
A) The only factor that causes the chick to weigh less than the egg when it is laid is the removal of the shell.
B) Not only does the hatchling have no shell, but it has lost some of its mass (weight) to the air during development.
C) During development, the chick gains new parts so the weight increases.
D) Egg weight at oviposition includes a lot of water that evaporates during development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Art Questions

Which of these shown in the figure below does NOT begin cellular respiration in the cytoplasm?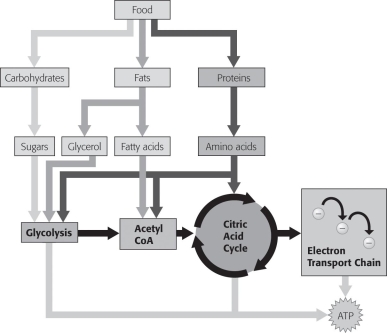
A) amino acids
B) fatty acids
C) glucose
D) glycerol

Which of these shown in the figure below does NOT begin cellular respiration in the cytoplasm?

A) amino acids
B) fatty acids
C) glucose
D) glycerol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Scenario Questions
Read the following scenario to answer the following questions.
An abundant and continual supply of ATP is necessary for all living cells. Active muscle cells require an extraordinary amount of ATP to permit strenuous exercise for prolonged periods. Toxins, reduced blood flow, and a compromised respiratory system can interfere with the transport of oxygen to active cells. A runner in a marathon faces multiple obstacles to continue to produce sufficient ATP to remain competitive.
When oxygen delivery becomes insufficient to support a runner's aerobic metabolism,cells switch to an emergency mode in which ________.
A) ATP is generated less efficiently by harvesting the heat energy in a cell
B) ATP is inefficiently produced and lactic acid is generated as a by-product
C) lactic acid is broken down to produce smaller amounts of ATP
D) carbon dioxide is joined with water to generate much smaller amounts of ATP
Read the following scenario to answer the following questions.
An abundant and continual supply of ATP is necessary for all living cells. Active muscle cells require an extraordinary amount of ATP to permit strenuous exercise for prolonged periods. Toxins, reduced blood flow, and a compromised respiratory system can interfere with the transport of oxygen to active cells. A runner in a marathon faces multiple obstacles to continue to produce sufficient ATP to remain competitive.
When oxygen delivery becomes insufficient to support a runner's aerobic metabolism,cells switch to an emergency mode in which ________.
A) ATP is generated less efficiently by harvesting the heat energy in a cell
B) ATP is inefficiently produced and lactic acid is generated as a by-product
C) lactic acid is broken down to produce smaller amounts of ATP
D) carbon dioxide is joined with water to generate much smaller amounts of ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Art Questions

Examine the figure above.Which of the following reactant(s)primarily come(s)from the air?
A) water
B) glucose
C) carbon dioxide
D) oxygen and carbon dioxide

Examine the figure above.Which of the following reactant(s)primarily come(s)from the air?
A) water
B) glucose
C) carbon dioxide
D) oxygen and carbon dioxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Art Questions

Examine the following figure.Which of these stages occur(s)in the cytoplasm?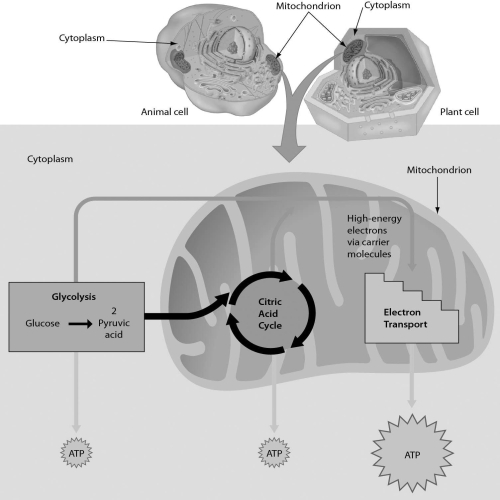
A) glycolysis
B) citric acid cycle
C) glycolysis and citric acid cycle
D) citric acid cycle and electron transport

Examine the following figure.Which of these stages occur(s)in the cytoplasm?

A) glycolysis
B) citric acid cycle
C) glycolysis and citric acid cycle
D) citric acid cycle and electron transport

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Art Questions

The figure below shows that ________.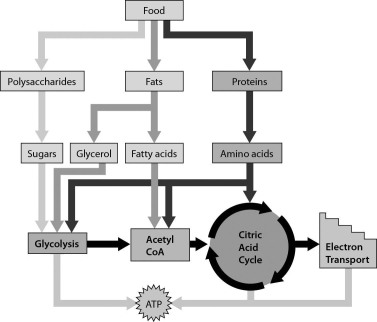
A) amino acids can move directly into the electron transport chain
B) our cells can use sugars, fatty acids, and amino acids to produce ATP
C) our cells can produce ATP only from glucose
D) our cells can produce ATP from sugars and glycerol, but not fatty acids

The figure below shows that ________.

A) amino acids can move directly into the electron transport chain
B) our cells can use sugars, fatty acids, and amino acids to produce ATP
C) our cells can produce ATP only from glucose
D) our cells can produce ATP from sugars and glycerol, but not fatty acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The table below shows experimental data from poultry scientists. Examine the table to answer the following questions.
Oviposition time, egg weight, chicken hatch weight and hatch weight/egg weight from young and mid-age broiler breeder flocks.


Which hypothesis were the poultry scientists likely testing?
A) The time of egg laying (oviposition) has an impact on egg weight.
B) Bigger eggs result in larger mature chickens.
C) Young hens have a harder time laying eggs than do older hens.
D) Egg weight is related to the weight of the hatchling (newly hatched chick).
Oviposition time, egg weight, chicken hatch weight and hatch weight/egg weight from young and mid-age broiler breeder flocks.


Which hypothesis were the poultry scientists likely testing?
A) The time of egg laying (oviposition) has an impact on egg weight.
B) Bigger eggs result in larger mature chickens.
C) Young hens have a harder time laying eggs than do older hens.
D) Egg weight is related to the weight of the hatchling (newly hatched chick).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Scenario Questions
Read the following scenario to answer the following questions.
An abundant and continual supply of ATP is necessary for all living cells. Active muscle cells require an extraordinary amount of ATP to permit strenuous exercise for prolonged periods. Toxins, reduced blood flow, and a compromised respiratory system can interfere with the transport of oxygen to active cells. A runner in a marathon faces multiple obstacles to continue to produce sufficient ATP to remain competitive.
Breathing faster when we exercise is necessary to expel ________.
A) carbon dioxide and bring in more oxygen to support aerobic metabolism
B) oxygen and bring in more carbon dioxide to support aerobic metabolism
C) carbon dioxide and bring in more oxygen to support anaerobic metabolism
D) oxygen and bring in more carbon dioxide to support anaerobic metabolism
Read the following scenario to answer the following questions.
An abundant and continual supply of ATP is necessary for all living cells. Active muscle cells require an extraordinary amount of ATP to permit strenuous exercise for prolonged periods. Toxins, reduced blood flow, and a compromised respiratory system can interfere with the transport of oxygen to active cells. A runner in a marathon faces multiple obstacles to continue to produce sufficient ATP to remain competitive.
Breathing faster when we exercise is necessary to expel ________.
A) carbon dioxide and bring in more oxygen to support aerobic metabolism
B) oxygen and bring in more carbon dioxide to support aerobic metabolism
C) carbon dioxide and bring in more oxygen to support anaerobic metabolism
D) oxygen and bring in more carbon dioxide to support anaerobic metabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



